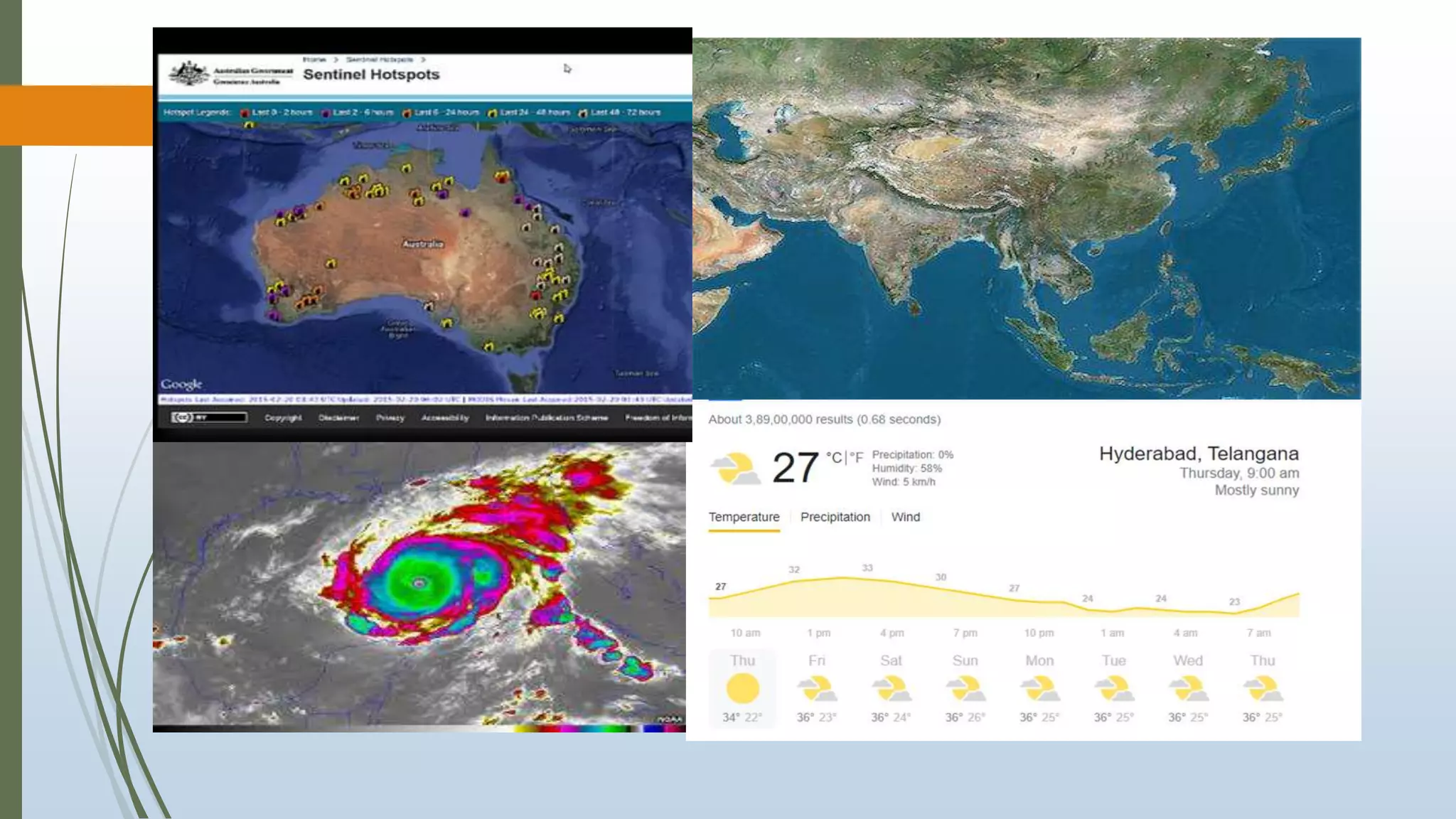
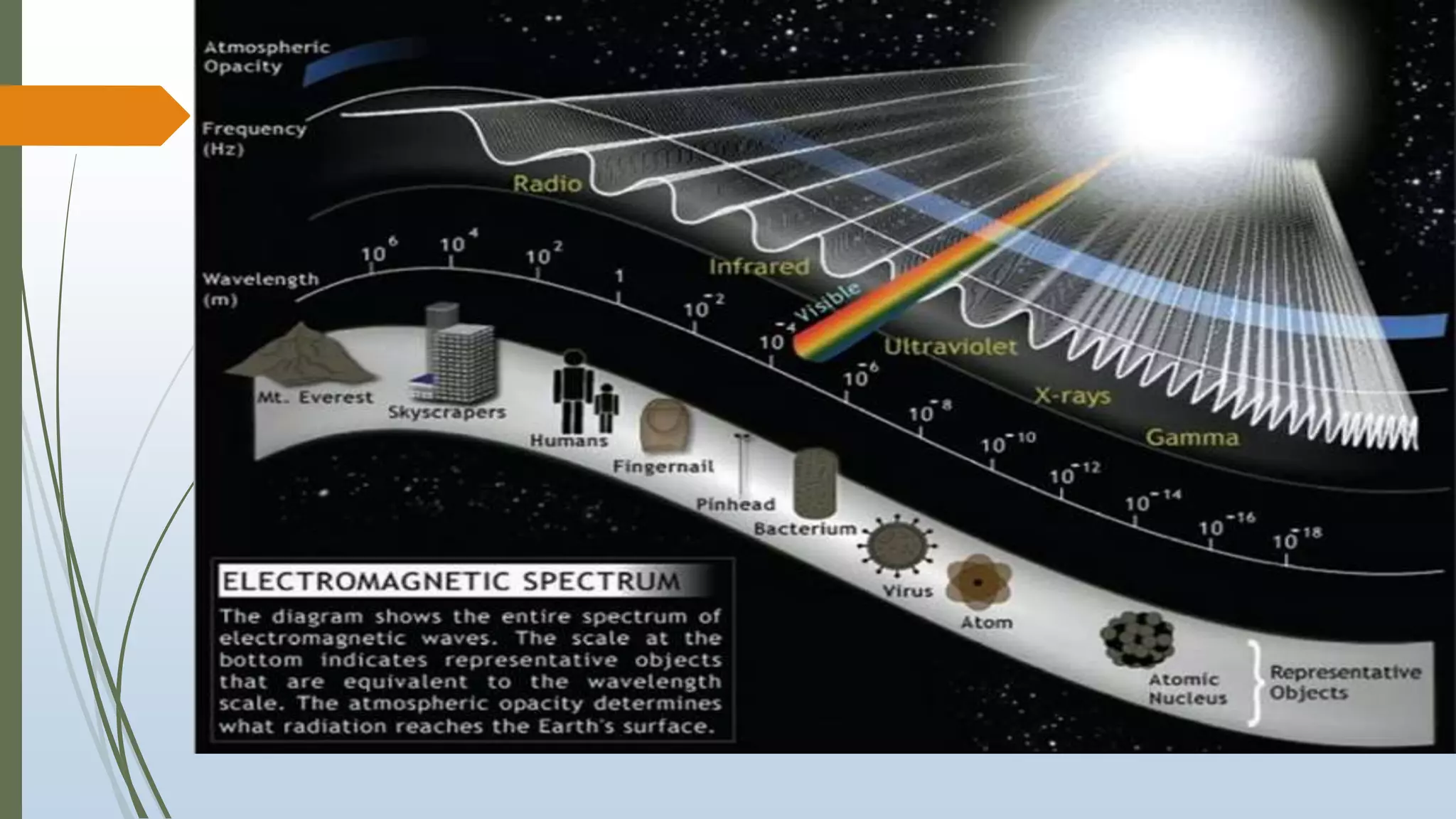
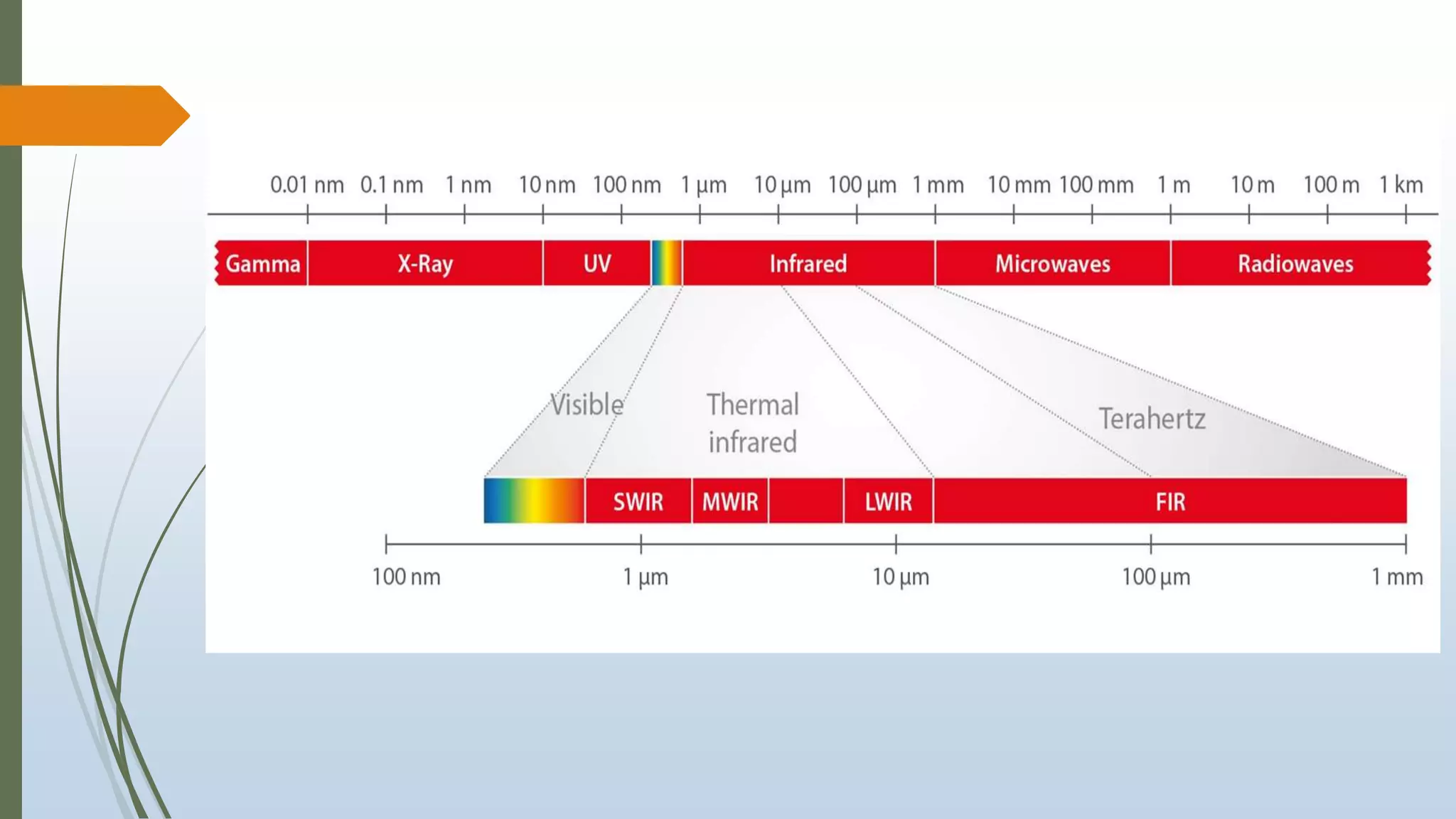
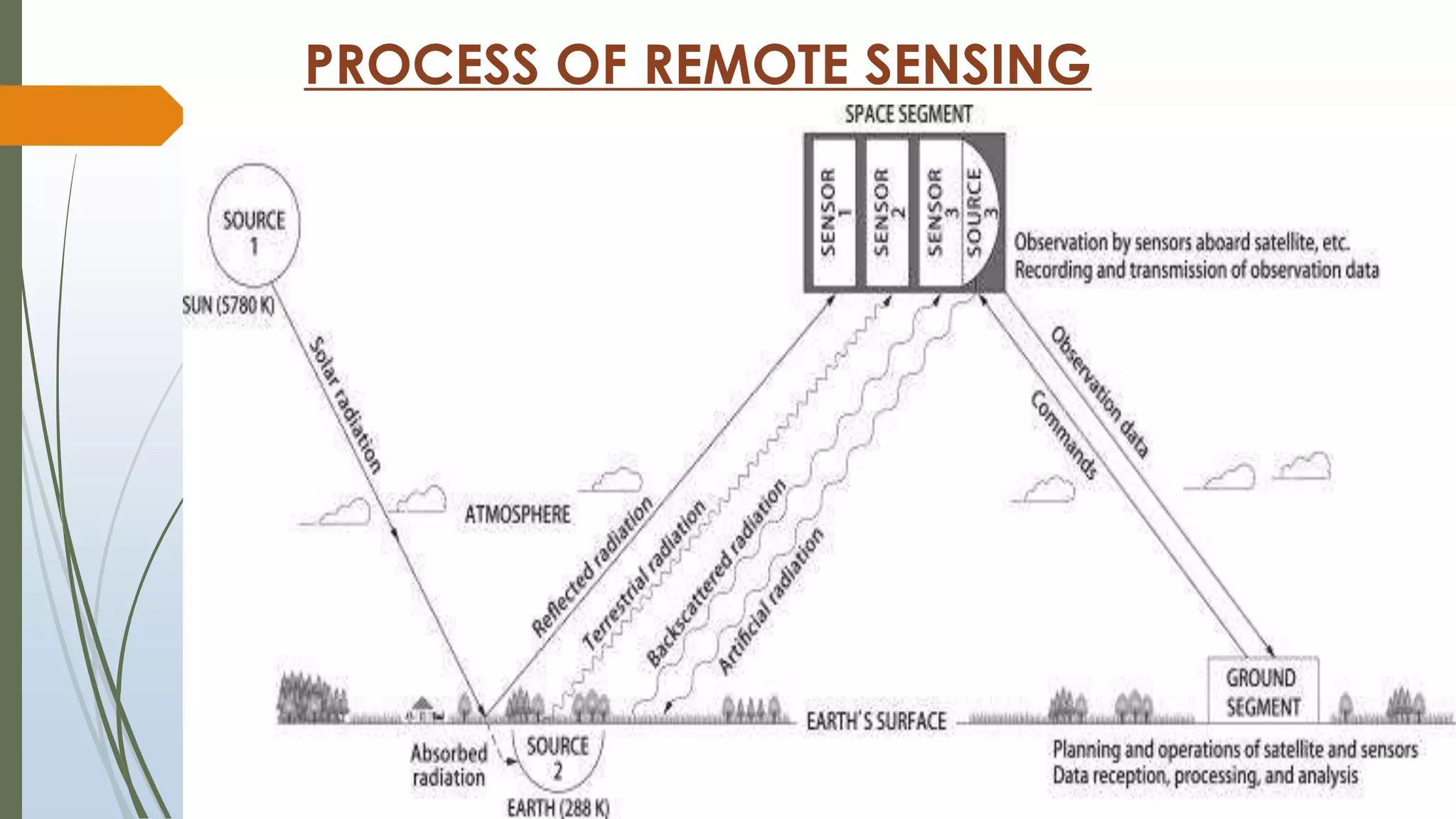
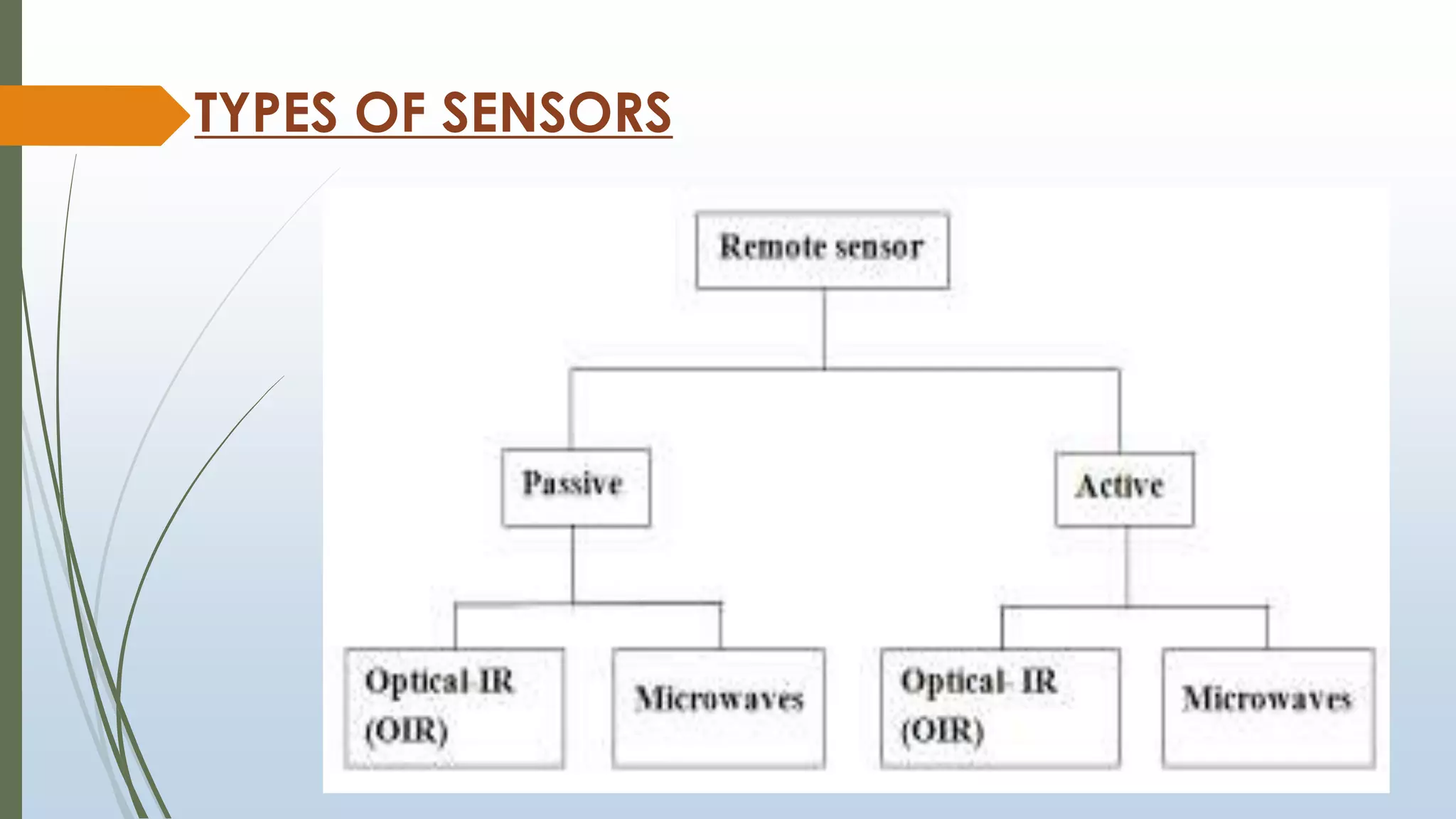
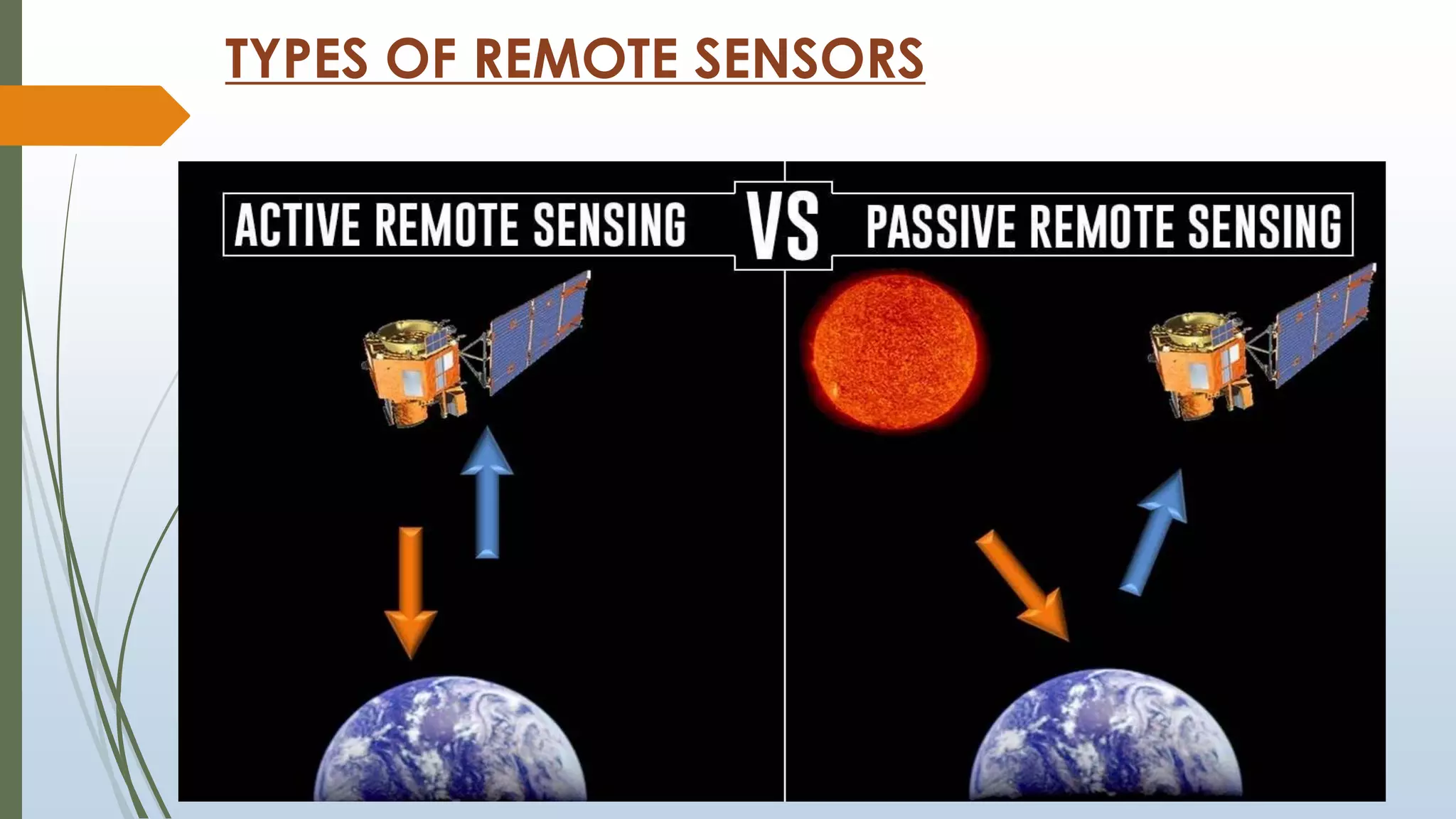
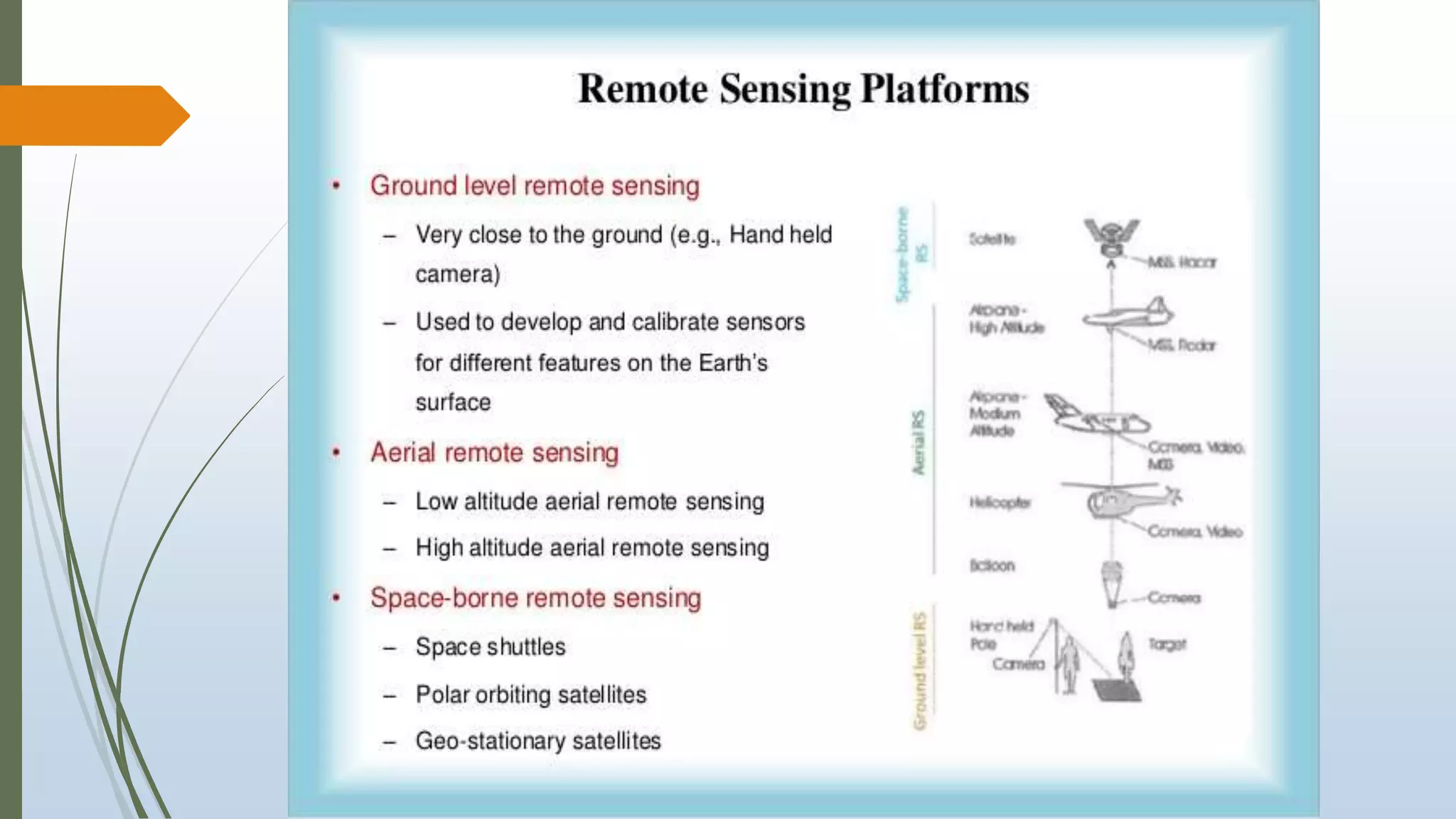
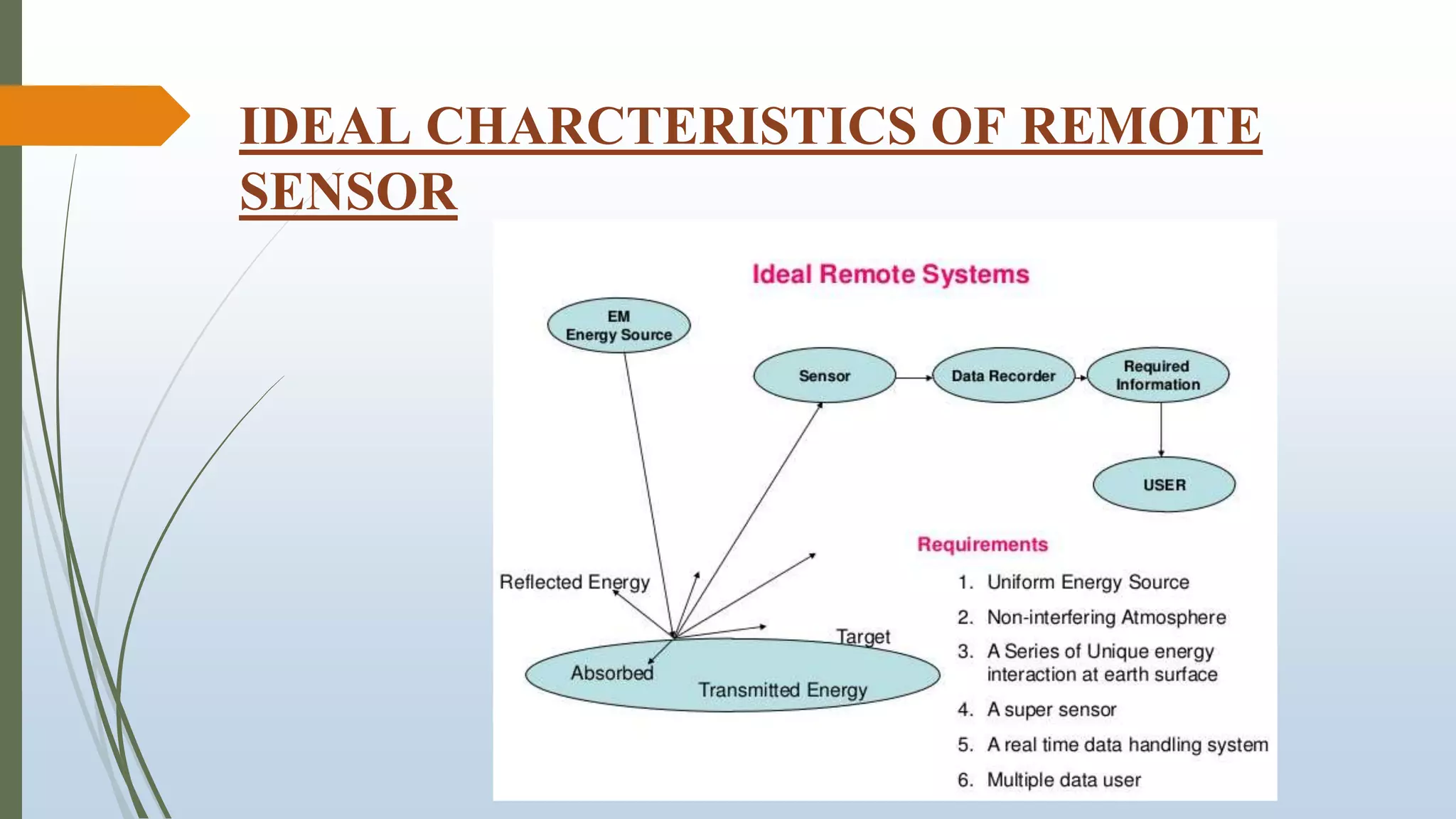
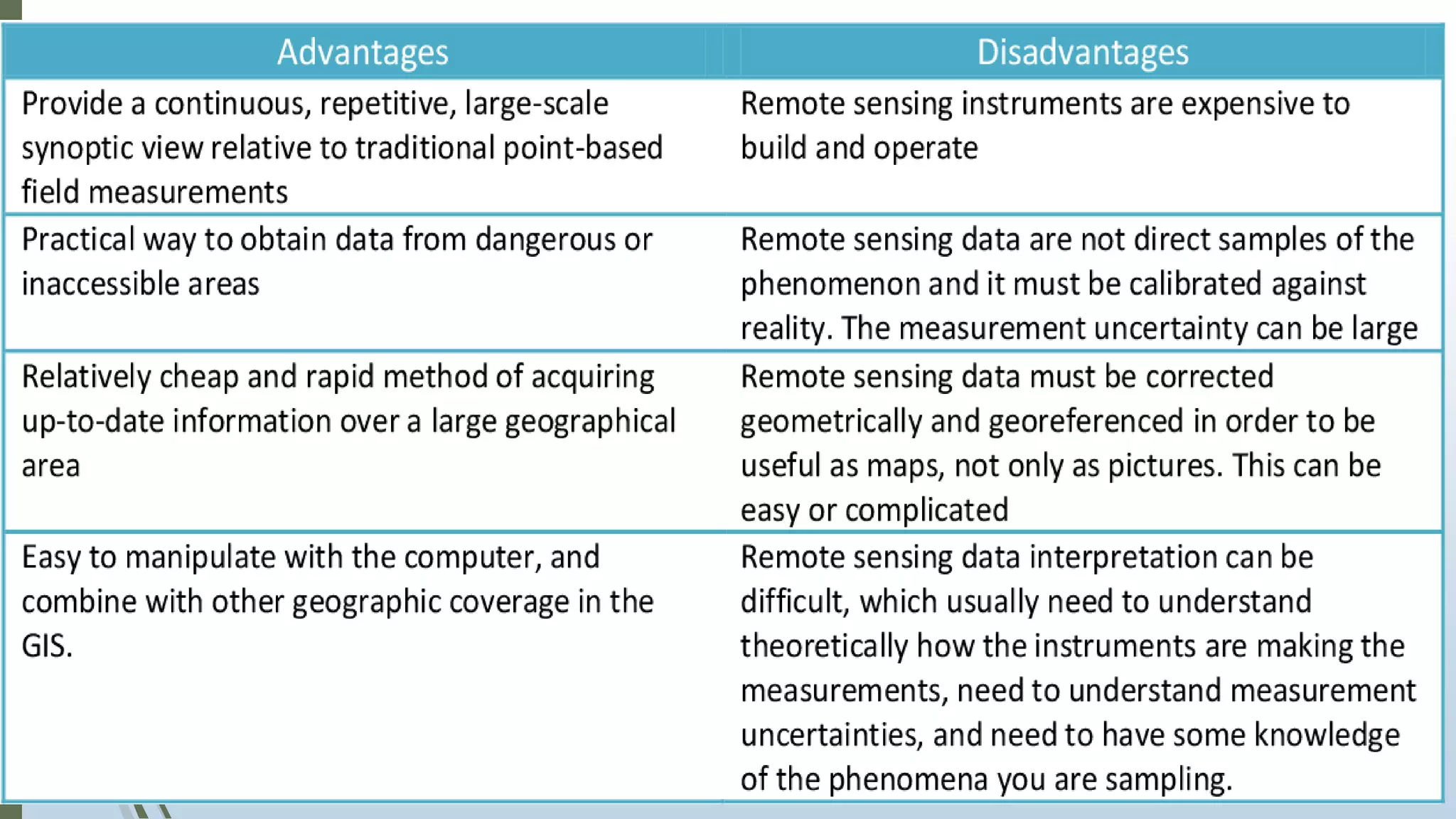
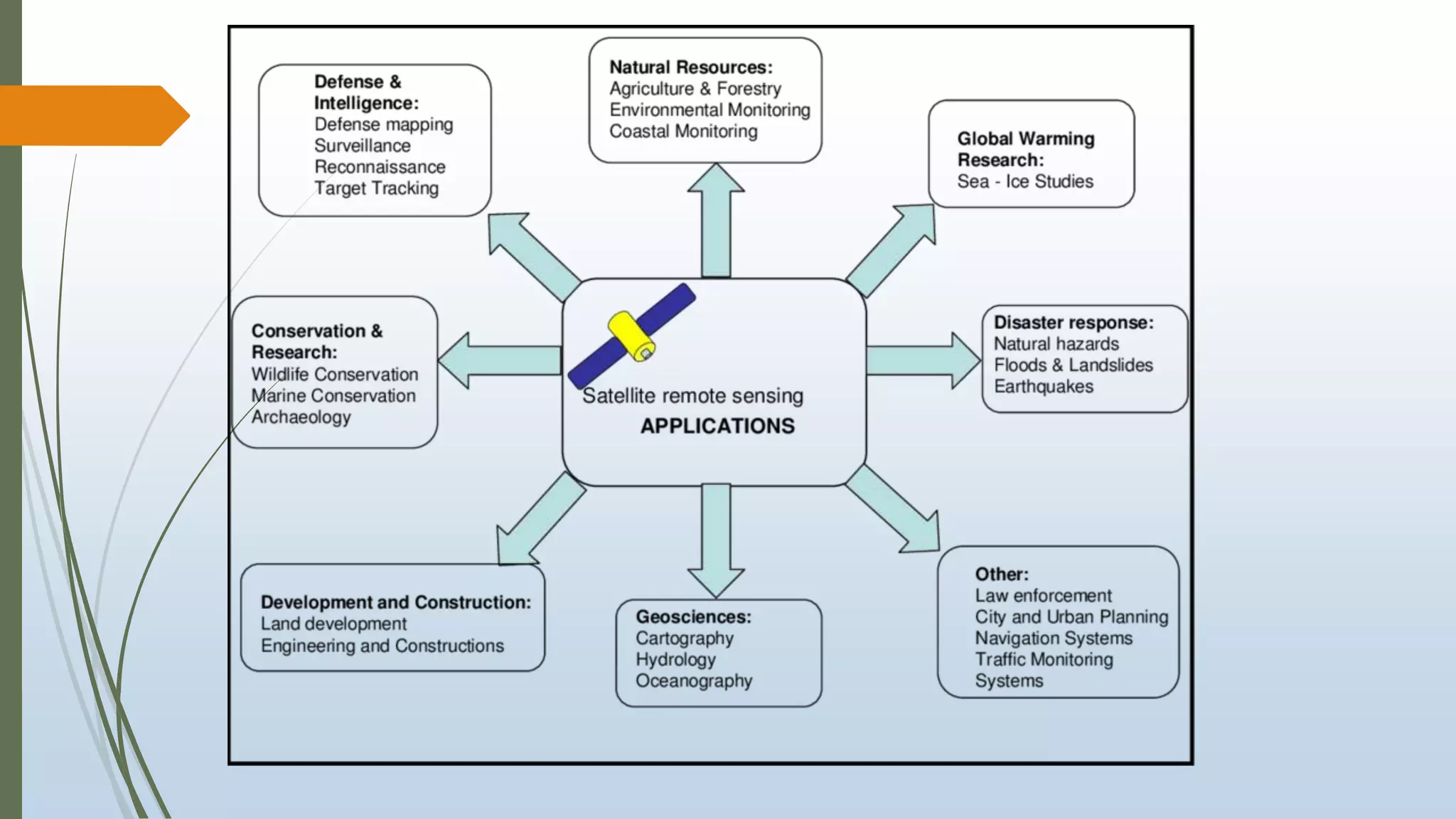
This document discusses infrared (IR) remote sensing technology. It provides an overview of remote sensing, including definitions and key principles. A group project on IR remote sensing is described, with members listed. The document outlines the importance of remote sensing, electromagnetic radiation spectrum, applications of IR, the remote sensing process, types of remote sensors and platforms, ideal sensor characteristics, and applications. Remote sensing allows data collection from dangerous or inaccessible areas and provides fast, repetitive coverage of large areas for applications like weather forecasts and disaster monitoring.