The document covers Object-Oriented Programming concepts in Java, focusing on inheritance, interfaces, and method overriding. It explains types of inheritance (single, multilevel, hierarchical, multiple, hybrid), the use of the super keyword, and the implementation of interfaces to achieve code reusability and abstraction. Additionally, the document discusses final classes and methods, dynamic method dispatch, and the difference between abstract classes and interfaces.






![10
Examples
class Employee{
float salary=40000;
}
class Programmer extends Employee{
int bonus=10000;
public static void main(String args[]){
Programmer p=new Programmer();
System.out.println("Programmer salary is:"+p.salary);
System.out.println("Bonus of Programmer is:"+p.bonus);
}
}
Programmer is a
Employee
09/18/2024](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-10-2048.jpg)

![12
Java
Inheritance
Types
Single Inheritance
Multilevel Inheritance
Hierarchical Inheritance
Multiple Inheritance
Hybrid Inheritance
• In single-Inheritance, a sub-class is derived
from only one super class
class One{
public void One_display() {
System.out.println(“Paavai Engineering College”); }
}
class Two extends One{
public void Two_display() {
System.out.println(“Department of CSE(IoT)”); }
}
public Class Main{
public Static void main(String args[]){
Two t=new Two();
t.One_display();
t.Two_display(); }}
09/18/2024](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-12-2048.jpg)
![13
Java
Inheritance
Types
Single Inheritance
Multilevel Inheritance
Hierarchical Inheritance
Multiple Inheritance
Hybrid Inheritance
• In Multilevel Inheritance, a derived class of a
base class can derive a sub class. (Chain of Inheritance).
class One{
public void One_display() {
System.out.println(“Paavai Engineering College”); } }
class Two extends One{
public void Two_display() {
System.out.println(“Department of CSE(IoT)”); } }
class Three extends Two{
public void Three_display() {
System.out.println(“2023 – 2027 Batch”); } }
Public Class Main{
public Static void main(String args[]){
Three t=new Three();
t.One_display();
t.Two_display();
t.Three_display(); }}
09/18/2024](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-13-2048.jpg)
![14
Java
Inheritance
Types
Single Inheritance
Multilevel Inheritance
Hierarchical Inheritance
Multiple Inheritance
Hybrid Inheritance
• In Hierarchical Inheritance, a super class derives
more than one class.
class One{
public void One_display() {
System.out.println(“Paavai Engineering College”); } }
class Two extends One{
public void Two_display() {
System.out.println(“Department of CSE(IoT)”); } }
class Three extends One{
public void Three_display() {
System.out.println(“Department of AI-ML”); } }
Public Class Main{
public Static void main(String args[]){
Two t=new Two();
t.One_display(); t.Two_display();
Three r=new Three();
r.One_display(); r.Three_display(); }}
09/18/2024](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-14-2048.jpg)
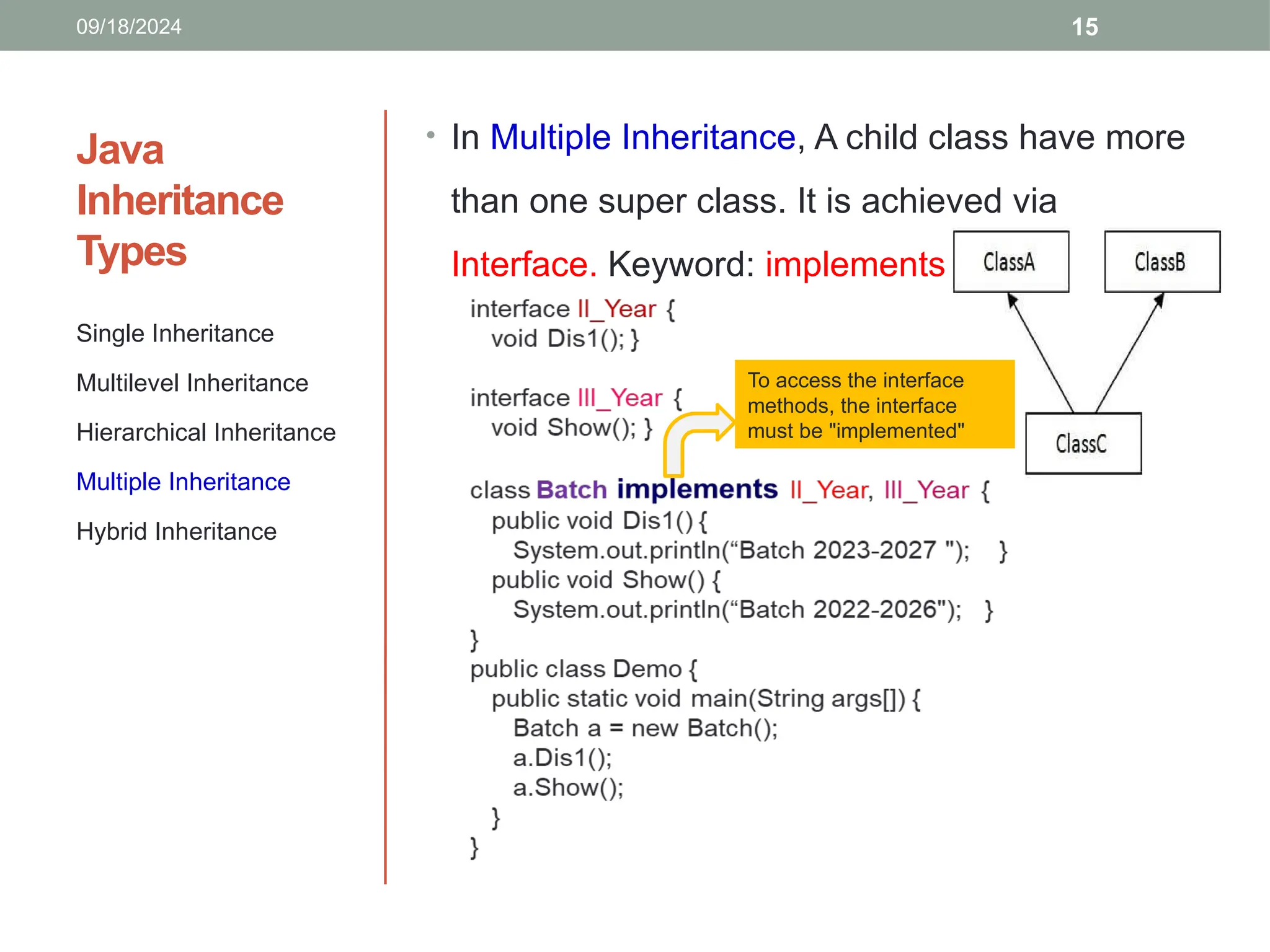
![16
Java
Inheritance
Types
Single Inheritance
Multilevel Inheritance
Hierarchical Inheritance
Multiple Inheritance
Hybrid Inheritance
• In Hybrid Inheritance, composition of two or
more types of inheritance.
class C {
public void disp() {
System.out.println("C"); } }
class A extends C {
public void disp() {
System.out.println("A"); } }
class B extends C {
public void disp() {
System.out.println("B"); } }
public class D extends A {
public void disp() {
System.out.println("D"); }
public static void main(String args[]) {
D obj = new D();
obj.disp(); } }
Hierarchical and Single Inheritance
09/18/2024
Class C
Class A Class B
Class D
• Single and Multiple Inheritance (not
supported but can be achieved
through interface)
• Multilevel and Hierarchical Inheritance
• Hierarchical and Single Inheritance
• Multiple and Multilevel Inheritance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-16-2048.jpg)



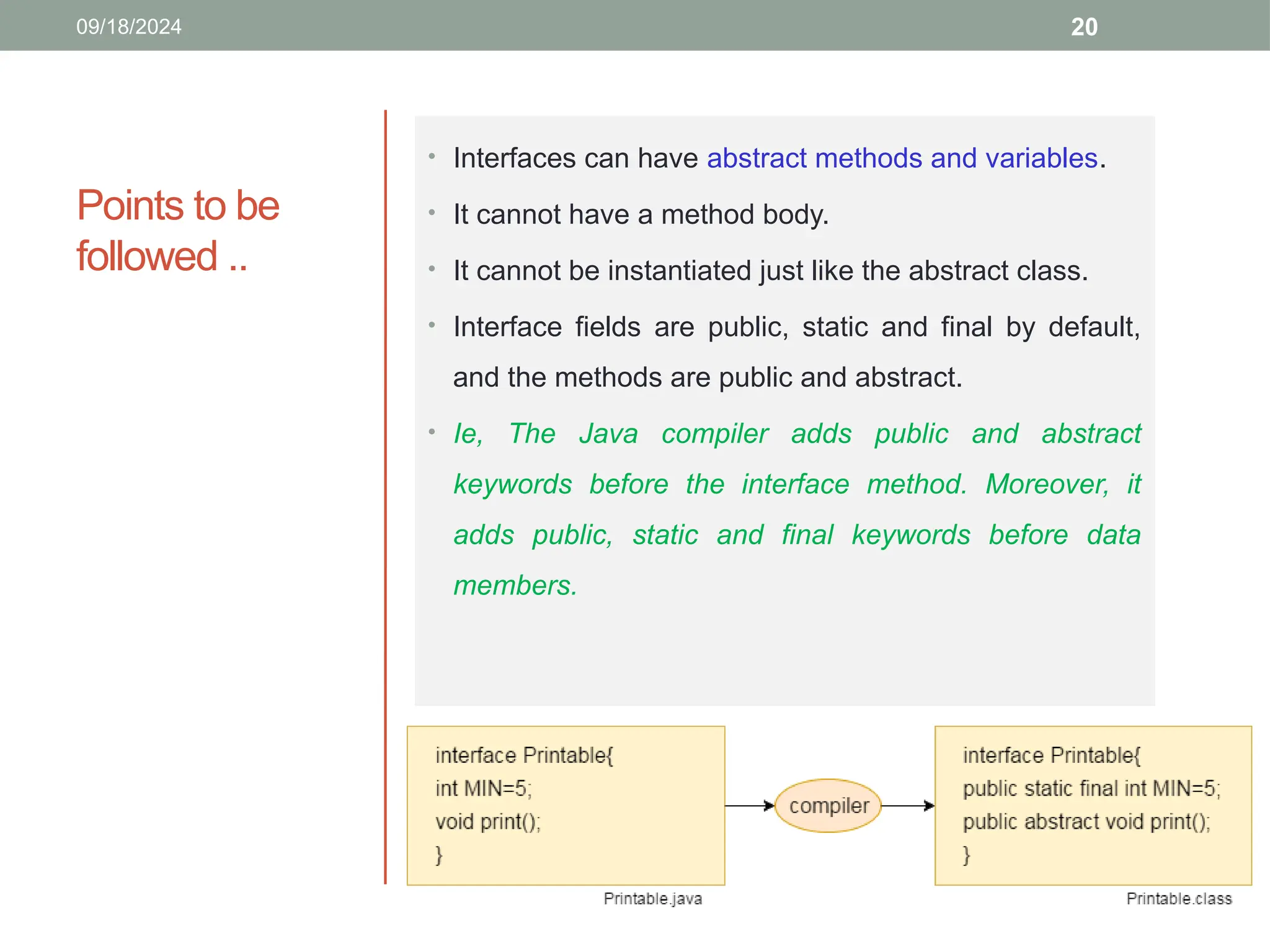
![21
Possible Java
Interfaces
Example
09/18/2024
interface printable{
void print();
}
class A6 implements printable{
public void print()
{System.out.println("Hello");}
public static void main(String args[]){
A6 obj = new A6();
obj.print();
}
}
the Printable interface
has only one method,
and its implementation is
provided in the A6 class.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-21-2048.jpg)
![22
An interface Examcell is
implemented at IoT
class
09/18/2024
interface Examcell {
public void internal(); // interface method (does not have a body)
public void CIA1(); // interface method (does not have a body)
}
// IoT "implements" the ExamCell interface
class IoT implements ExamCell {
public void internal() {
// The body of internal() is provided here
System.out.println(“This is Internal Test Assessment"); }
public void CIA1() {
// The body of CIA1 is provided here
System.out.println(“CIA 1"); }
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IoT s = new IoT(); // Create a Pig object
s.internal();
s.CIA1();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-22-2048.jpg)

![24
Scenario 2
09/18/2024
the Bank interface has
only one method. Its
implementation is
provided by SBI and IOB
classes.
interface Bank{
float rateOfInterest();
}
class SBI implements Bank{
public float rateOfInterest(){return 9.15f;}
}
class PNB implements Bank{
public float rateOfInterest(){return 9.7f;}
}
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Bank b=new SBI();
System.out.println("ROI: "+b.rateOfInterest());
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-24-2048.jpg)
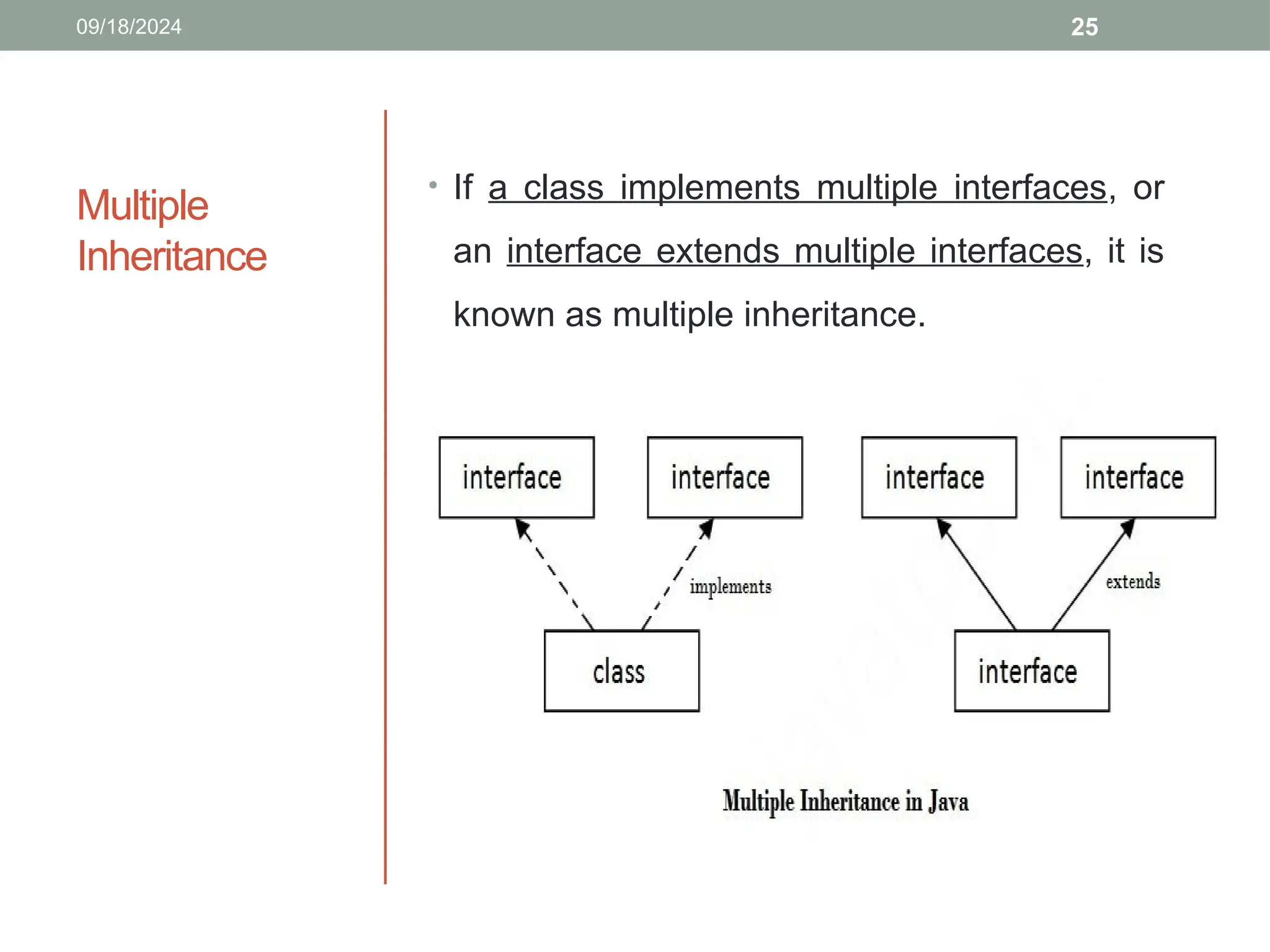
![26
Example,
interface Printable{
void print(); }
interface Showable{
void show(); }
class A7 implements Printable,Showable{
public void print(){System.out.println("Hello");}
public void show(){System.out.println("Welcome");}
public static void main(String args[]){
A7 obj = new A7();
obj.print();
obj.show(); } }
09/18/2024](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-26-2048.jpg)
![27
Interface
Inheritance
interface Printable{
void print(); }
interface Showable extends Printable{
void show(); }
class TestInterface4 implements Showable{
public void print(){System.out.println("Hello");}
public void show(){System.out.println("Welcome");}
public static void main(String args[]){
TestInterface4 obj = new TestInterface4();
obj.print();
obj.show(); } }
A class implements
an interface, but
one interface
extends another
interface.
09/18/2024](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-27-2048.jpg)
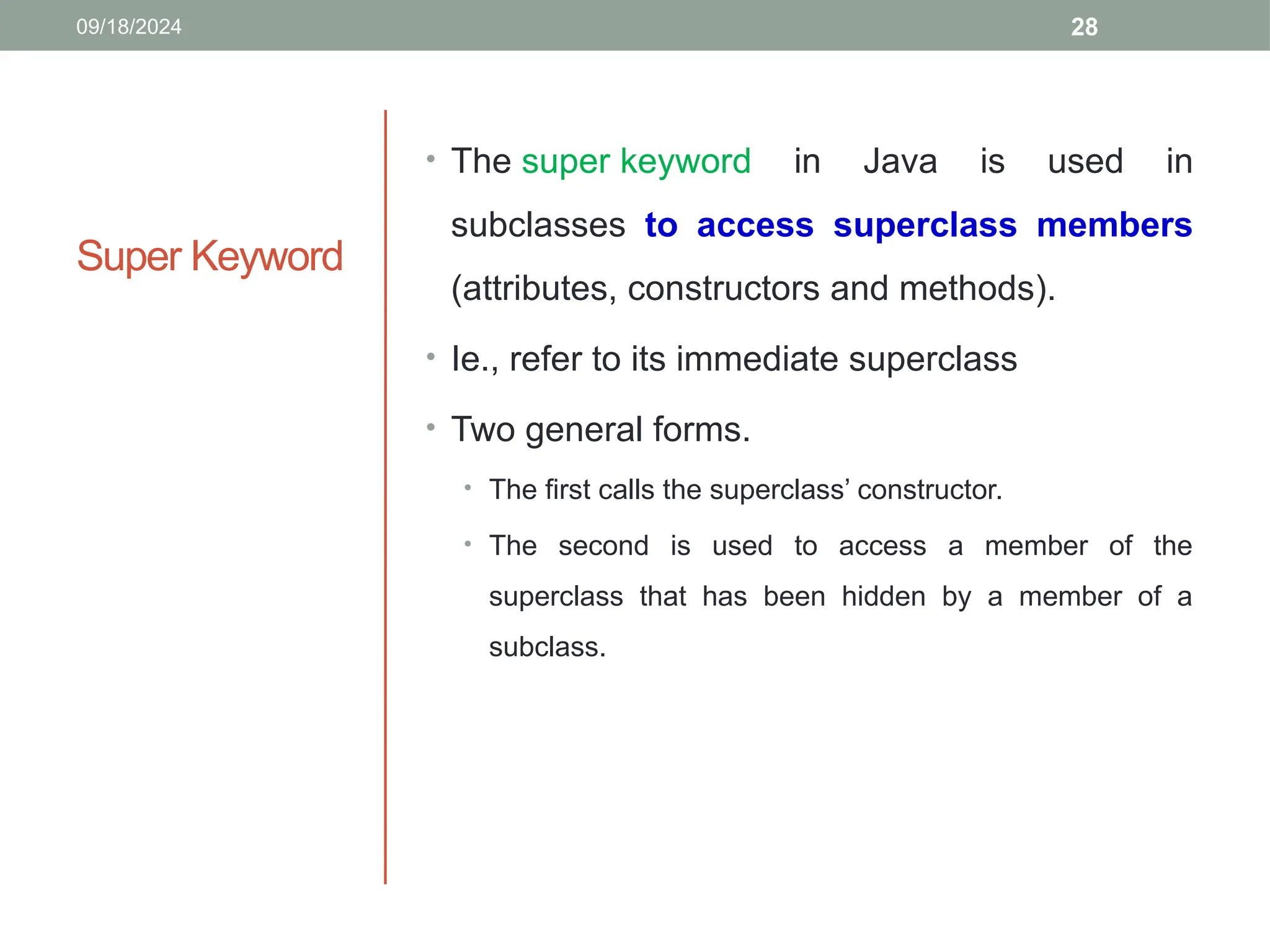

![30
Accessing
Parent Class
Fields
class Animal
{
String name = "Animal"; }
class Dog extends Animal
{
String name = "Dog";
void printNames()
{
System.out.println("Name in Dog class: " + name);
System.out.println("Name in Animal class: " + super.name); } }
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Dog dog = new Dog(); dog.printNames();
} }
To access a field
from the parent class
when it is hidden by a
field with the same
name in the child
class.
09/18/2024](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-30-2048.jpg)
![31
Parent
Methods
access
class Animal
{
void makeSound()
{ System.out.println("Animal makes a sound."); } }
class Dog extends Animal
{
void makeSound()
{
super.makeSound();
System.out.println("Dog barks."); } }
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Dog dog = new Dog(); dog.makeSound();
}
}
09/18/2024](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-31-2048.jpg)
![32
Accessing
Parent Class
Constructor
To explicitly call a
constructor of the parent
class from the child
class constructor.
09/18/2024
class Person{
int id;
String name;
Person(int id,String name){
this.id=id;
this.name=name; } }
class Emp extends Person{
float salary;
Emp(int id,String name,float salary){
super(id,name);//reusing parent constructor
this.salary=salary; }
void display(){System.out.println(id+" "+name+" "+salary);} }
class TestSuper5{
public static void main(String[] args){
Emp e1=new Emp(1,"ankit",45000f);
e1.display();
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-32-2048.jpg)
![33
Calling Parent
Class Methods
from Overridden
Methods
class Base
{
void display() {
System.out.println("Display method in Base"); } }
class Derived extends Base {
void display() {
super.display(); // Calls the display method of Base class
System.out.println("Display method in Derived"); } }
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Derived obj = new Derived();
obj.display(); } }
To invoke the original
implementation of a
method in the parent
class when it is
overridden in the child
class.
09/18/2024](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-33-2048.jpg)

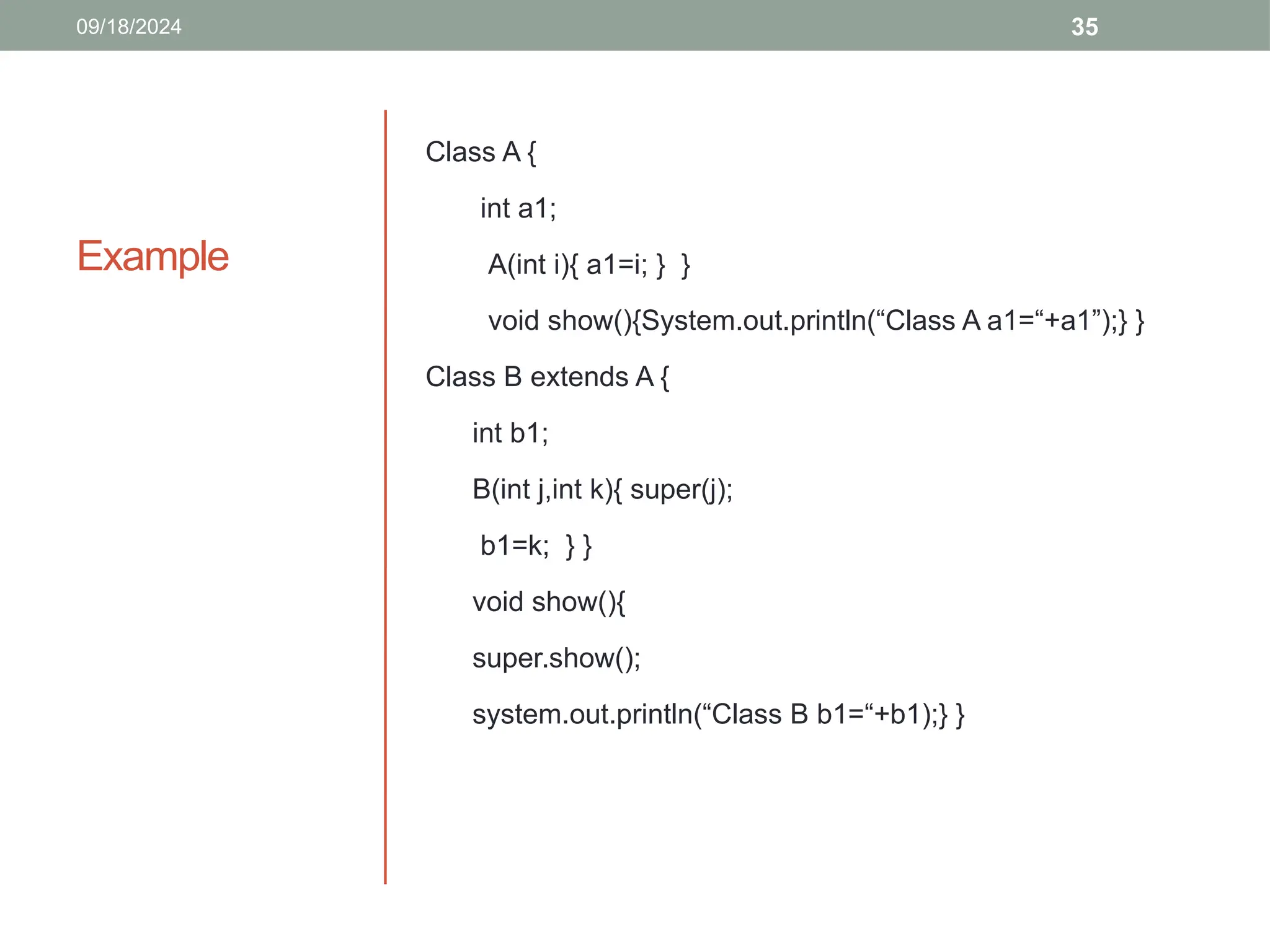




![41
09/18/2024
abstract class Animal {
public abstract void animalSound();
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("Zzz"); } }
class Pig extends Animal {
public void animalSound() {
System.out.println("The pig says: wee wee"); } }
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pig myPig = new Pig();
myPig.animalSound();
myPig.sleep(); } }
// Abstract class
// Abstract method (does not have a body)
// Regular method
// Subclass (inherit from Animal)
// The body of animalSound() is provided here
// Create a Pig object](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-41-2048.jpg)
![42
Final
Set a variable to final, to
prevent it from being
overridden/modified.
09/18/2024
public class Main {
final int x = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main myObj = new Main();
myObj.x = 25;
System.out.println(myObj.x);
}
}
// will generate an error: cannot assign a
value to a final variable
• The final keyword in java is used to restrict the user.
• The java final keyword can be used in many context.
Final can be:
• variable
• method
• class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-42-2048.jpg)
![43
09/18/2024
If you make any
method as final,
you cannot
override it.
class Bike{
final void run(){System.out.println("running");}
}
class Honda extends Bike{
void run()
{System.out.println("running safely with 100kmph");}
public static void main(String args[]){
Honda honda= new Honda();
honda.run();
}
}
Output: Compile Time Error](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-43-2048.jpg)
![44
If you make any
class as final, you
cannot extend it.
09/18/2024
final class Bike{}
class Honda1 extends Bike{
void run(){System.out.println("running safely with 100kmph");}
public static void main(String args[]){
Honda1 honda= new Honda1();
honda.run();
}
}
Output: Compile Time Error](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-44-2048.jpg)

![46
09/18/2024
import java.util.Scanner;
class MyClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner myObj = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter username");
String userName = myObj.nextLine();
System.out.println("Username is: " + userName);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-46-2048.jpg)
![47
User-defined
Packages
To create a package,
use
the package keyword
09/18/2024
package mypack;
public class ClassOne {
public void methodClassOne() {
System.out.println("Hello there its ClassOne"); } }
└── root
└── mypack
└── ClassOne.java
import mypack.ClassOne;
public class Testing {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ClassOne b = new ClassOne();
b.methodClassOne();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance1-241014170708-efb92648/75/inheritance-Packages-and-Interfaces-pptx-47-2048.jpg)
