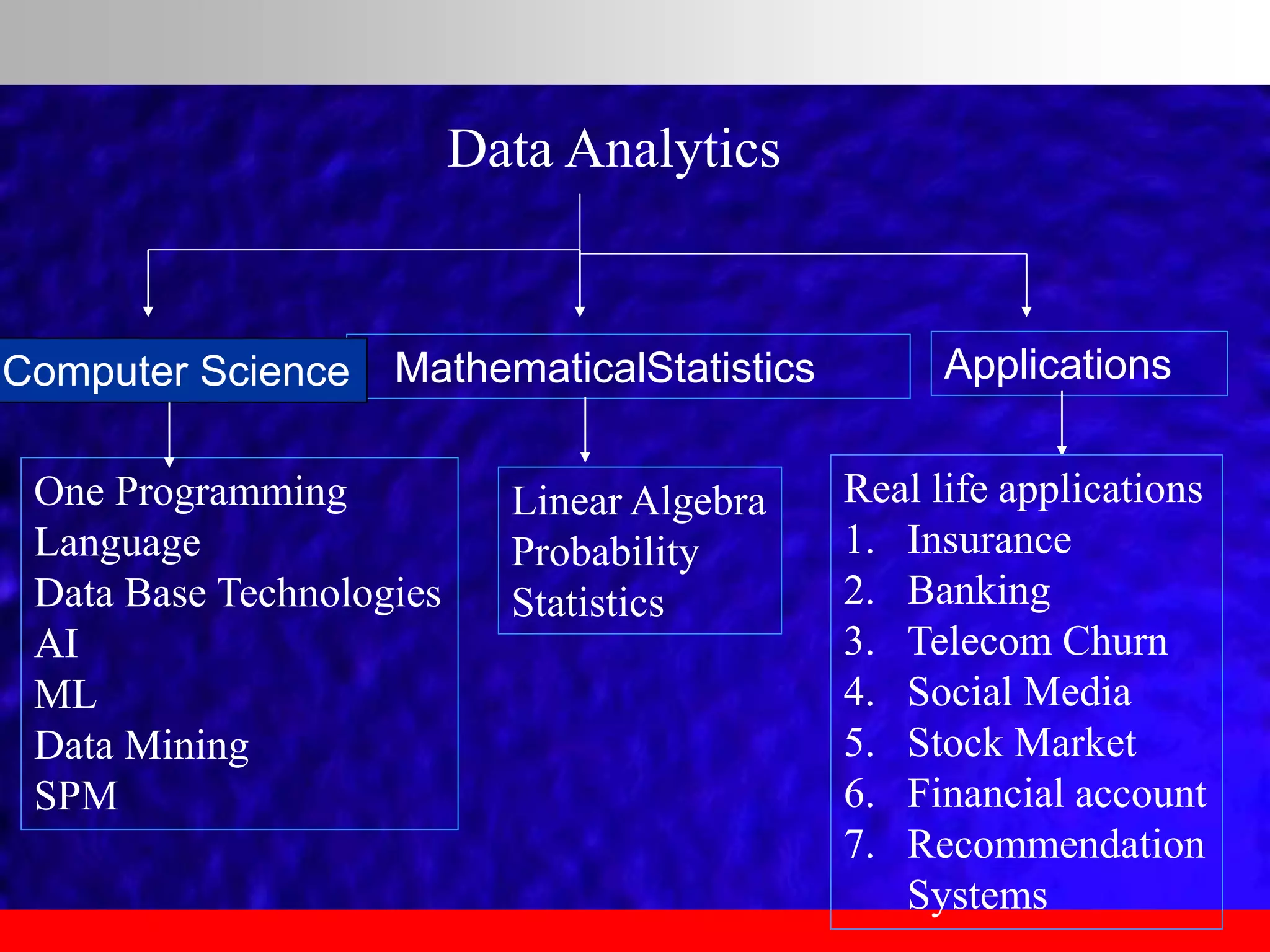
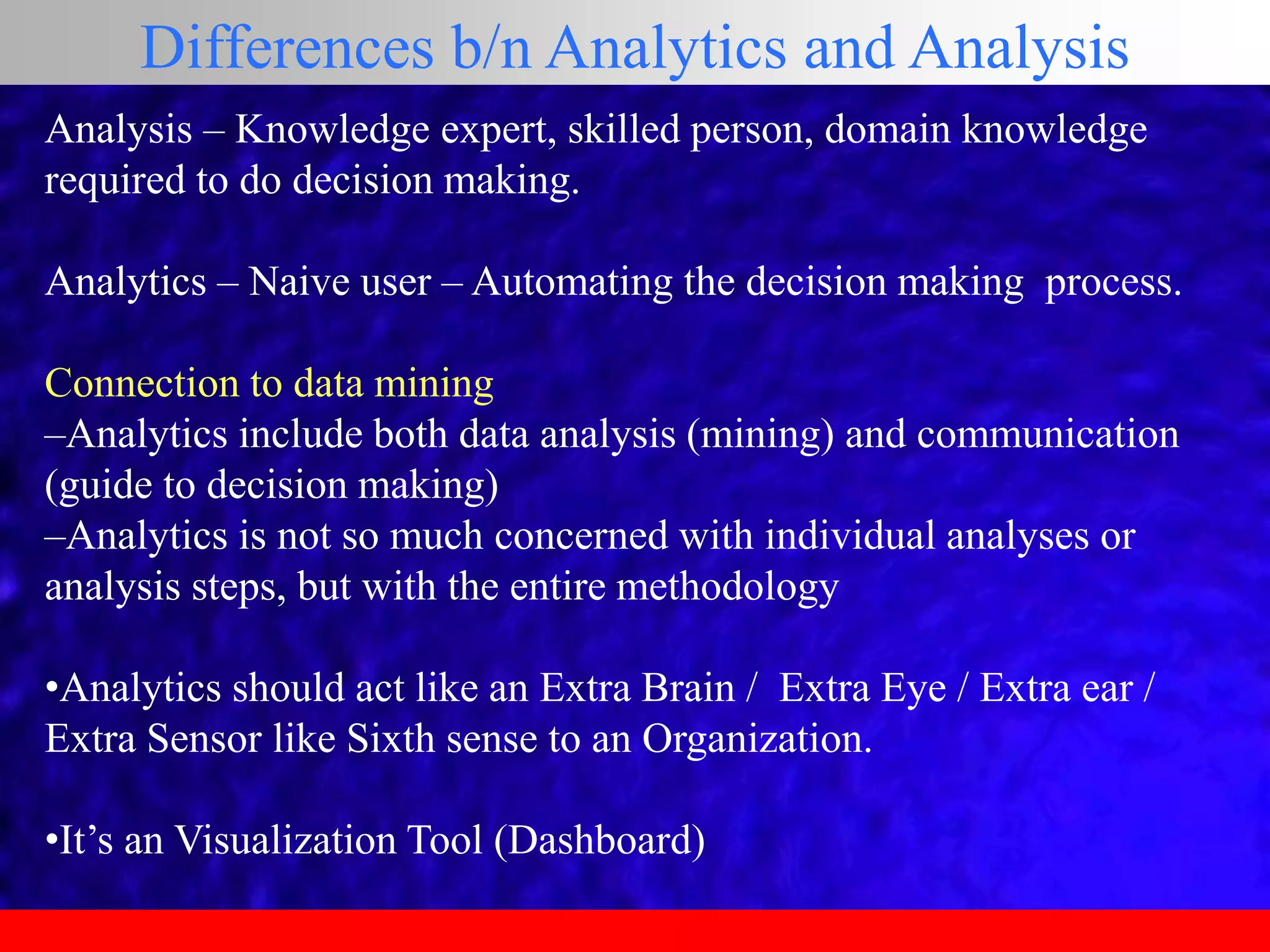
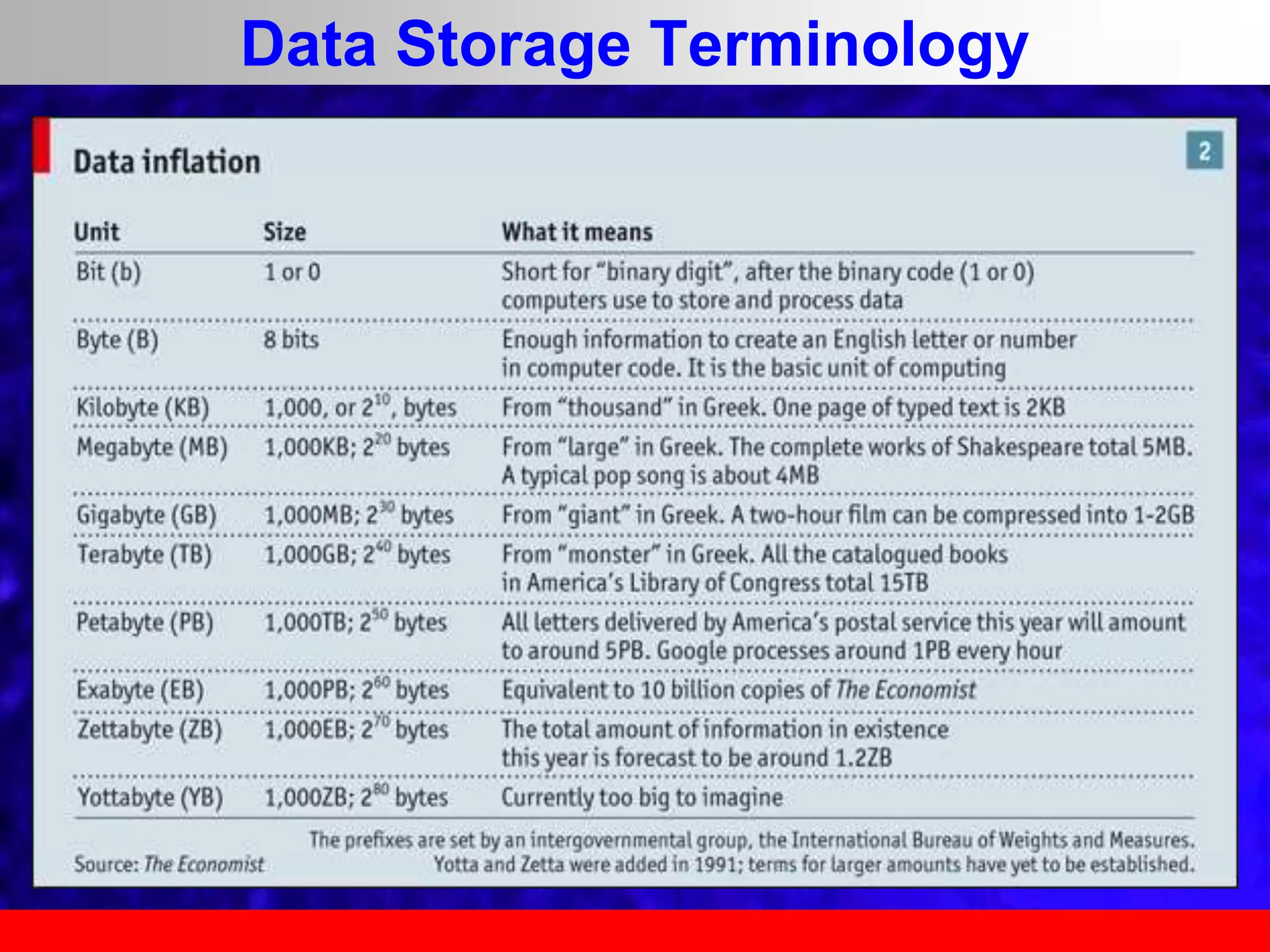
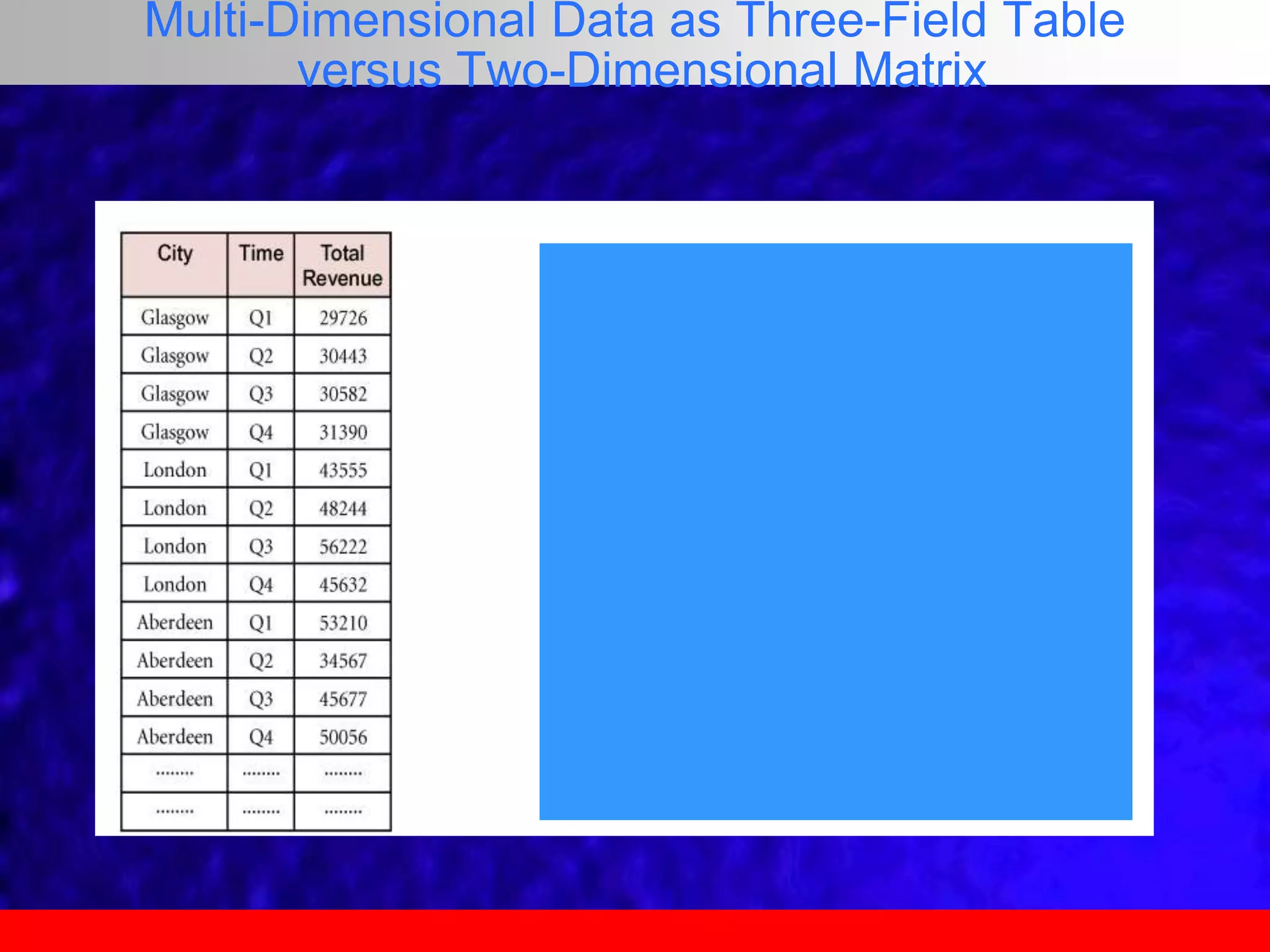
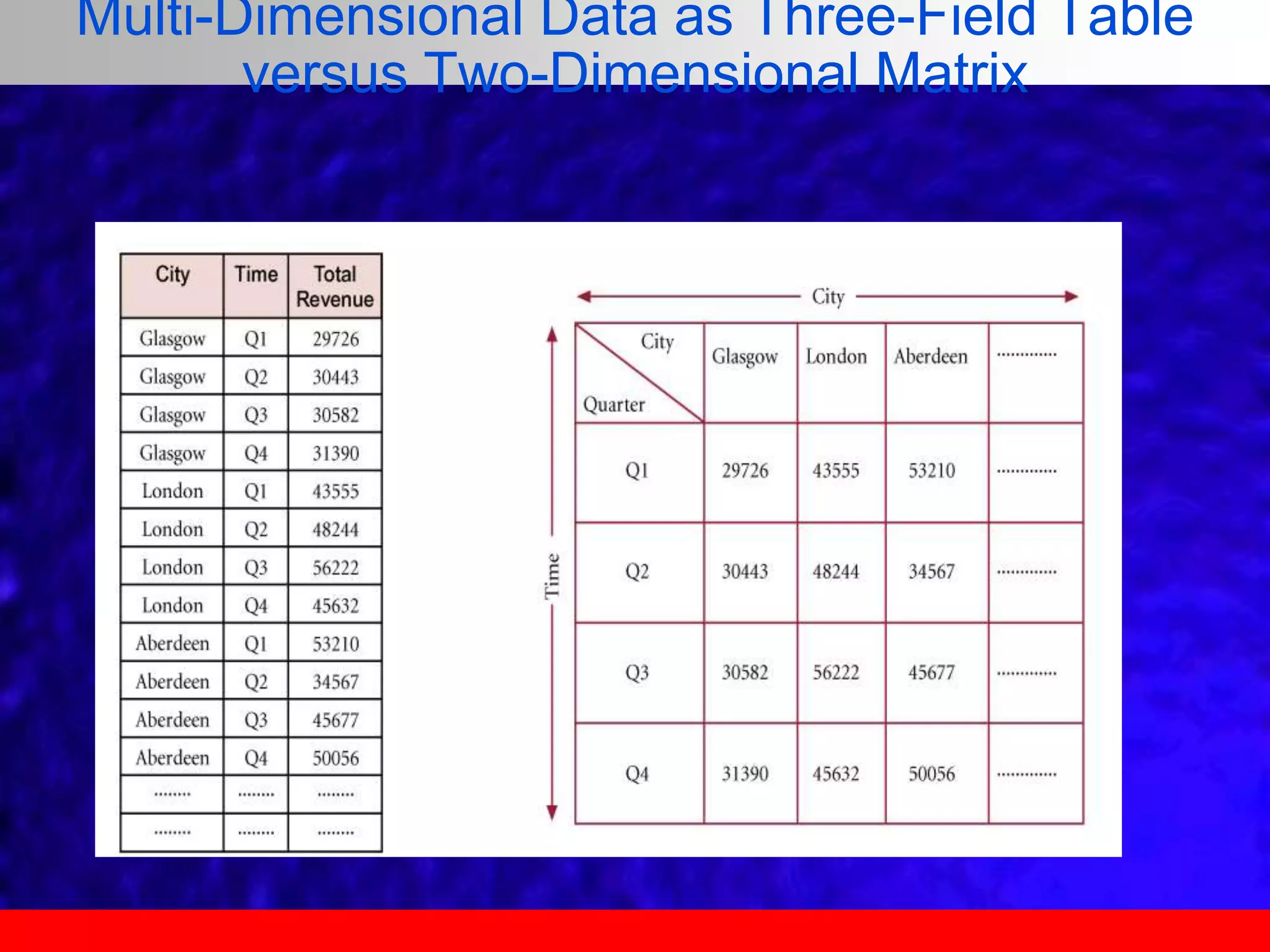
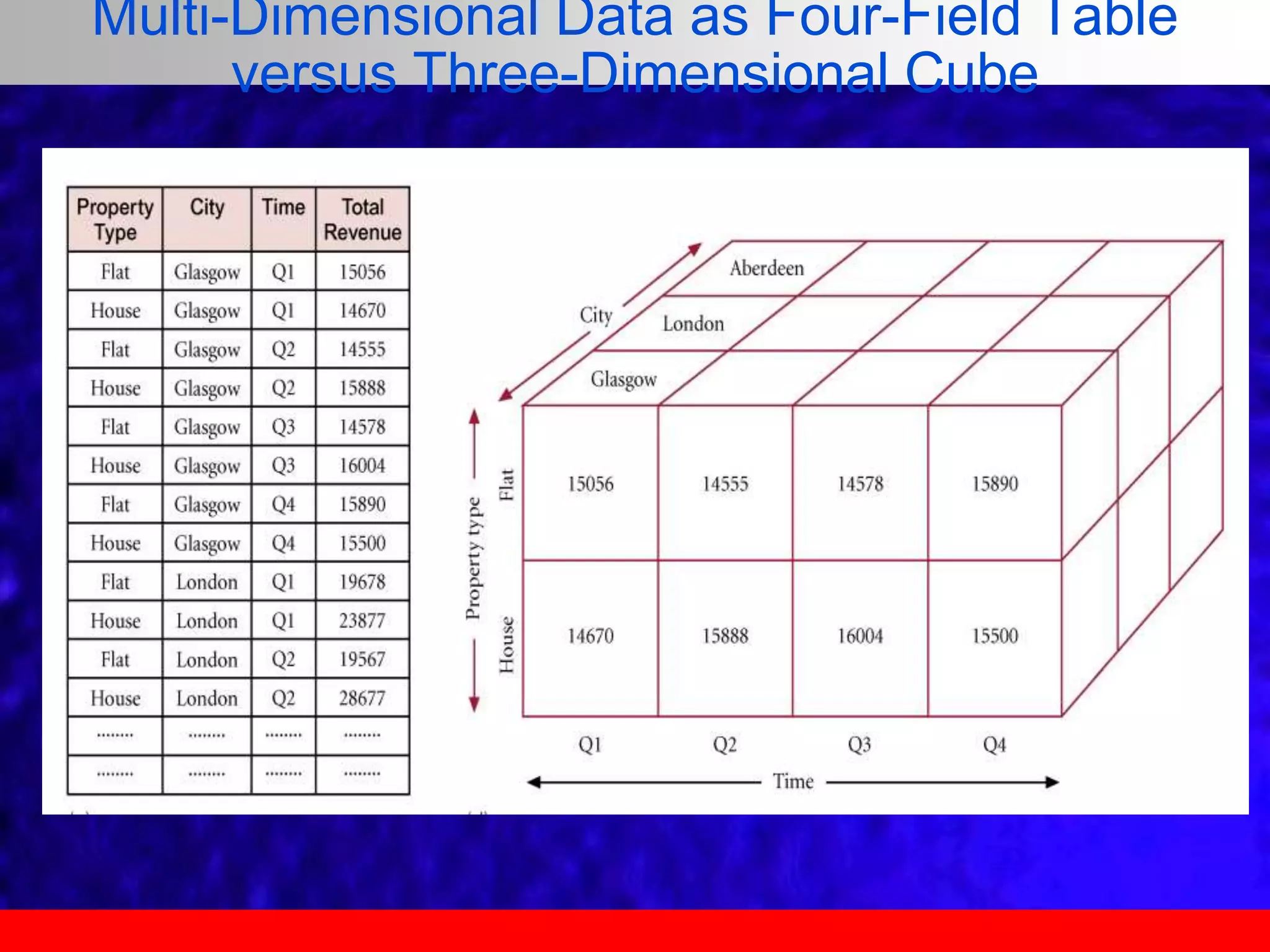
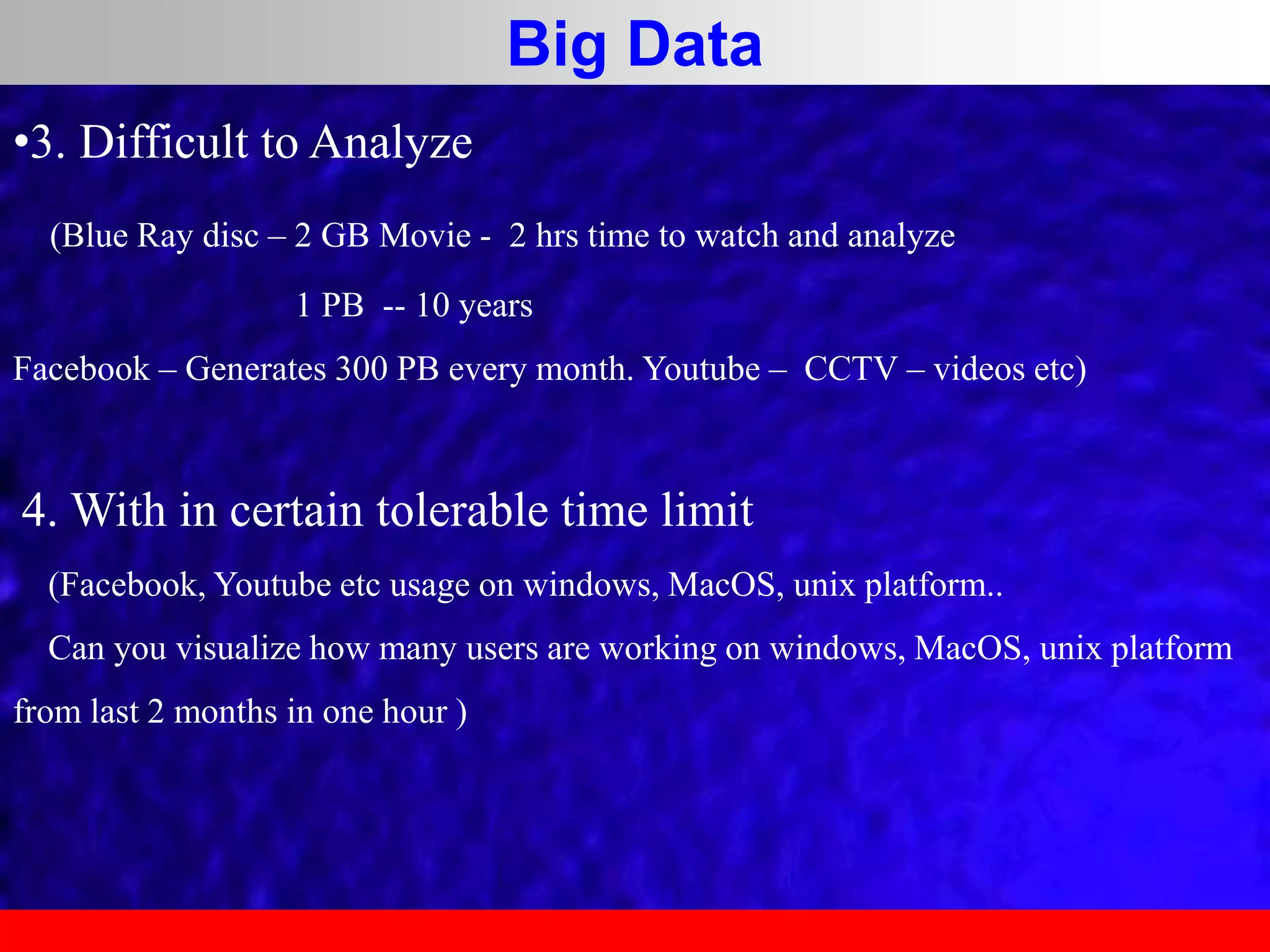
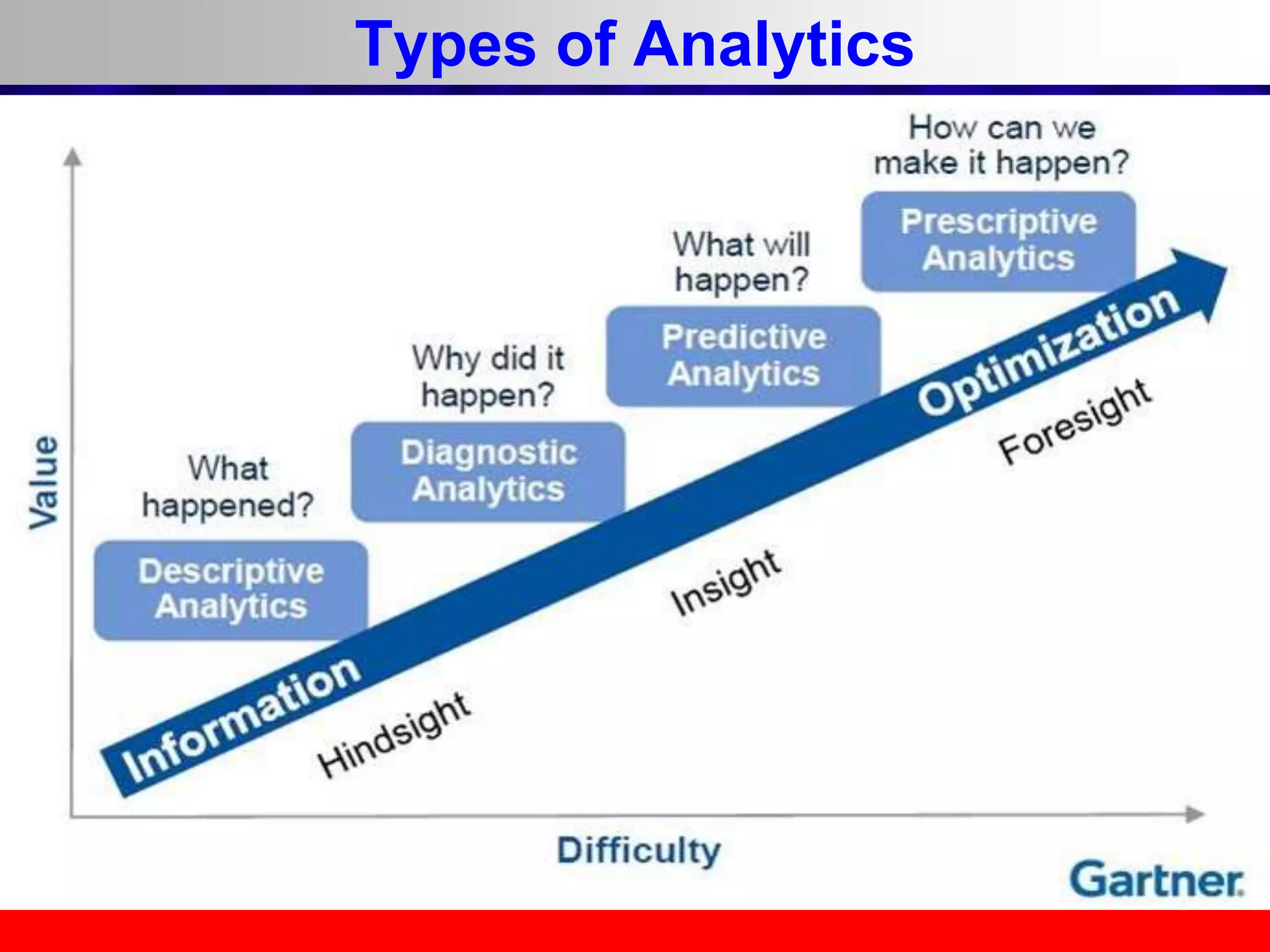
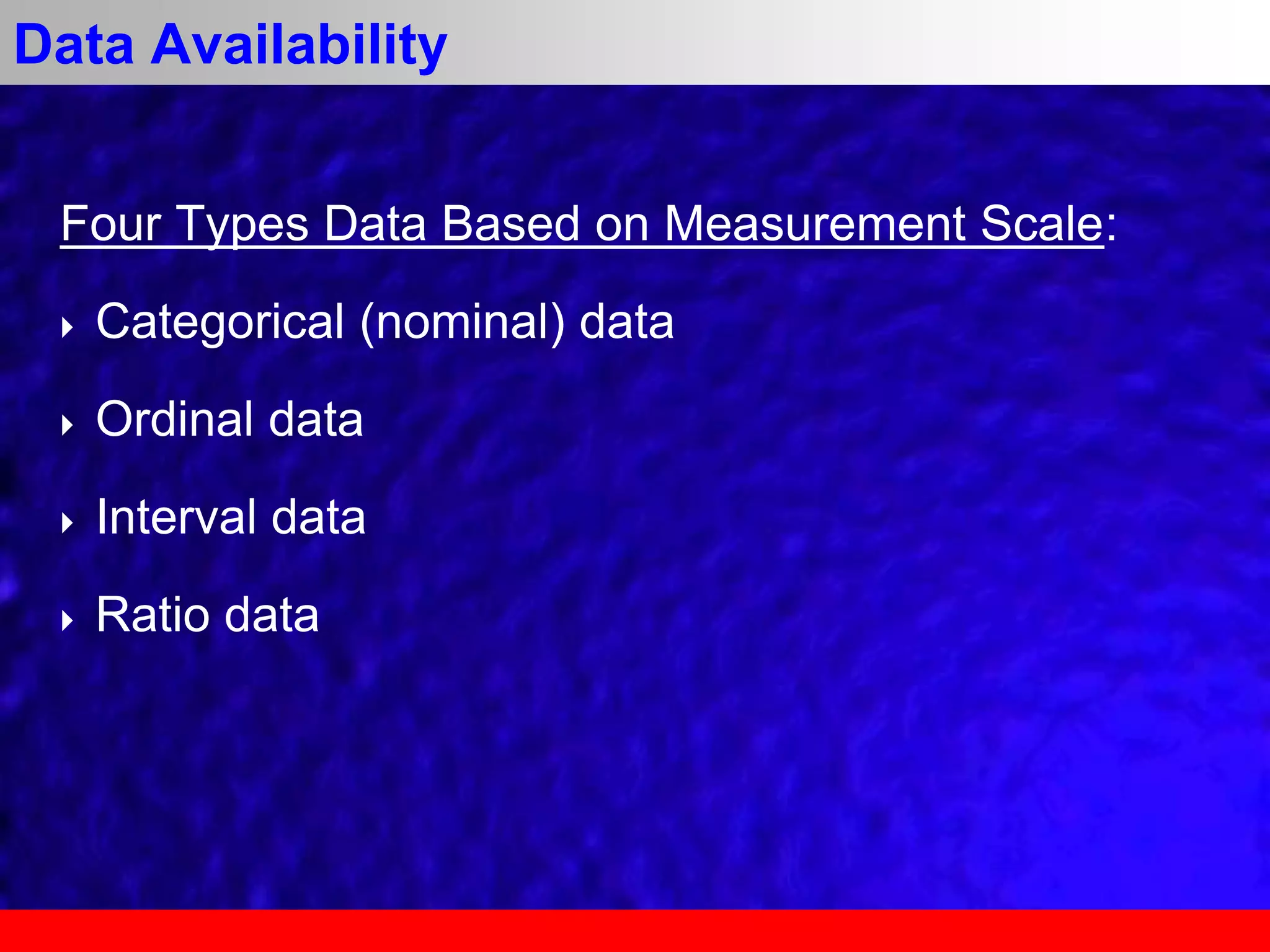
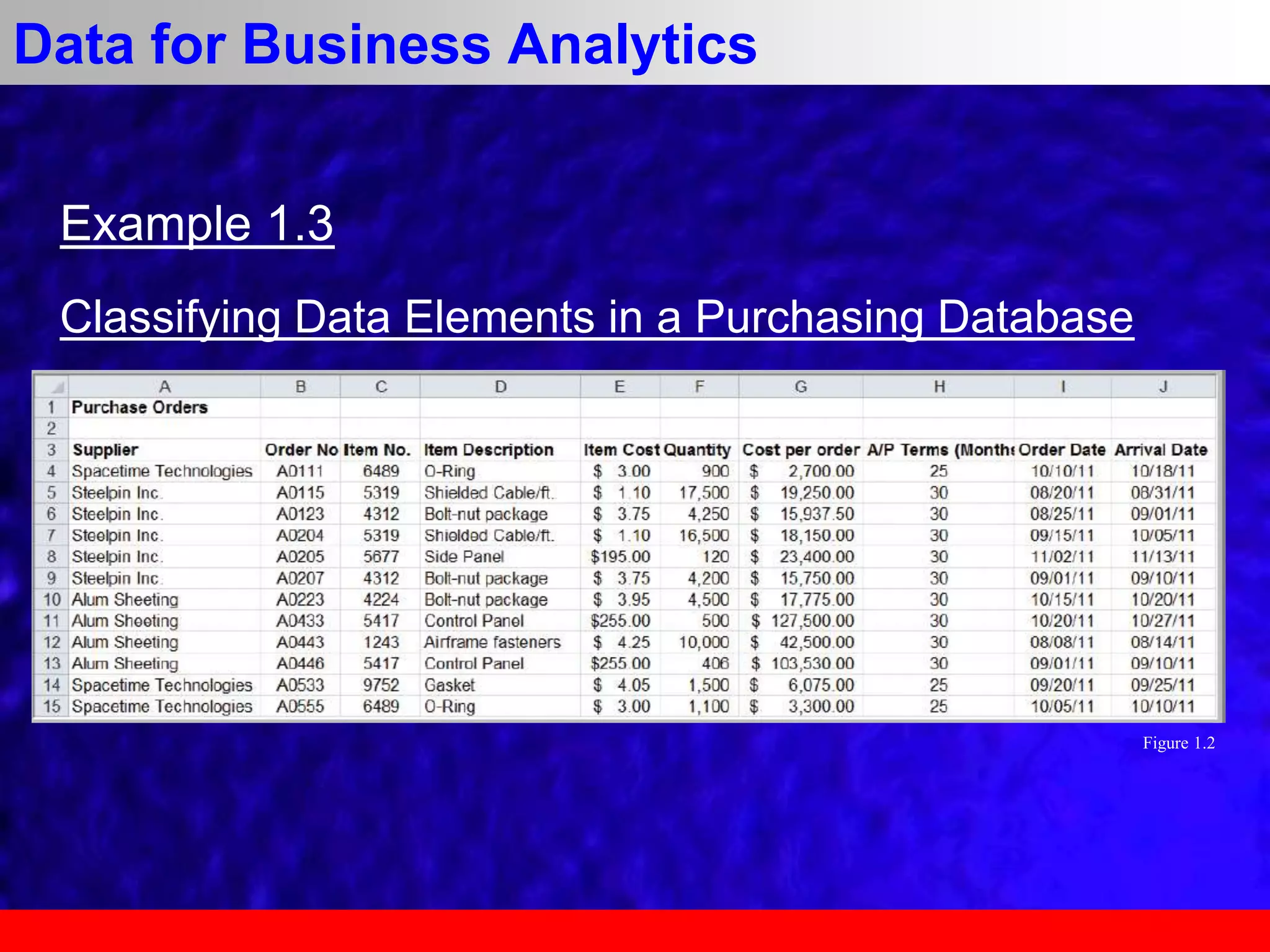
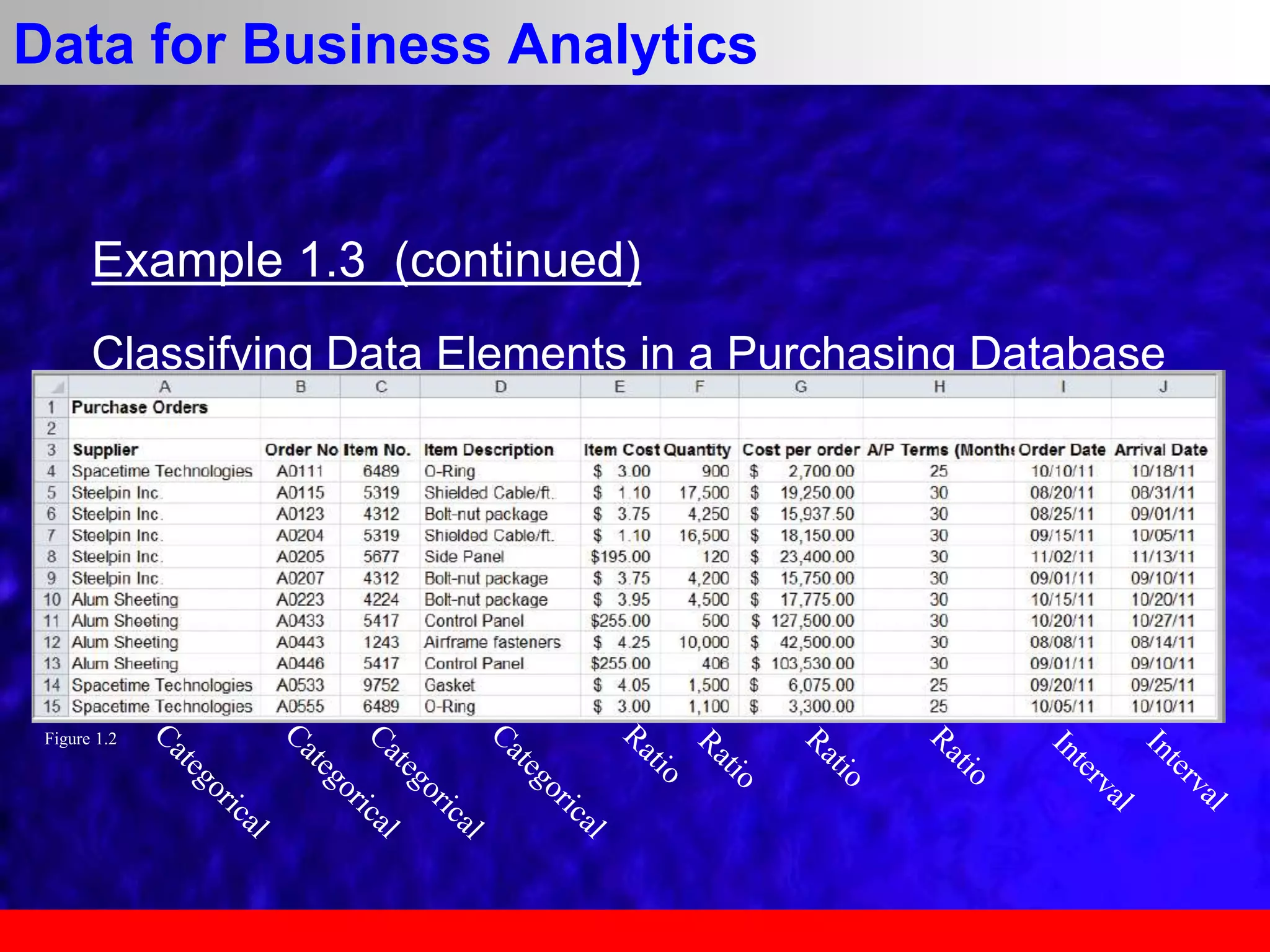
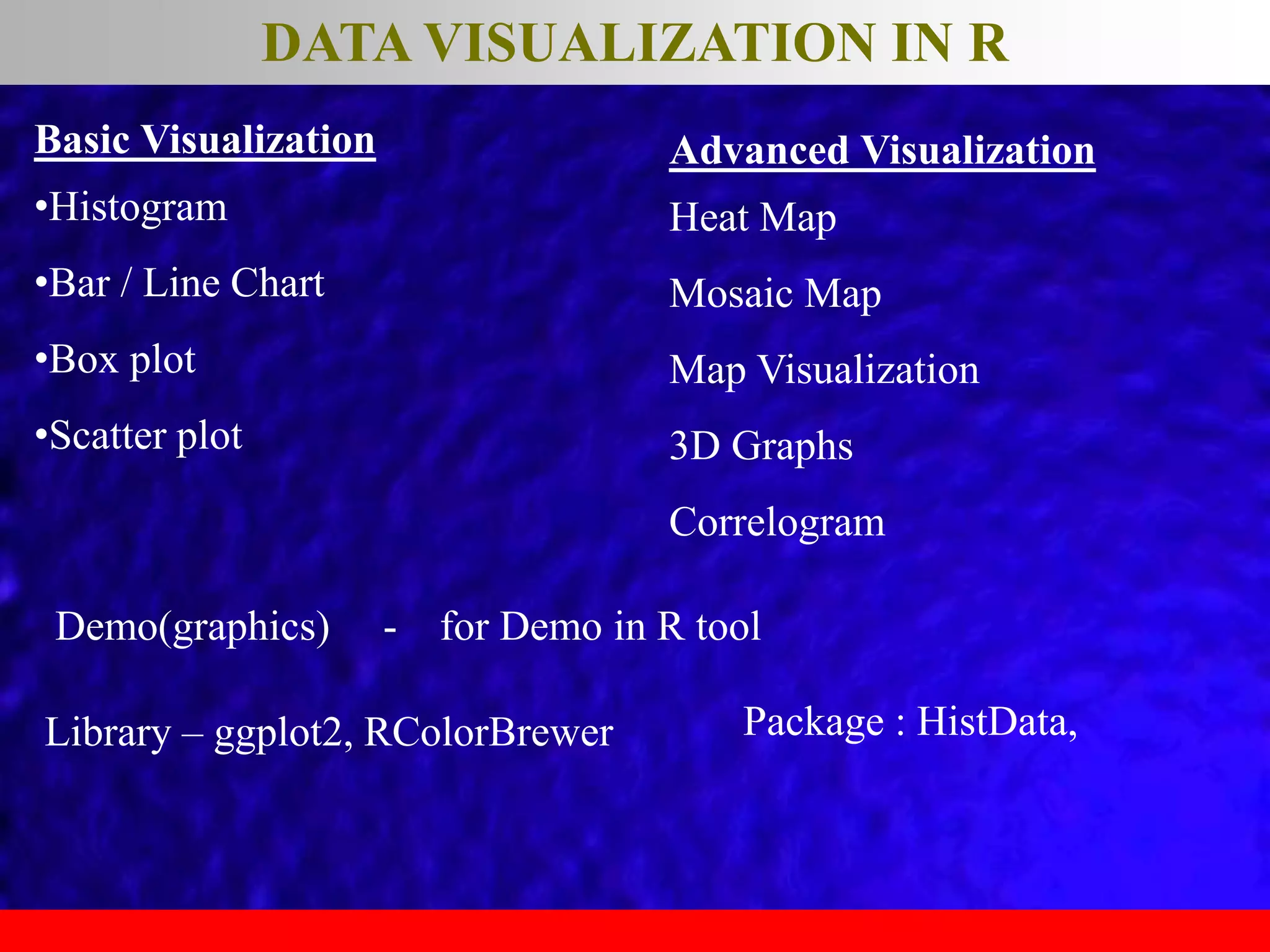
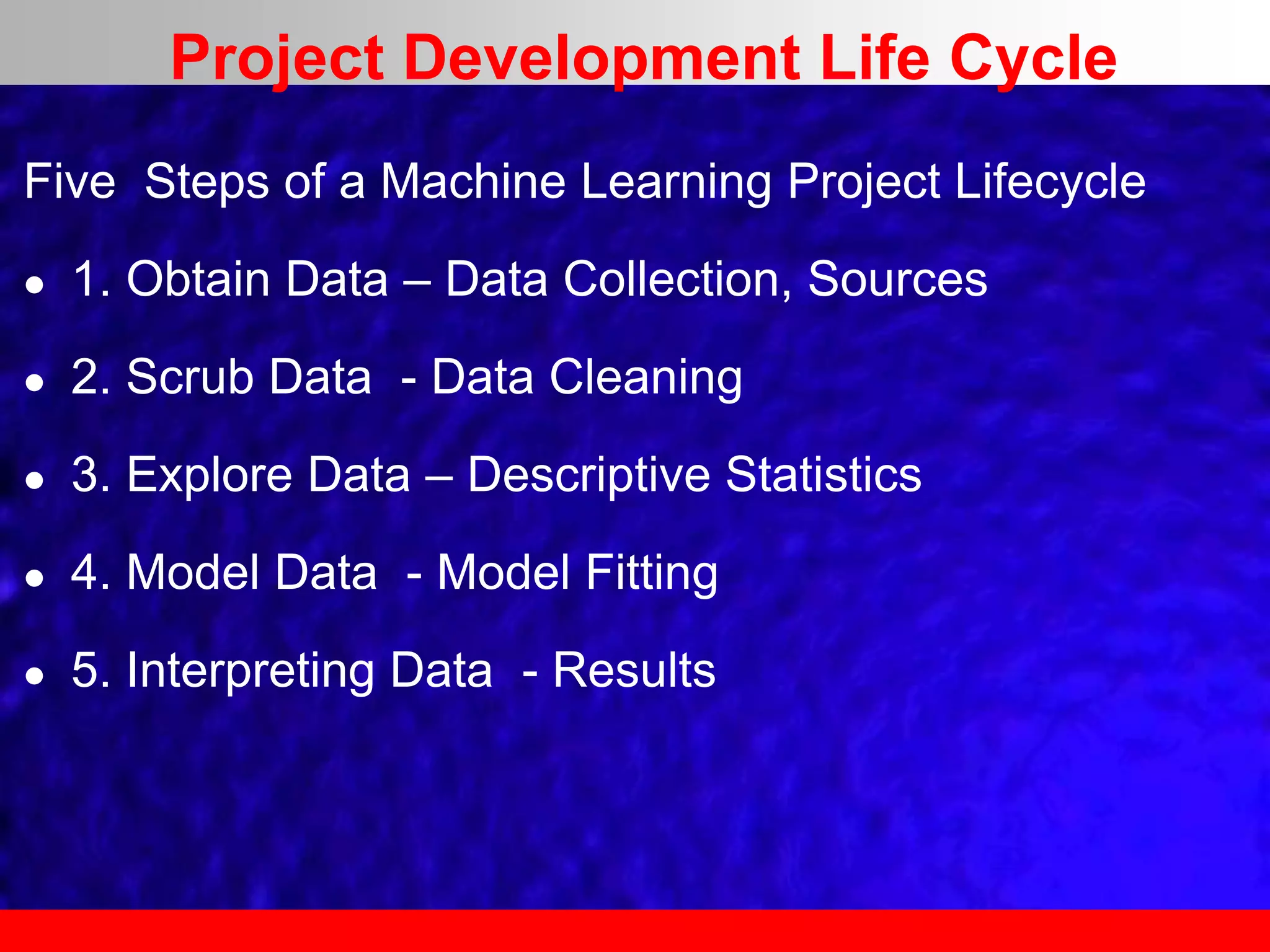
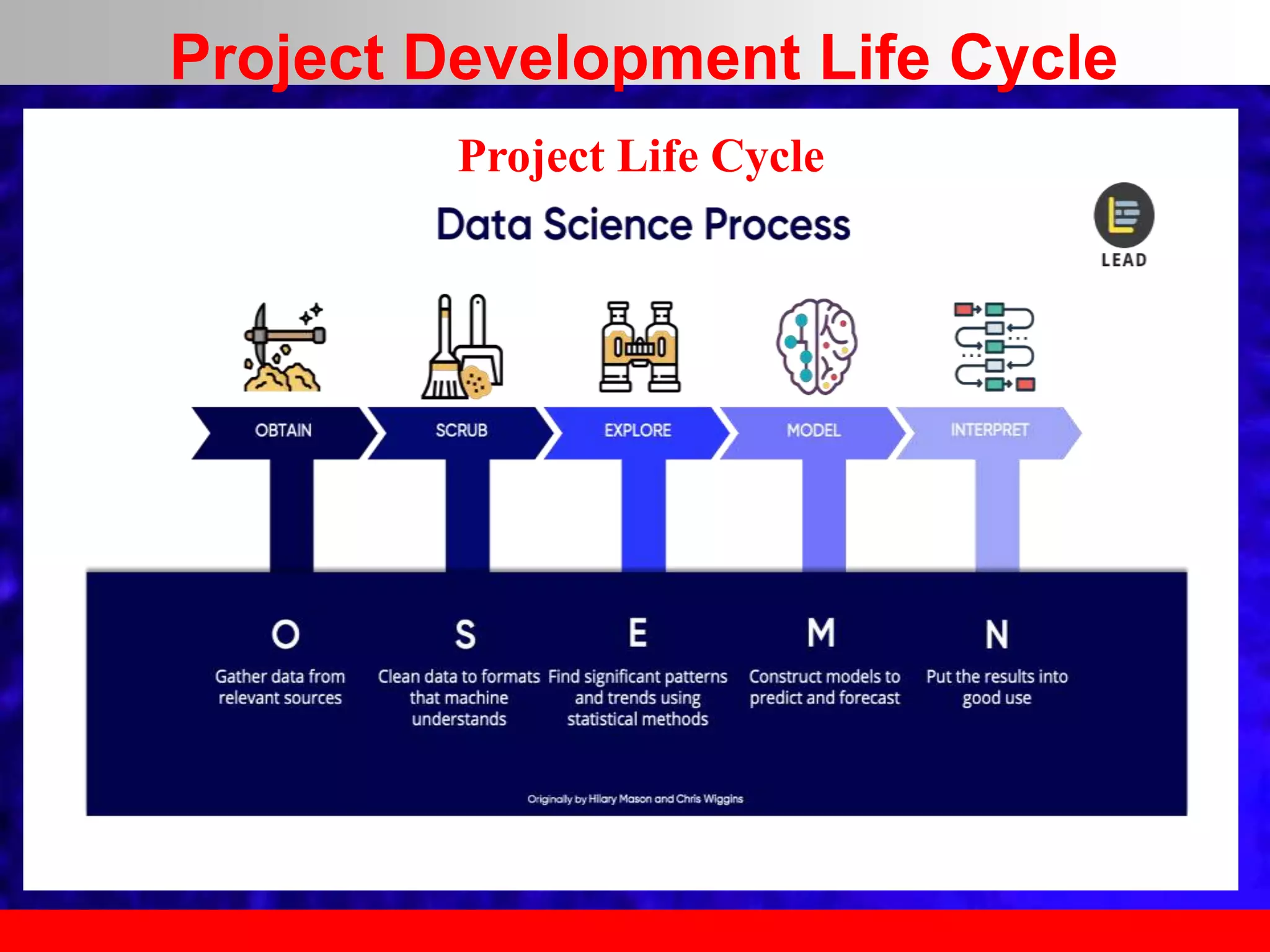
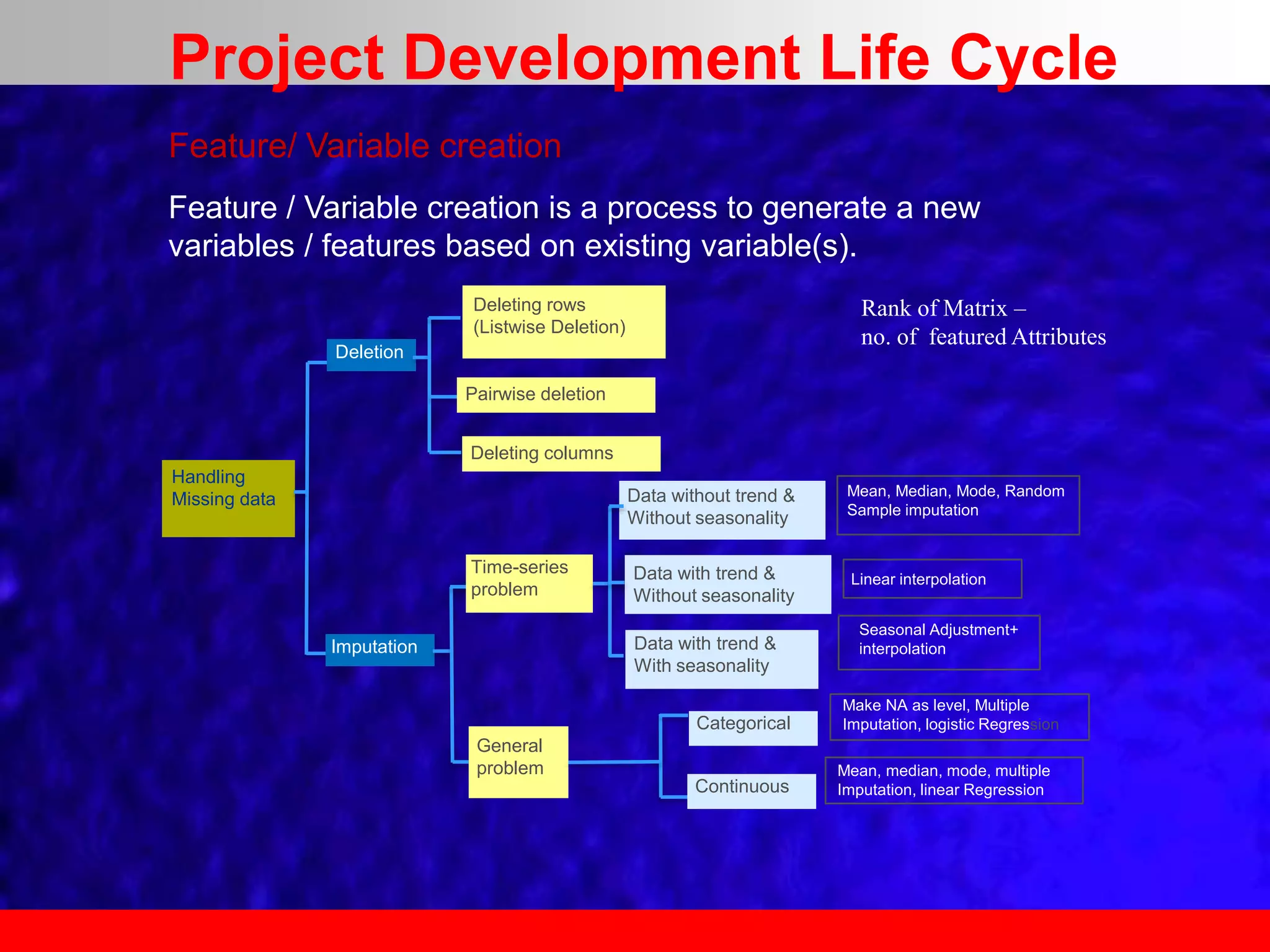
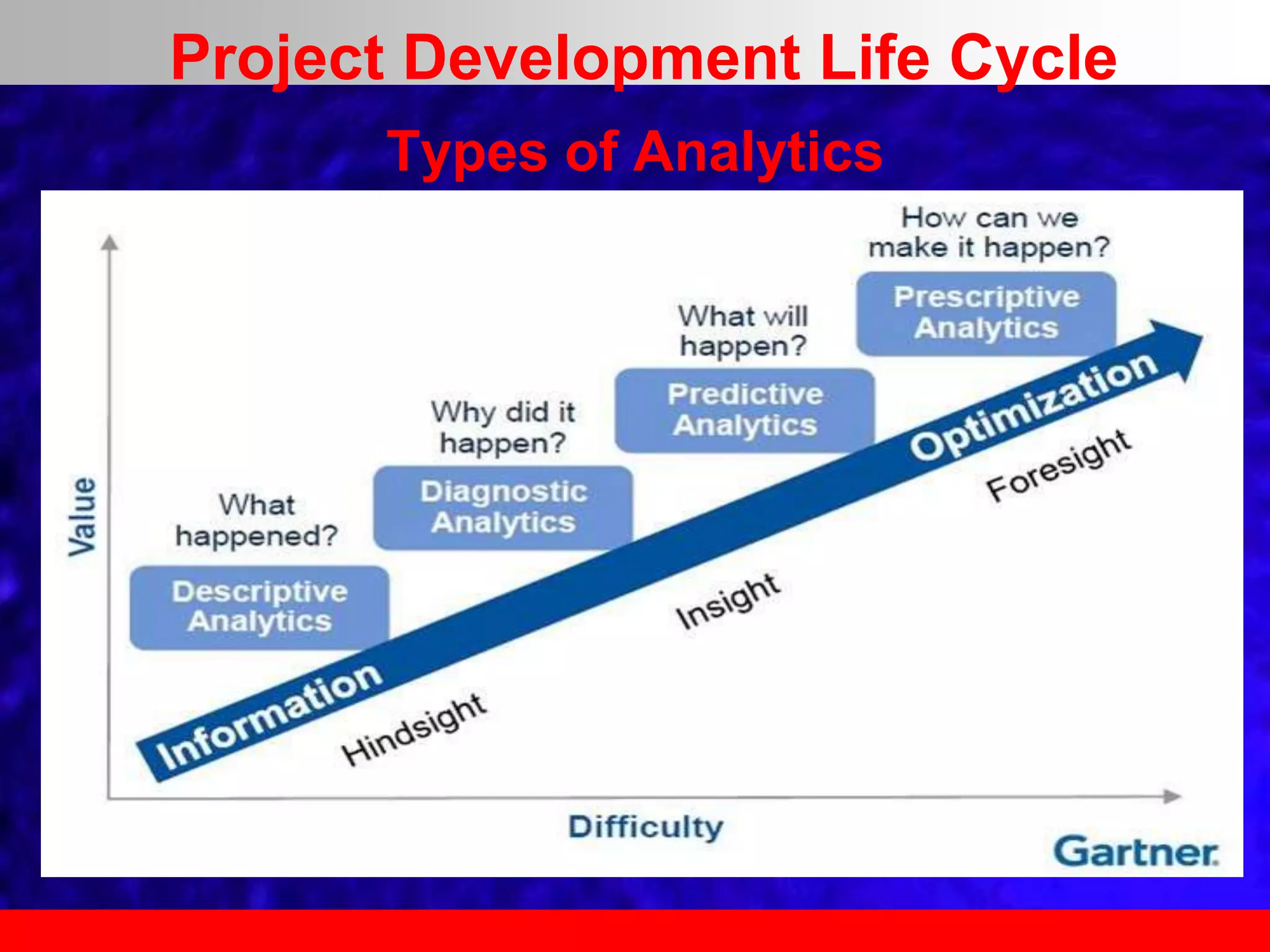
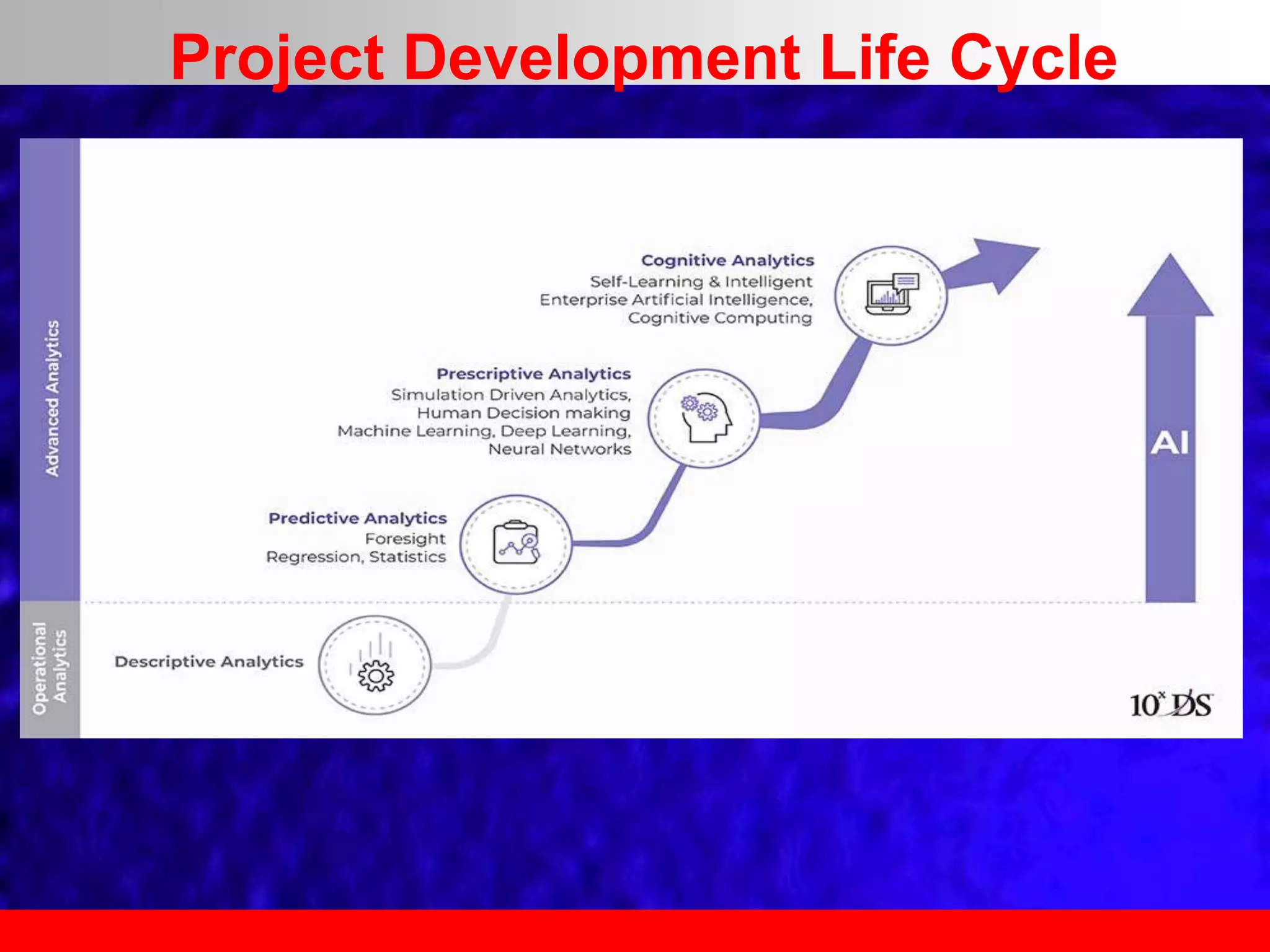
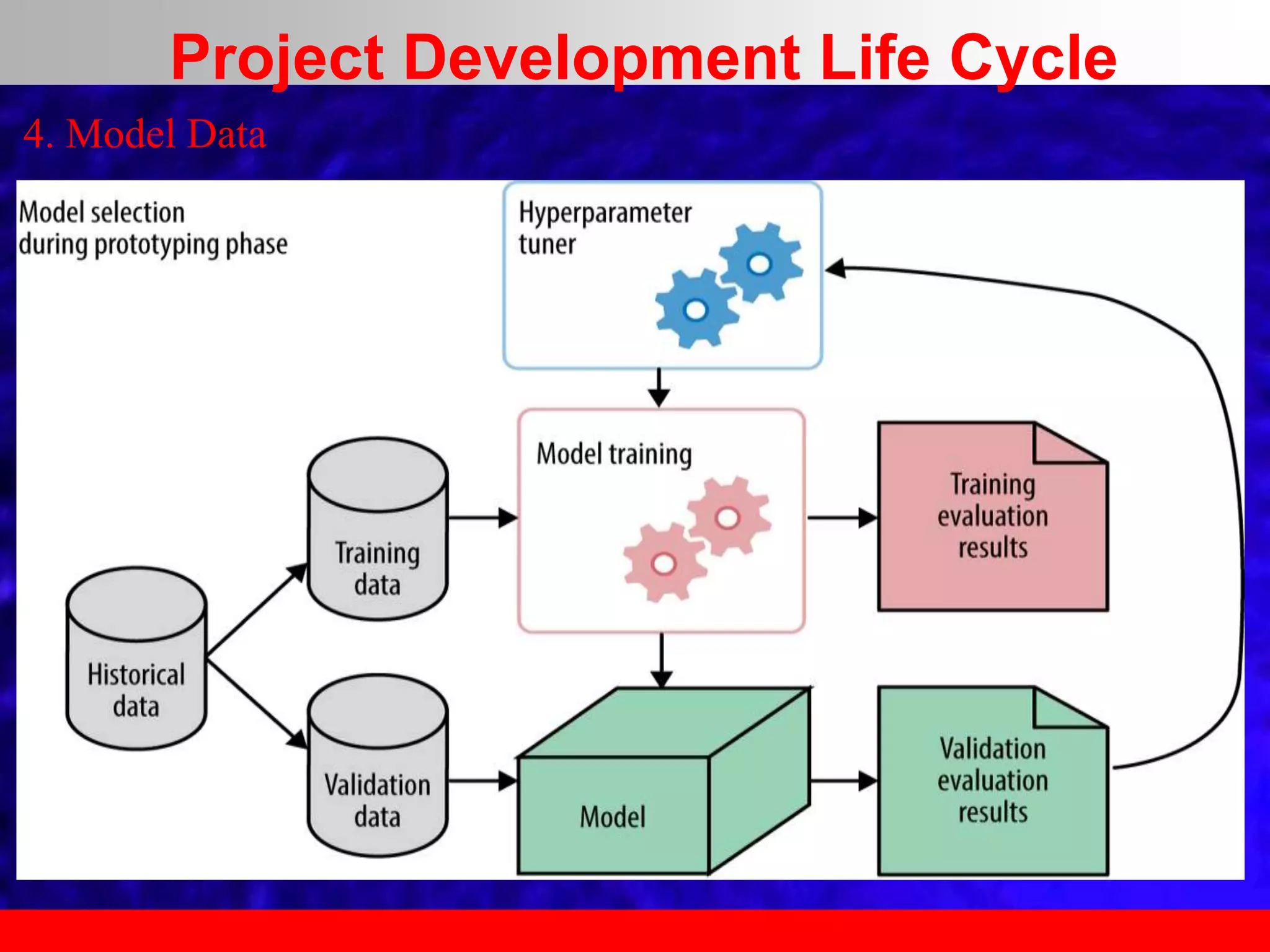
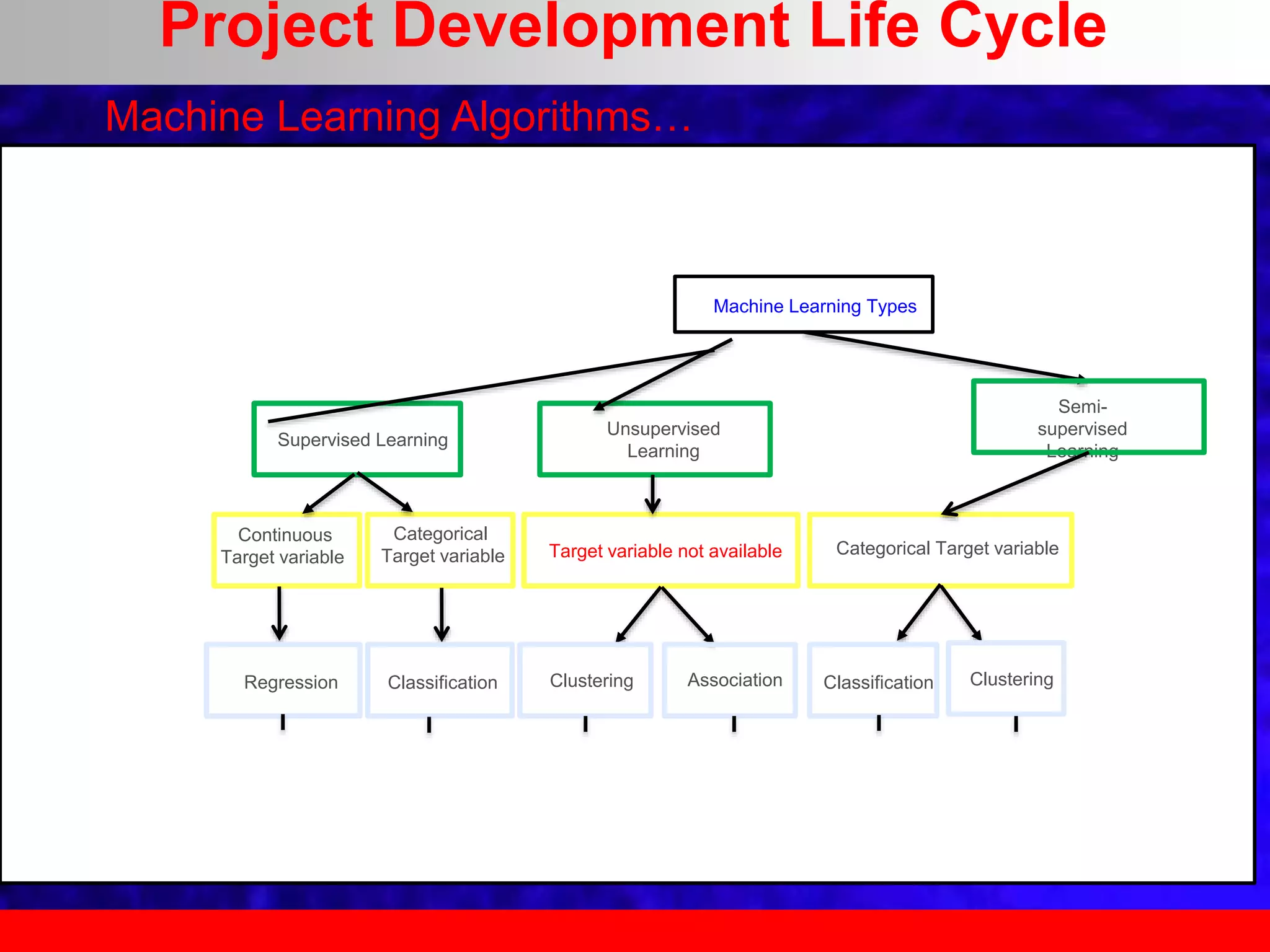
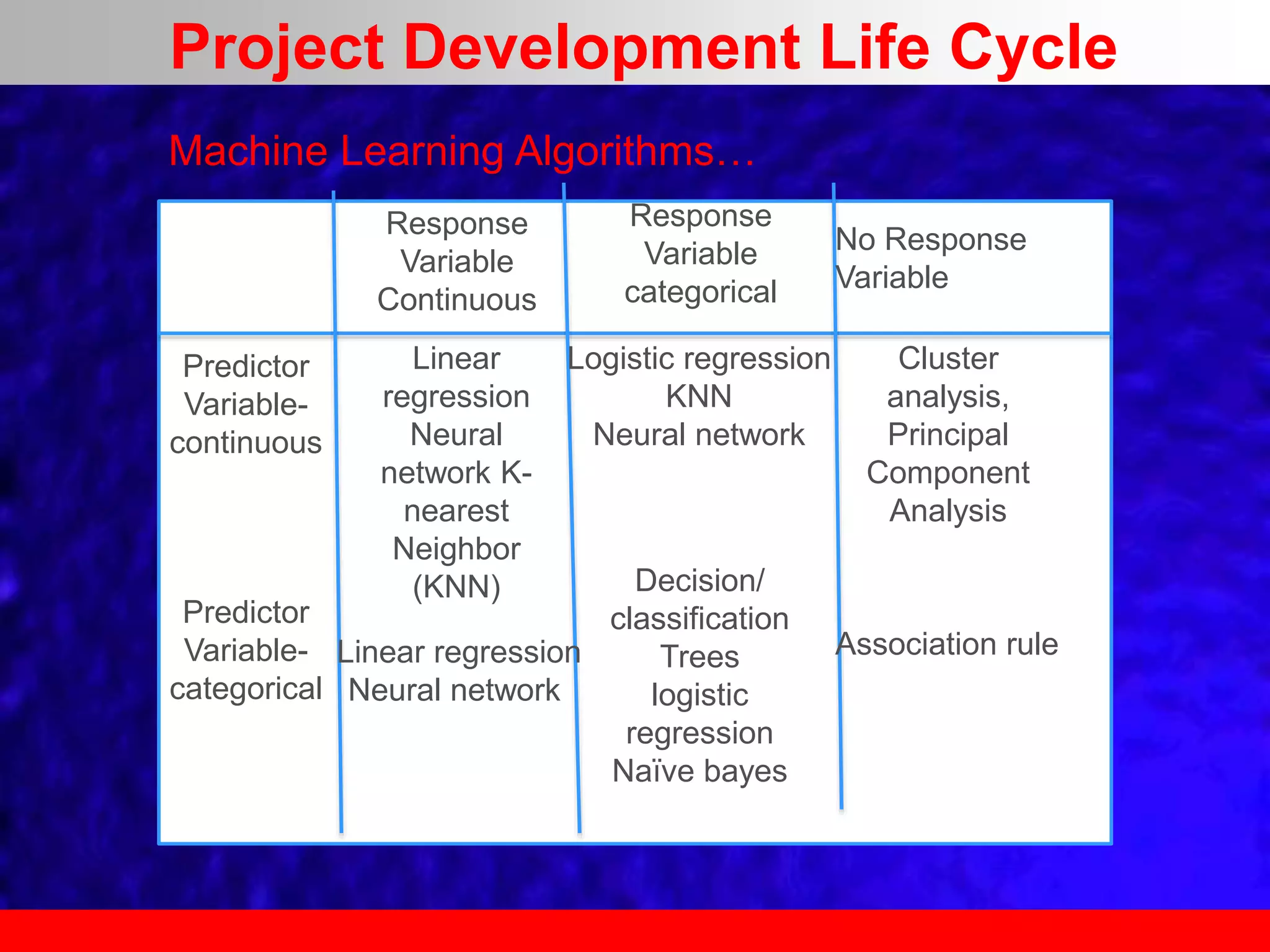
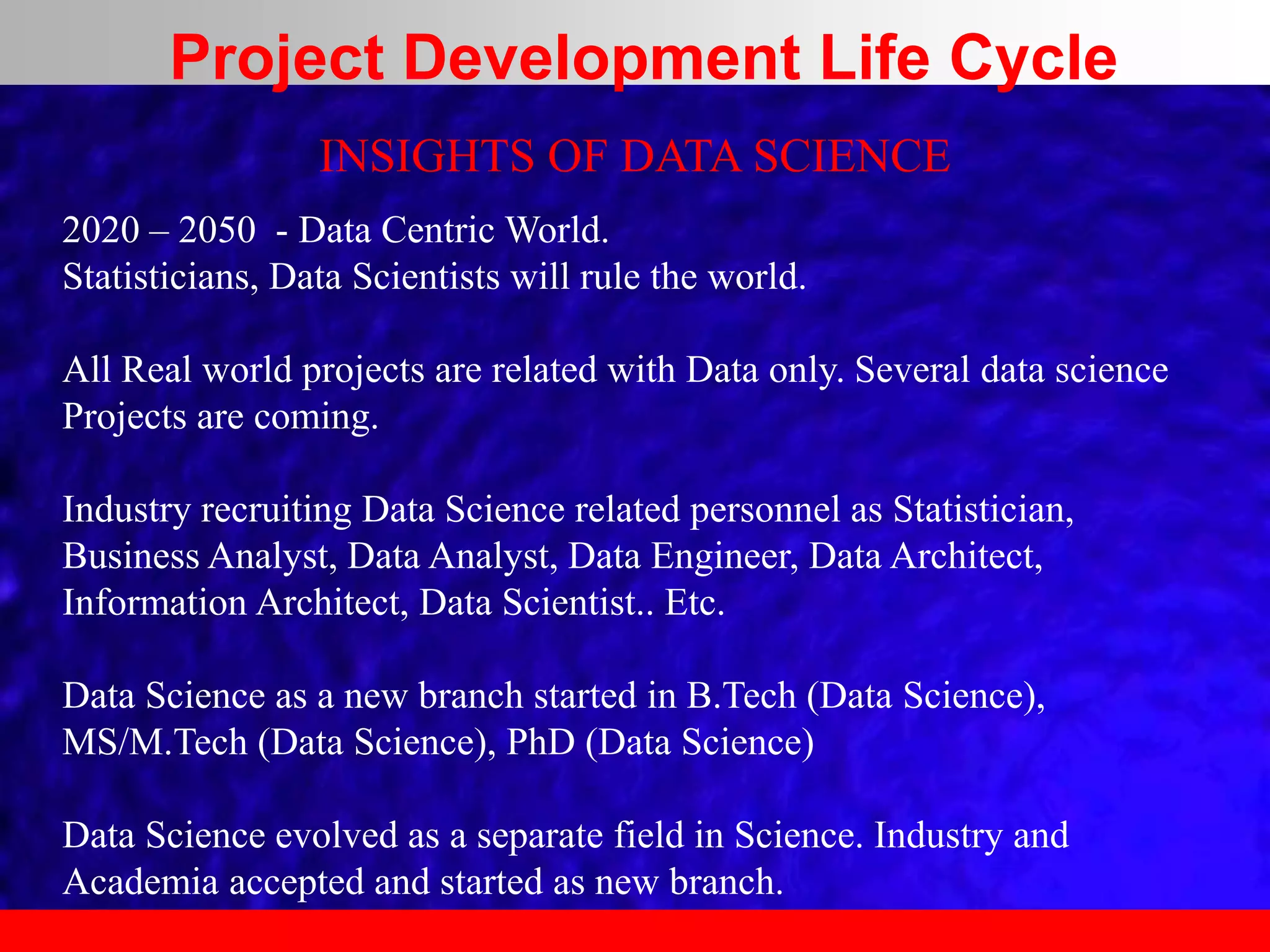
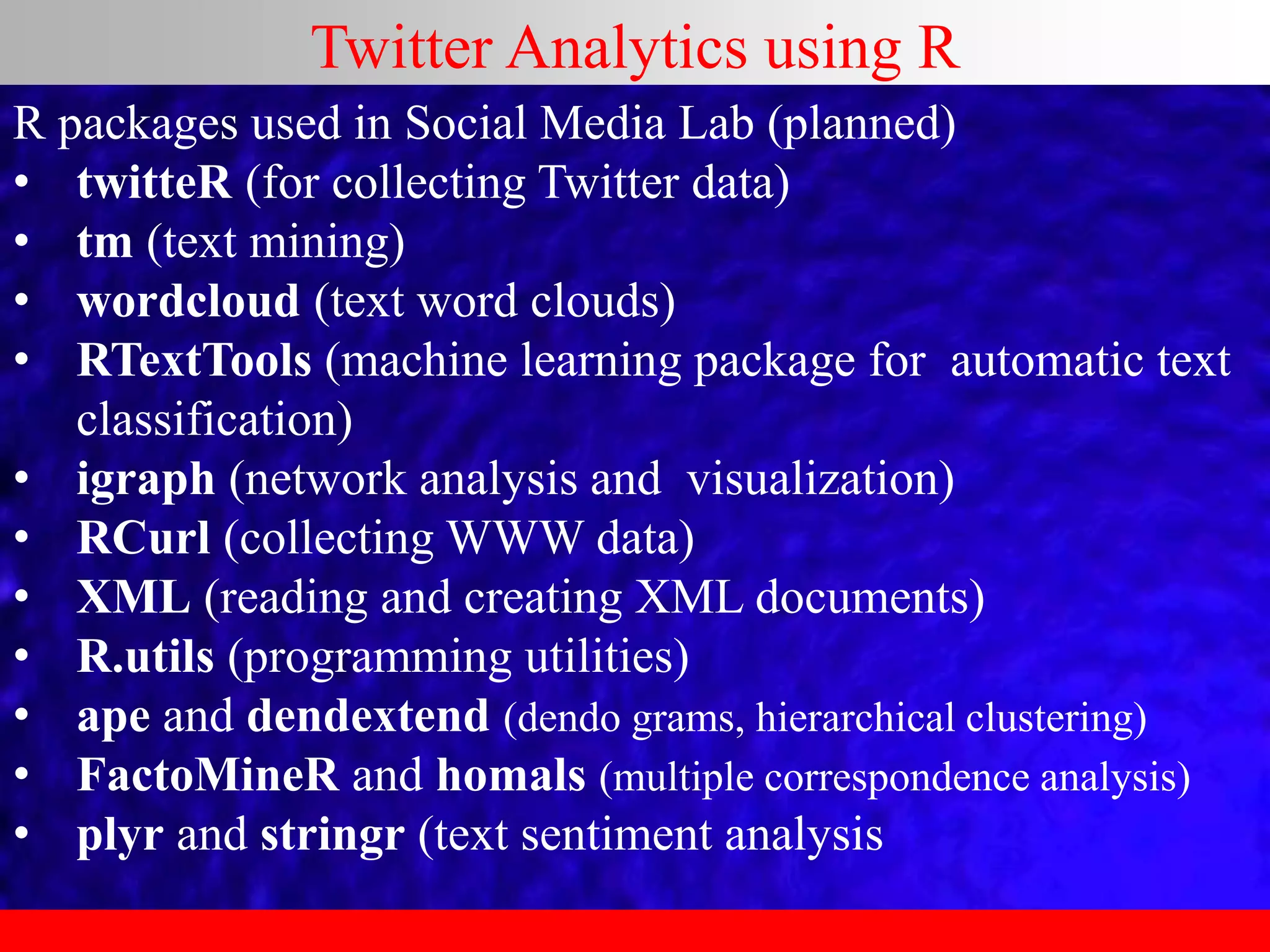
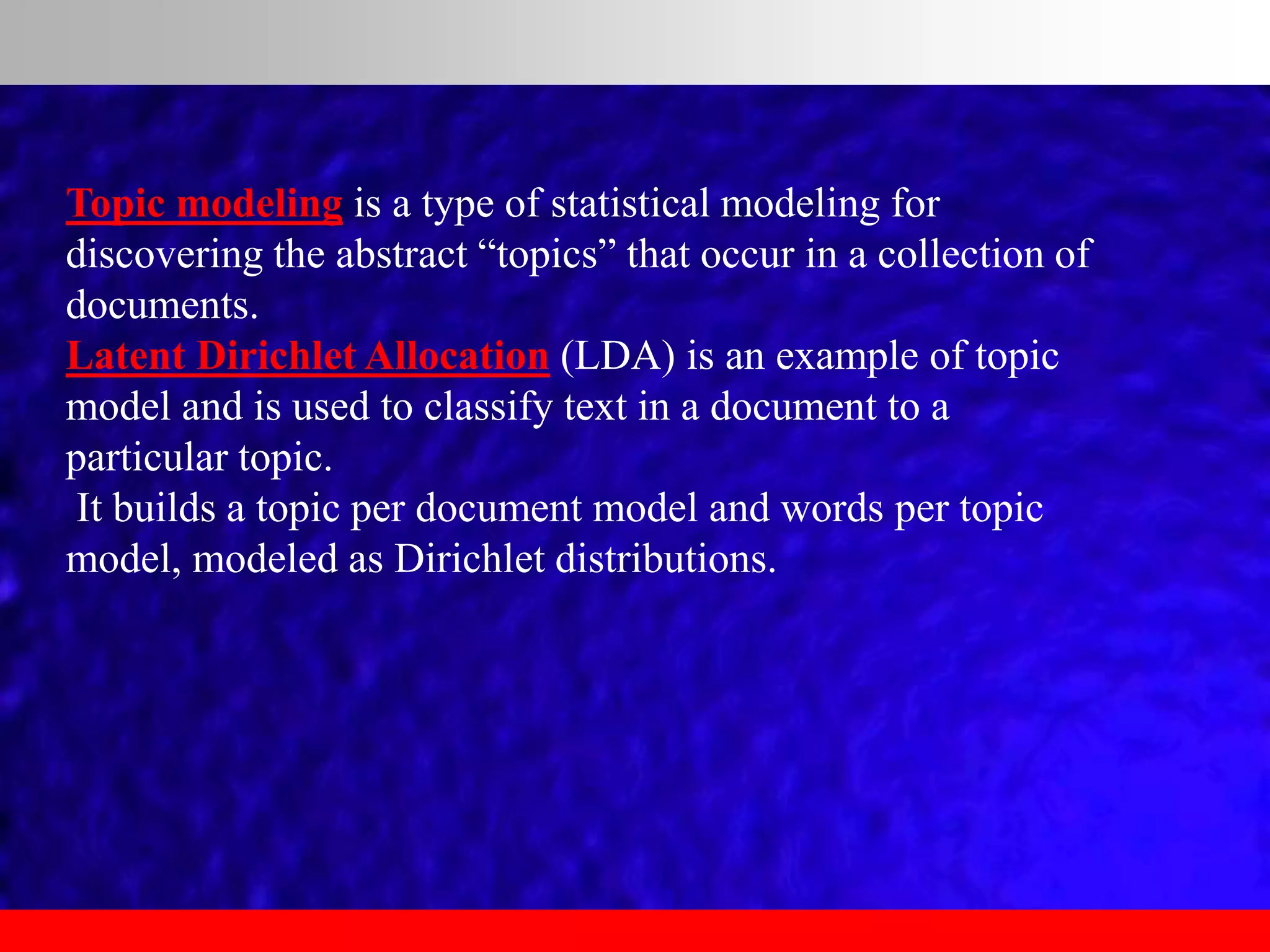
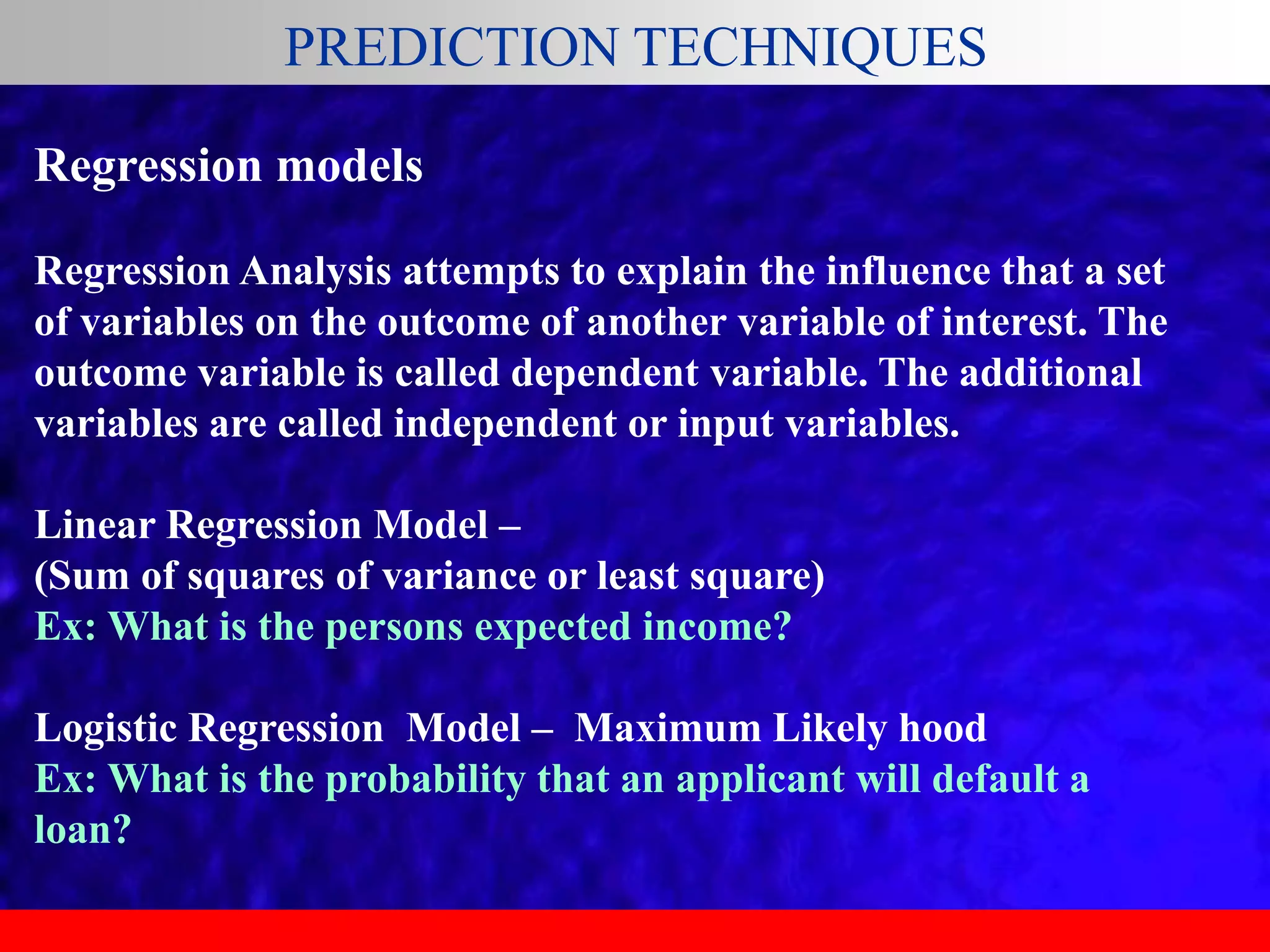
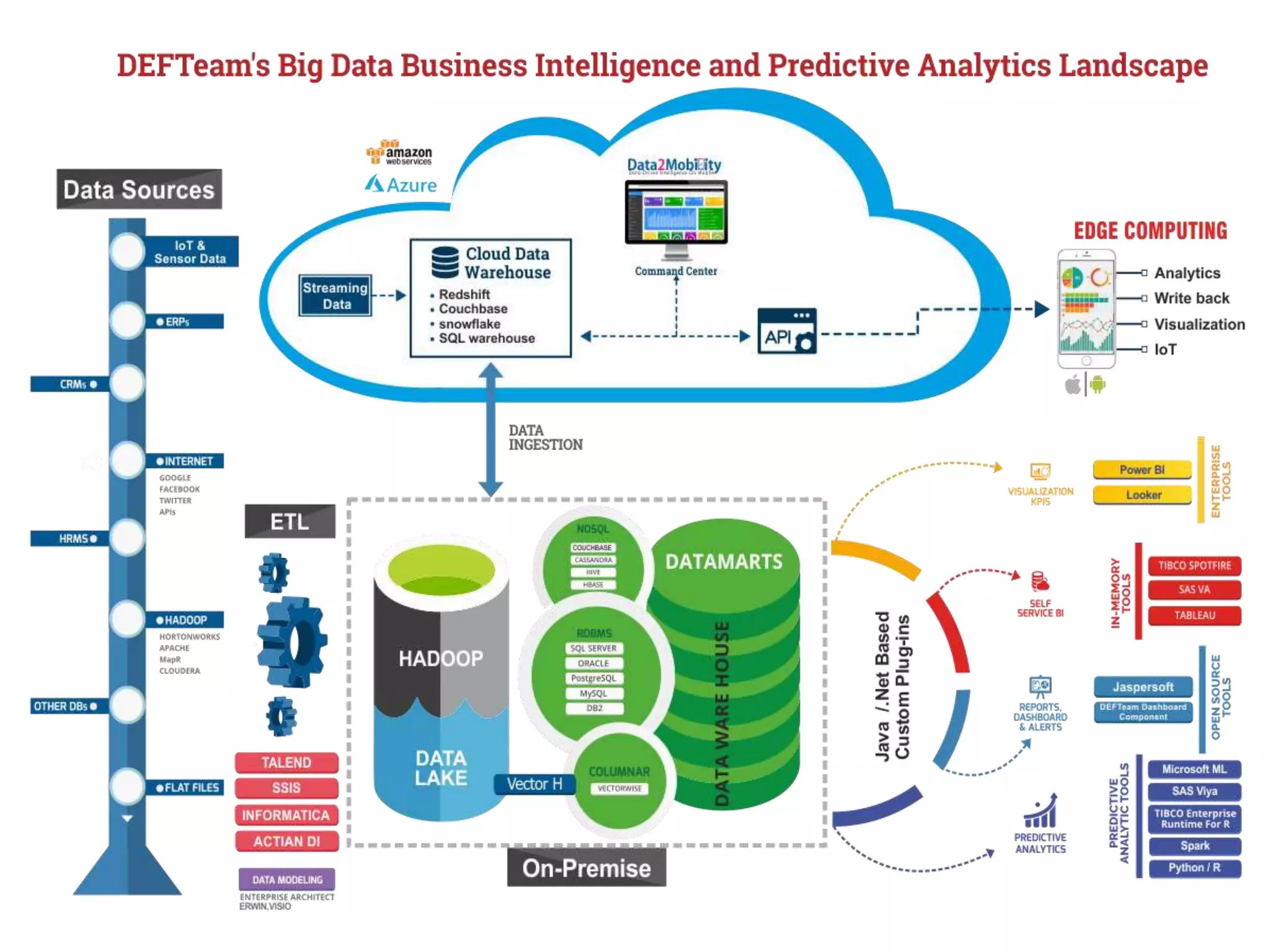
This document provides an overview of data analytics and time series analysis. It discusses the importance of topics like data science, analytics, and analysis. It covers key concepts in data analytics including data types, storage, visualization, and big data. It also discusses machine learning, predictive modeling techniques, and the typical lifecycle of a machine learning project including obtaining data, data cleaning, exploration, modeling, and interpreting results. The goal is to understand and discover useful insights from data to support decision making.