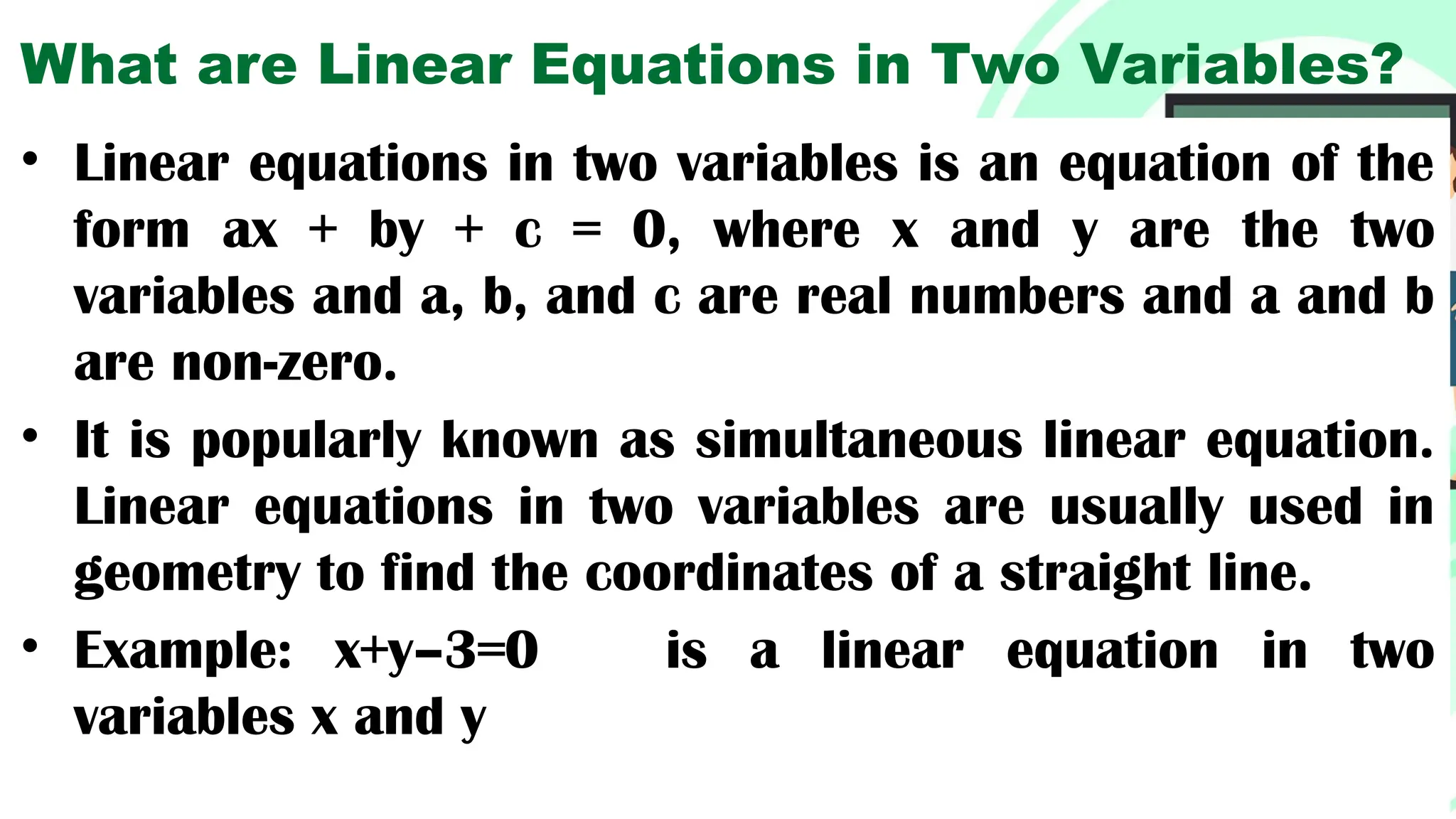
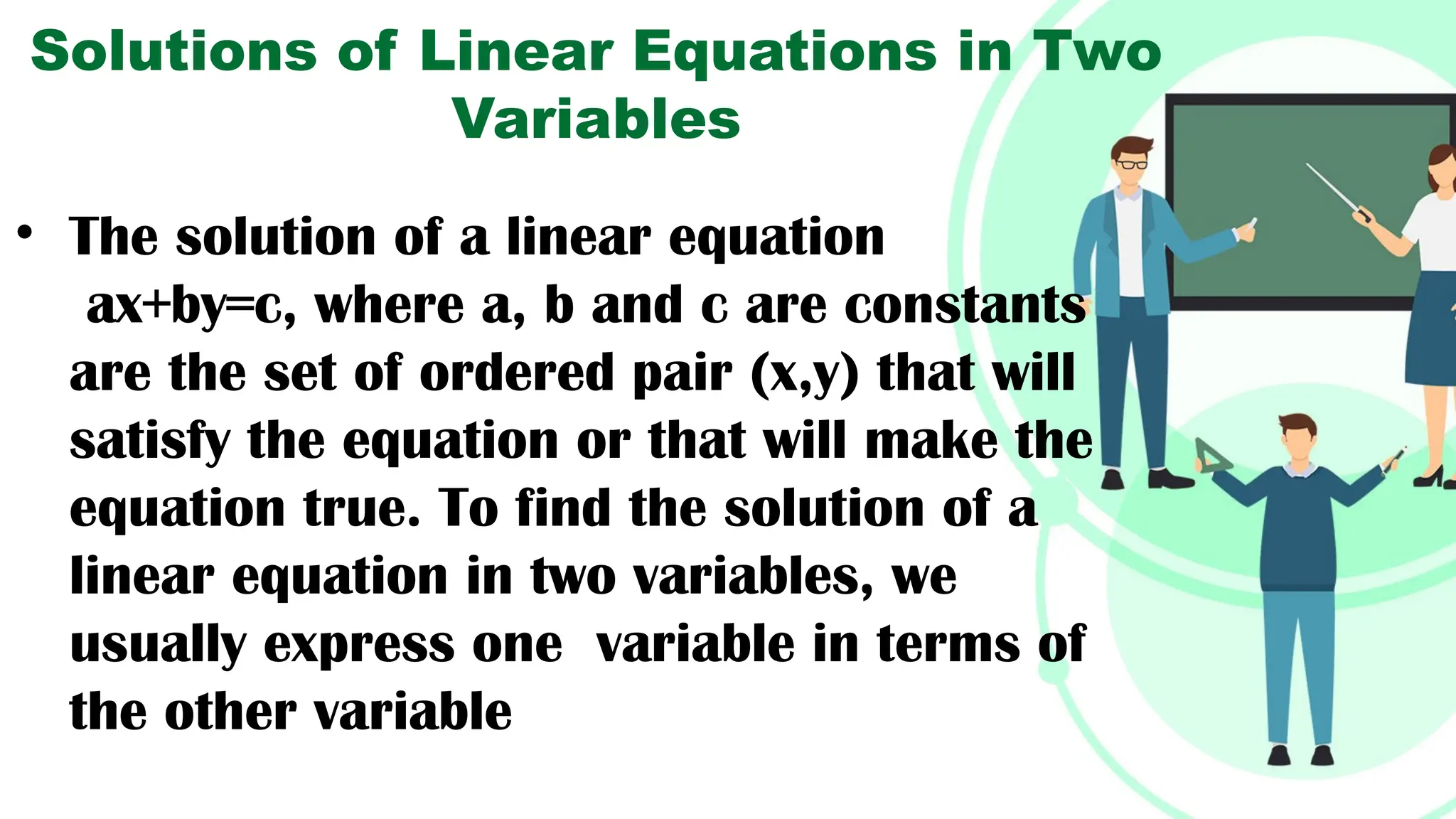
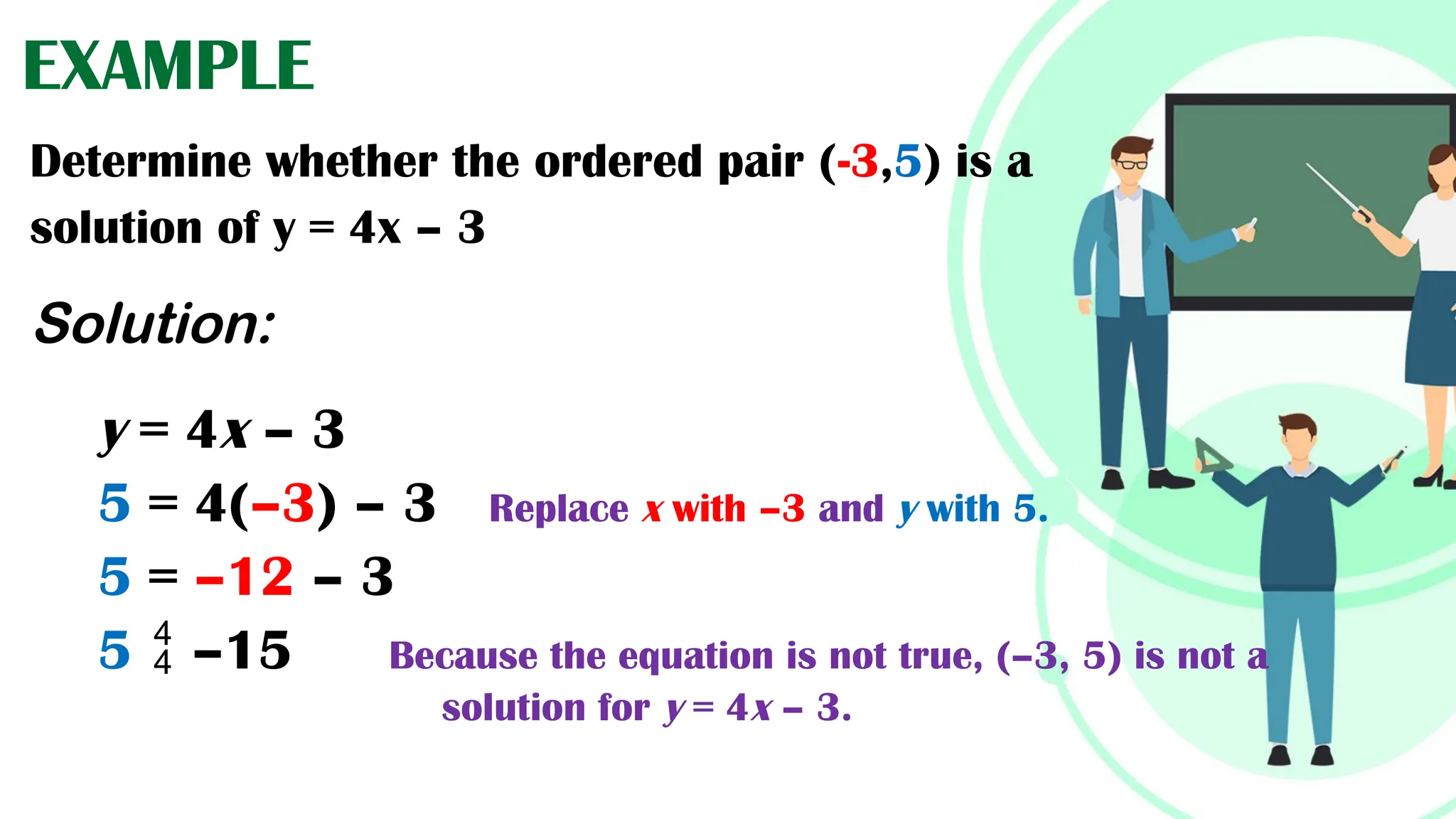
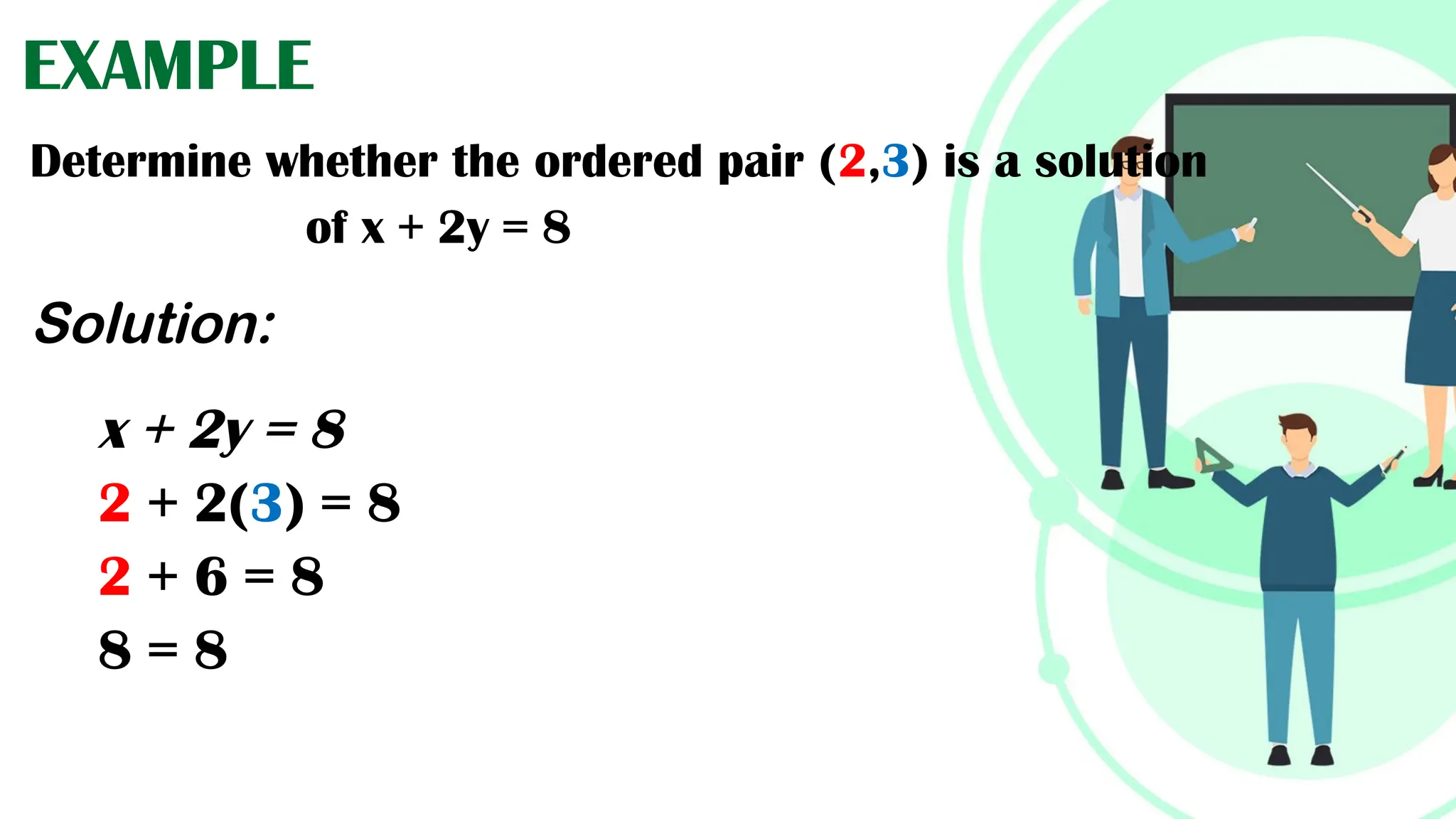
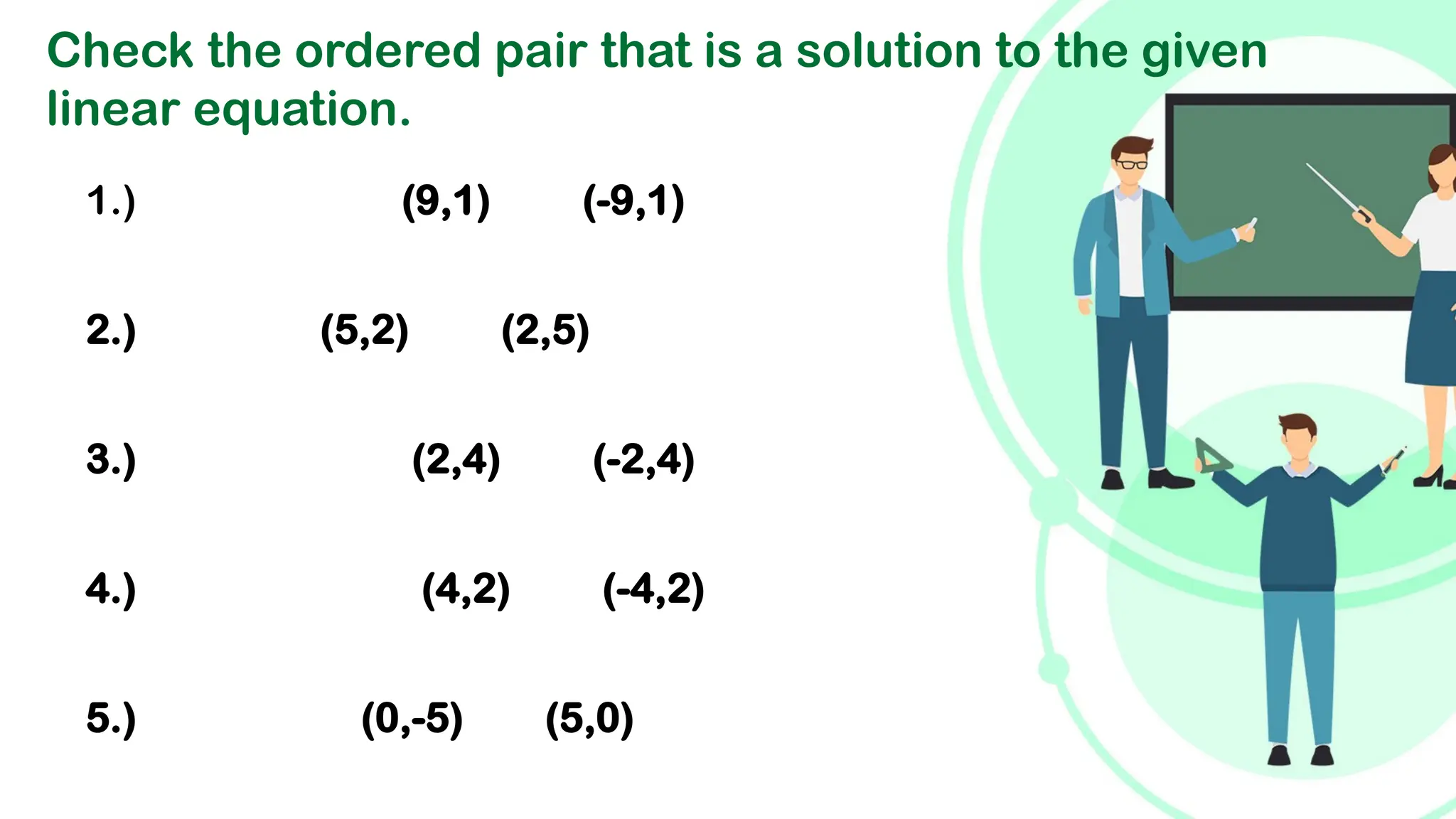
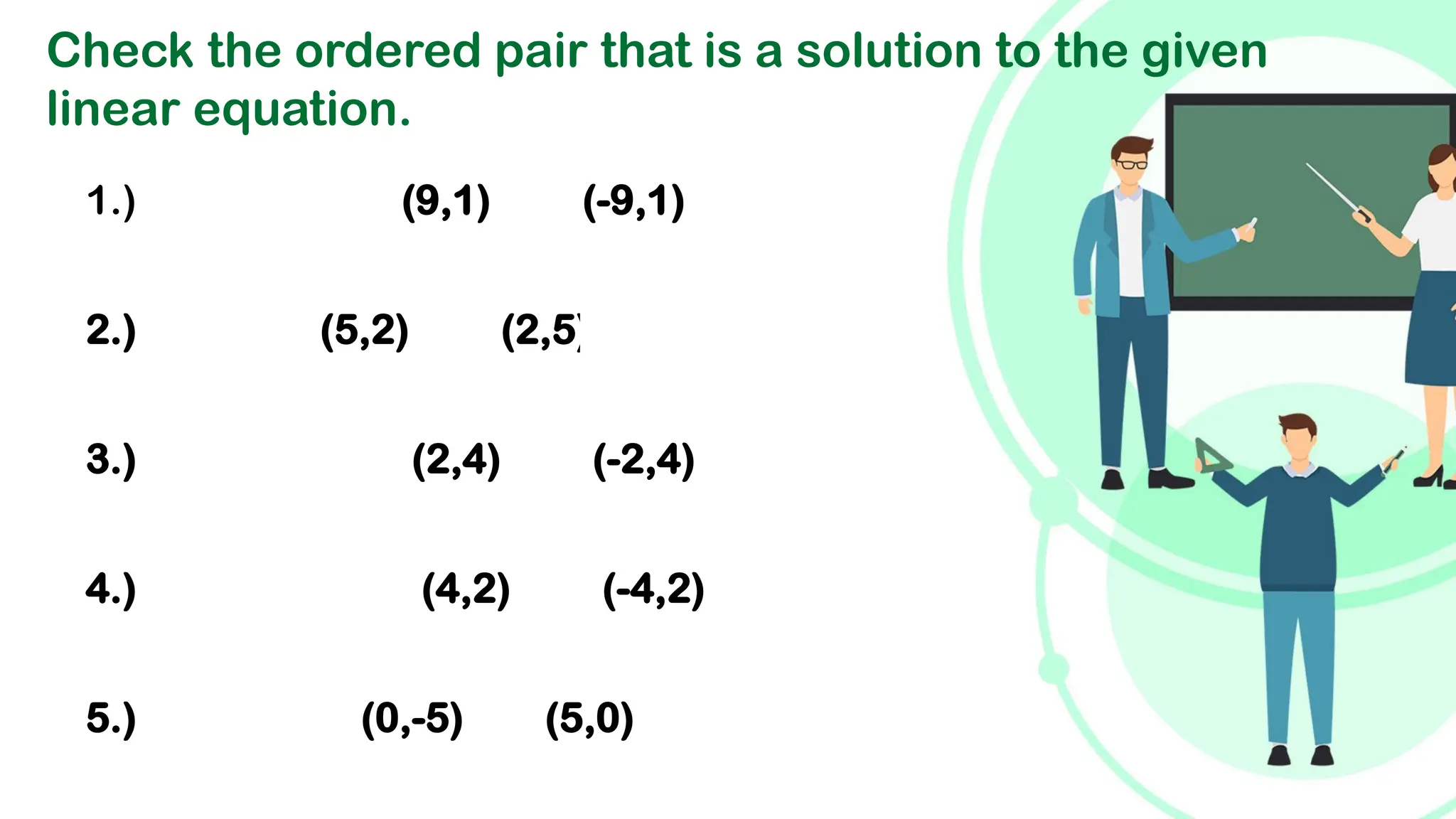
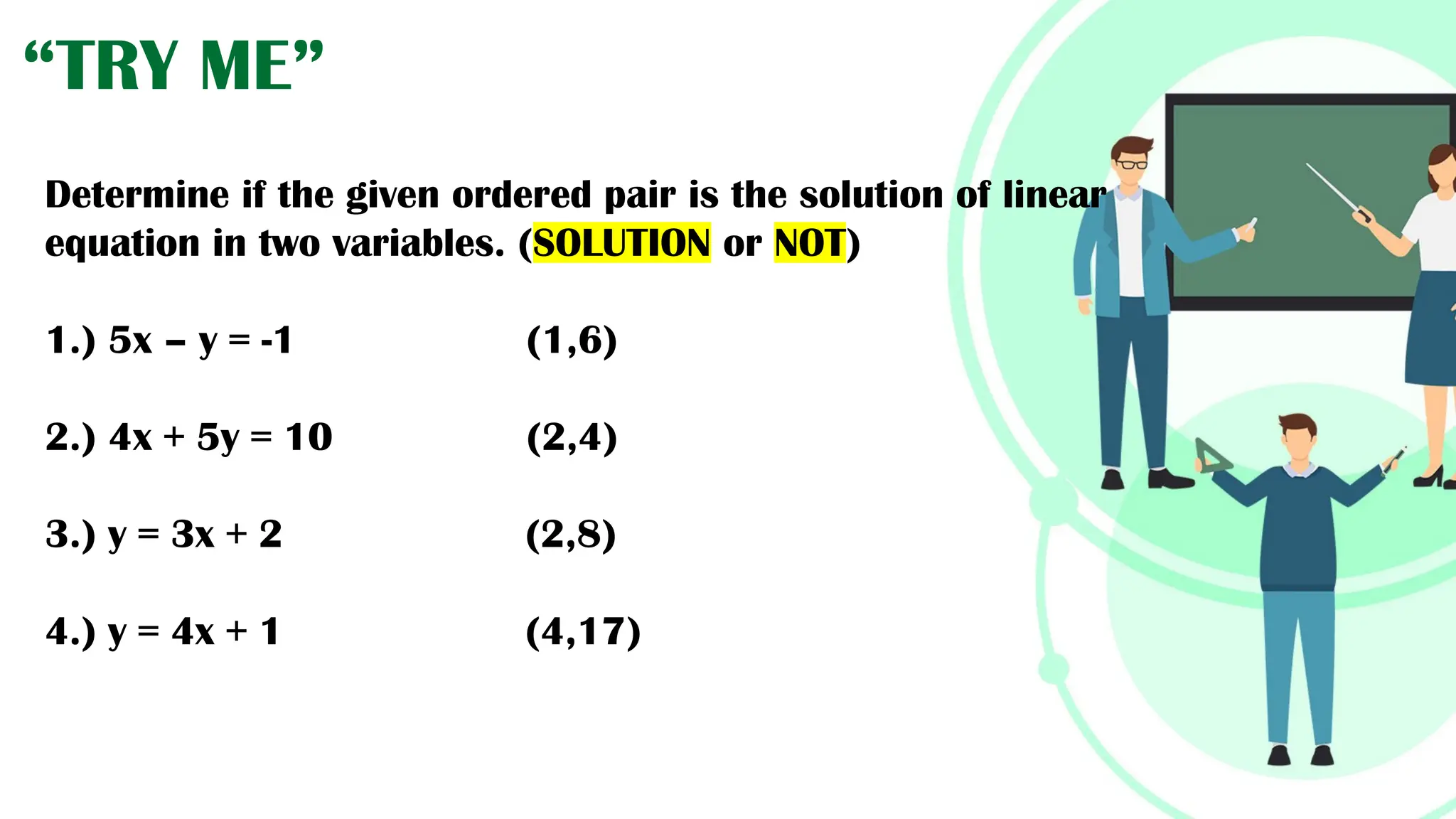
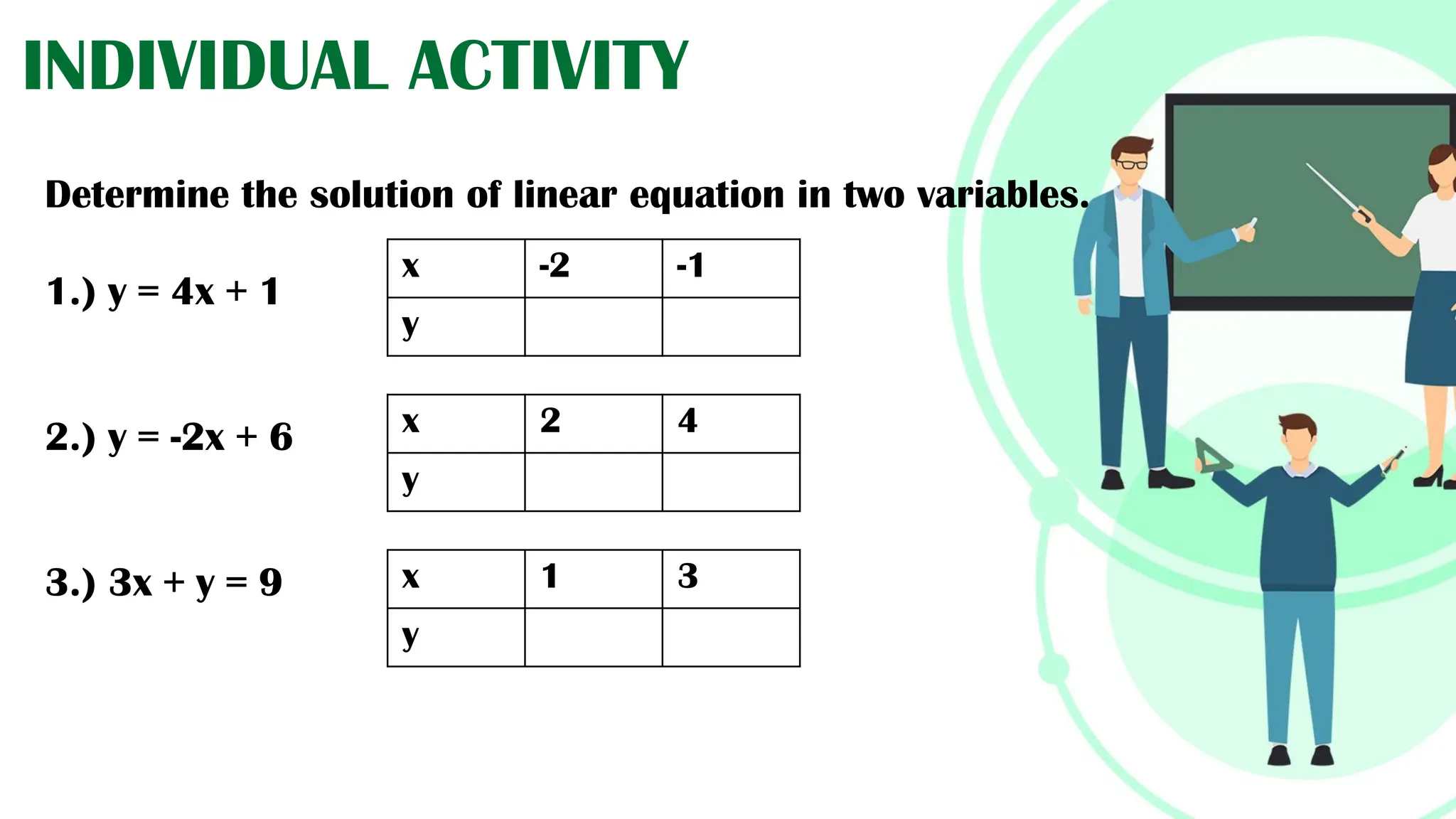
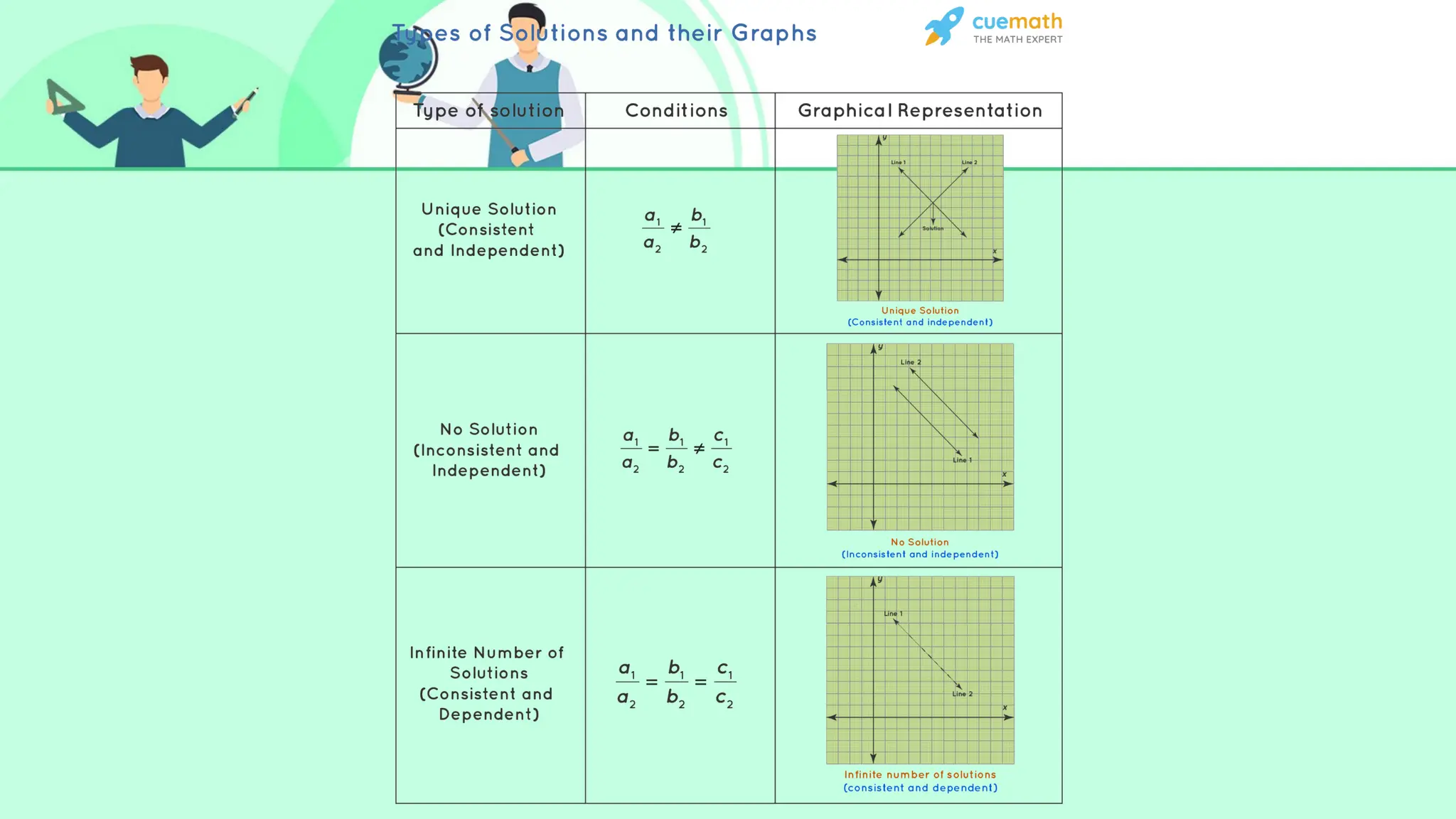
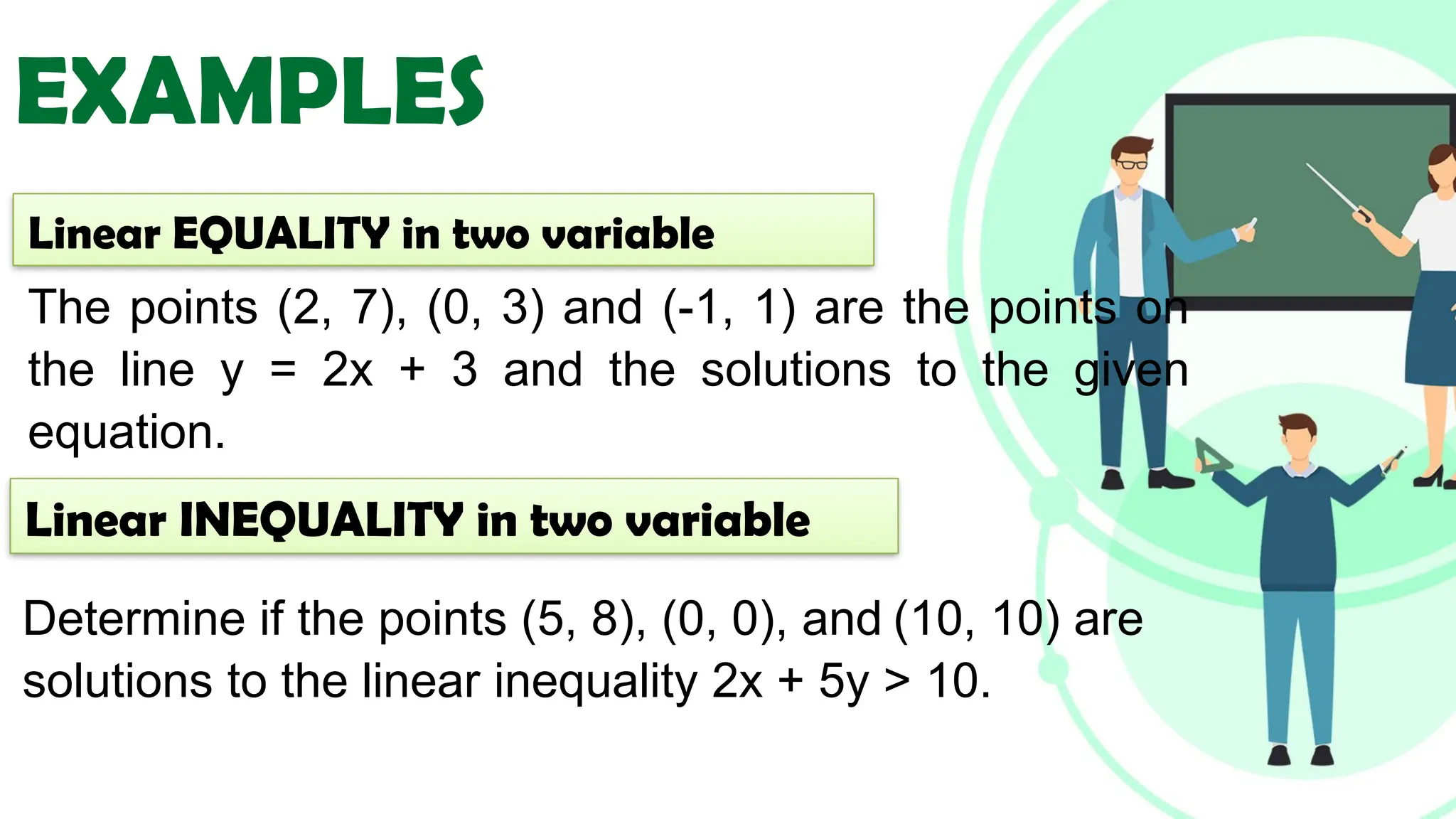
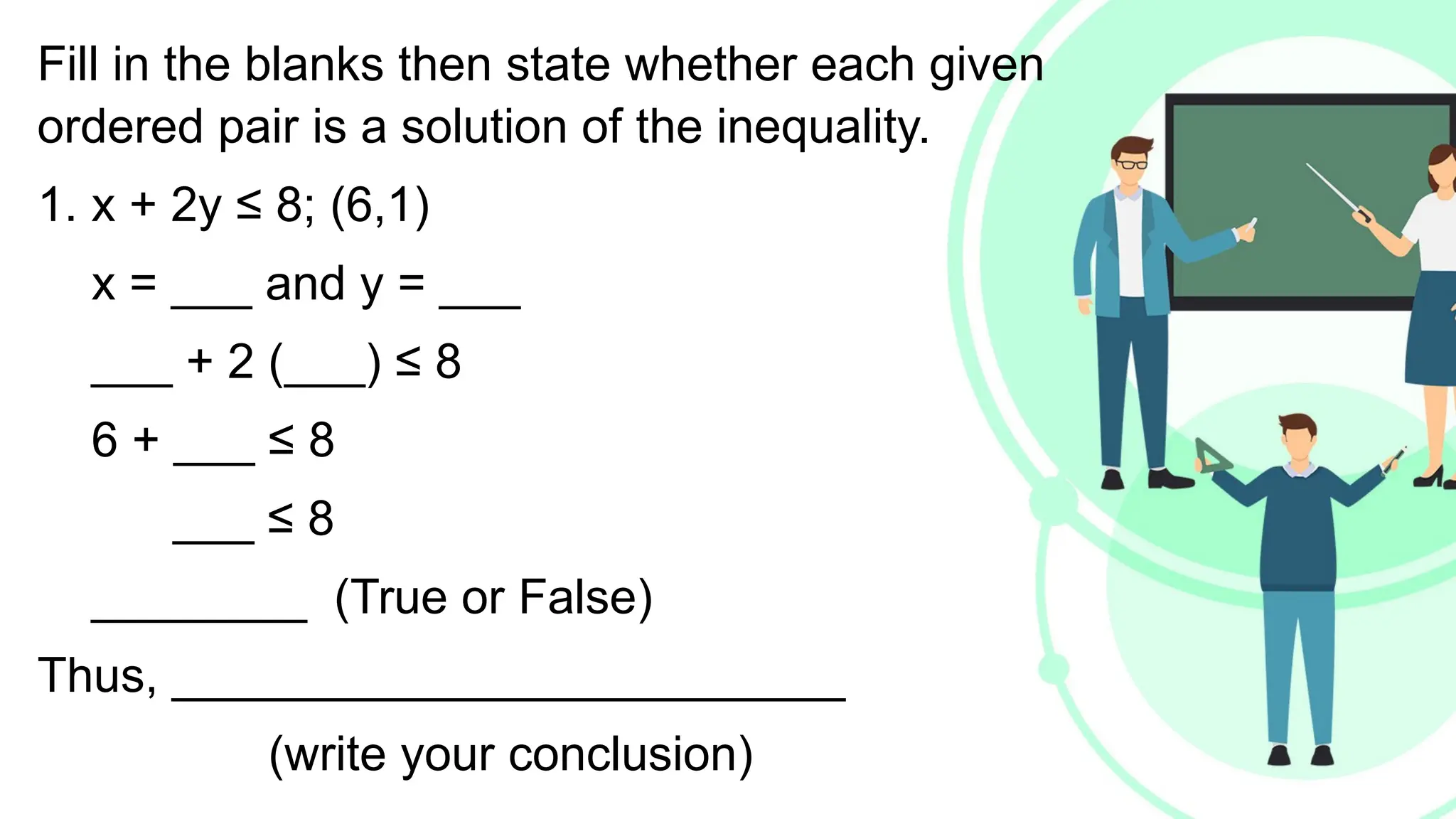
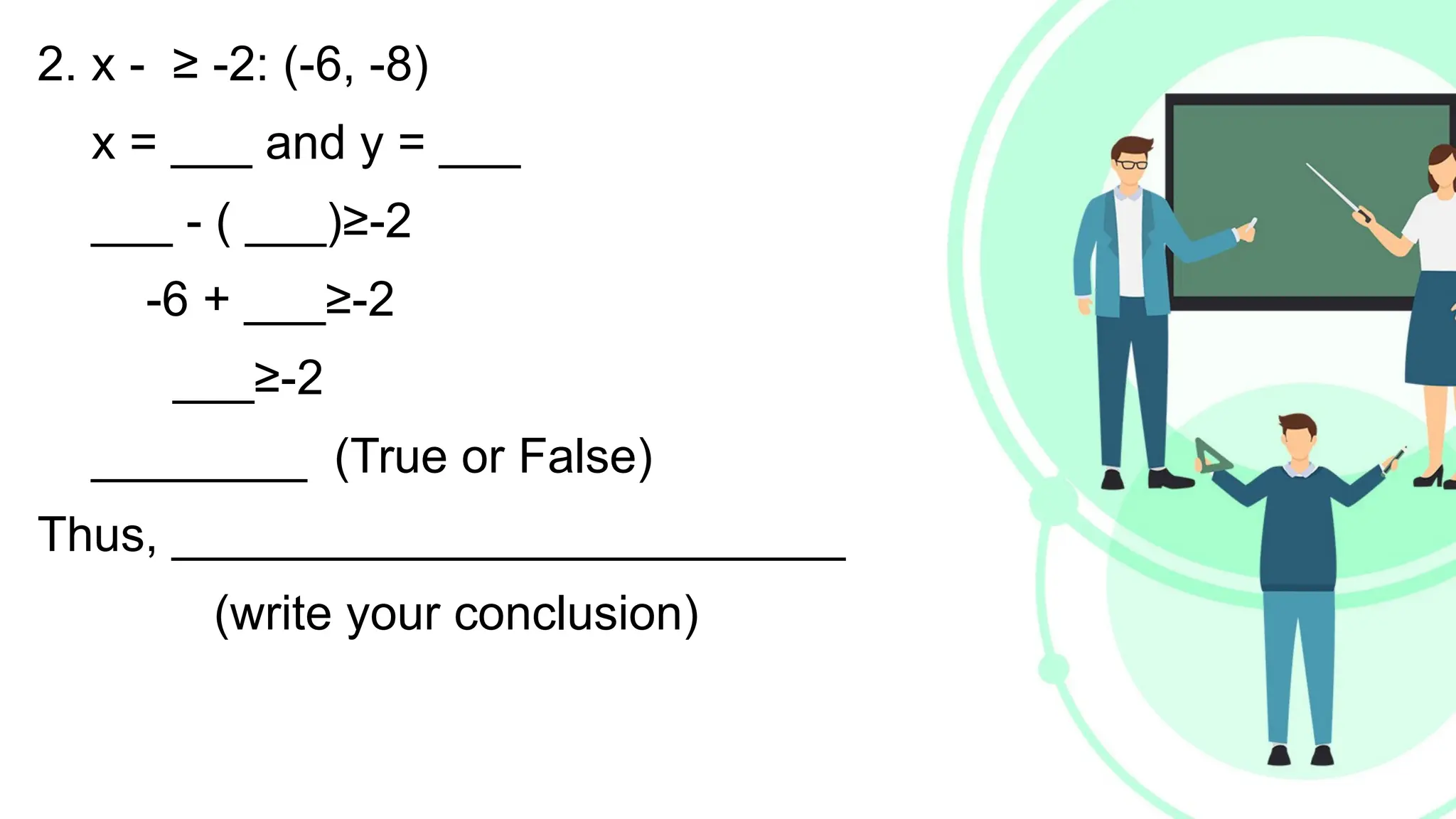
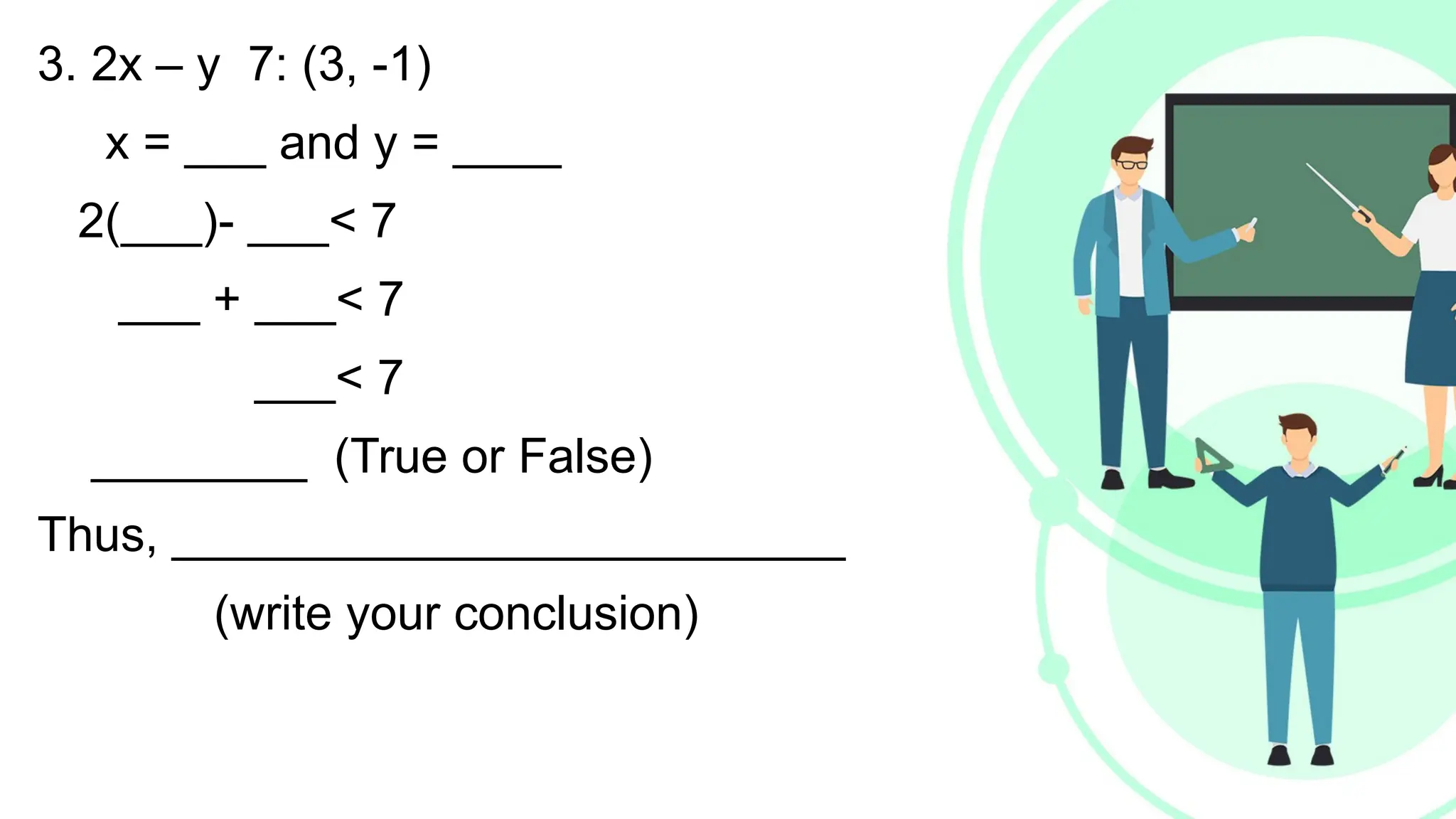
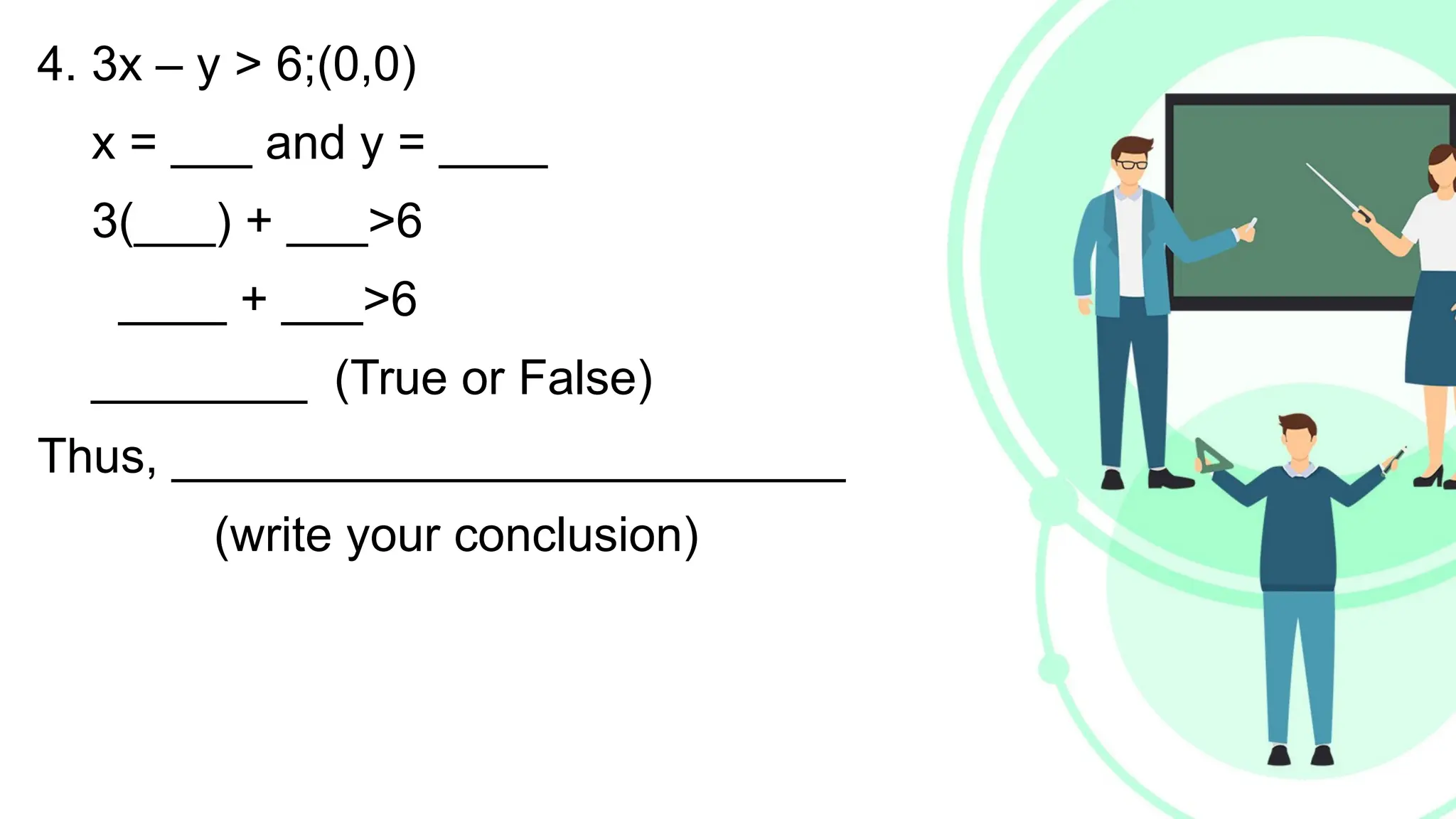
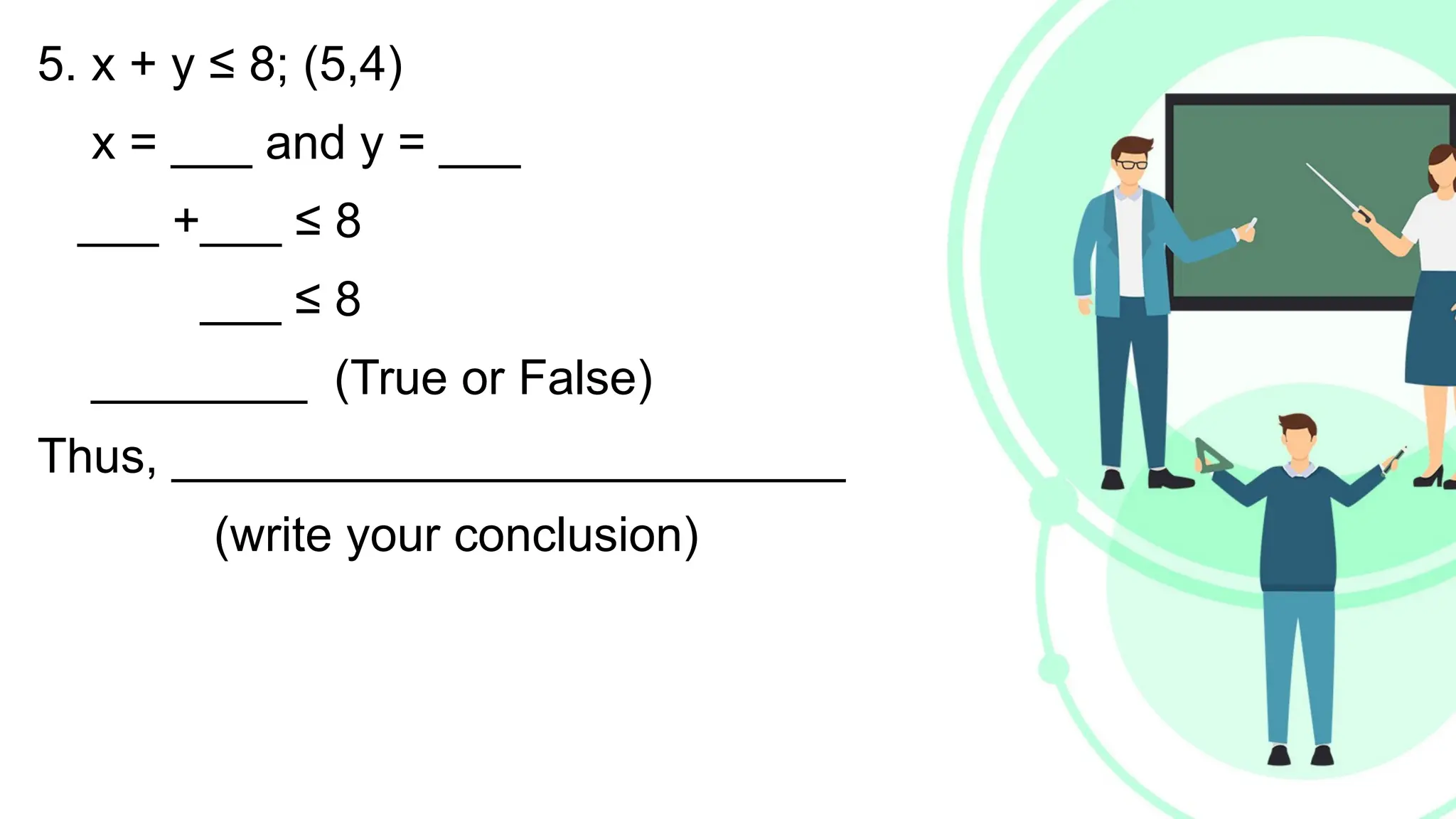
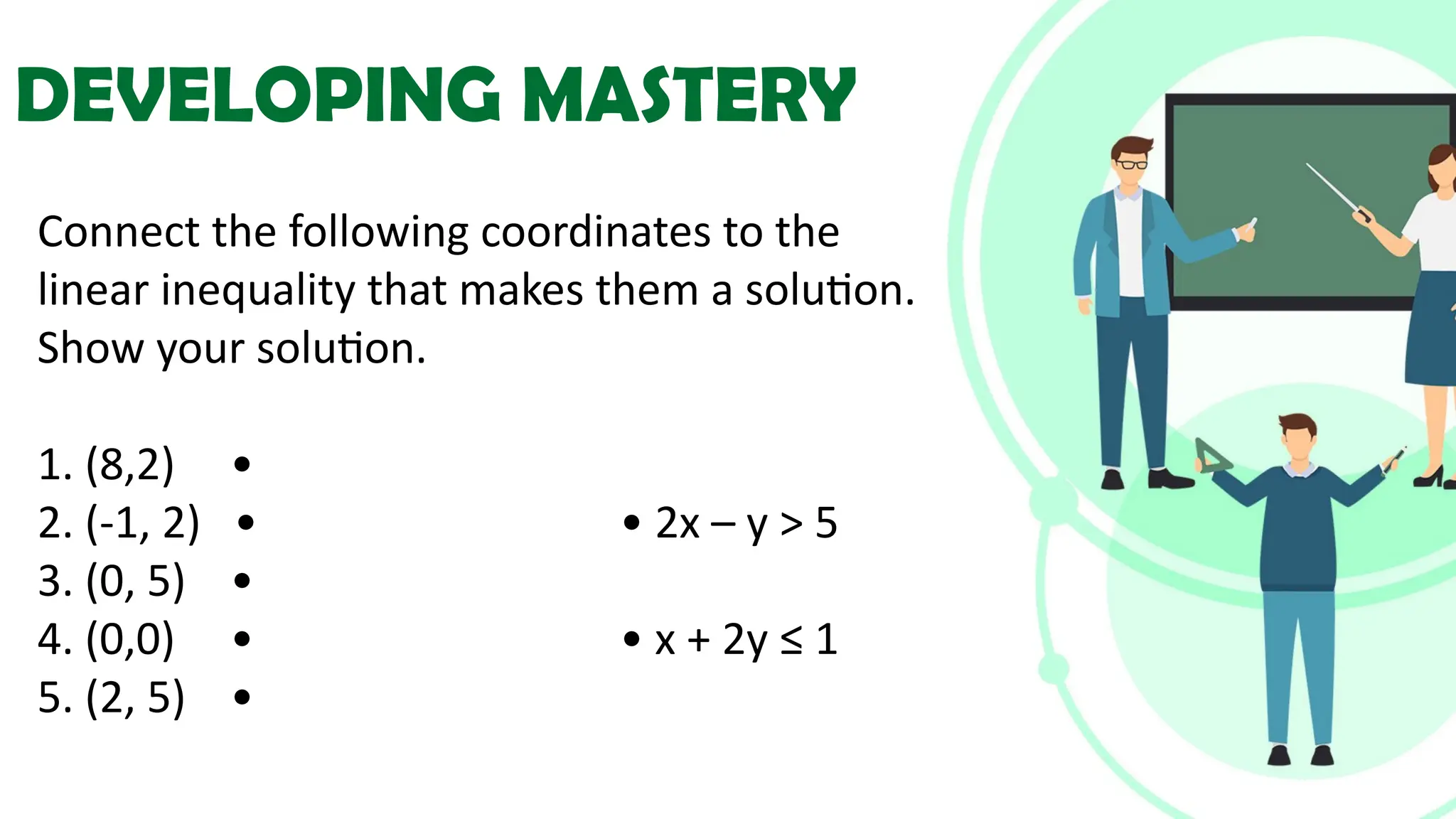
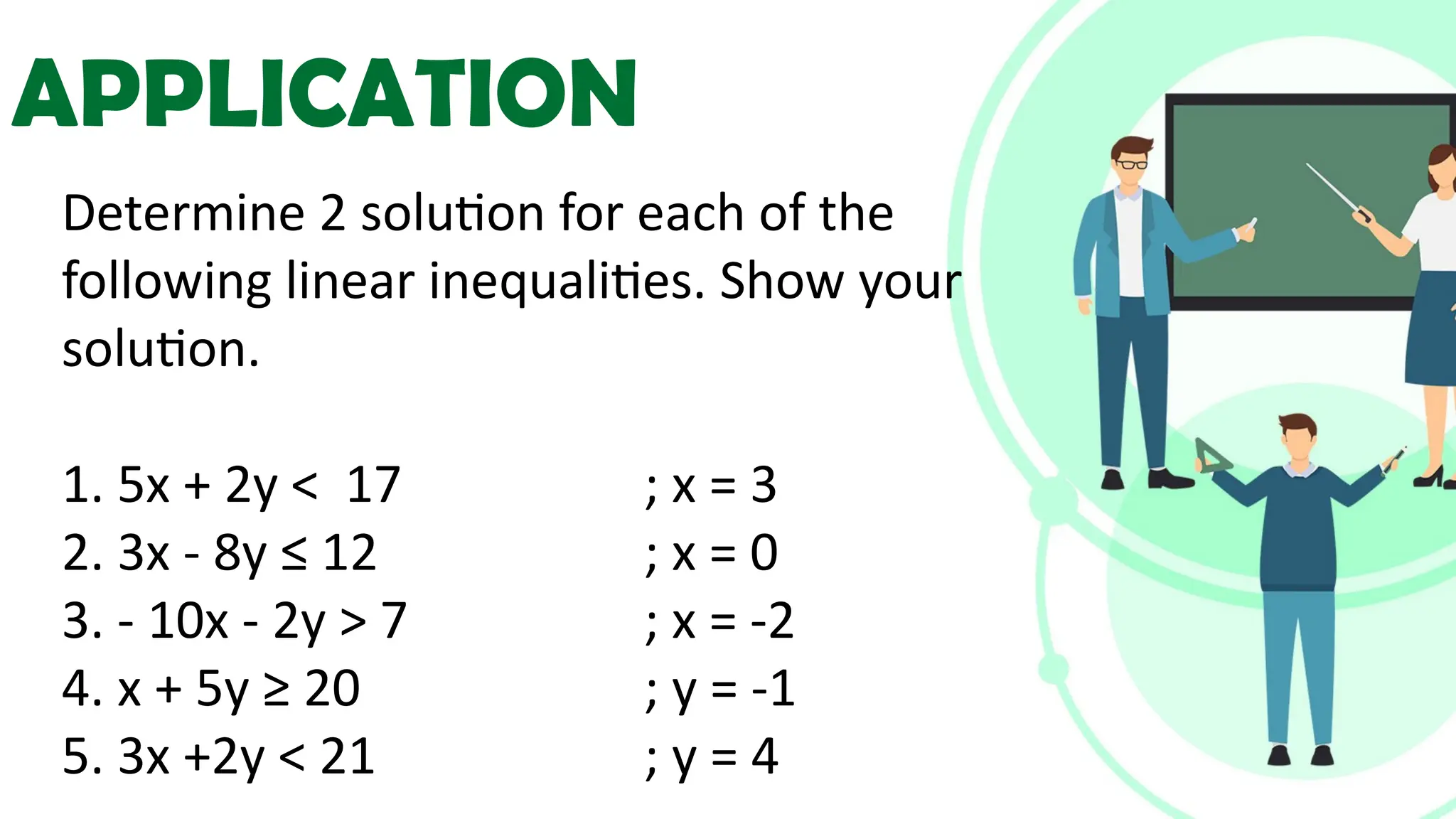
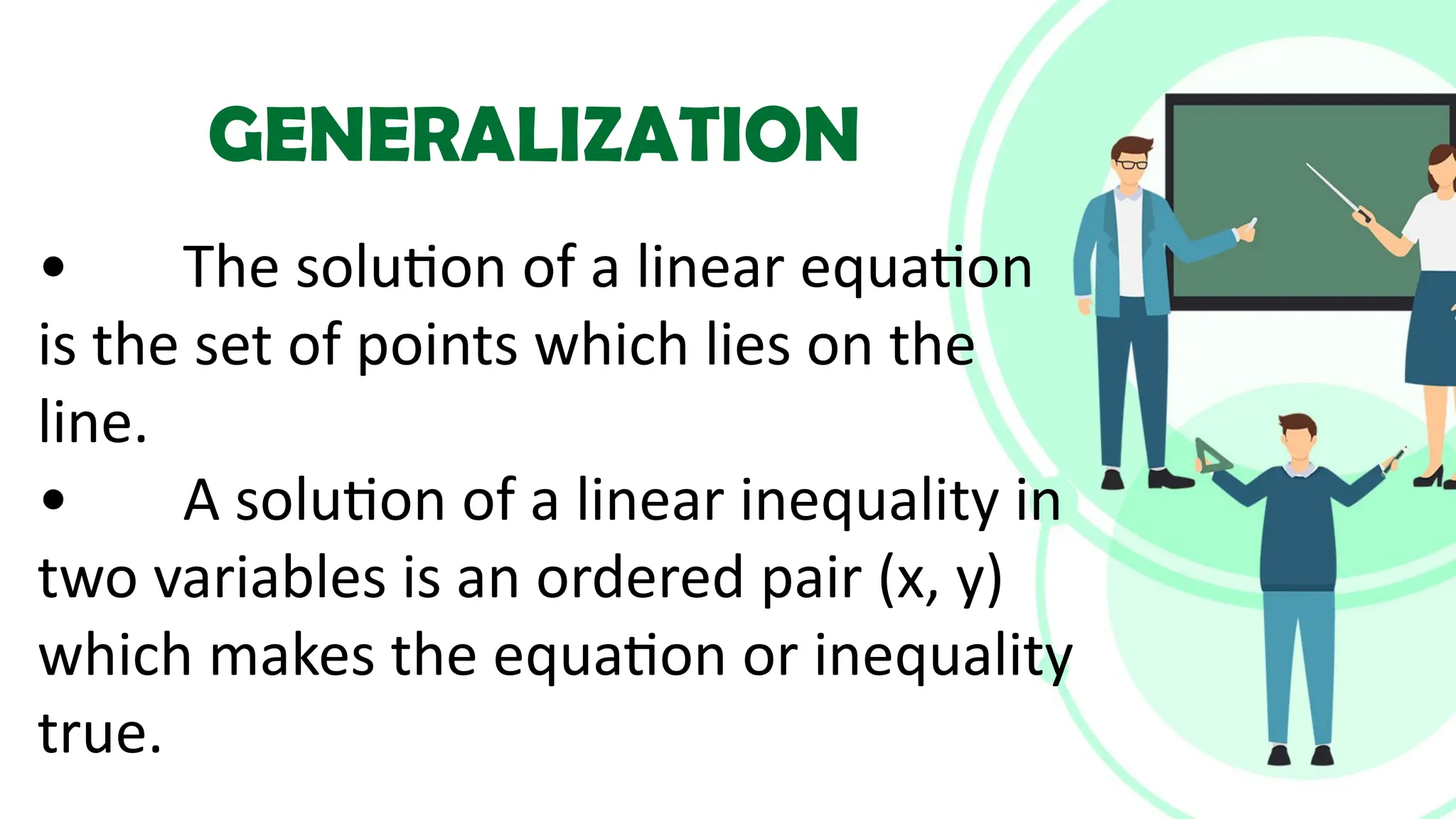
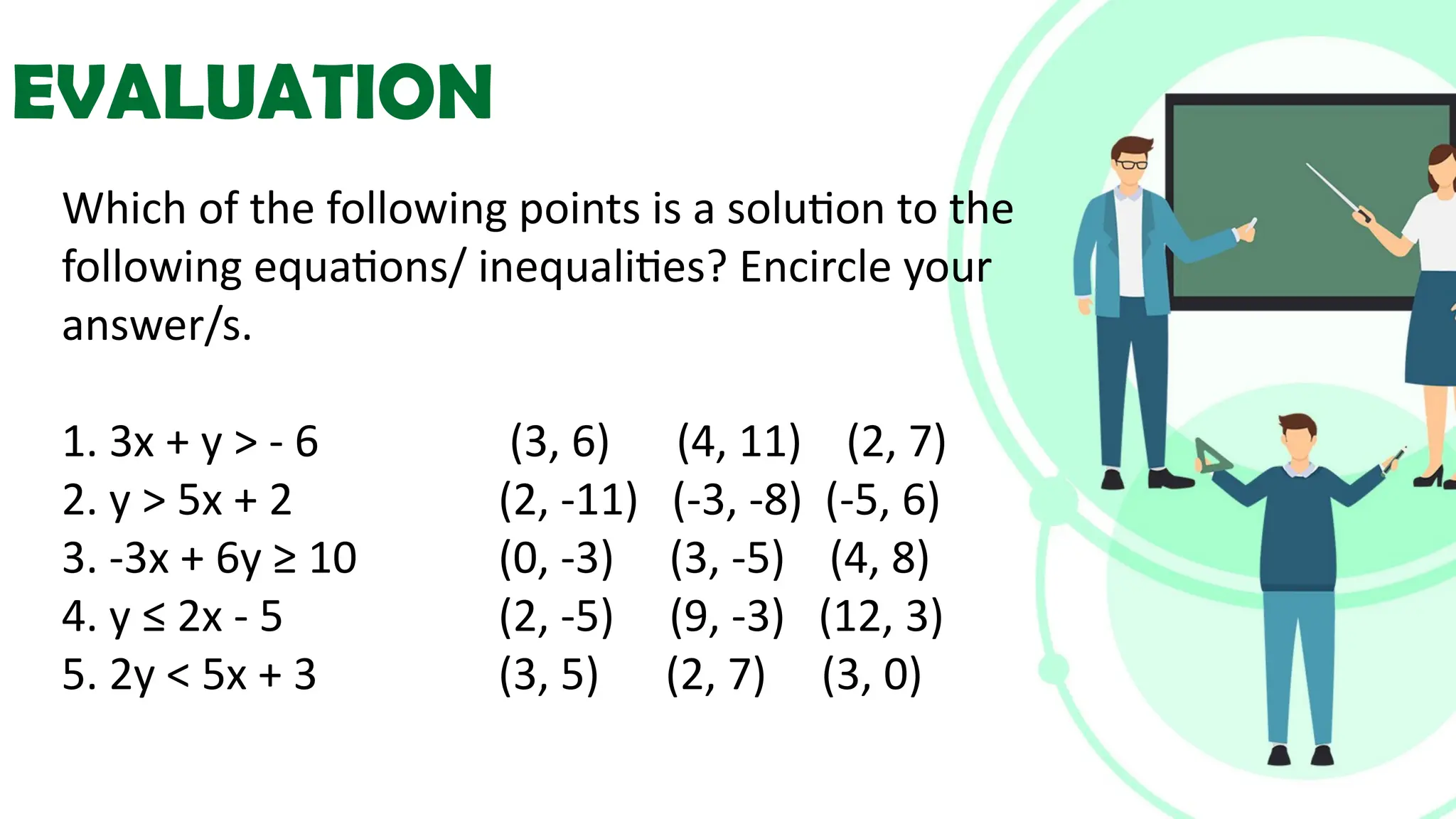
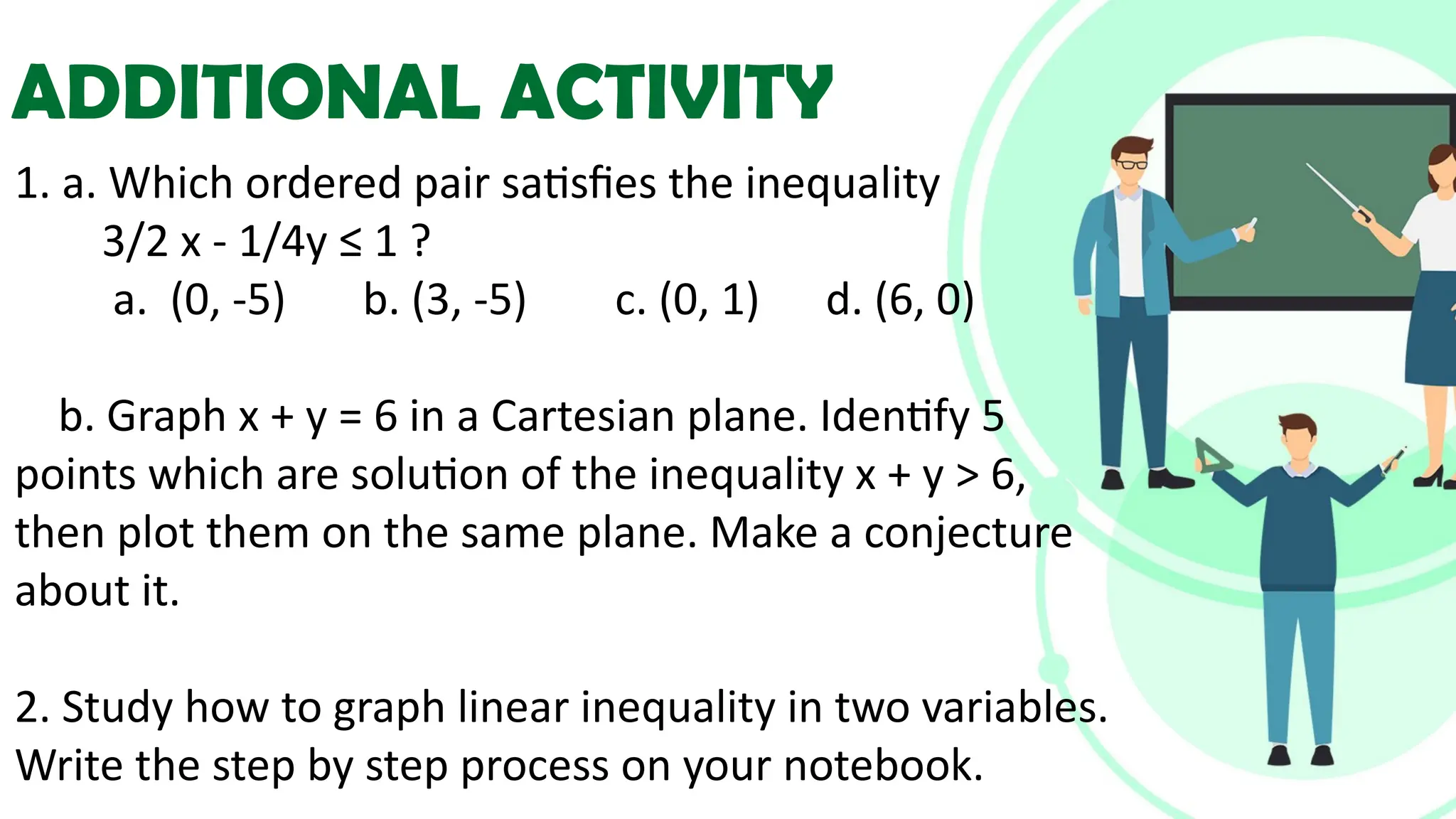
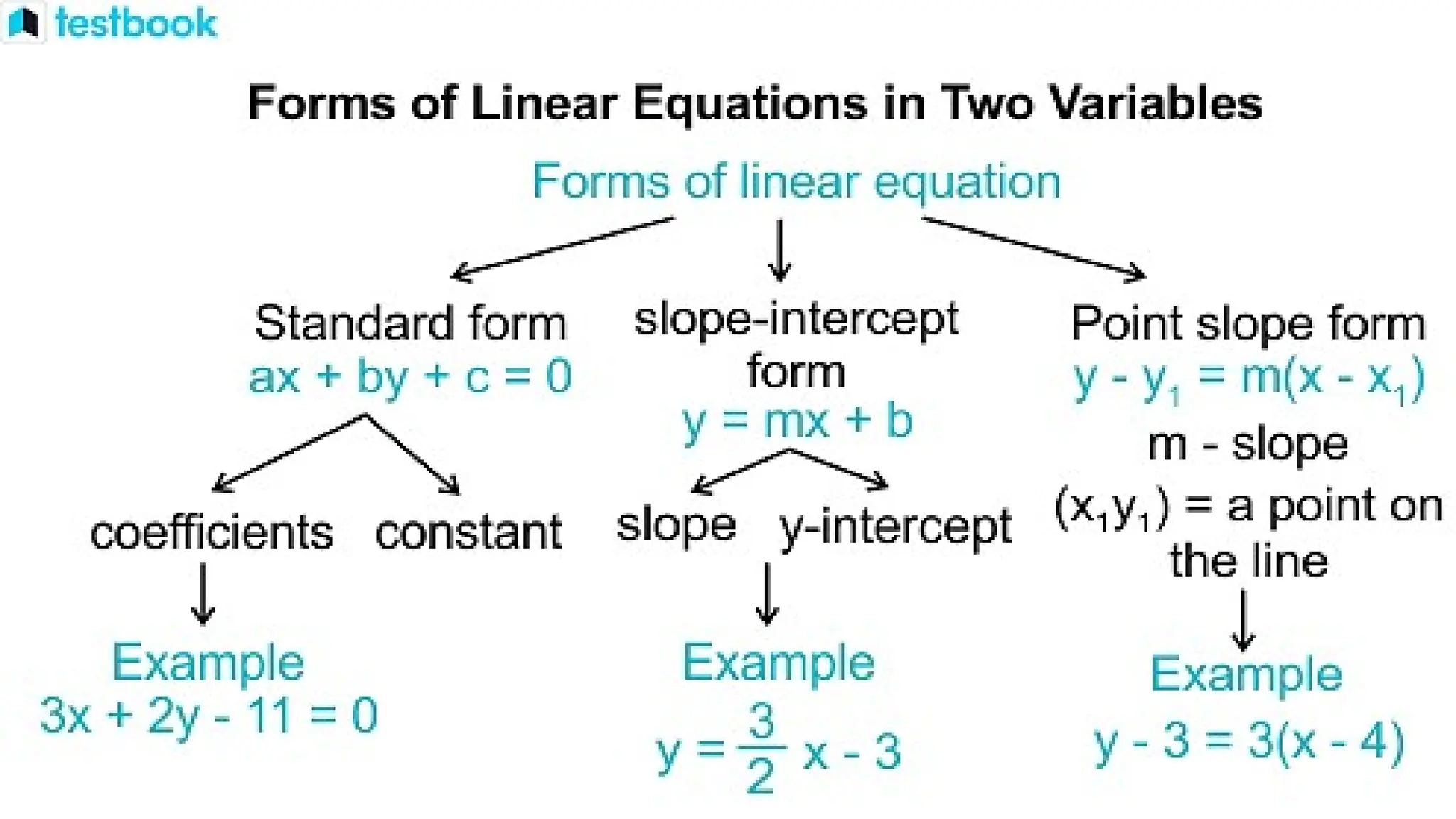
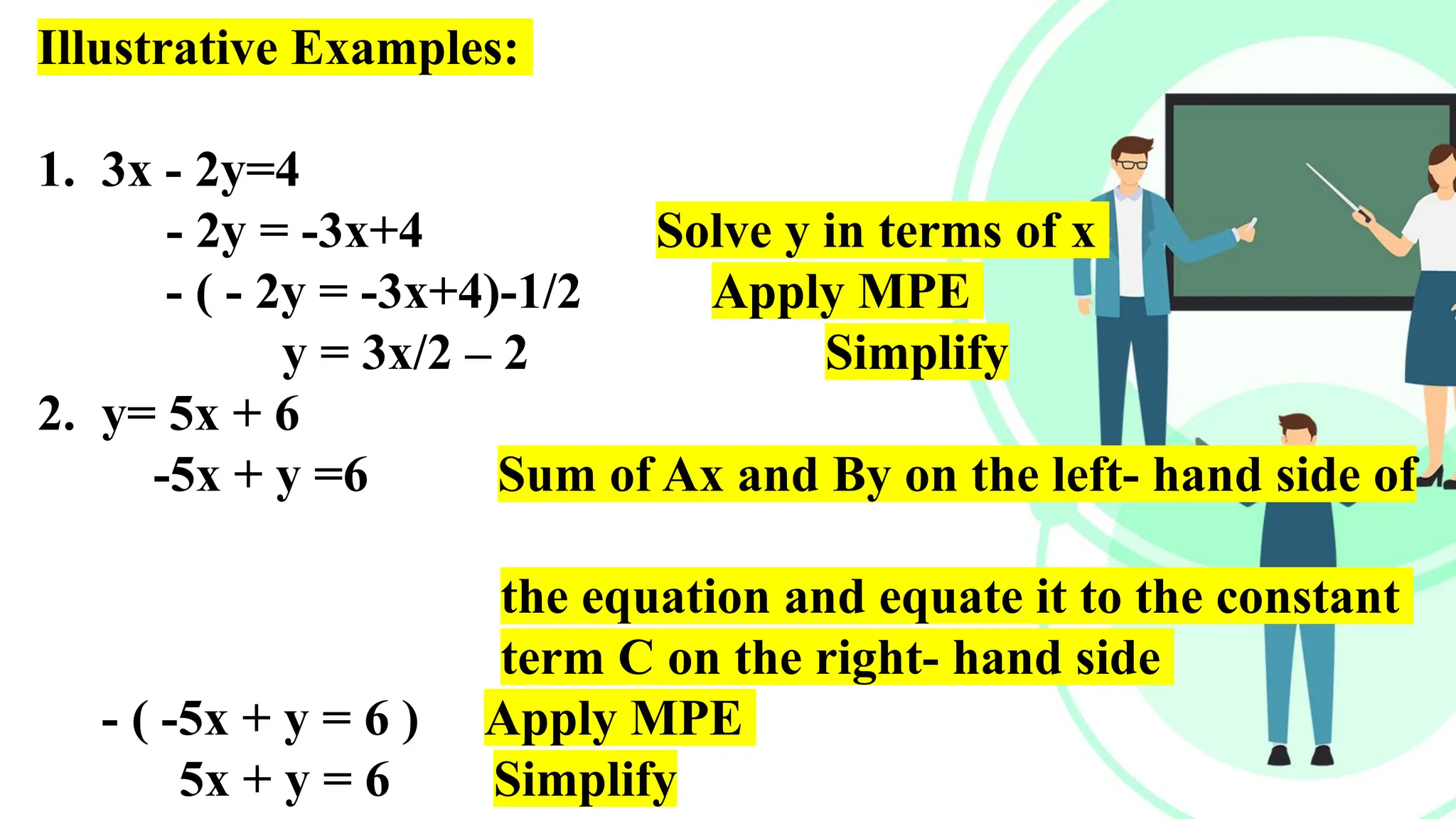
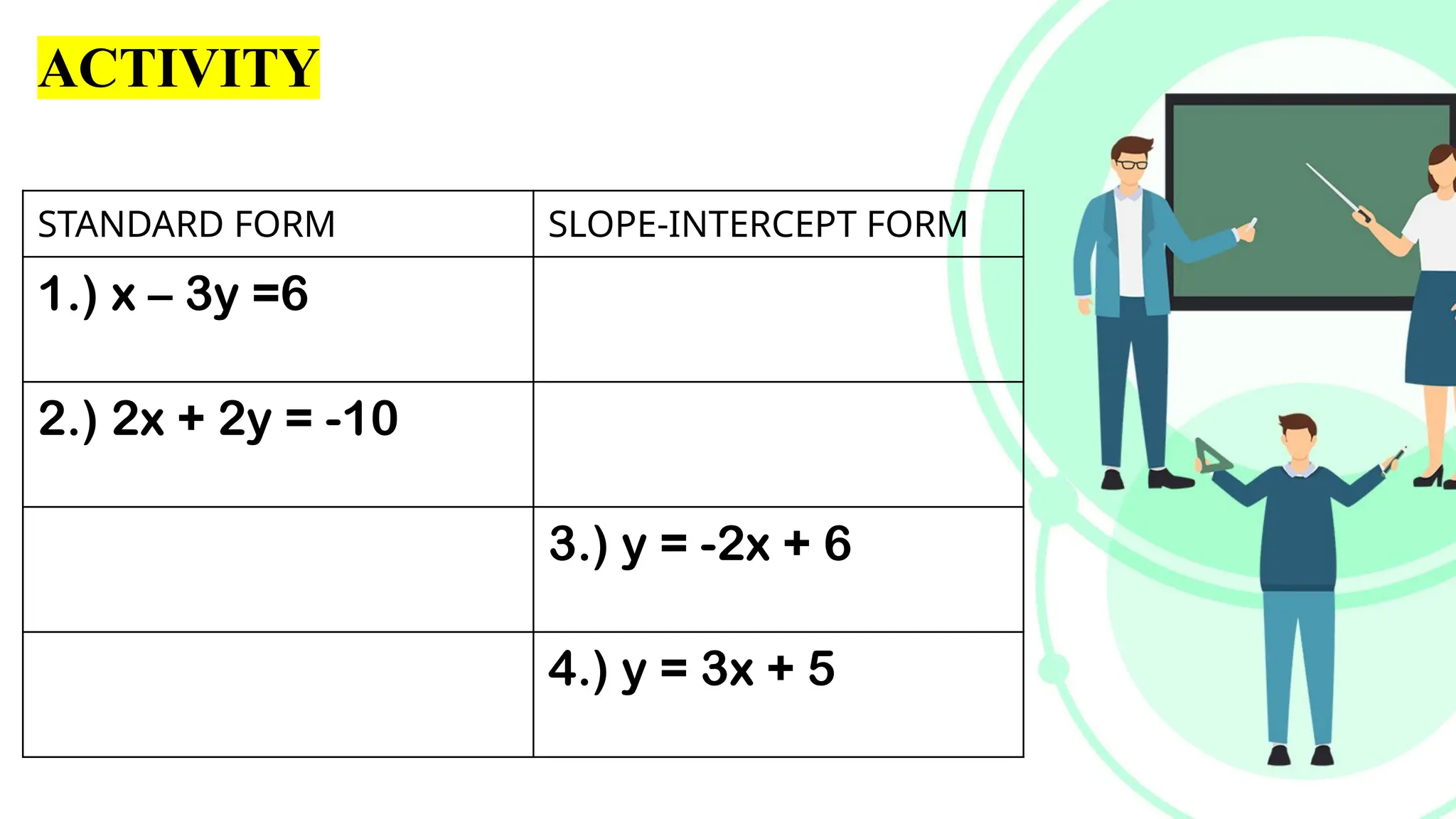
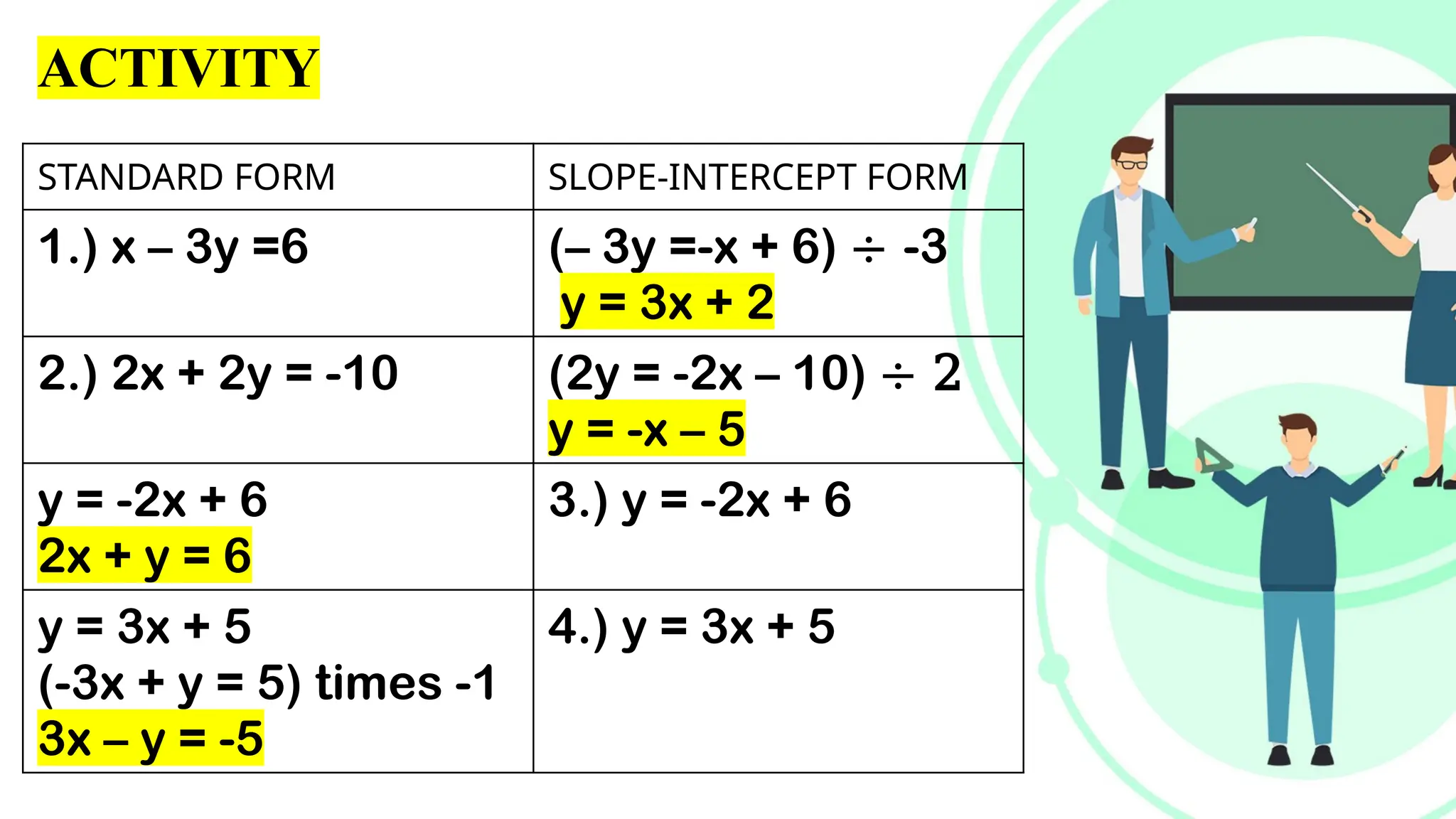
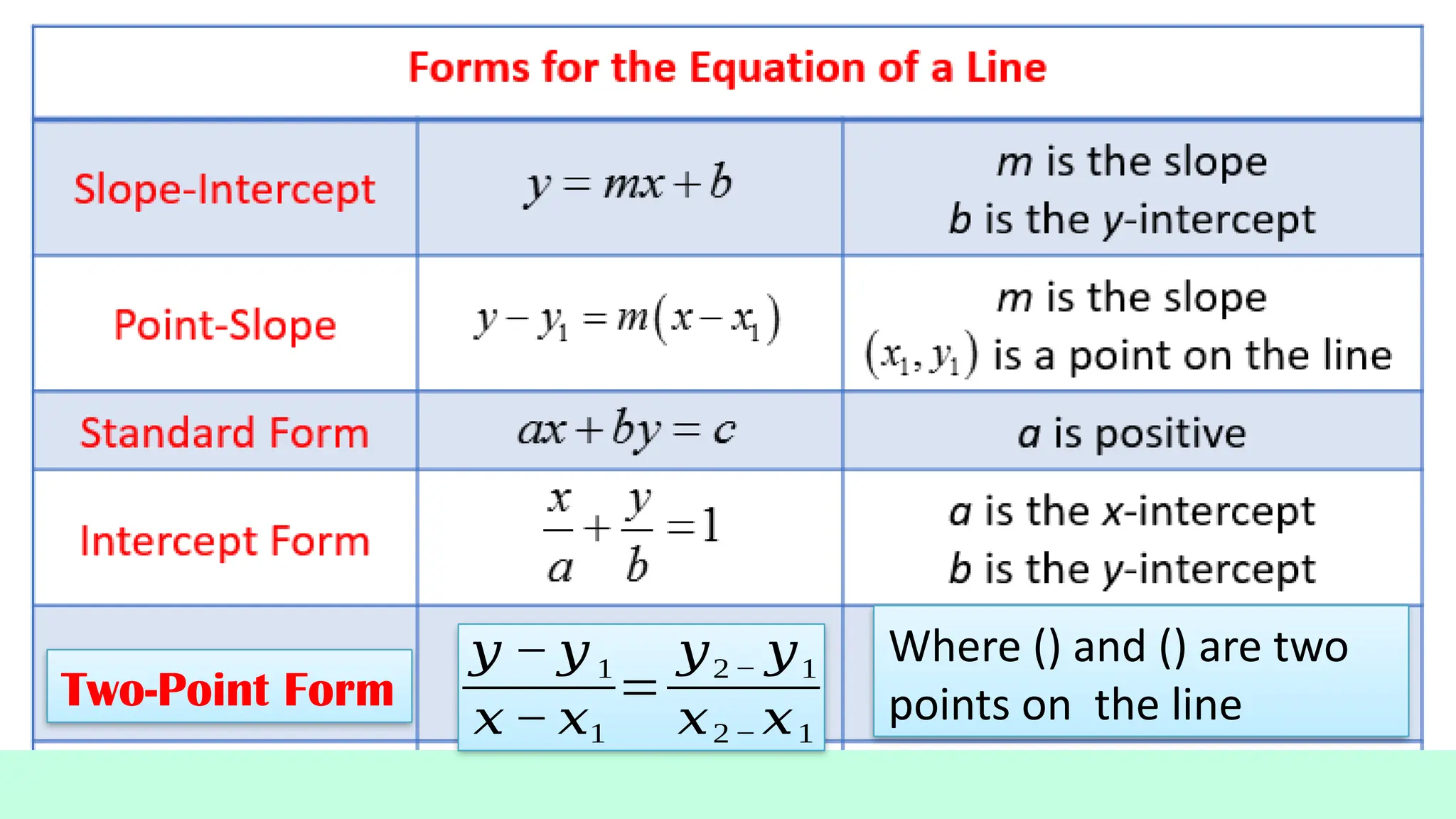
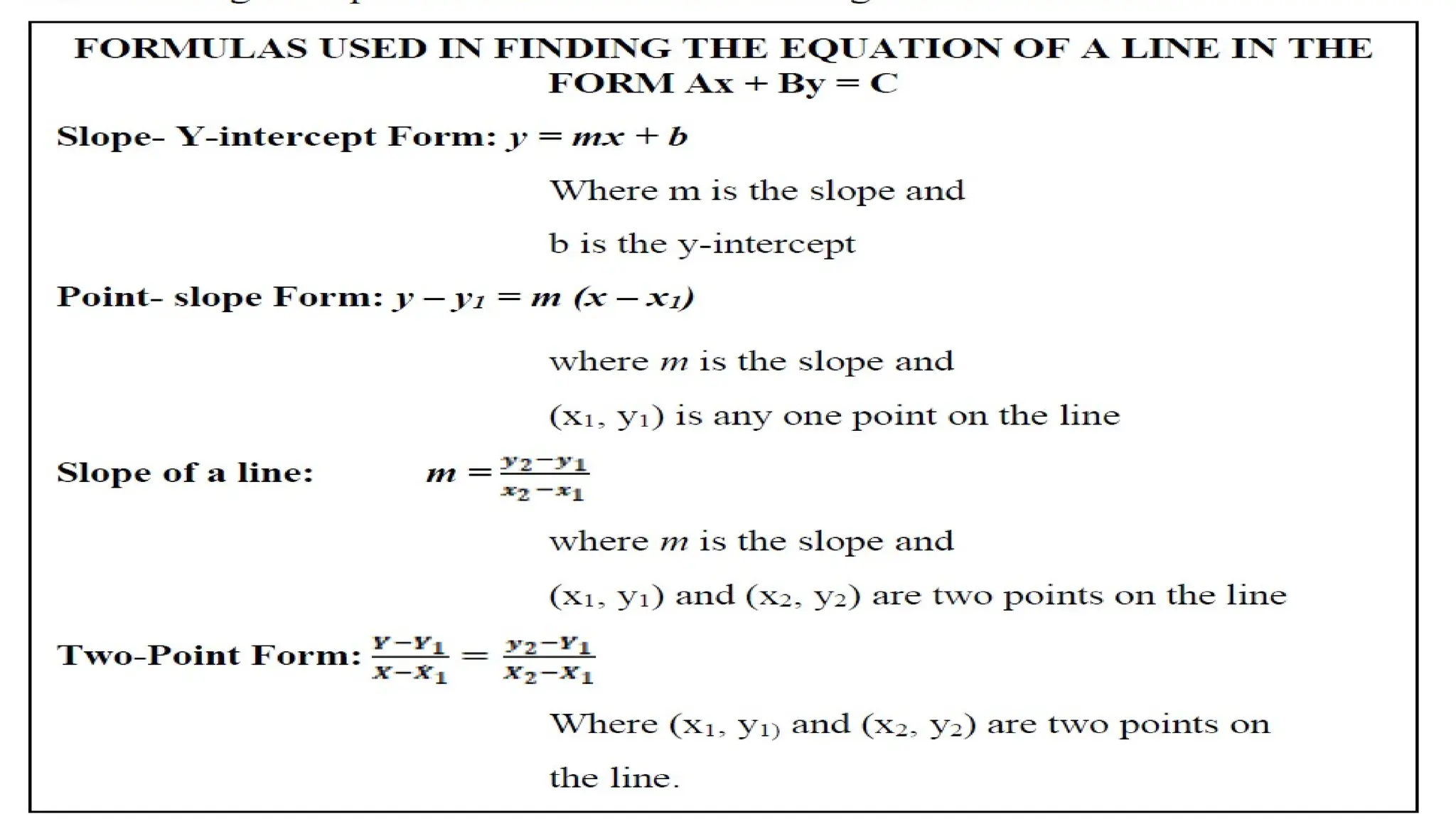
Linear equations in two variables are expressed as ax + by + c = 0, where a, b, and c are real numbers and a and b are non-zero, commonly used in geometry for line coordinates. Solutions are ordered pairs (x, y) that satisfy the equation, with techniques to verify and determine solutions for given points or inequalities. The document also covers converting equations between standard and slope-intercept forms, alongside examples and applications involving linear inequalities.