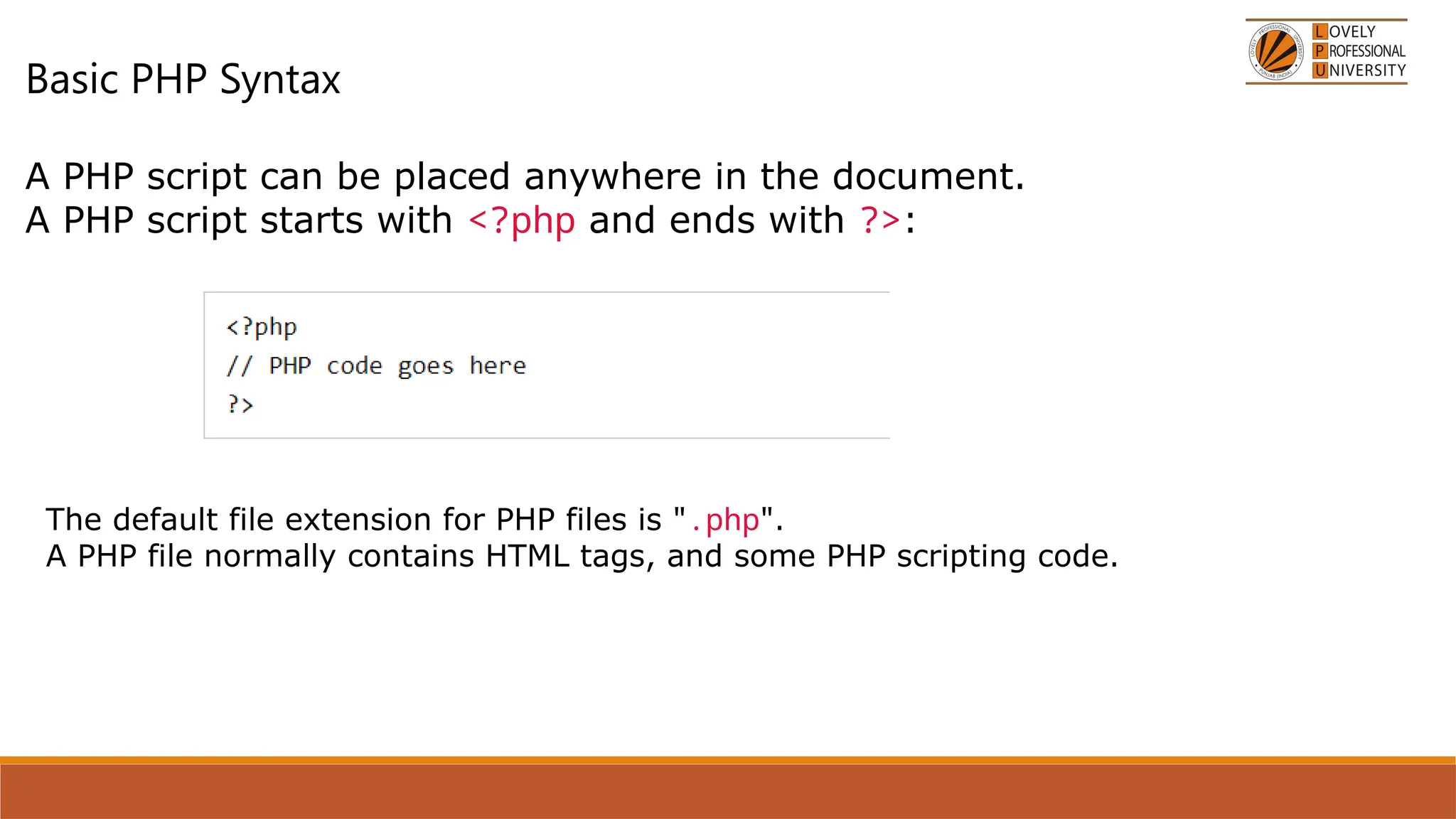
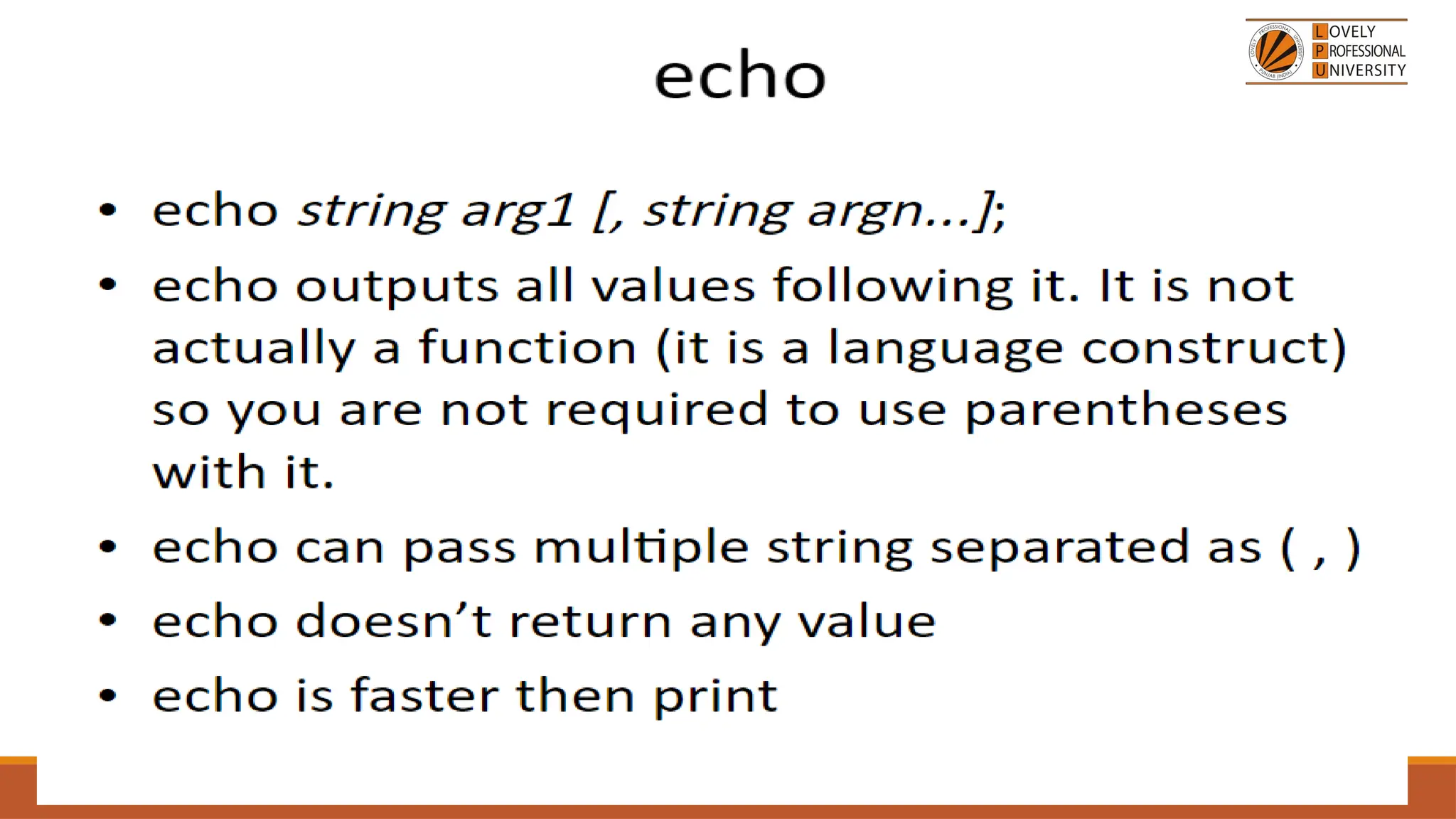
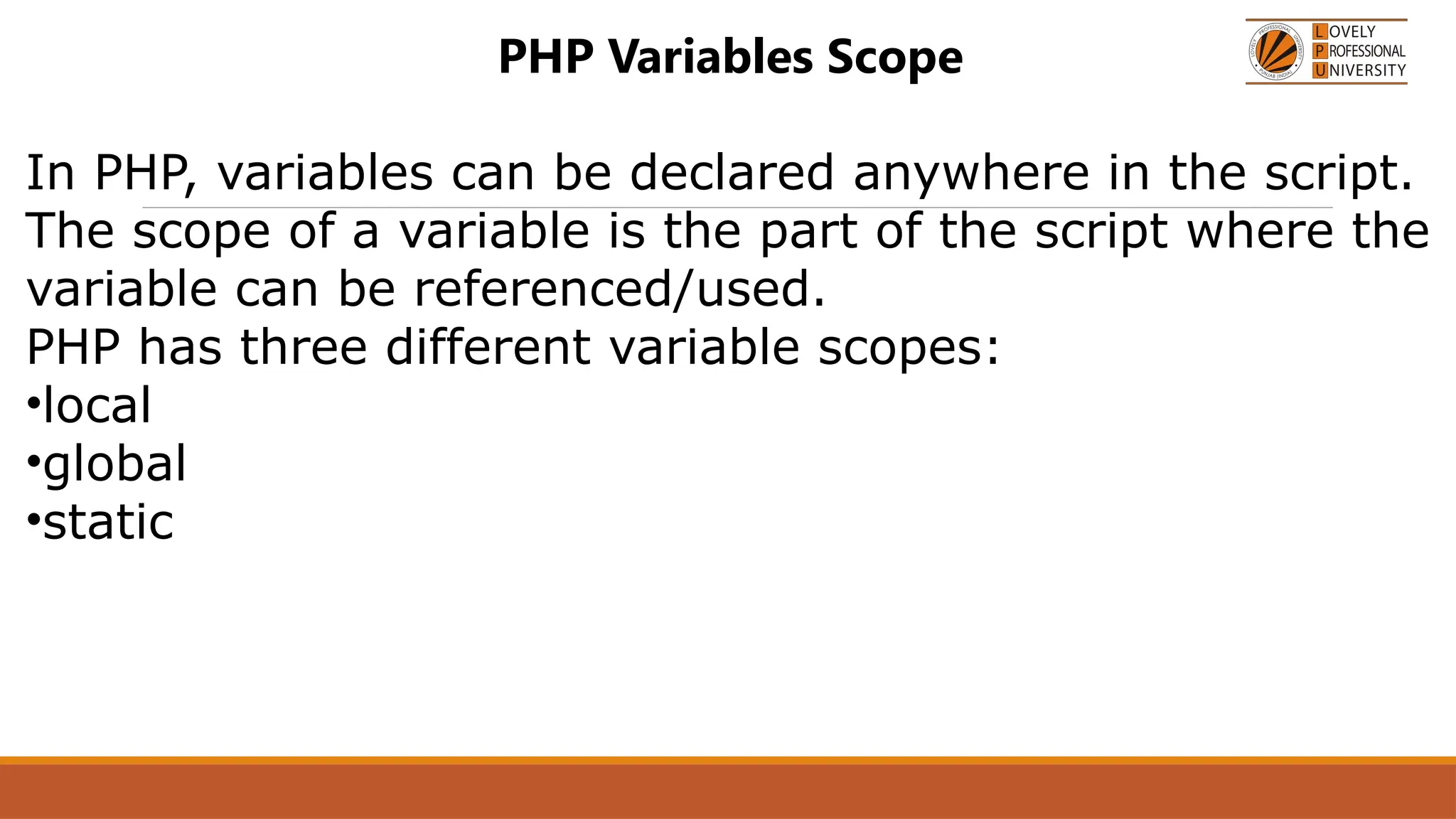
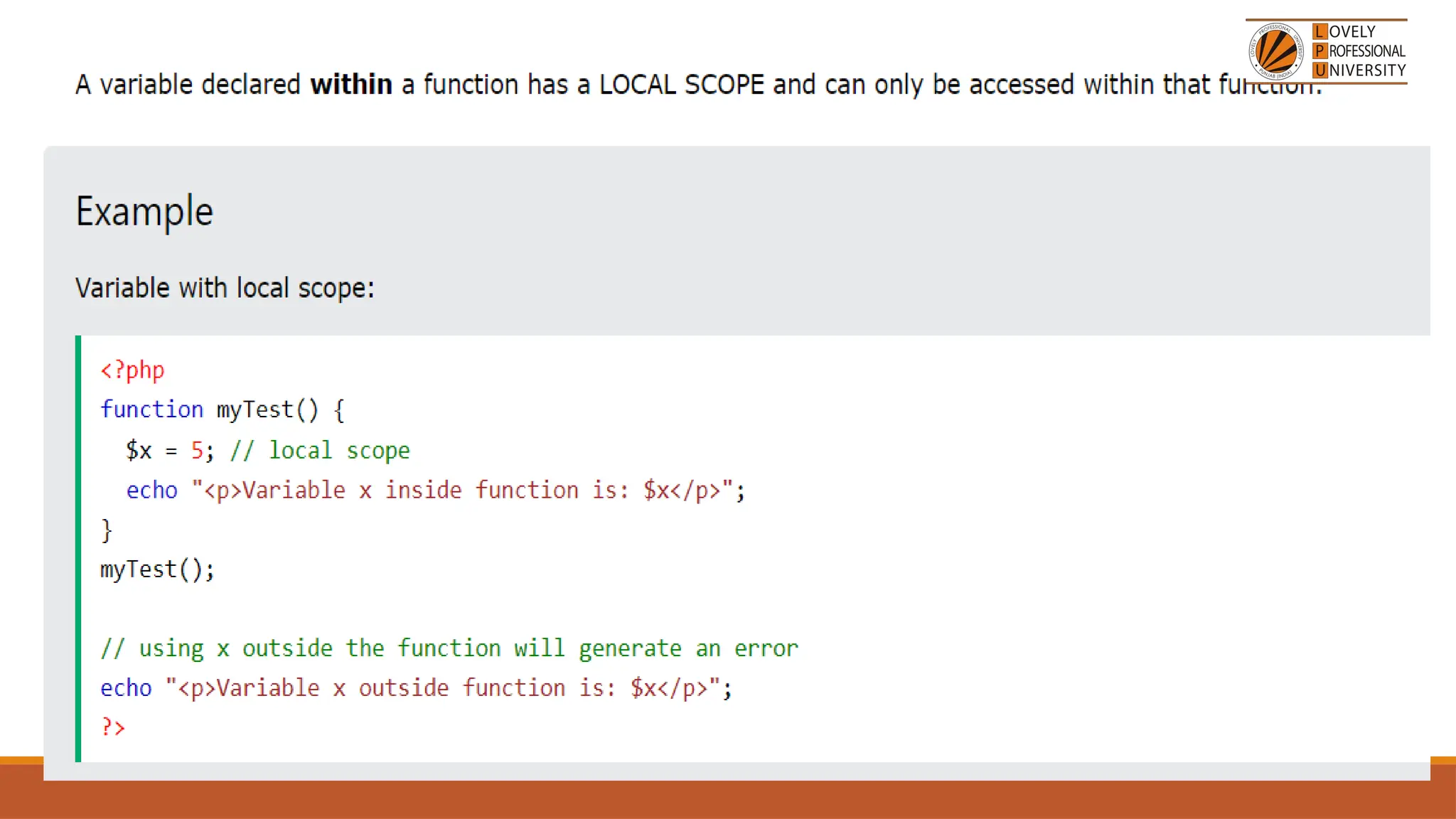
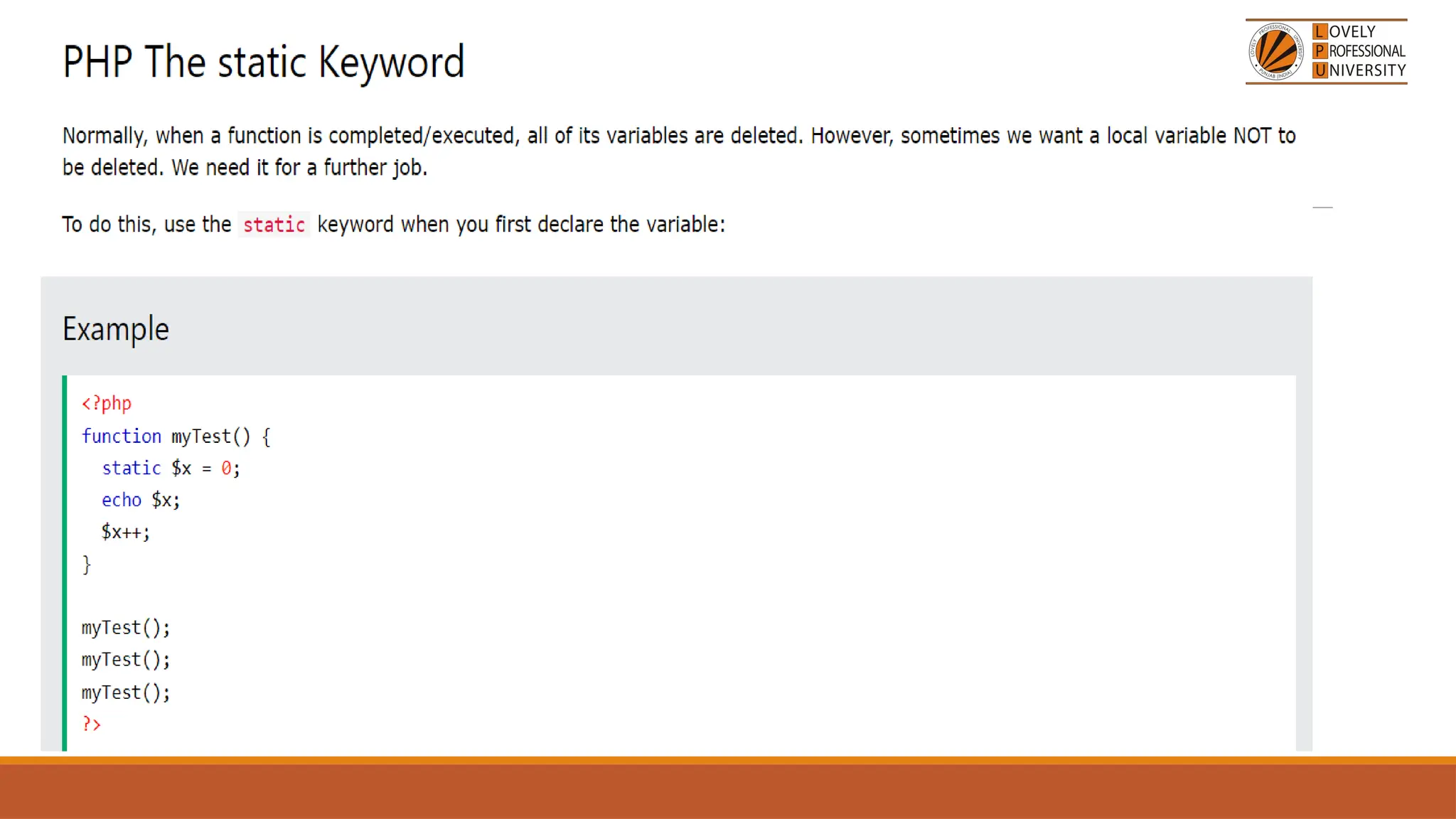
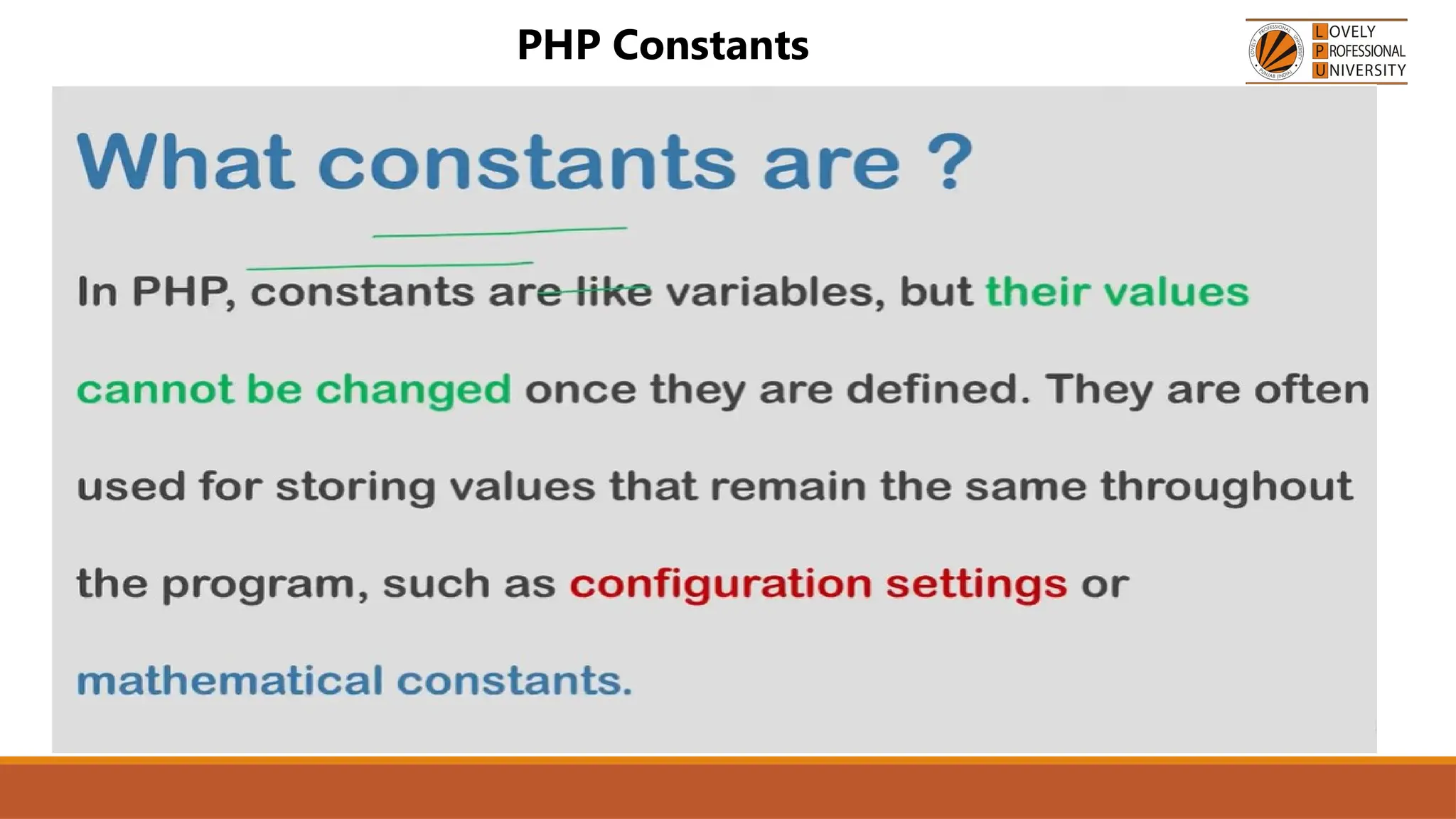
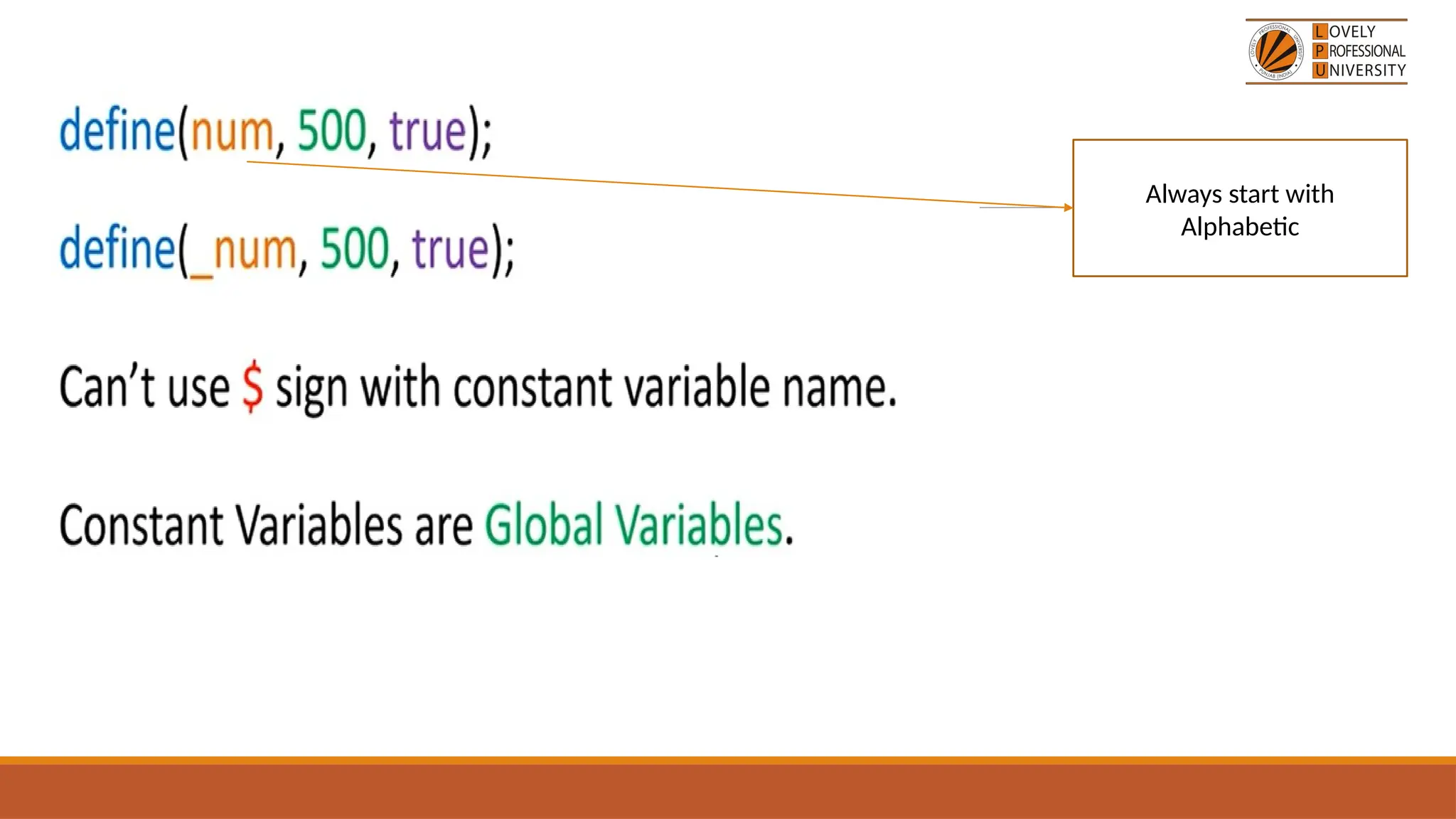
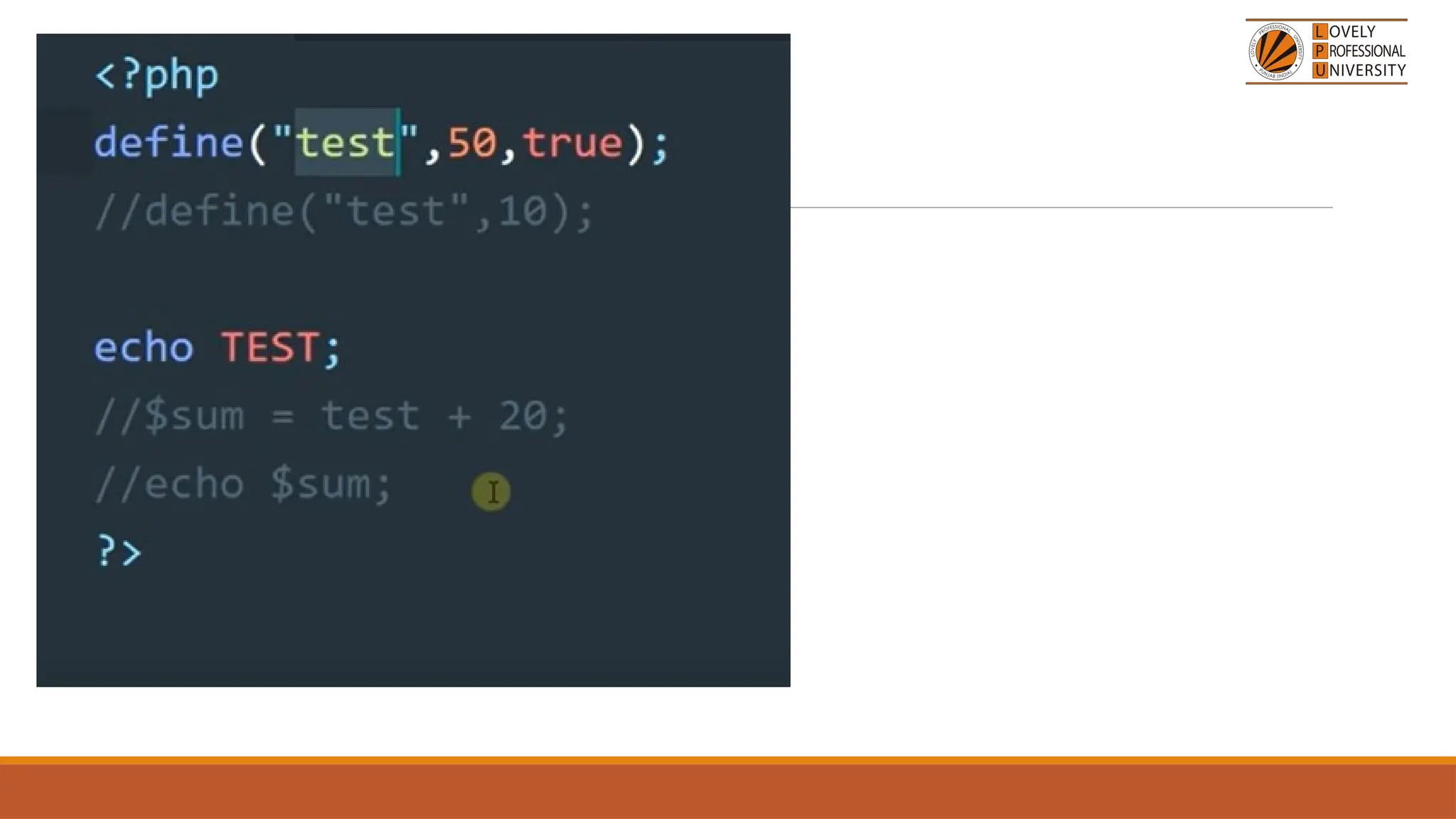
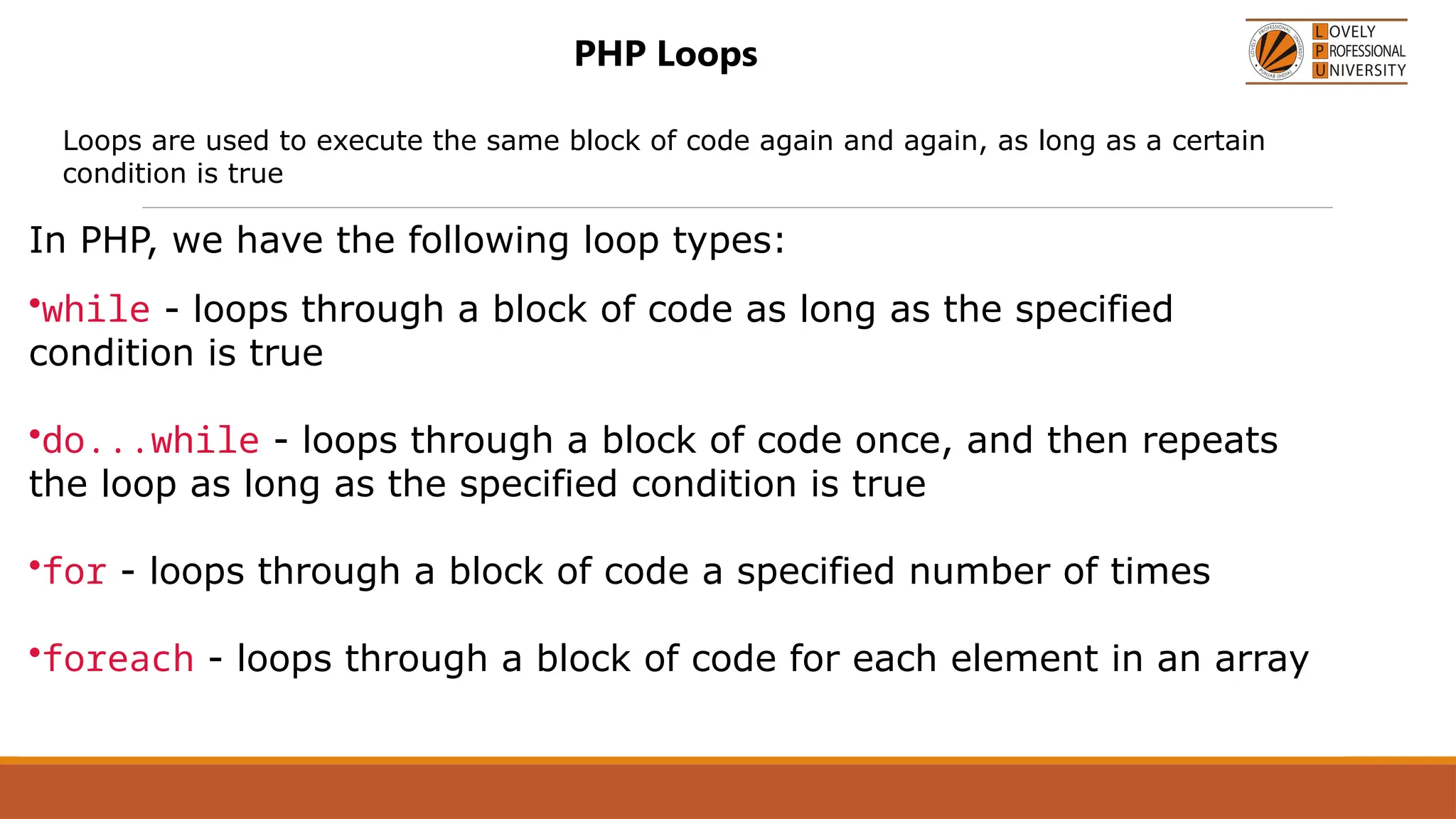
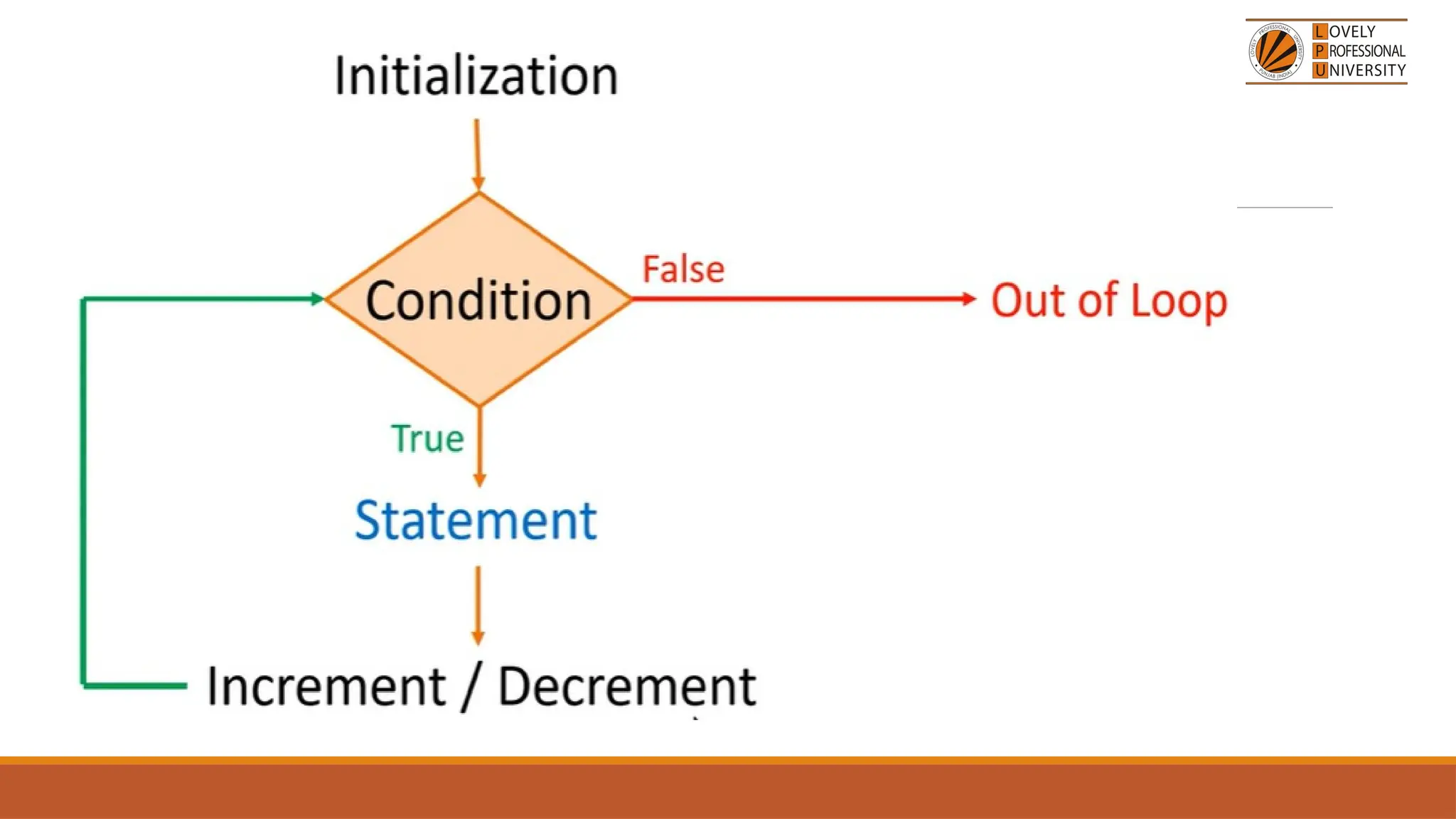
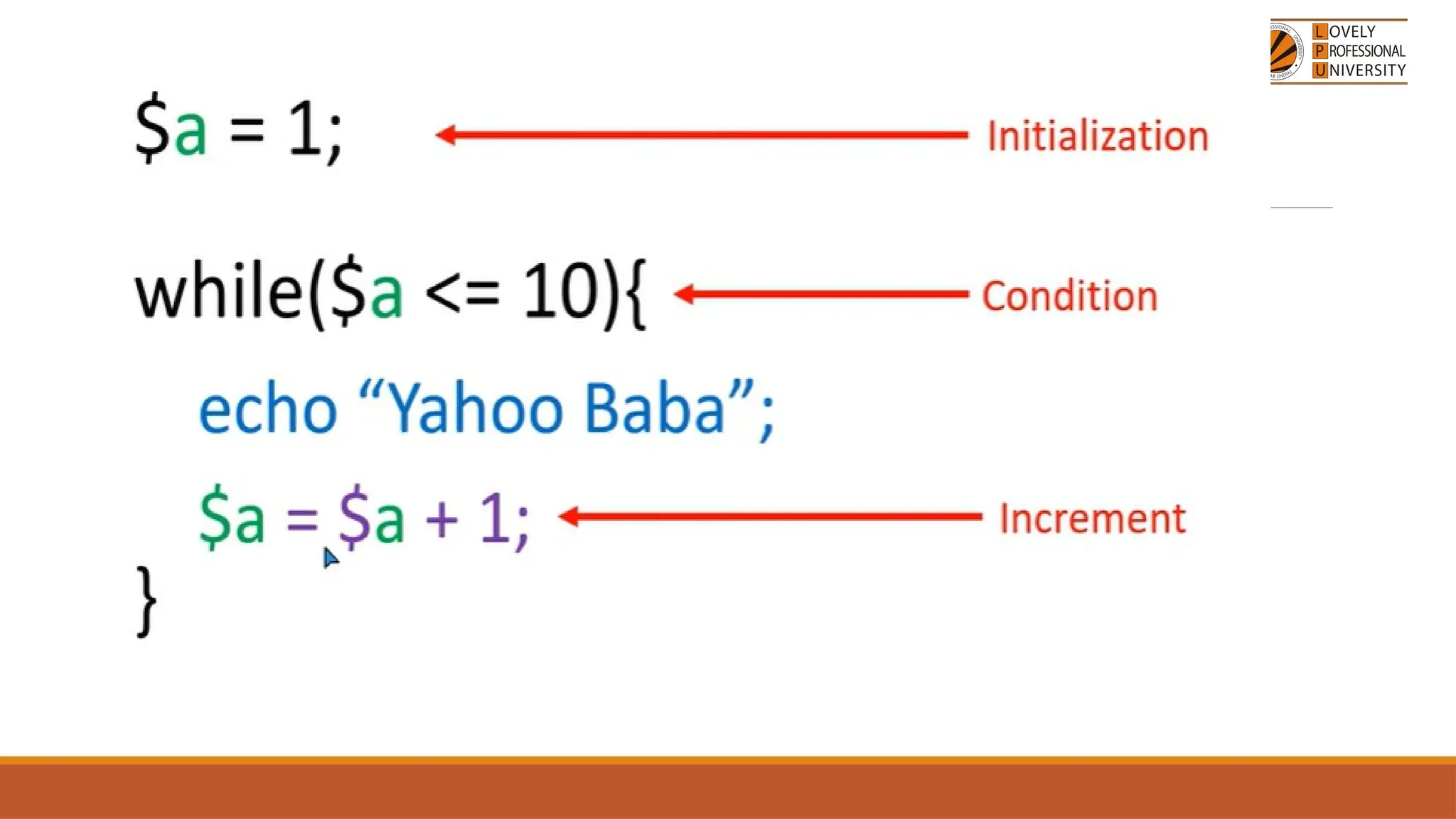
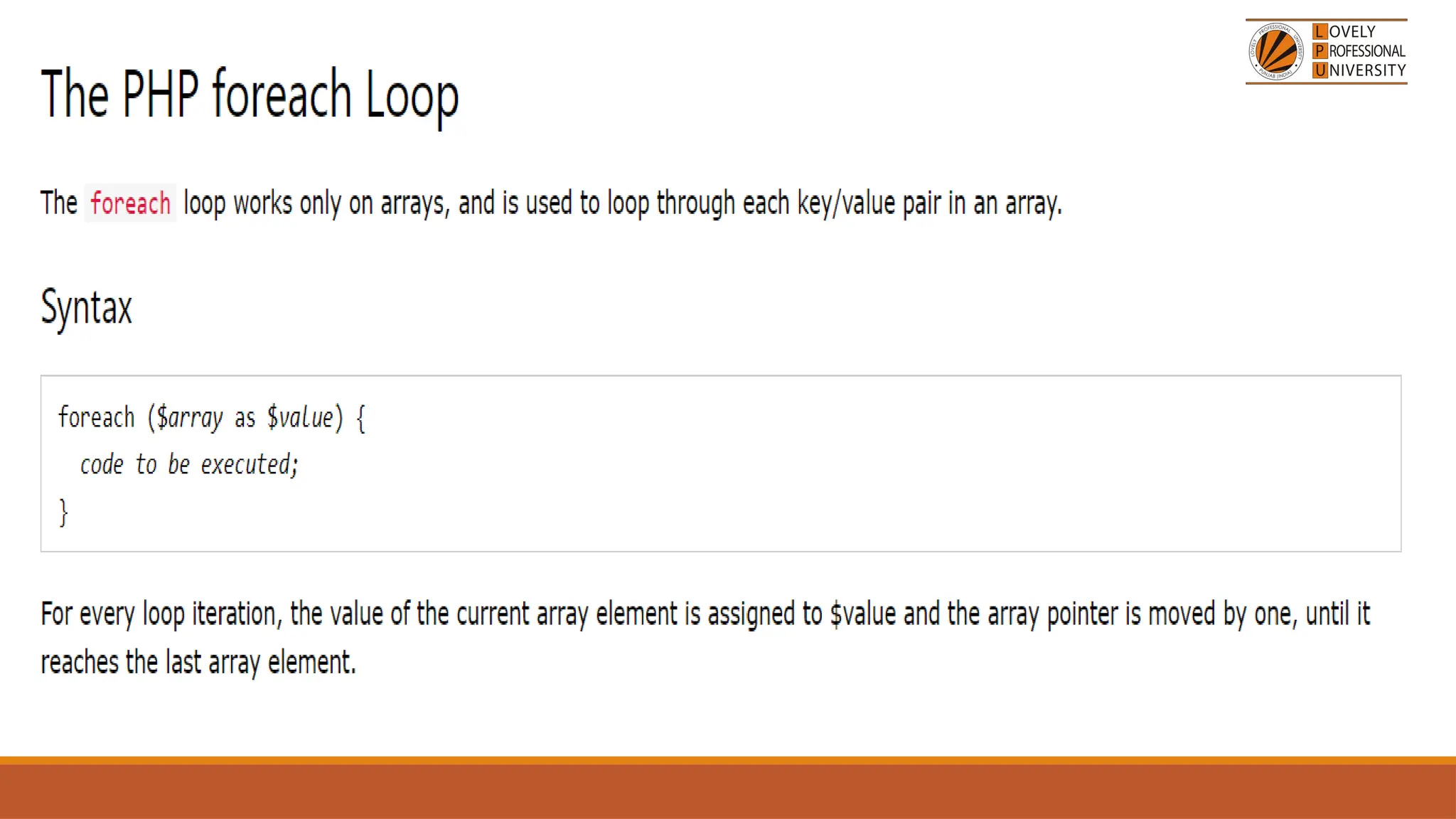
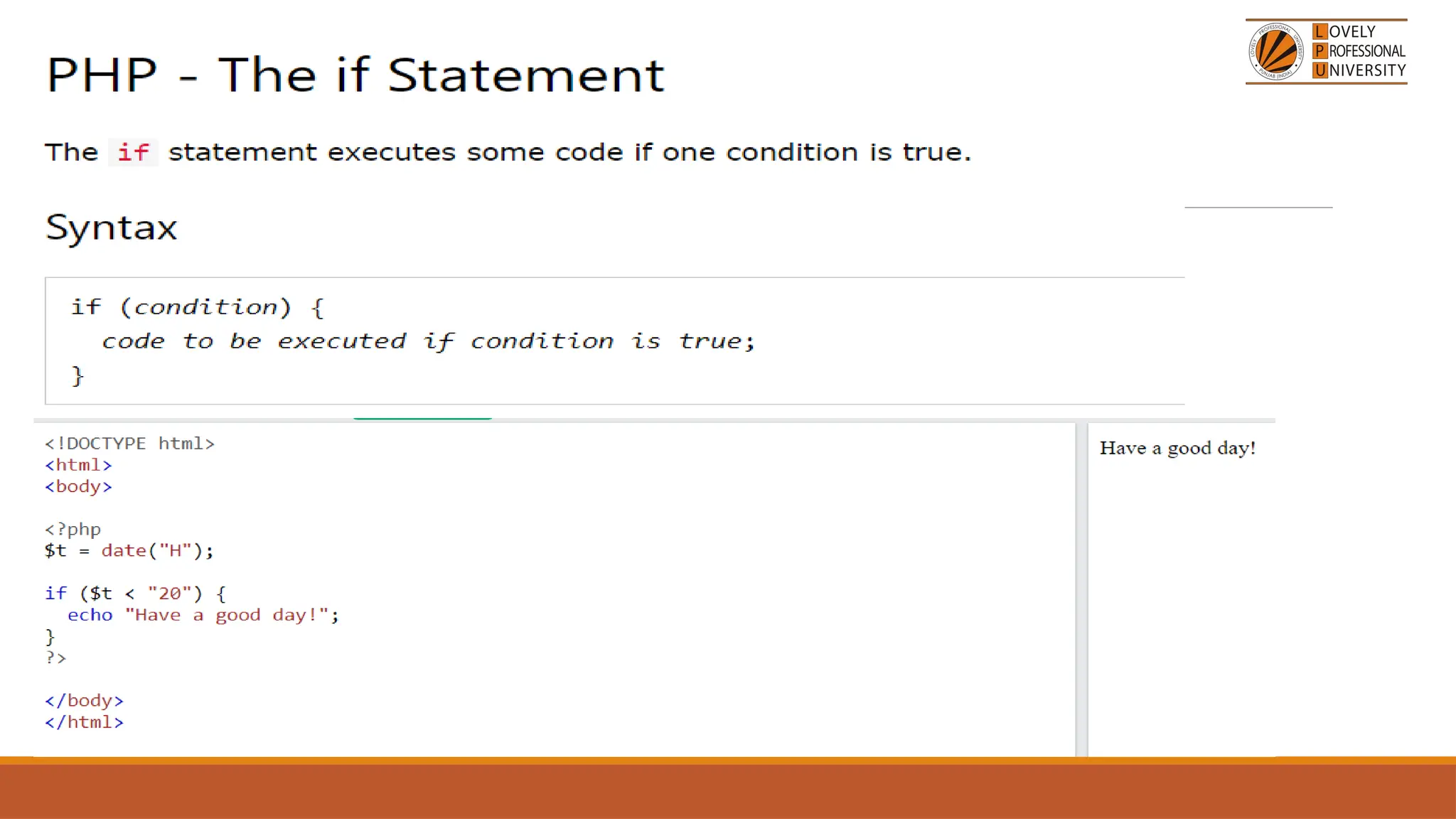
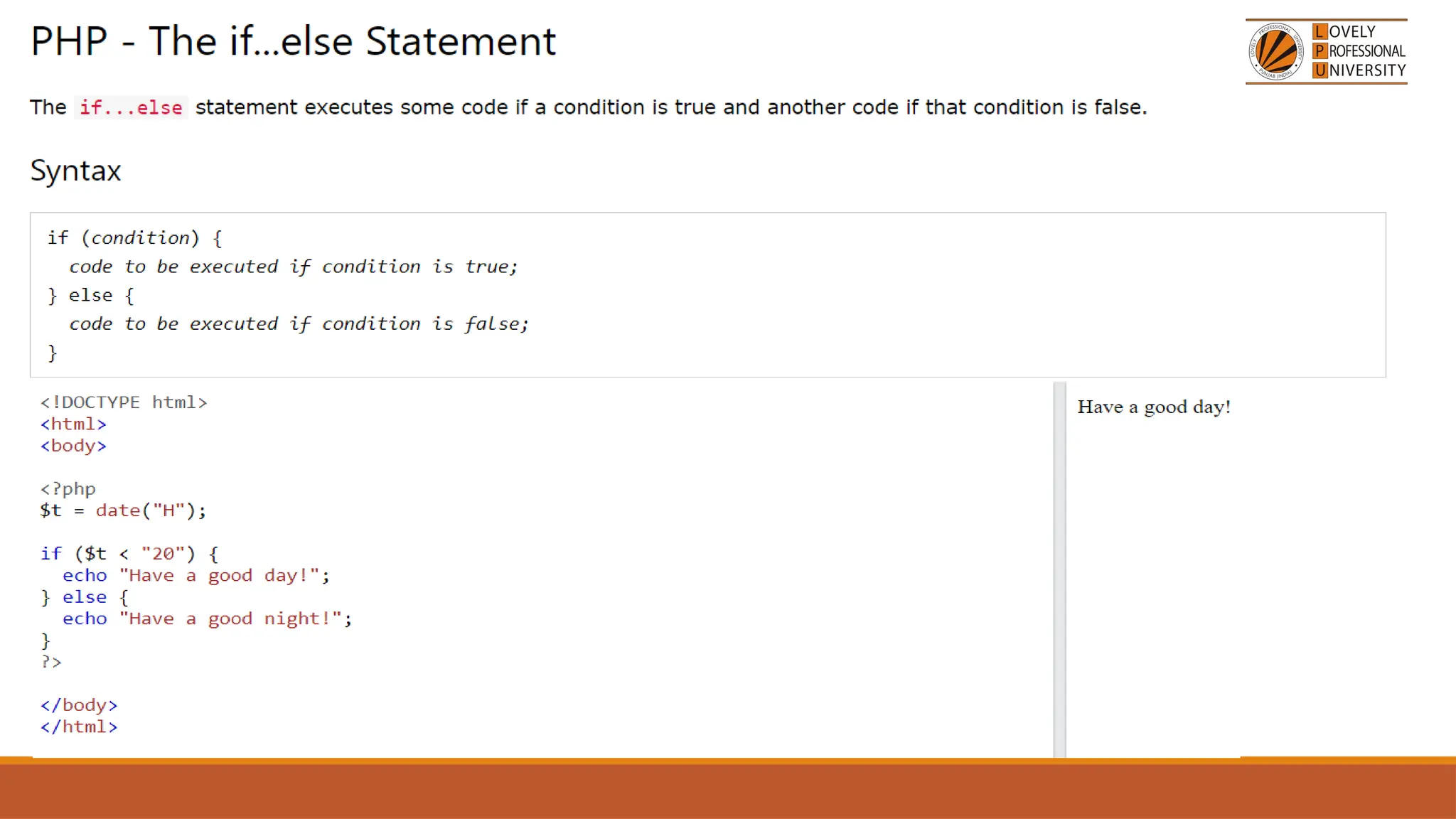
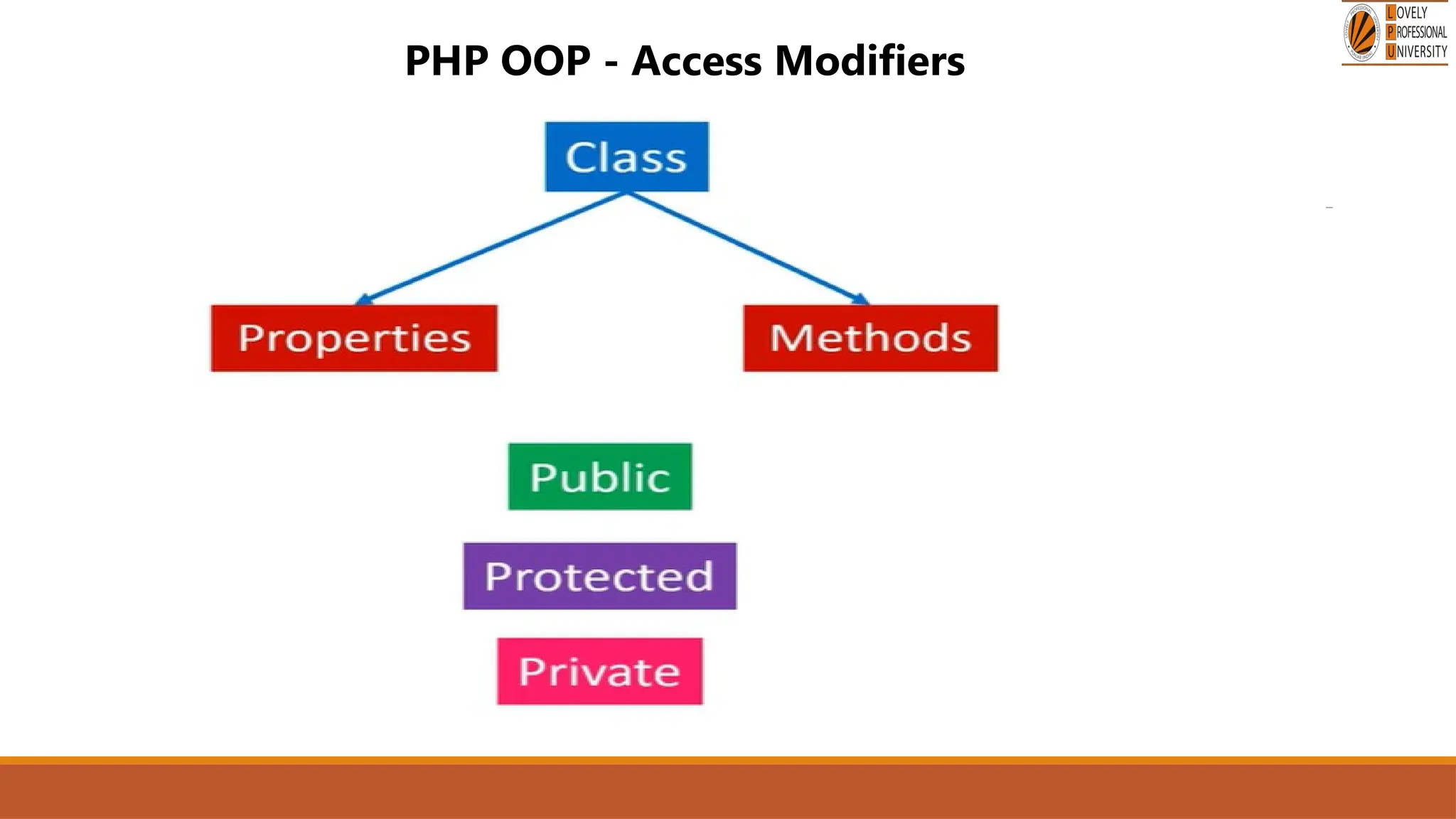
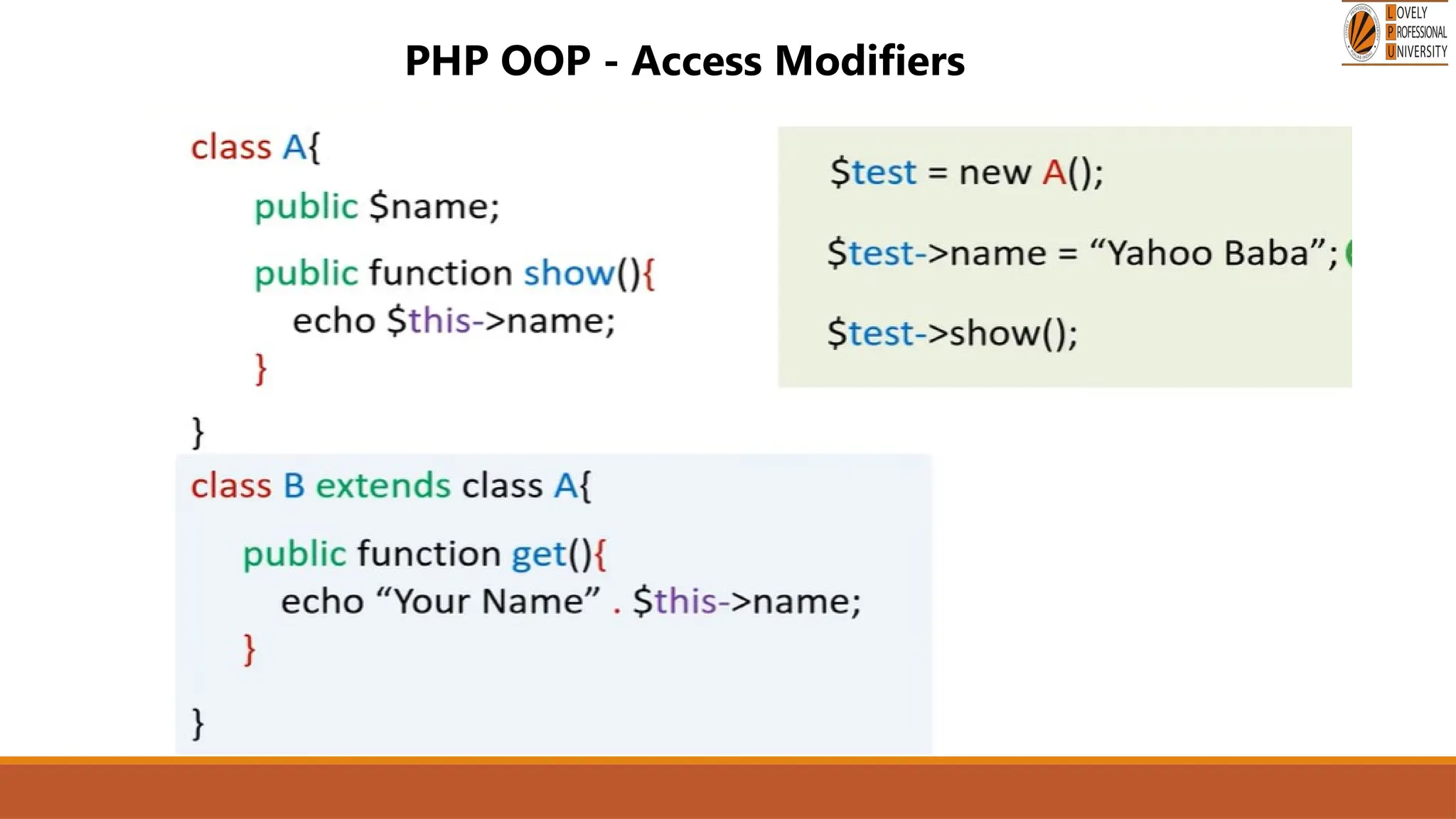
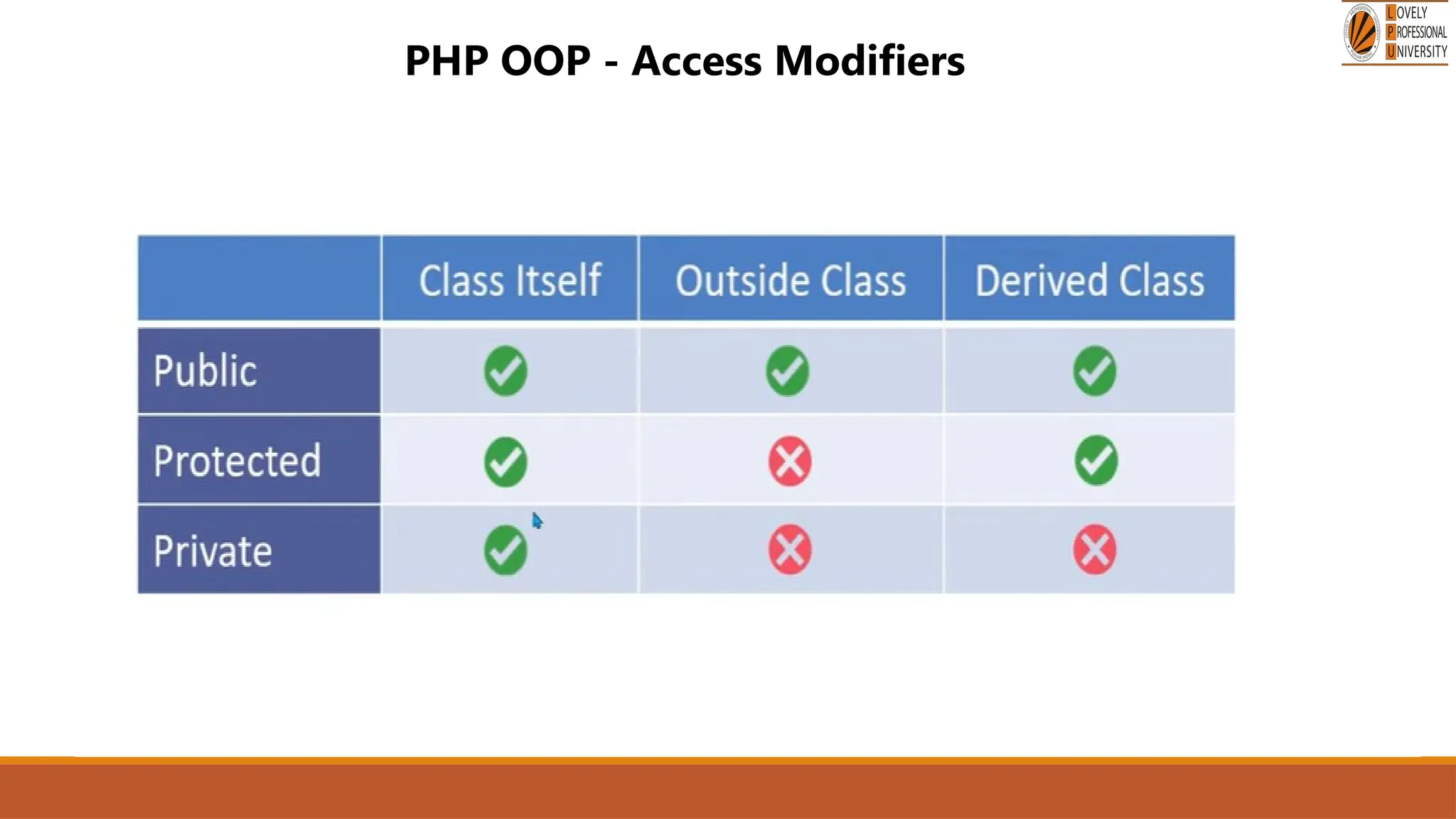
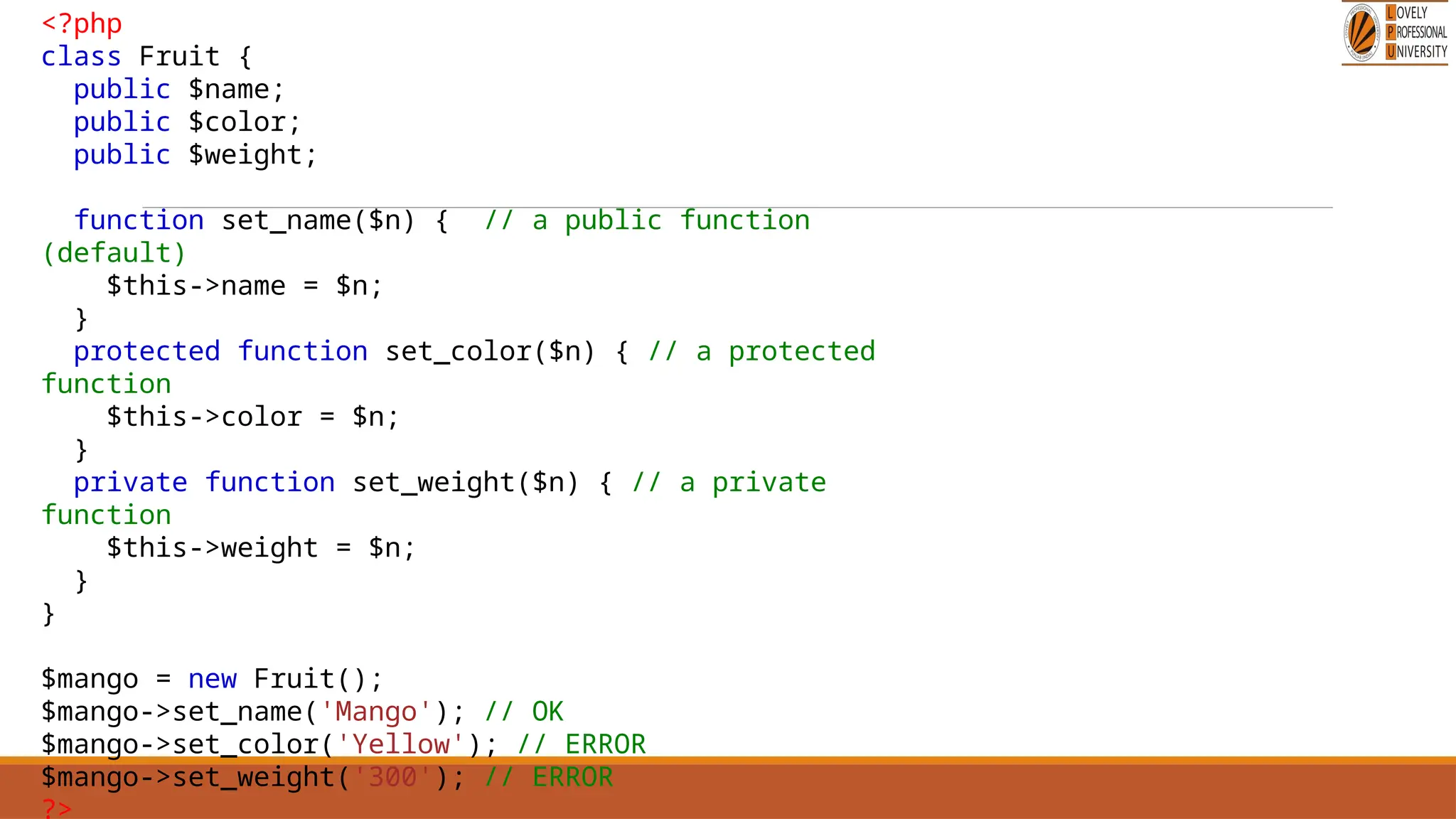
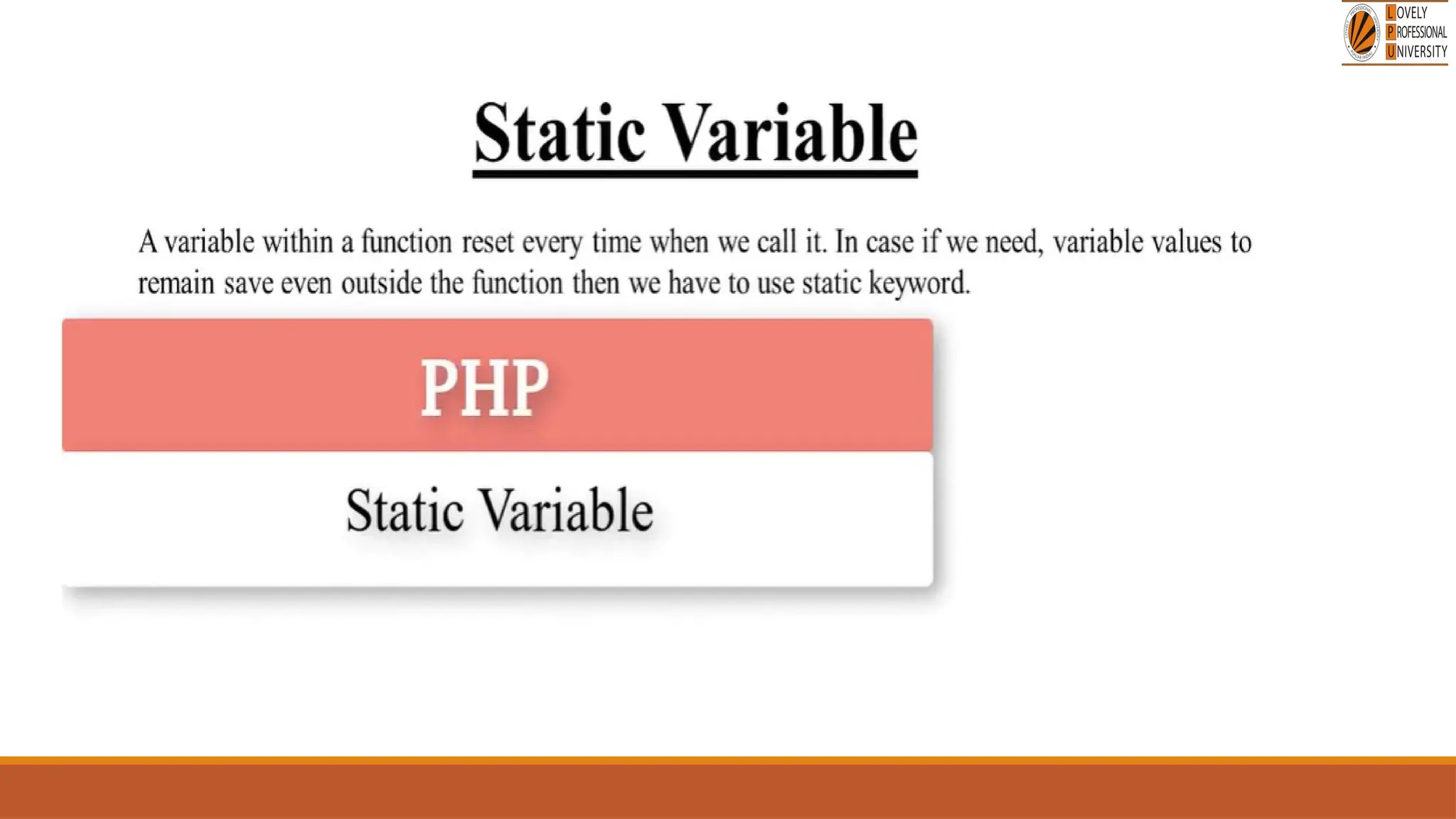
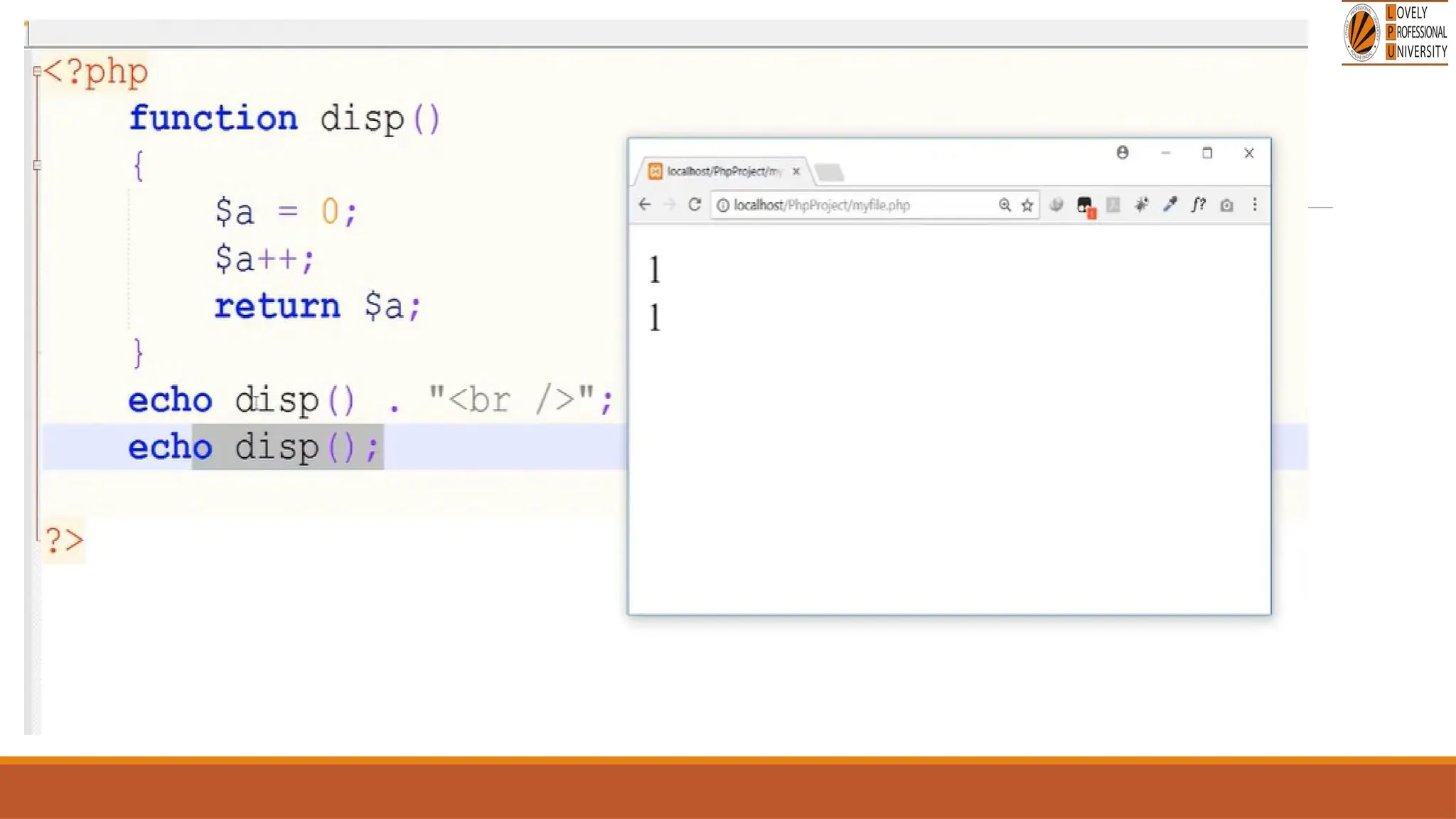
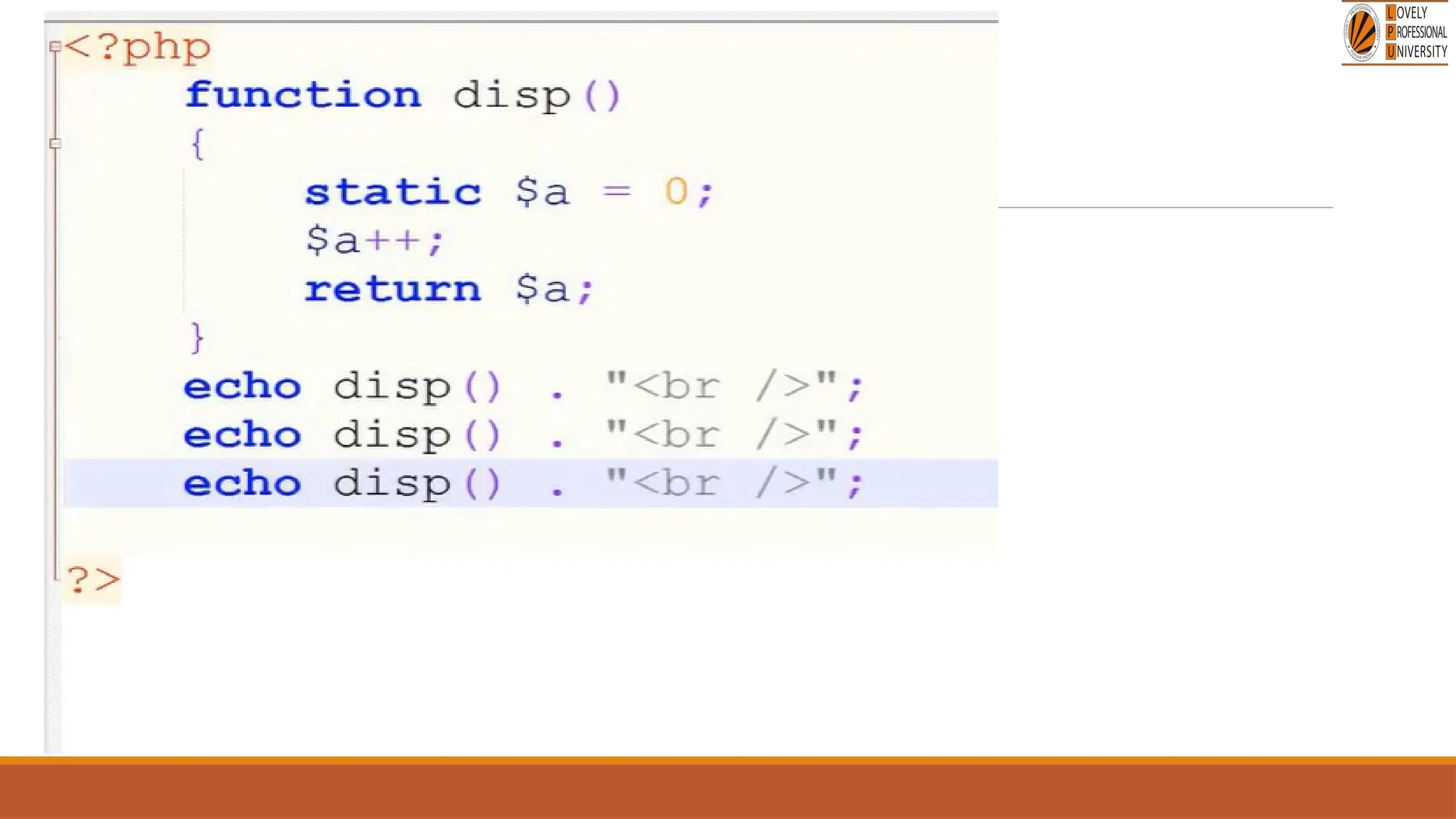
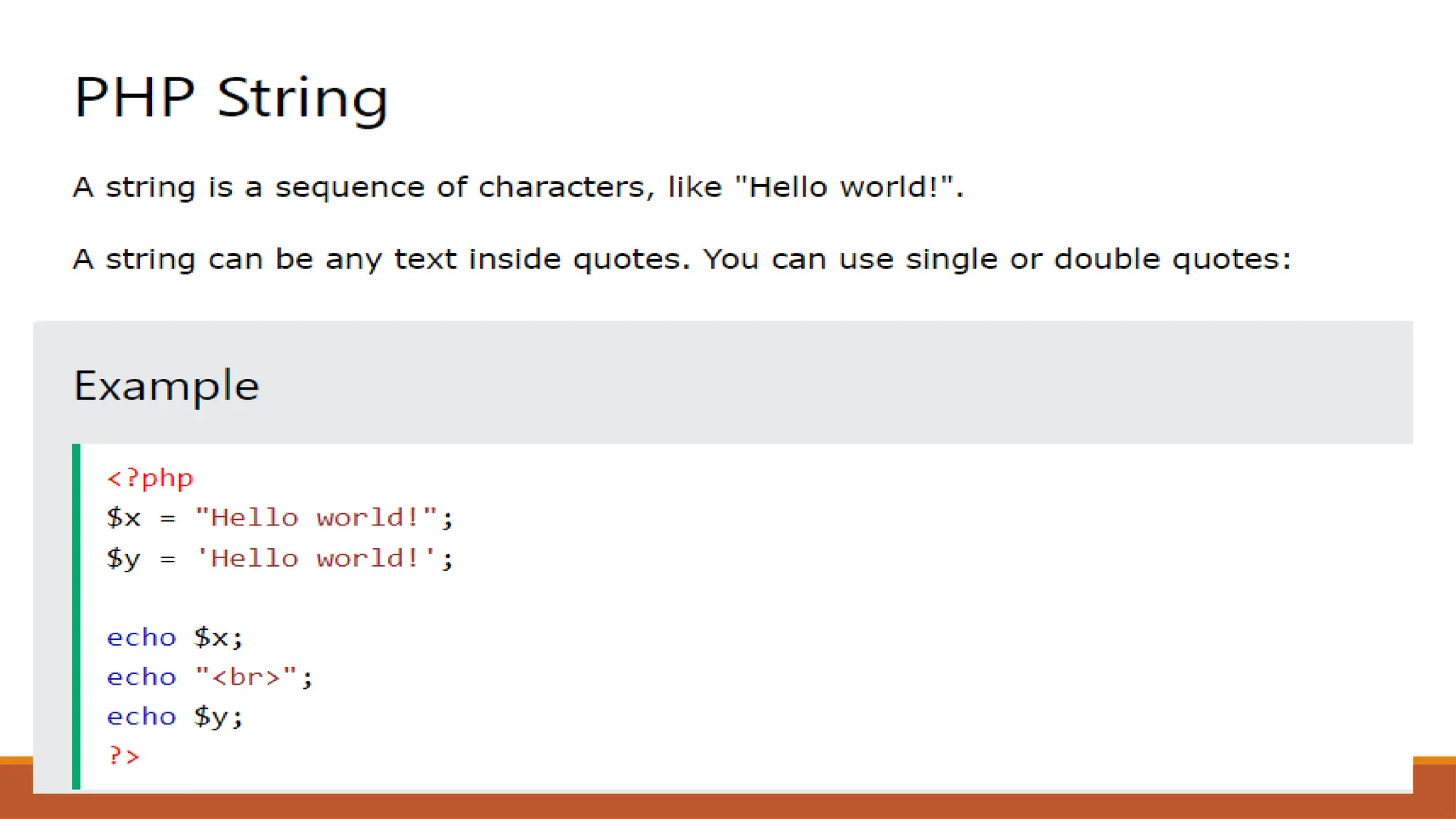
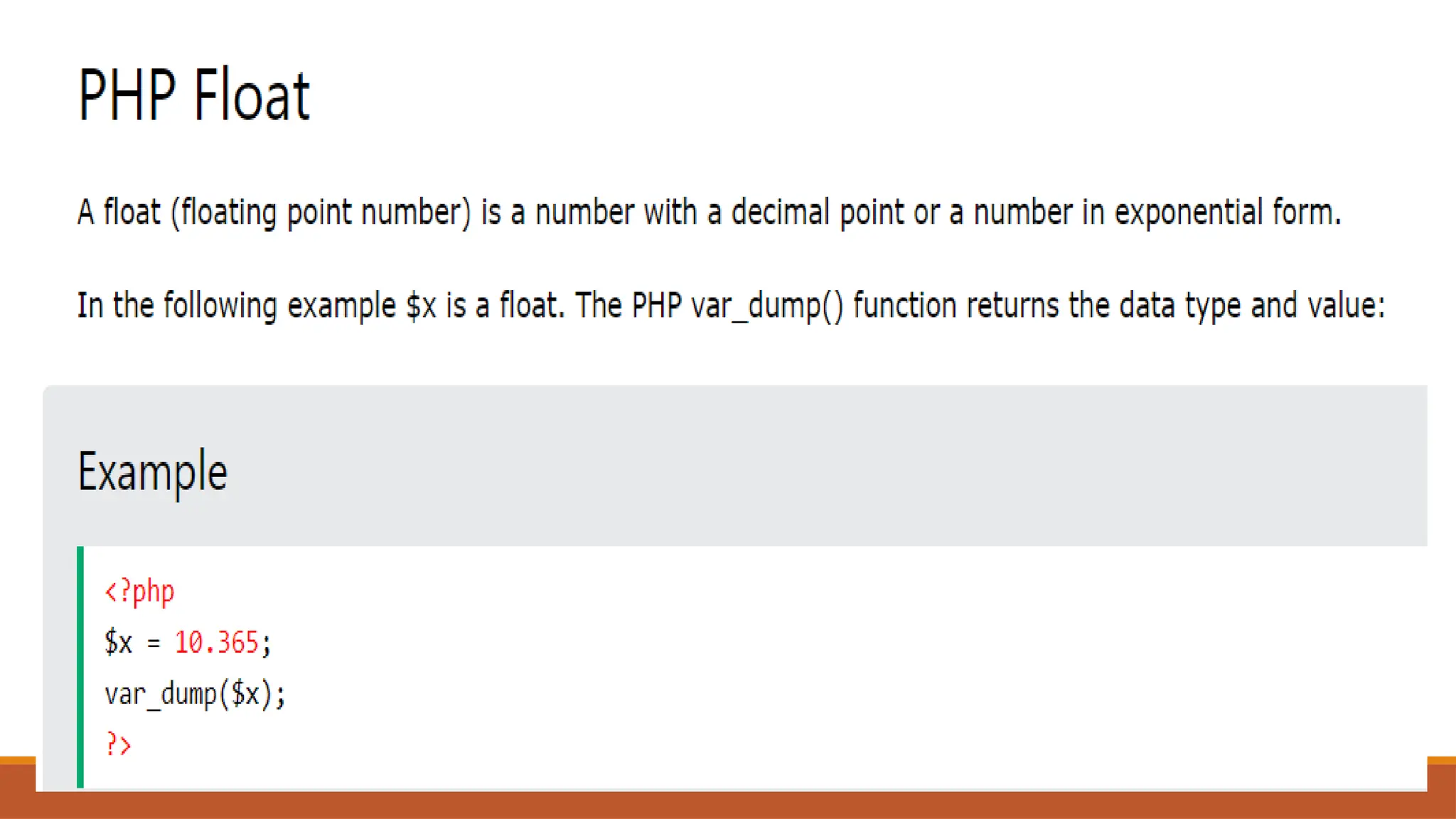
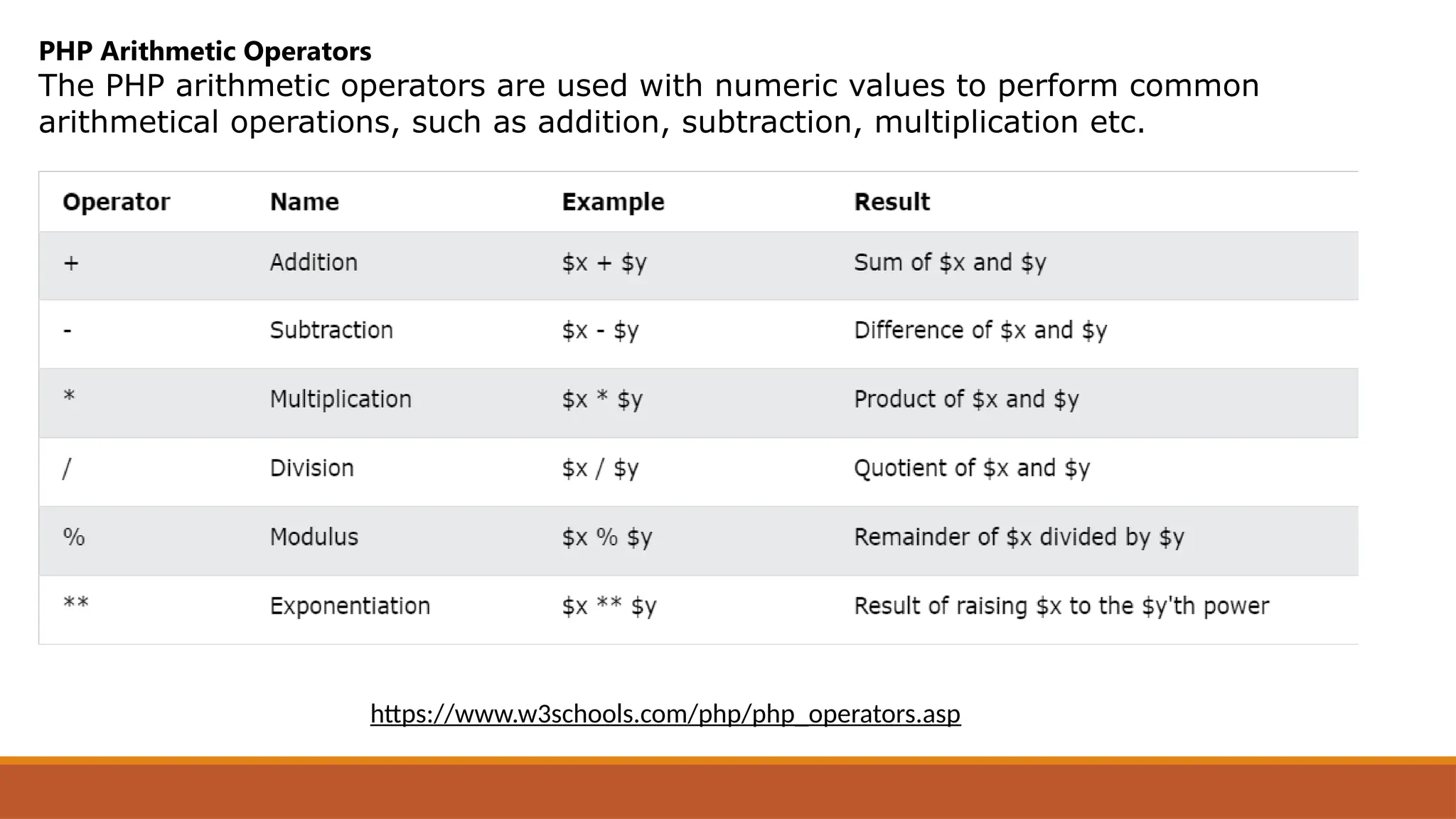
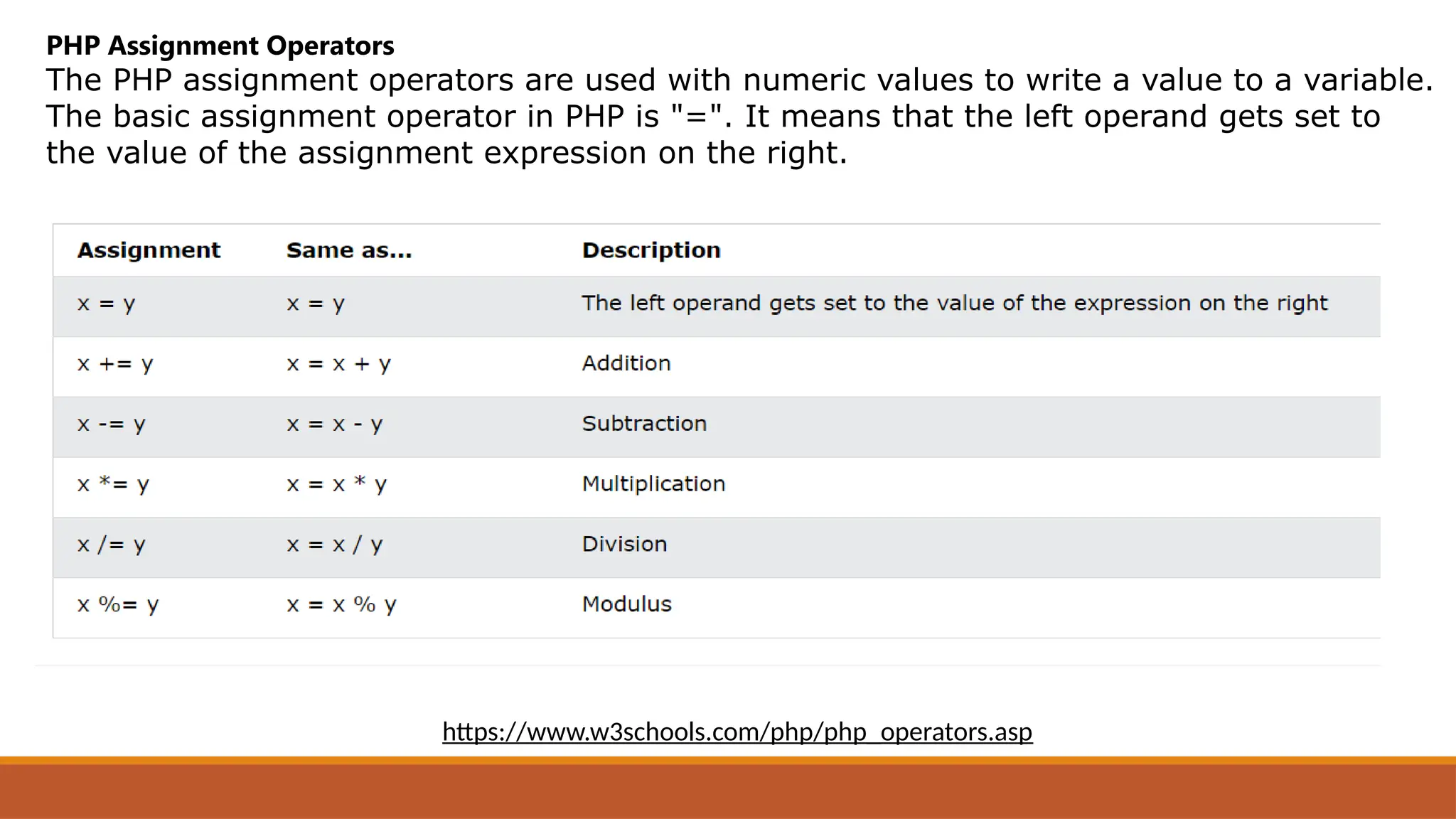
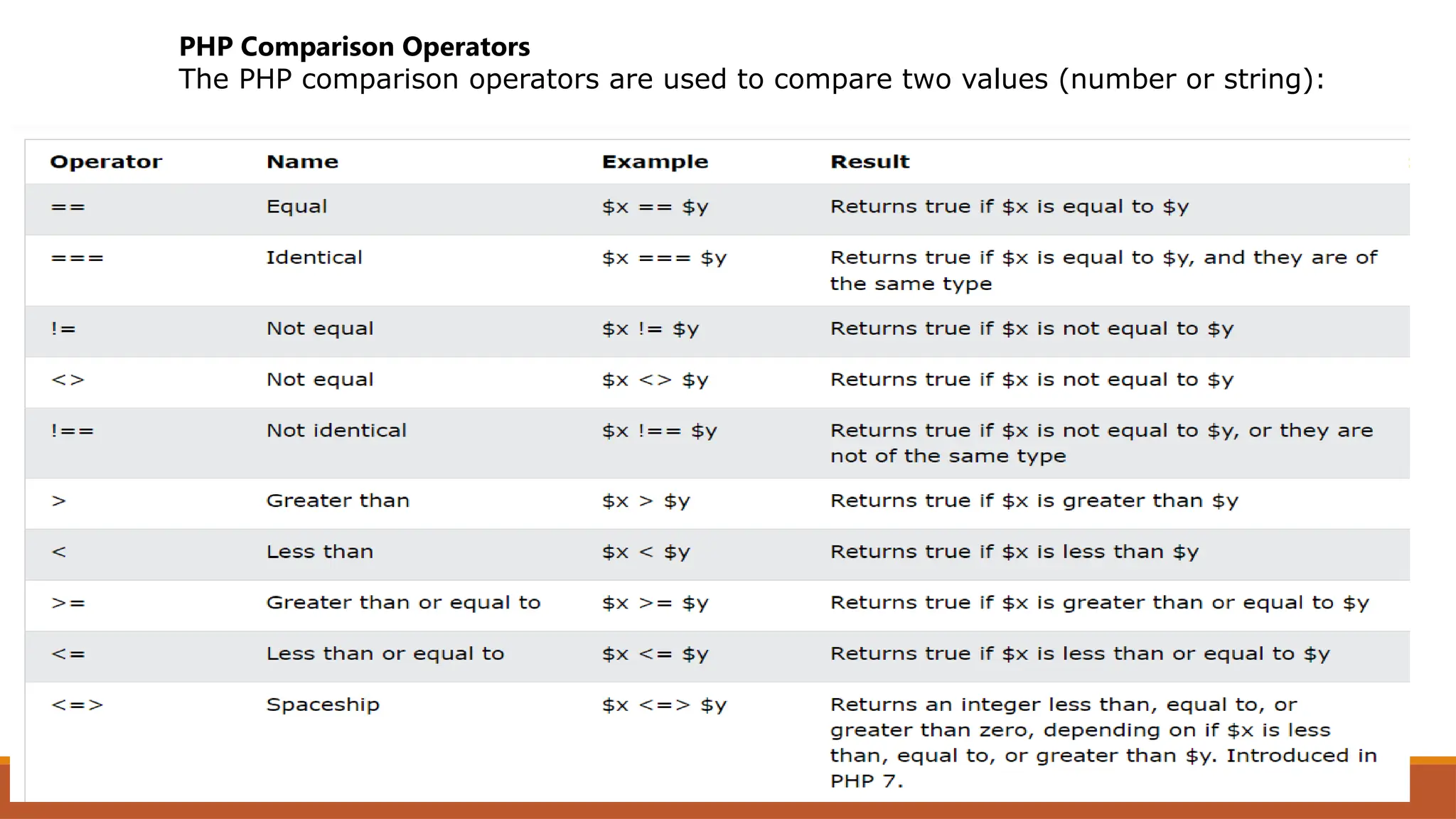
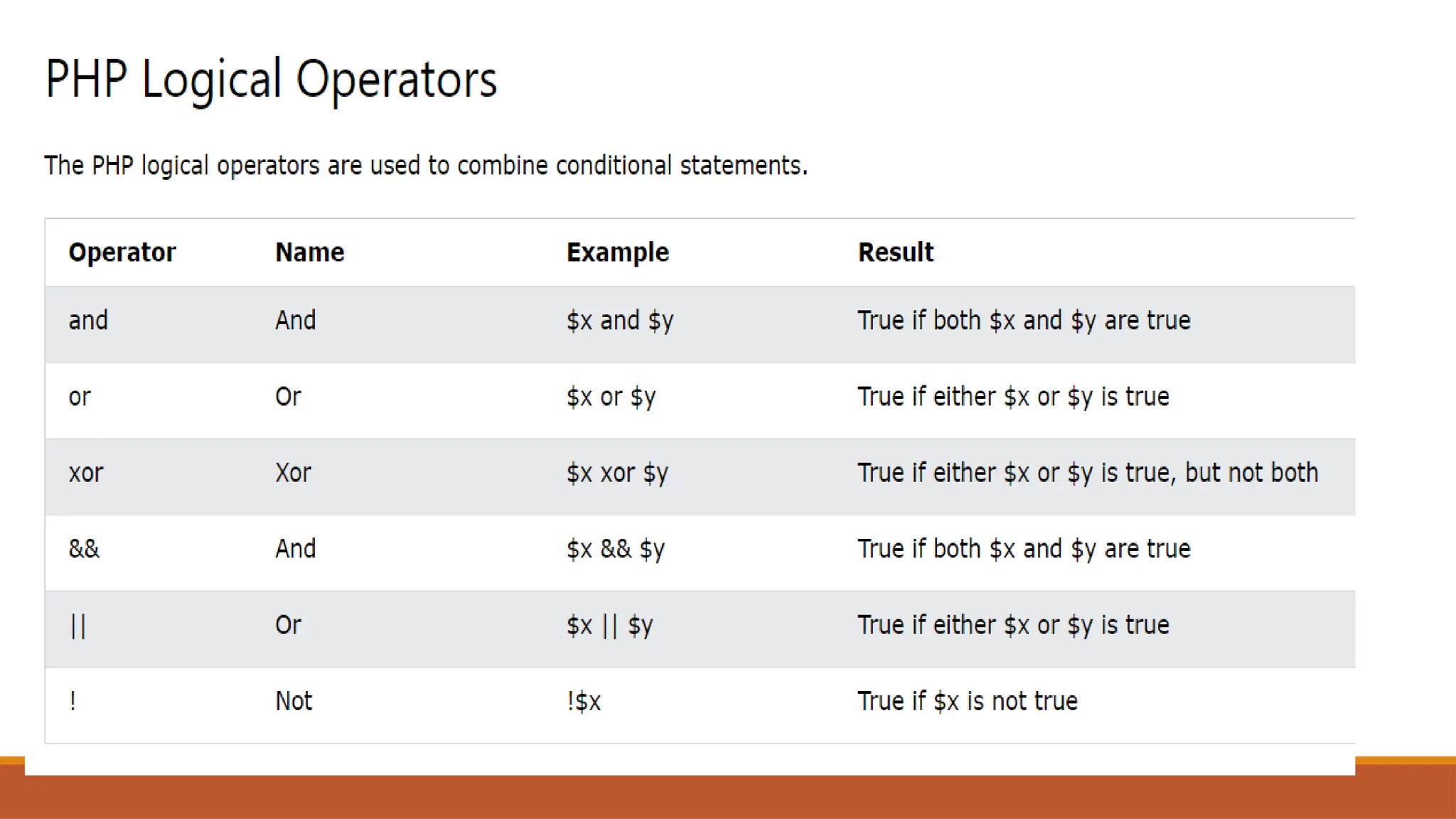
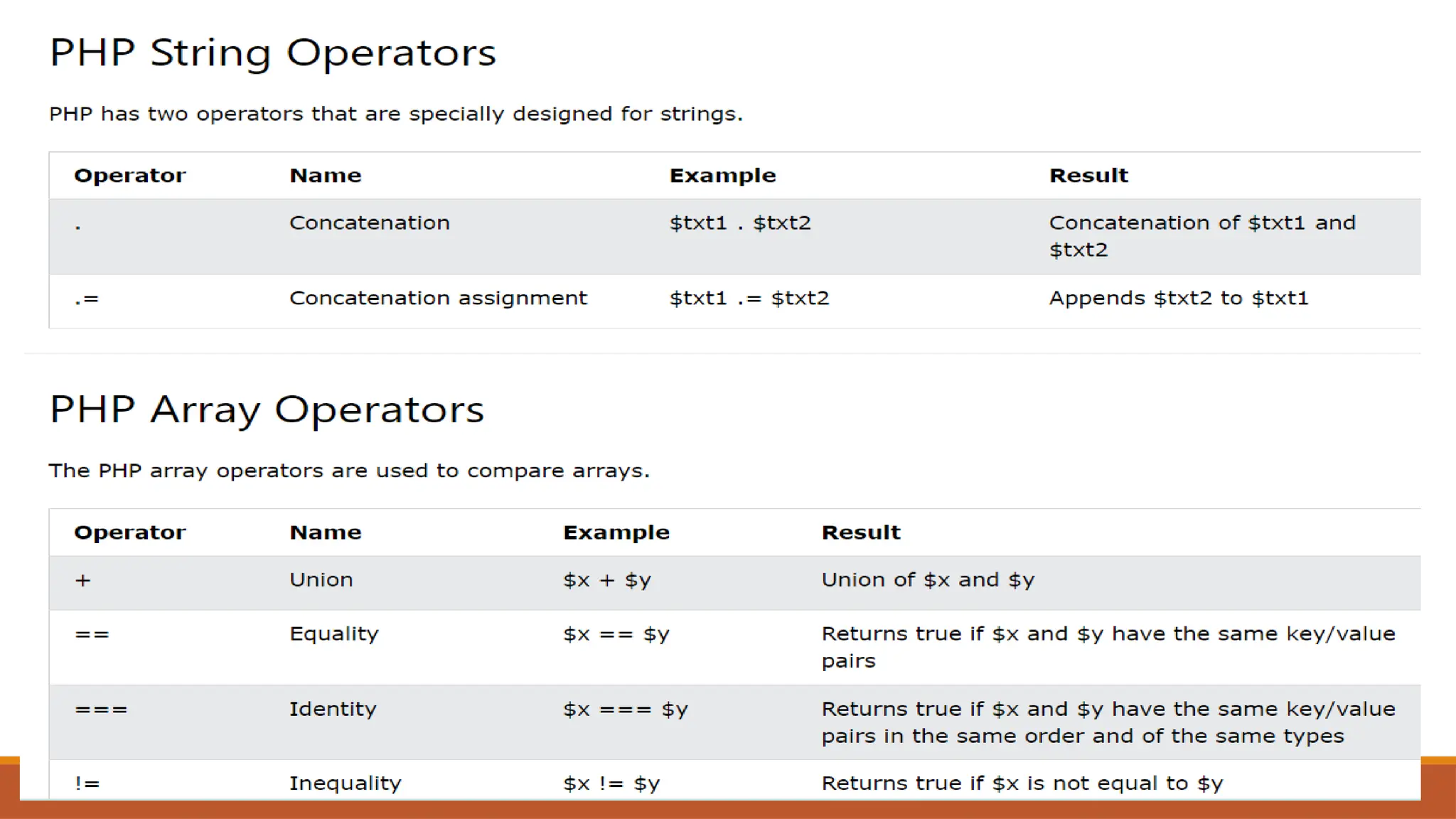
The document provides an overview of PHP, a widely-used open-source server-side scripting language, detailing its capabilities, installation requirements, and basic syntax. It covers essential topics such as PHP variables, loops, conditional statements, and object-oriented programming (OOP) principles, including access modifiers and operators. The content also contrasts server-side and client-side scripting, emphasizing the advantages of using PHP for dynamic web applications.