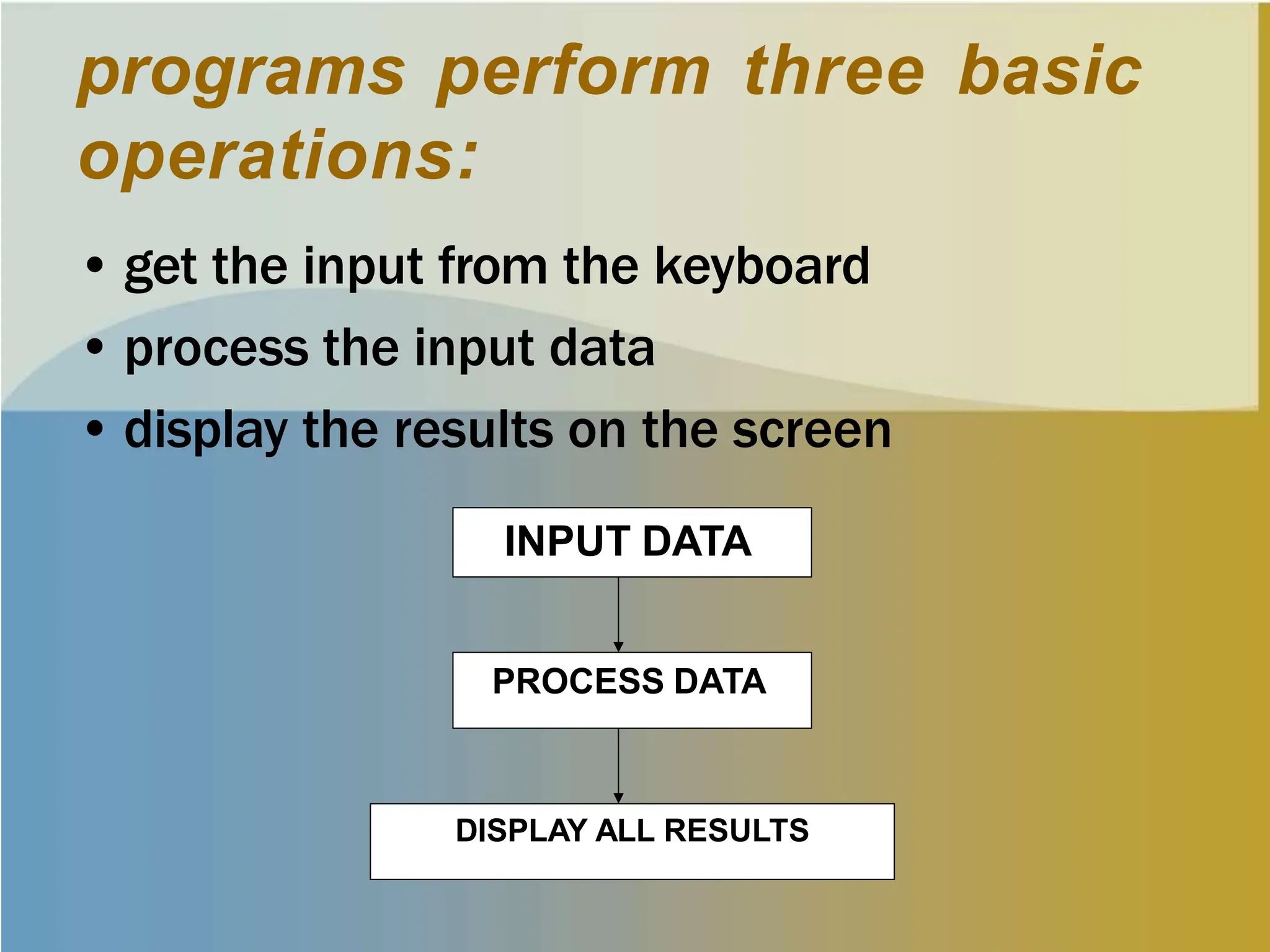
This document provides an introduction to computer programming. It discusses what a computer program and programming language are, and describes the two major classes of programs - application programs and operating systems. It explains the process a programmer goes through to write a program, including using a text editor to create source code files and translating it into machine-readable object code. It also gives an overview of the basic components of a computer and different types of memory. Finally, it provides examples of common programming languages and the basic structure of a simple C program.