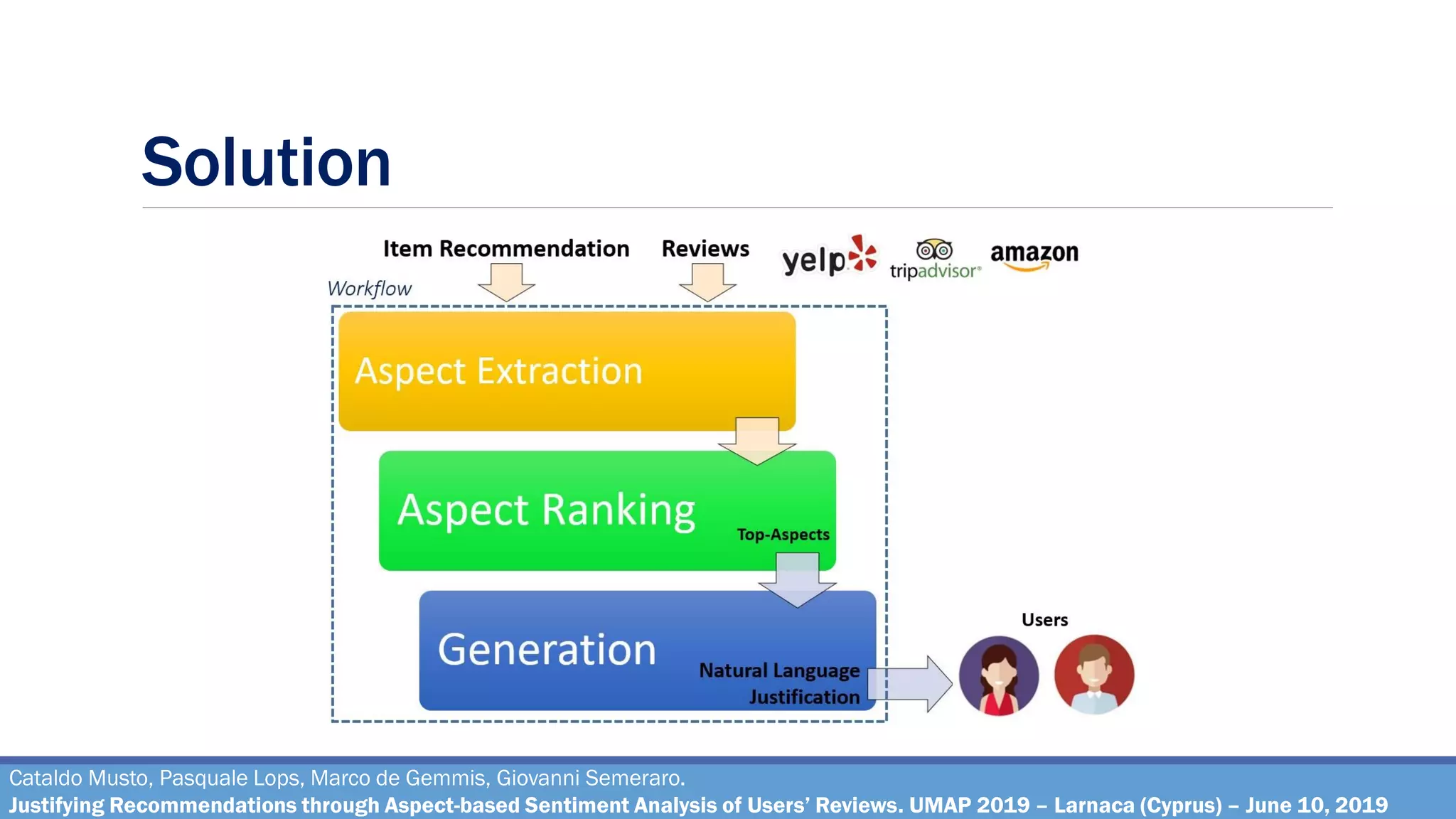
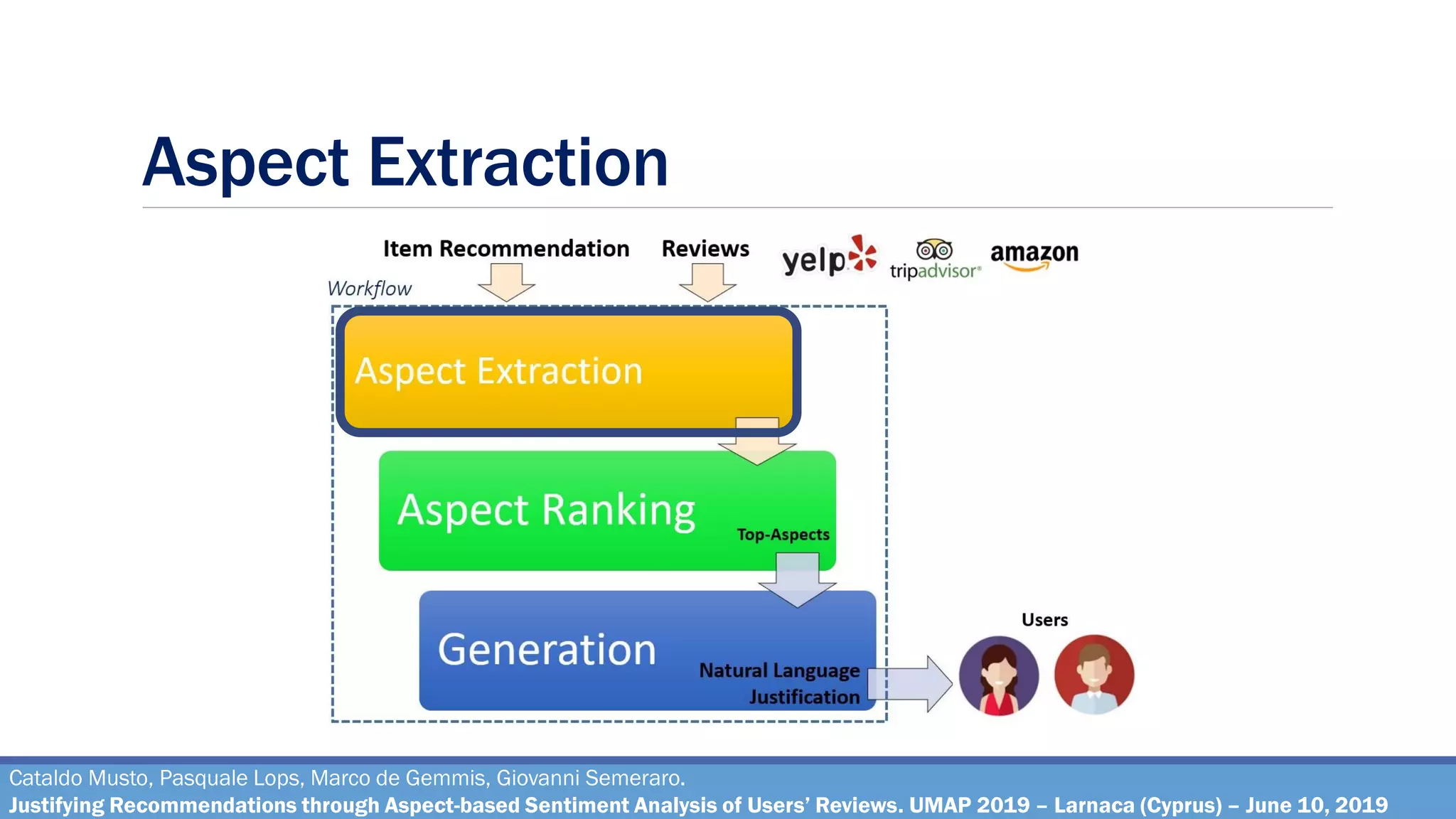
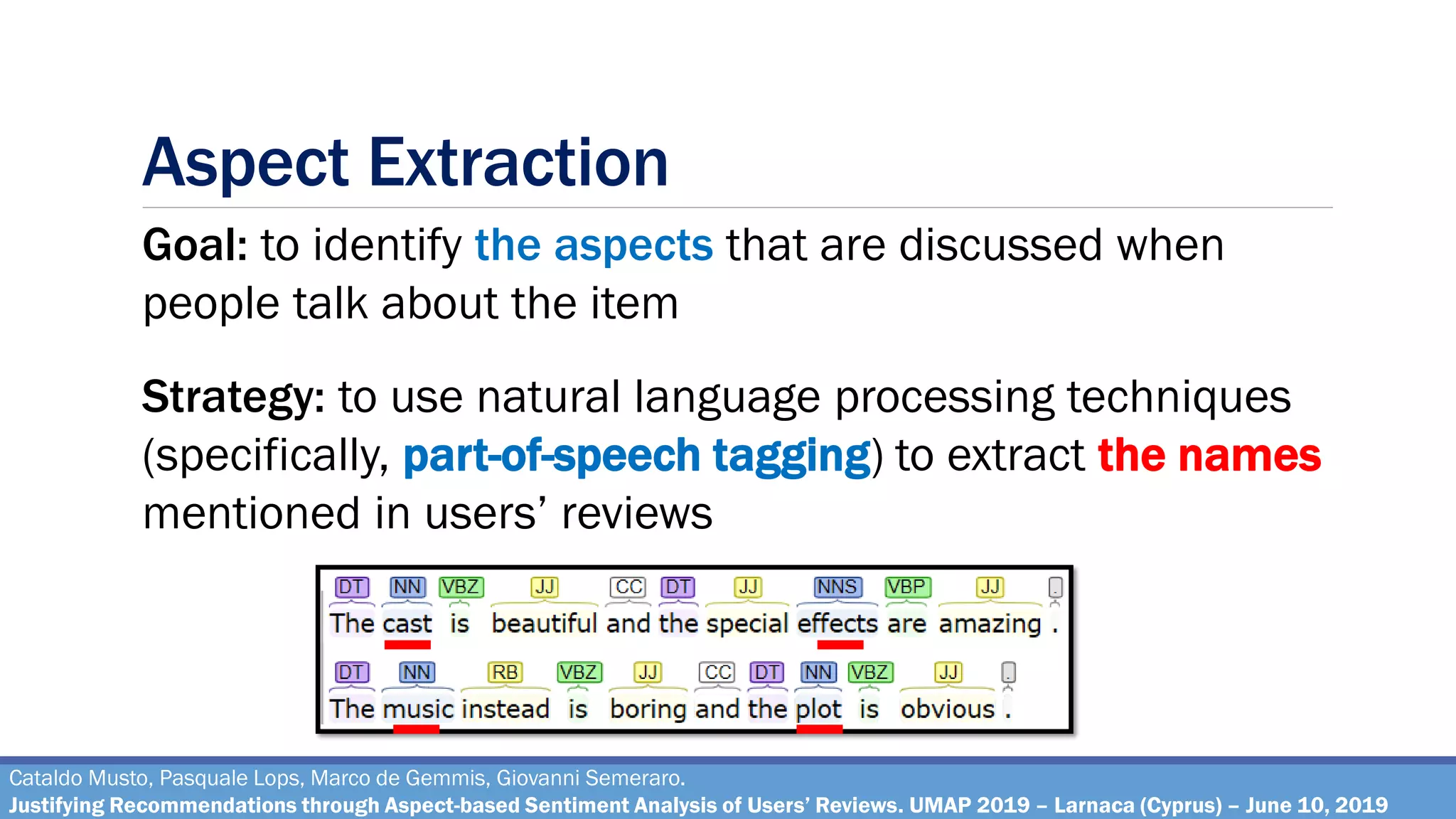
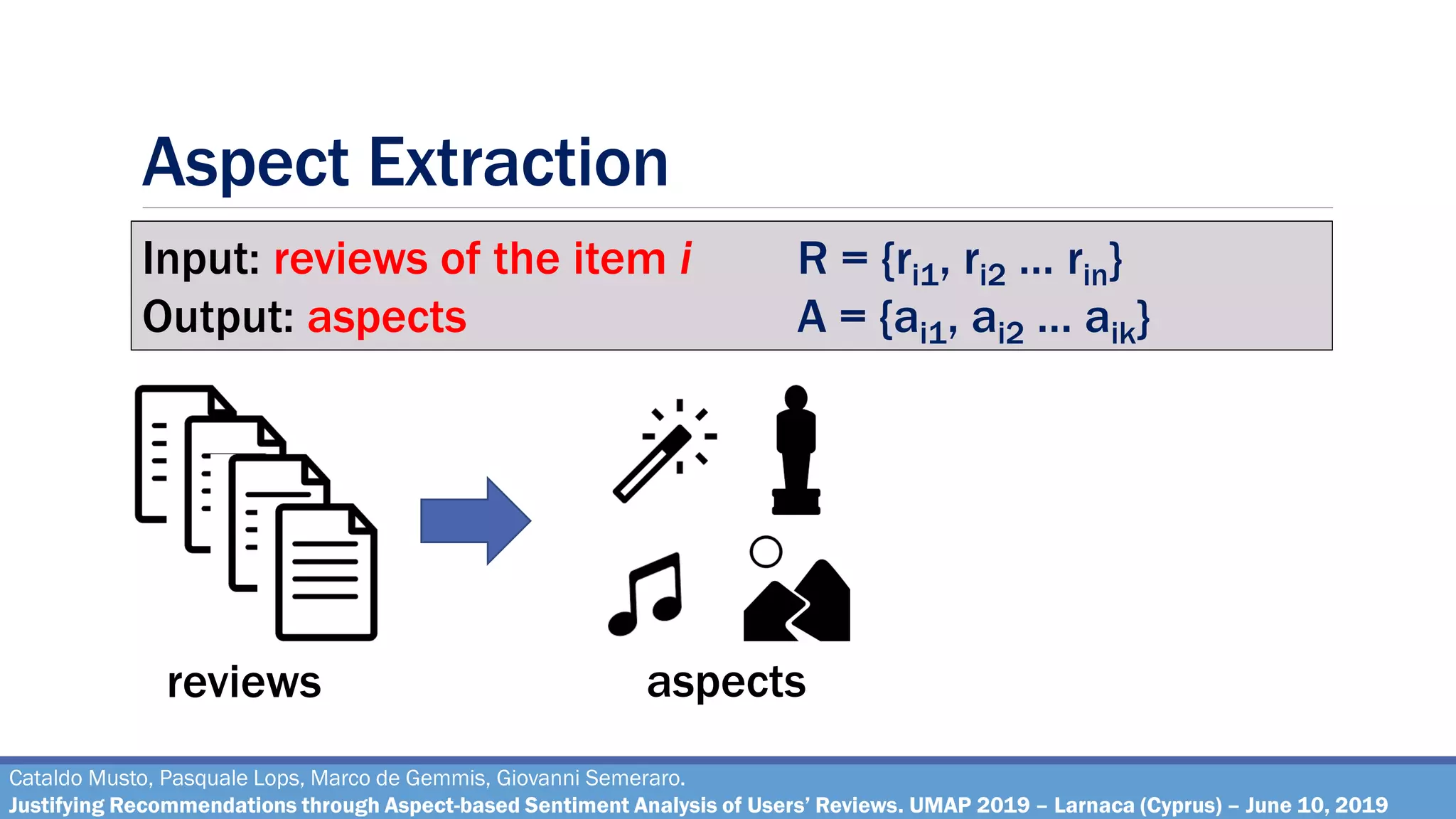
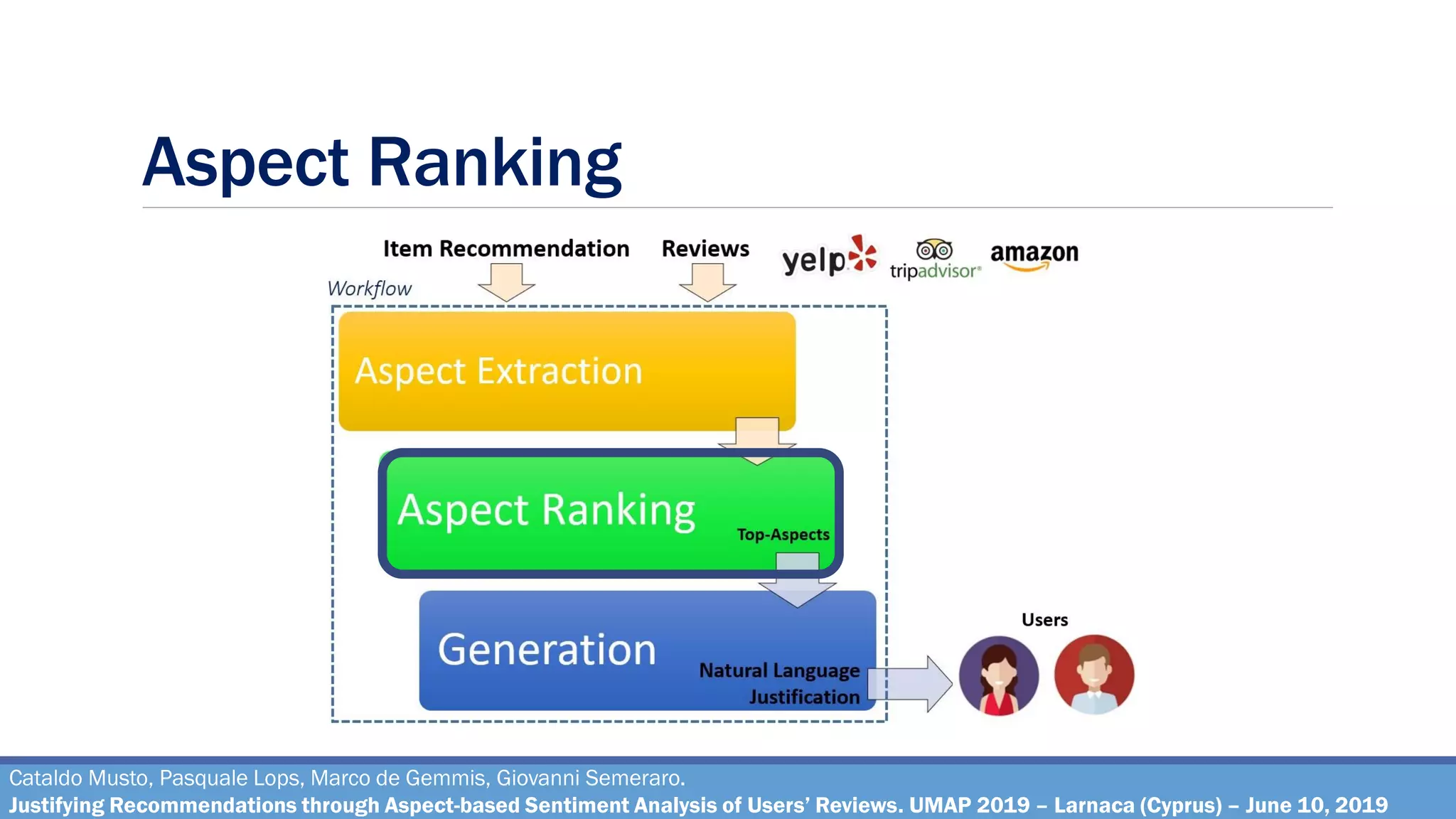
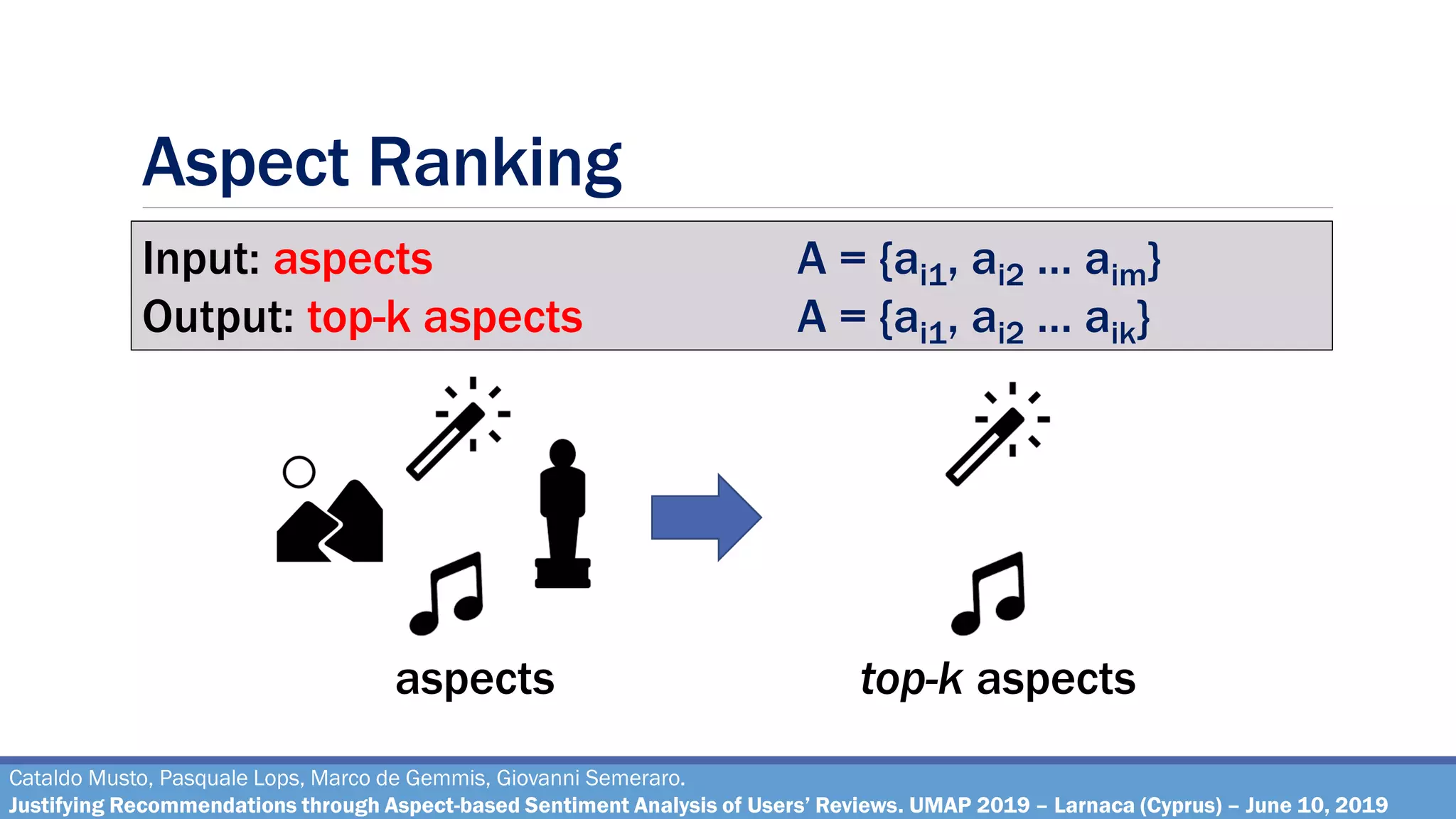
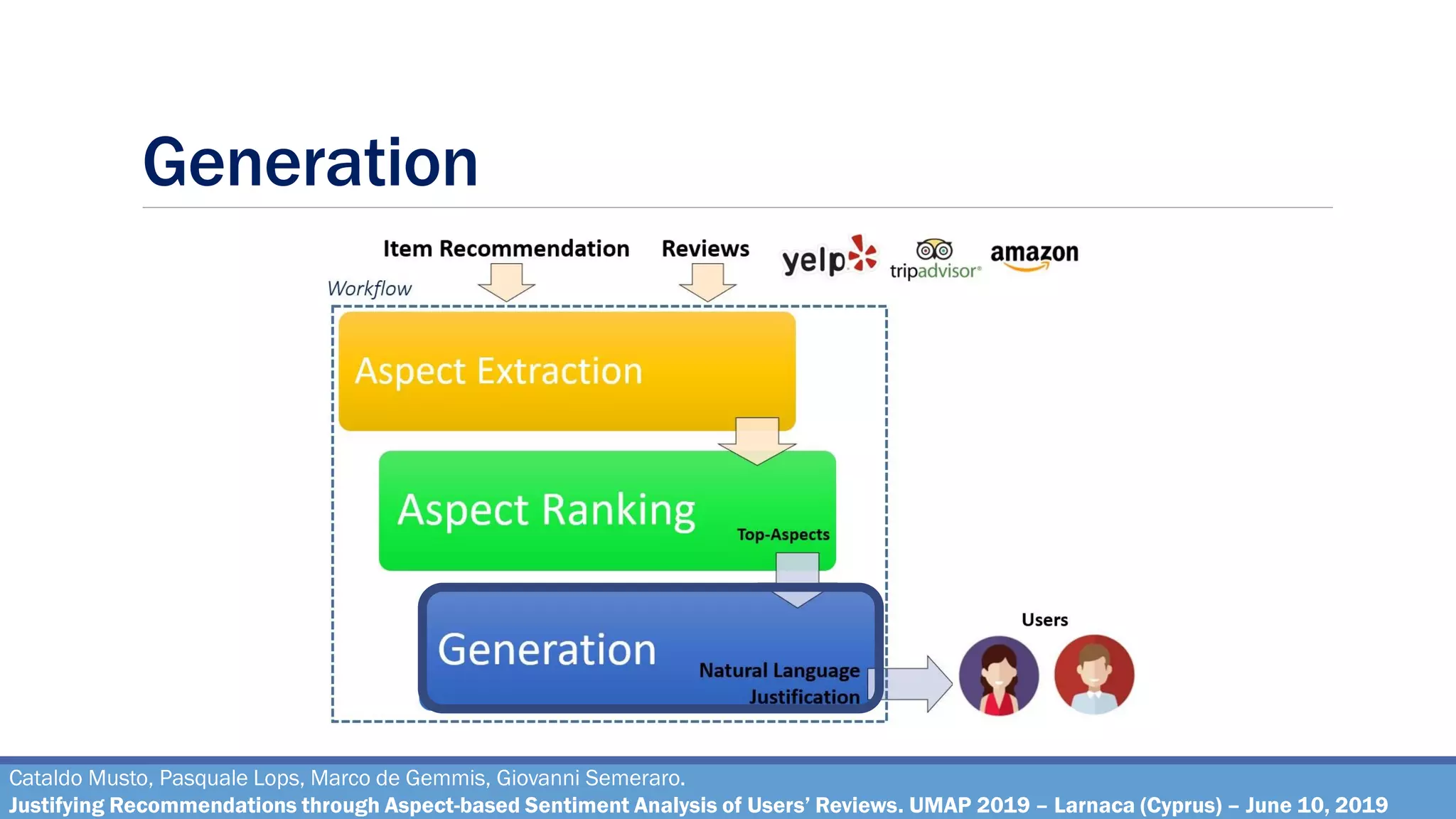
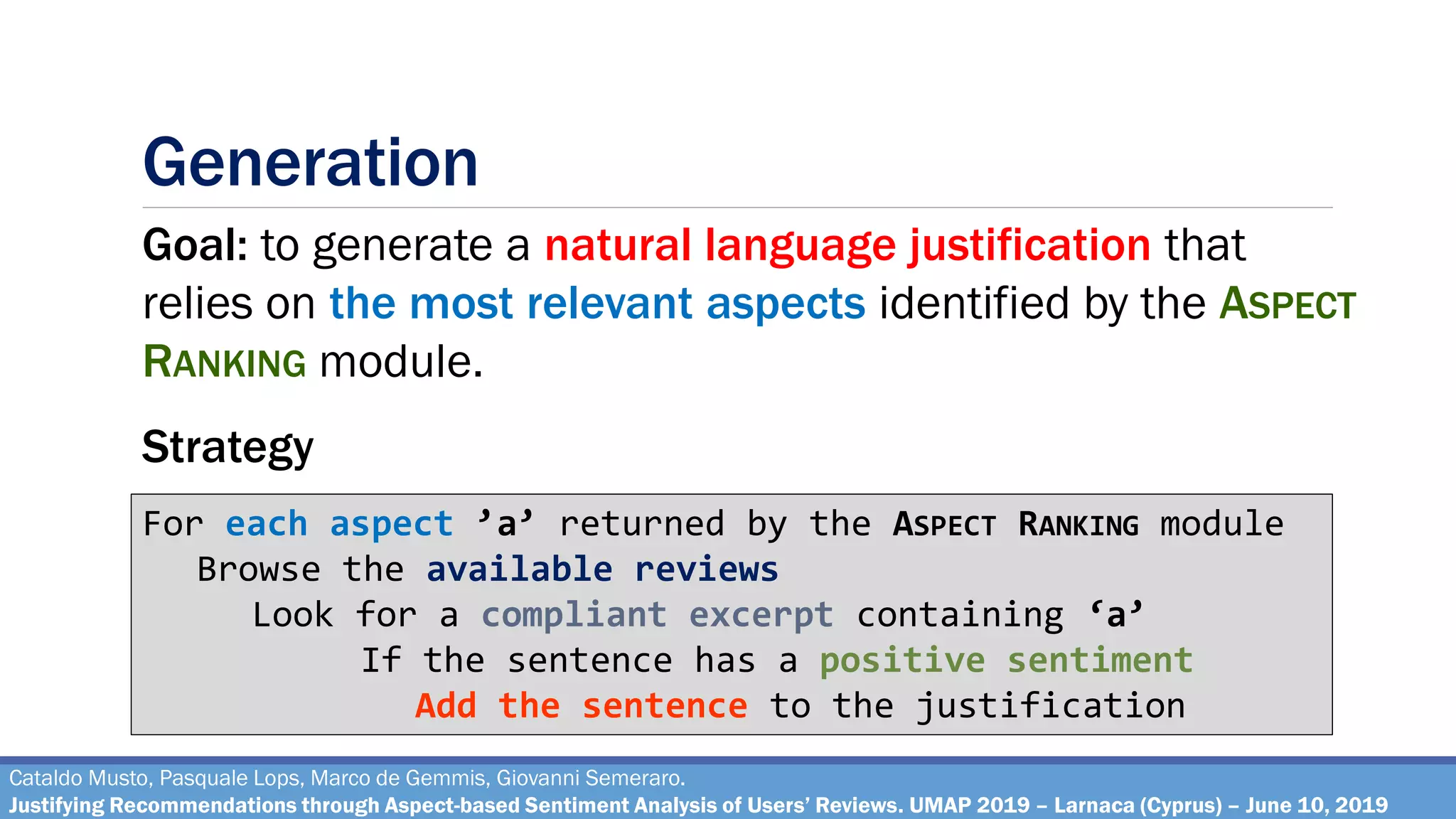
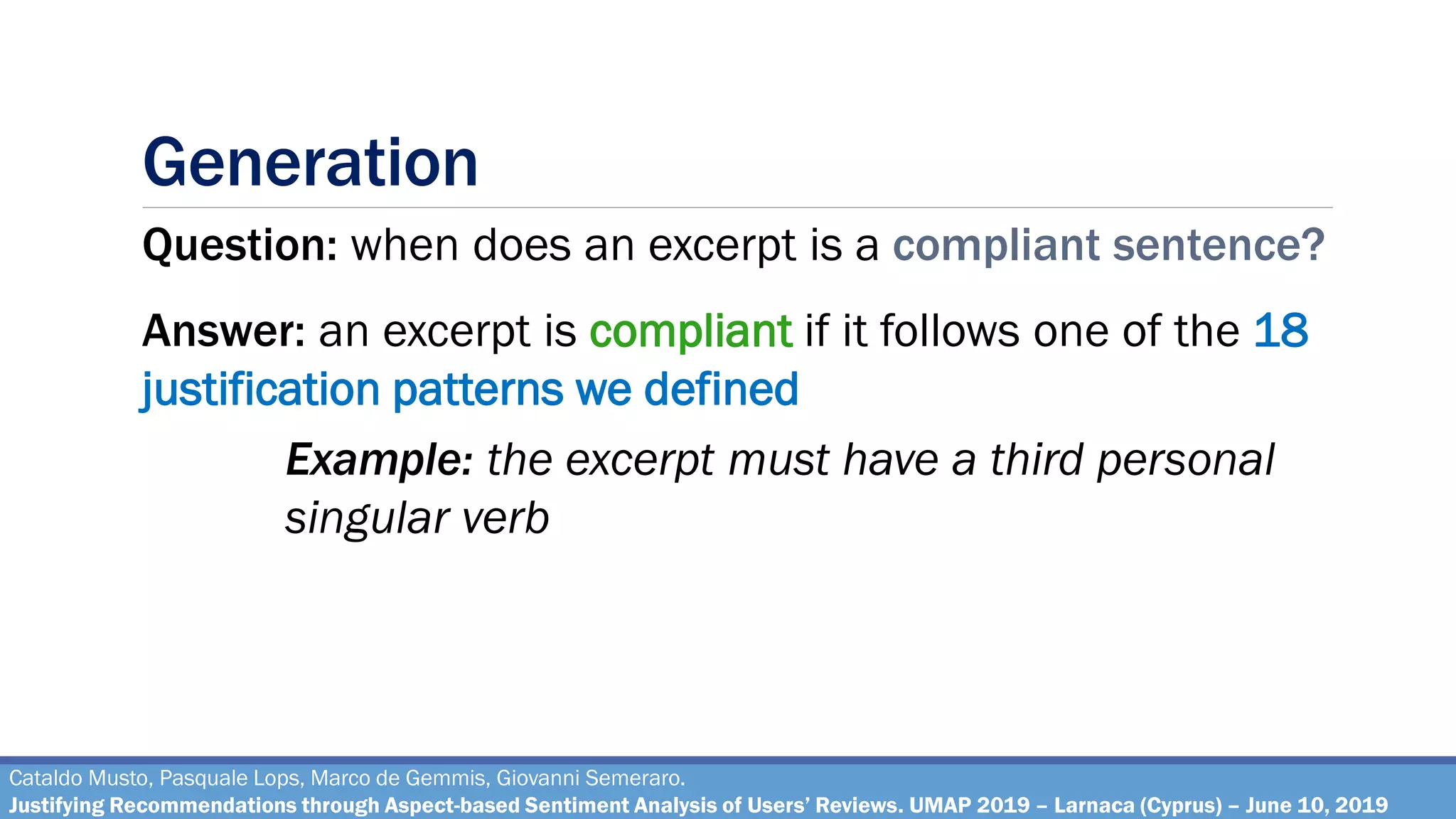
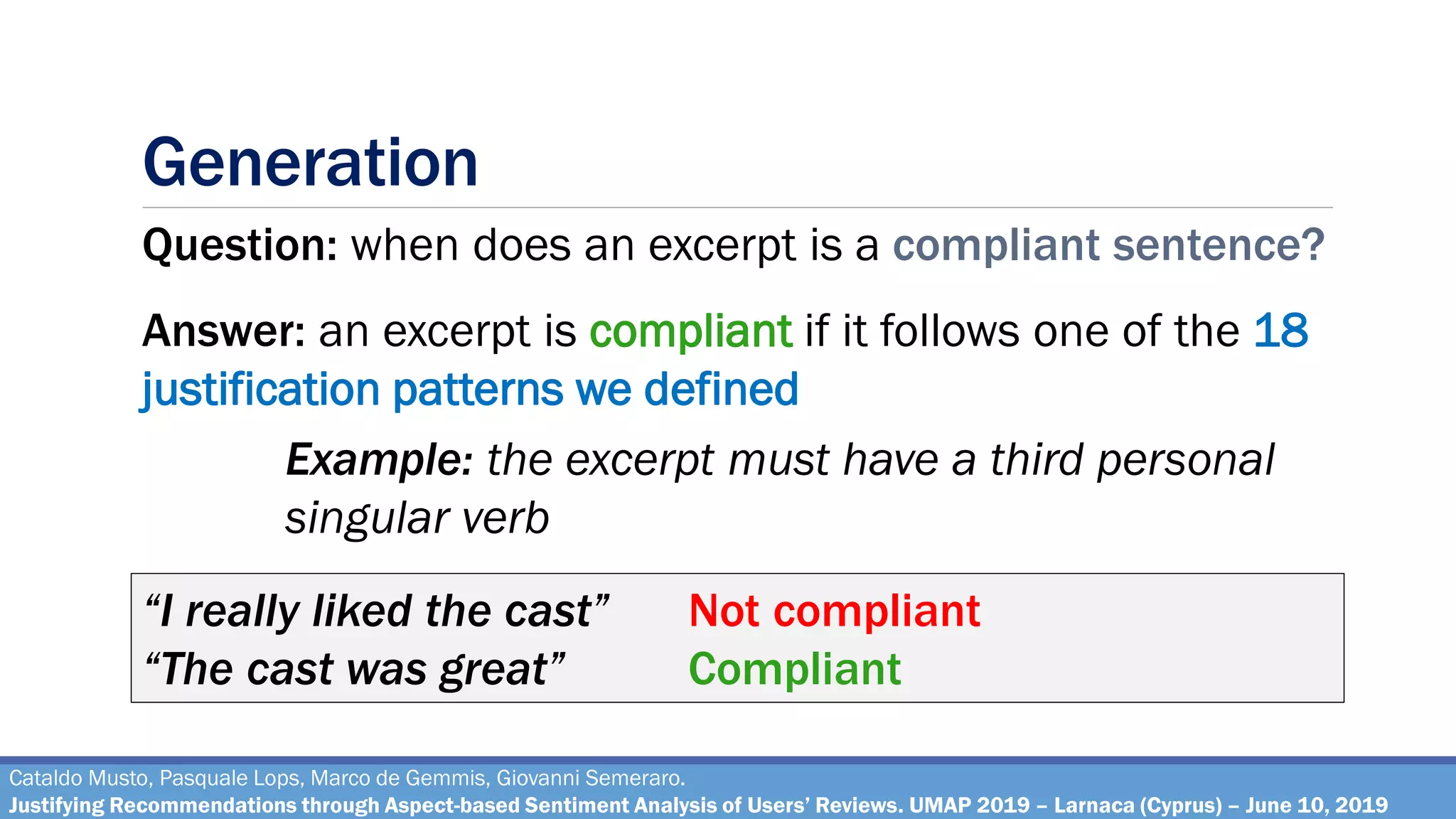
The document describes a method for justifying recommendations through aspect-based sentiment analysis of users' reviews. It involves extracting aspects from reviews using natural language processing, ranking aspects by relevance and sentiment polarity, and generating a natural language justification using positive excerpts about high-ranking aspects. An experimental evaluation with 286 subjects compared justifications from different combinations of parameters and to a feature-based baseline. Results showed that review-based justifications scored higher than the baseline in terms of transparency, persuasion, engagement, trust and effectiveness.
















![Experimental Evaluation
Cataldo Musto, Pasquale Lops, Marco de Gemmis, Giovanni Semeraro.
Justifying Recommendations through Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis of Users’ Reviews. UMAP 2019 – Larnaca (Cyprus) – June 10, 2019
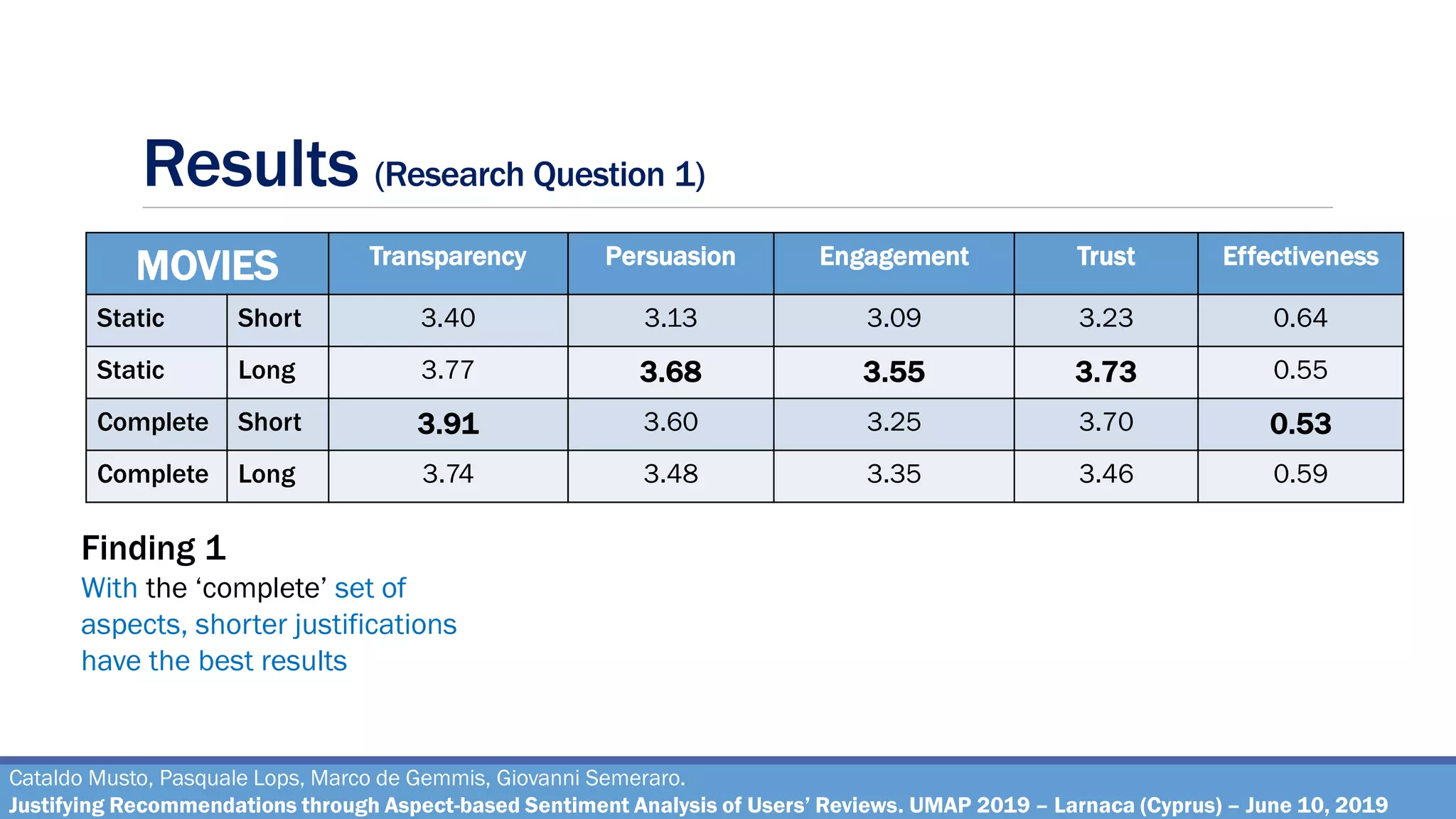
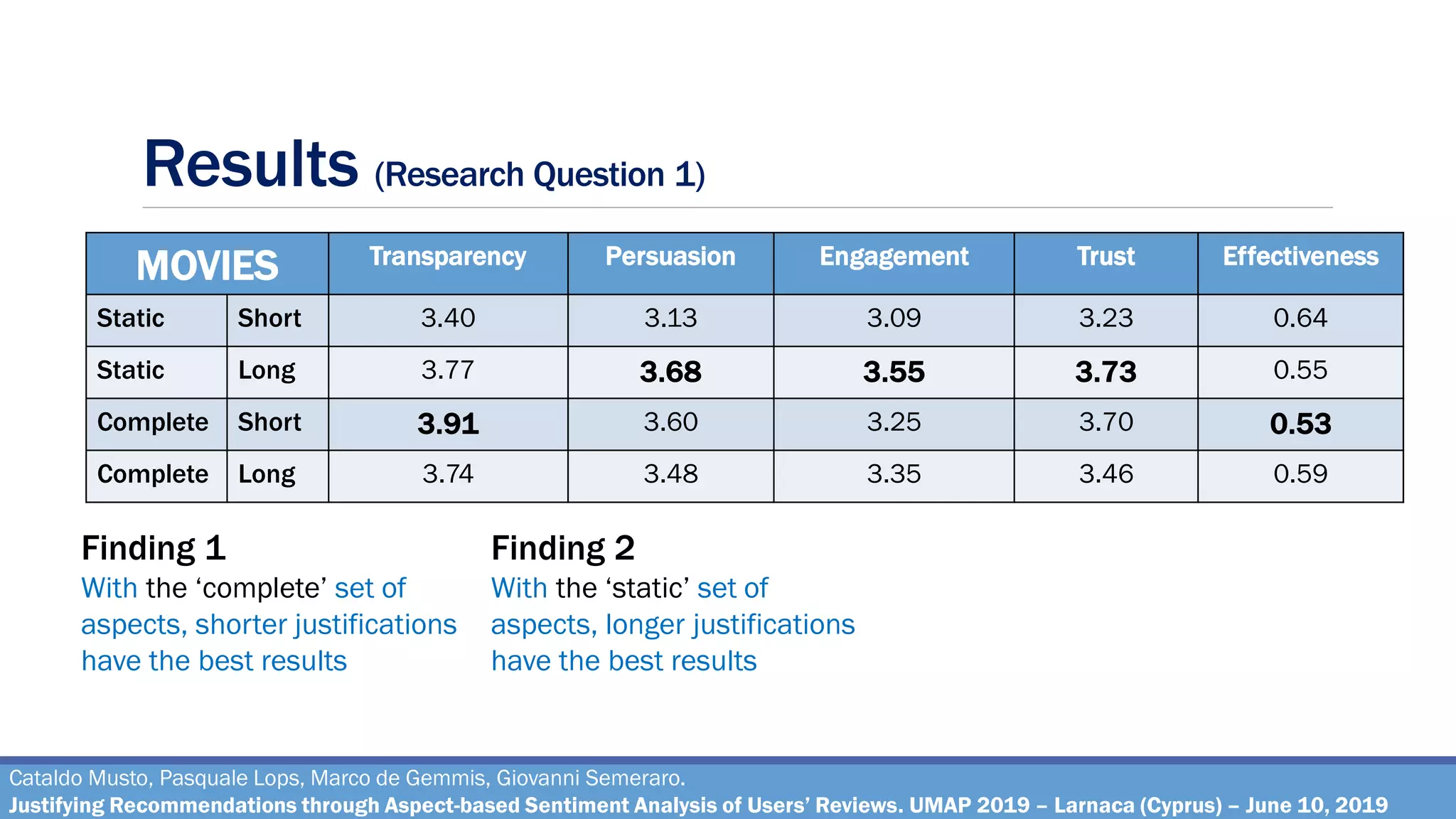
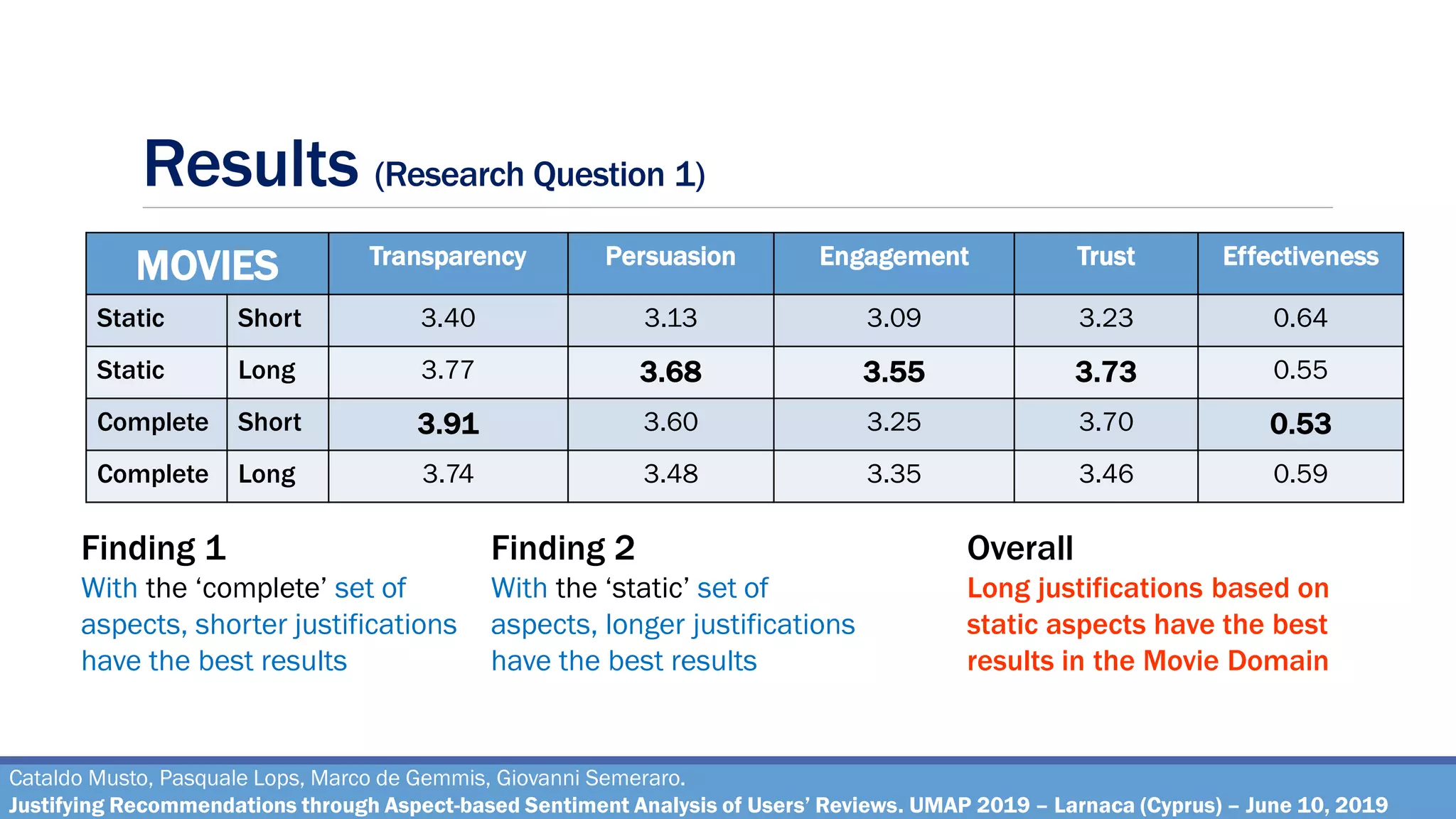
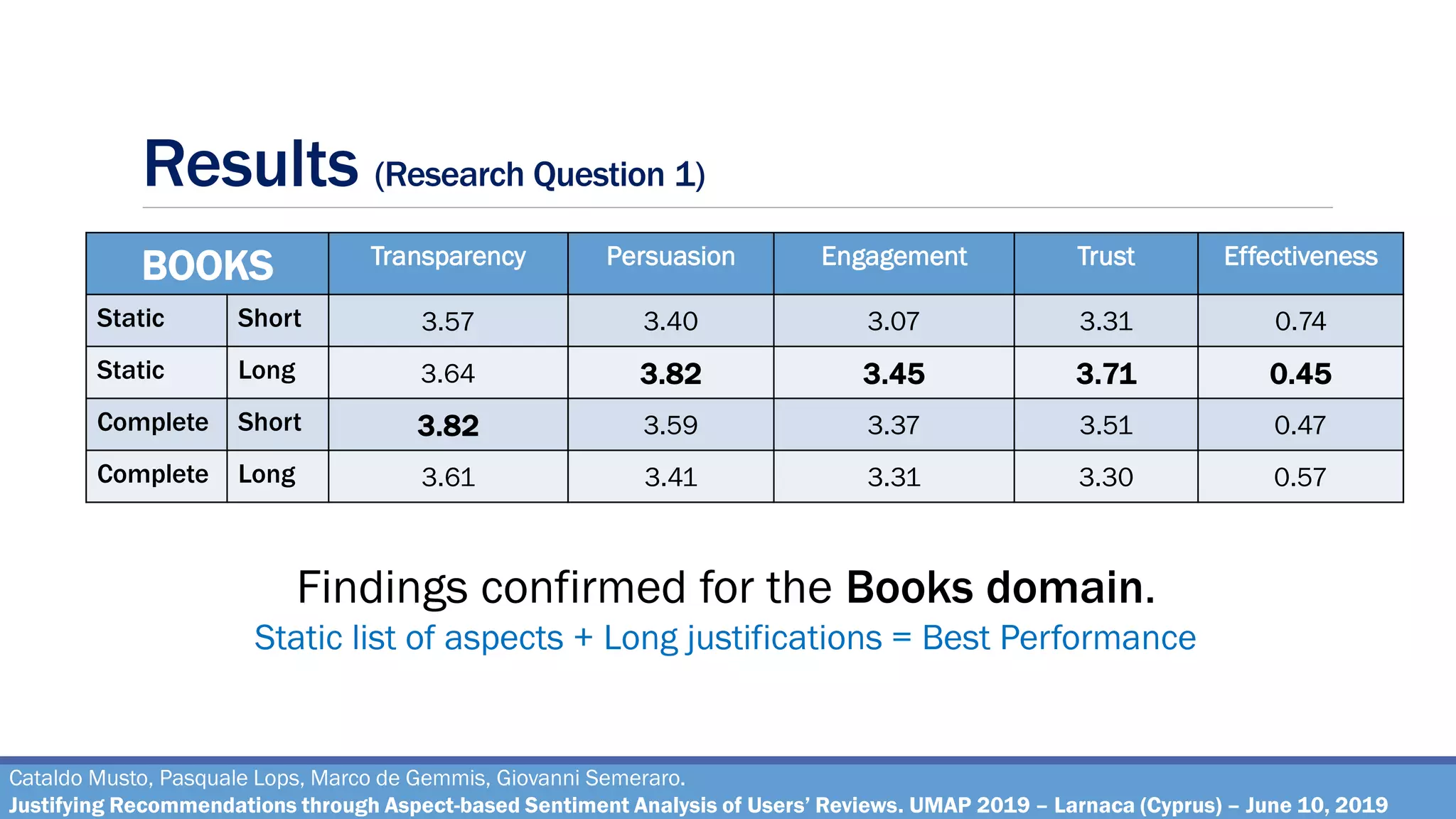
Research Question 1
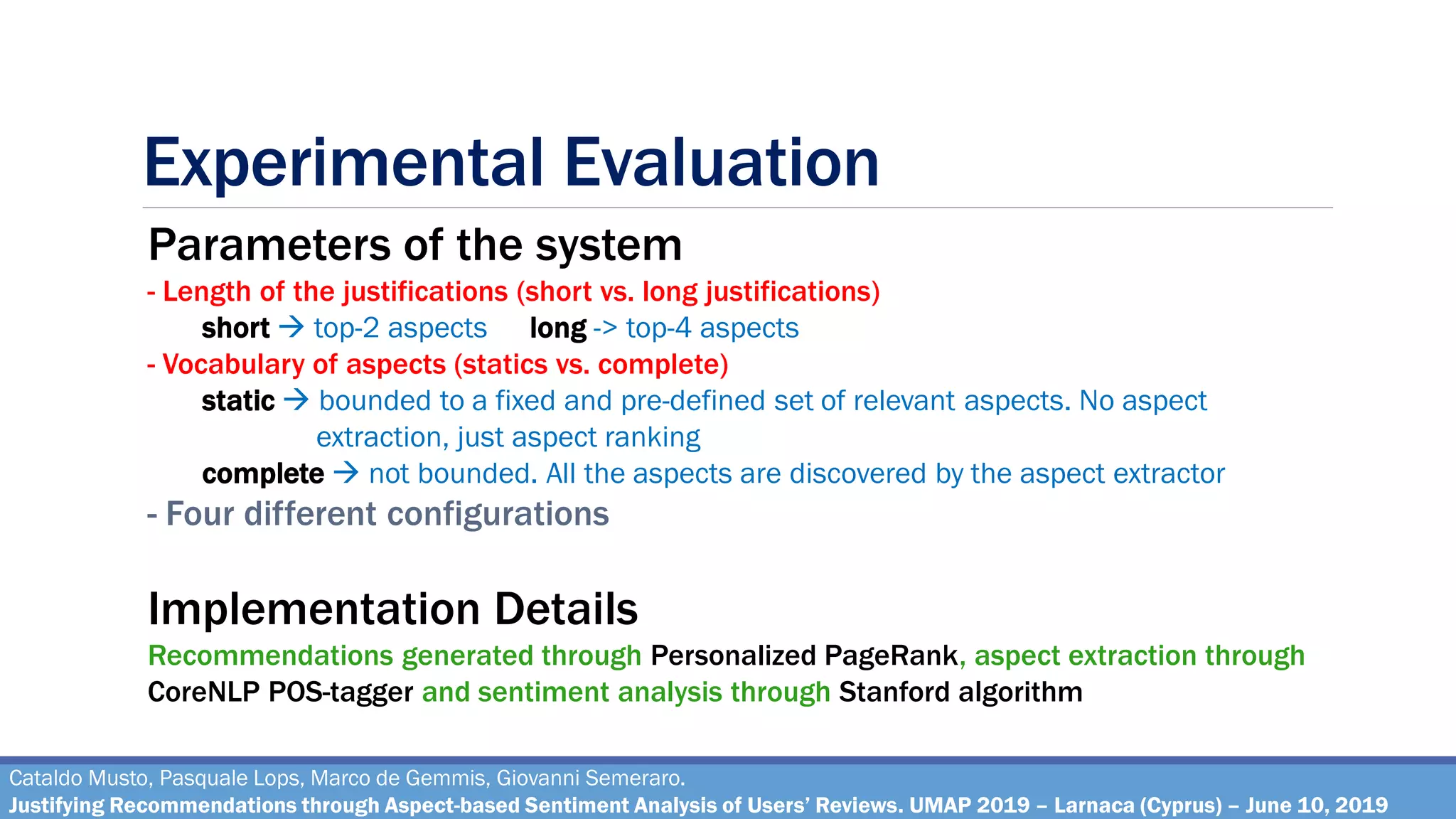
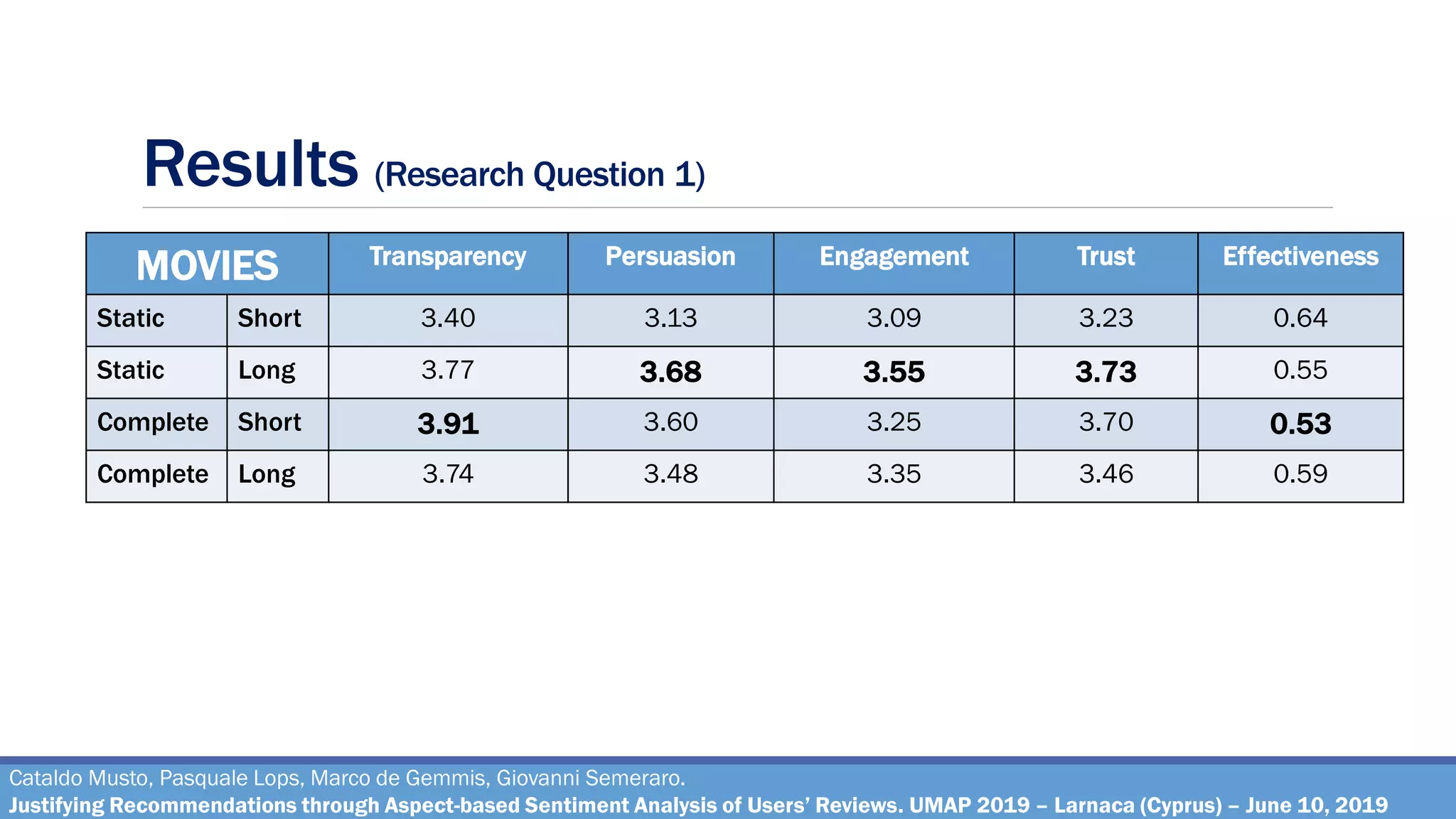
How effective are the justifications generated through the pipeline, on varying of different
combinations of the parameters?
Research Question 2
How does our justifications perform with respect to a classic feature-based explanation [*] ?
(e.g.) “I suggest you 300 since you like other movies by Zack Snyder, as Watchmen”
Experimental Design
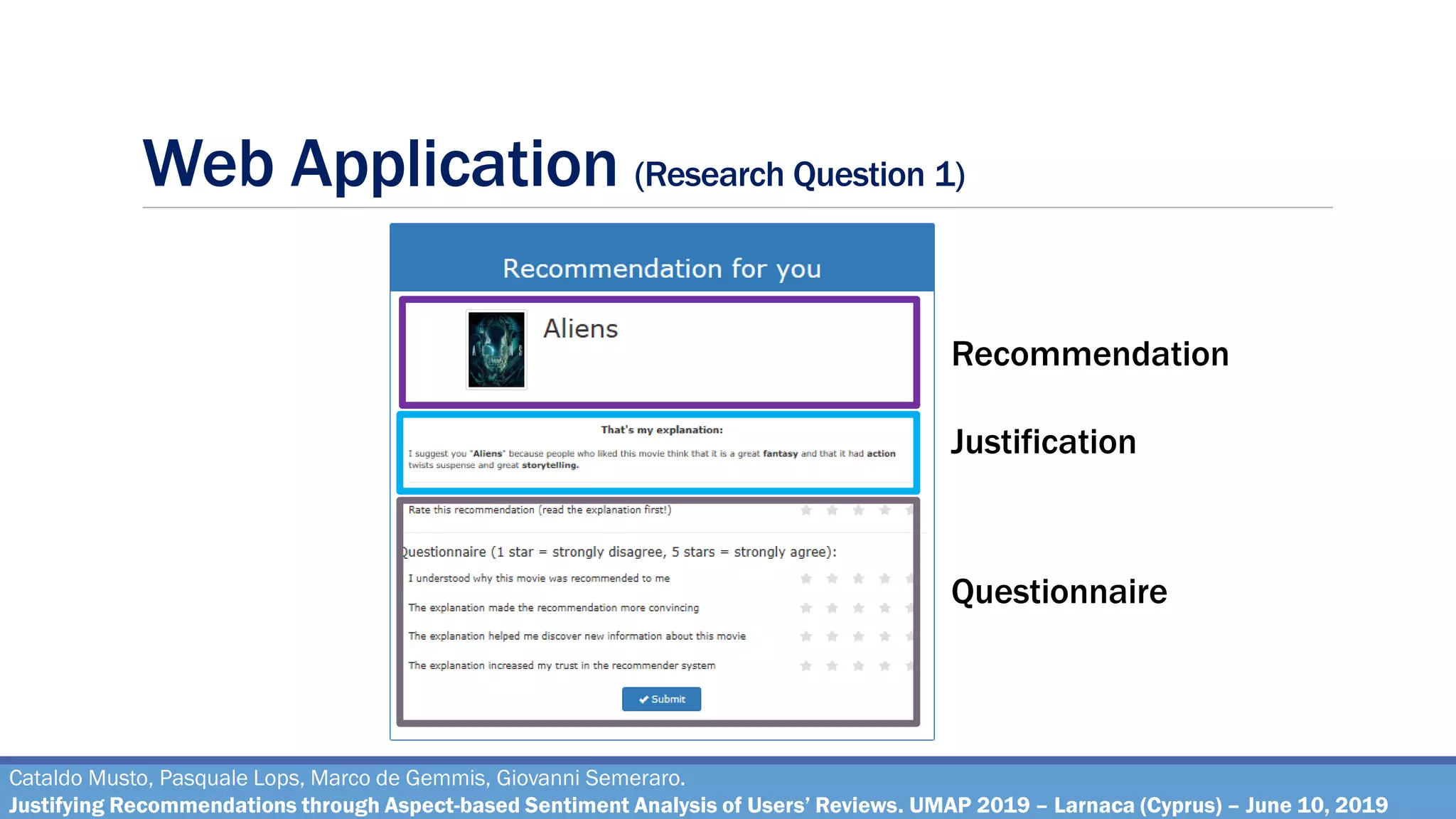
User Study with a Web Application
286 subjects
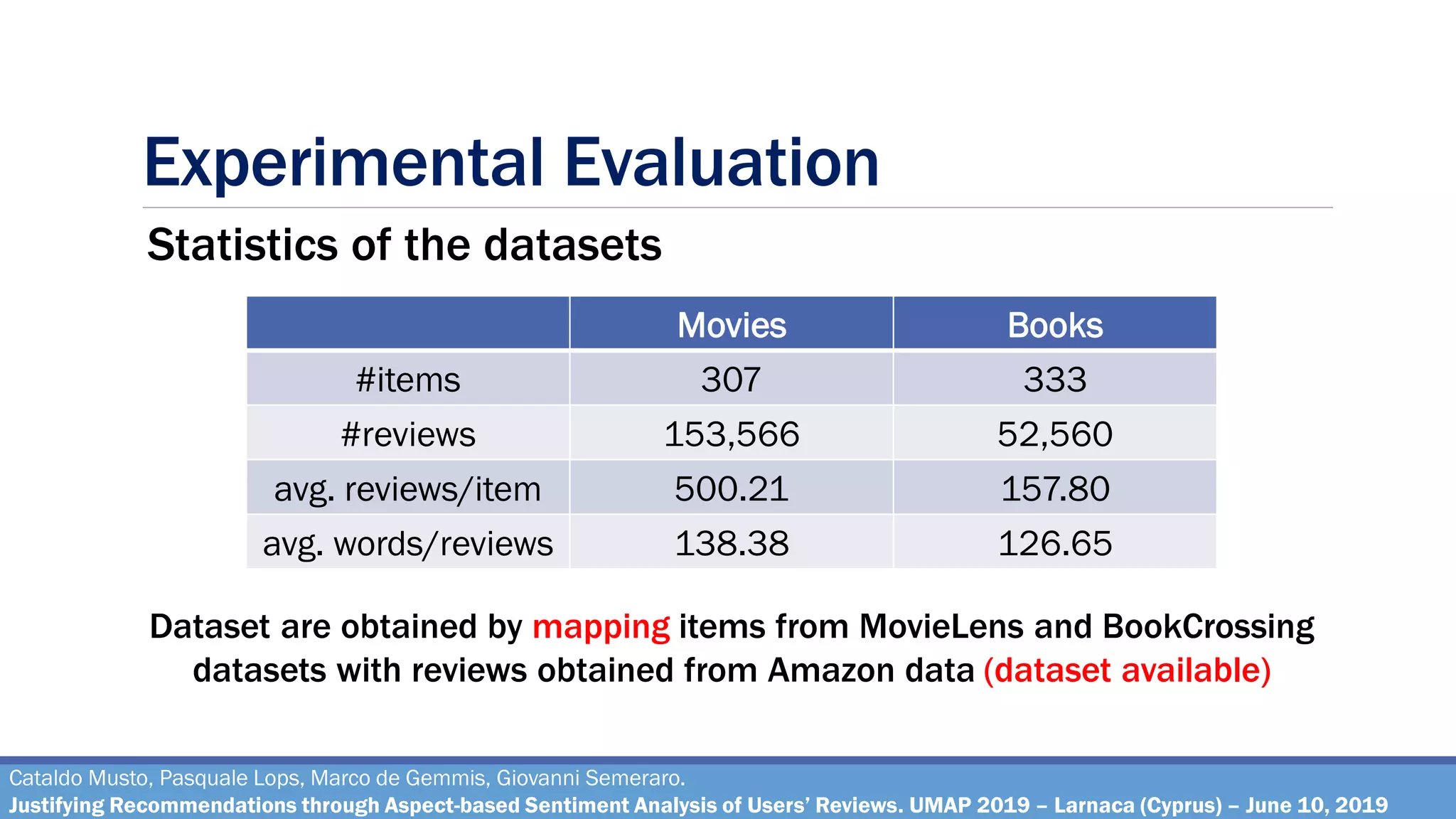
Movie and Books Domain
Metrics: Transparency, Engagement, Persuasion, Trust, Effectiveness [^]
Between-subjects for Research Question 1, Within-subjects for Research Question 2
[*] Musto, C., Narducci, F., Lops, P., De Gemmis, M., Semeraro G.
ExpLOD: A Framework for Explaining Recommendations based on
the Linked Open Data Cloud. In Proceedings of the 10th ACM
Conference on Recommender Systems. pp. 151-154. 2016
[^] Tintarev, N., & Masthoff, J. Designing and evaluating
explanations for recommender systems. In Recommender
systems handbook. pp. 479-510. Springer, Boston, MA. 2011](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umap19-explanation-190609211950/75/Justifying-Recommendations-through-Aspect-based-Sentiment-Analysis-of-Users-Reviews-28-2048.jpg)