Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX


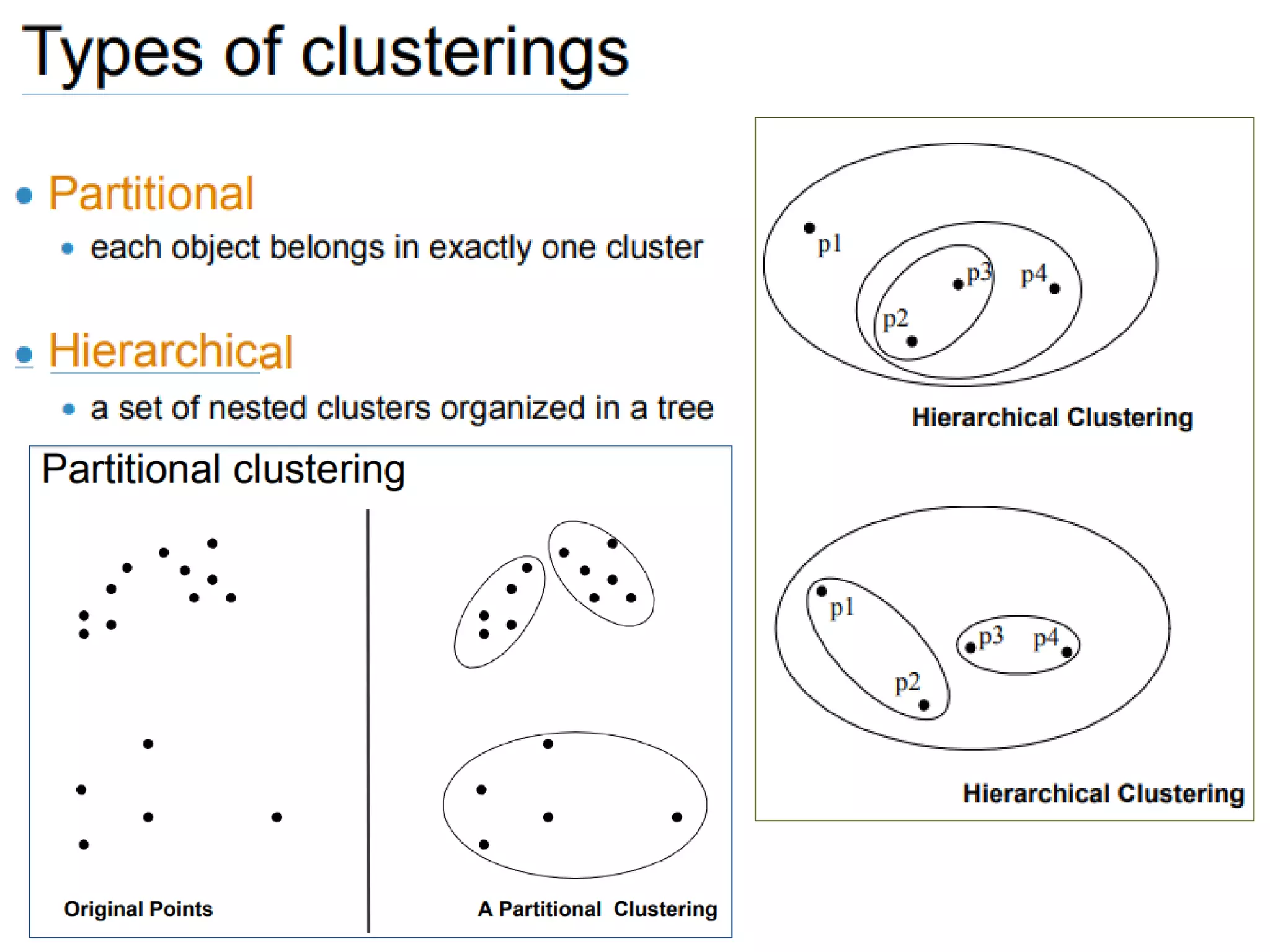
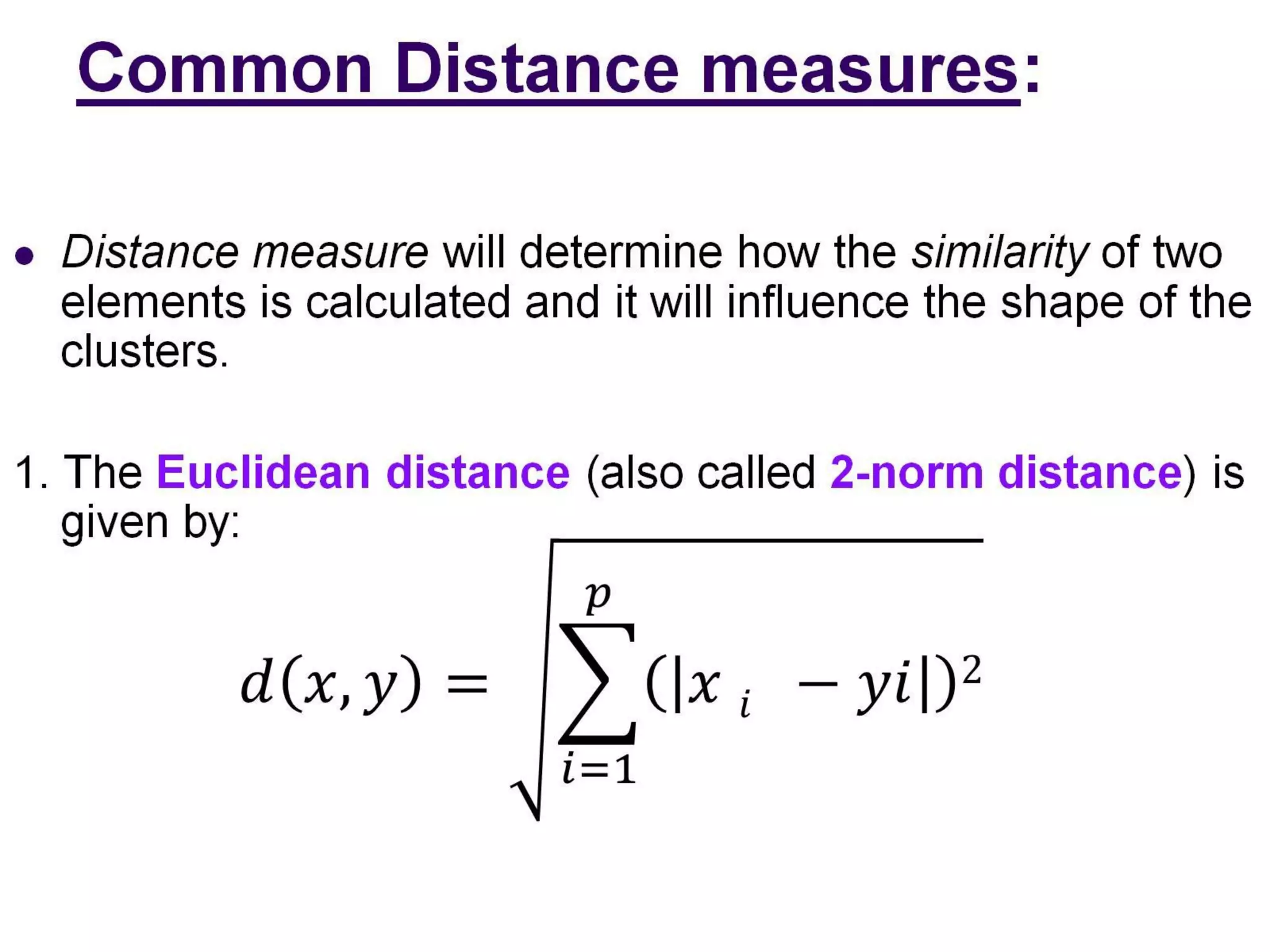

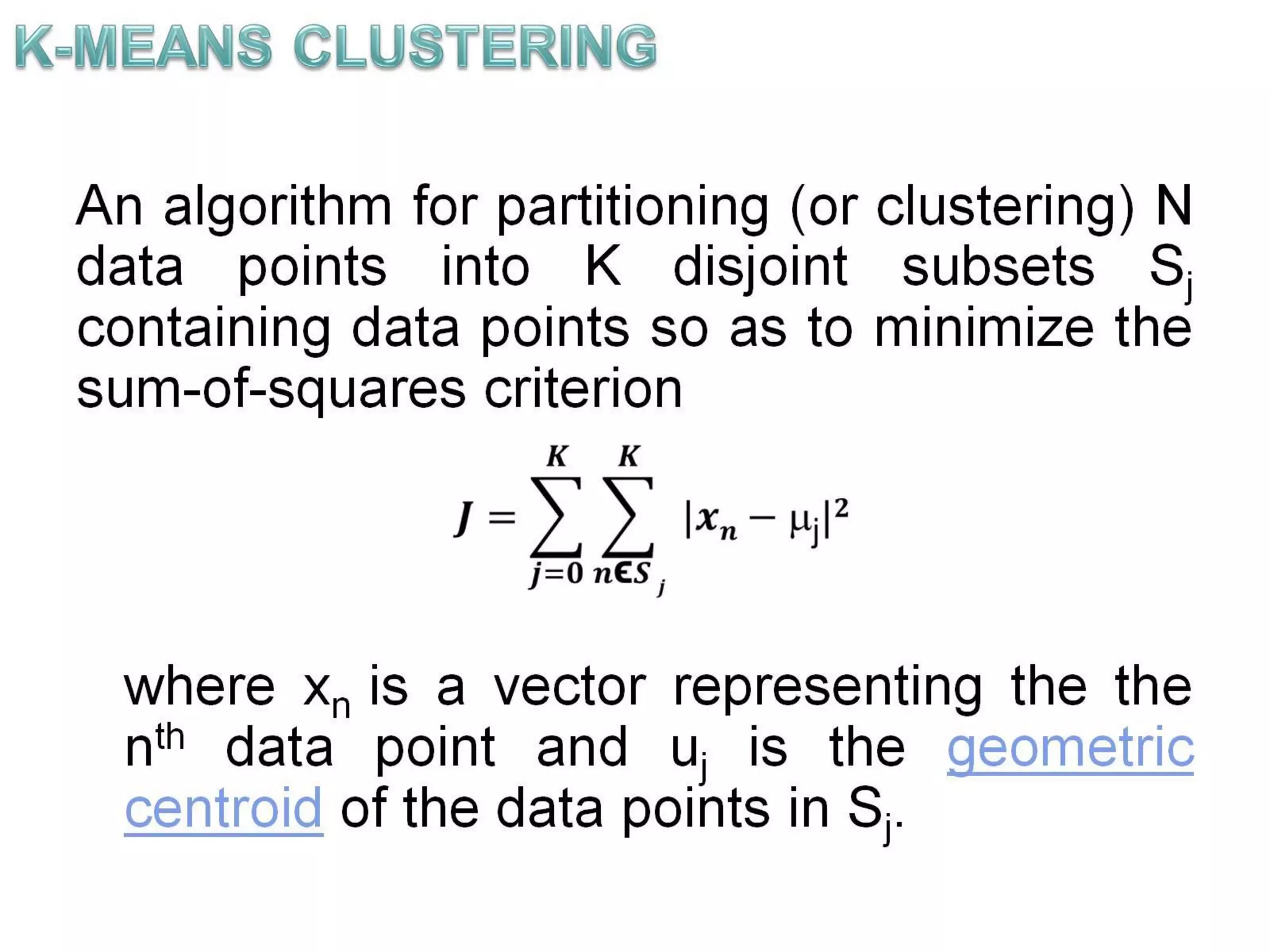

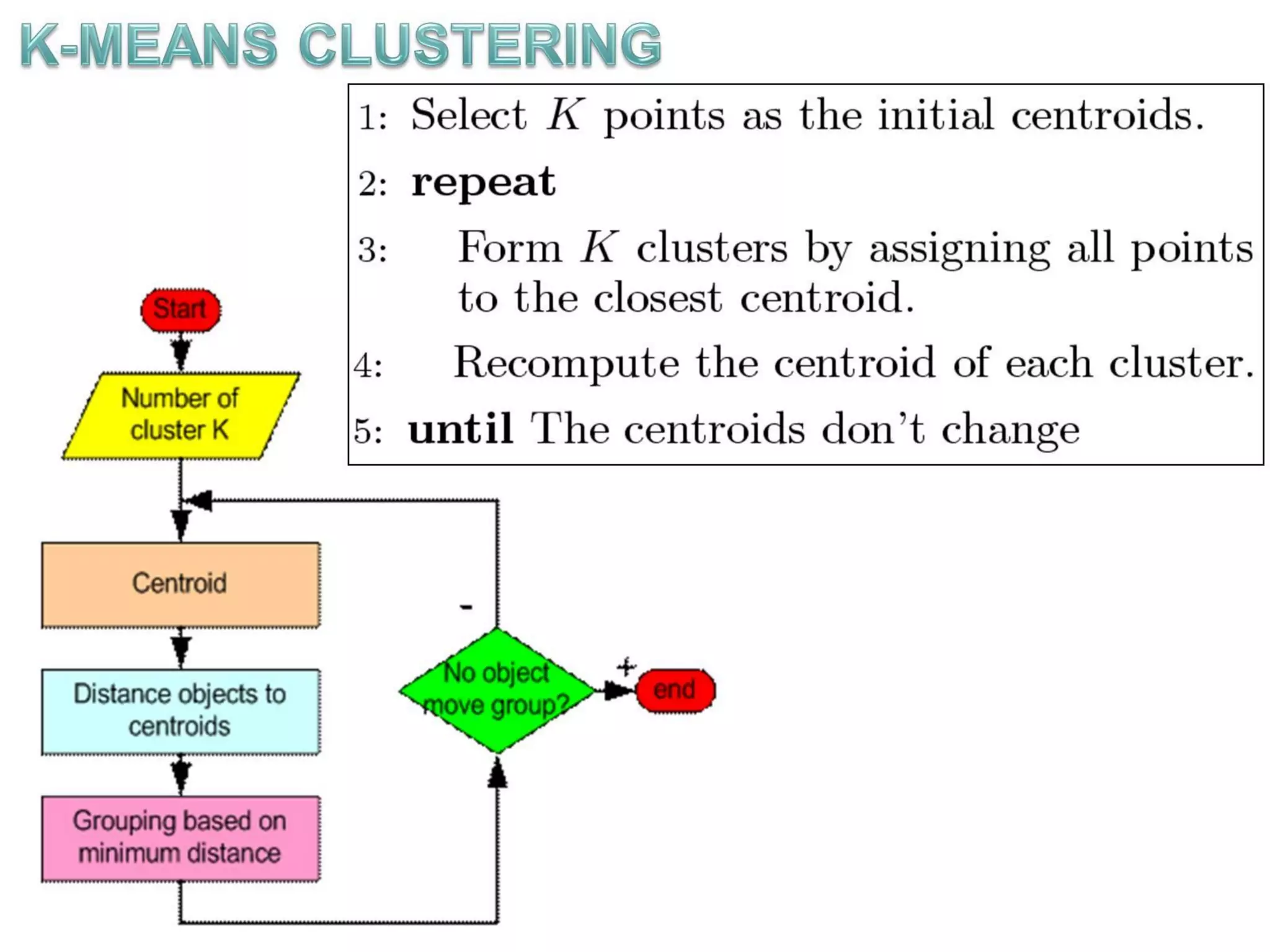

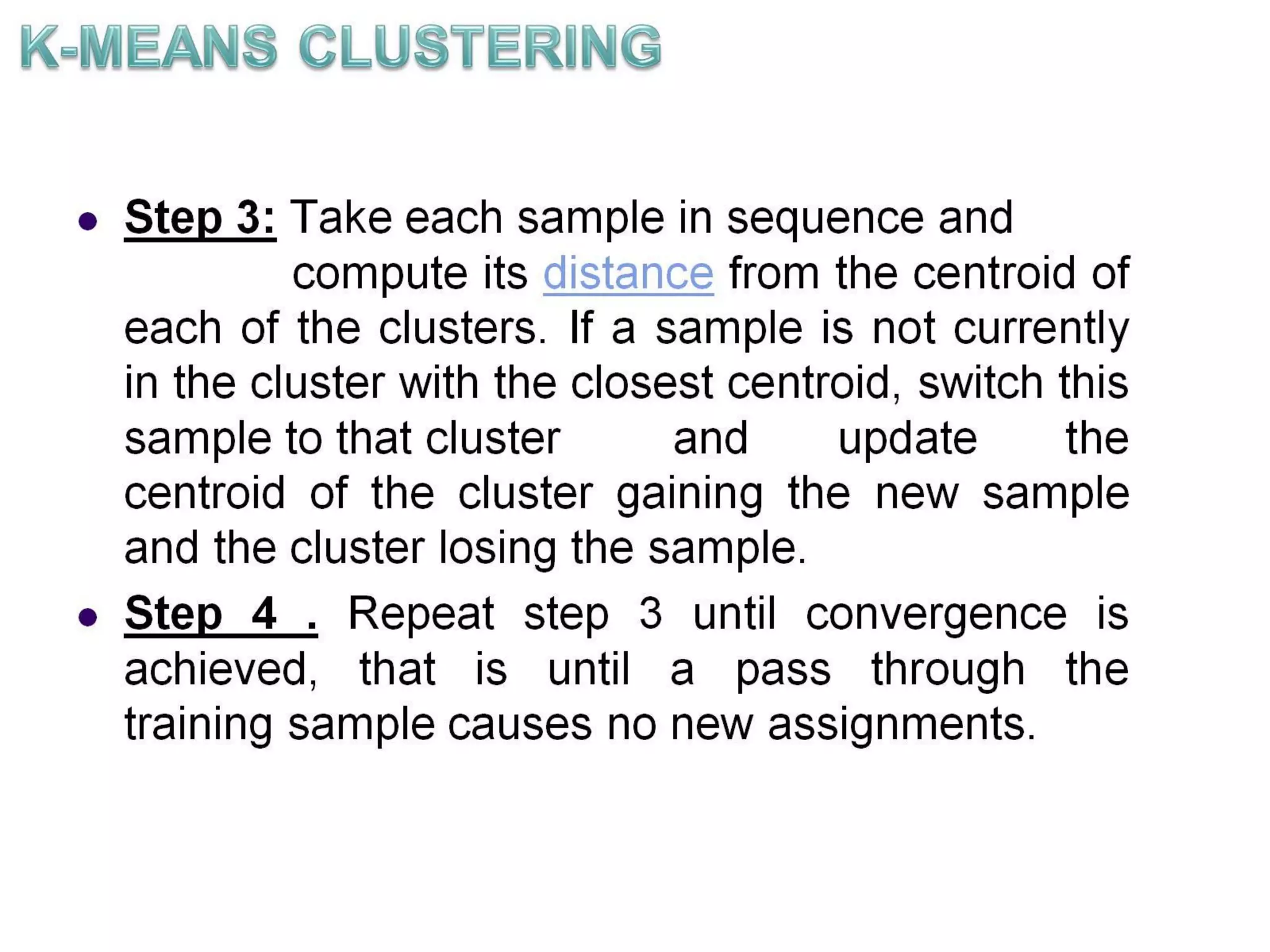
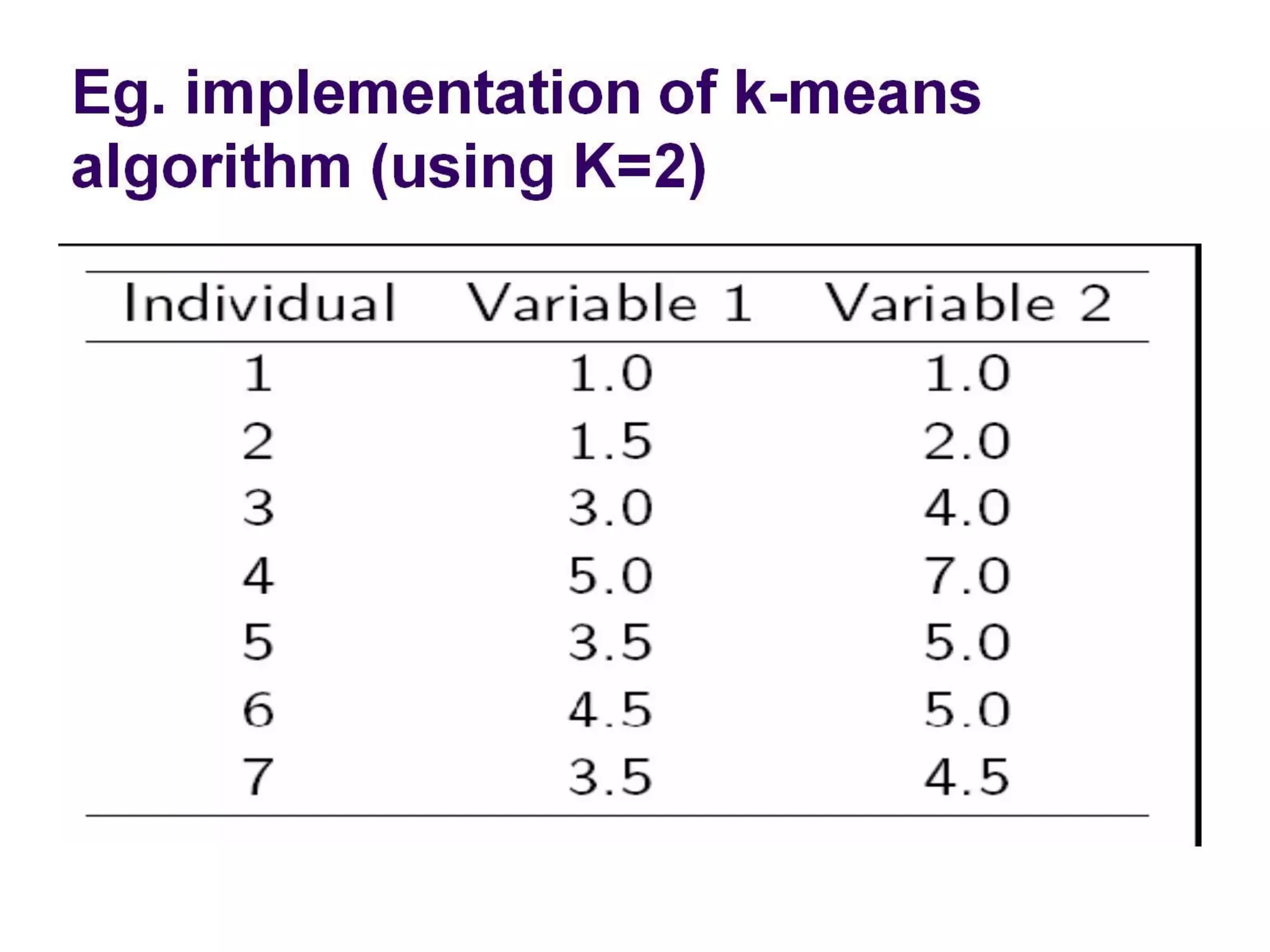
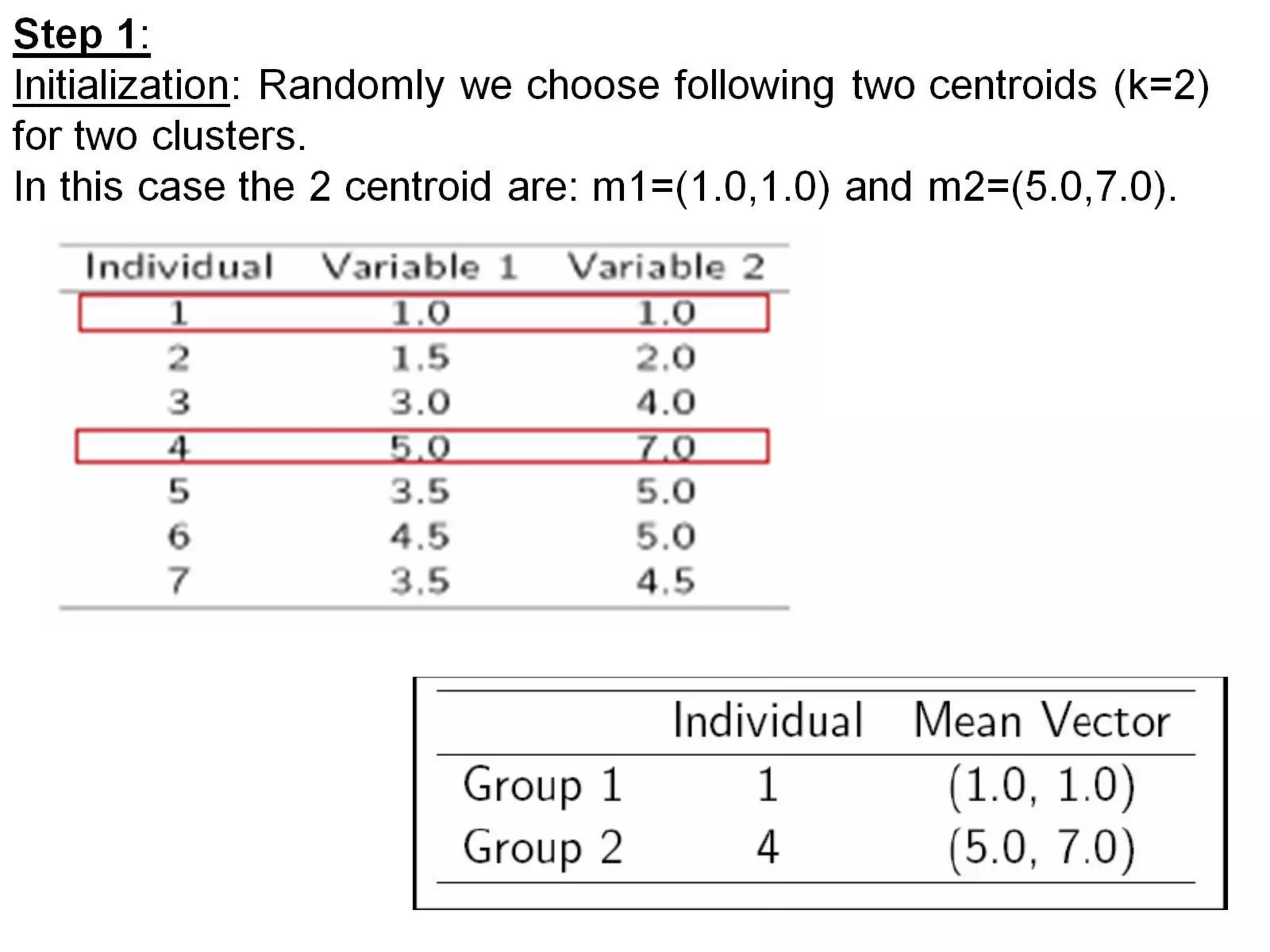
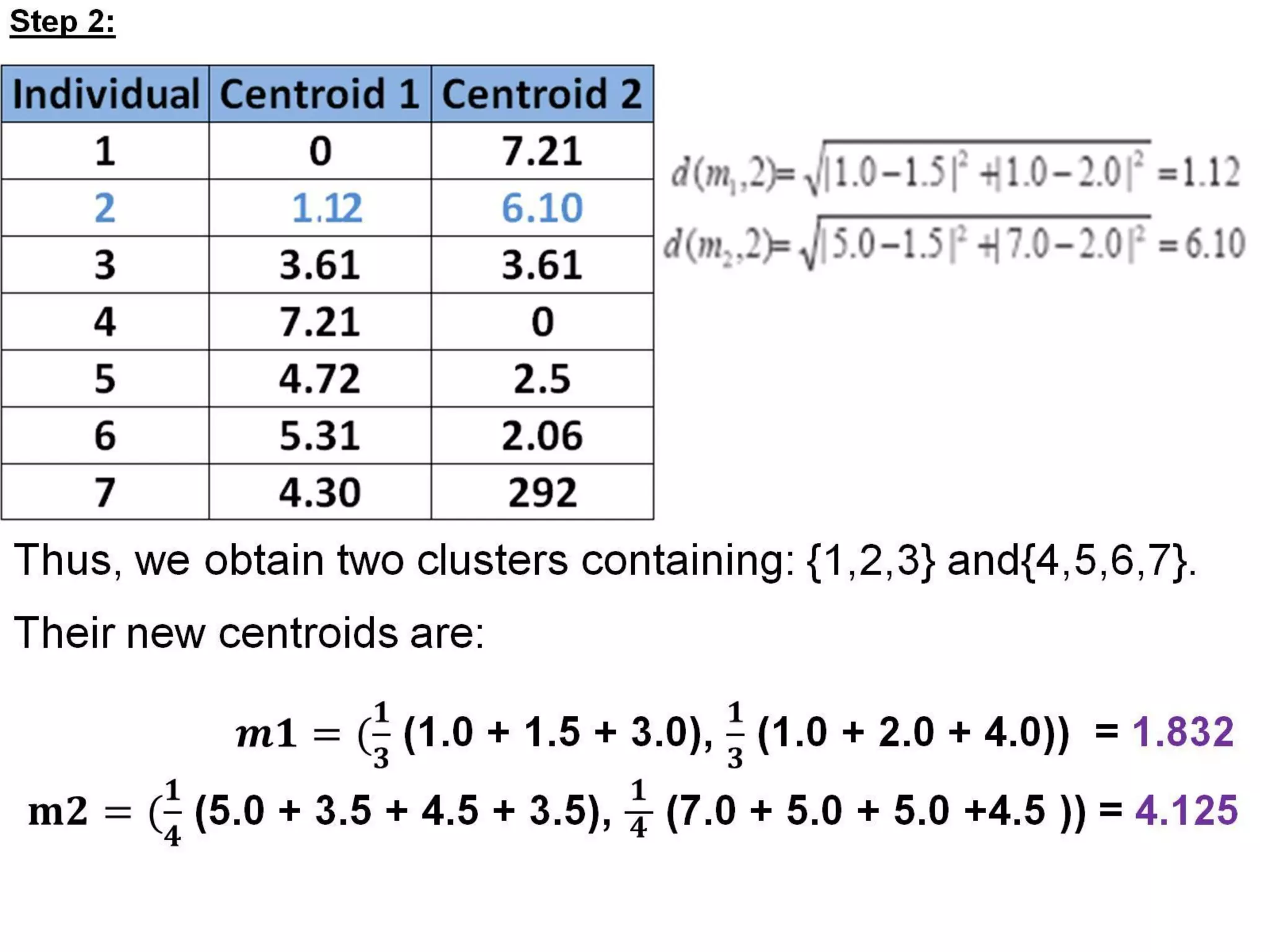
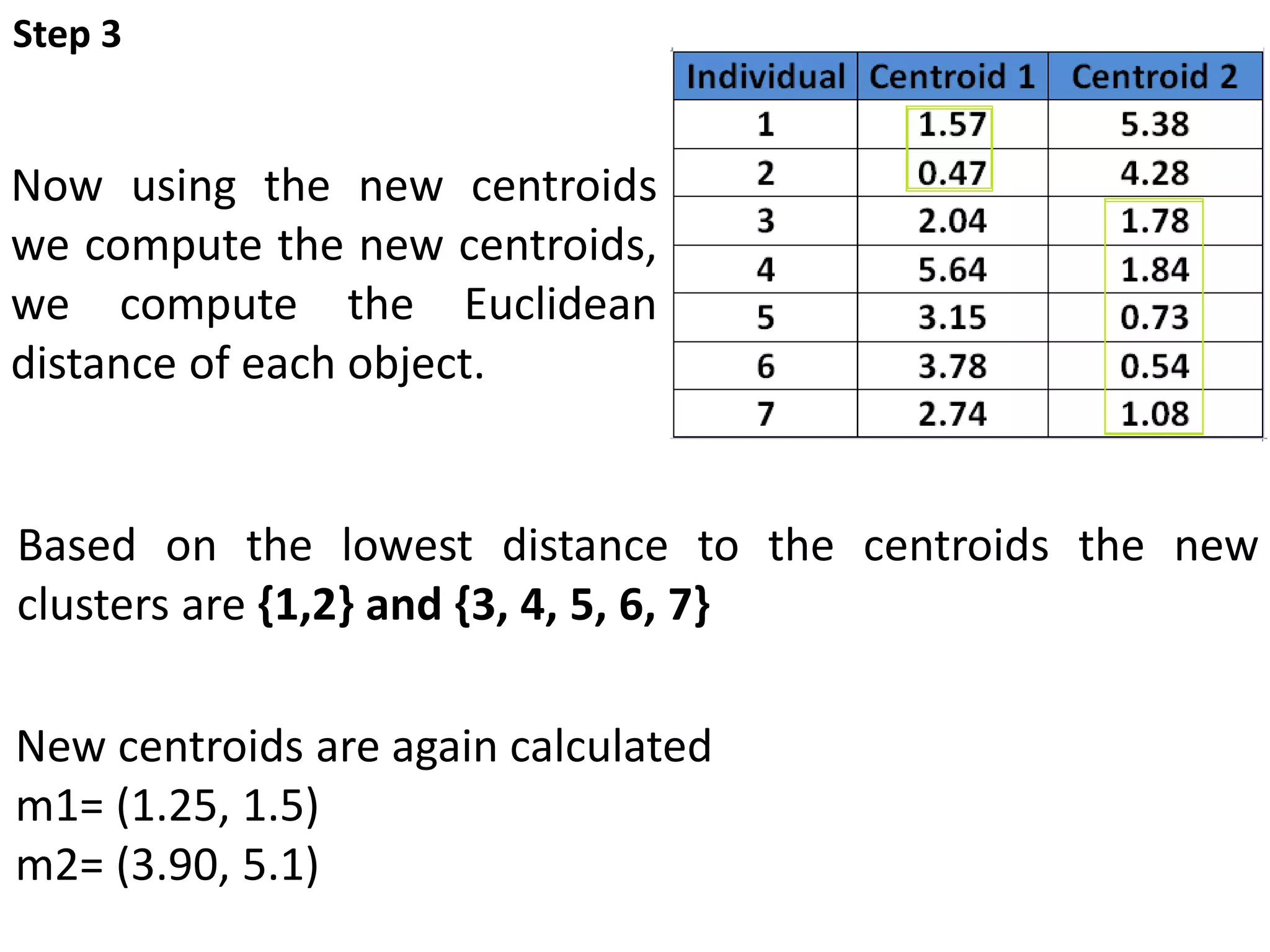
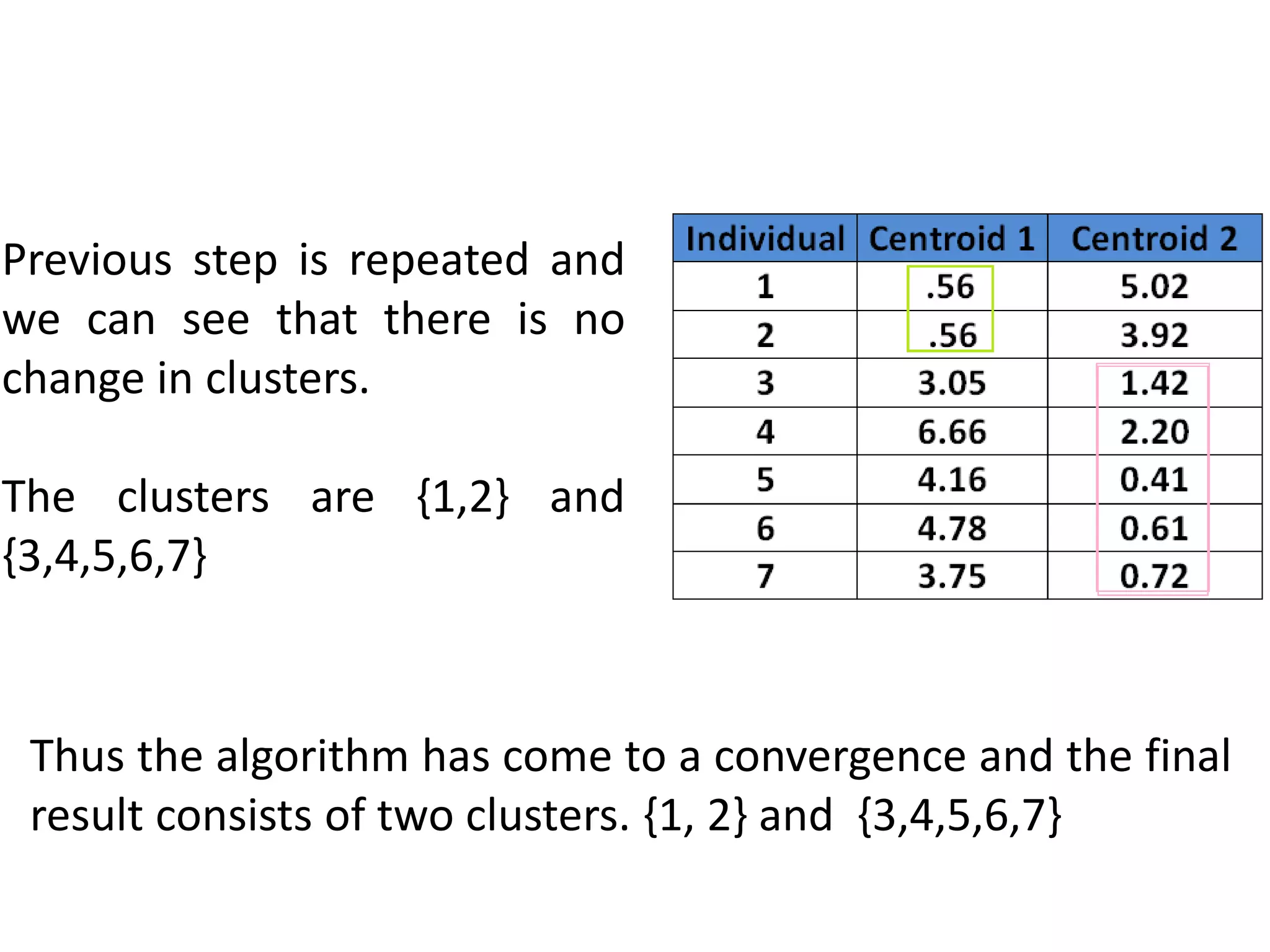
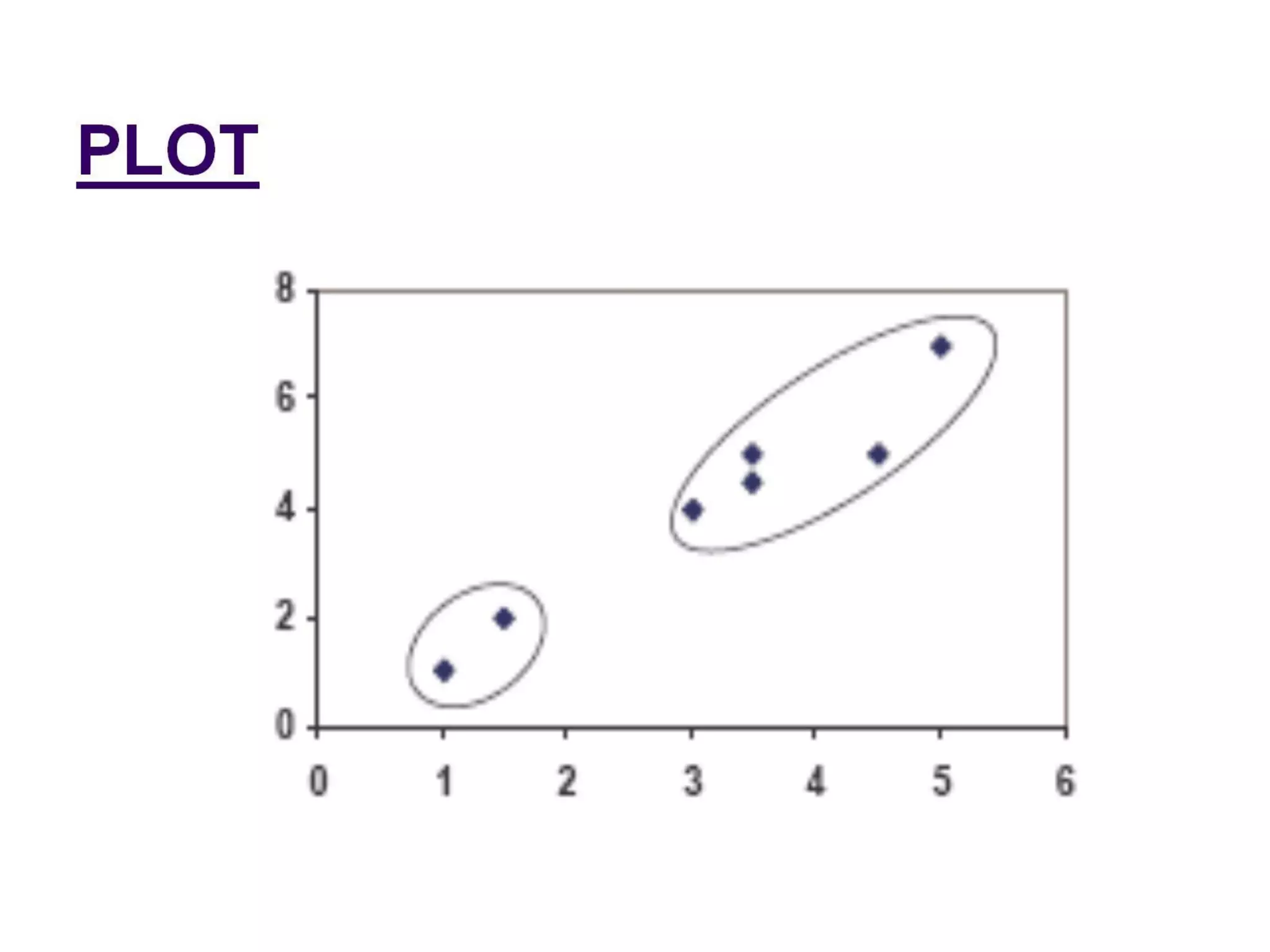


The document describes the k-means clustering algorithm, detailing the process of computing centroids, assigning clusters based on Euclidean distances, and achieving convergence with final clusters {1,2} and {3,4,5,6,7}. It highlights the algorithm's efficiency with a time complexity of O(tkn) and its applications in machine learning, data mining, speech understanding, image segmentation, and color palette selection. Overall, k-means is regarded as a simple yet powerful tool for various fields, including artificial intelligence and pattern recognition.


















