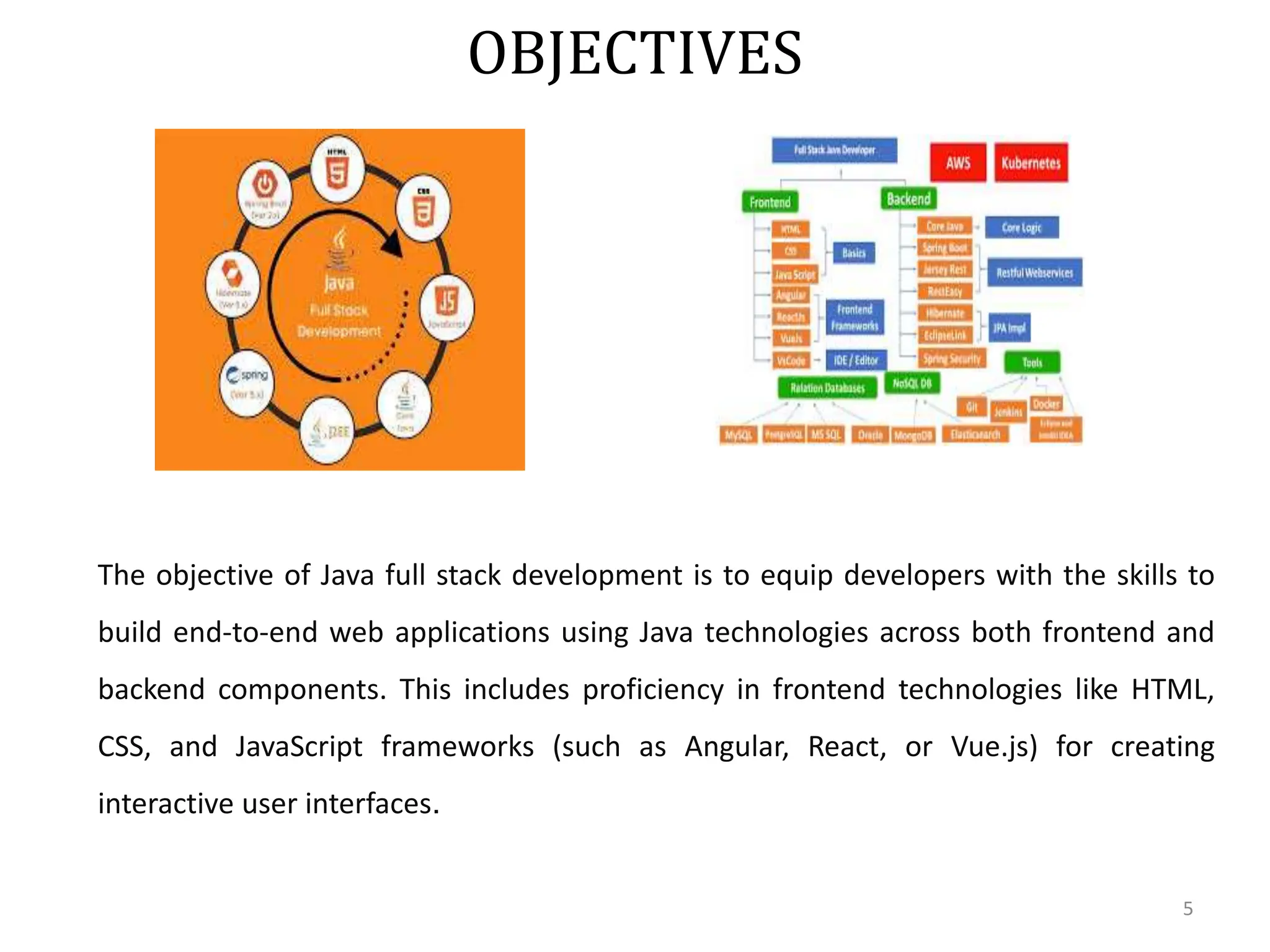
The document outlines a Java Full Stack internship that provides training in both frontend and backend technologies, emphasizing essential skills for building end-to-end web applications using Java. It details the company's profile, the objectives of the internship, key technologies involved (like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Spring Boot, and various databases), and the outcomes expected for participants. Ultimately, the internship aims to equip individuals with the necessary expertise to pursue entry-level software development roles or further education in the field.