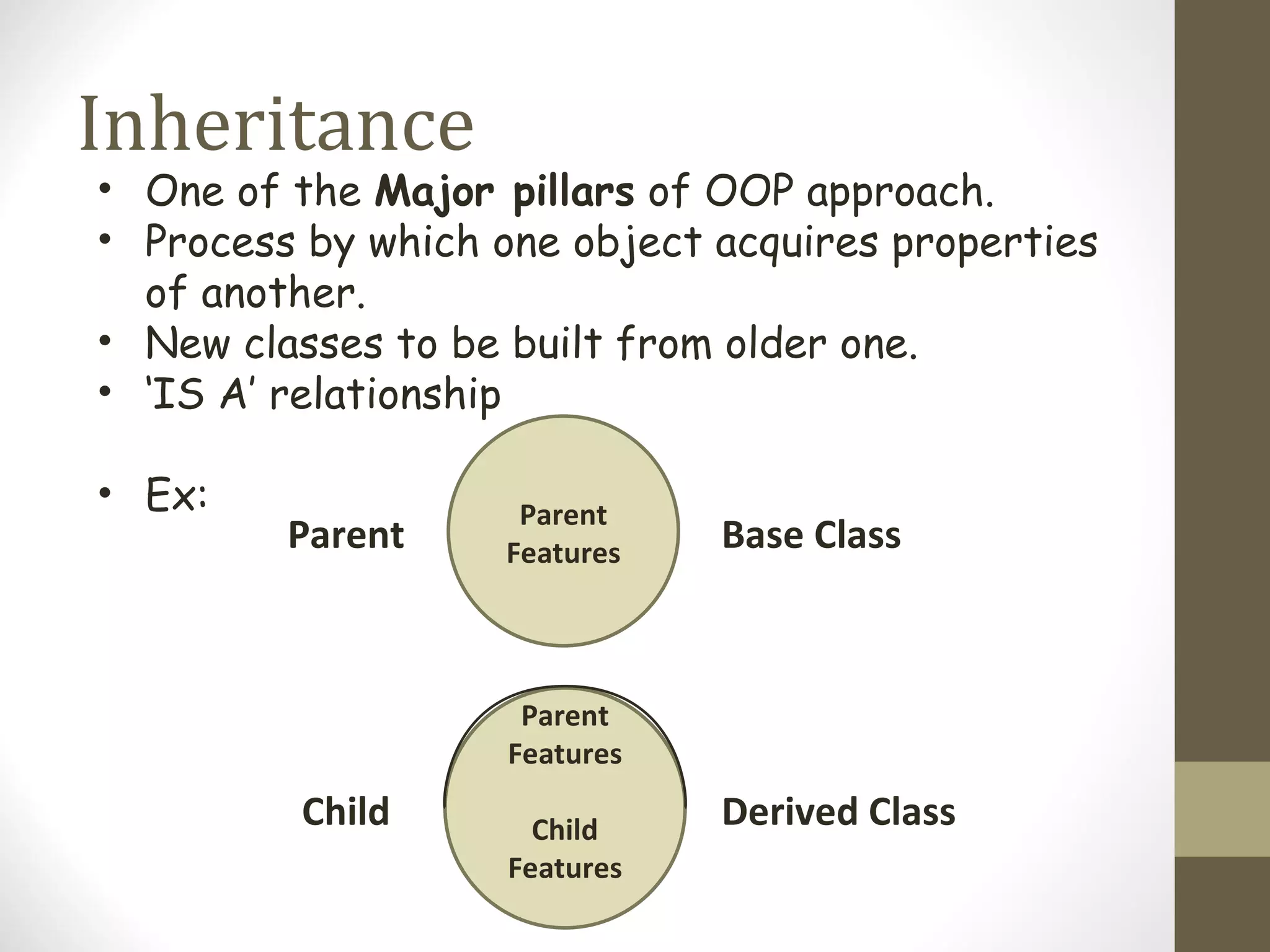
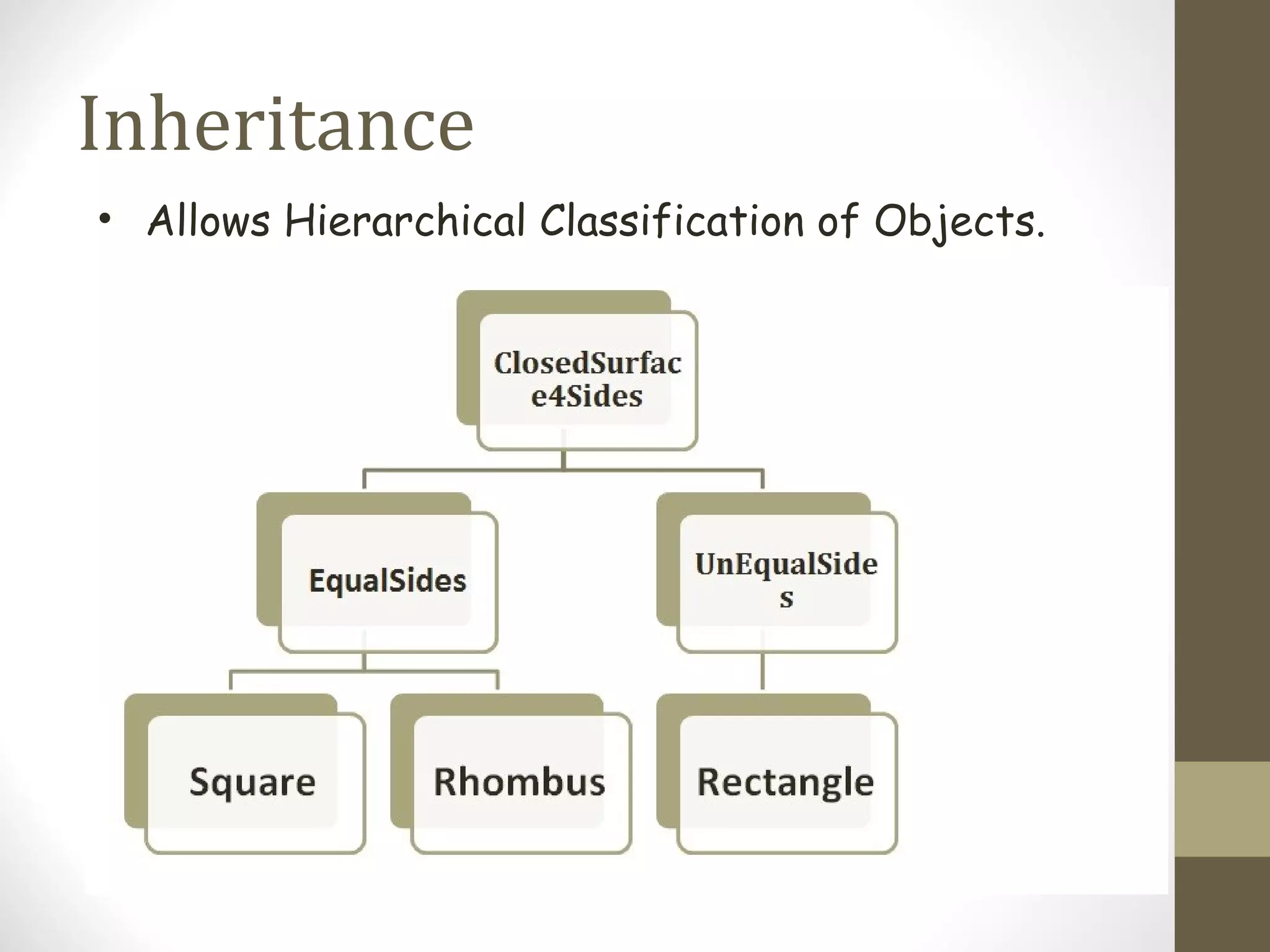
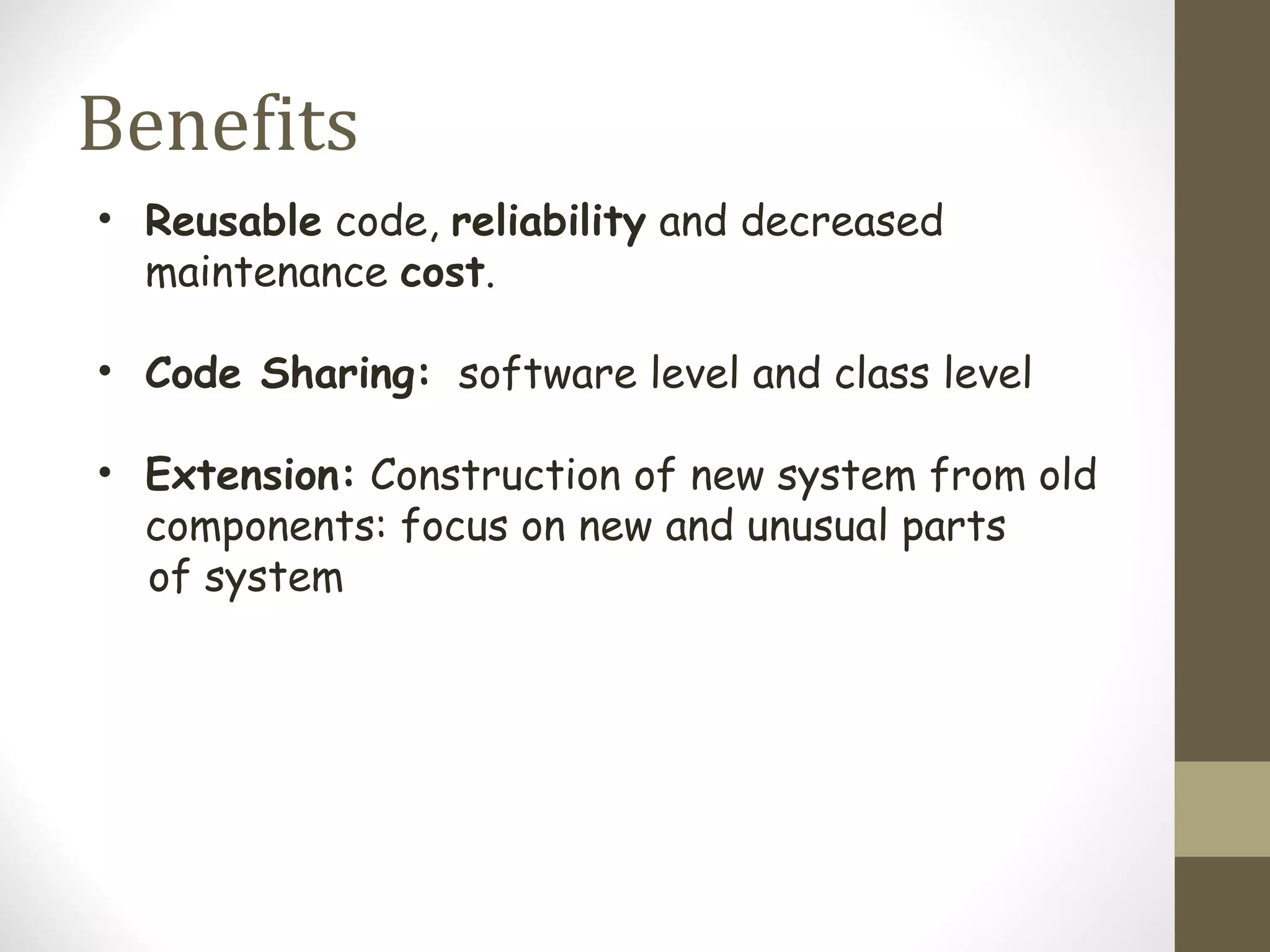
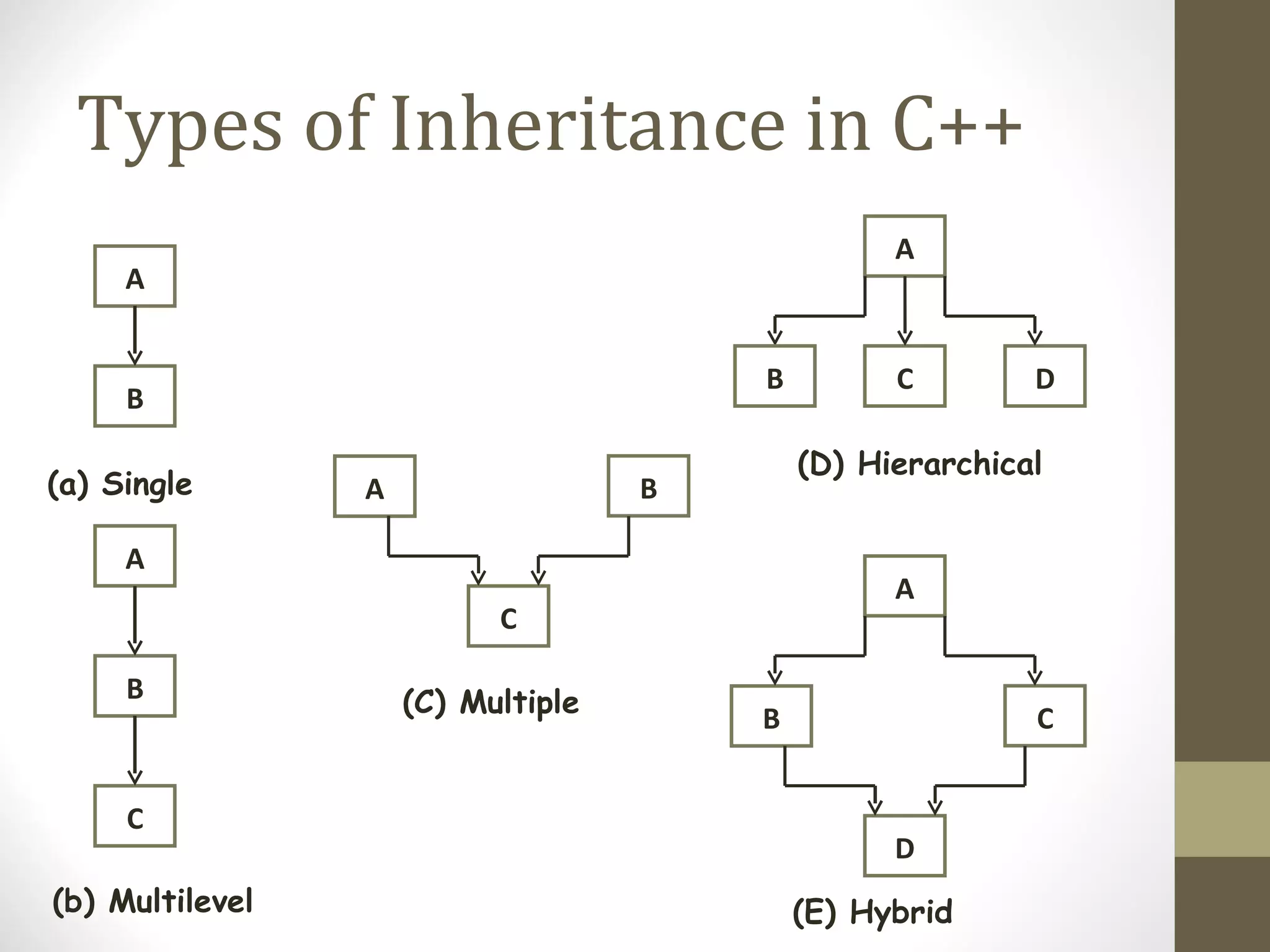
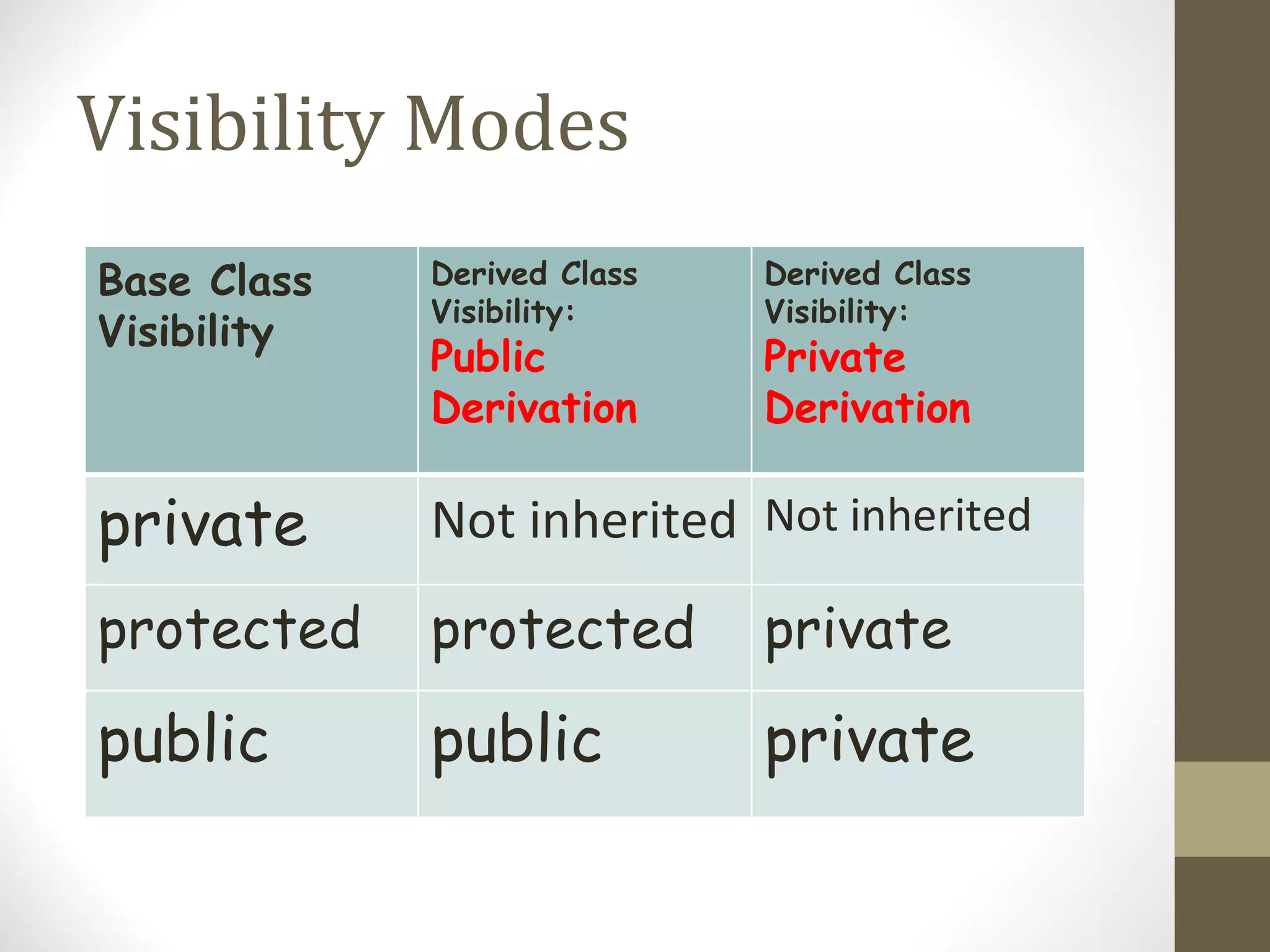
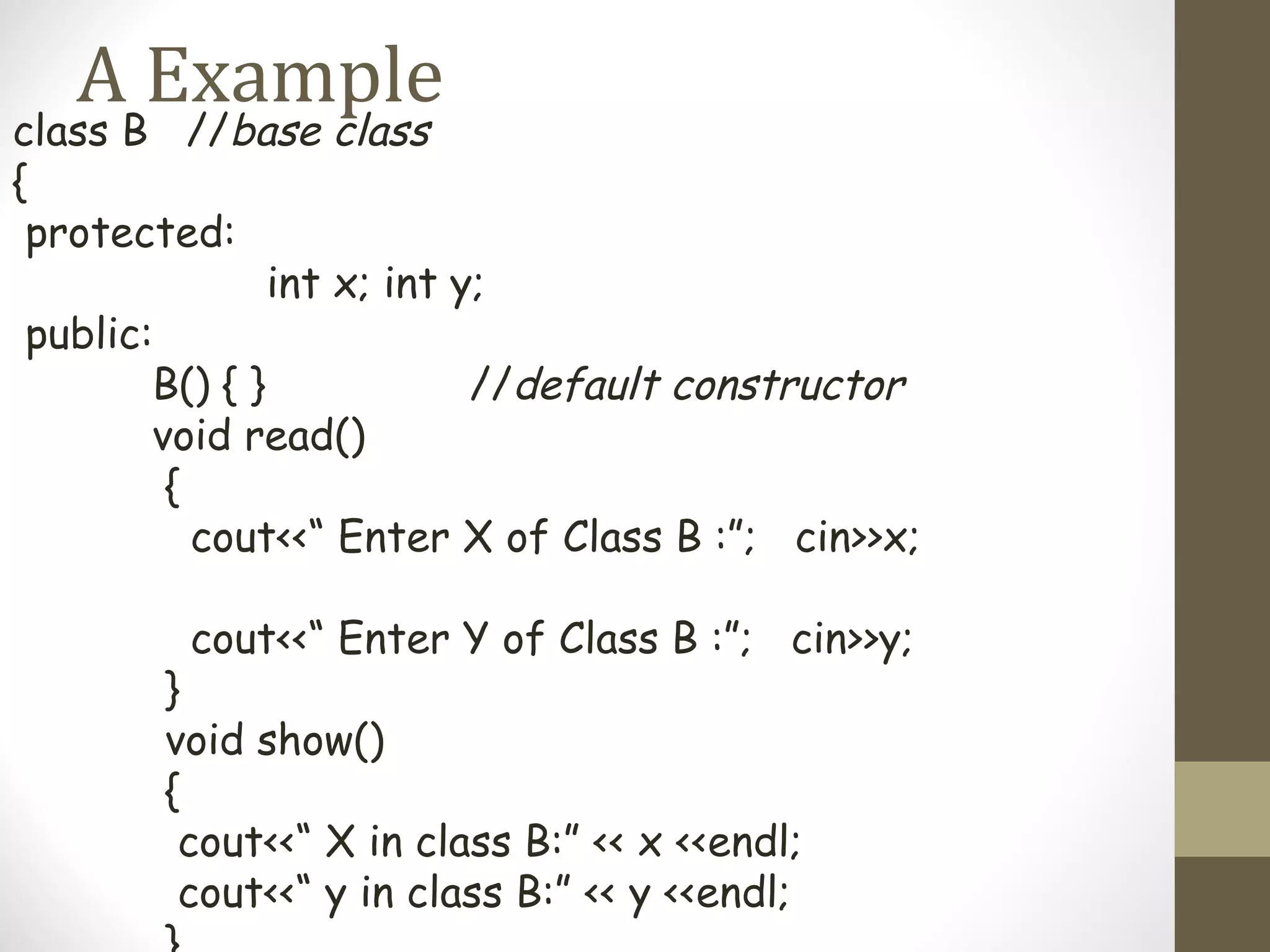
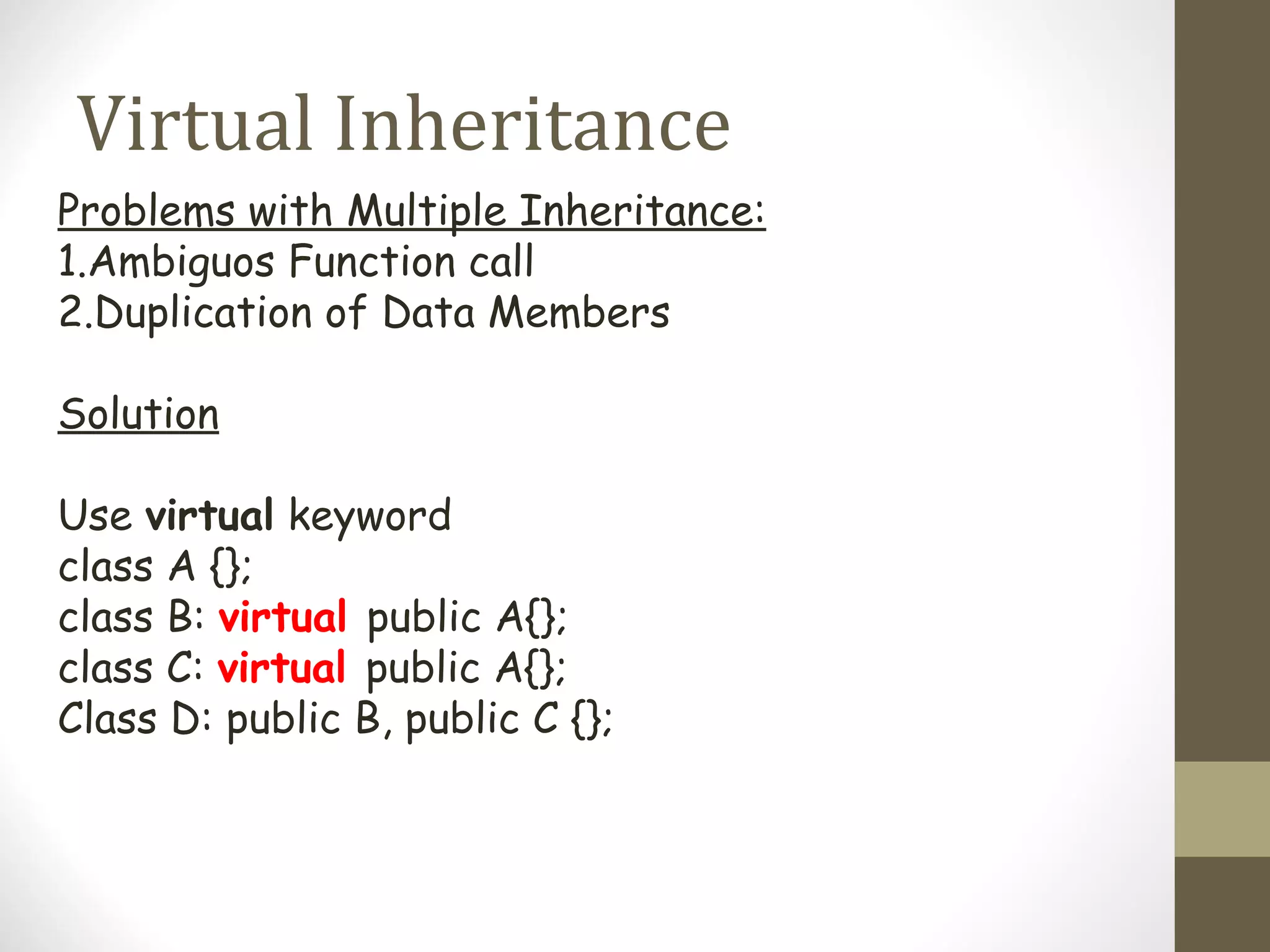
Inheritance allows hierarchical classification of objects by allowing new classes to acquire properties from older base classes. This allows for code sharing and reuse, which increases reliability and decreases maintenance costs. There are different types of inheritance like single, multilevel, multiple, and hierarchical. Inheritance is implemented using the derived class and base class syntax where the derived class inherits visibility of members defined in the base class depending on the visibility mode being private, protected, or public. Virtual inheritance solves issues like ambiguous function calls and duplication of data members that can occur with multiple inheritance.