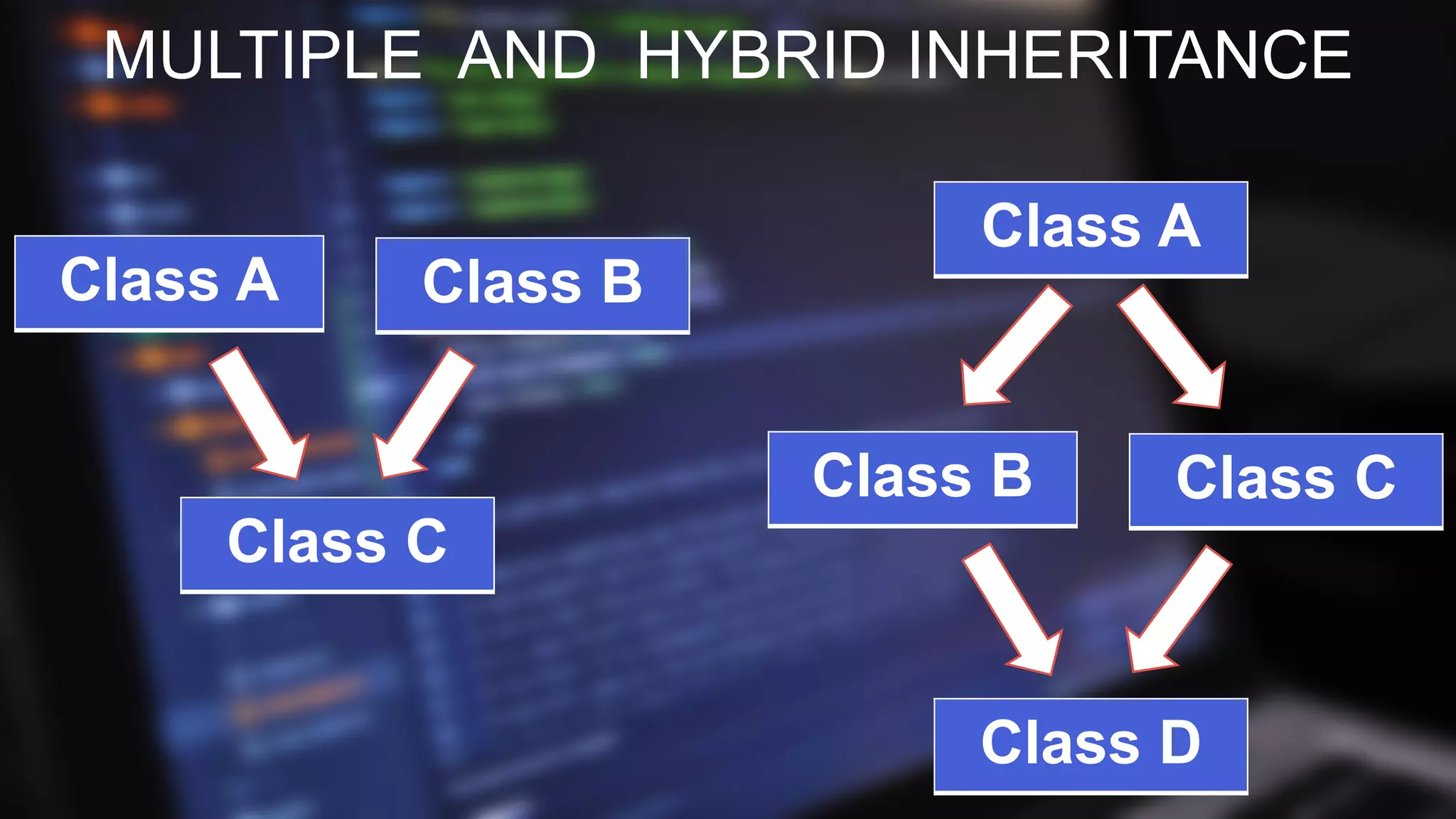
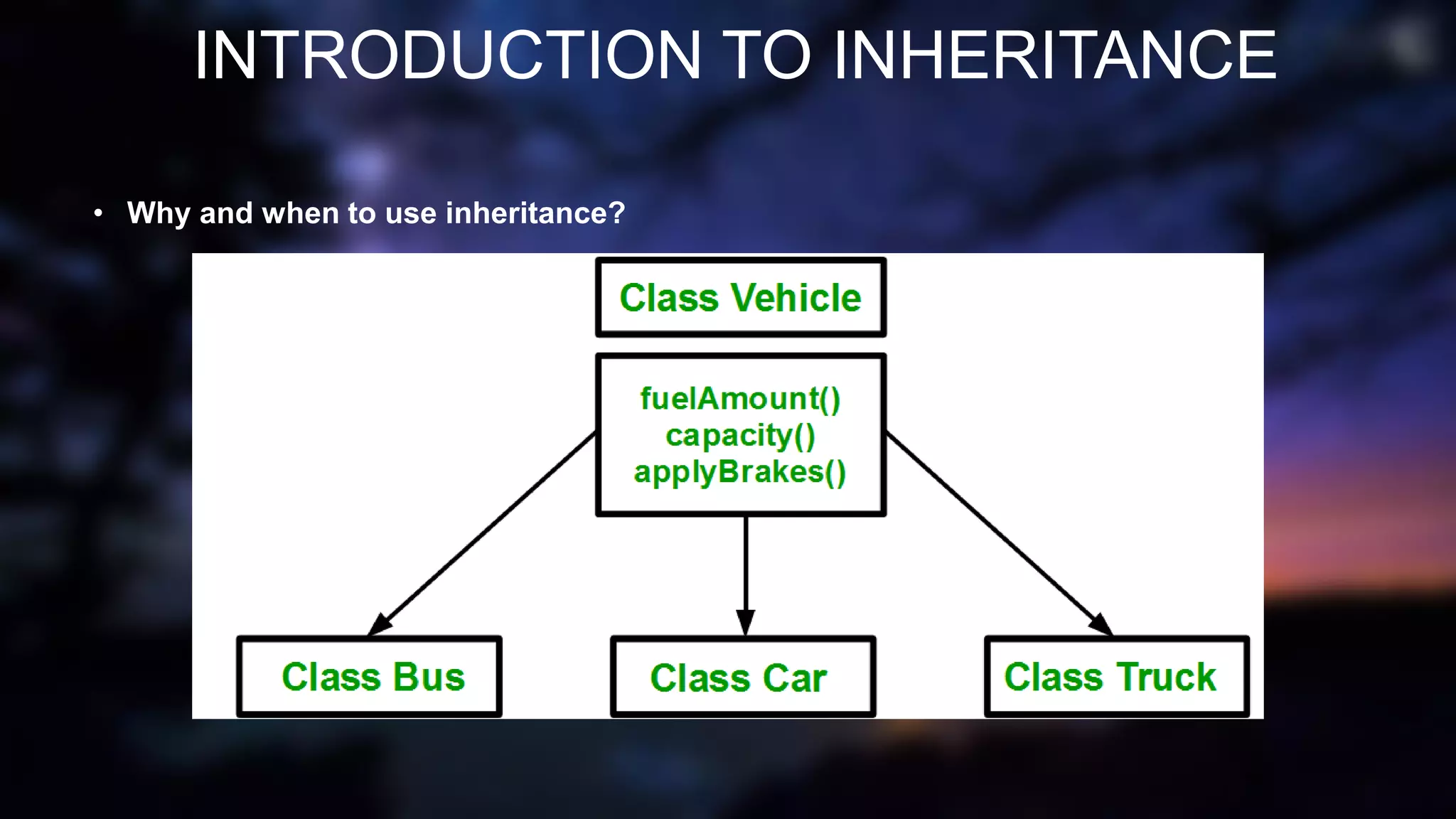
This document discusses inheritance in Java programming. It defines inheritance as a mechanism where a subclass acquires the properties and behaviors of a superclass. It describes the key types of inheritance in Java including single, multilevel, and hierarchical inheritance. It also outlines some advantages, such as code reusability and reliability, and disadvantages, such as increased coupling between classes.






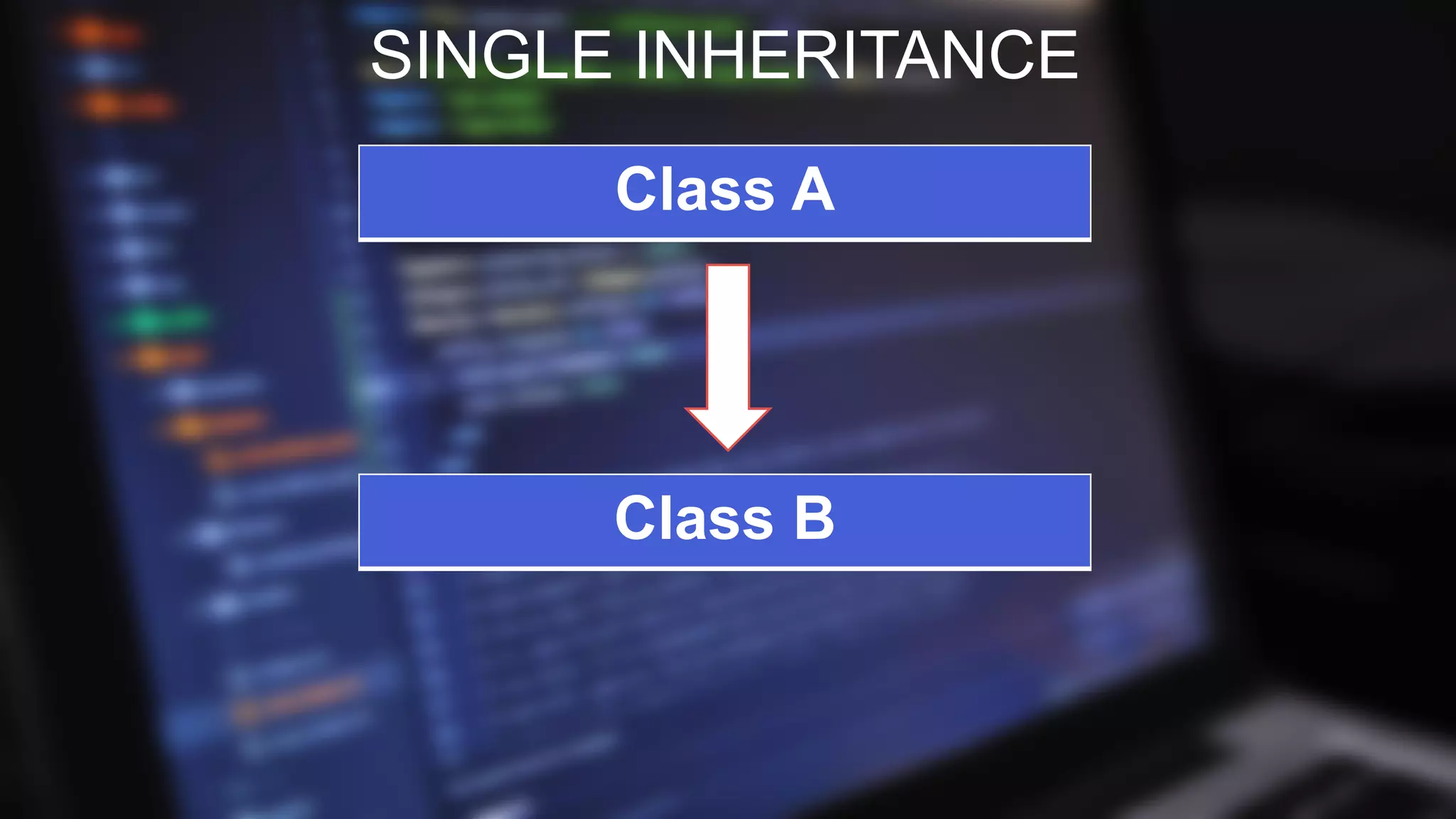
![SINGLE INHERITANCE
PROGRAM
class Animal {
void eat() {
System.out.println("eating...");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
void bark() {
System.out.println("barking...");
}
}
class TestInheritance {
public static void main(String args[ ]) {
Dog d=new Dog();
d.bark();
d.eat();
}
}
OUTPUT
barking...
eating...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/editededitedinheritanceinjava1-180924231647/75/Inheritance-In-Java-10-2048.jpg)
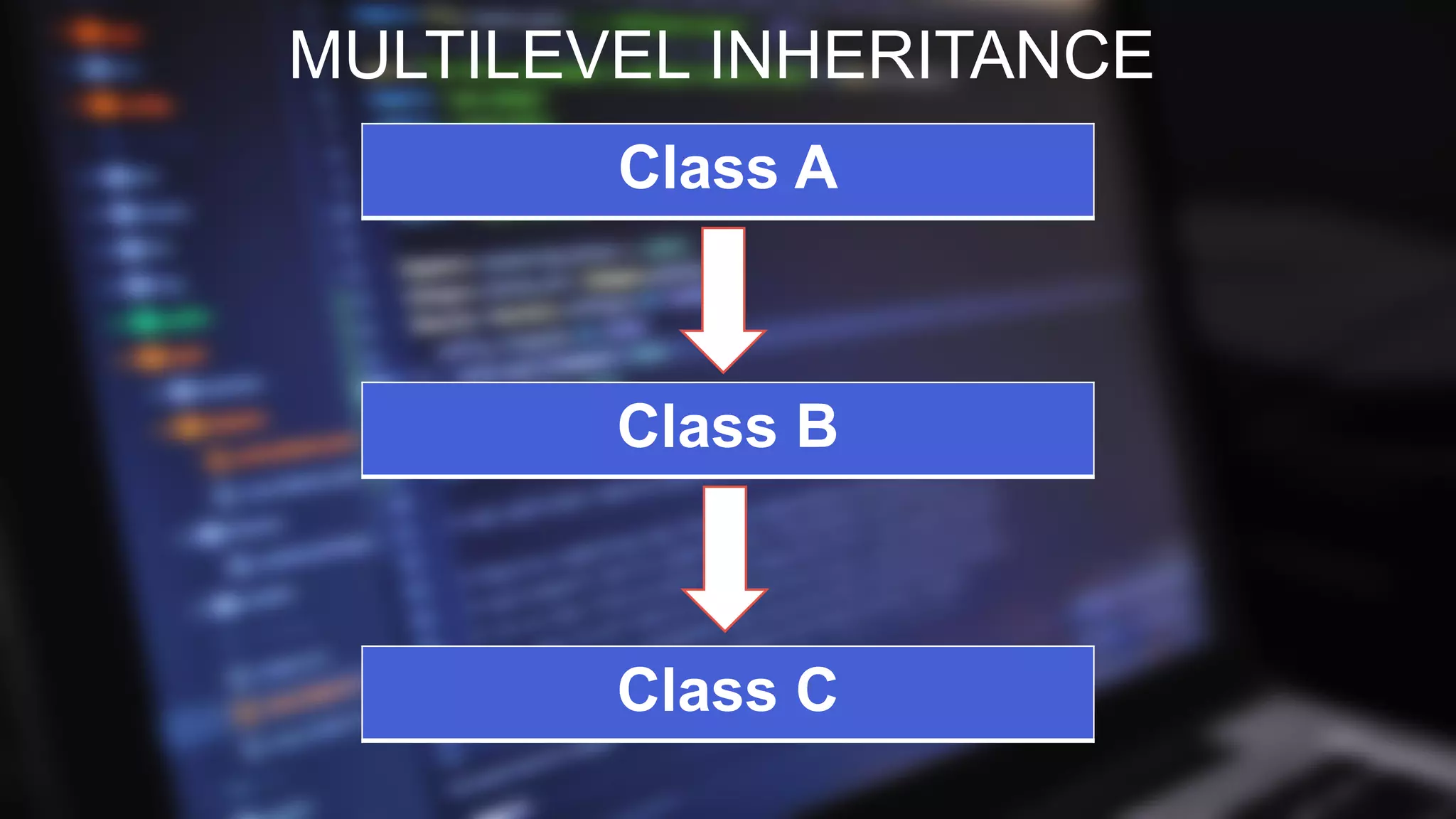
![MULTILEVEL INHERITANCE
PROGRAM
class Animal {
void eat() {
System.out.println("eating...");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
void bark() {
System.out.println("barking...");
}
}
class BabyDog extends Dog {
void weep() {
System.out.println("weeping...");
}
}
class TestInheritance2 {
public static void main(String args[ ]) {
BabyDog d=new BabyDog();
d.weep();
d.bark();
d.eat();
}
}
OUTPUT
weeping...
barking...
eating...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/editededitedinheritanceinjava1-180924231647/75/Inheritance-In-Java-12-2048.jpg)
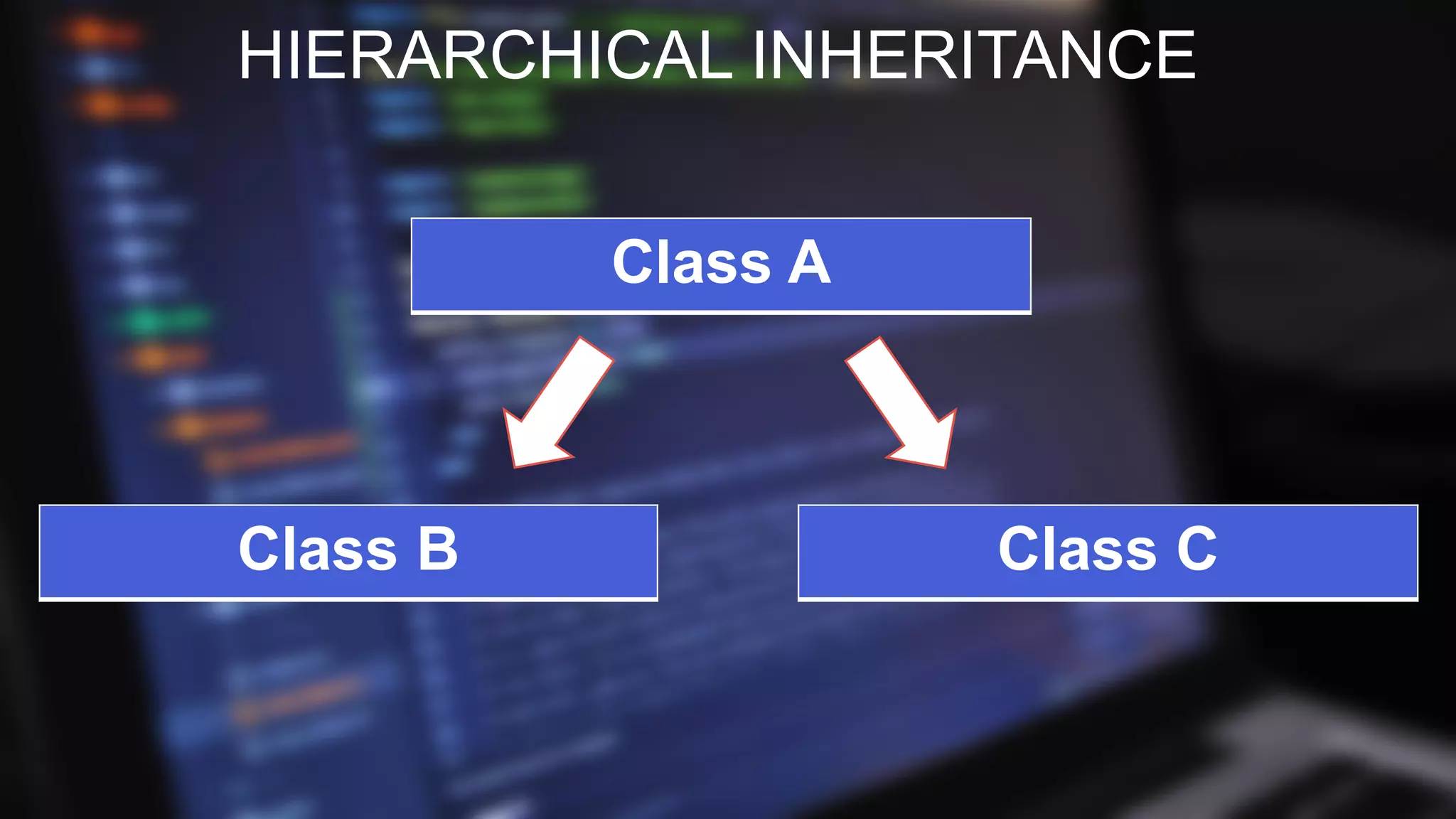
![HIERARCHICAL INHERITANCE
PROGRAM
class Animal {
void eat() {
System.out.println("eating...");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
void bark() {
System.out.println("barking...");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
void meow() {
System.out.println("meowing...");
}
}
class TestInheritance3 {
public static void main(String args[ ]) {
Cat c=new Cat();
Dog d=new Dog();
c.meow();
c.eat();
d.bark();
d.eat();
}
}
OUTPUT
meowing...
eating...
barking…
eating…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/editededitedinheritanceinjava1-180924231647/75/Inheritance-In-Java-14-2048.jpg)