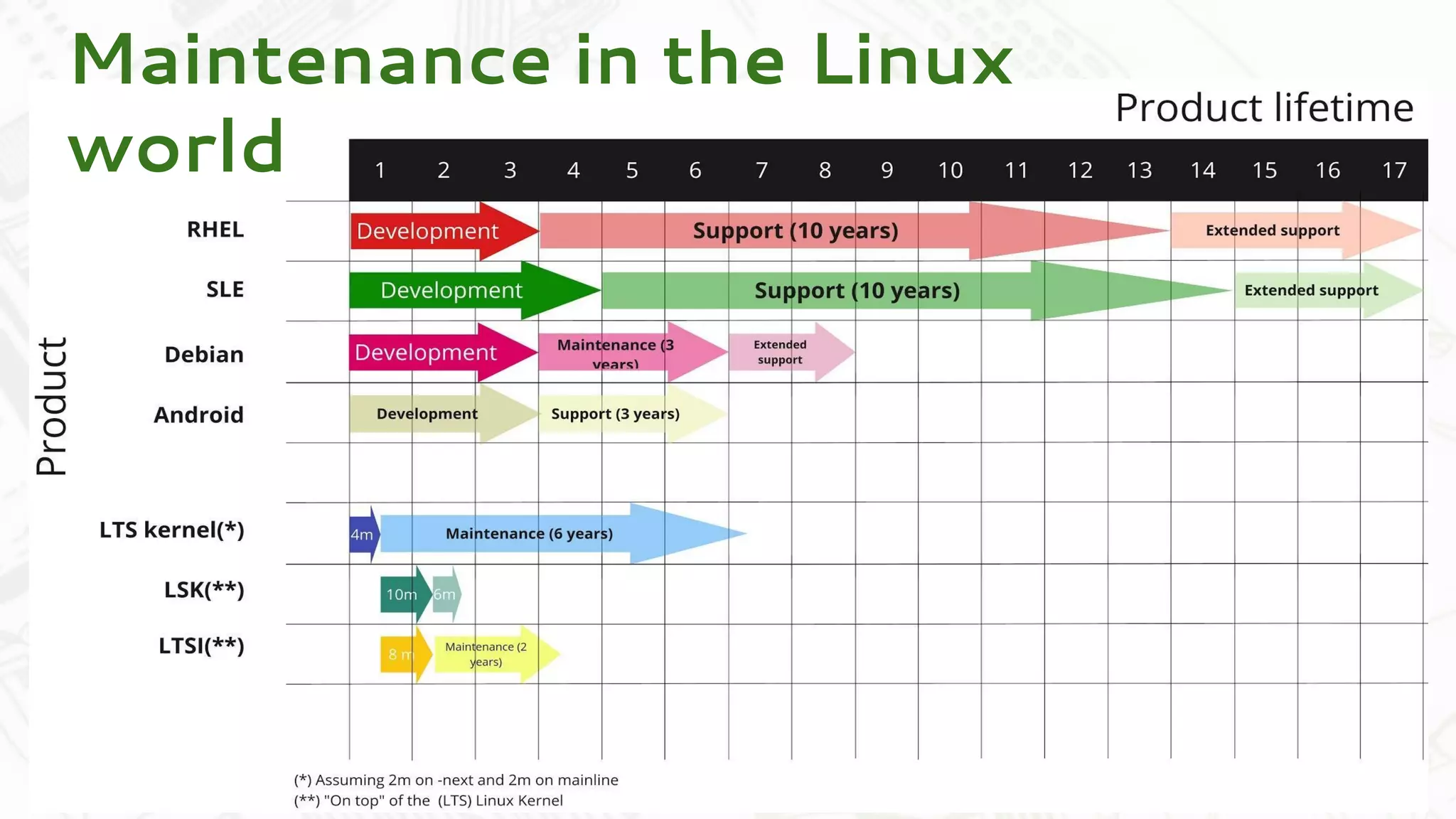
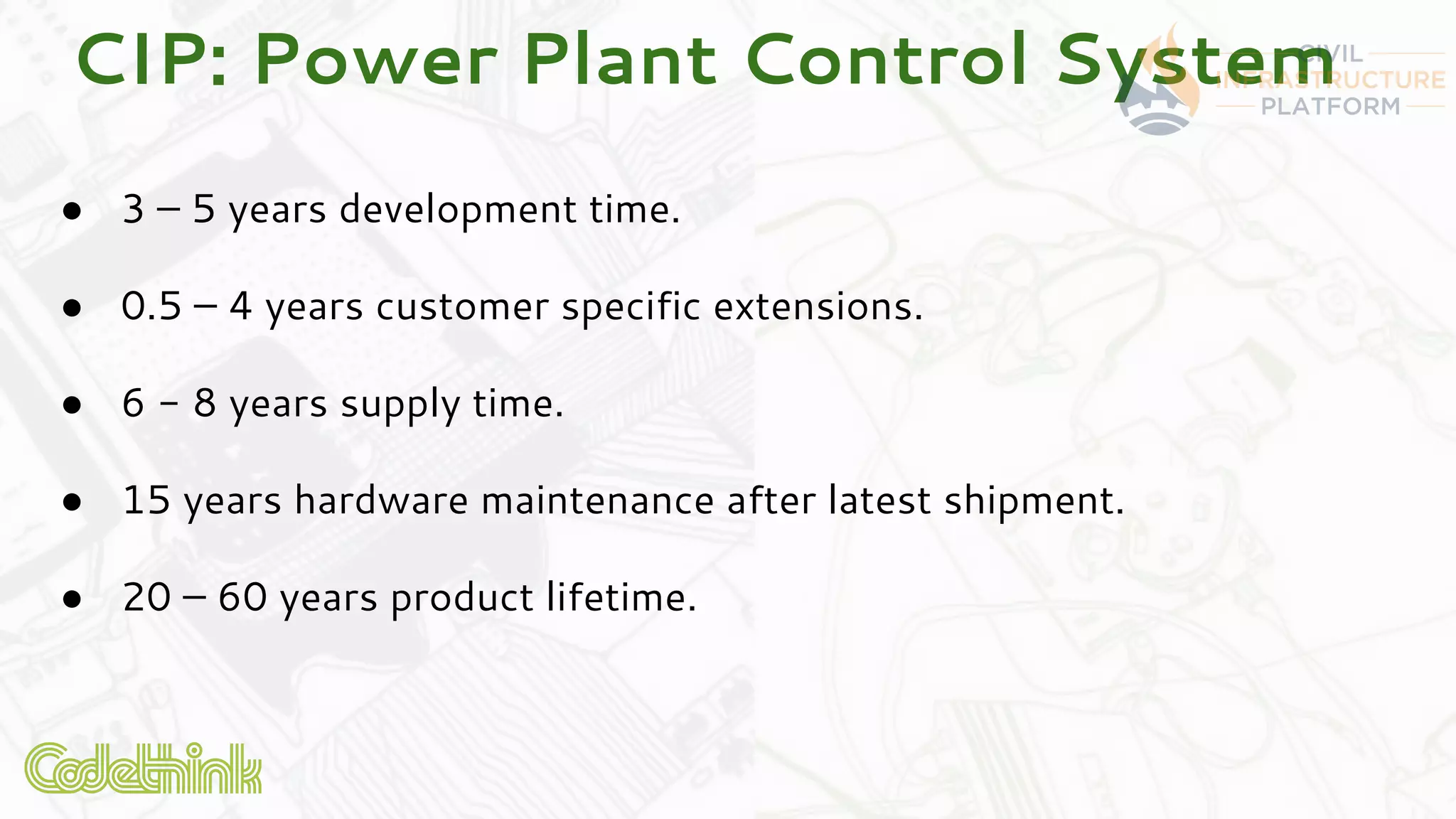
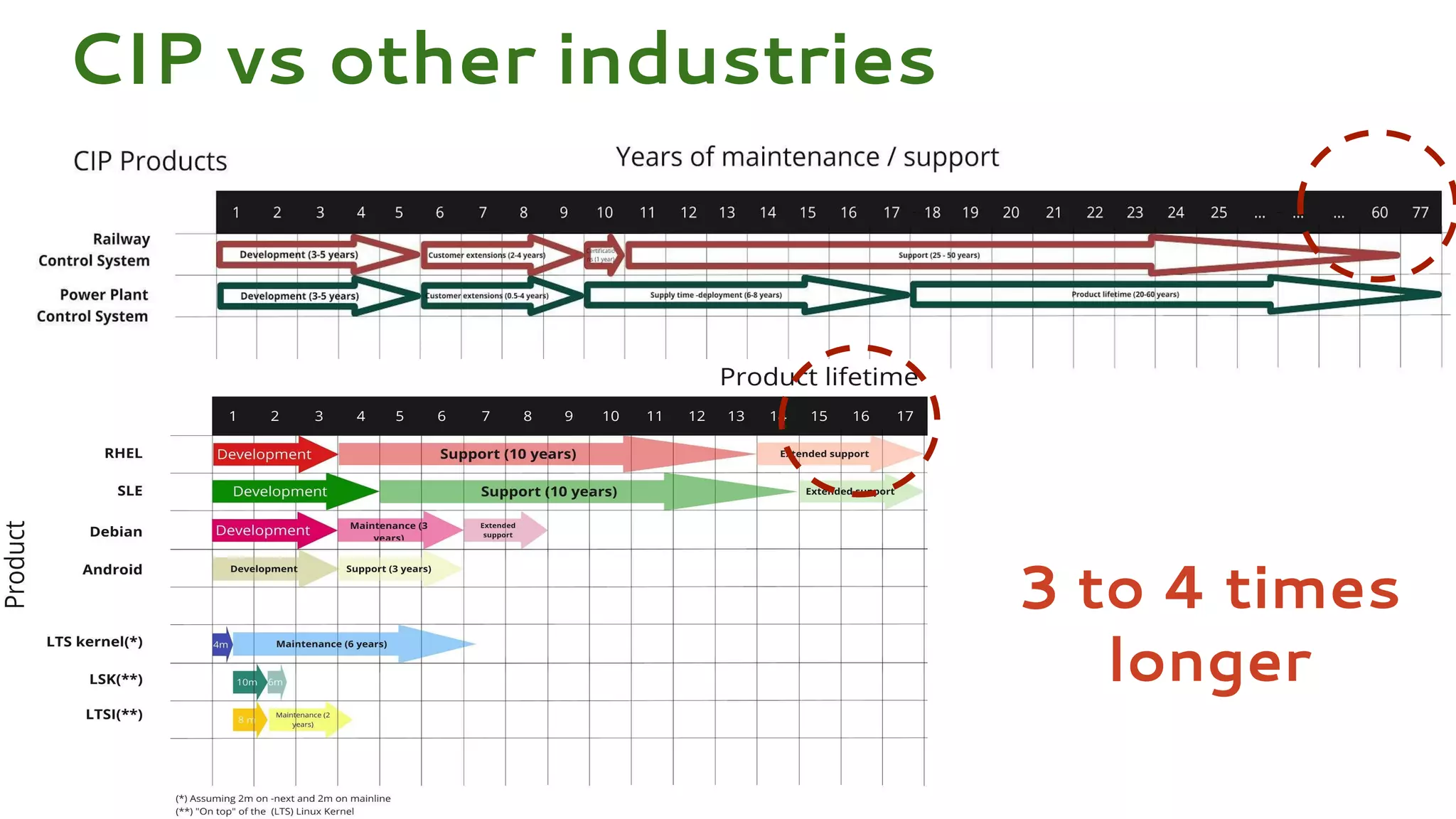
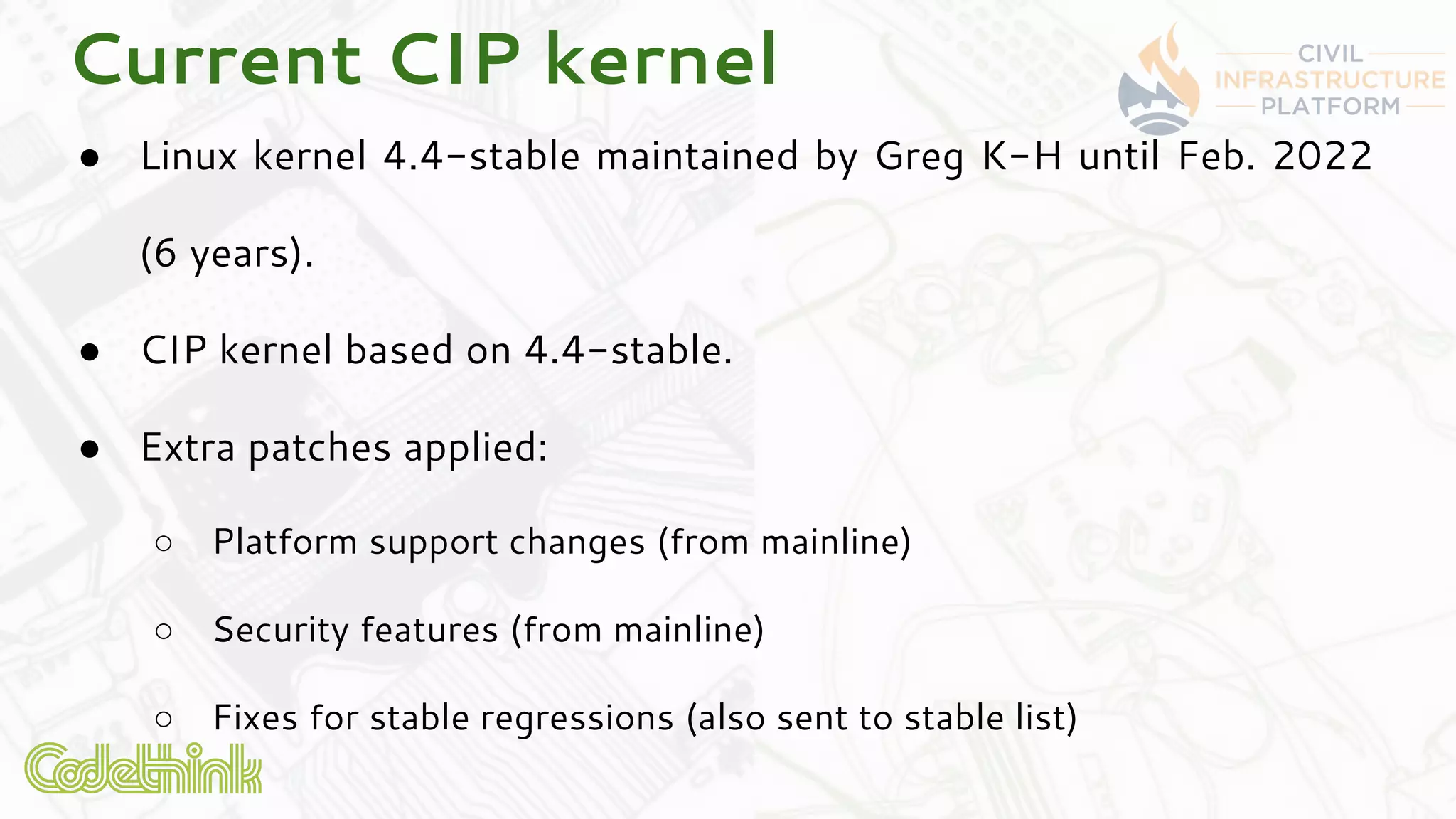
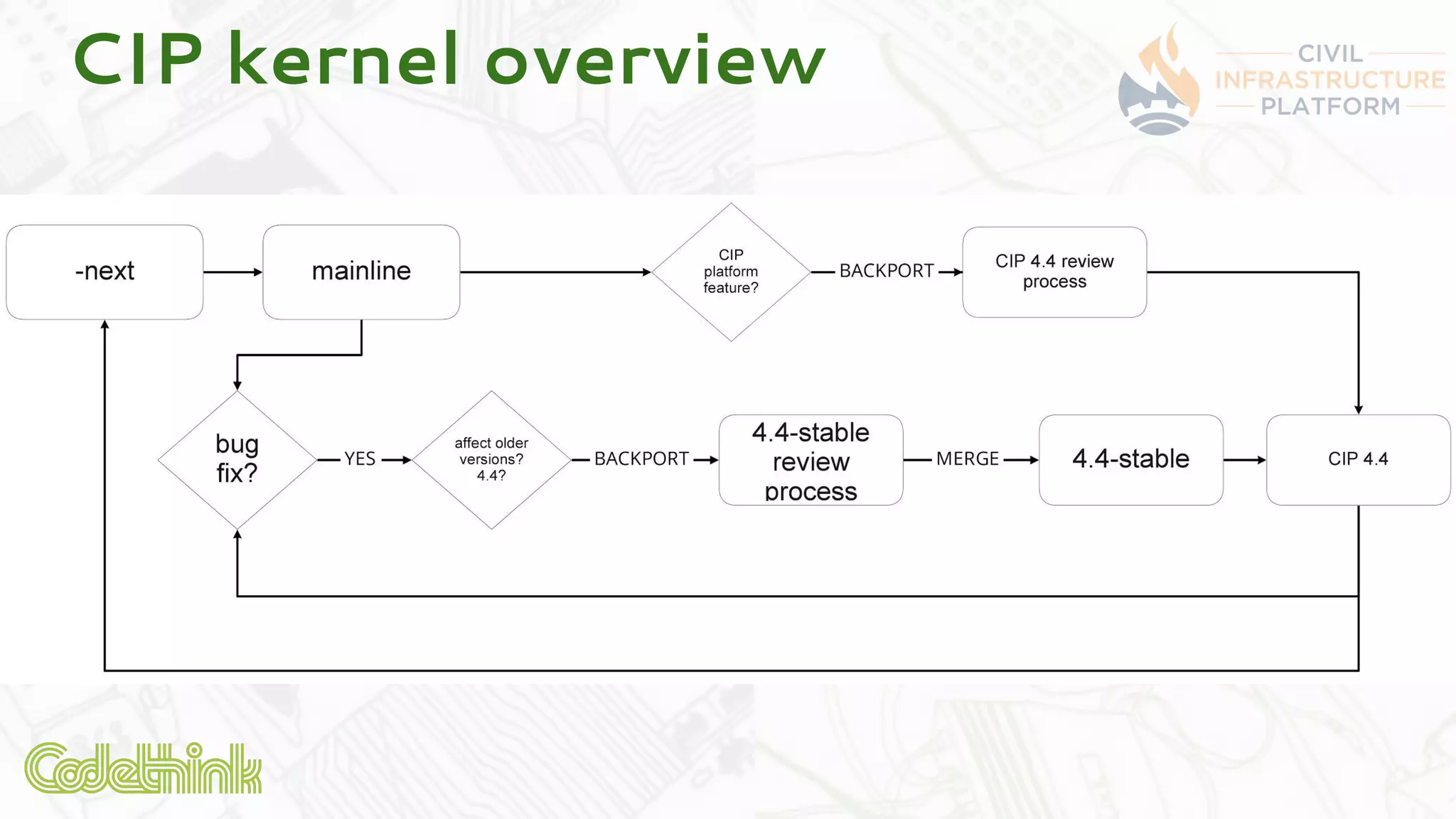
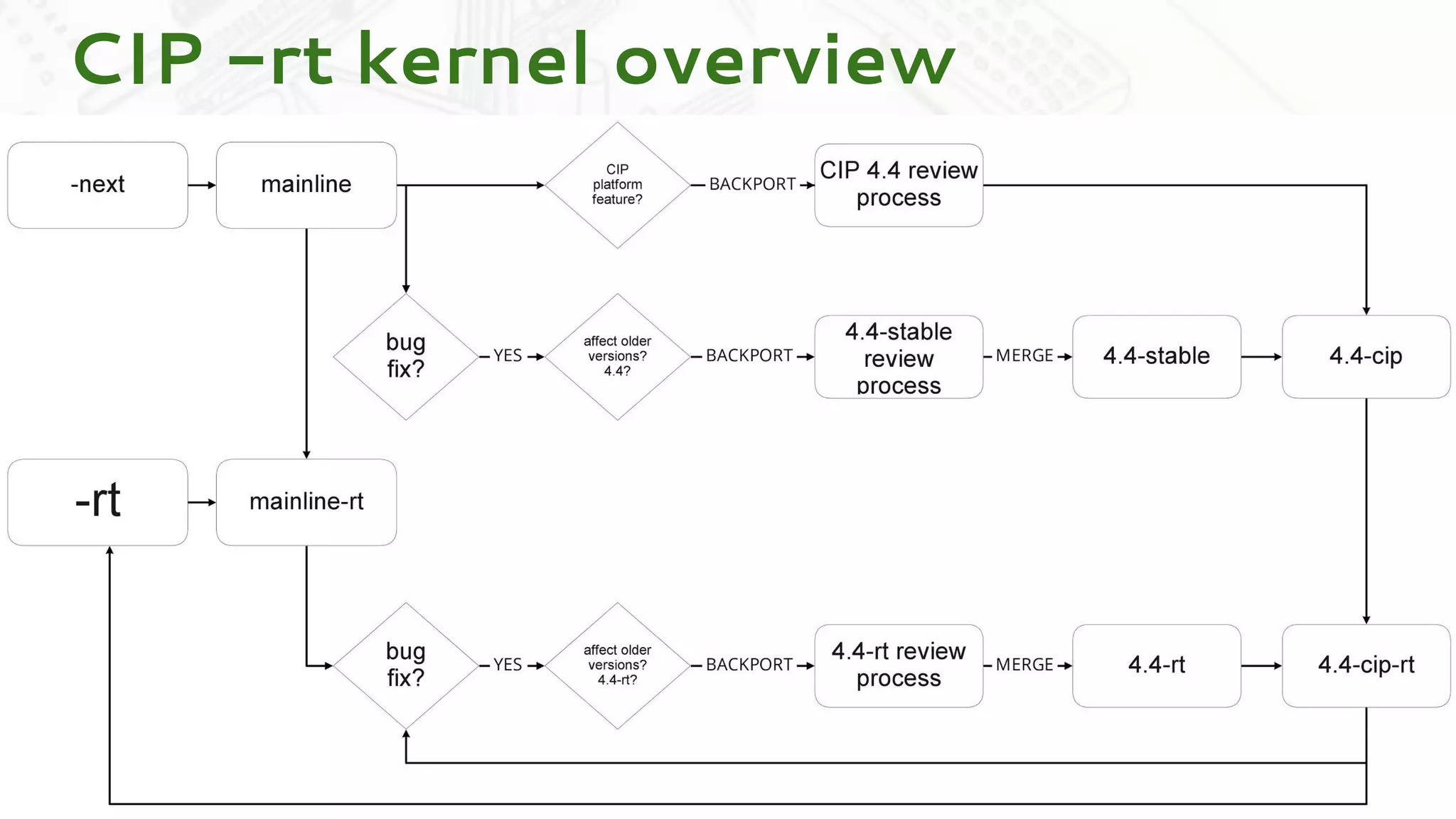
Codethink Ltd, an expert in open source software, offers long-term Linux kernel maintenance through its participation in the Civil Infrastructure Project (CIP), which aims to support industrial-grade Linux systems. The CIP, formed by major companies like Hitachi and Siemens, focuses on creating a stable, maintainable Linux core with specific strategies for product maintenance, opting for a long-term support (LTS) approach. The presentation outlines the benefits of collaboration and open-source methodologies in maintaining complex systems while addressing the challenges and strategies associated with the CIP kernel.