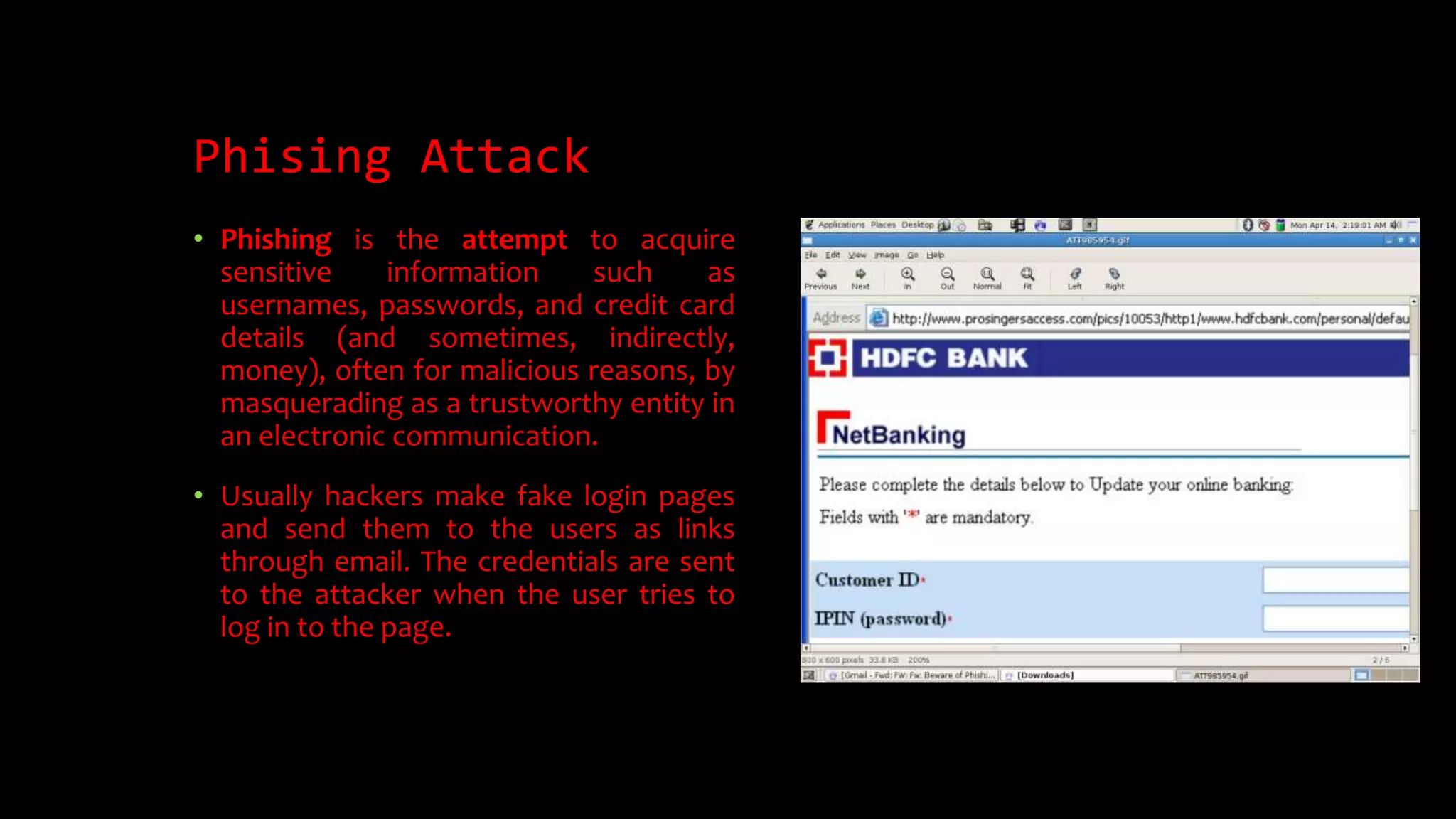
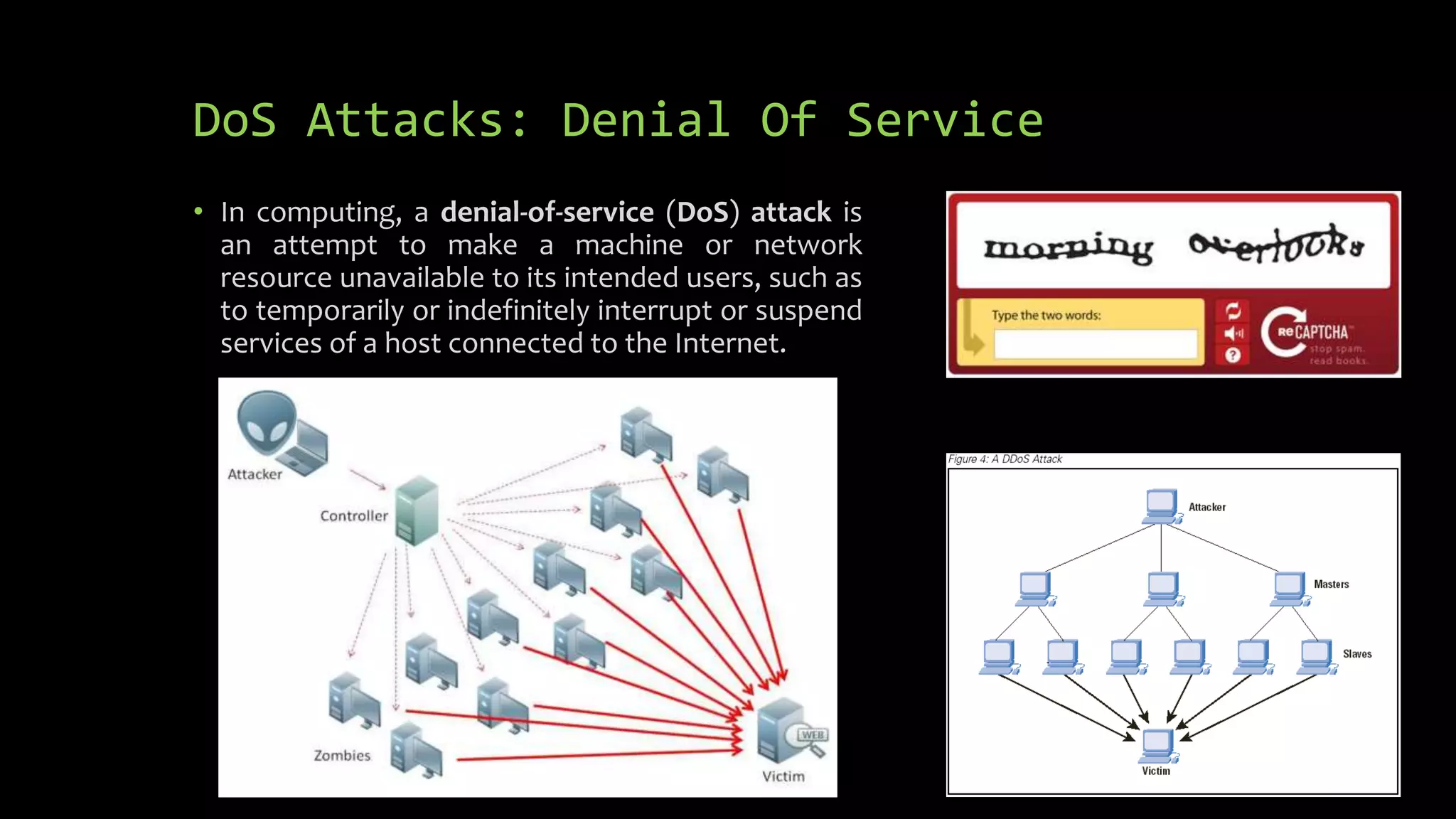
Computer Security: Vulnerabilities and Solutions is a document that discusses computer and internet security. It begins with an introduction to hacking, including the different types of hackers like white hat, black hat, and grey hat hackers. It then discusses common vulnerabilities like viruses, worms, Trojan horses, phishing attacks, and denial of service attacks. The document concludes by providing some common solutions for improving security, such as using antivirus software, firewalls, being cautious of unknown links and apps, and educating yourself on computer security best practices.