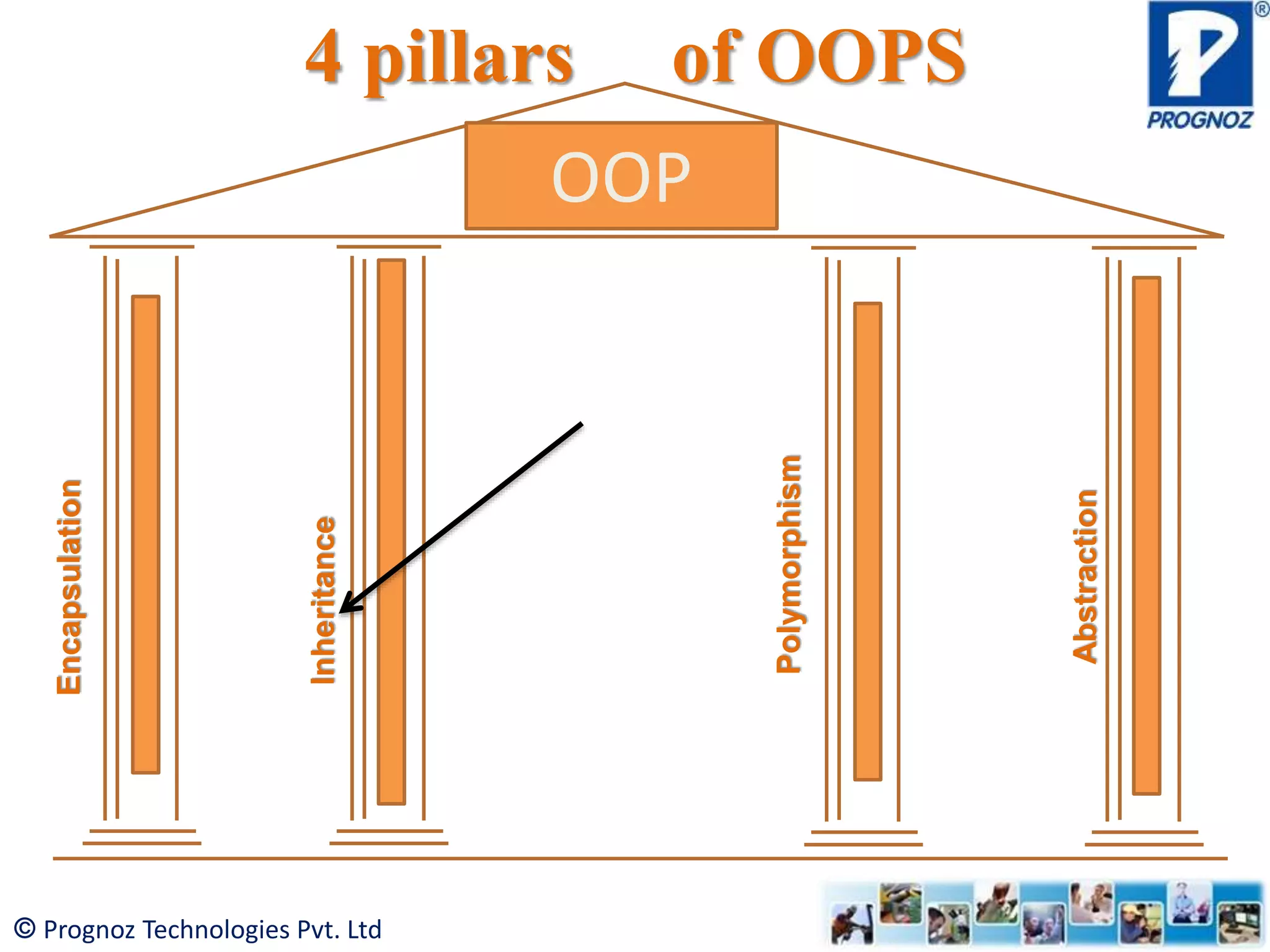
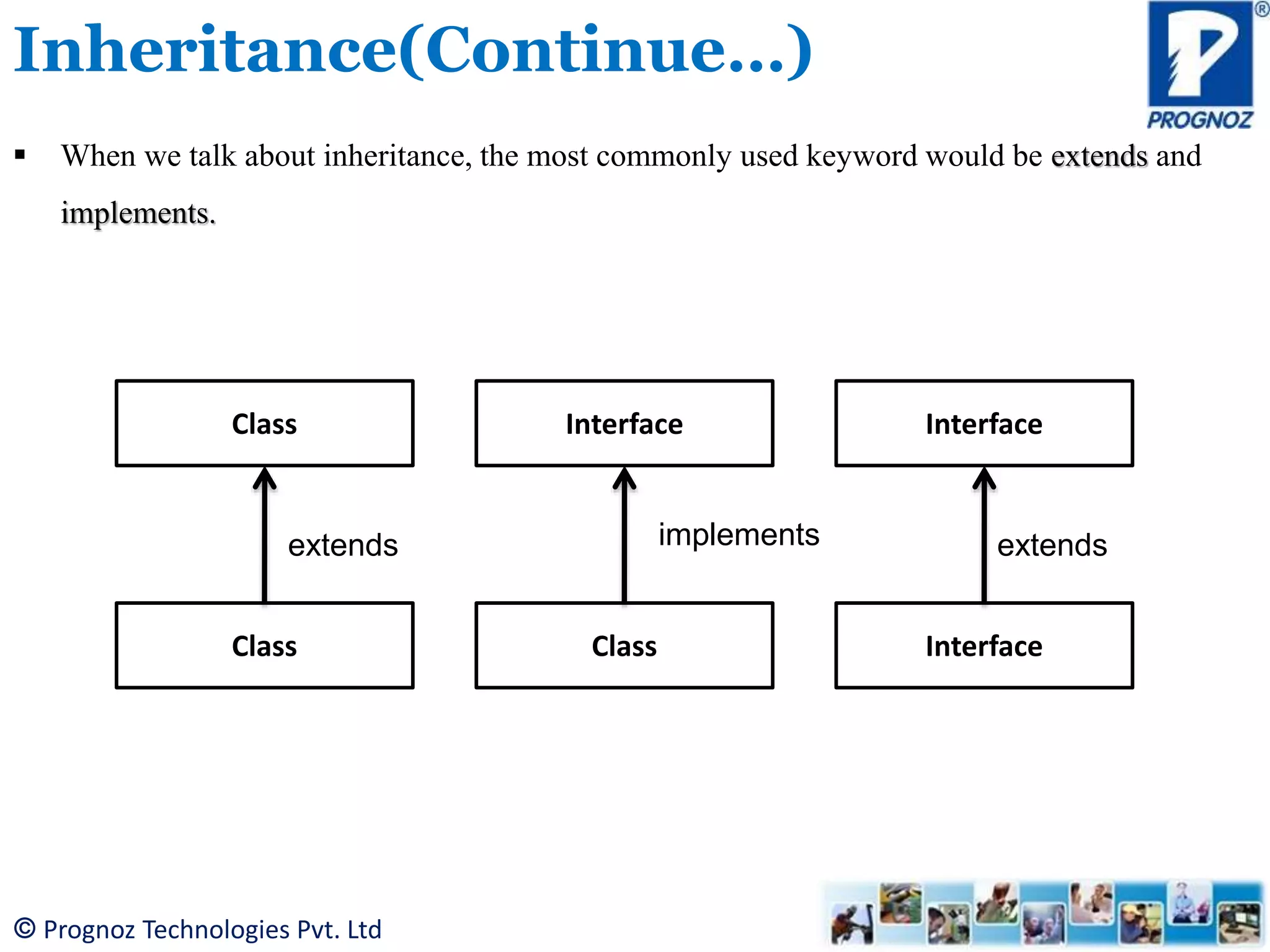
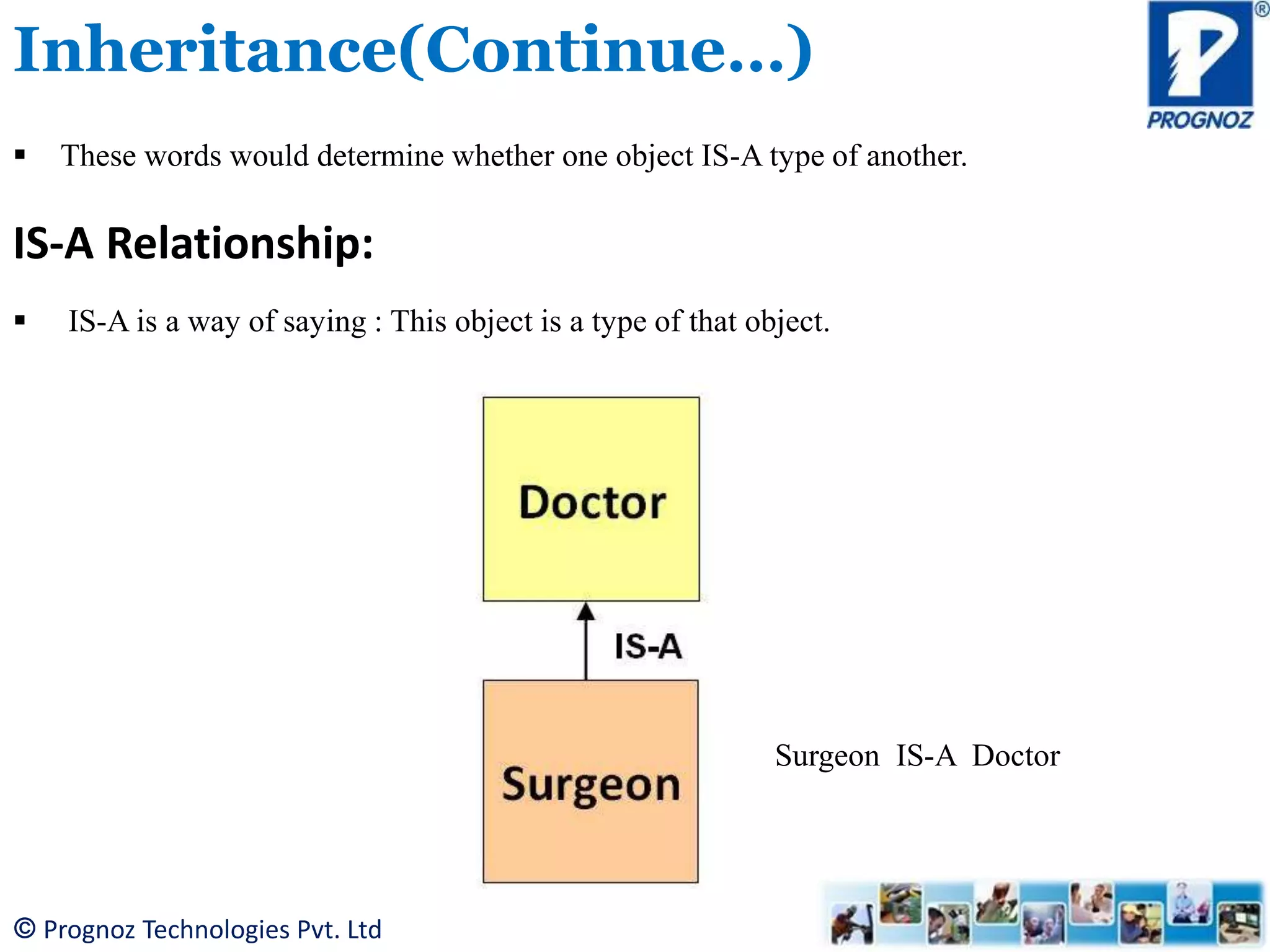
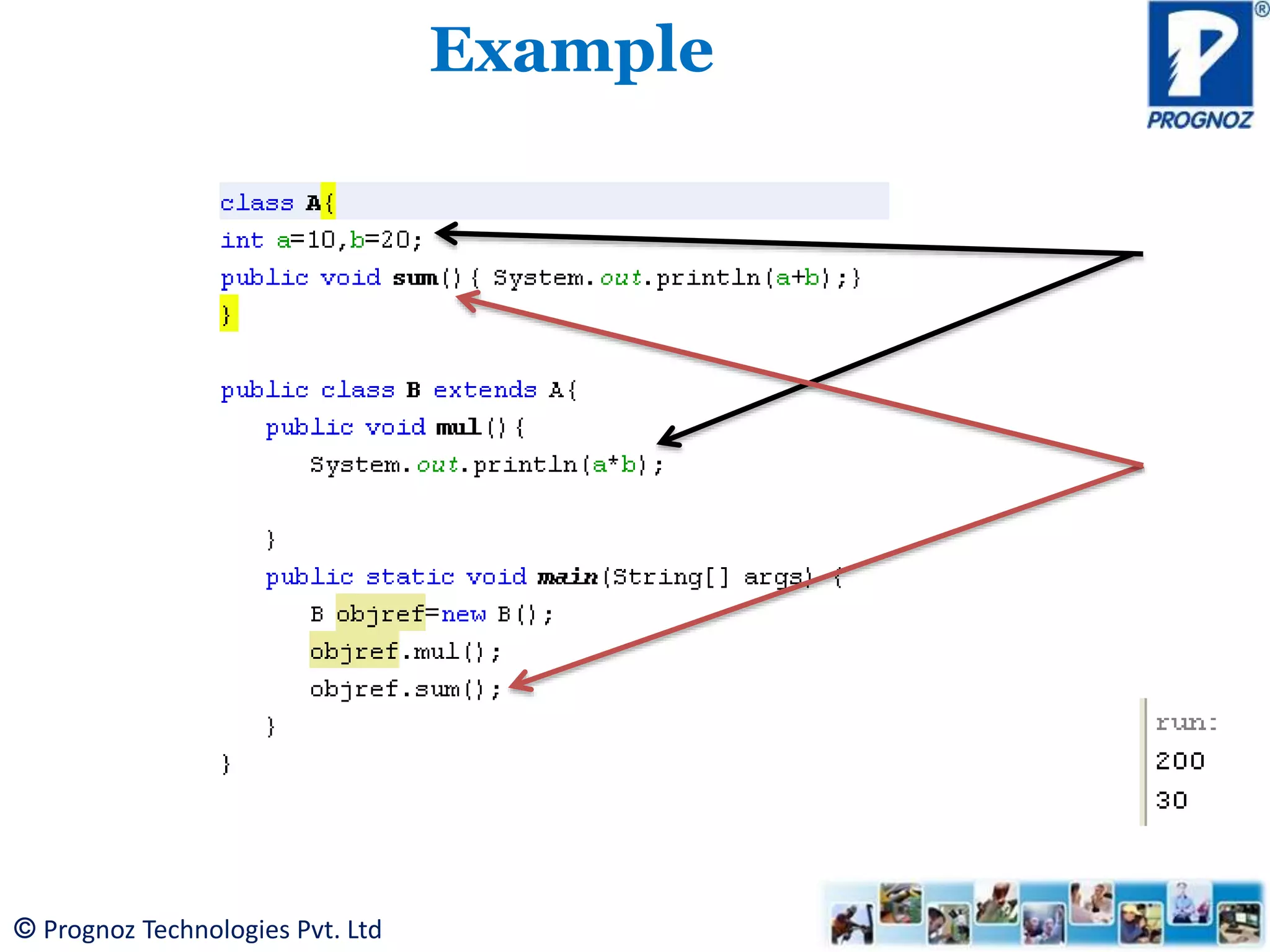
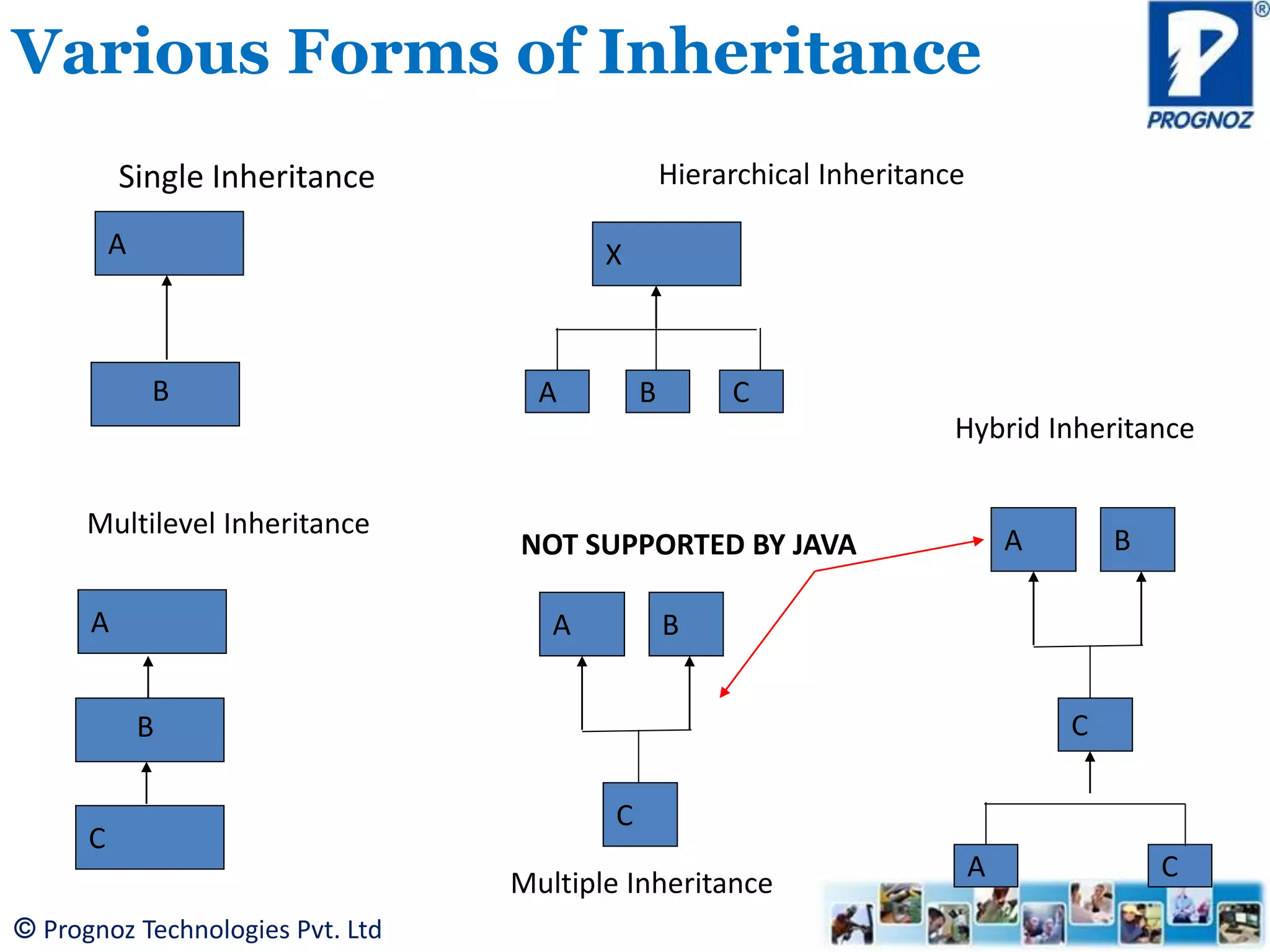
The document discusses the concept of inheritance in object-oriented programming (OOP), highlighting its importance in reusability and defining relationships between classes. It explains the is-a relationship and types of inheritance in Java, including single, multilevel, and hierarchical inheritance, while also addressing why multiple inheritance is not supported. The document emphasizes that inheritance allows subclasses to inherit attributes and methods from their superclasses, enabling better code management.