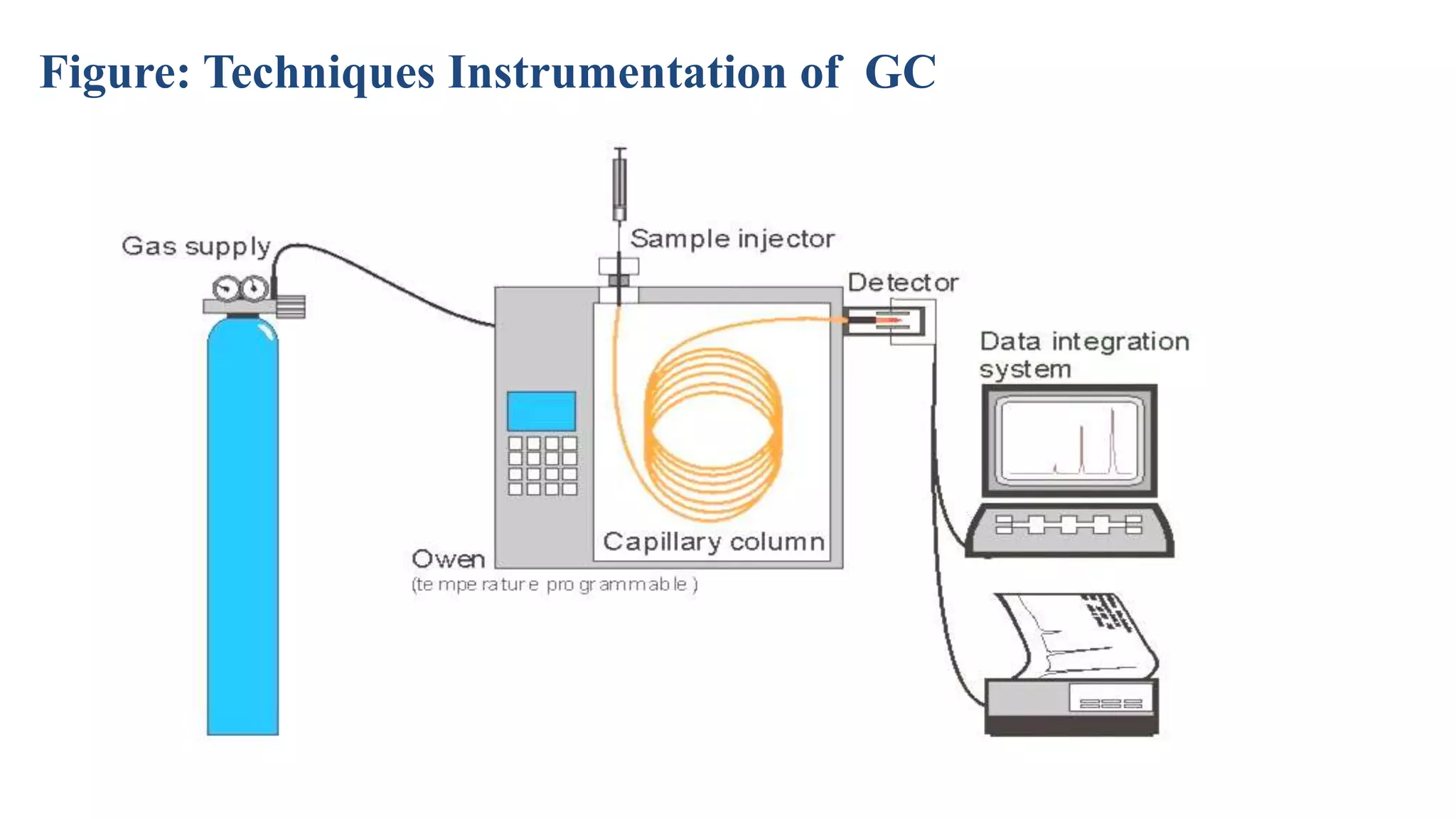
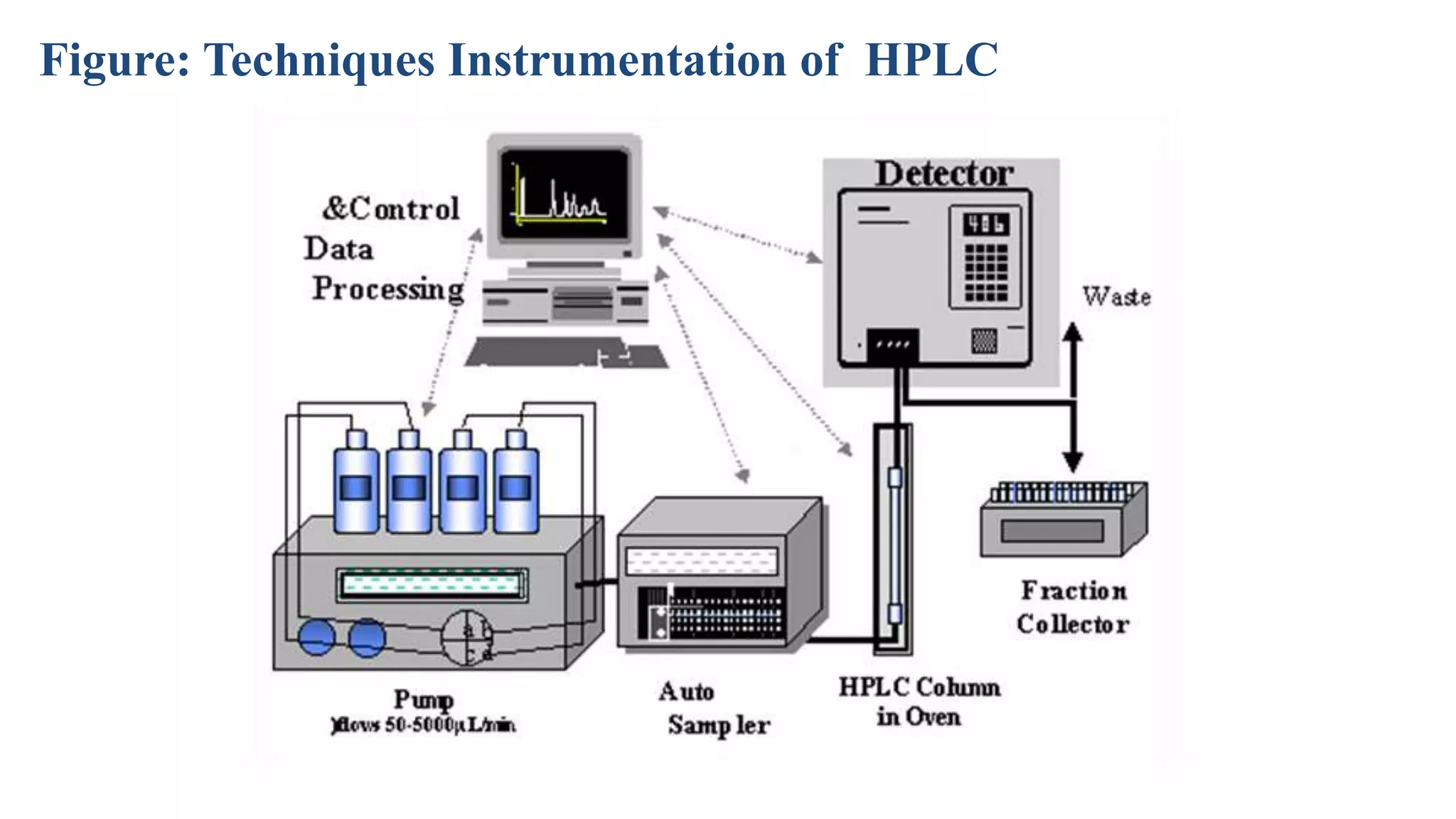
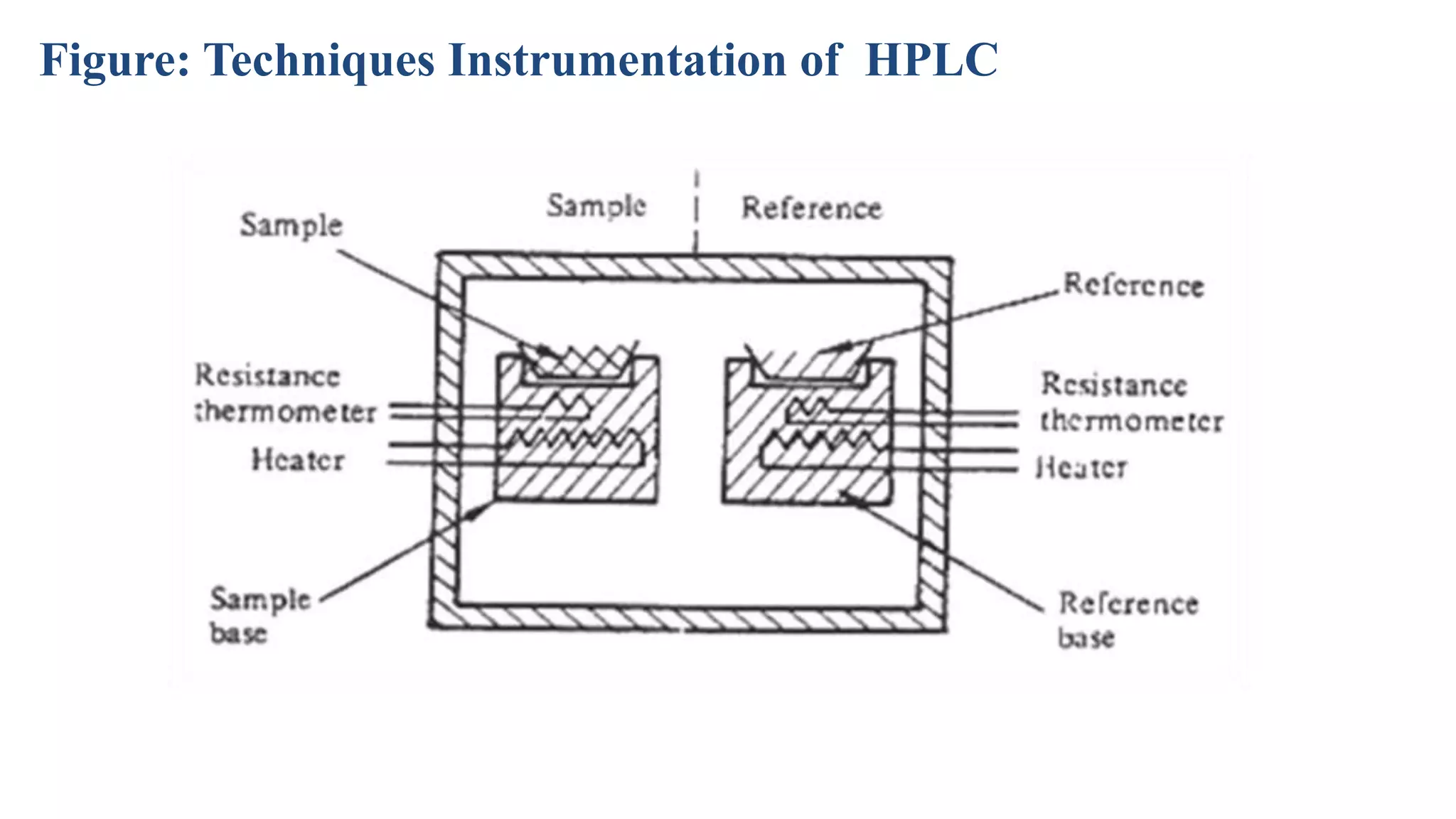
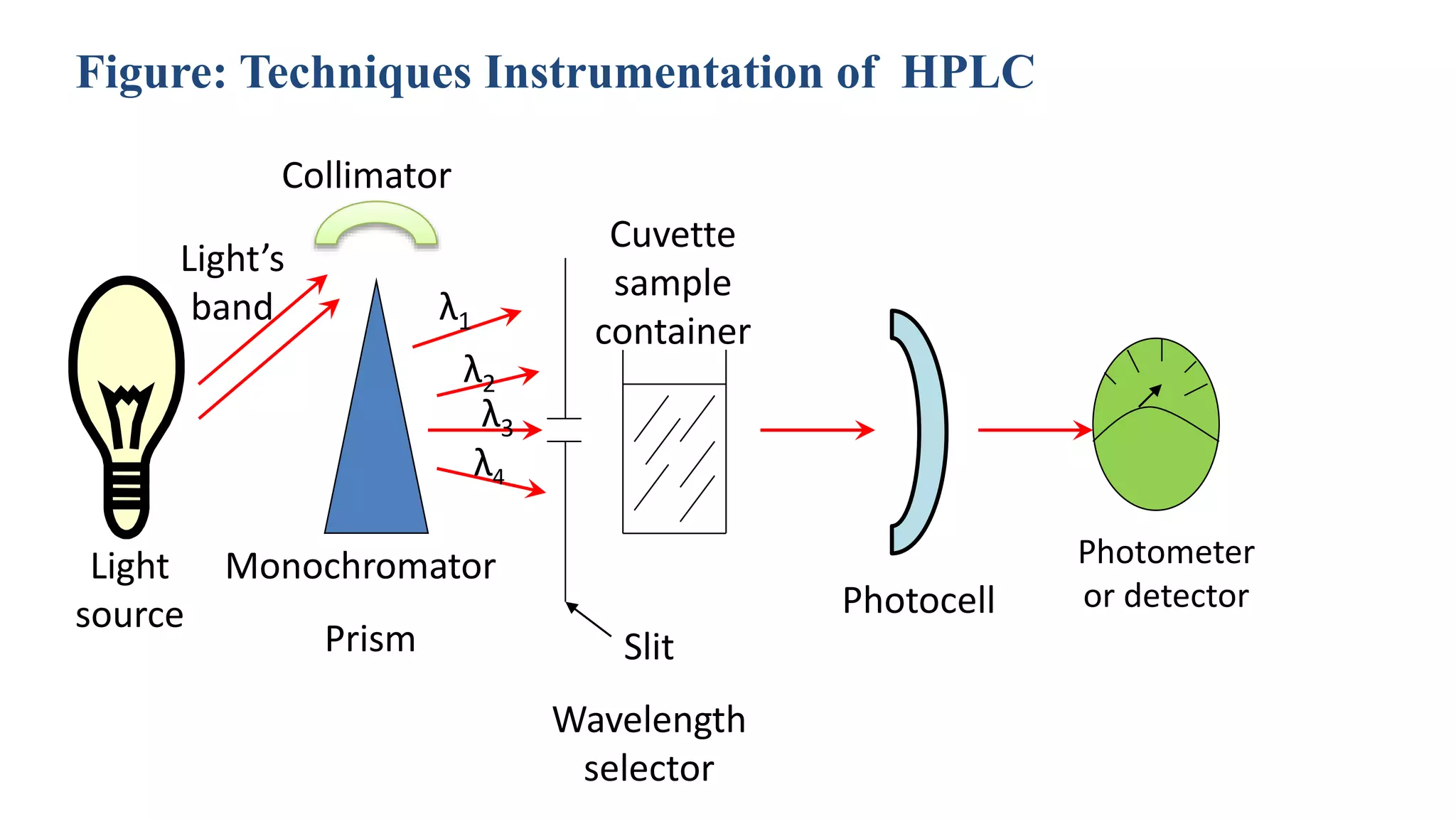
This document discusses four main analytical instrument techniques used in food chemical composition analysis: gas chromatography (GC), high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), differential scanning calorimeter (DSC), and ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer. It provides an overview of each technique, including their aims and uses in food analysis. GC is used to separate and analyze compounds that can be vaporized, HPLC separates mixtures using liquid mobile and stationary phases, DSC measures heat flows during material transitions, and UV-VIS spectrophotometry determines substance identities and concentrations by measuring light absorption.