Recommended
PDF
PDF
ODT
KEY
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
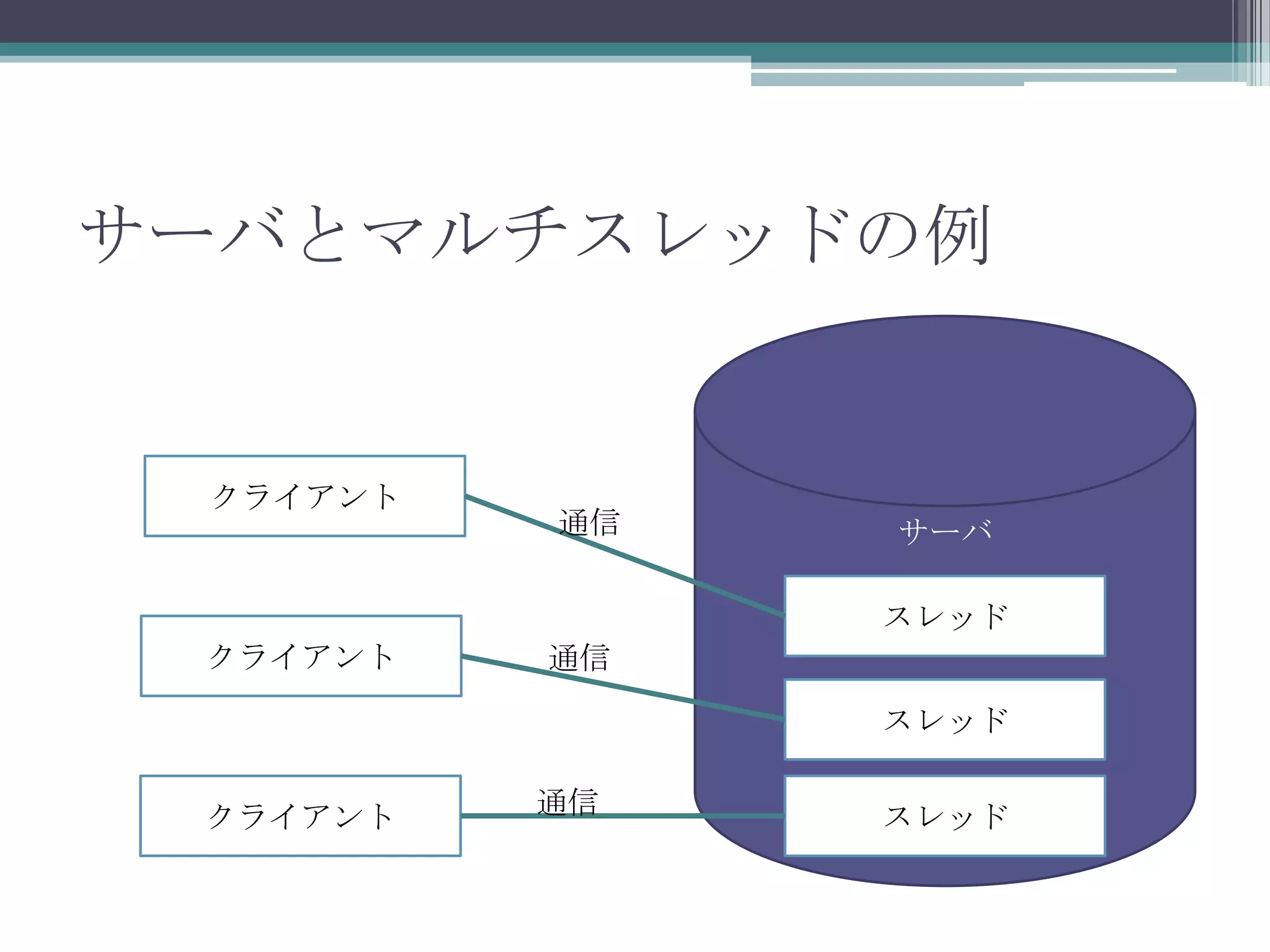
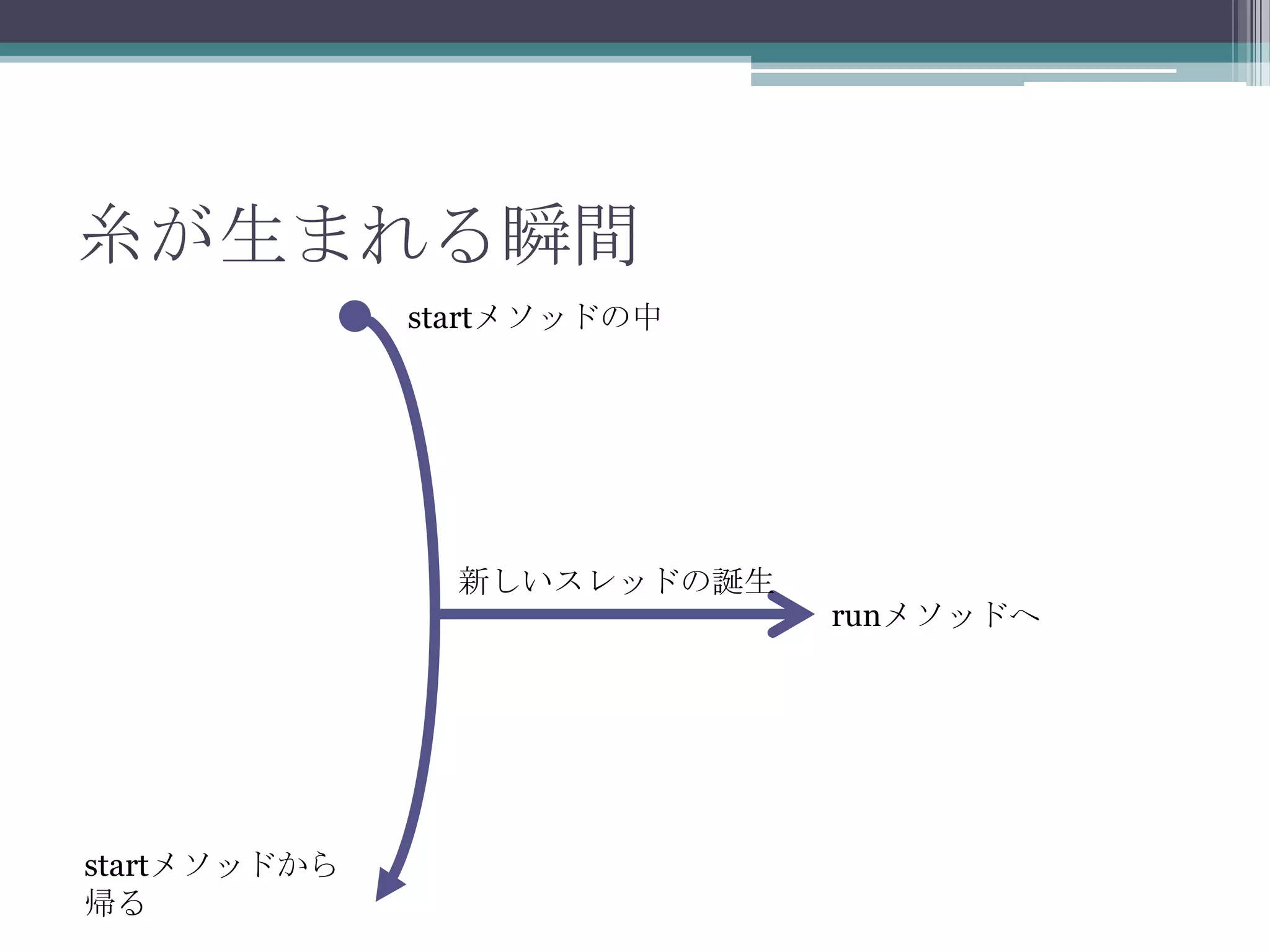
20120609 java oo道場(ネタのメモ)
PPTX
PPTX
PDF
Project Loom - 限定継続と軽量スレッド -
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
PPTX
Jvm reading-synchronization
PDF
HotSpot のロック: A Peek Under the Hood [JJUG ナイトセミナ JVM 特集 2015年8月]
PDF
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
Introduction to conccrent_lock
PDF
KEY
PDF
PDF
Project Loom + Project Panama
PPTX
Effective Java 輪読会 項目66-68
PDF
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
More Related Content
PDF
PDF
ODT
KEY
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
20120609 java oo道場(ネタのメモ)
Similar to Javaプログラミング入門【第8回】
PPTX
PPTX
PDF
Project Loom - 限定継続と軽量スレッド -
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
PPTX
Jvm reading-synchronization
PDF
HotSpot のロック: A Peek Under the Hood [JJUG ナイトセミナ JVM 特集 2015年8月]
PDF
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
Introduction to conccrent_lock
PDF
KEY
PDF
PDF
Project Loom + Project Panama
PPTX
Effective Java 輪読会 項目66-68
PDF
PPTX
More from Yukiko Kato
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
DOCX
PDF
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
DOCX
PPTX
DOCX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
Recently uploaded
PPTX
socialization in fundamentals of sociology.pptx
PDF
ПЛАН_профілактика правопорушень02.09.25.pdf
PDF
Seminar midterm presentation by Chihana Usui
PDF
ПЛАН_навчально_профілактичні_заходи_запобігання_негативним_проявам.pdf
PDF
ПОЛОЖЕННЯ_протидія насильству_підписане.pdf
PDF
Bases especialista admen rrhh minedu.pdf
PDF
ГРАФІК ГУРТКОВОЇ РОБОТИ 2025 kg72 grafik
Javaプログラミング入門【第8回】 1. 2. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Threadクラスでスレッドを作る例
• CountTenA.java
public class CountTenA extends Thread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CountTenA ct = new CountTenA();
ct.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("main:i = " + i);
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("run:i = " + i);
}
}
}
16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Runnableインターフェースを使ったス
レッドを作る例
• CountTenB.java
public class CountTenB implements Runnable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CountTenB ct = new CountTenB();
Thread th = new Thread(ct);
th.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("main:i = " + i);
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("run:i = " + i);
}
}
}
22. 23. スレッド開始の違い
• CountTenAは
CountTenA ct = new CountTenA();
ct.start();
▫ CountTenAのメソッドstartを呼び出している
▫ CountTenAにはstartメソッドは宣言されていないが、
スーパークラスのメソッドを呼び出している
• CountTenBは
CountTenB ct = new CountTenB();
Thread th = new Thread(ct);
th.start();
▫ CountTenBのオブジェクト(インスタンス)を引数に渡
してThreadのオブジェクトを生成し、Threadクラス
のstartメソッドを呼び出している
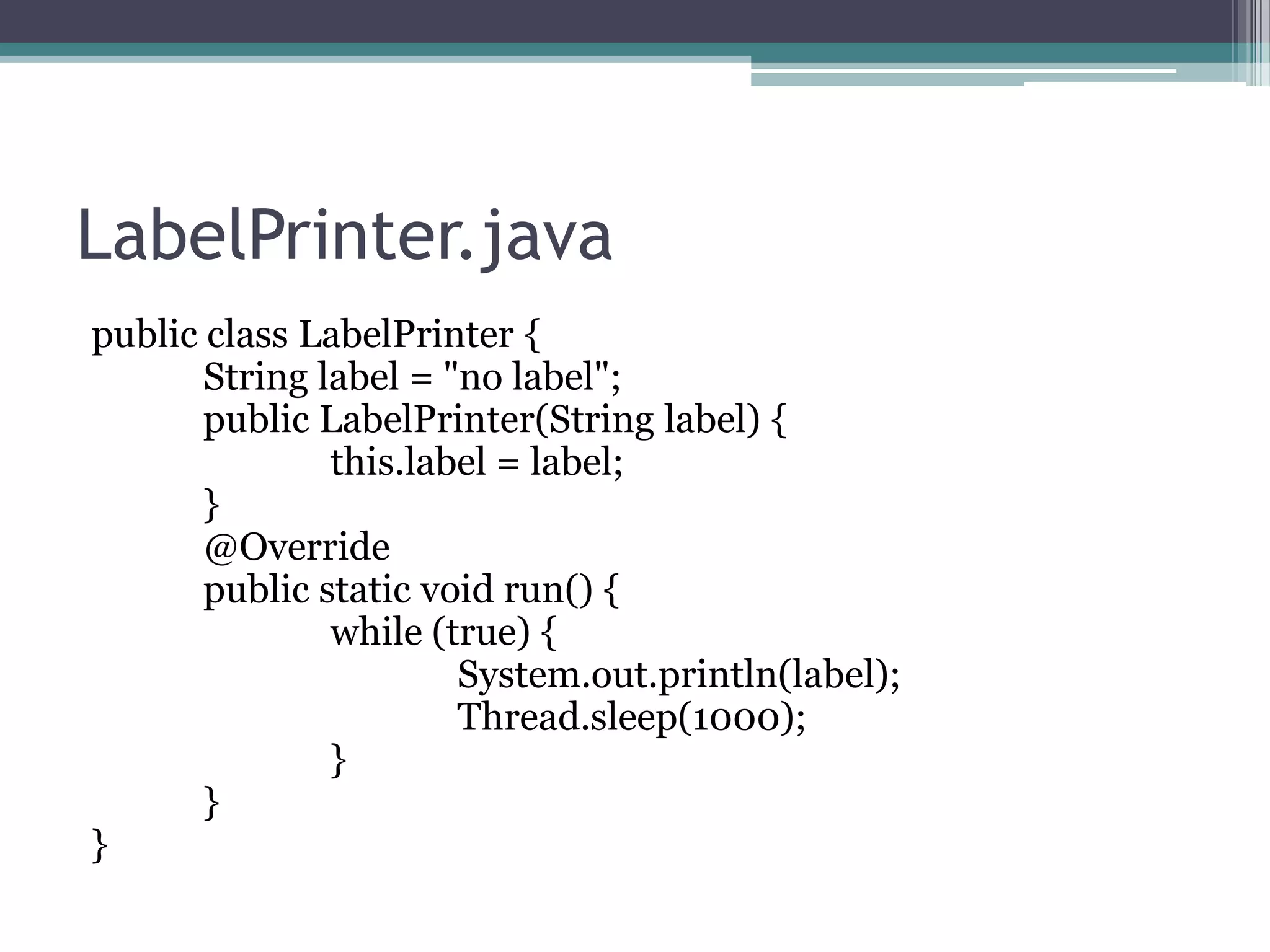
24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. LabelPrinter.java
public class LabelPrinter {
String label = "no label";
public LabelPrinter(String label) {
this.label = label;
}
@Override
public static void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println(label);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
}
30. 31. 32. 2つのスレッドが同じフィールドに代入
する例
• BadBank.java
public class BadBank {
// 預金残高
private int value = 0;
// 預入・引き出し
public void addMoney(int money) {
// 現在残高を保存
int currentValue = value;
// 状況を表示
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "がaddMoneyに入りました");
// 現在残高を変更
value += money;
if (currentValue + money != value) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "で矛盾が発生しました");
System.exit(-1);
}
// 状況を表示
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "がaddMoneyから出ました");
}
}
33. BadBankを使う例
public class BadBankTest extends Thread {
BadBank bank;
public BadBankTest(BadBank bank) {
this.bank = bank;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true) {
// 100円預入
bank.addMoney(100);
// 100円引出し
bank.addMoney(-100);
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
BadBank bank = new BadBank();
// 2つのスレッドで同じインスタンスを扱う
new BadBankTest(bank).start();
new BadBankTest(bank).start();
}
}
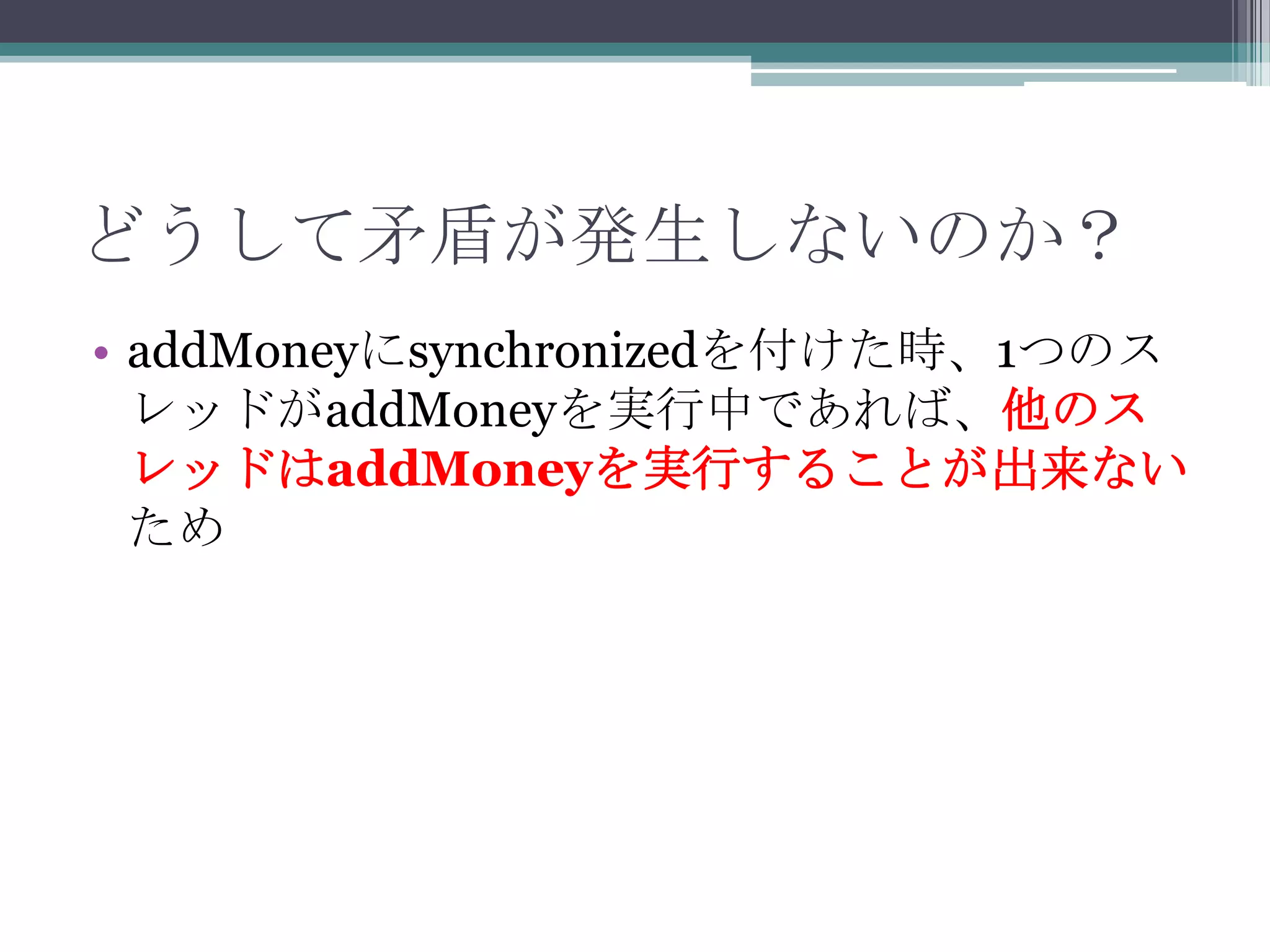
34. なぜ矛盾は発生するのか?
• 現在残高を保存する
int currentValue = value;
という部分と、矛盾チェックを行う
if (currentValue + money != value) {
....
}
という部分の間で、「スレッドの切り替え」が起こ
る可能性があるから
▫ 1つのスレッドが現在残高を保存し、矛盾がないか
チェックする前に、別のスレッドがvalueにmoneyを
足し込んでしまうから!
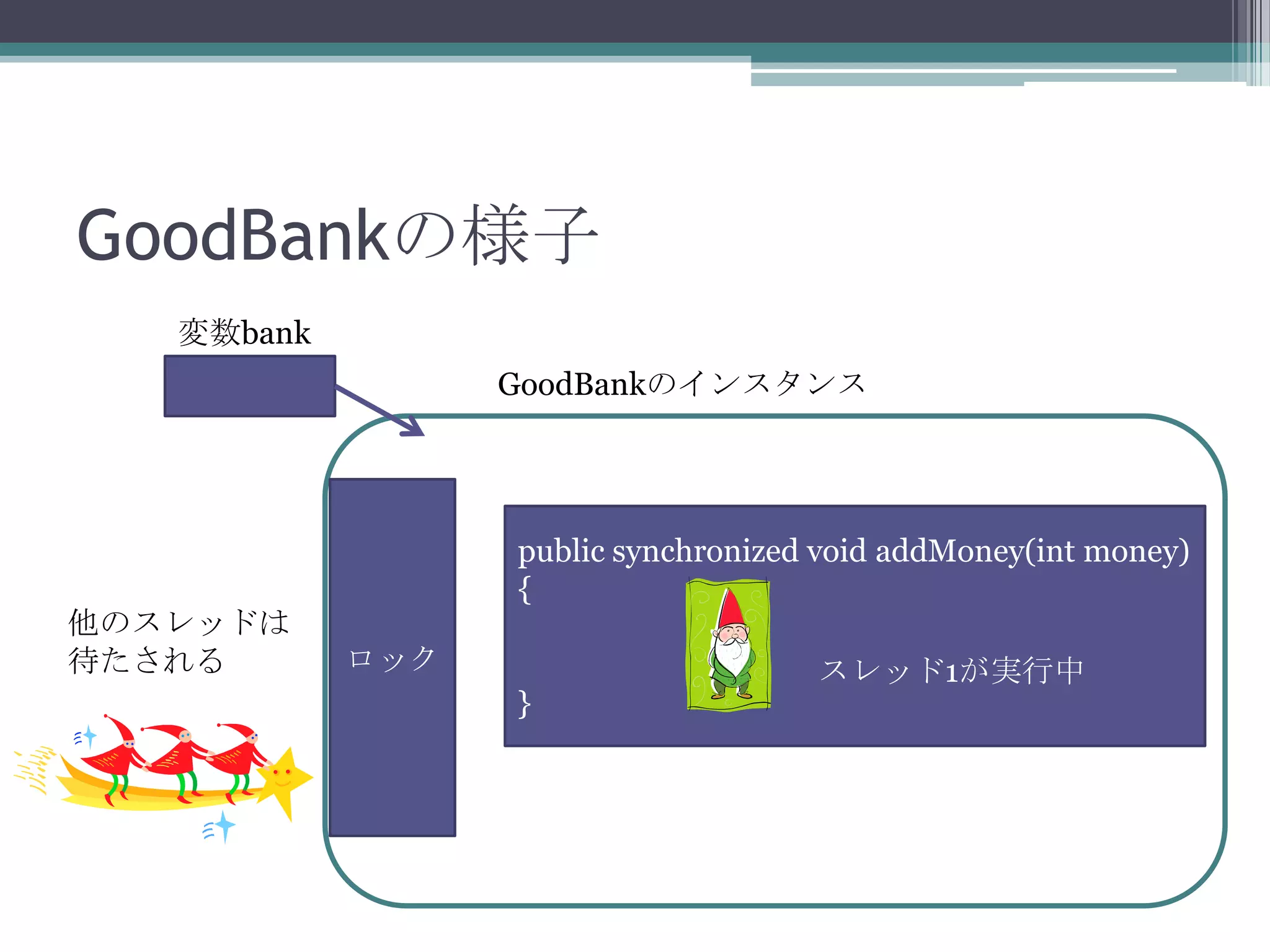
35. 36. BadBankを直したGoodBank
public class GoodBank {
// 預金残高
private int value = 0;
// 預入・引き出し
public synchronized void addMoney(int money) {
// 現在残高を保存
int currentValue = value;
// 状況を表示
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "がaddMoneyに入りました");
// 現在残高を変更
value += money;
if (currentValue + money != value) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "で矛盾が発生しました");
System.exit(-1);
}
// 状況を表示
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "がaddMoneyから出ました");
}
}
37. GoodBankを使う例
public class GoodBankTest extends Thread {
GoodBank bank;
public GoodBankTest(GoodBank bank) {
this.bank = bank;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true) {
// 100円預入
bank.addMoney(100);
// 100円引出し
bank.addMoney(-100);
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
GoodBank bank = new GoodBank();
new GoodBankTest(bank).start();
new GoodBankTest(bank).start();
}
}
38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. addMoneyの例
public void addMoney(int money) {
synchronized (this) {
// 現在残高を保存
int currentValue = value;
// 状況を表示
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "がaddMoneyに入りました
");
// 現在残高を変更
value += money;
if (currentValue + money != value) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "で矛盾が発生し
ました");
System.exit(-1);
}
// 状況を表示
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "がaddMoneyから出ました
");
}
}
45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 待ちたいときにはThread.sleep
public class Periodic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int tm = i * 1000;
System.out.println("Start sleep:tm = " +
tm);
try {
Thread.sleep(tm);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
}
52. 53. 54. 55. スレッドの終了を待つjoin
public class JoinTest extends Thread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JoinTest th = new JoinTest();
System.out.println("main:はじめ");
th.start();
System.out.println("main:終了待ちに入る");
try {
th.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("main:おわり");
}
56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. MyQueue.java(1)
public class MyQueue {
int[] intbuf;
int start;
int count;
public MyQueue(int size) {
intbuf = new int[size];
start = 0;
count = 0;
}
public synchronized void put(int n) throws InterruptedException {
while (count >= intbuf.length) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " wait : バッ
ファの空きを待つ");
wait();
}
int end = (start + count) % intbuf.length;
intbuf[end] = n;
count++;
notifyAll();
}
62. MyQueue.java(2)
public synchronized int take() throws InterruptedException {
while (count == 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "
wait : データを待つ");
wait();
}
int n = intbuf[start];
start = (start + 1) % intbuf.length;
count--;
notifyAll();
return n;
}
}
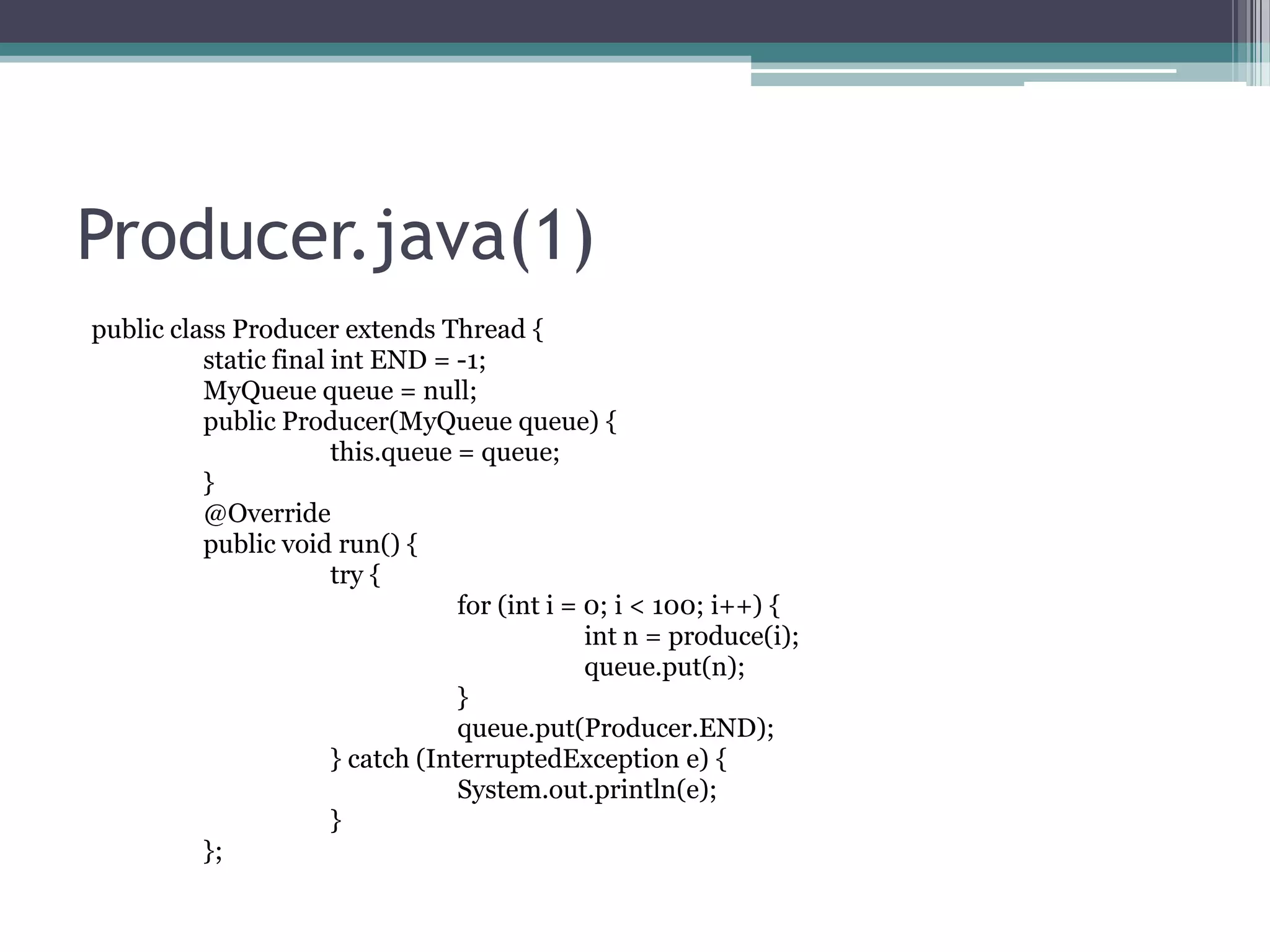
63. Producer.java(1)
public class Producer extends Thread {
static final int END = -1;
MyQueue queue = null;
public Producer(MyQueue queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
int n = produce(i);
queue.put(n);
}
queue.put(Producer.END);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
};
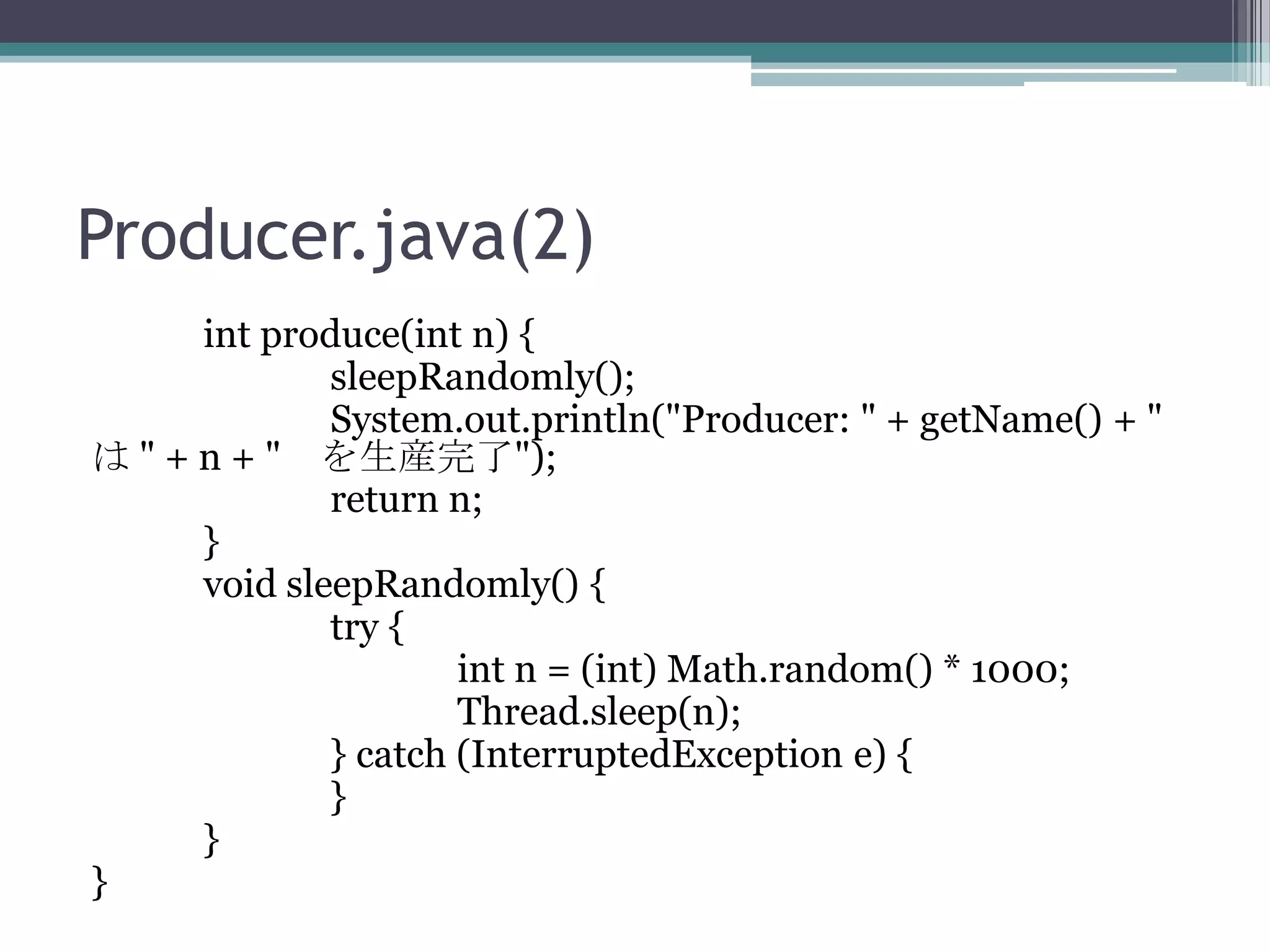
64. Producer.java(2)
int produce(int n) {
sleepRandomly();
System.out.println("Producer: " + getName() + "
は " + n + " を生産完了");
return n;
}
void sleepRandomly() {
try {
int n = (int) Math.random() * 1000;
Thread.sleep(n);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
65. Consumer.java(1)
public class Consumer extends Thread {
MyQueue queue = null;
public Consumer(MyQueue queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while(true) {
int n = queue.take();
if (n == Producer.END) {
break;
}
consume(n);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
66. Consumer.java(2)
void consume(int n) {
System.out.println("Consumer: " +
getName() + " は " + n + " を消費中");
sleepRandomly();
}
void sleepRandomly() {
try {
int n = (int) Math.random() * 1000;
Thread.sleep(n);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
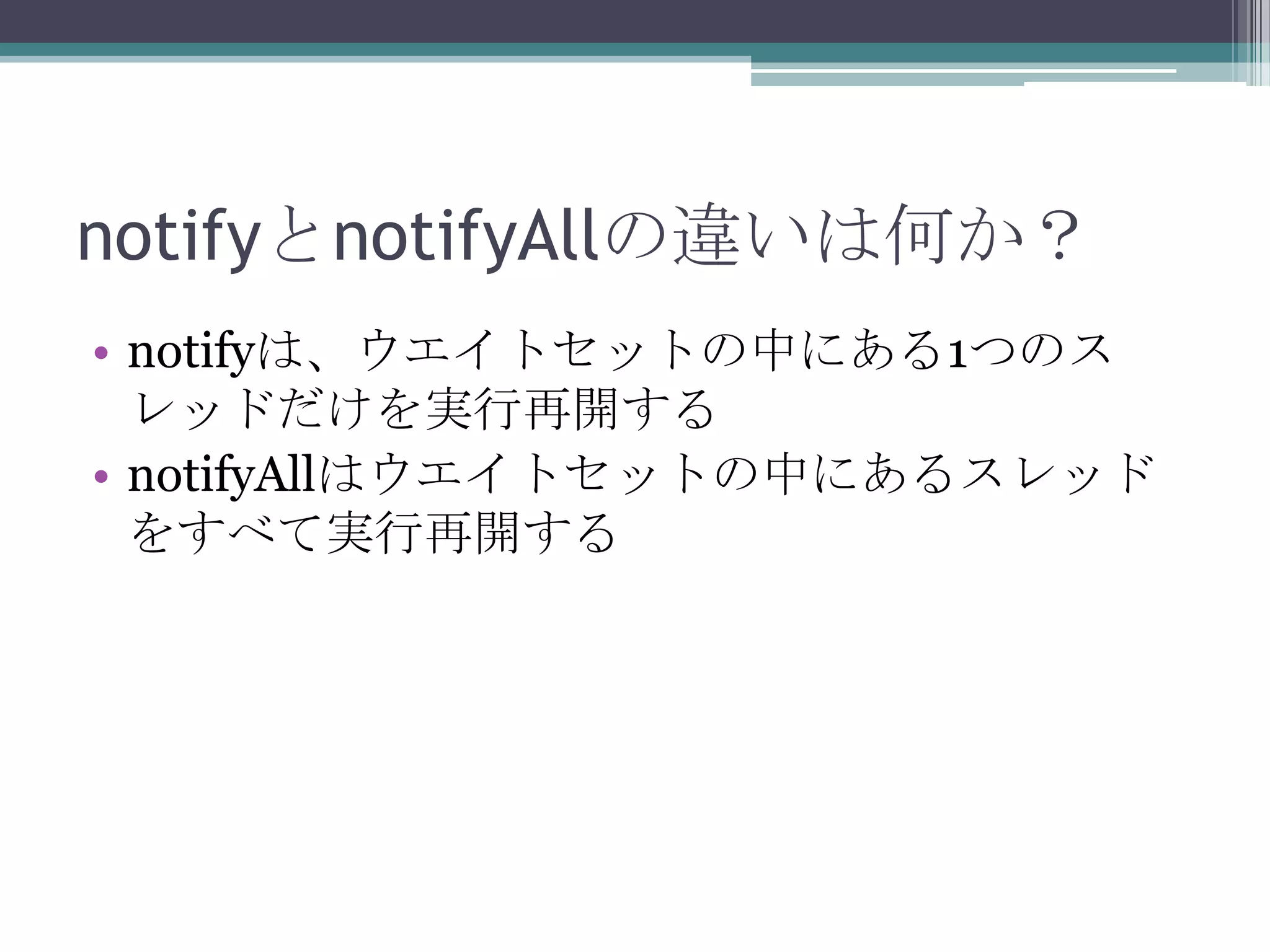
67. 68. 69. 70. MyQueueクラス
• putメソッド
▫ 引数nをデータとして格納するメソッド
▫ intbufが一杯ならば、そのスレッドは待ち状態になる
▫ 他のスレッドがnotifyAllすると、スレッドは動作可能
状態になる
• takeメソッド
▫ キューからデータを抜き出すメソッド
▫ キューが空だったら、waitメソッドで待ち状態に入る
▫ 他のスレッドがnotifyAllすると、動き始め、条件がみ
たされたことを確認するとwhile文を抜ける
71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. Job.java
public class Job {
int num;
public Job(int n) {
num = n;
}
public void work() {
System.out.println(this + " is working." );
try {
int n = (int) Math.random() * 10000;
Thread.sleep(n);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
public String toString() {
return "[Job " + num + "]";
}
}
81. SingleThreadProgram.java
public class SingleThreadProgram {
Job[] jobs;
public SingleThreadProgram(int jobcount) {
jobs = new Job[jobcount];
for (int i = 0; i< jobcount; i++) {
jobs[i] = new Job(i);
}
}
public void workAllJobs() {
for (int i = 0; i < jobs.length; i++) {
jobs[i].work();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleThreadProgram self = new SingleThreadProgram(10);
while(true) {
self.workAllJobs();
}
}
}
82.












![Threadクラスでスレッドを作る例
• CountTenA.java
public class CountTenA extends Thread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CountTenA ct = new CountTenA();
ct.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("main:i = " + i);
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("run:i = " + i);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java8-131216102632-phpapp01/75/Java-8-15-2048.jpg)




![Runnableインターフェースを使ったス
レッドを作る例
• CountTenB.java
public class CountTenB implements Runnable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CountTenB ct = new CountTenB();
Thread th = new Thread(ct);
th.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("main:i = " + i);
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("run:i = " + i);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java8-131216102632-phpapp01/75/Java-8-21-2048.jpg)







![PrintHello.java
public class PrintHello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LabelPrinter th = new LabelPrinter("こ
んにちは!");
th.start();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java8-131216102632-phpapp01/75/Java-8-30-2048.jpg)


![BadBankを使う例
public class BadBankTest extends Thread {
BadBank bank;
public BadBankTest(BadBank bank) {
this.bank = bank;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true) {
// 100円預入
bank.addMoney(100);
// 100円引出し
bank.addMoney(-100);
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
BadBank bank = new BadBank();
// 2つのスレッドで同じインスタンスを扱う
new BadBankTest(bank).start();
new BadBankTest(bank).start();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java8-131216102632-phpapp01/75/Java-8-33-2048.jpg)



![GoodBankを使う例
public class GoodBankTest extends Thread {
GoodBank bank;
public GoodBankTest(GoodBank bank) {
this.bank = bank;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true) {
// 100円預入
bank.addMoney(100);
// 100円引出し
bank.addMoney(-100);
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
GoodBank bank = new GoodBank();
new GoodBankTest(bank).start();
new GoodBankTest(bank).start();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java8-131216102632-phpapp01/75/Java-8-37-2048.jpg)










![待ちたいときにはThread.sleep
public class Periodic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int tm = i * 1000;
System.out.println("Start sleep:tm = " +
tm);
try {
Thread.sleep(tm);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java8-131216102632-phpapp01/75/Java-8-51-2048.jpg)


![スレッドの終了を待つjoin
public class JoinTest extends Thread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JoinTest th = new JoinTest();
System.out.println("main:はじめ");
th.start();
System.out.println("main:終了待ちに入る");
try {
th.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("main:おわり");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java8-131216102632-phpapp01/75/Java-8-55-2048.jpg)




![ProducerConsumer.java
public class ProducerConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyQueue queue = new MyQueue(3);
Producer producer = new
Producer(queue);
Consumer consumer = new
Consumer(queue);
producer.start();
consumer.start();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java8-131216102632-phpapp01/75/Java-8-60-2048.jpg)
![MyQueue.java(1)
public class MyQueue {
int[] intbuf;
int start;
int count;
public MyQueue(int size) {
intbuf = new int[size];
start = 0;
count = 0;
}
public synchronized void put(int n) throws InterruptedException {
while (count >= intbuf.length) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " wait : バッ
ファの空きを待つ");
wait();
}
int end = (start + count) % intbuf.length;
intbuf[end] = n;
count++;
notifyAll();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java8-131216102632-phpapp01/75/Java-8-61-2048.jpg)
![MyQueue.java(2)
public synchronized int take() throws InterruptedException {
while (count == 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "
wait : データを待つ");
wait();
}
int n = intbuf[start];
start = (start + 1) % intbuf.length;
count--;
notifyAll();
return n;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java8-131216102632-phpapp01/75/Java-8-62-2048.jpg)












![Job.java
public class Job {
int num;
public Job(int n) {
num = n;
}
public void work() {
System.out.println(this + " is working." );
try {
int n = (int) Math.random() * 10000;
Thread.sleep(n);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
public String toString() {
return "[Job " + num + "]";
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java8-131216102632-phpapp01/75/Java-8-80-2048.jpg)
![SingleThreadProgram.java
public class SingleThreadProgram {
Job[] jobs;
public SingleThreadProgram(int jobcount) {
jobs = new Job[jobcount];
for (int i = 0; i< jobcount; i++) {
jobs[i] = new Job(i);
}
}
public void workAllJobs() {
for (int i = 0; i < jobs.length; i++) {
jobs[i].work();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleThreadProgram self = new SingleThreadProgram(10);
while(true) {
self.workAllJobs();
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java8-131216102632-phpapp01/75/Java-8-81-2048.jpg)
![参考文献
• Java言語 プログラミングレッスン[第3版]下
▫ 結城浩[著]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java8-131216102632-phpapp01/75/Java-8-82-2048.jpg)