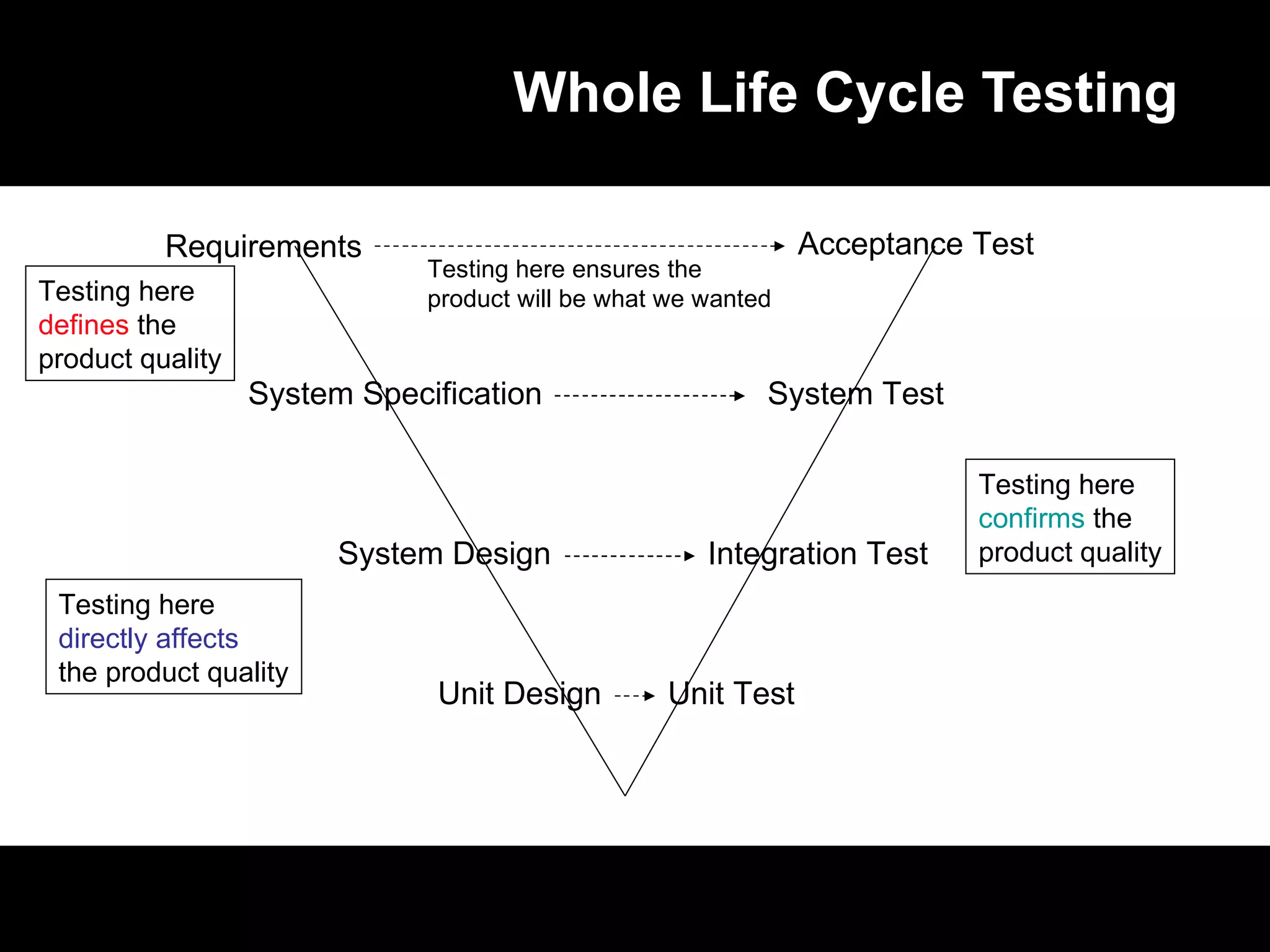
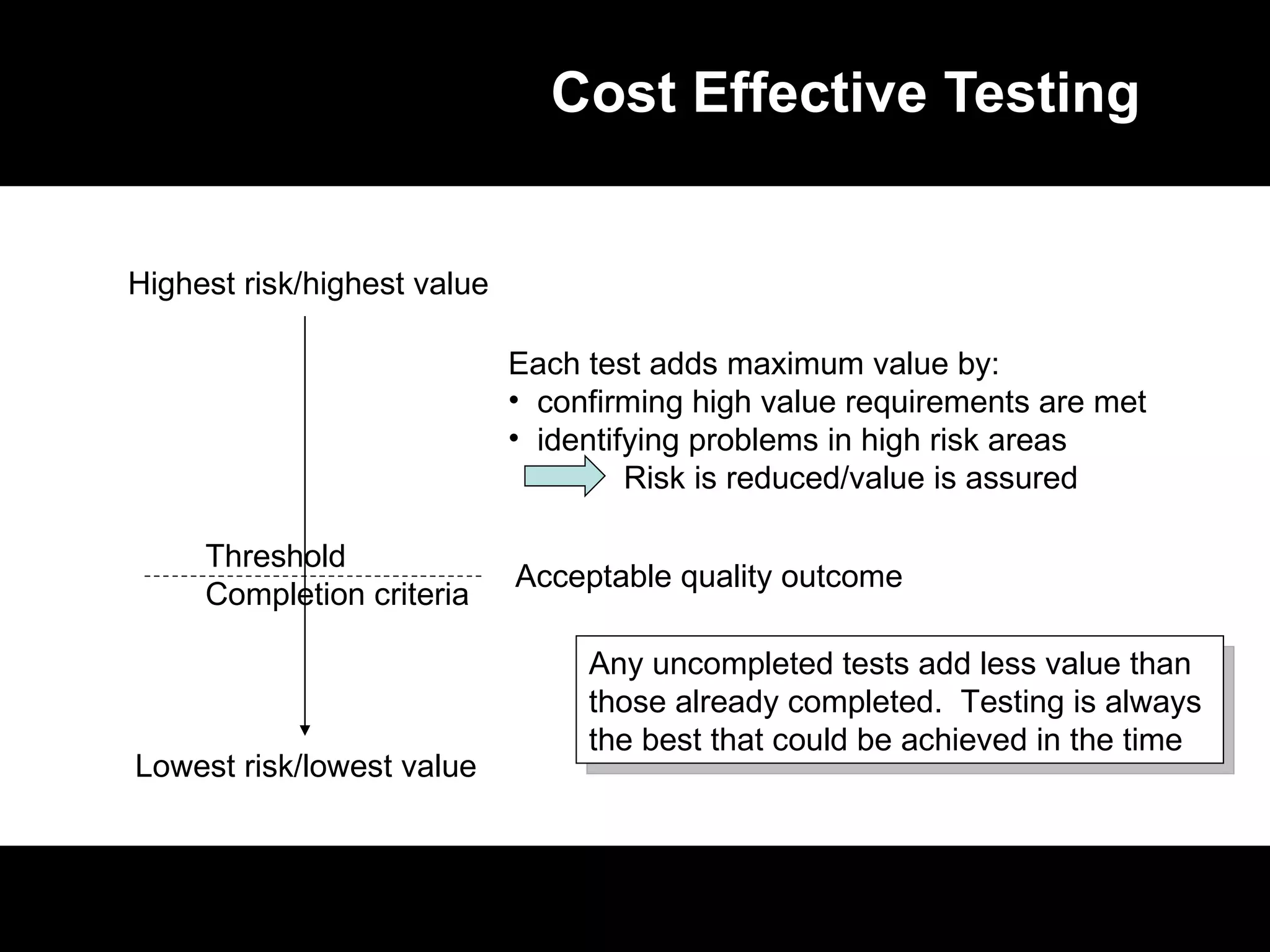
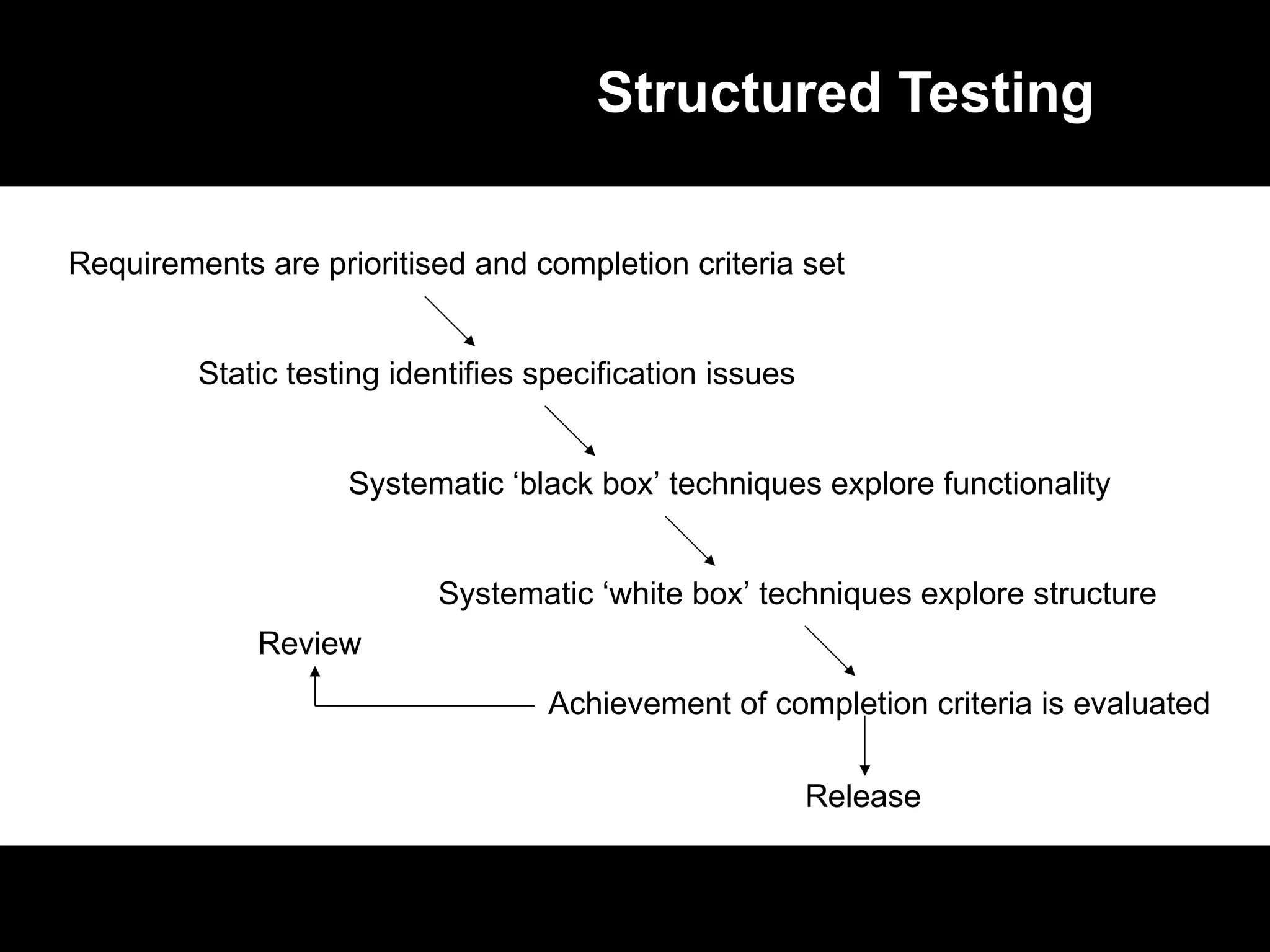
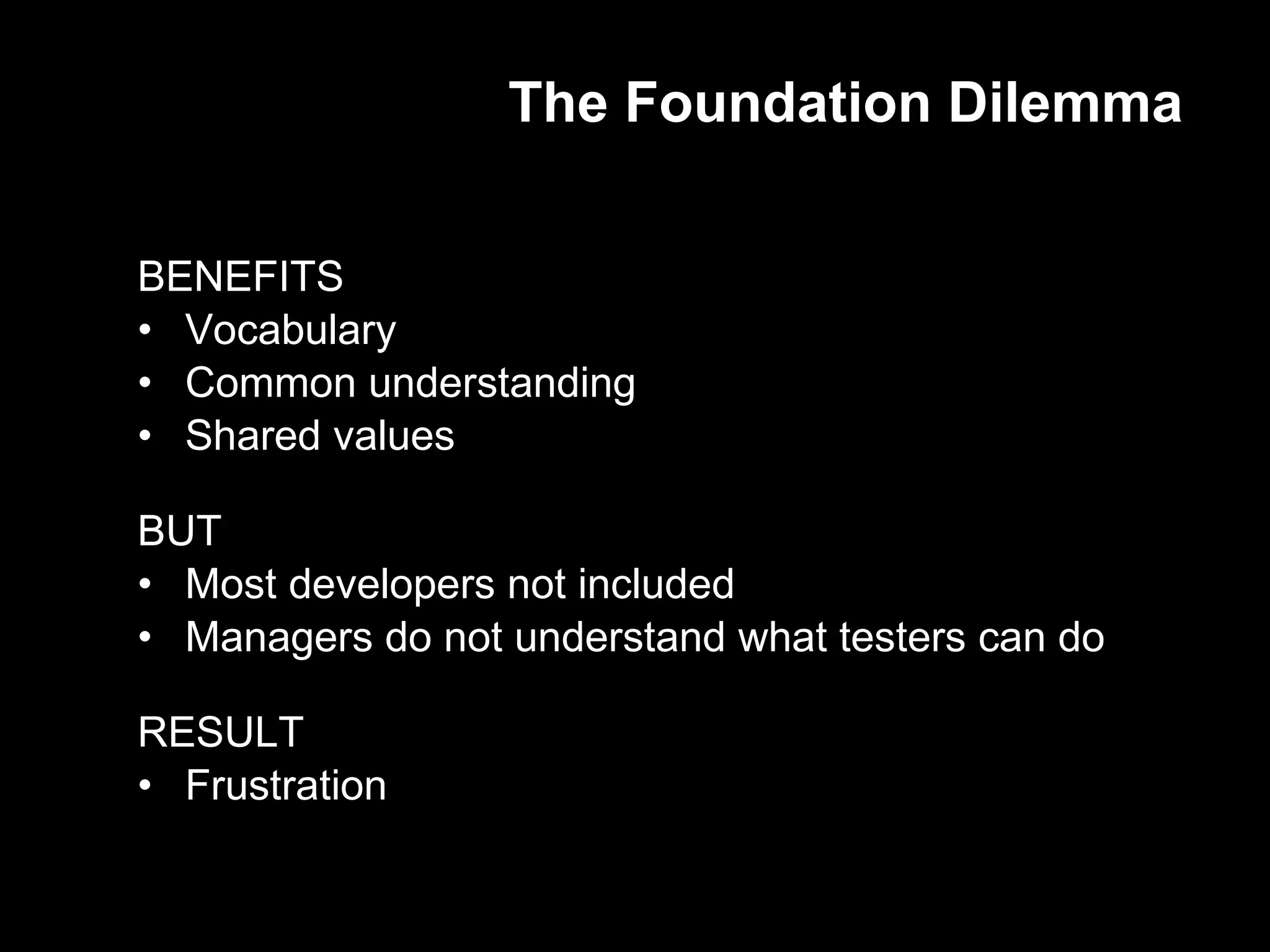
The document discusses the history and current state of software testing certification. It covers:
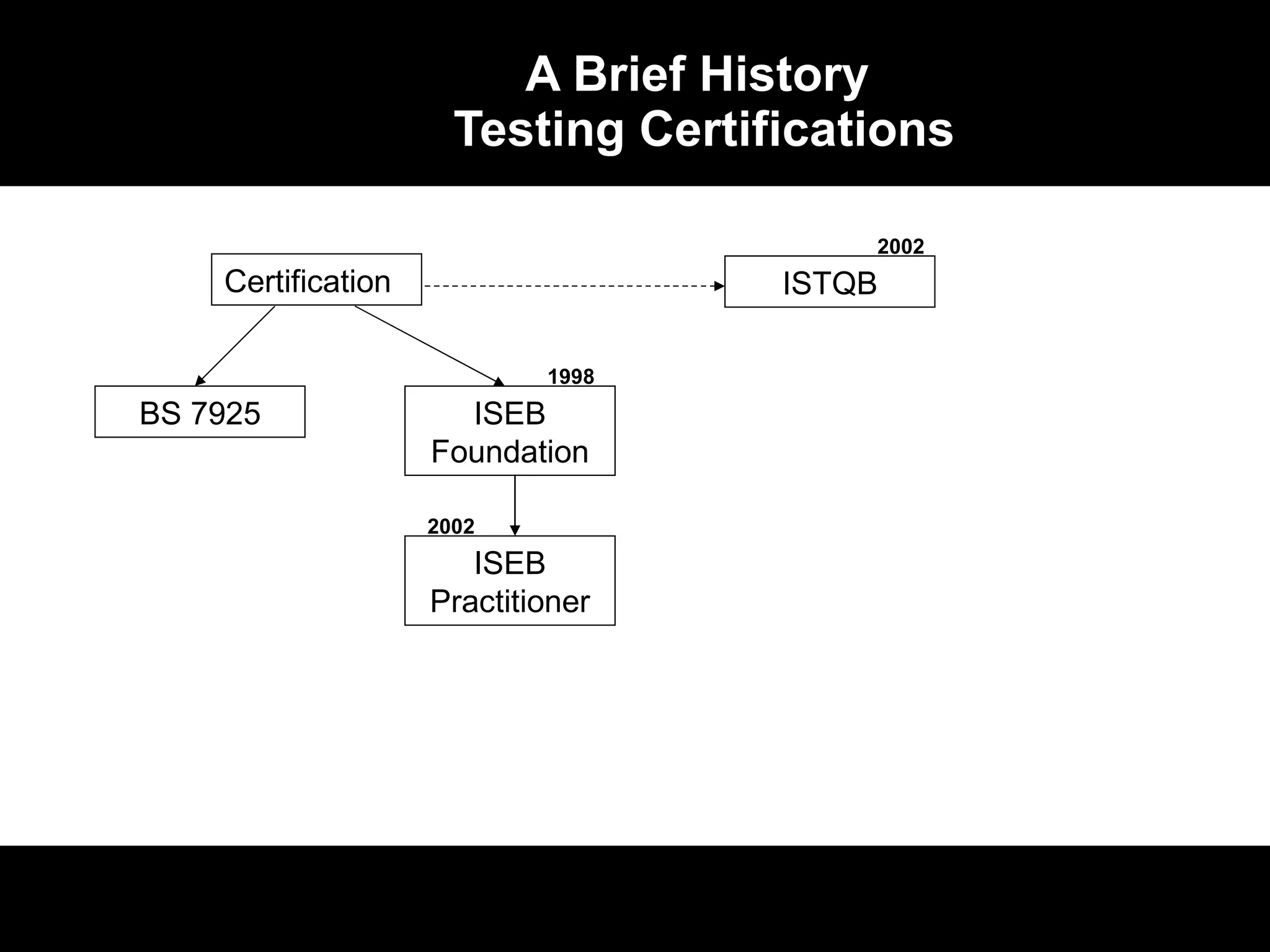
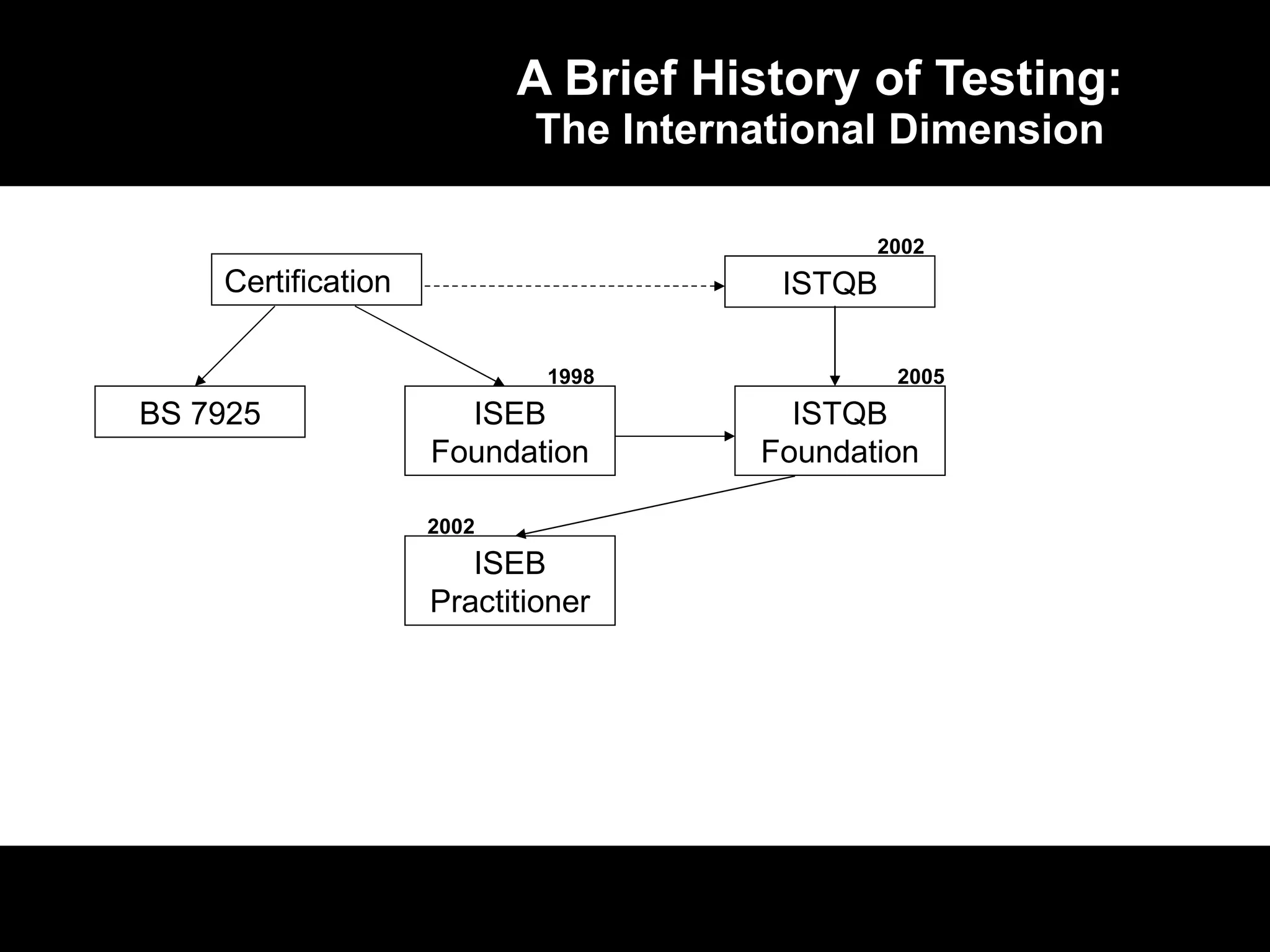
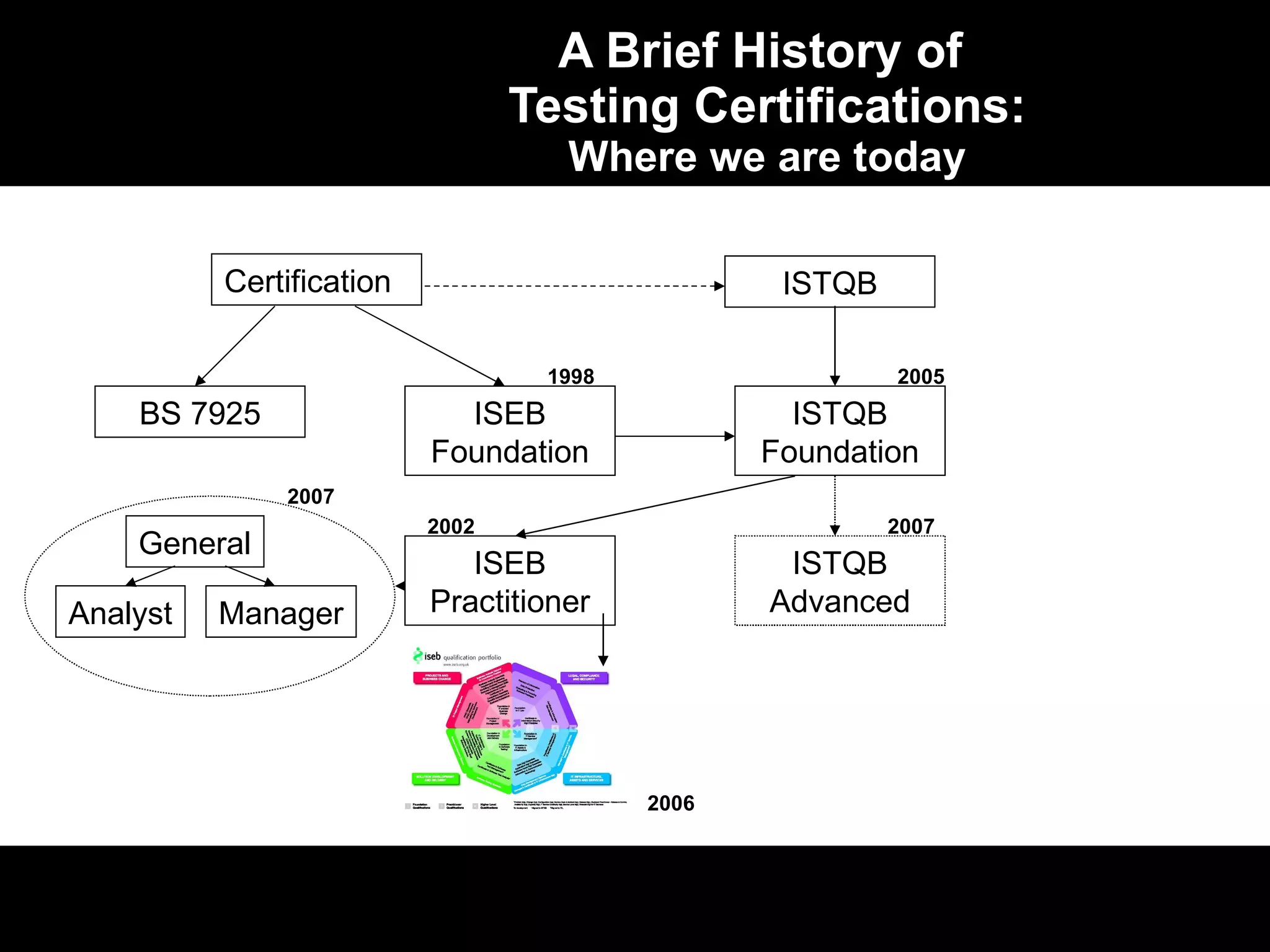
1) The ISTQB/ISEB certification program began in the late 1990s and early 2000s to standardize software testing knowledge and professionalize the field.
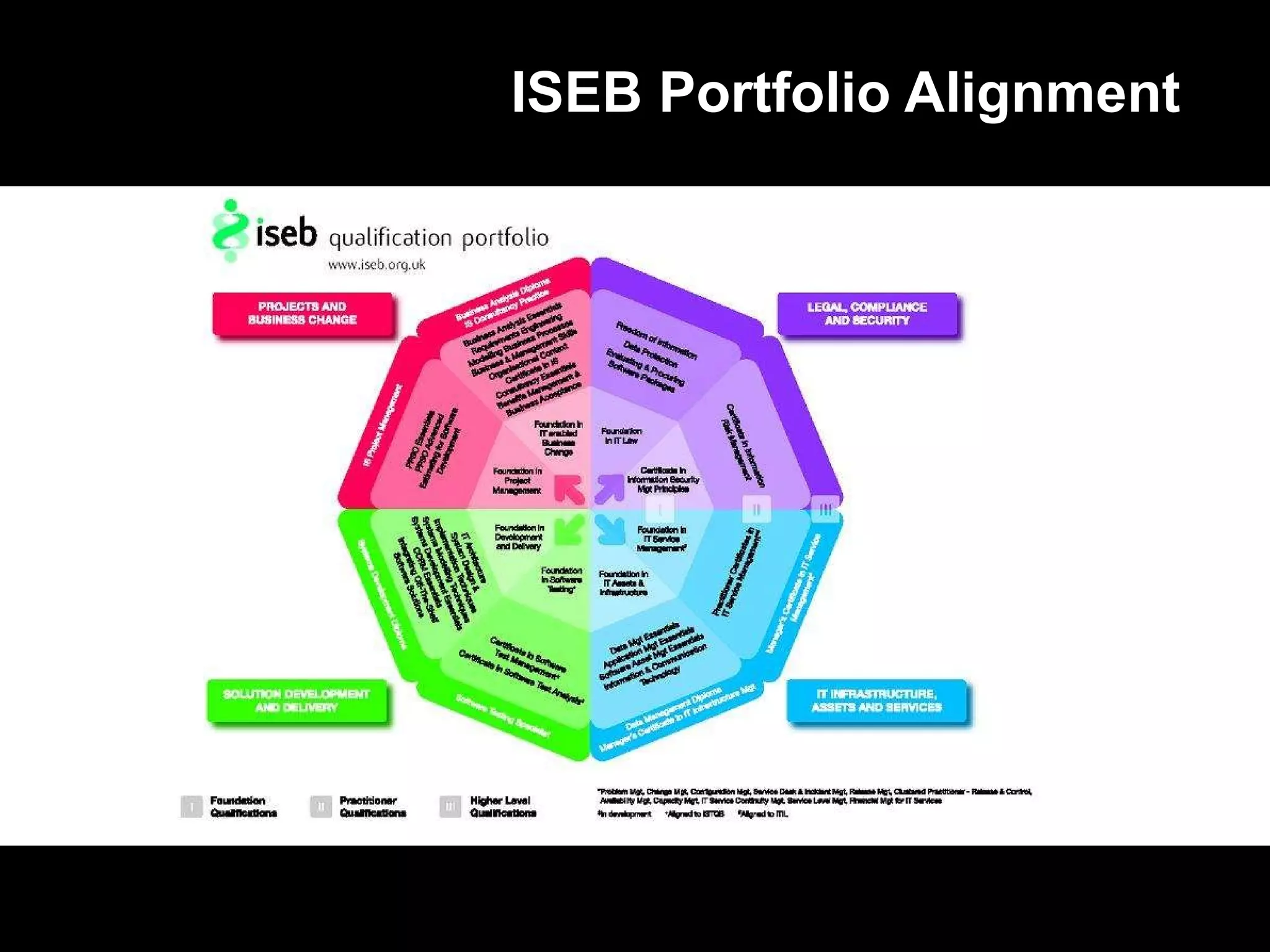
2) The certifications include Foundation, Practitioner, and Specialist levels to cater to candidates with different experience levels.
3) International collaboration through the ISTQB has led to widespread adoption of a common certification syllabus across many countries.