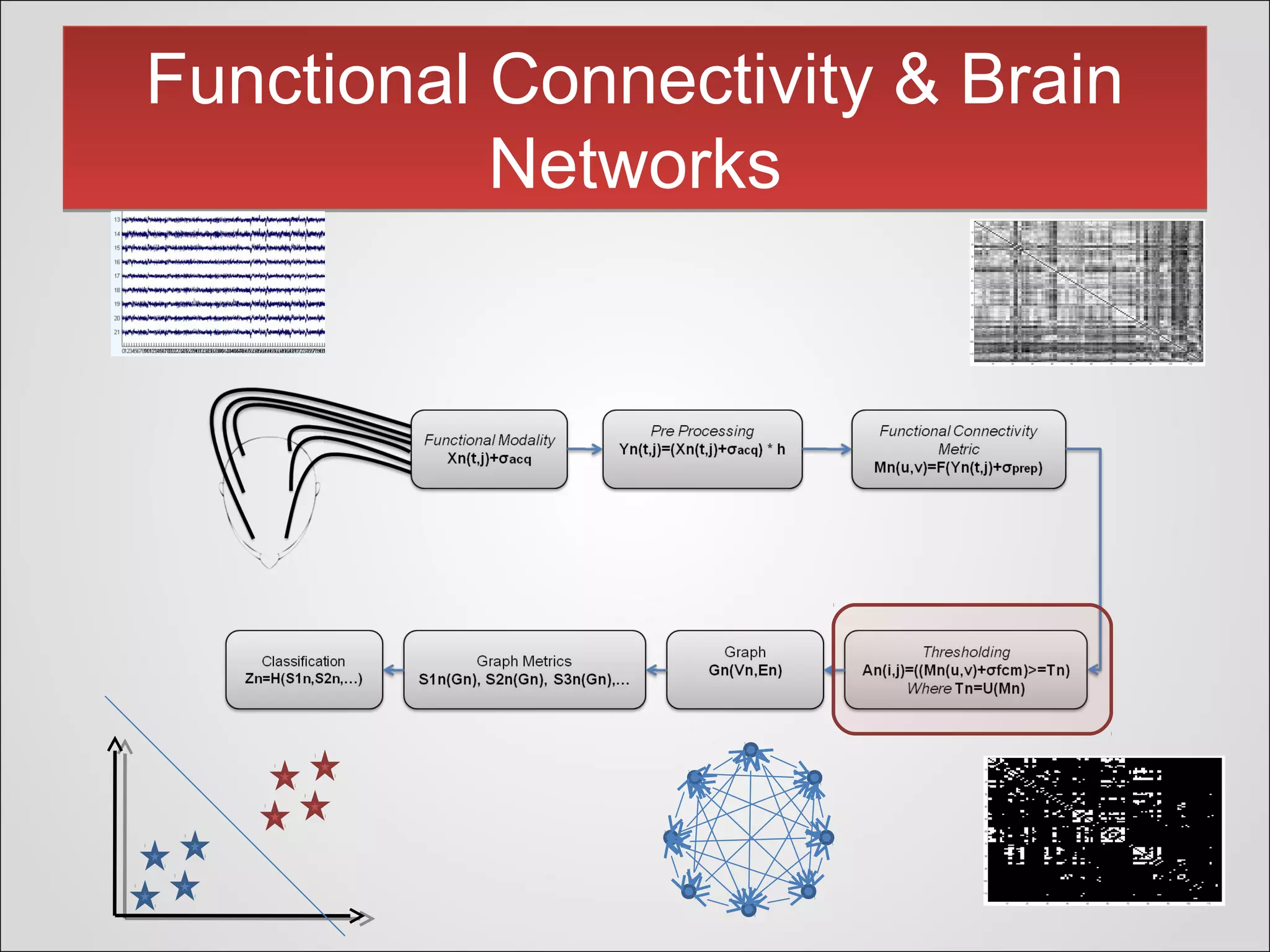
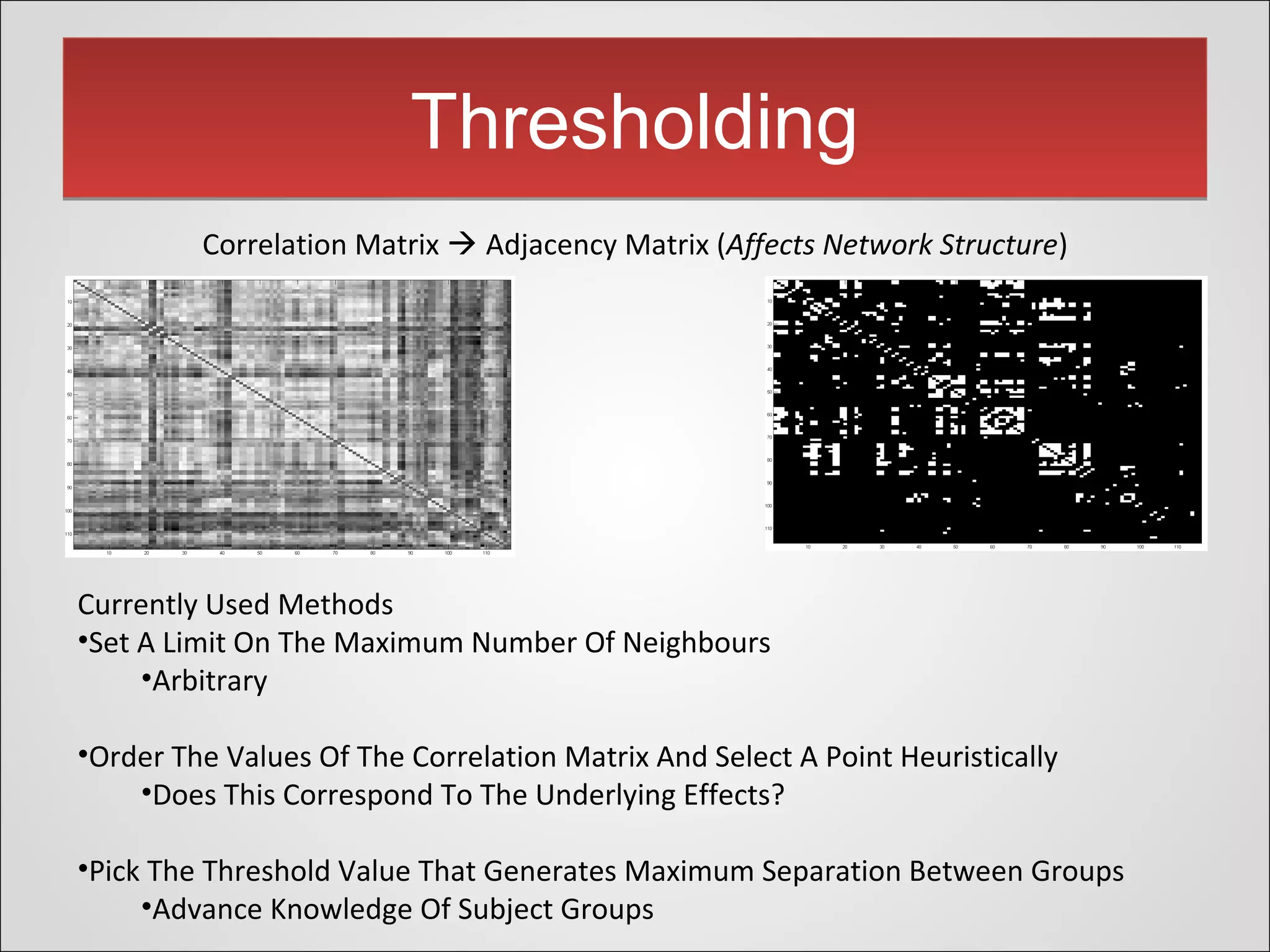
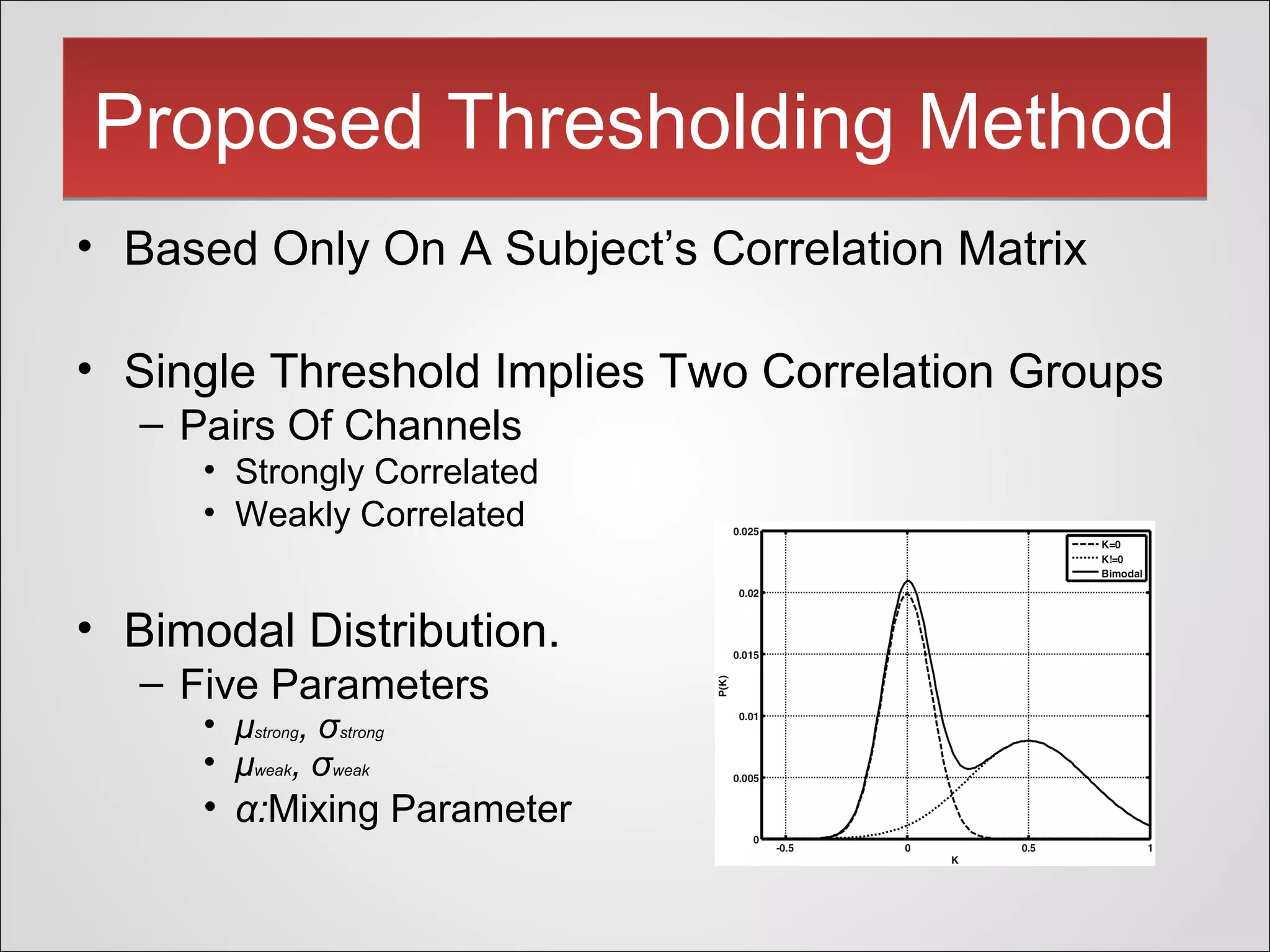
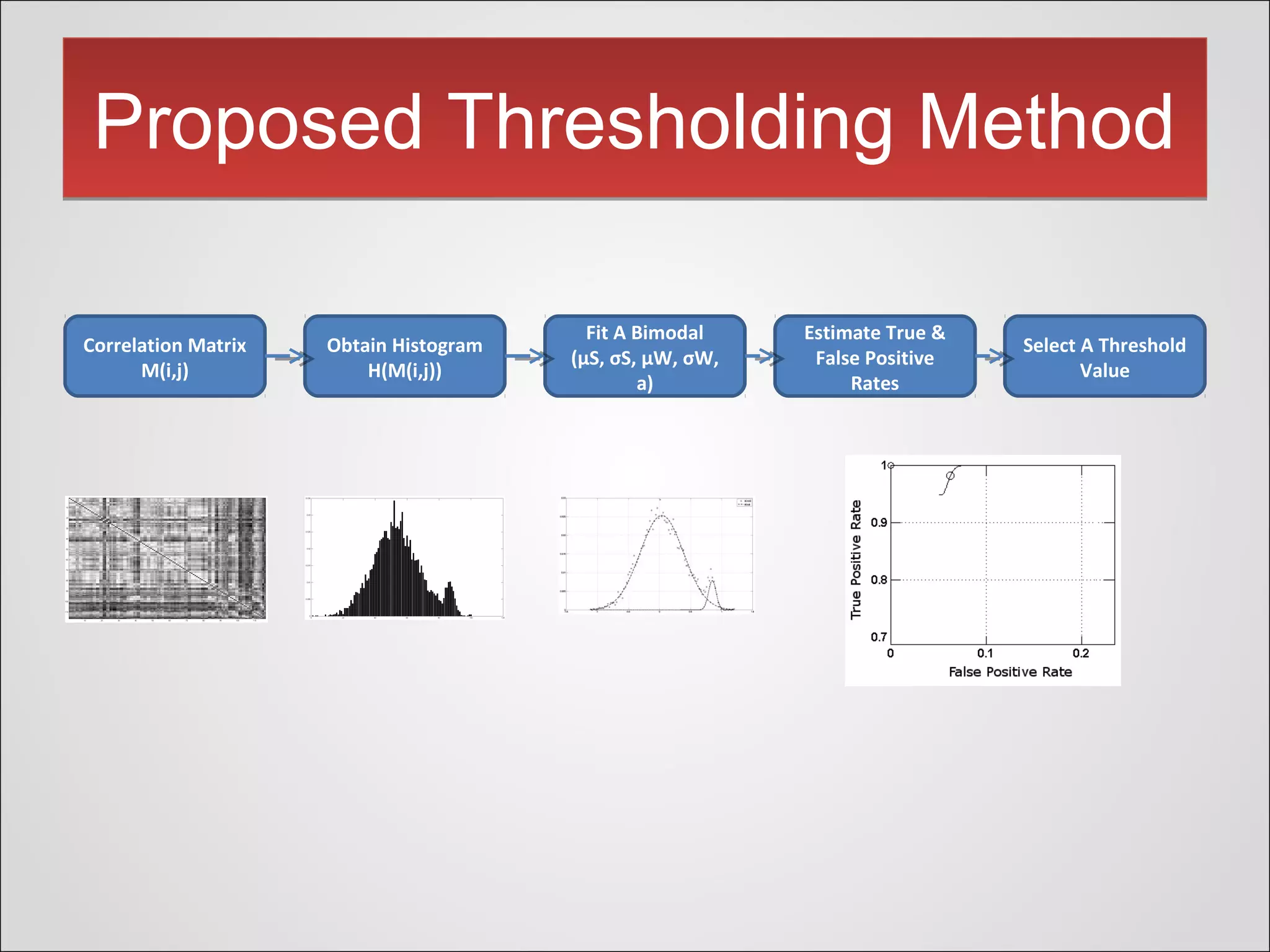
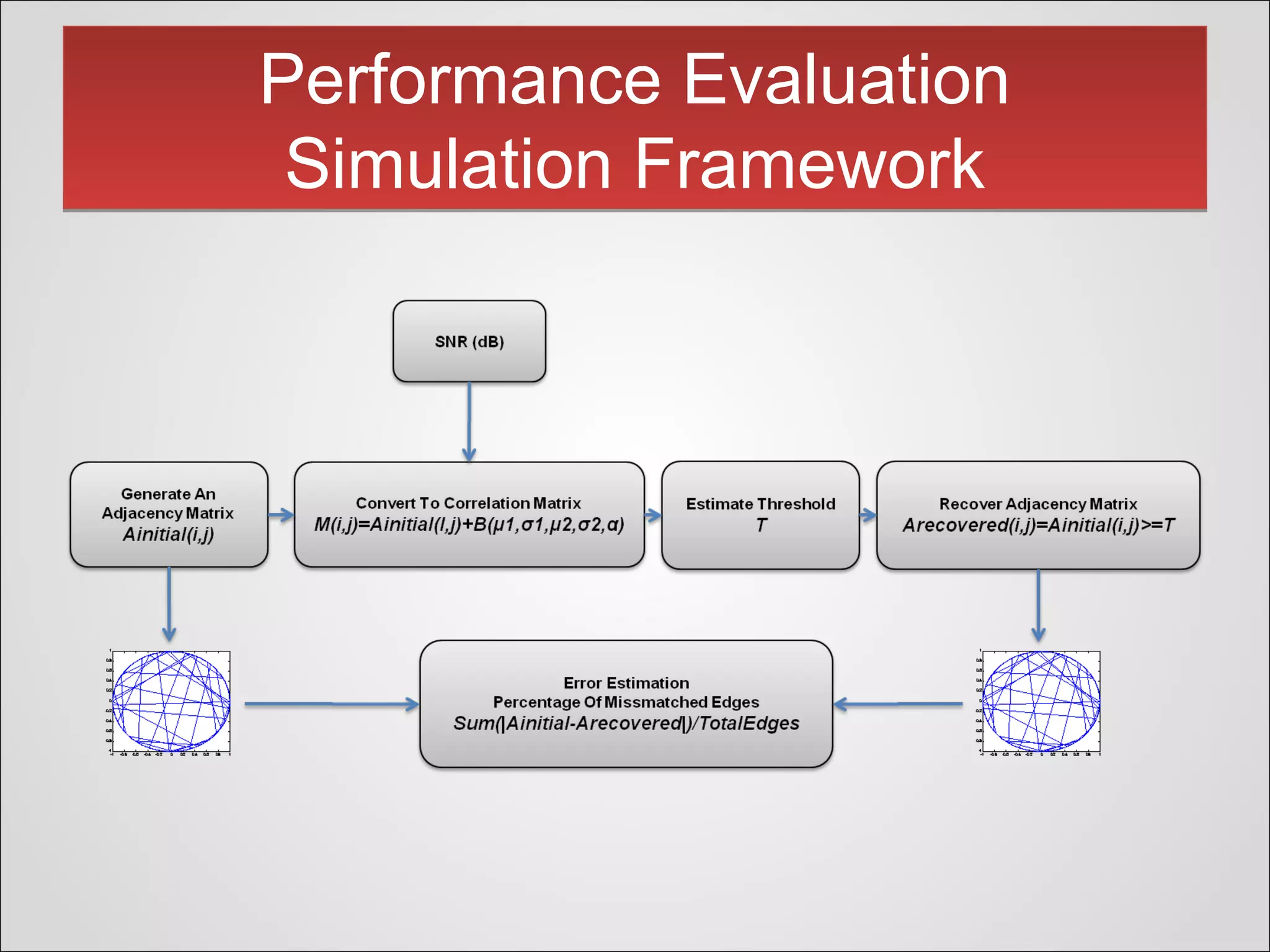
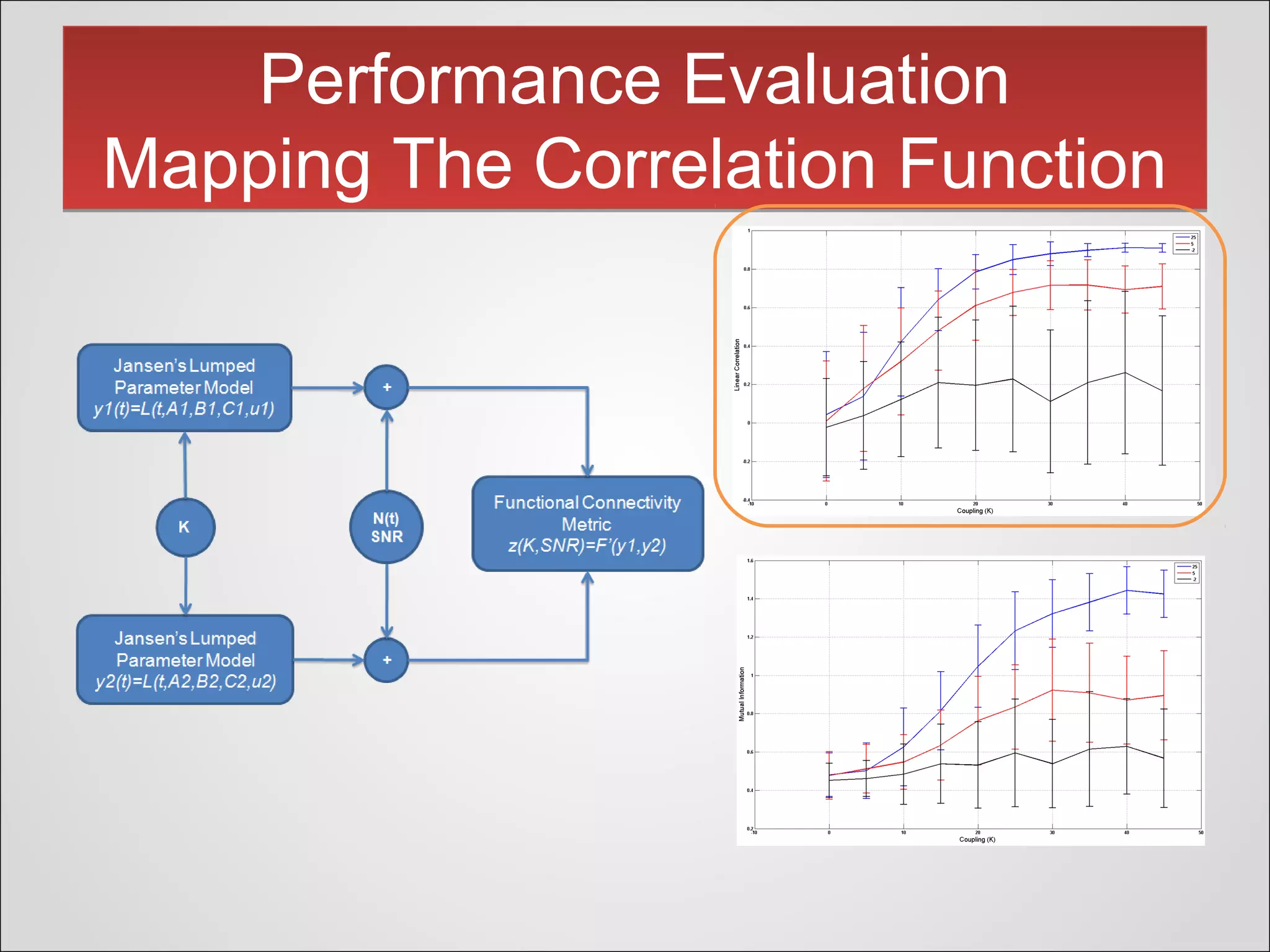
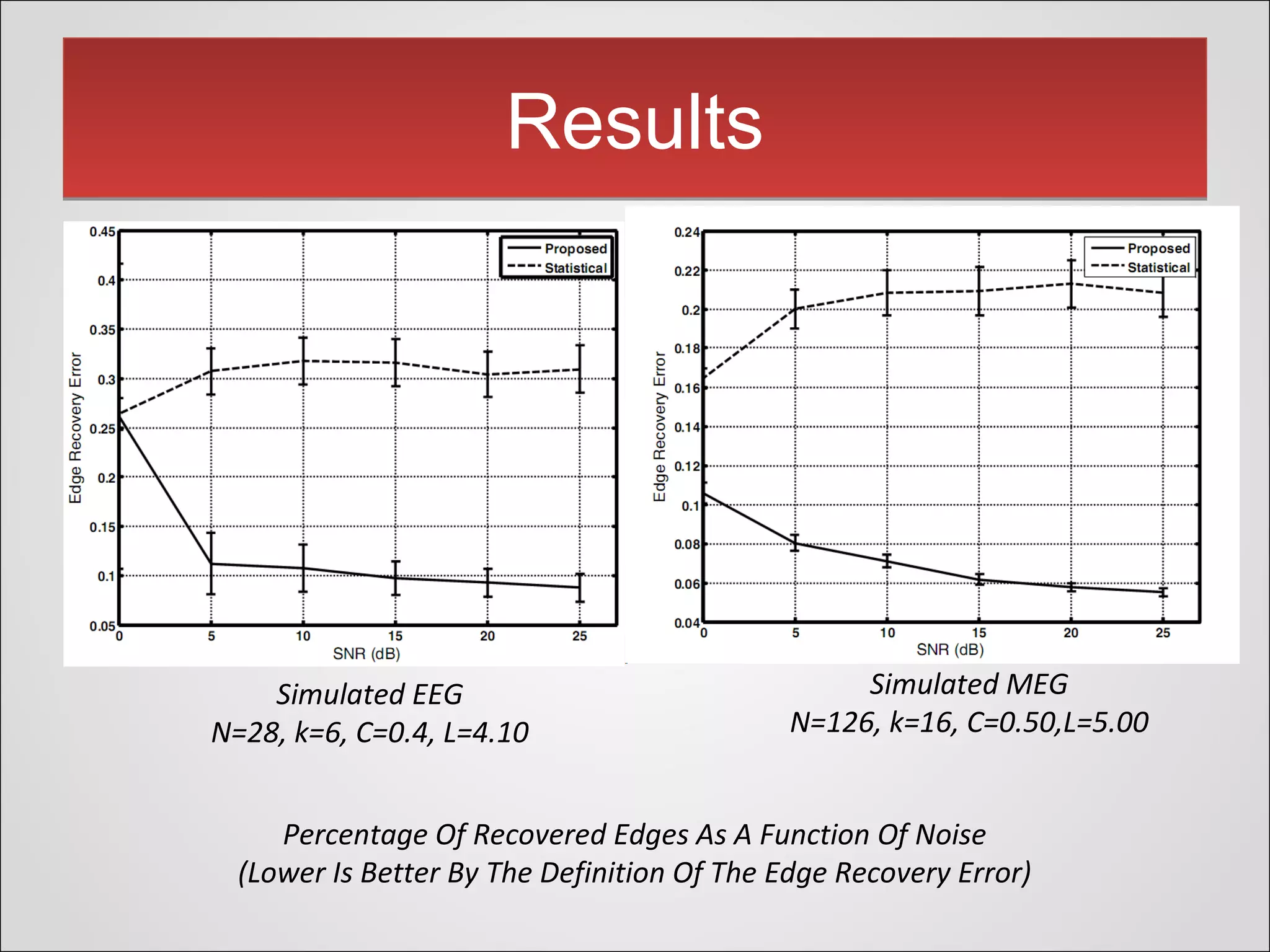
This document presents a novel thresholding method for analyzing functional connectivity networks in the brain, which is based on the subject's correlation matrix to identify strongly and weakly correlated pairs of channels. The proposed method utilizes a bimodal distribution to optimize the threshold value and demonstrates improved edge recovery in simulations compared to current techniques. The findings highlight the challenges of thresholding in low signal-to-noise ratio conditions and question the necessity of a threshold in some analyses.