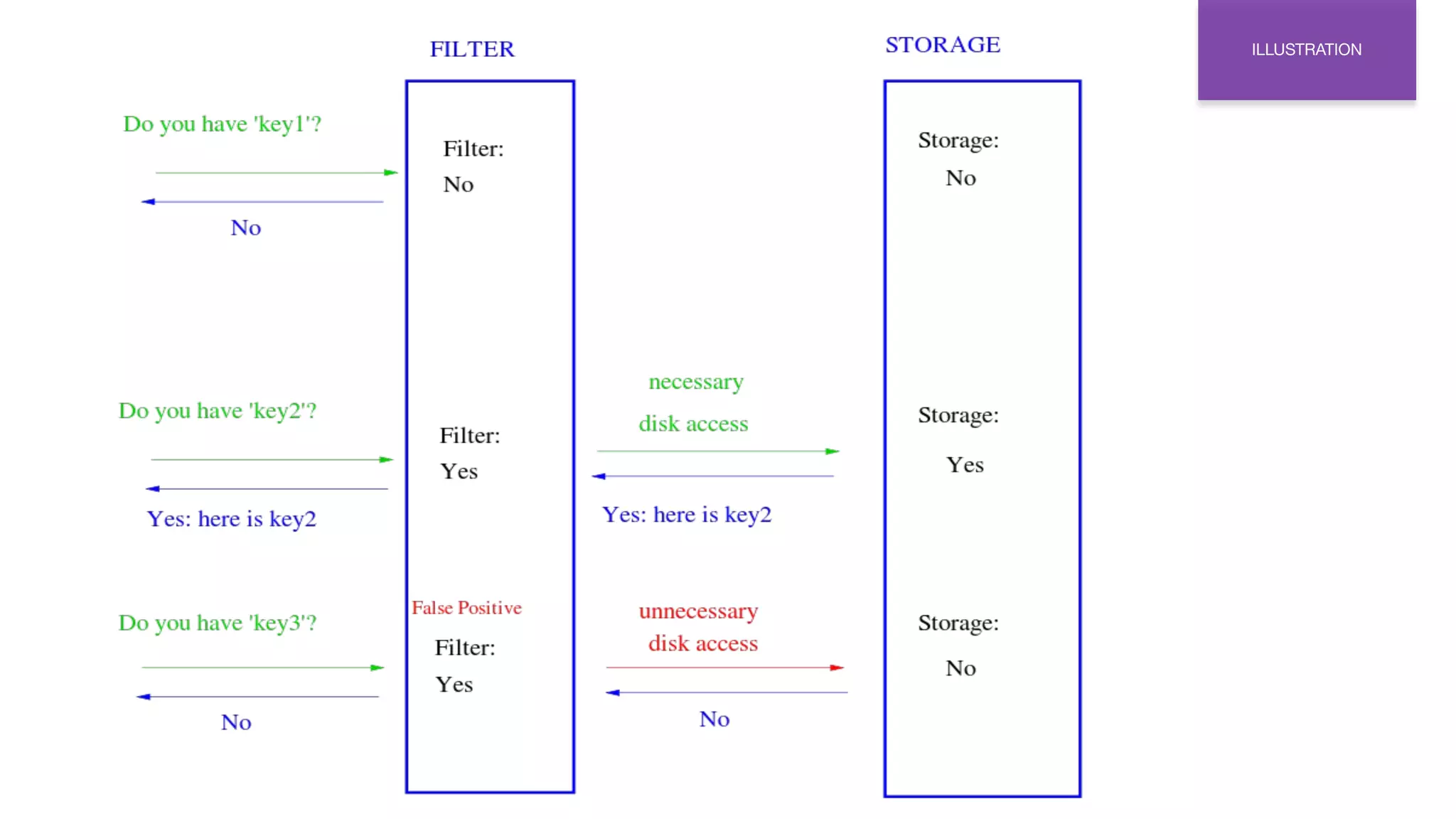
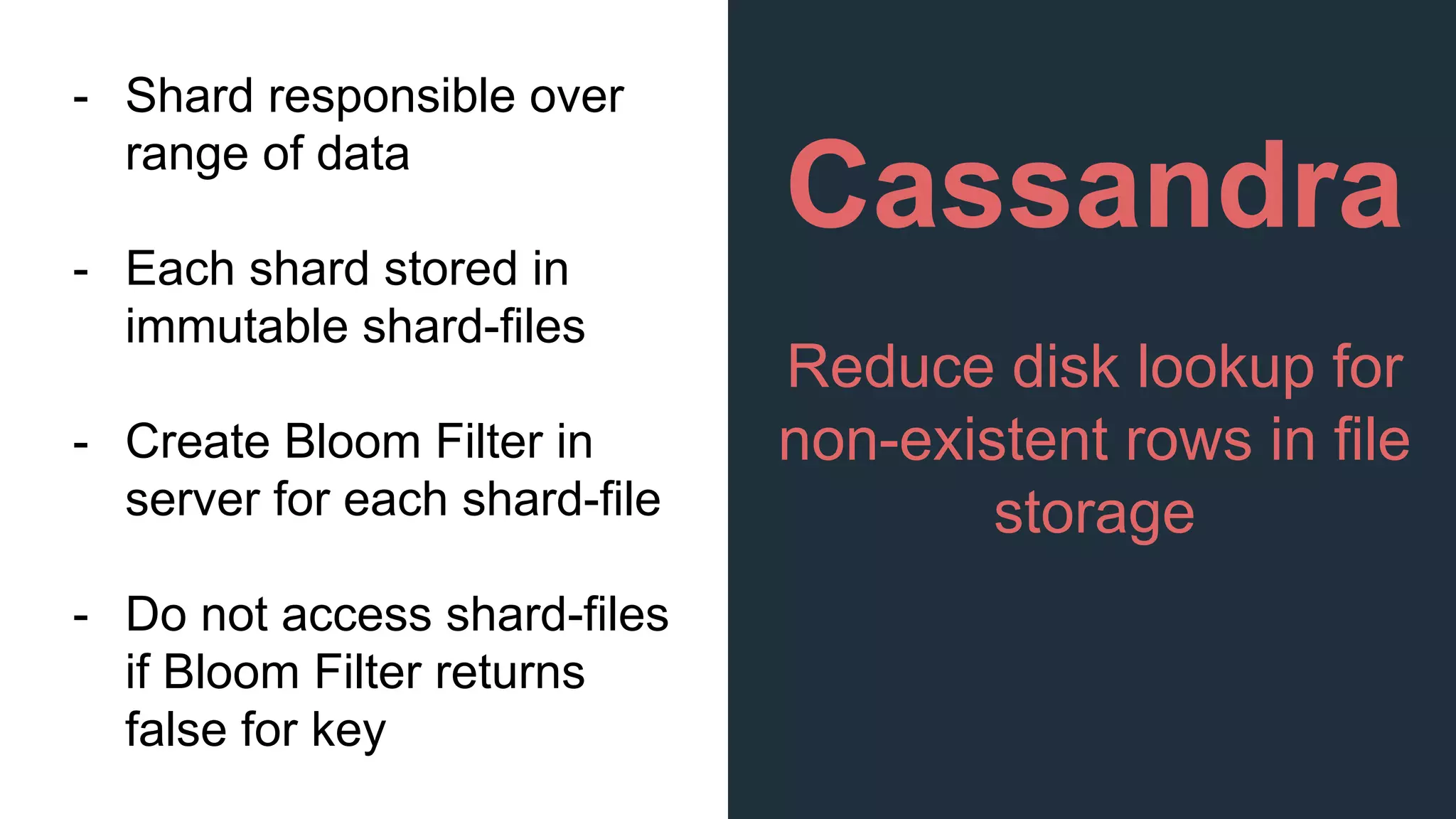
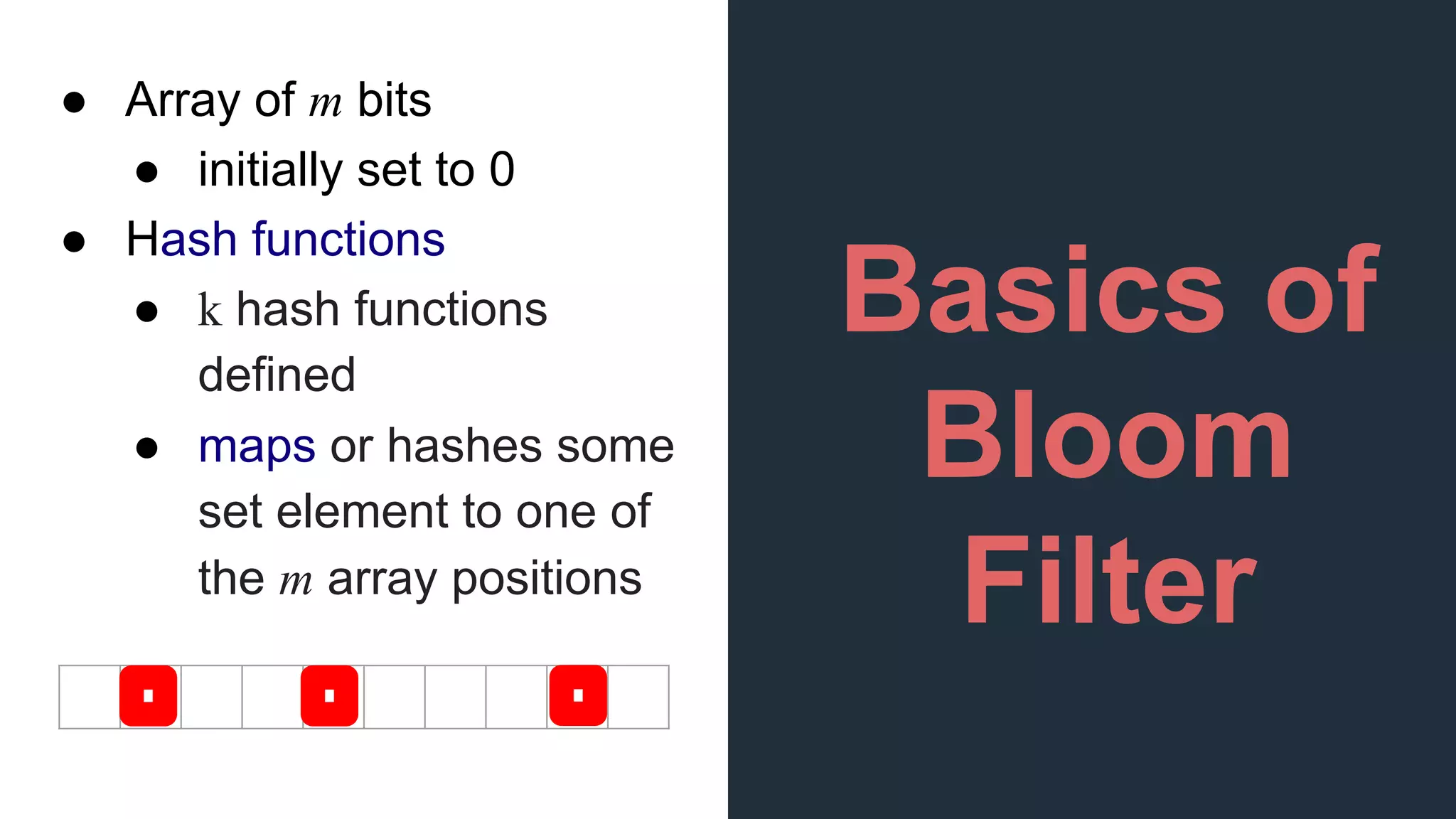
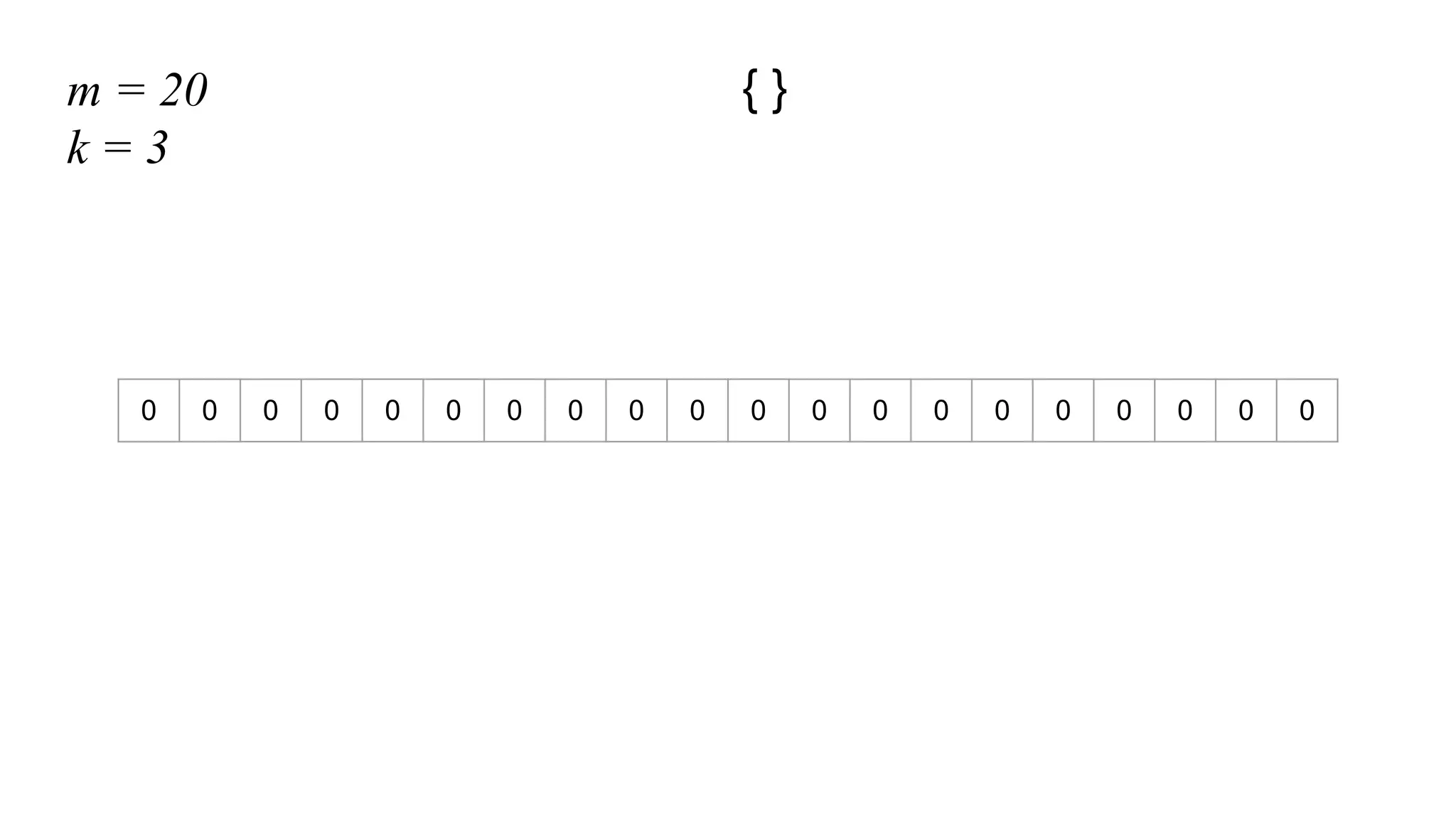
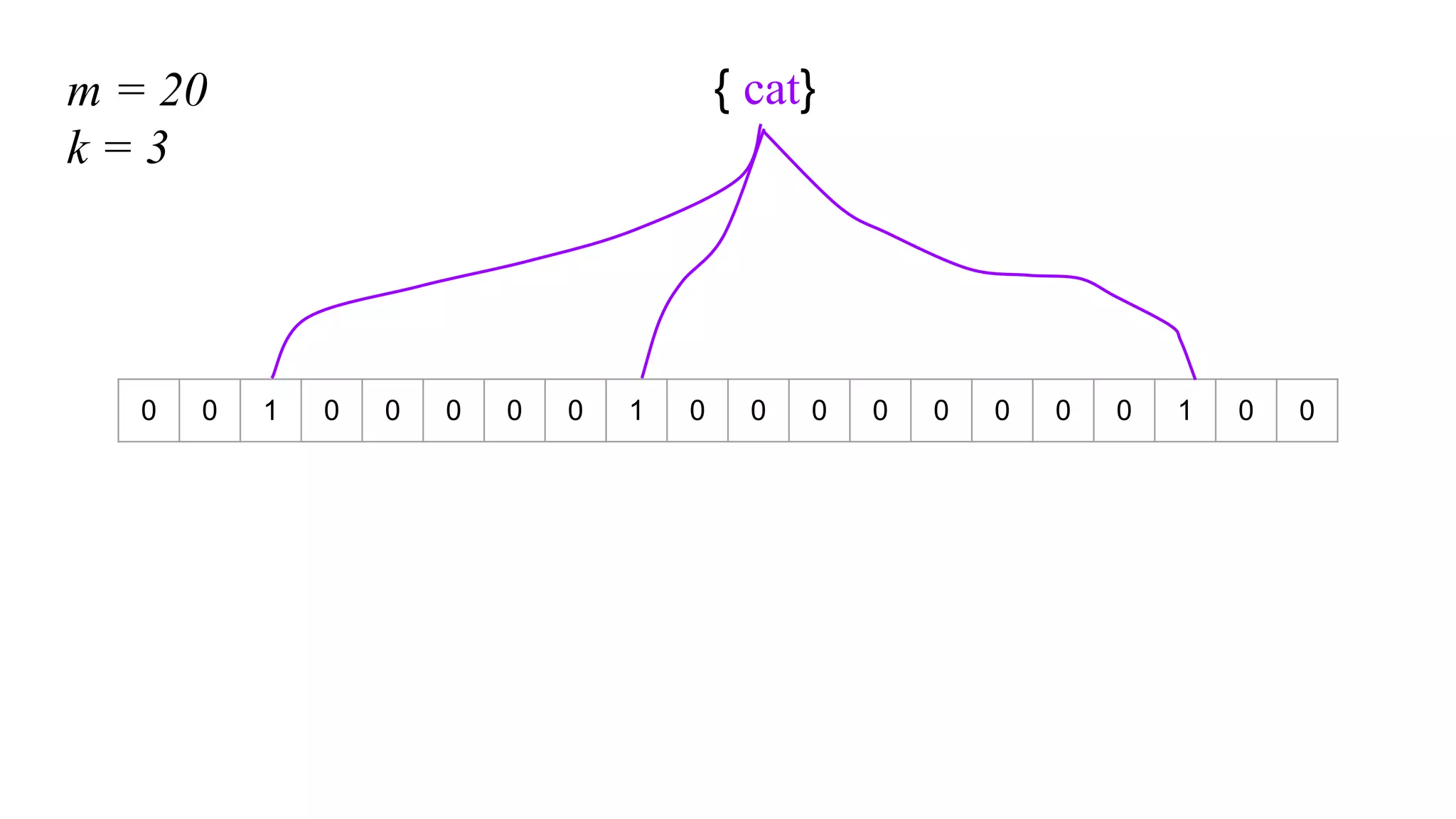
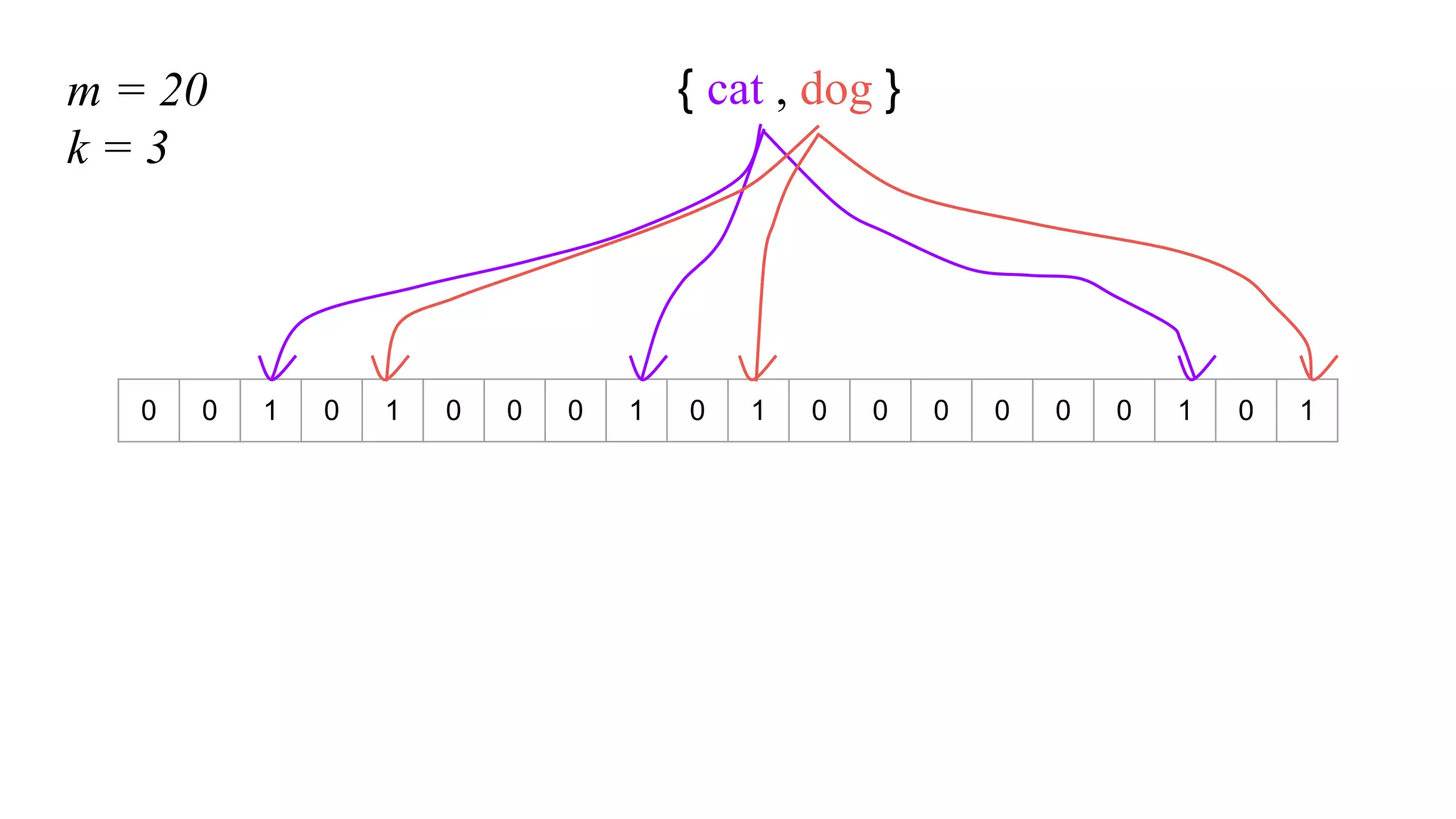
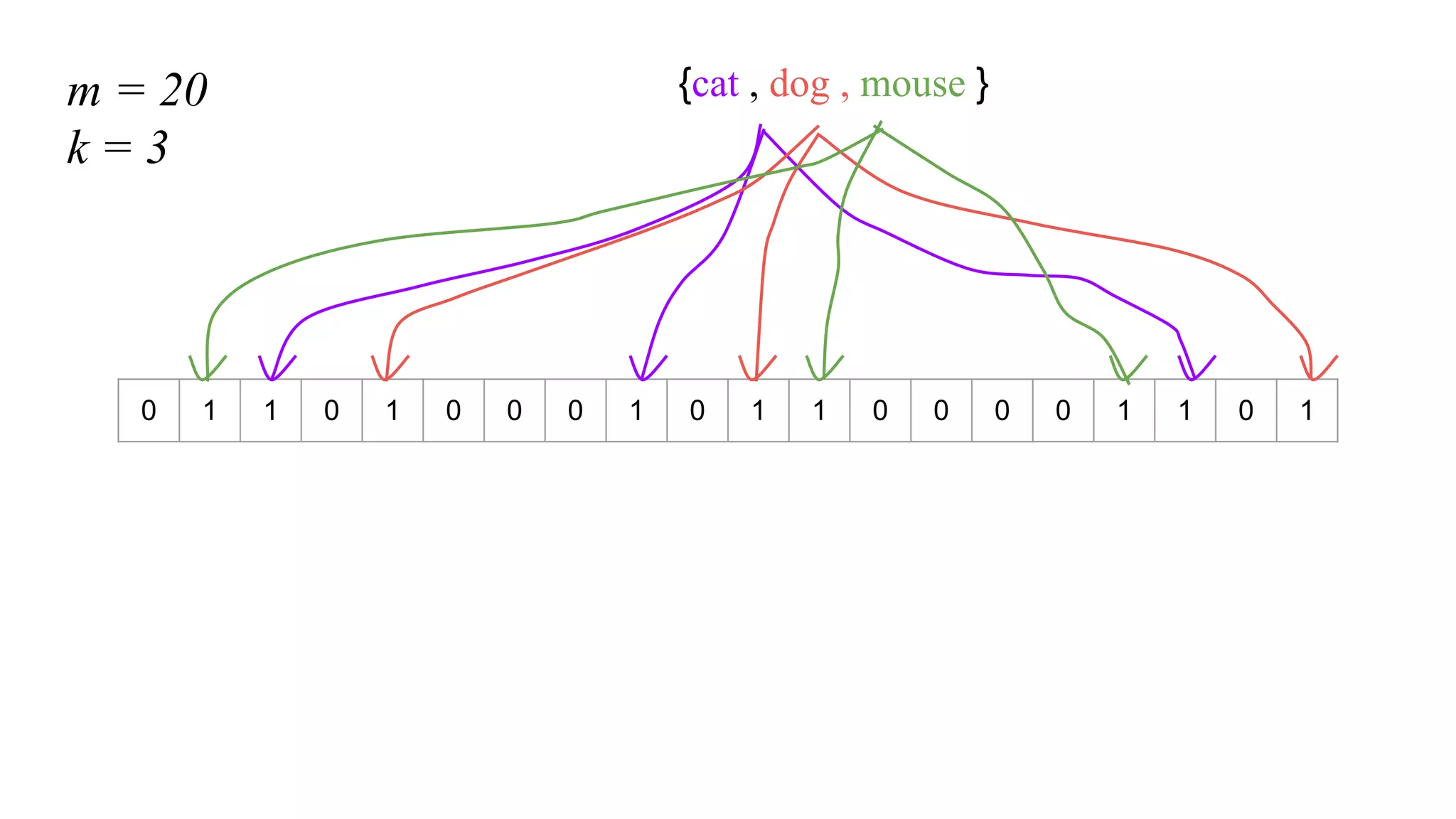
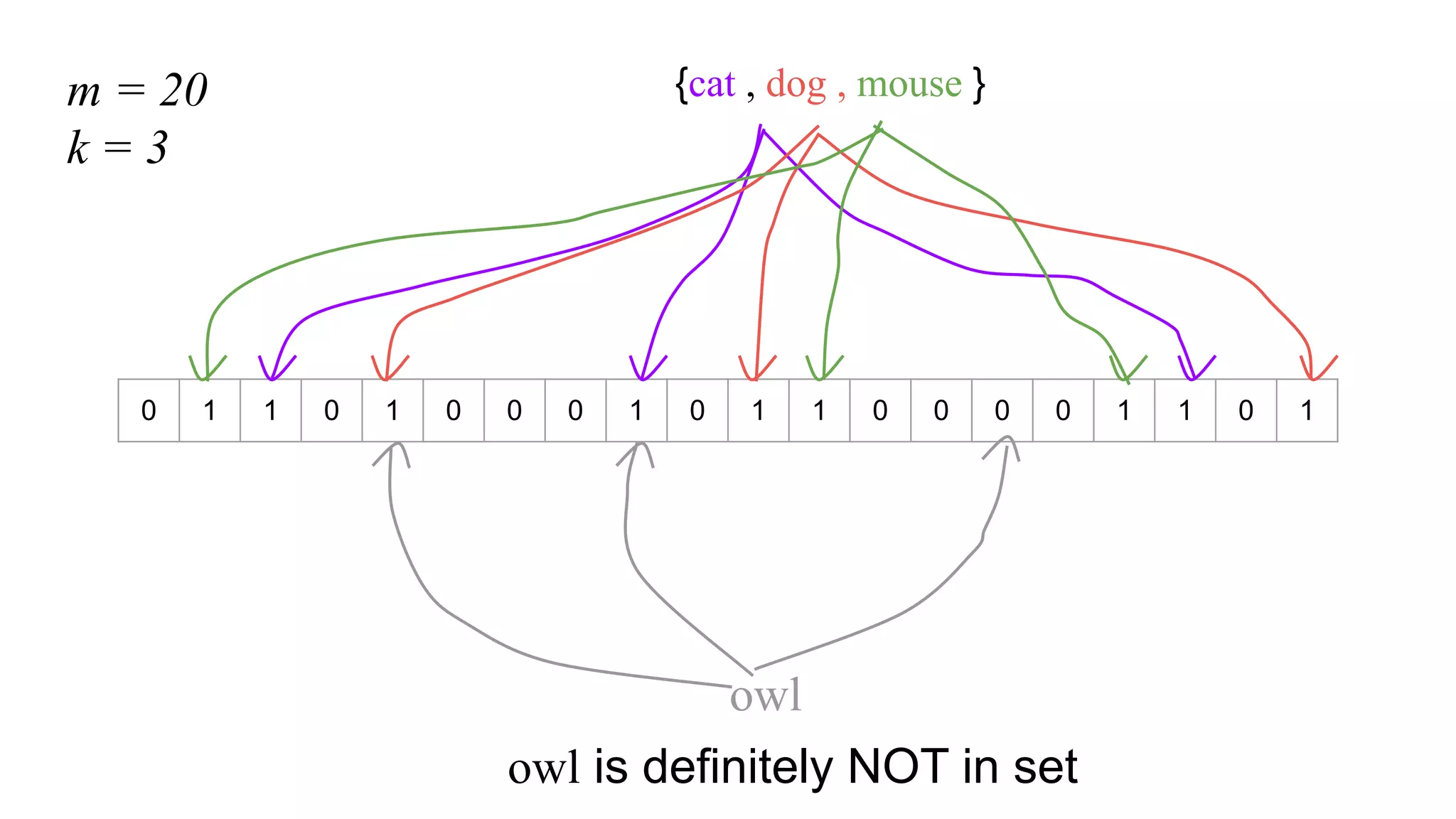
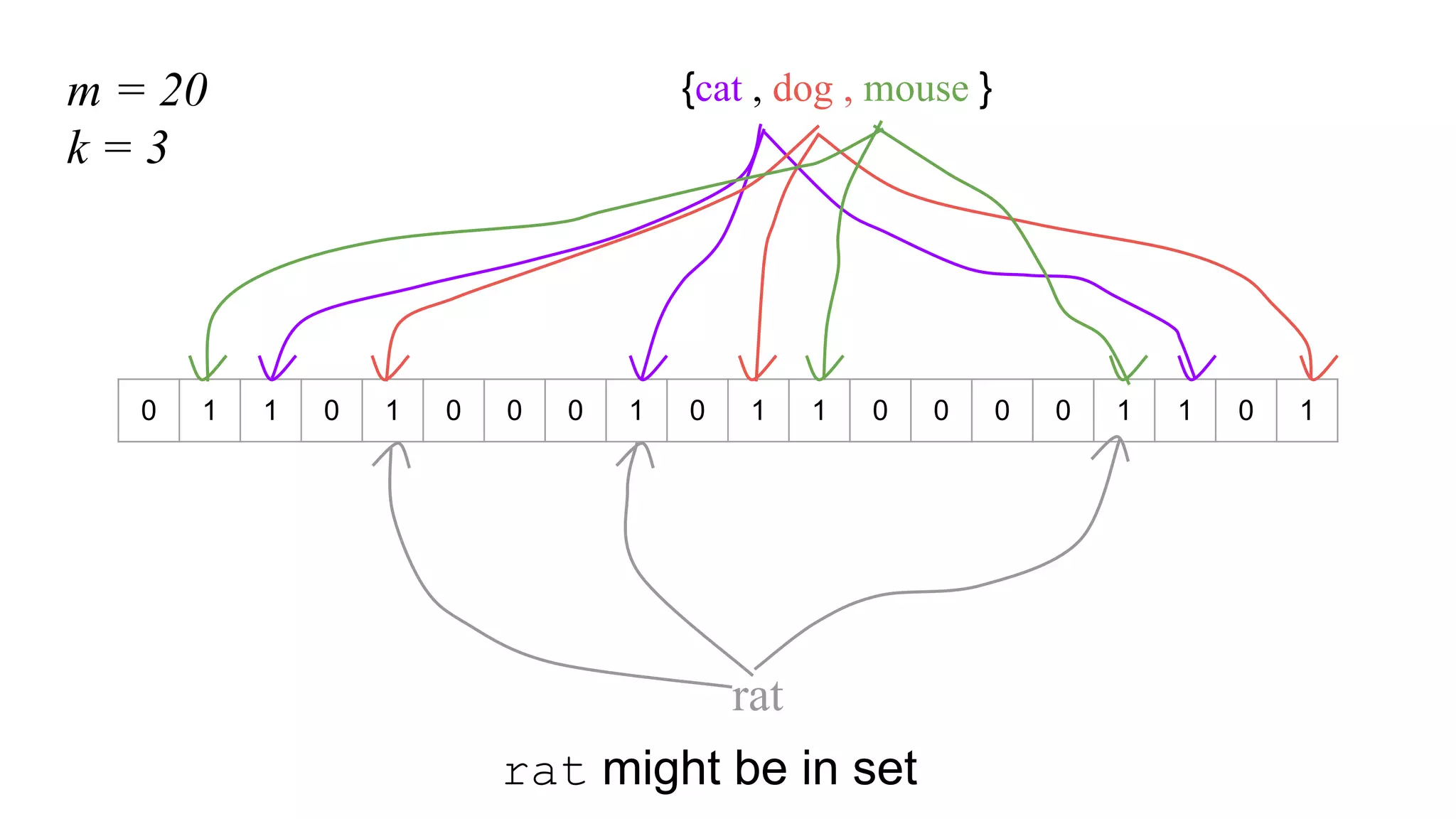
This document provides an overview of Bloom filters, including what they are, why you would want to use one, practical examples of their use, and how they work. Bloom filters are a data structure that can be used to test if an element is present in a set. They have a tiny memory footprint compared to storing the full set, use constant memory, and allow extremely fast lookups. However, they can produce false positives. The document discusses examples of Bloom filters being used by companies like Akamai, Medium, and Cassandra to reduce storage usage and improve performance. It also explains how Bloom filters work under the hood using hash functions and bit arrays.