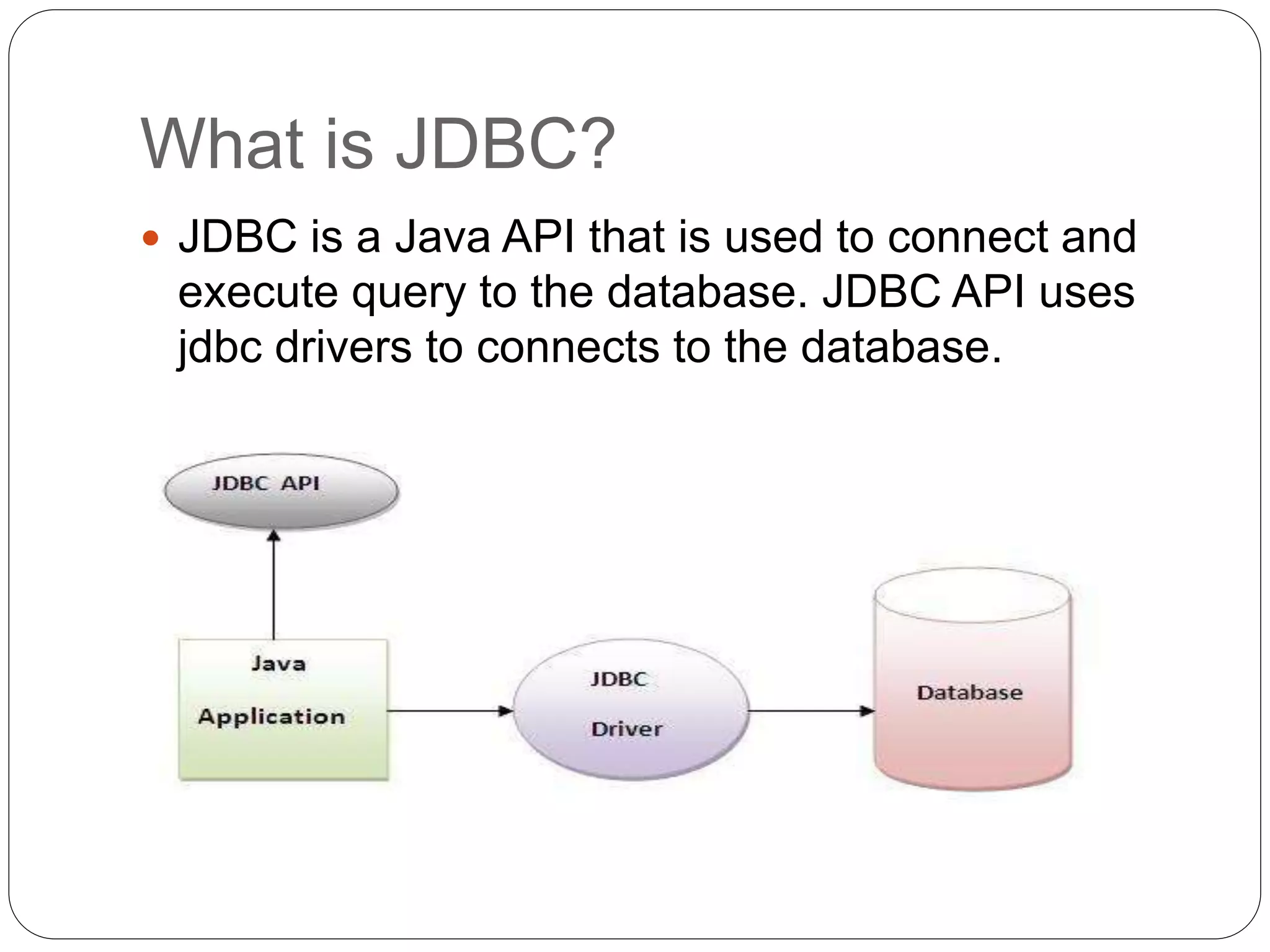
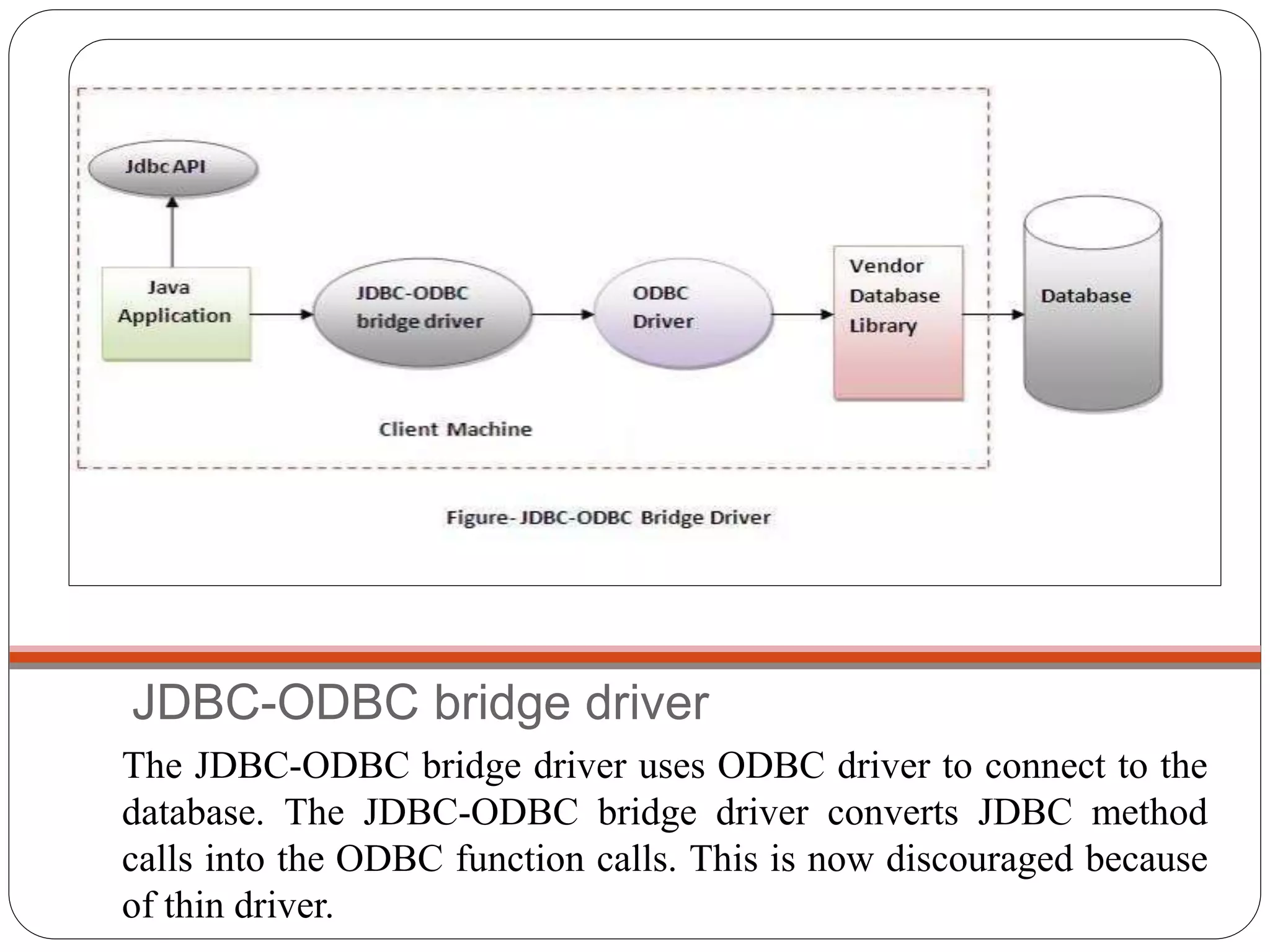
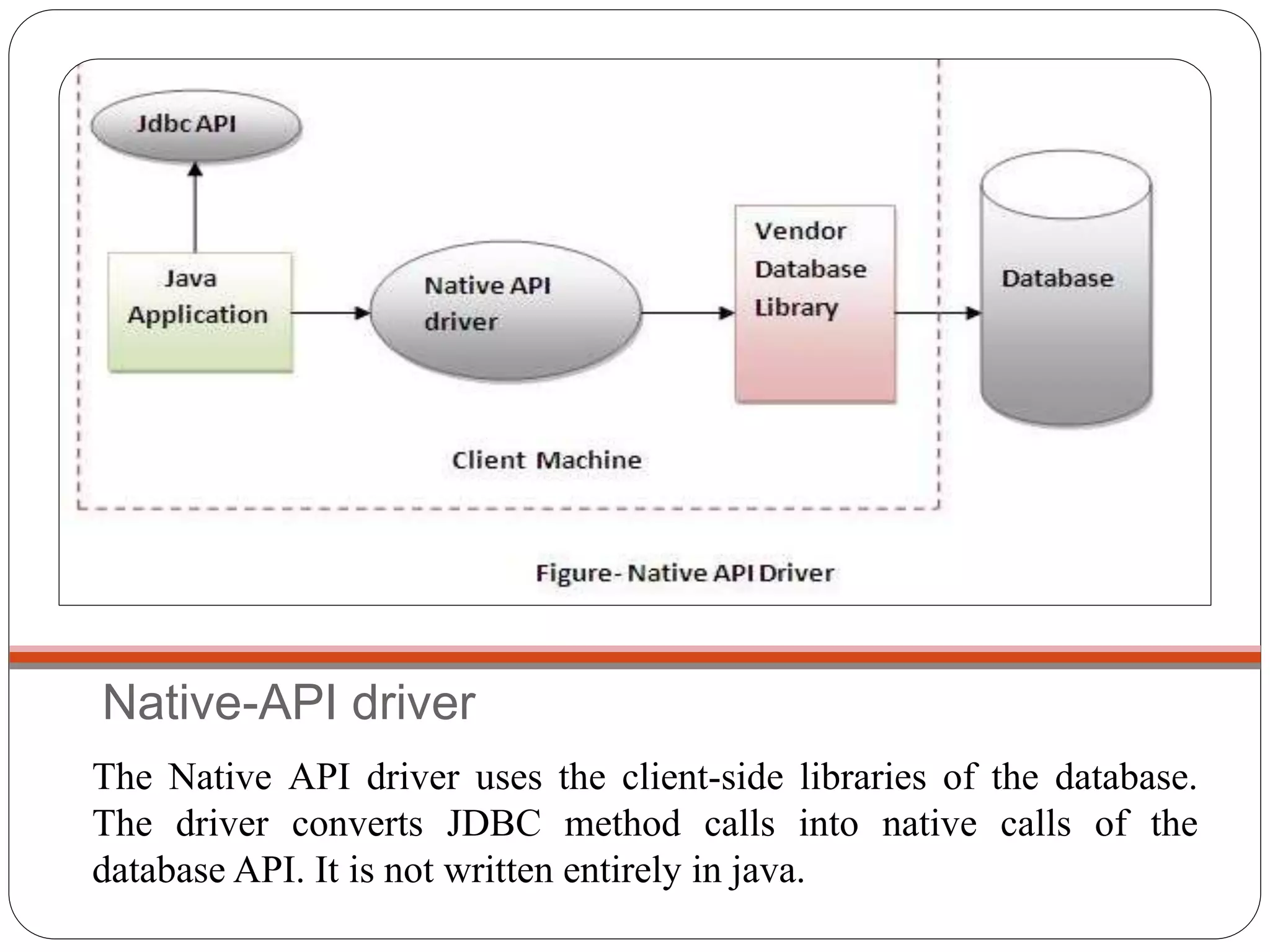
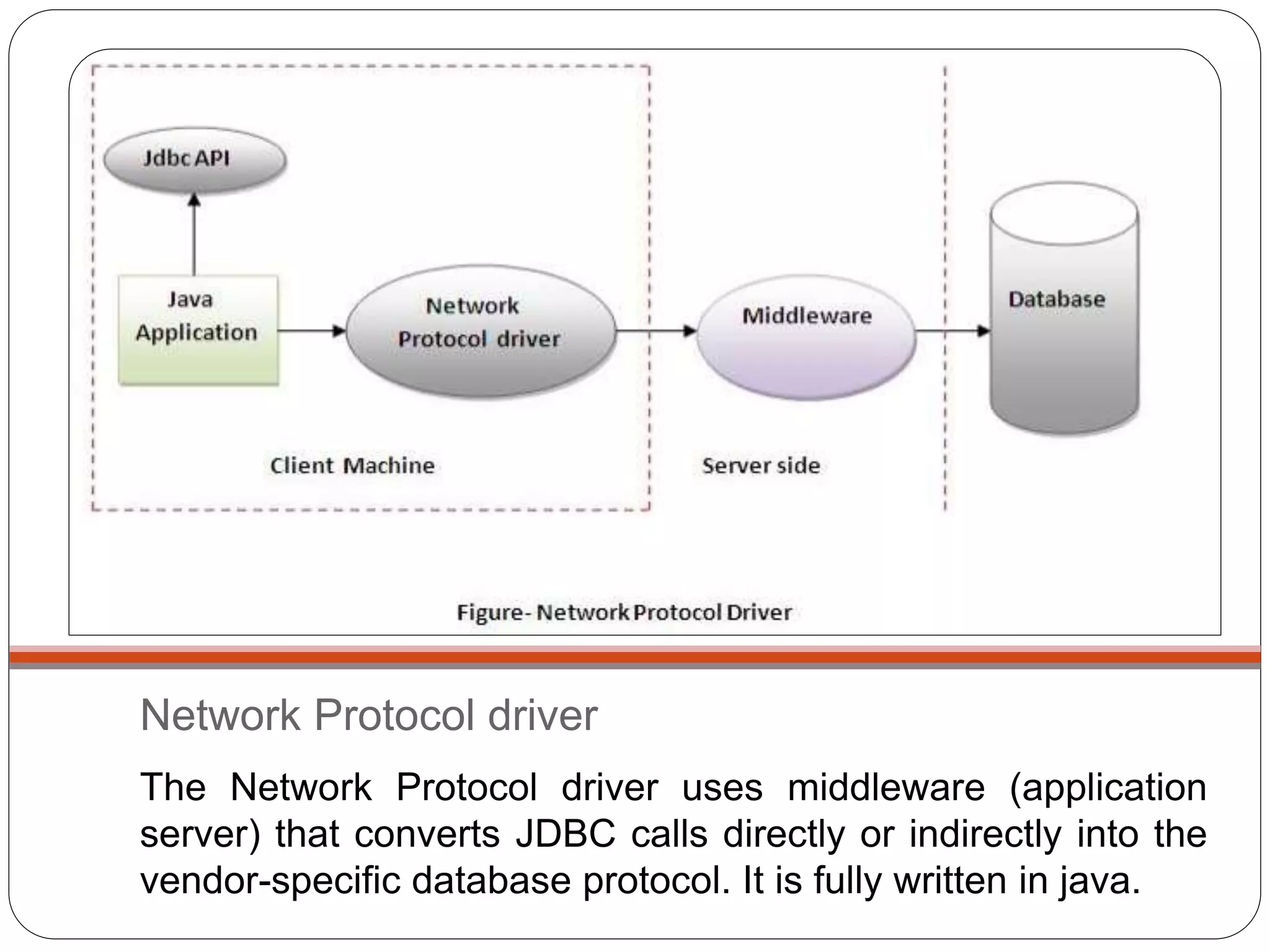
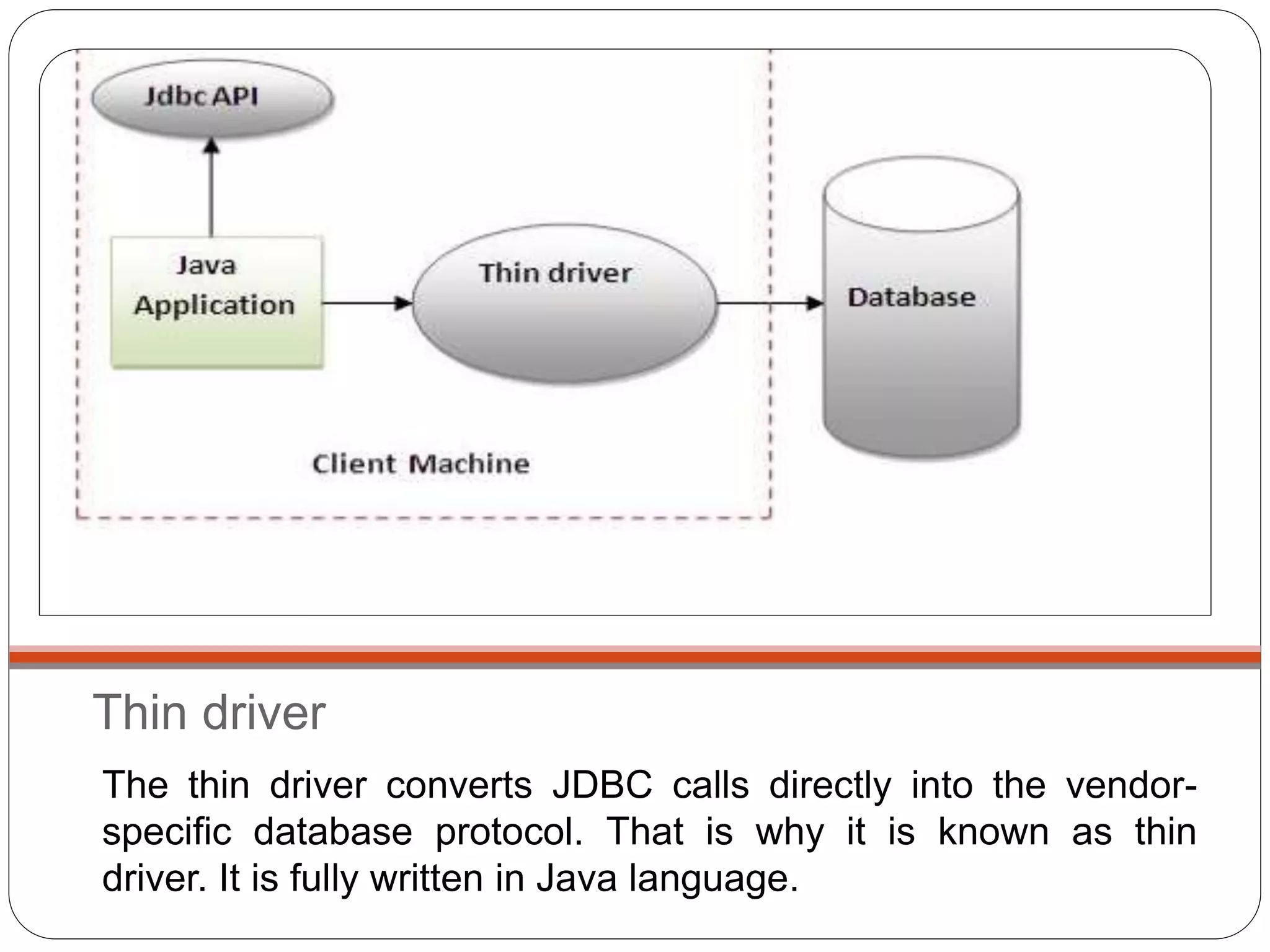
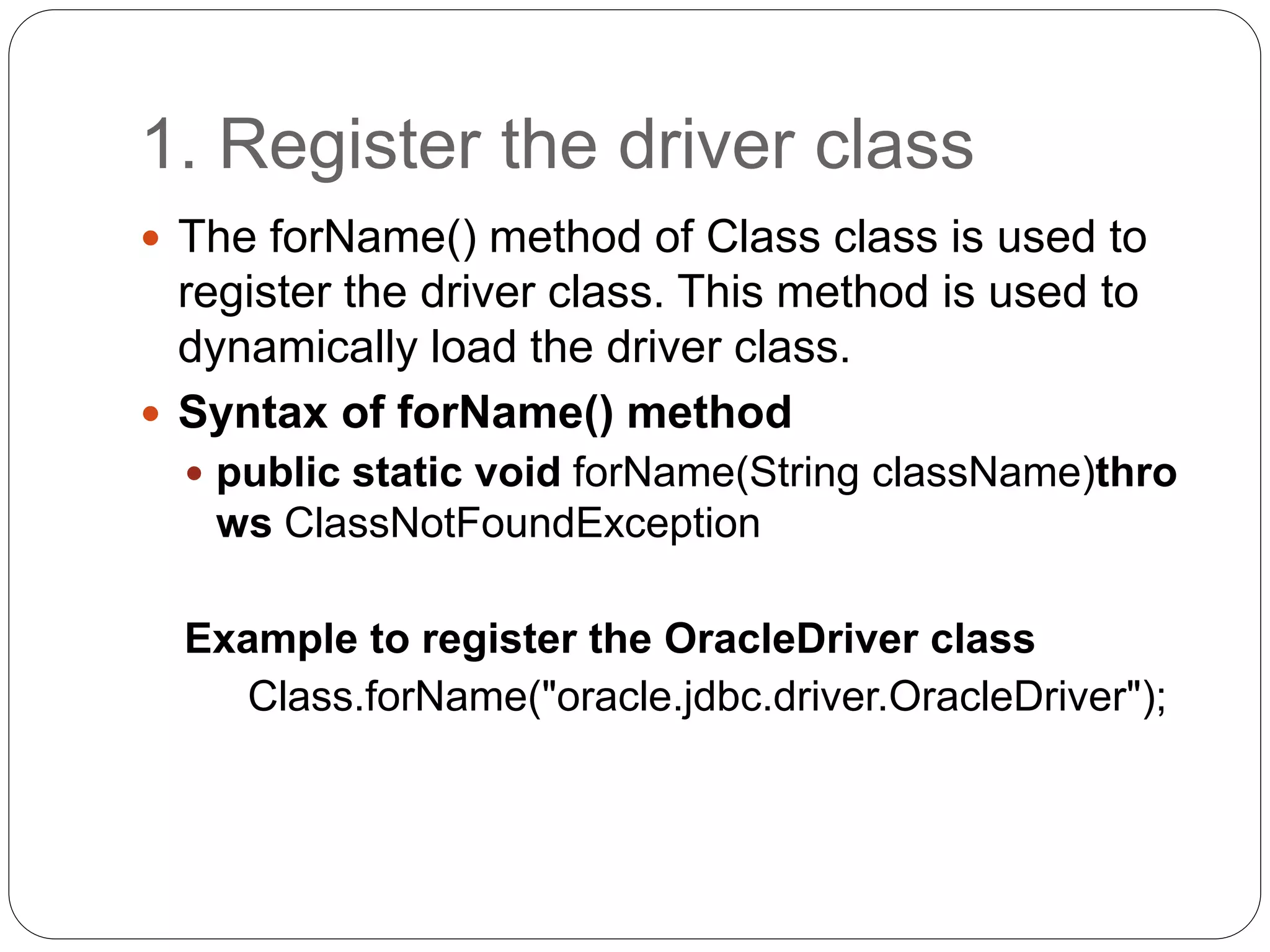
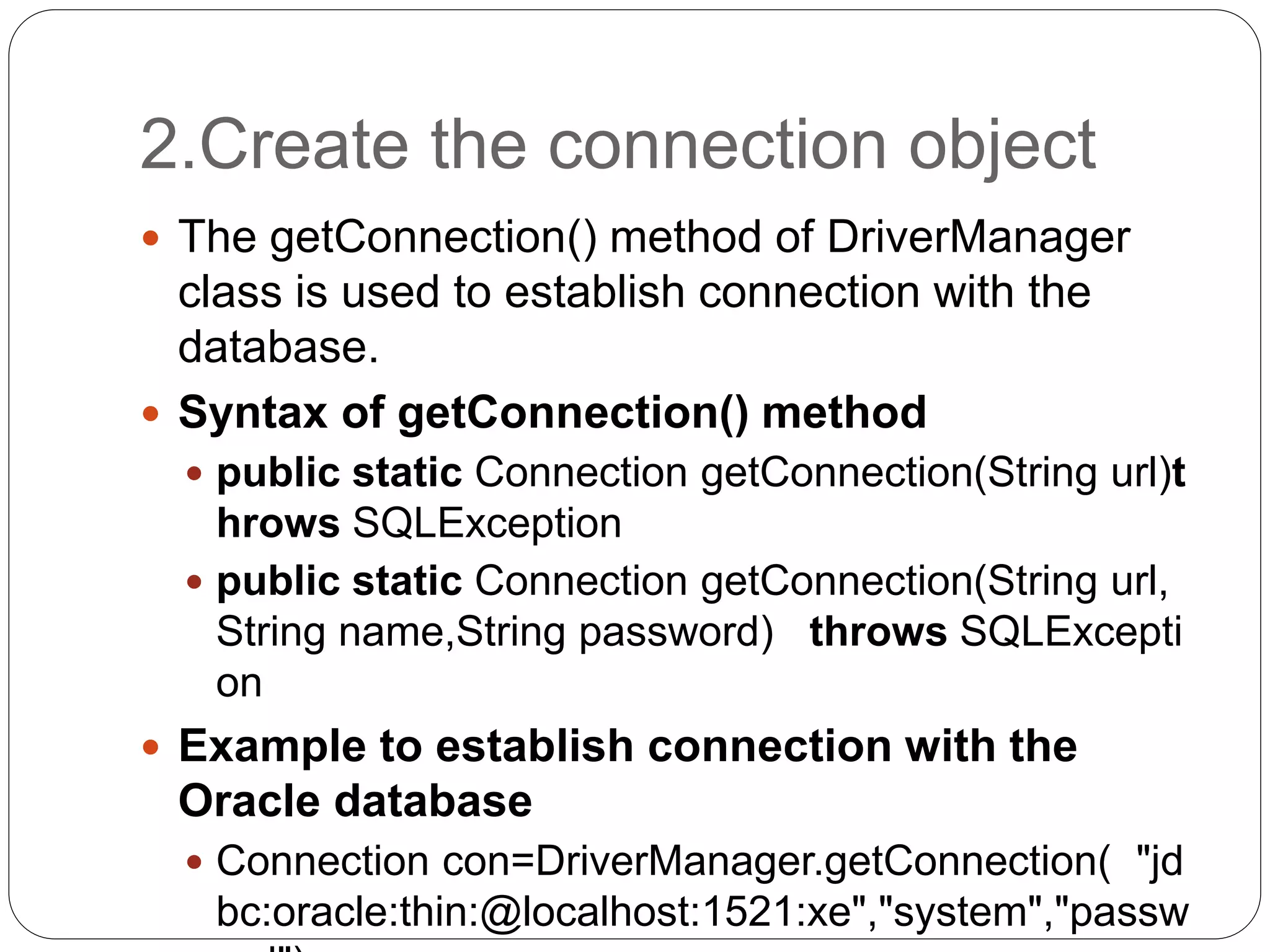
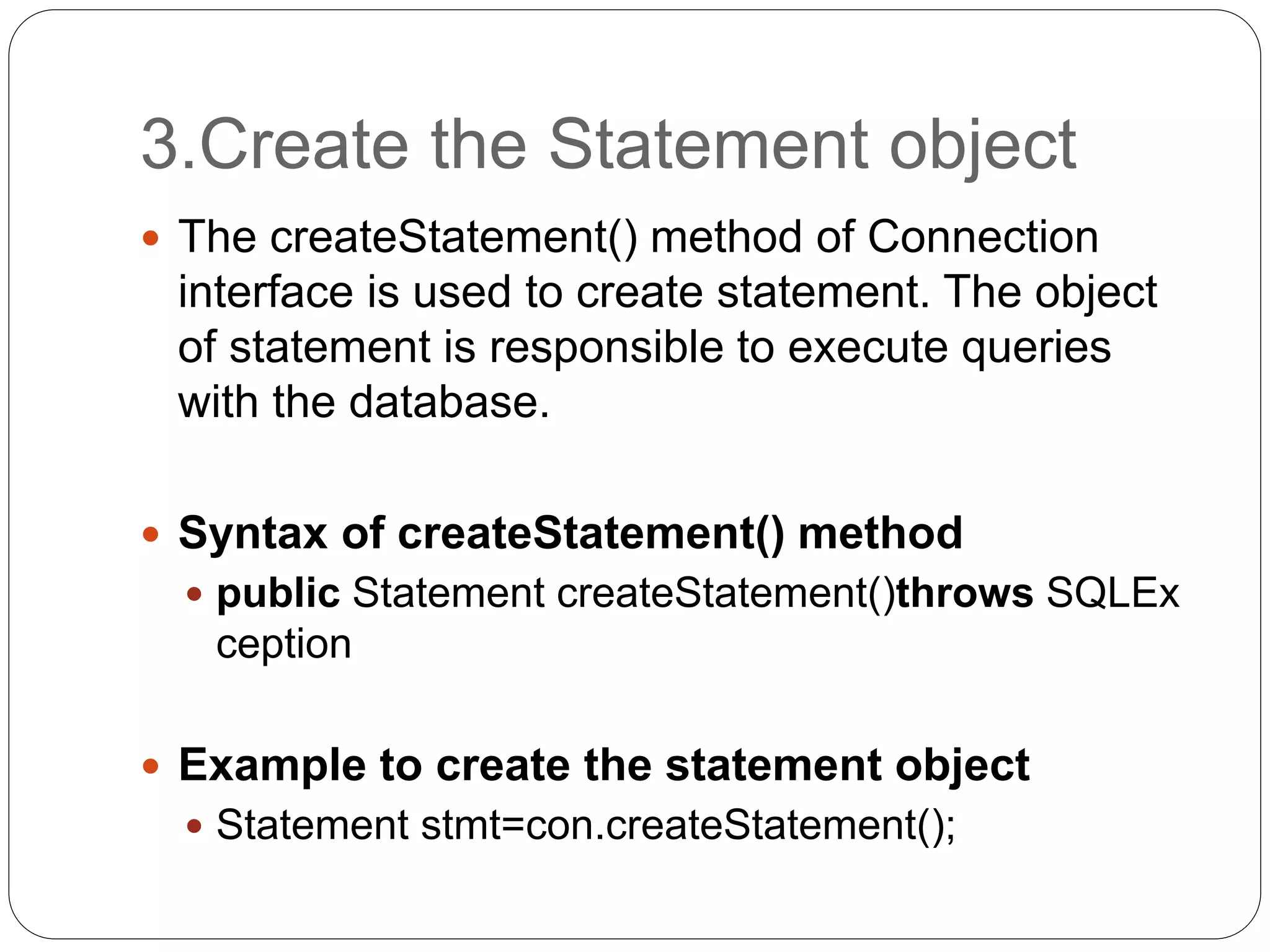
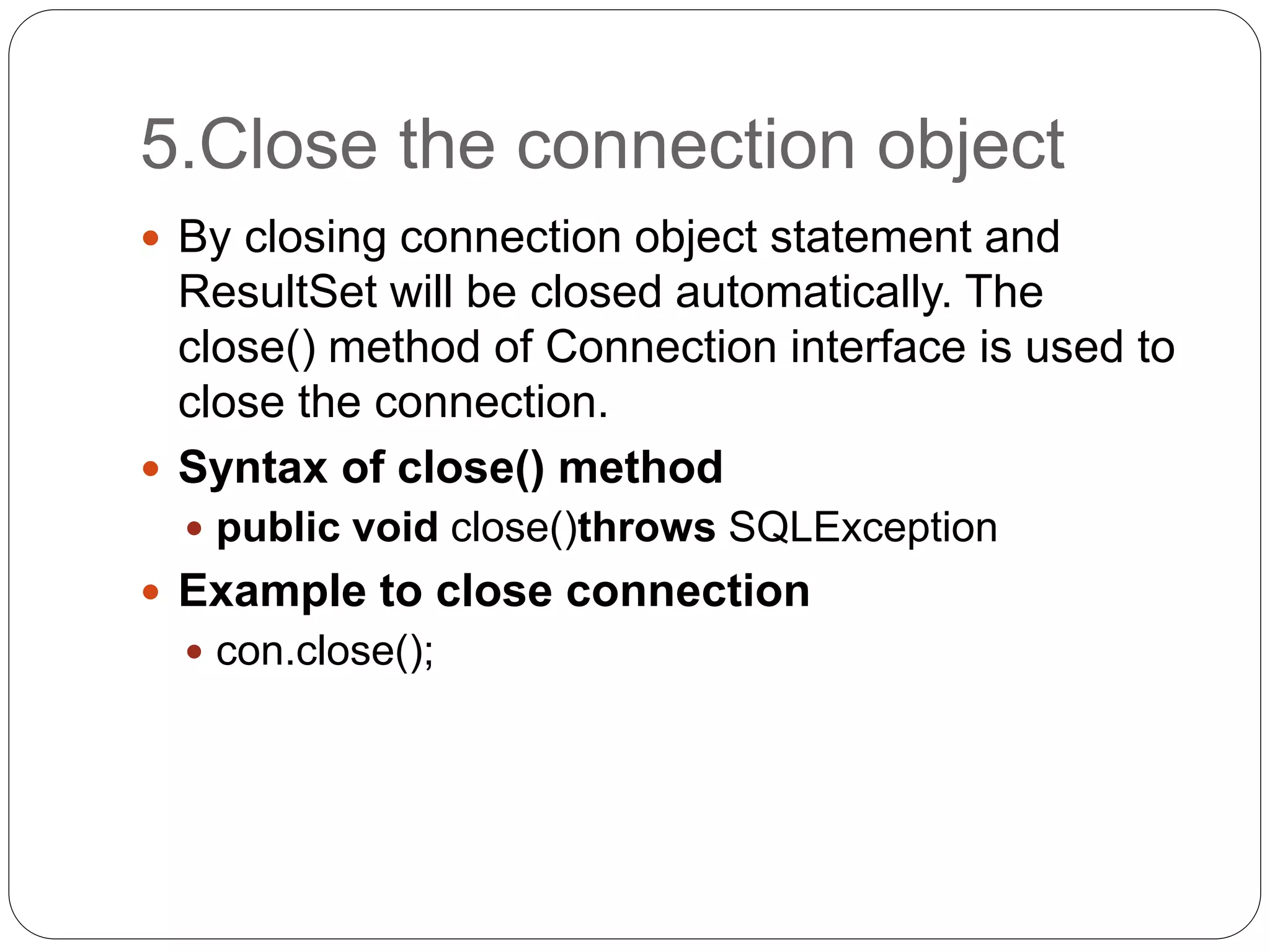
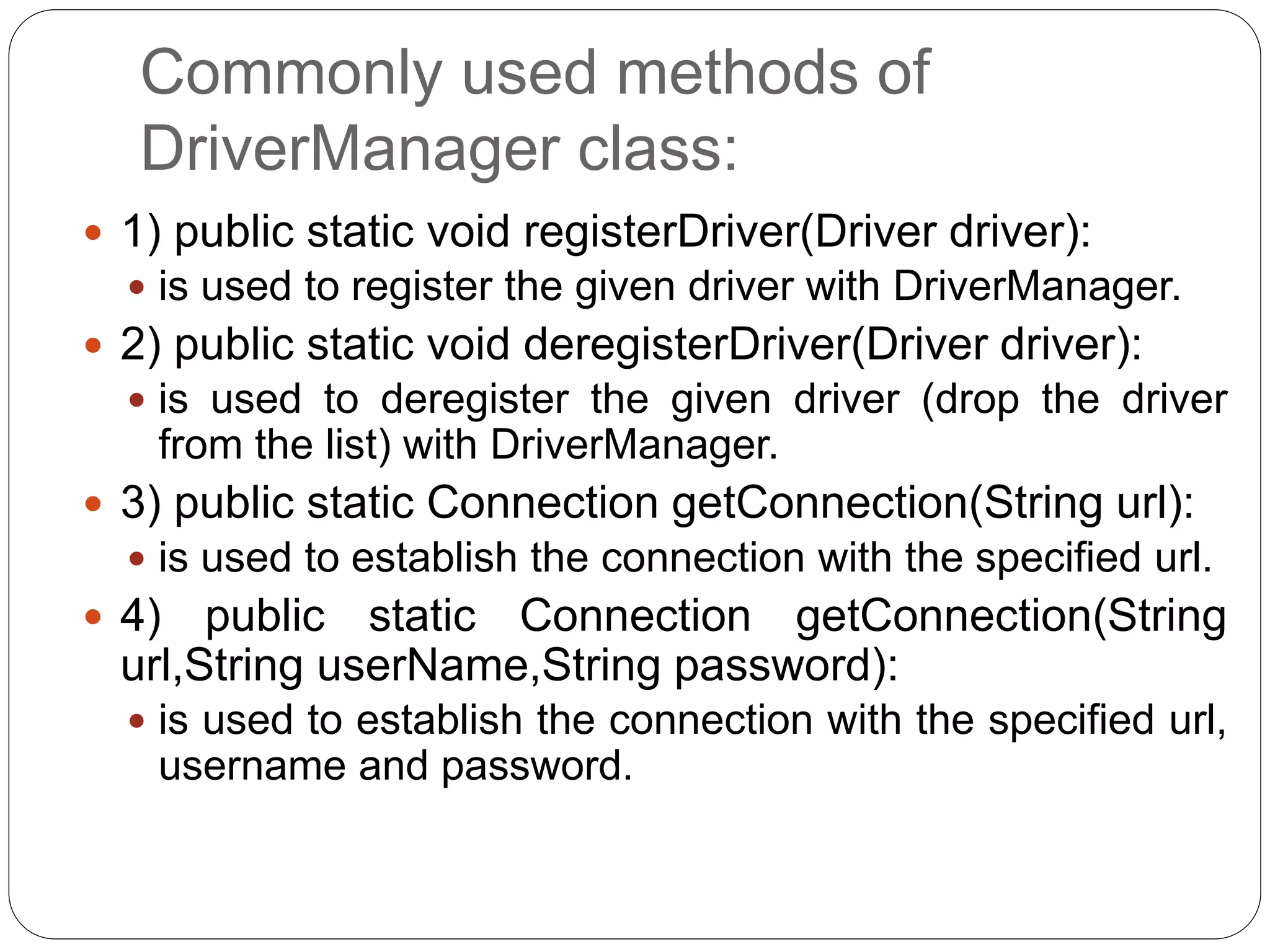
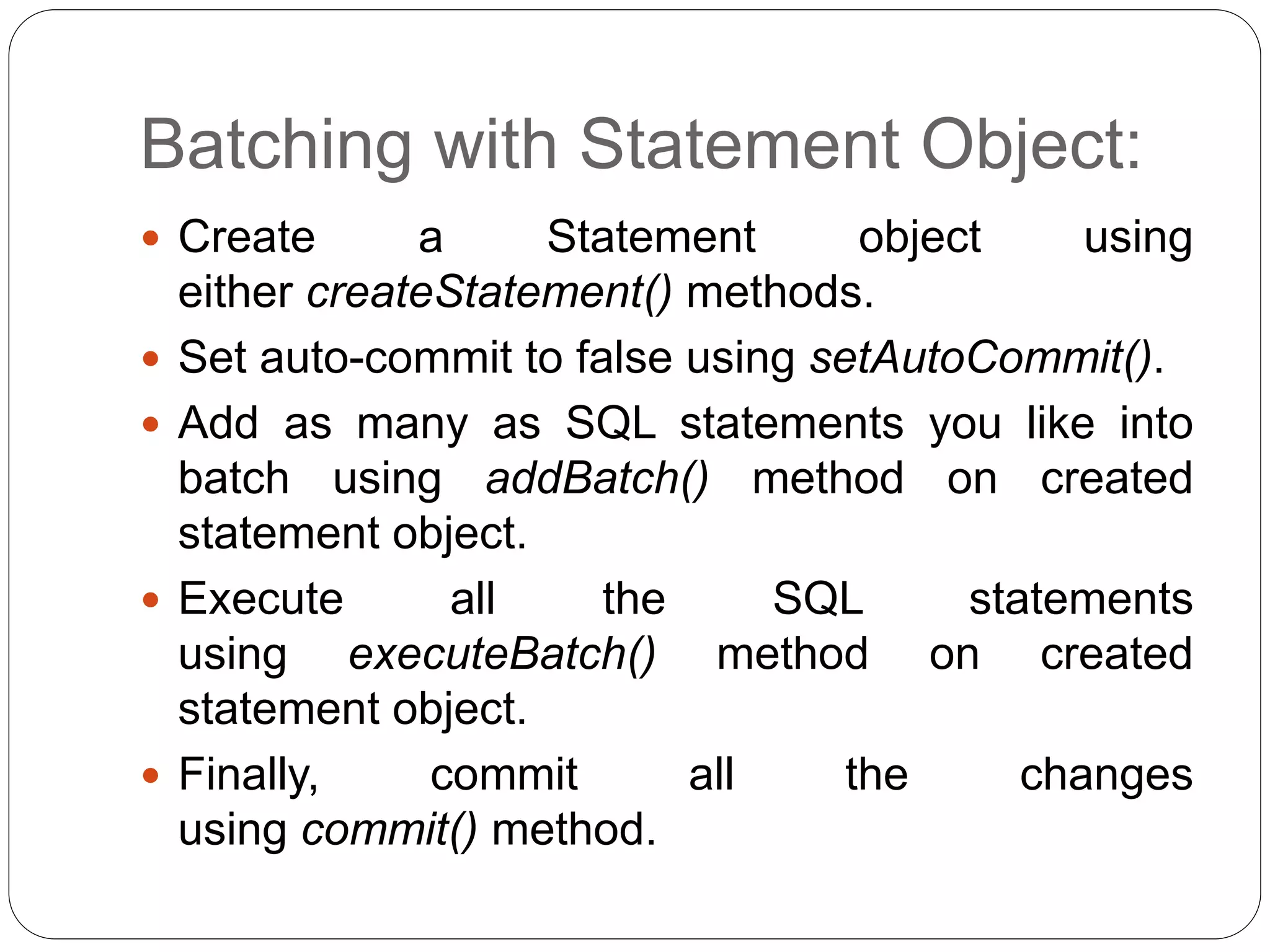
This document discusses Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) which is an API used to connect Java applications to databases. It describes the different types of JDBC drivers including bridge, native, network protocol, and thin drivers. It also outlines the basic steps to connect to a database using JDBC including registering the driver, getting a connection, creating statements, executing queries, and closing the connection. Key interfaces like Connection, Statement, PreparedStatement, and ResultSet are also summarized.