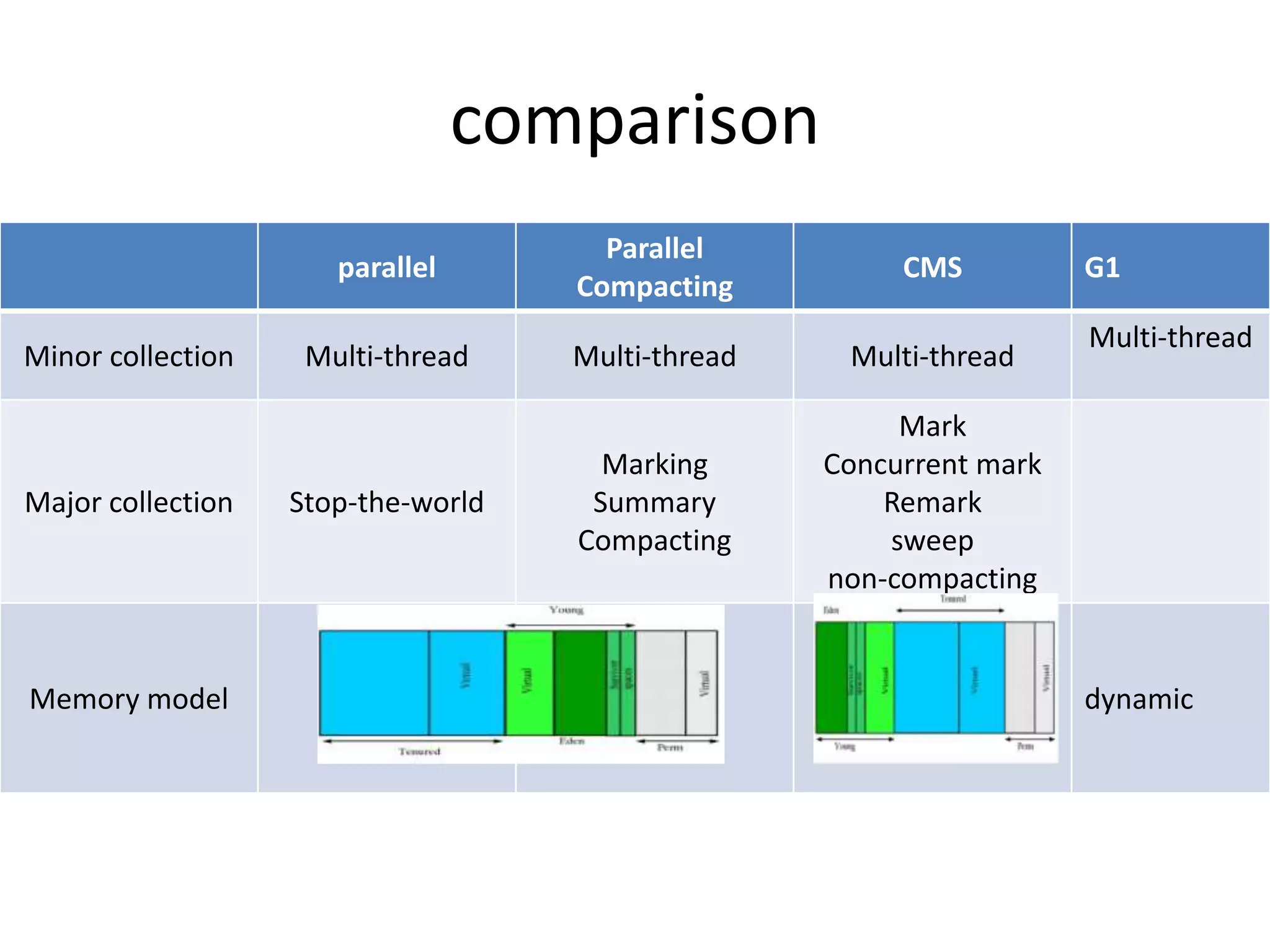
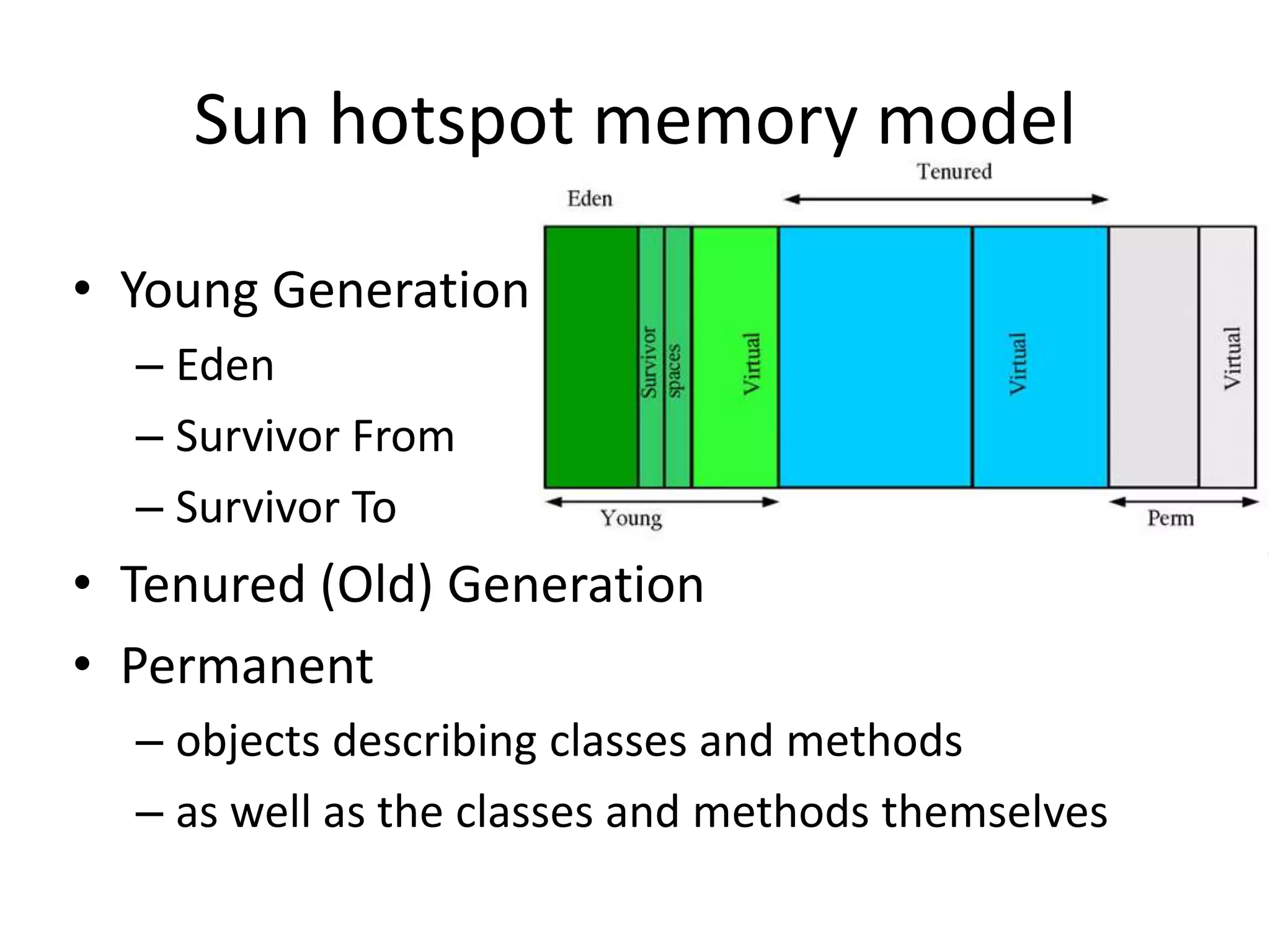
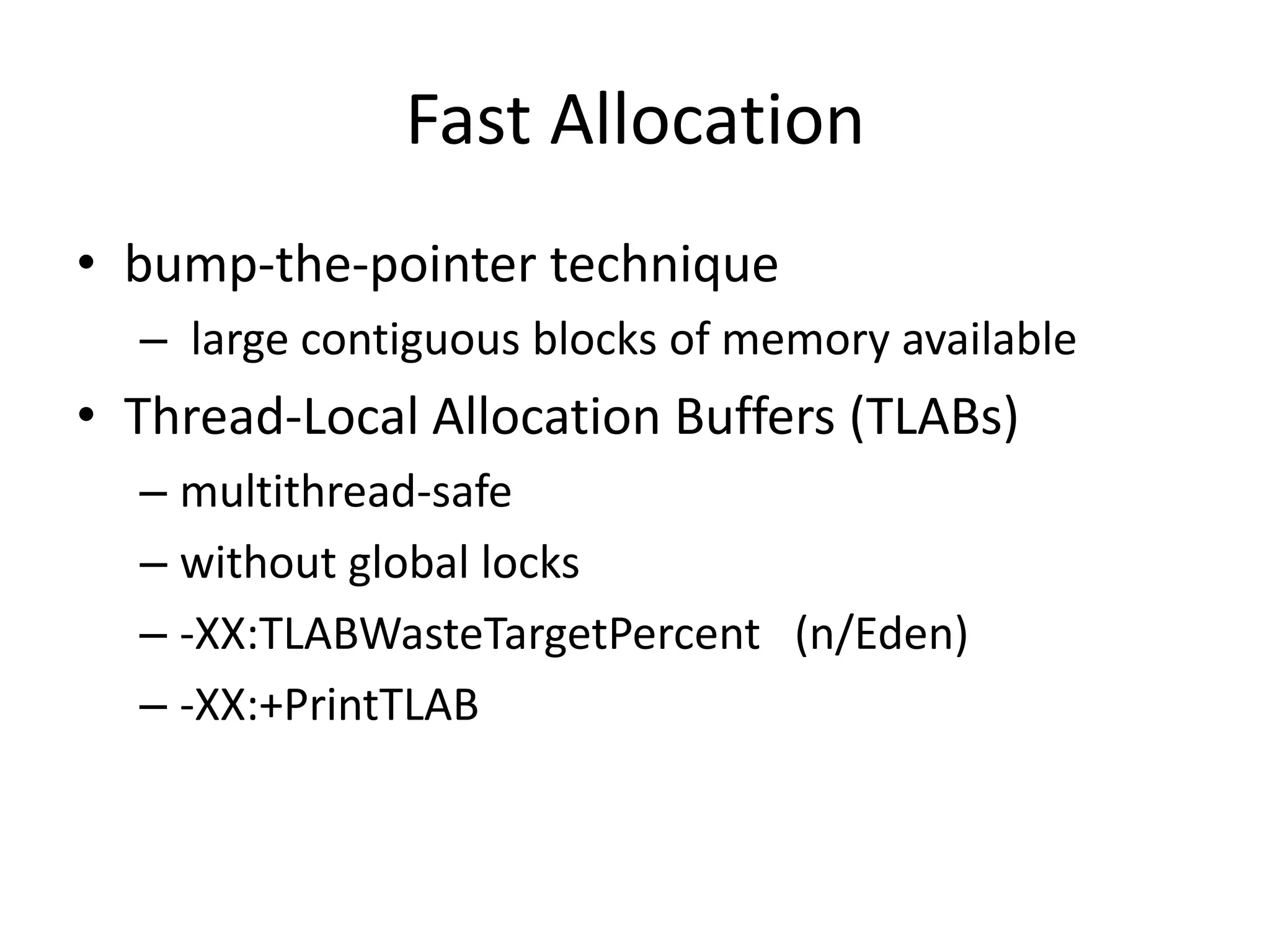
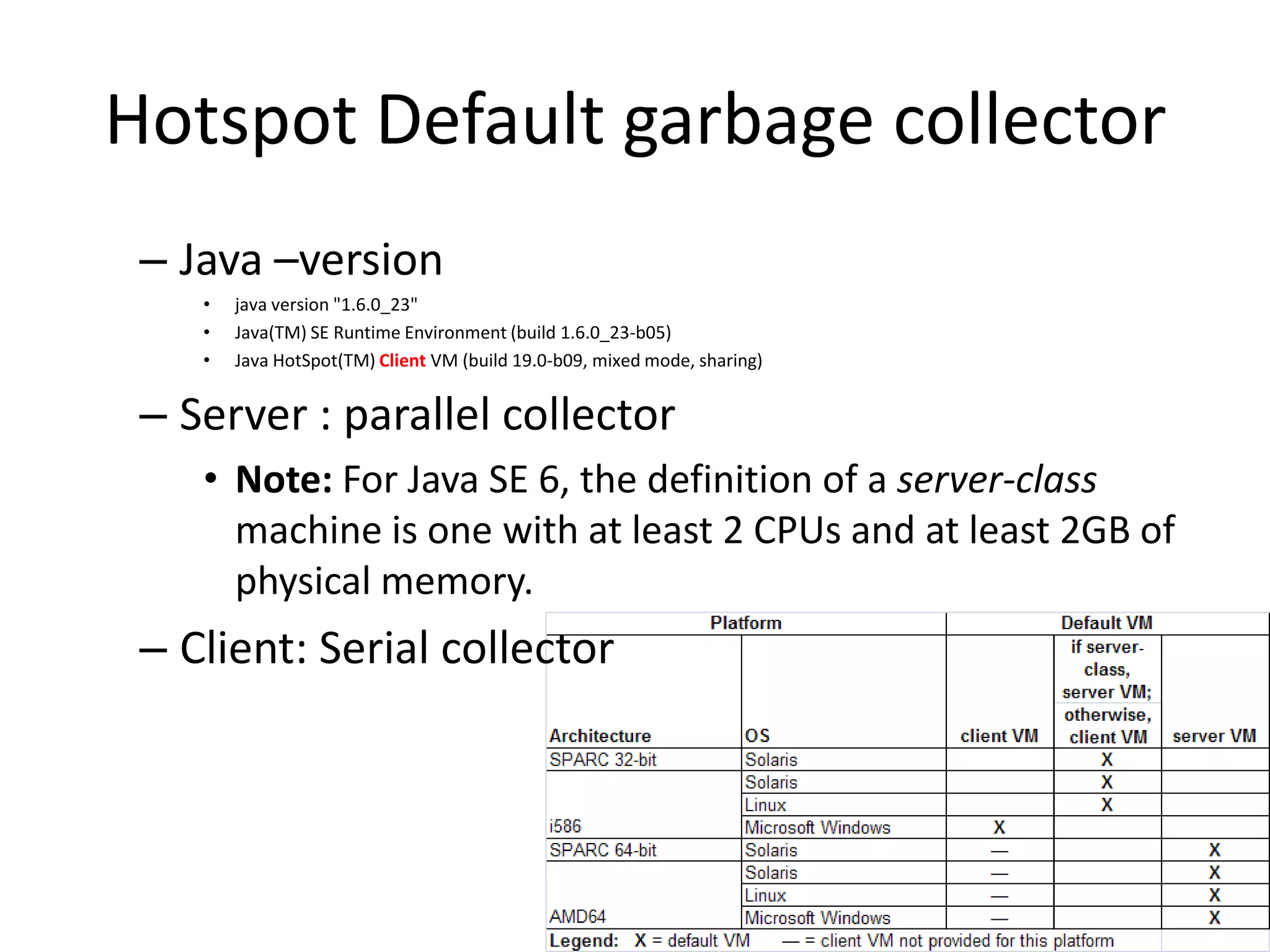
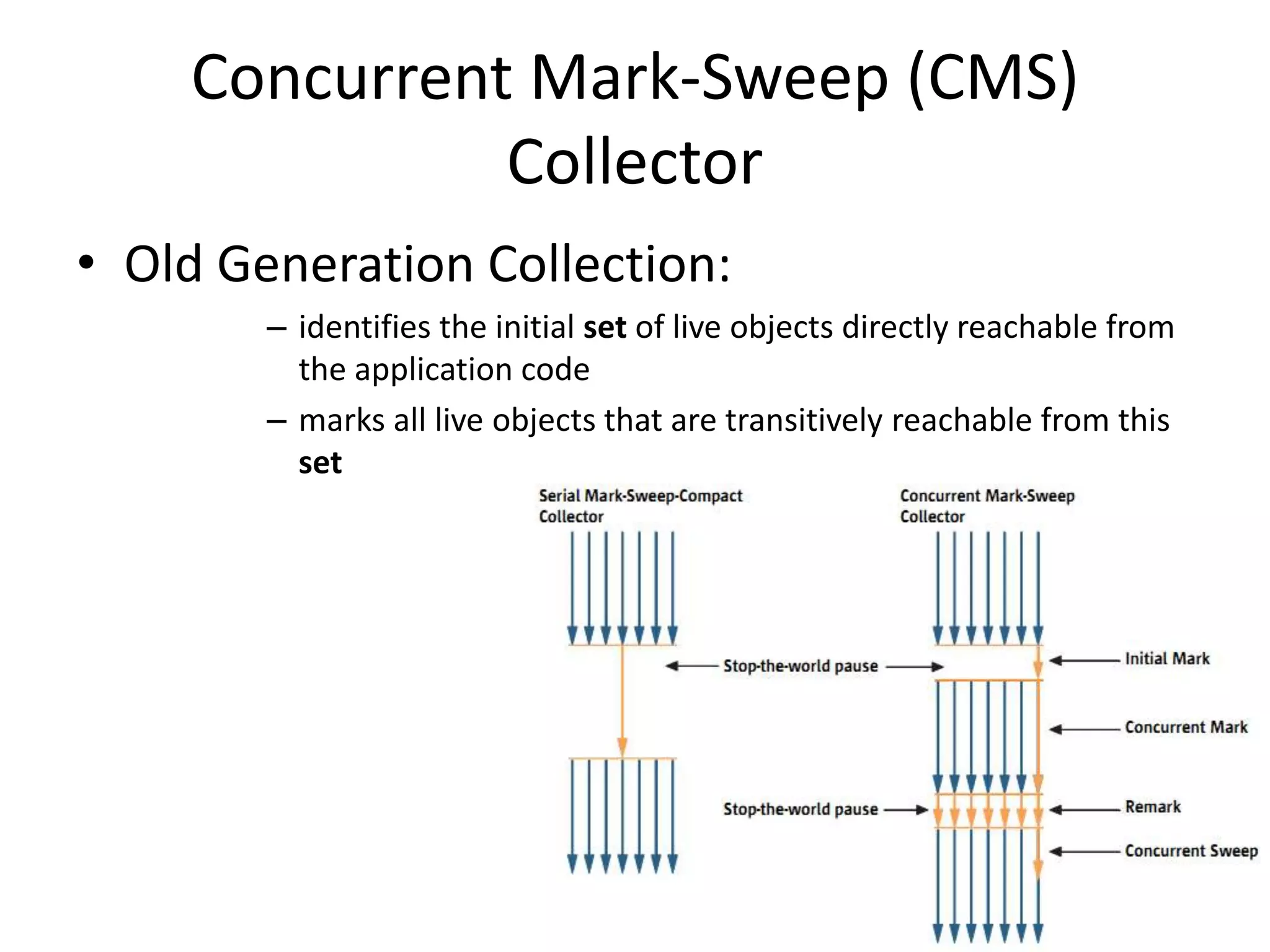
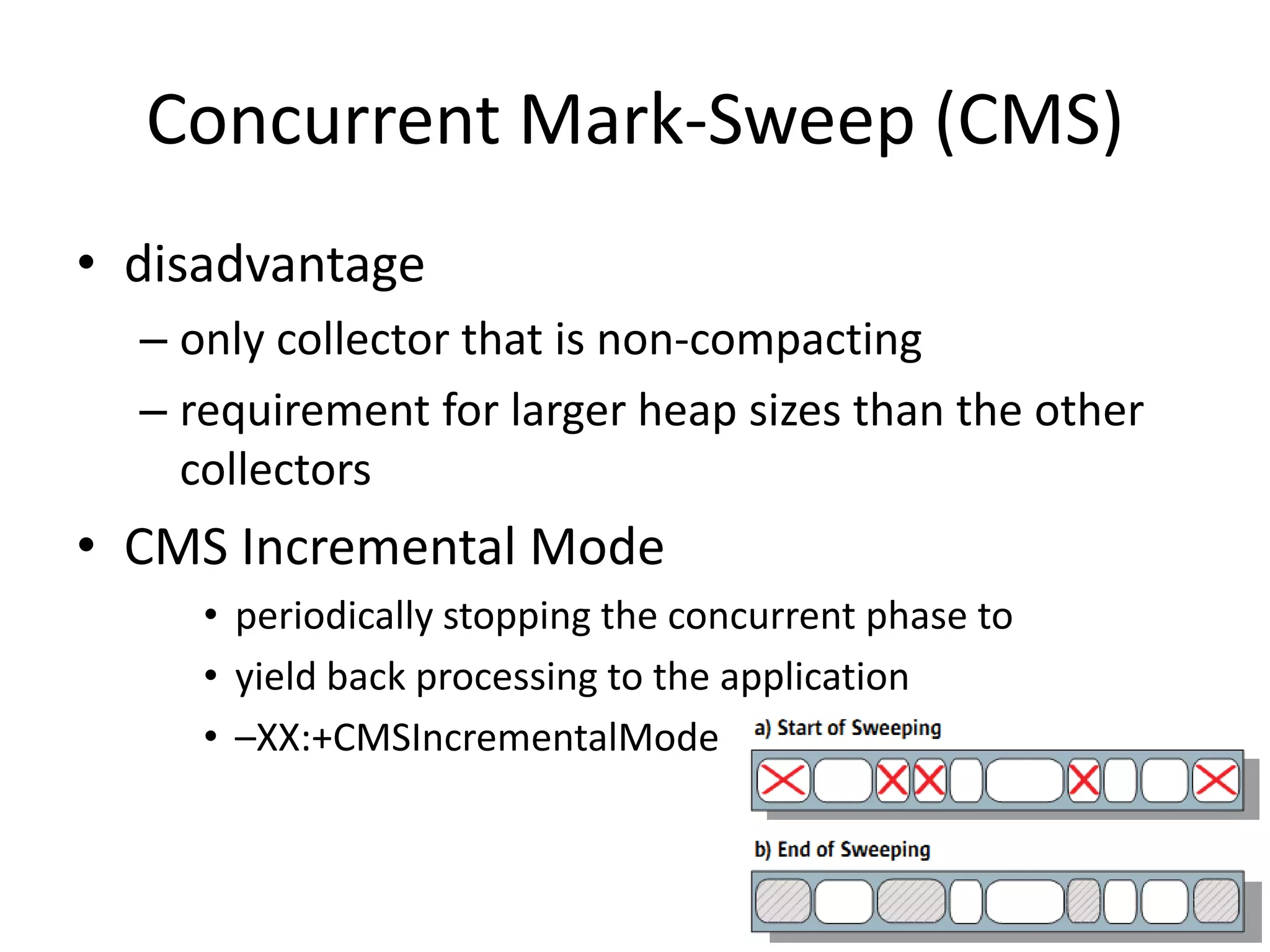
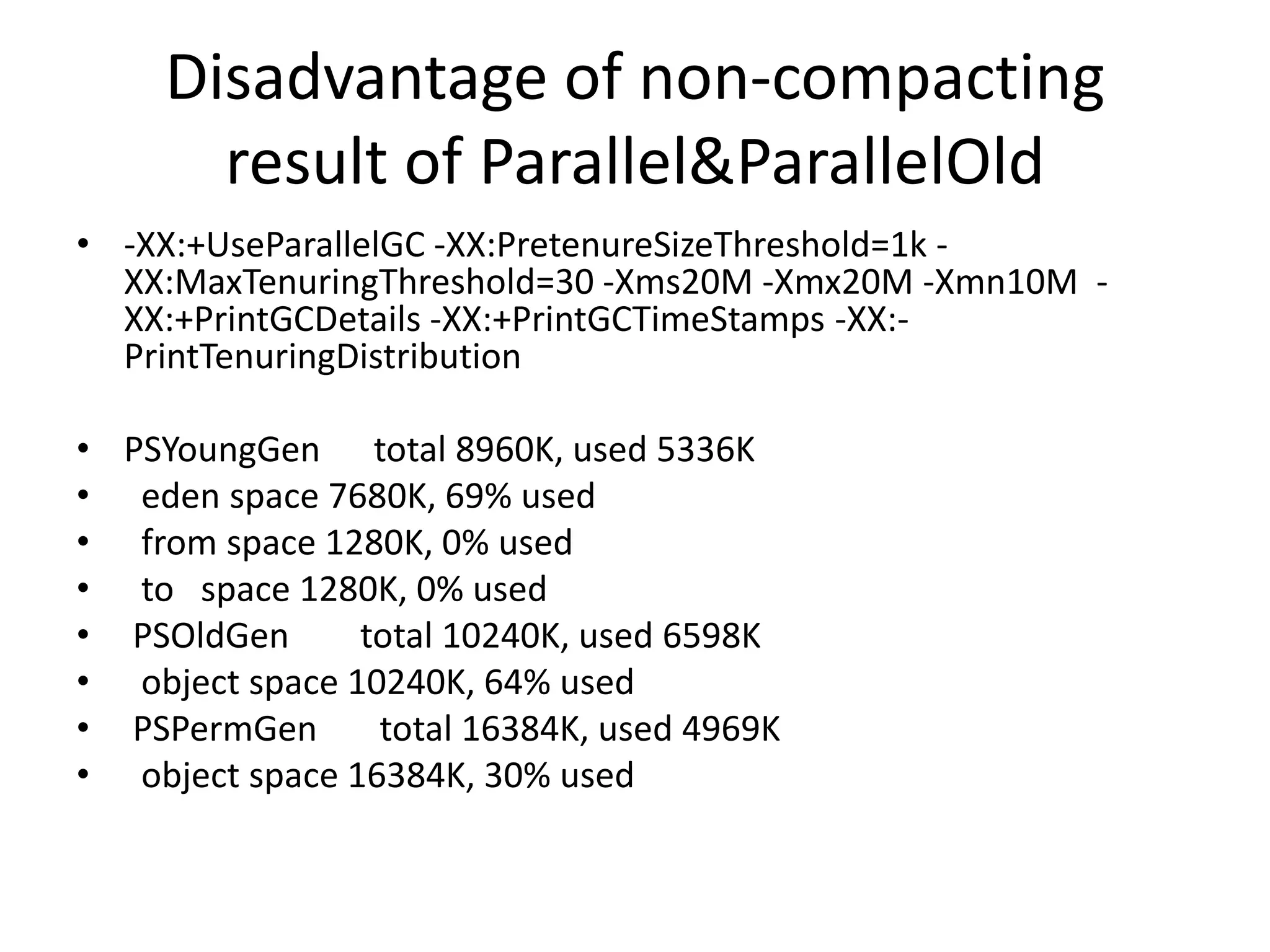
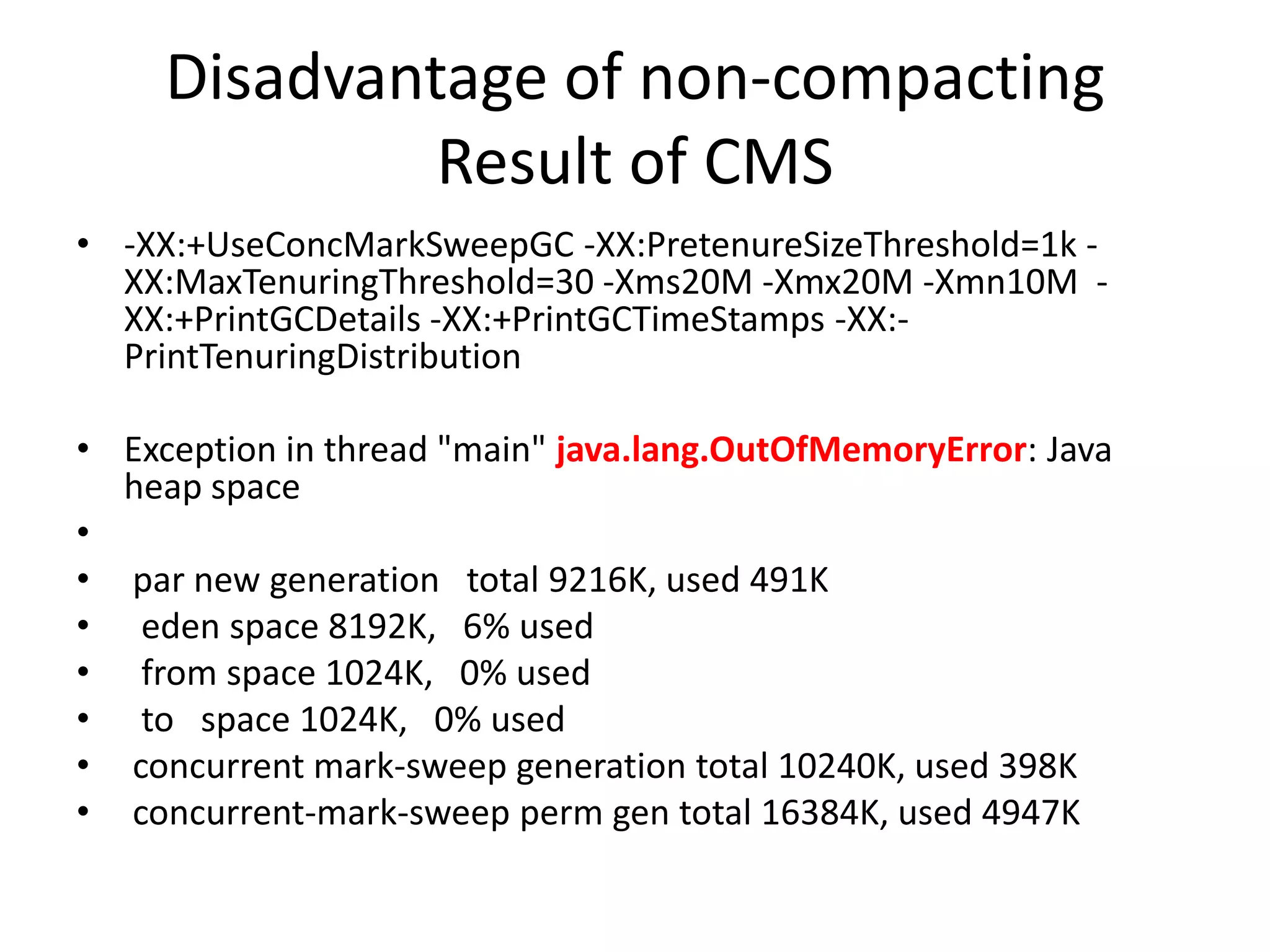
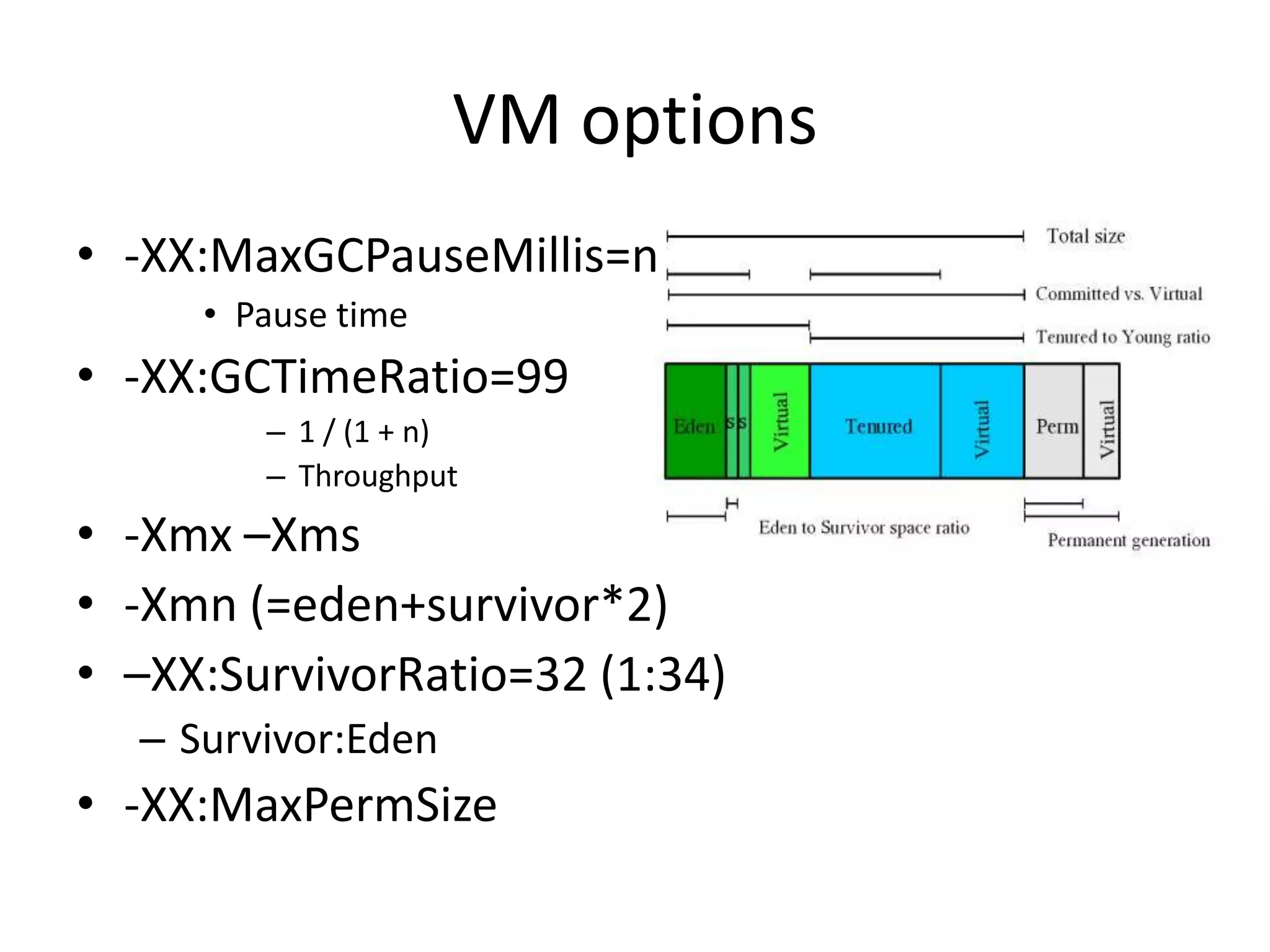
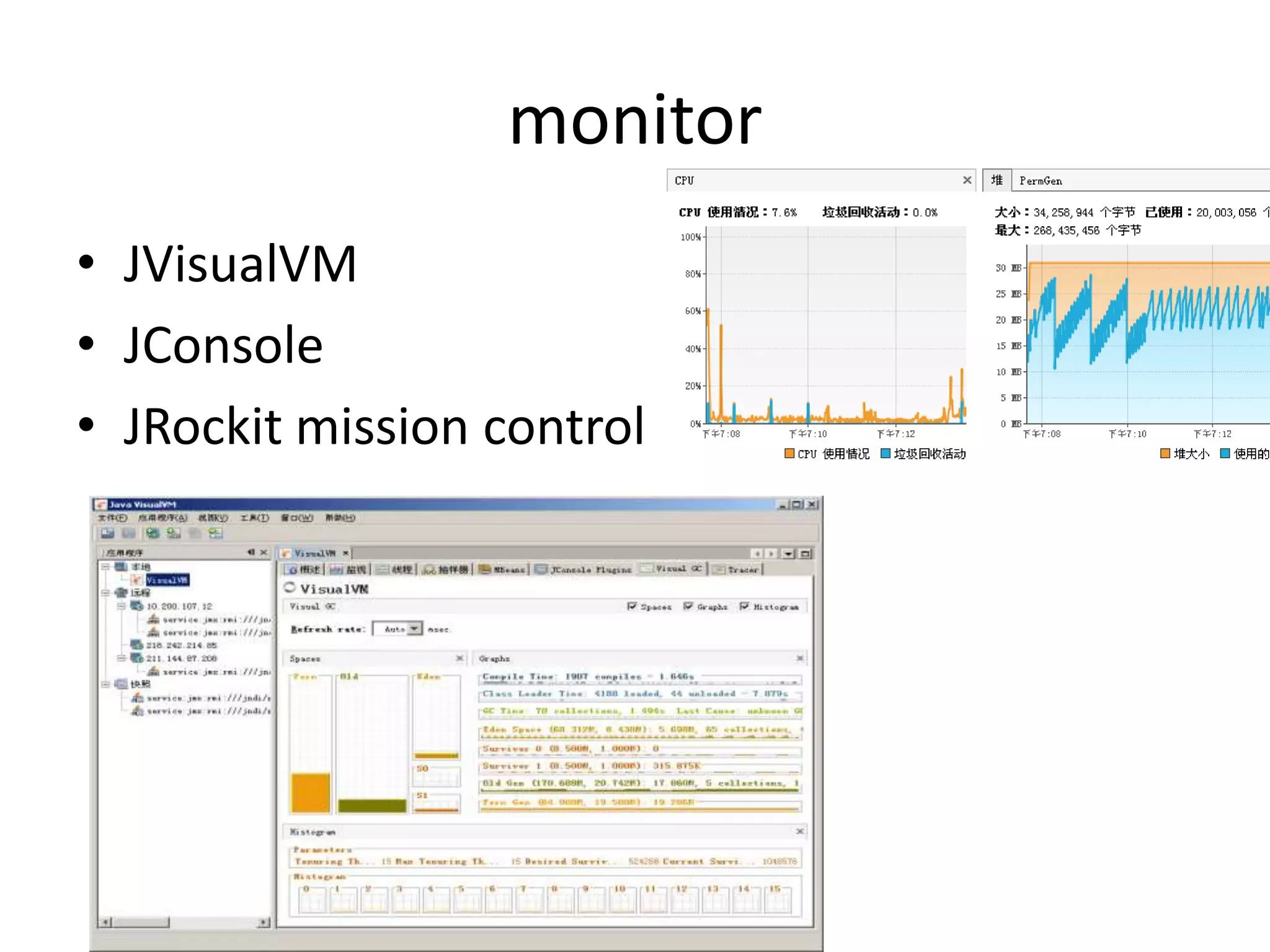
The document discusses Java memory management and garbage collection. It describes the responsibilities of garbage collection as allocating memory, ensuring referenced objects remain in memory, and recovering memory from unreachable objects. It discusses generation collection and the Hotspot memory model with young and old generations. The major garbage collectors are described as serial, parallel, parallel compacting, and concurrent mark-sweep collectors. The document provides examples of VM options and logging output.













![CMS log2.259: [GC [1 CMS-initial-mark: 4280K(5120K)] 6042K(18944K), 0.0003876 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] 2.260: [CMS-concurrent-mark-start]2.267: [CMS-concurrent-mark: 0.007/0.007 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] 2.267: [CMS-concurrent-preclean-start]2.267: [CMS-concurrent-preclean: 0.001/0.001 secs] [Times: user=0.01 sys=0.00, real=0.02 secs] 2.267: [GC[YG occupancy: 1761 K (13824 K)]2.268: [Rescan (parallel) , 0.0001977 secs]2.268: [weak refs processing, 0.0000046 secs] [1 CMS-remark: 4280K(5120K)] 6042K(18944K), 0.0003386 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] 2.268: [CMS-concurrent-sweep-start]2.269: [CMS-concurrent-sweep: 0.001/0.001 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] 2.269: [CMS-concurrent-reset-start]2.269: [CMS-concurrent-reset: 0.001/0.001 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/techsharemm-110802213733-phpapp01/75/java-memory-management-gc-23-2048.jpg)
![Disadvantage of non-compactingCodestatic int alloc_1MB = 1024 * 1024 * 1;public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //UseConcMarkSweepGC byte[] bytes10 = alloc(); alloc(); byte[] bytes12 = alloc(); alloc(); byte[] bytes14 = alloc(); alloc(); byte[] bytes16 = alloc(); alloc(); byte[] bytes18 = alloc(); alloc(); byte[] bytes20 = alloc(); alloc(); byte[] bytes22 = alloc();alloc(3); }static int count = 0; private static byte[] alloc() { return alloc(1); } private static byte[] alloc(inti) { count = count + 1 * i ;System.out.println(count + "M"); return new byte[alloc_1MB * i]; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/techsharemm-110802213733-phpapp01/75/java-memory-management-gc-24-2048.jpg)
![Print gc–XX:+PrintGC–XX:+PrintGCDetails–XX:+PrintGCTimeStamps-verbose:gc[GC 325407K->83000K(776768K), 0.2300771 secs][GC 325816K->83372K(776768K), 0.2454258 secs][Full GC 267628K->83769K(776768K), 1.8479984 secs]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/techsharemm-110802213733-phpapp01/75/java-memory-management-gc-28-2048.jpg)

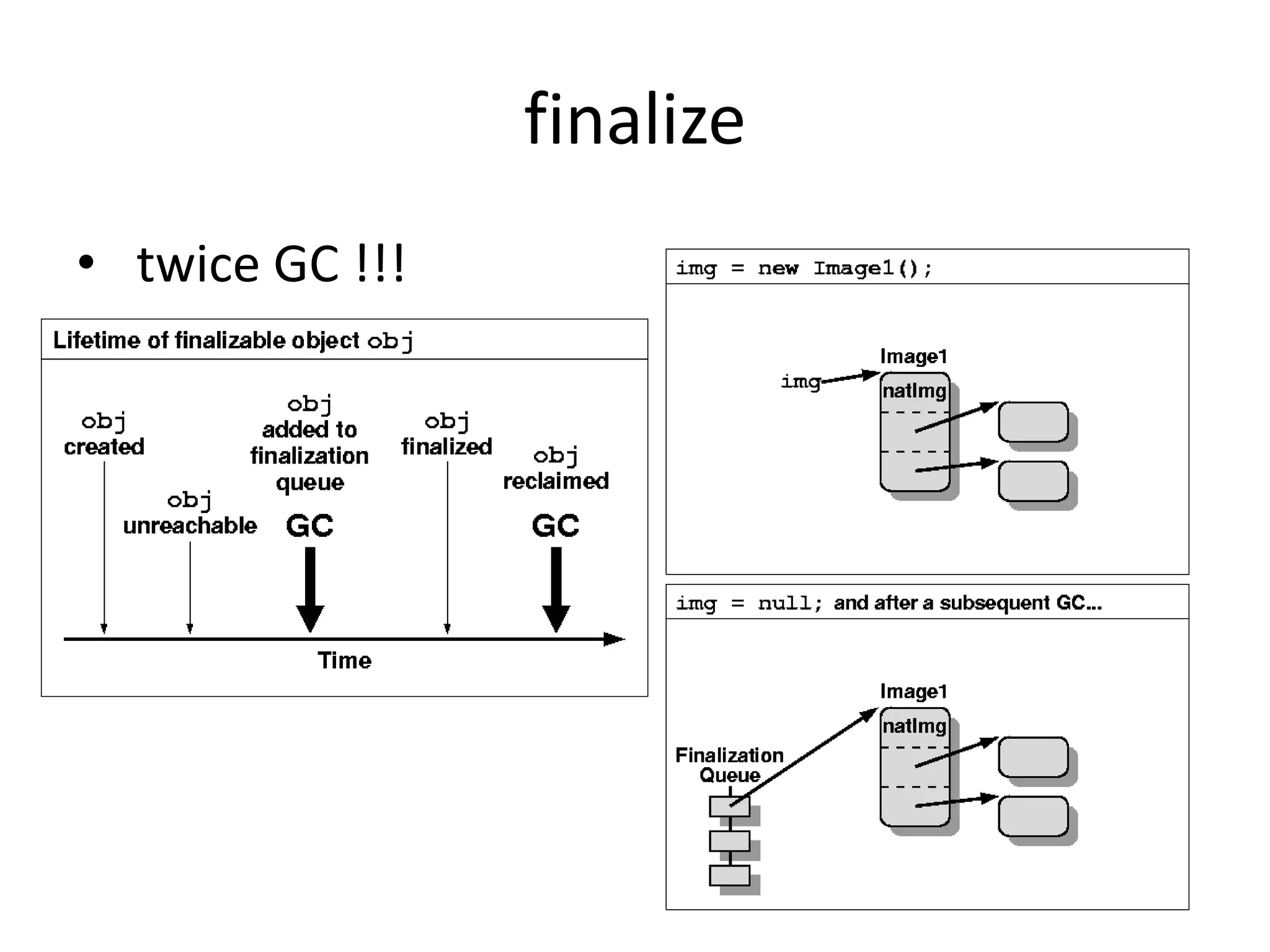
![System.gc() & finalize()Code:public class SerialTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { new SerialTest();System.gc();Thread.sleep(10);System.out.println("123"); }@Override protected void finalize() throws Throwable {System.out.println("heloo================finalize"); }}Result:0.227: [Full GC (System) TLAB: gc thread: 0x08839400 [id: 5820] ………..heloo================finalize123](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/techsharemm-110802213733-phpapp01/75/java-memory-management-gc-30-2048.jpg)


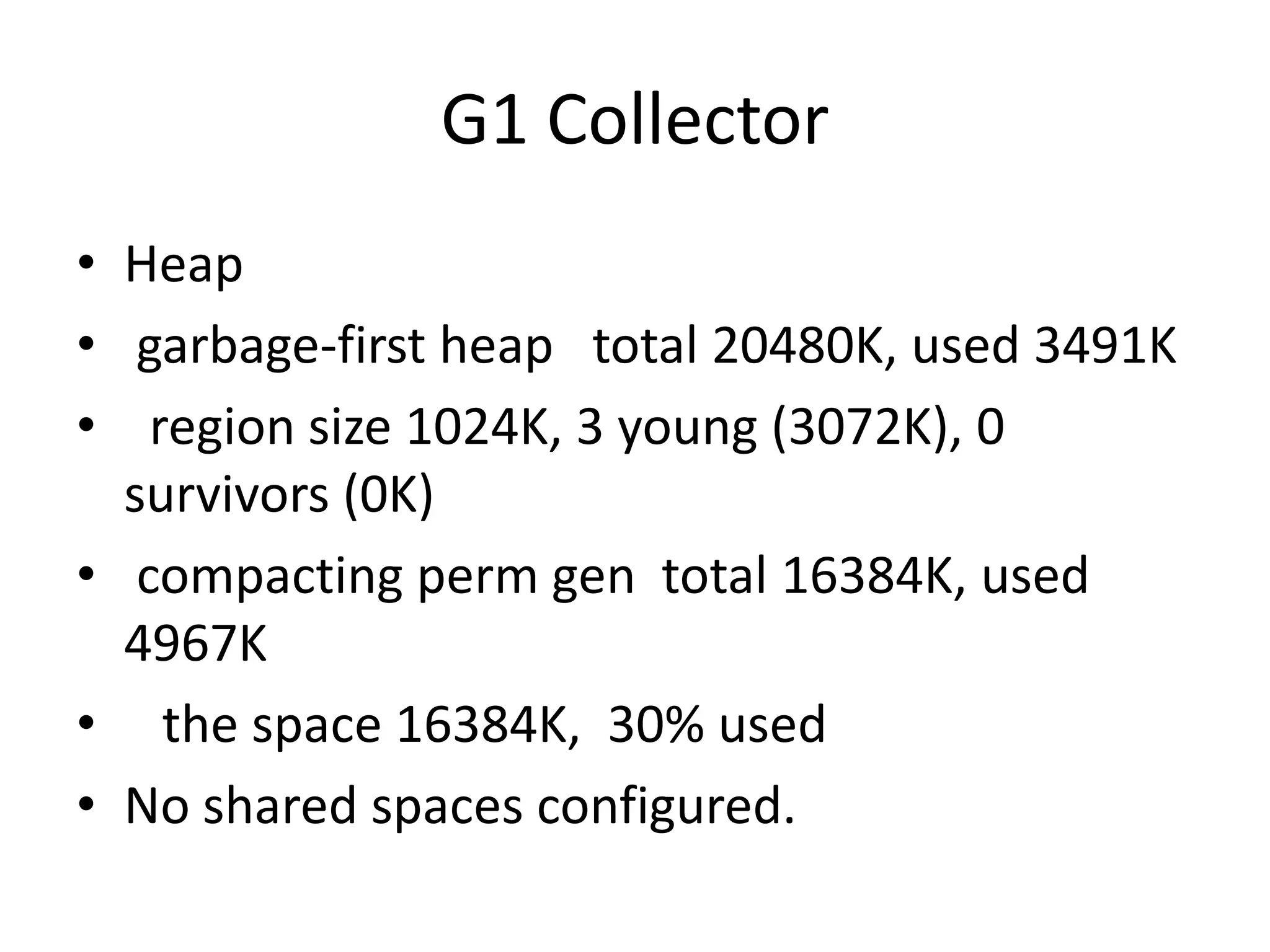
![G1 CollectorRS: regon set0.634: [GC pause (young), 0.00846287 secs] [Parallel Time: 8.3 ms] [GC Worker Start Time (ms): 633.9 634.3] [Update RS (ms): 0.0 0.0Avg: 0.0, Min: 0.0, Max: 0.0] [Processed Buffers : 0 5 Sum: 5, Avg: 2, Min: 0, Max: 5] [Ext Root Scanning (ms): 3.6 3.3Avg: 3.5, Min: 3.3, Max: 3.6] [Mark Stack Scanning (ms): 0.0 0.0Avg: 0.0, Min: 0.0, Max: 0.0] [Scan RS (ms): 0.0 0.0Avg: 0.0, Min: 0.0, Max: 0.0] [Object Copy (ms): 3.8 3.6Avg: 3.7, Min: 3.6, Max: 3.8] [Termination (ms): 0.0 0.0Avg: 0.0, Min: 0.0, Max: 0.0] [Termination Attempts : 1 1 Sum: 2, Avg: 1, Min: 1, Max: 1] [GC Worker End Time (ms): 641.3 641.3] [Other: 1.1 ms] [Clear CT: 0.0 ms] [Other: 0.2 ms] [Choose CSet: 0.0 ms] [ 2868K->1763K(20M)] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/techsharemm-110802213733-phpapp01/75/java-memory-management-gc-36-2048.jpg)