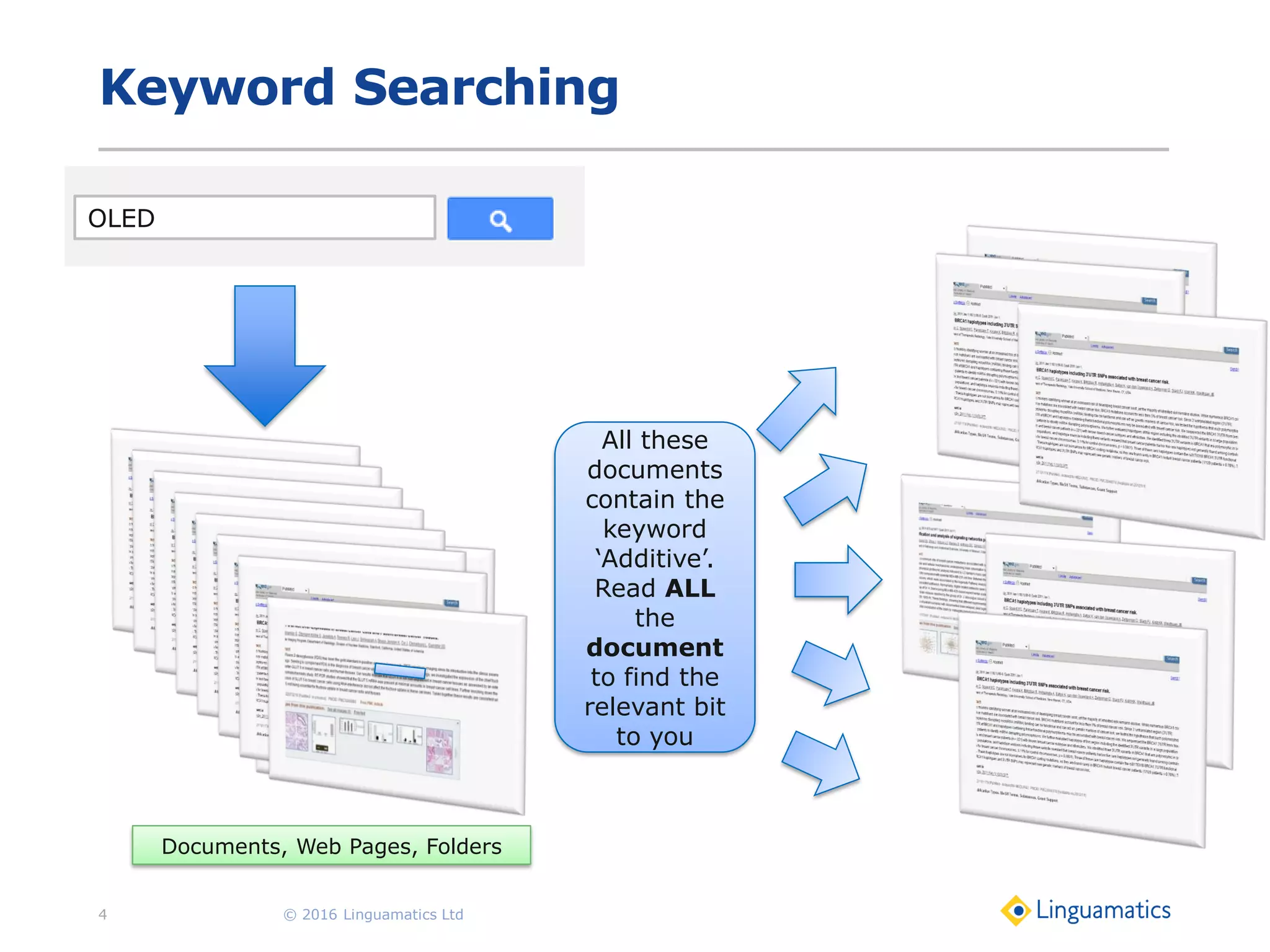
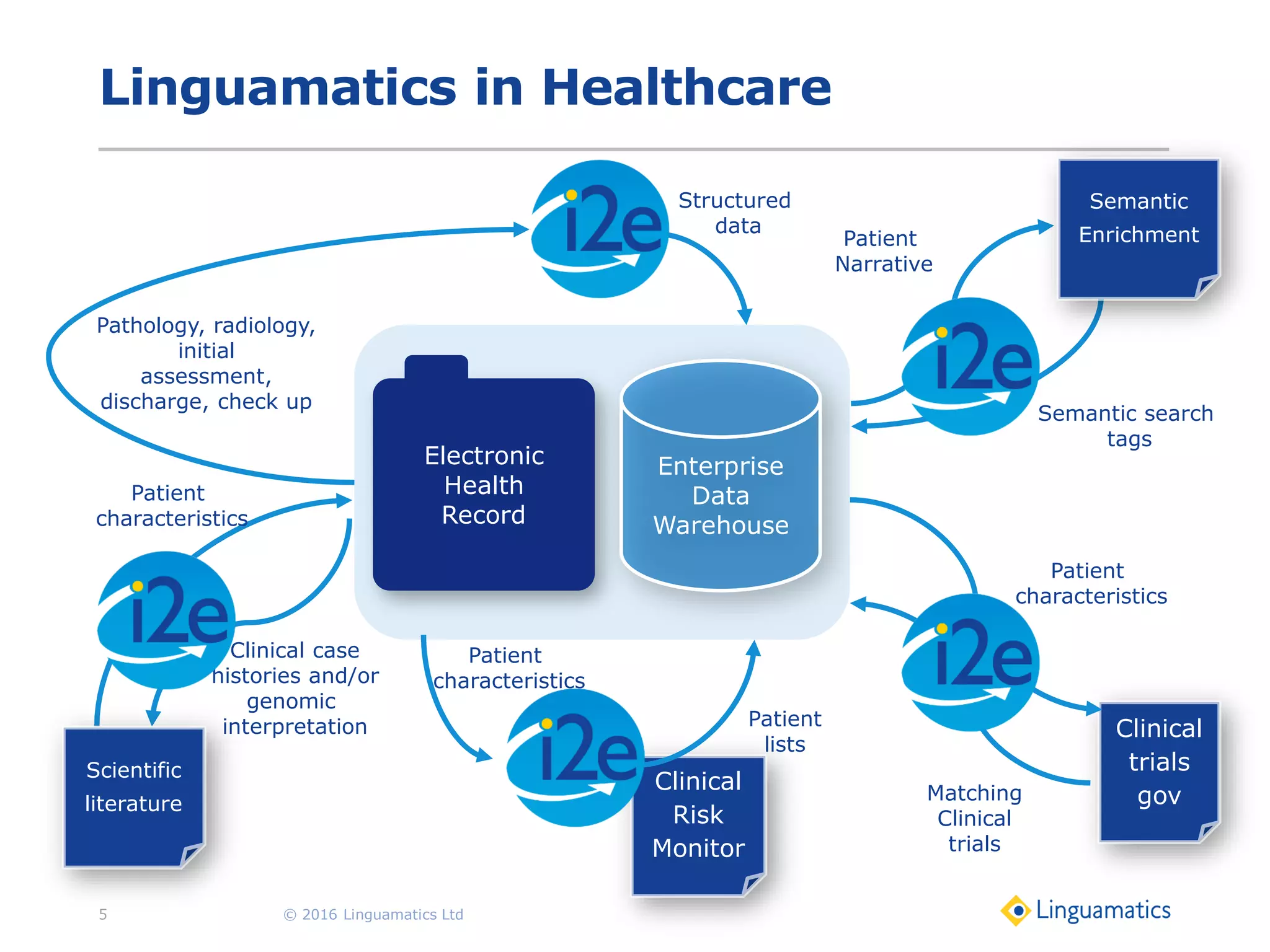
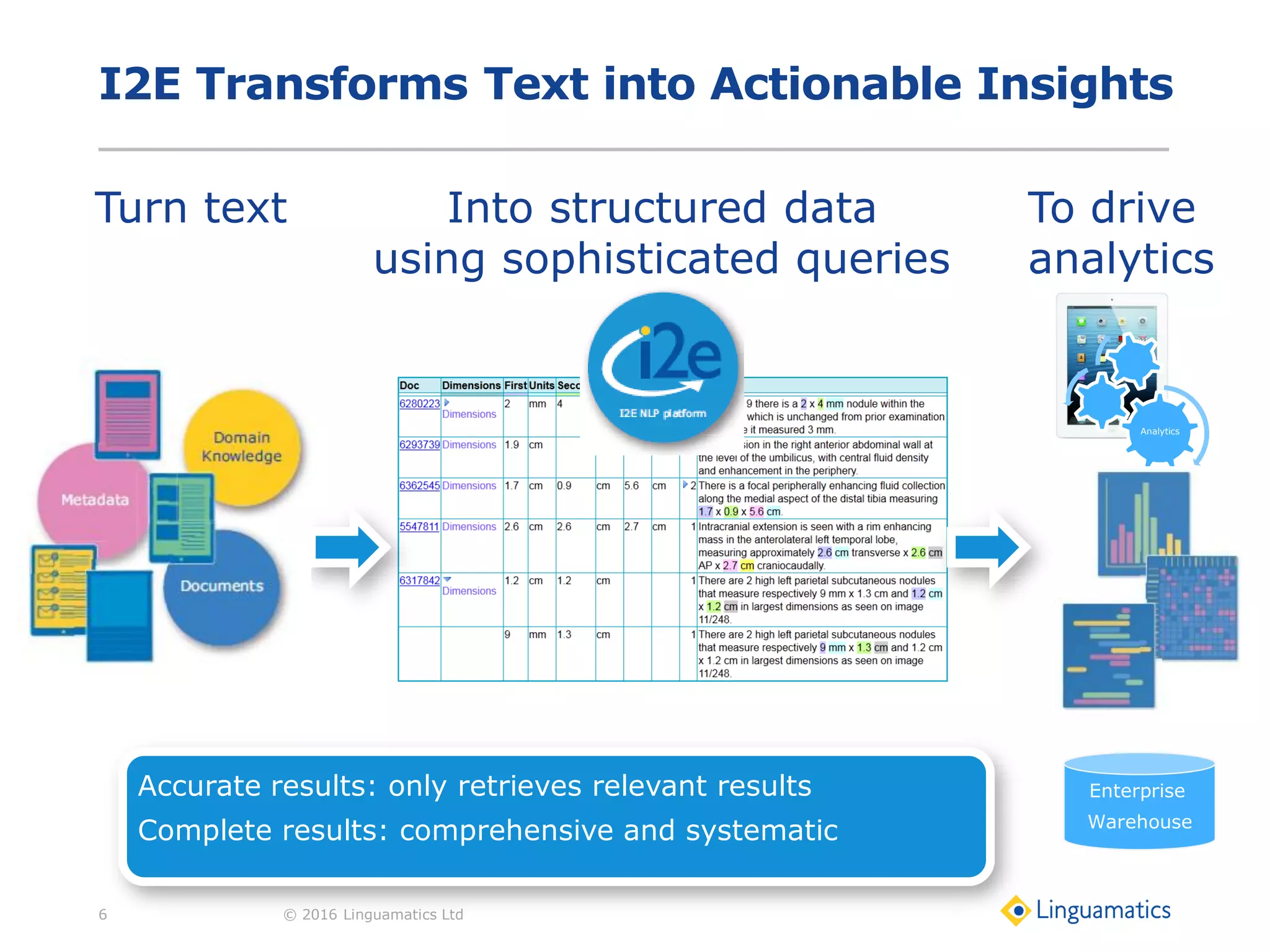
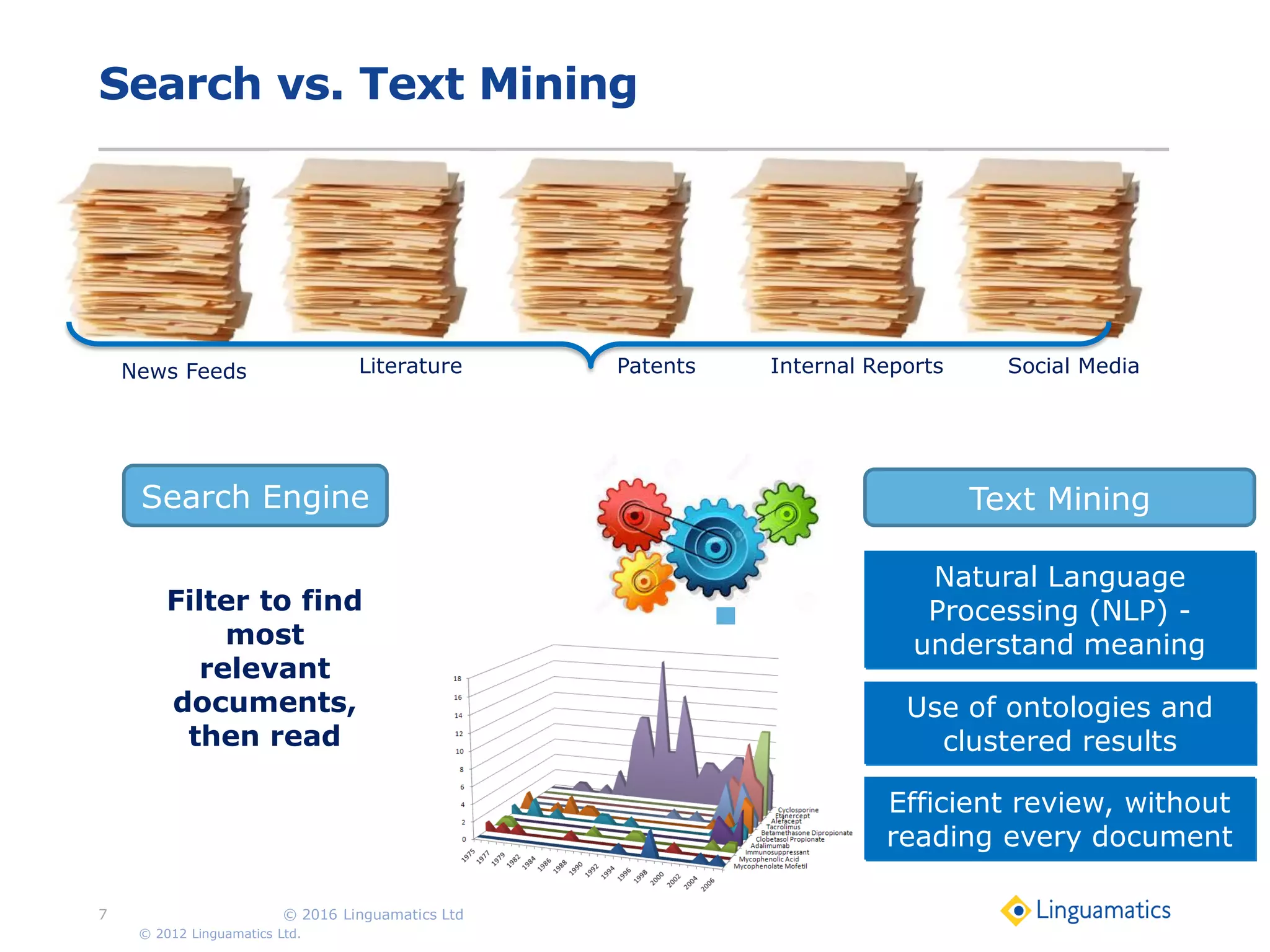
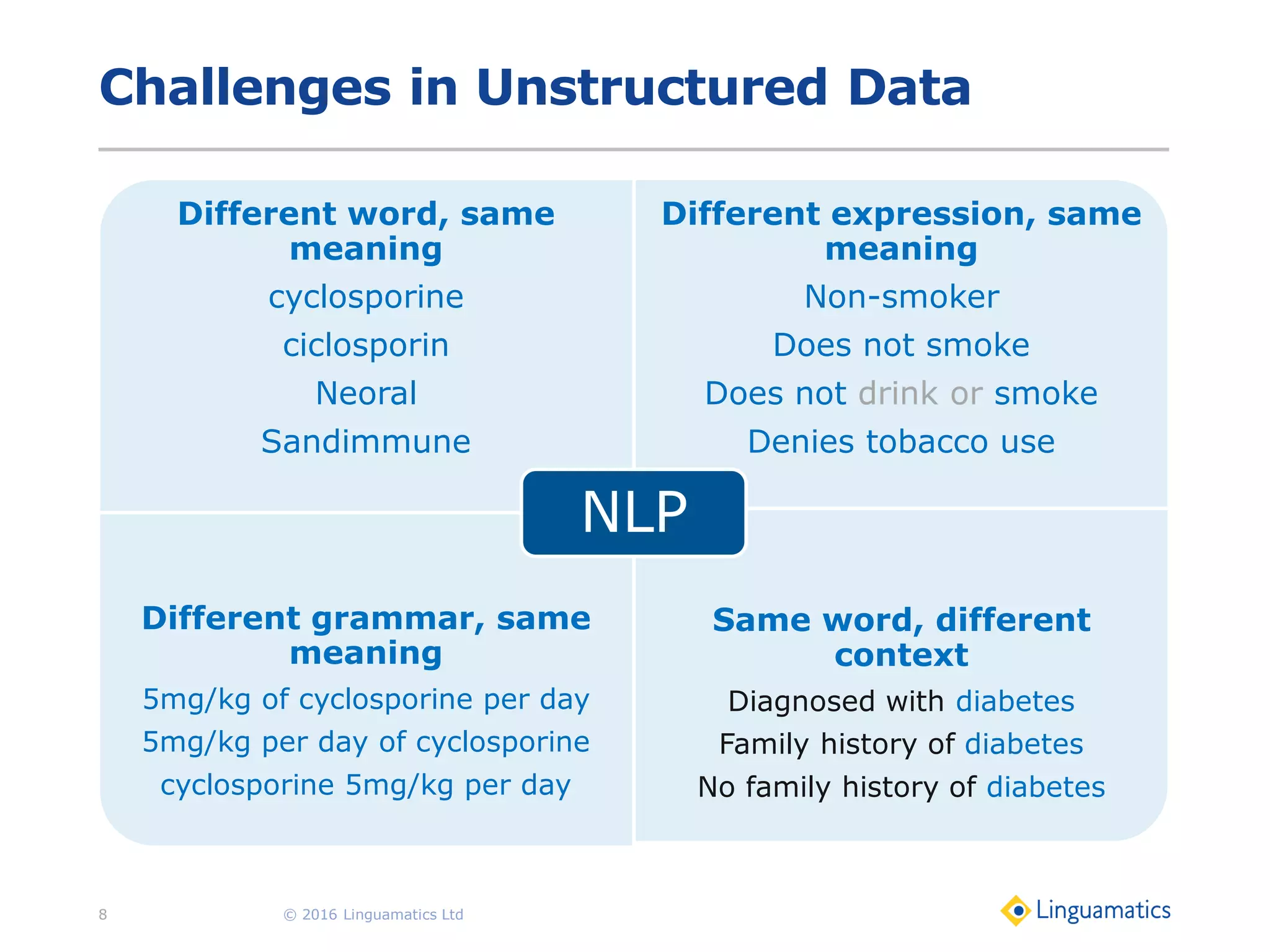
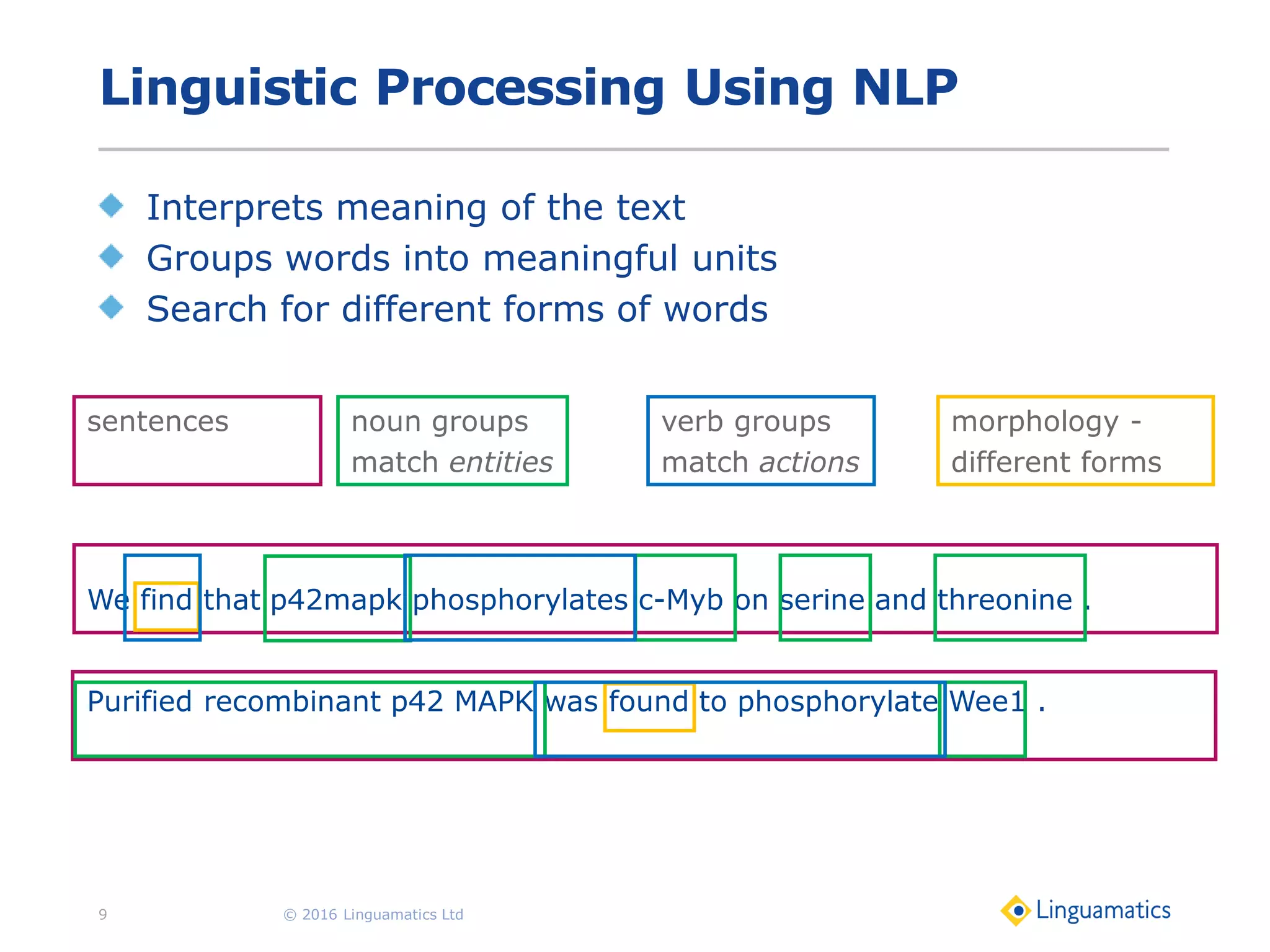
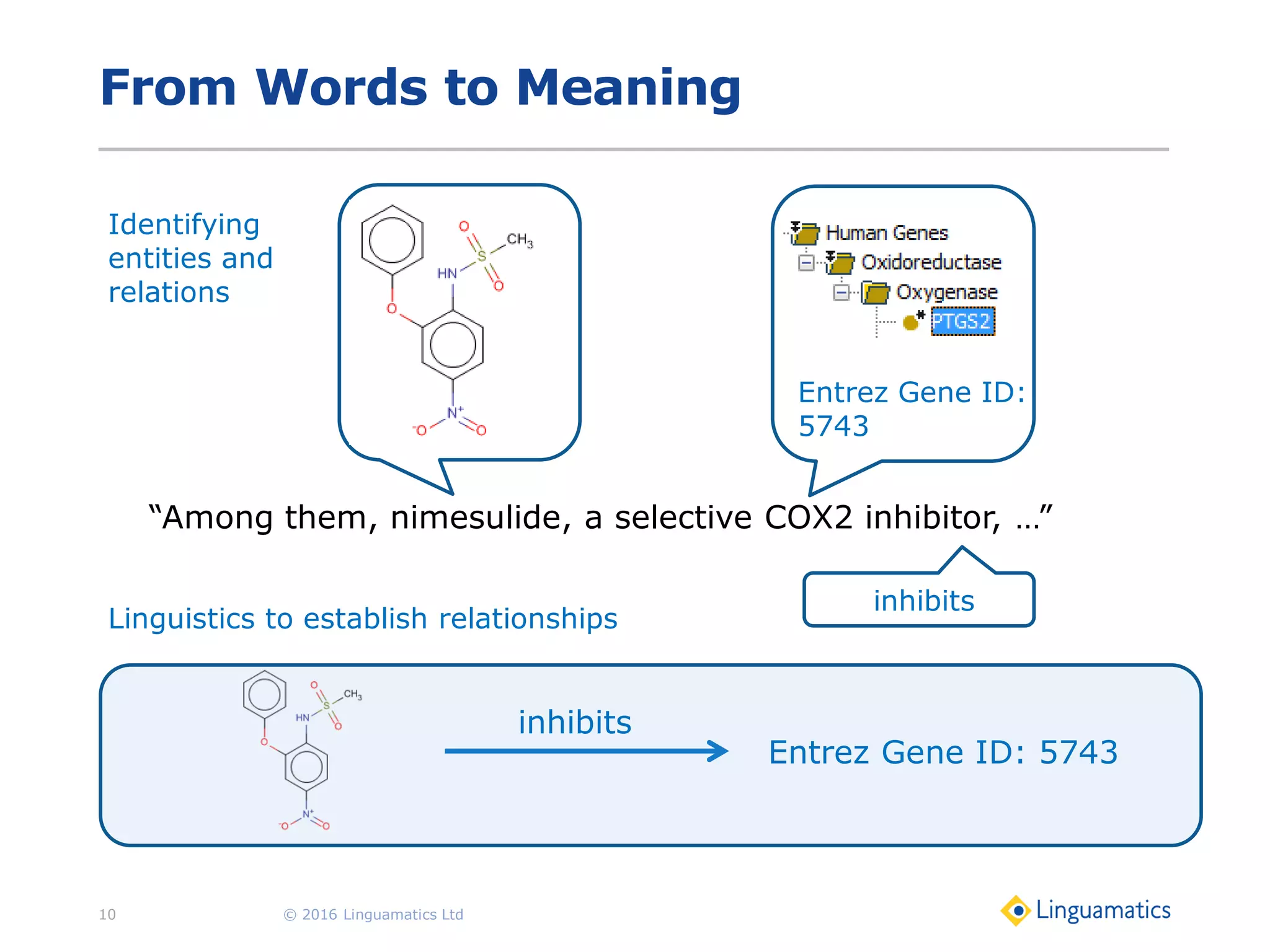
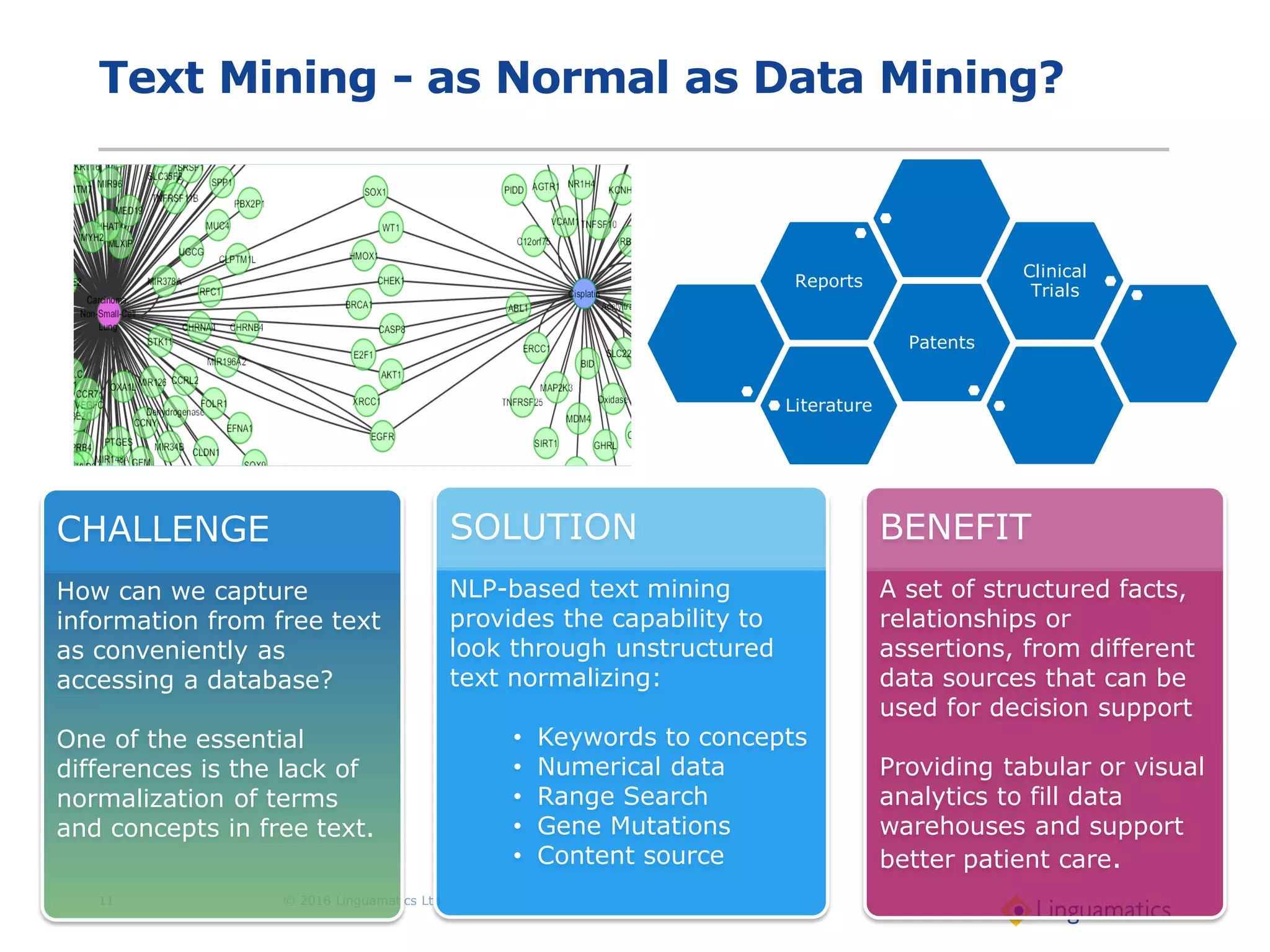
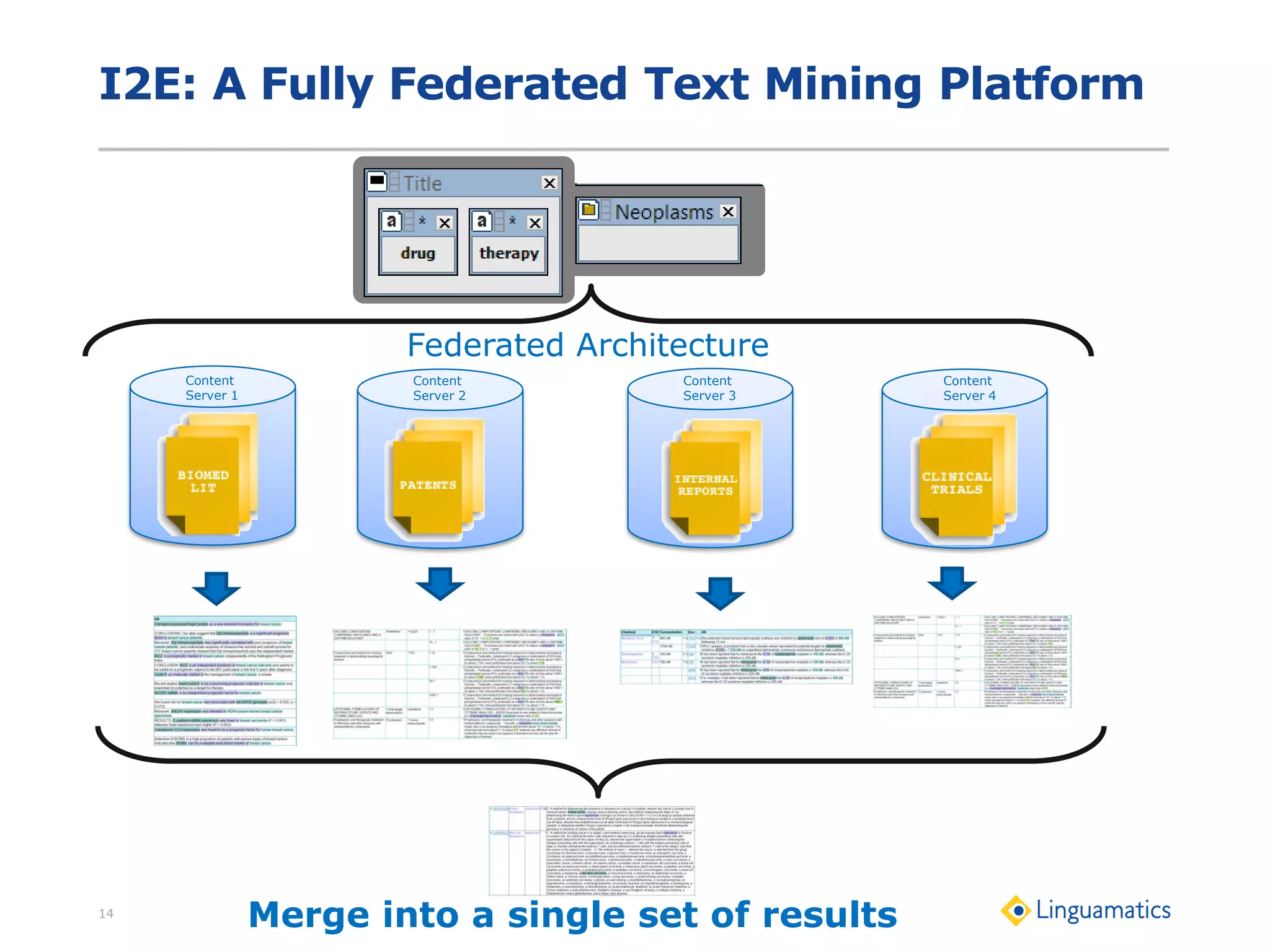
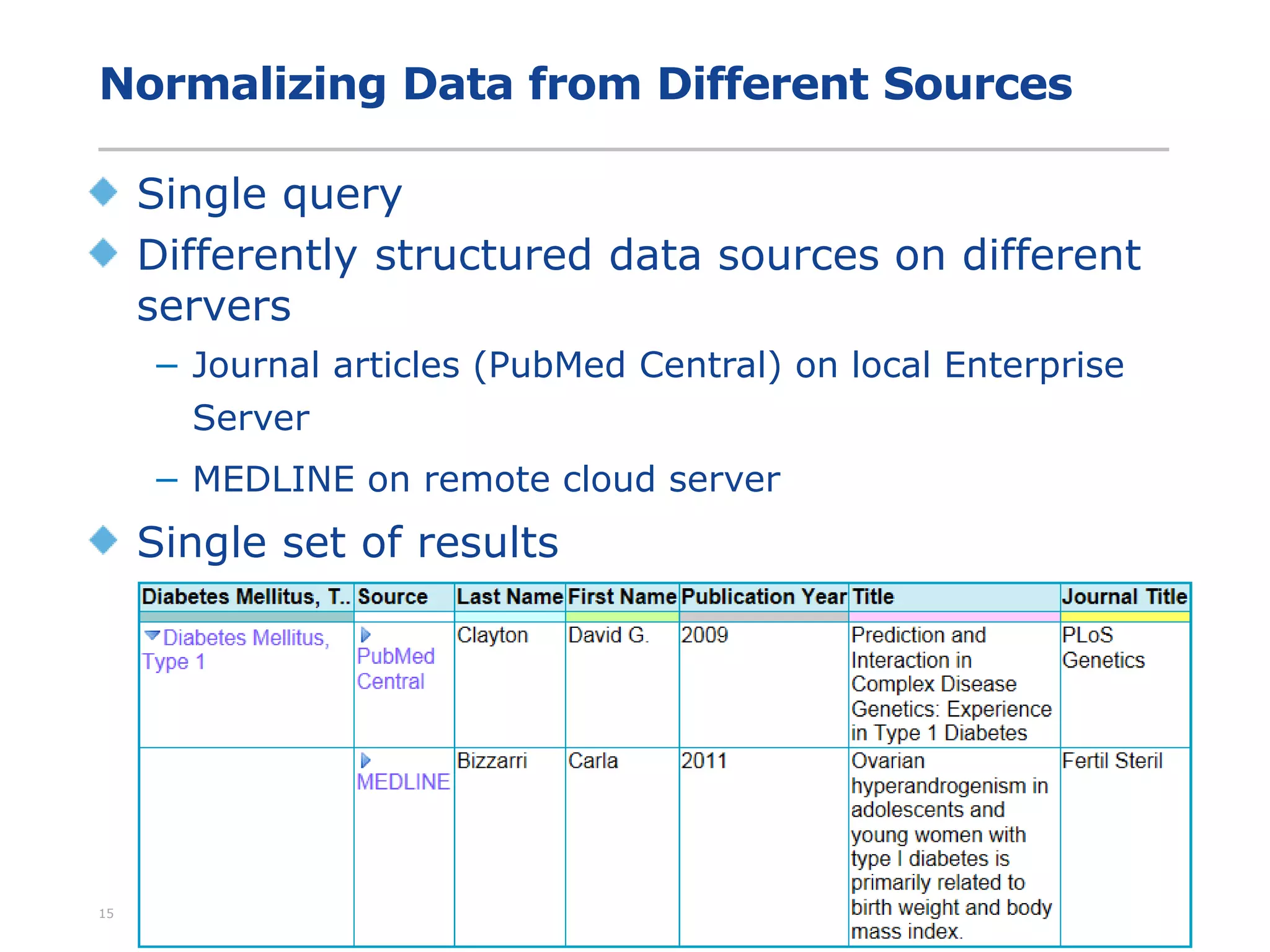
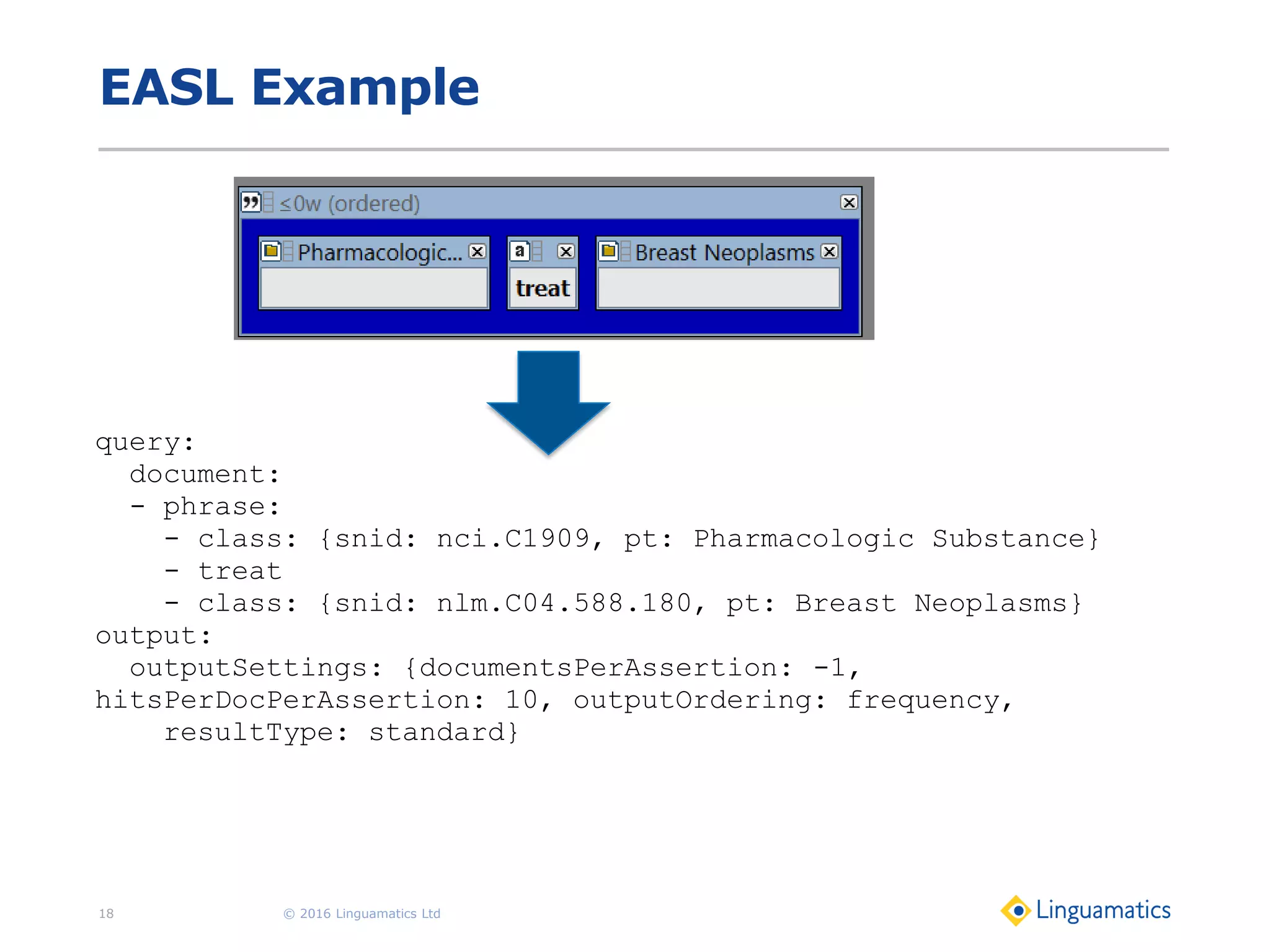
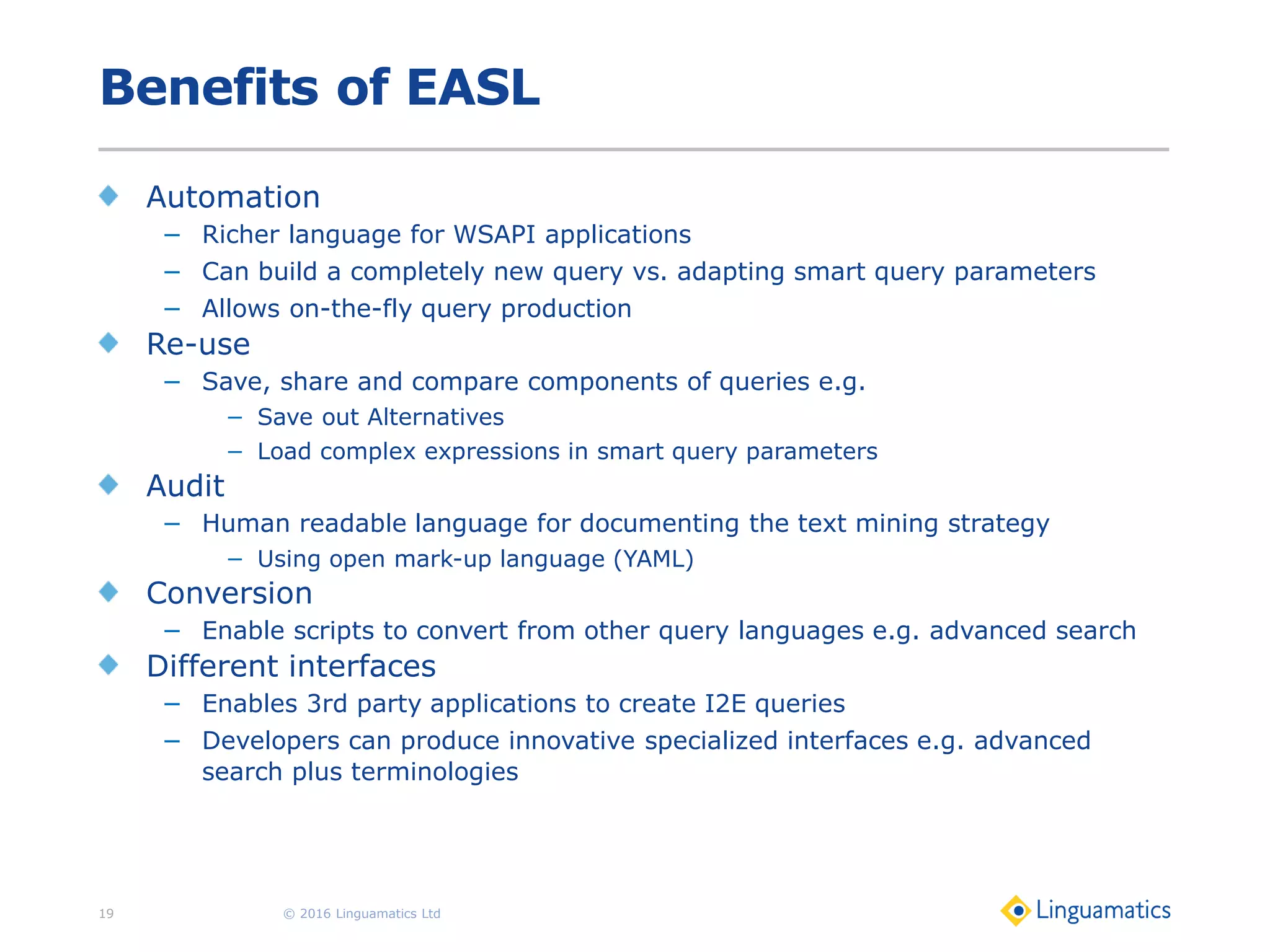
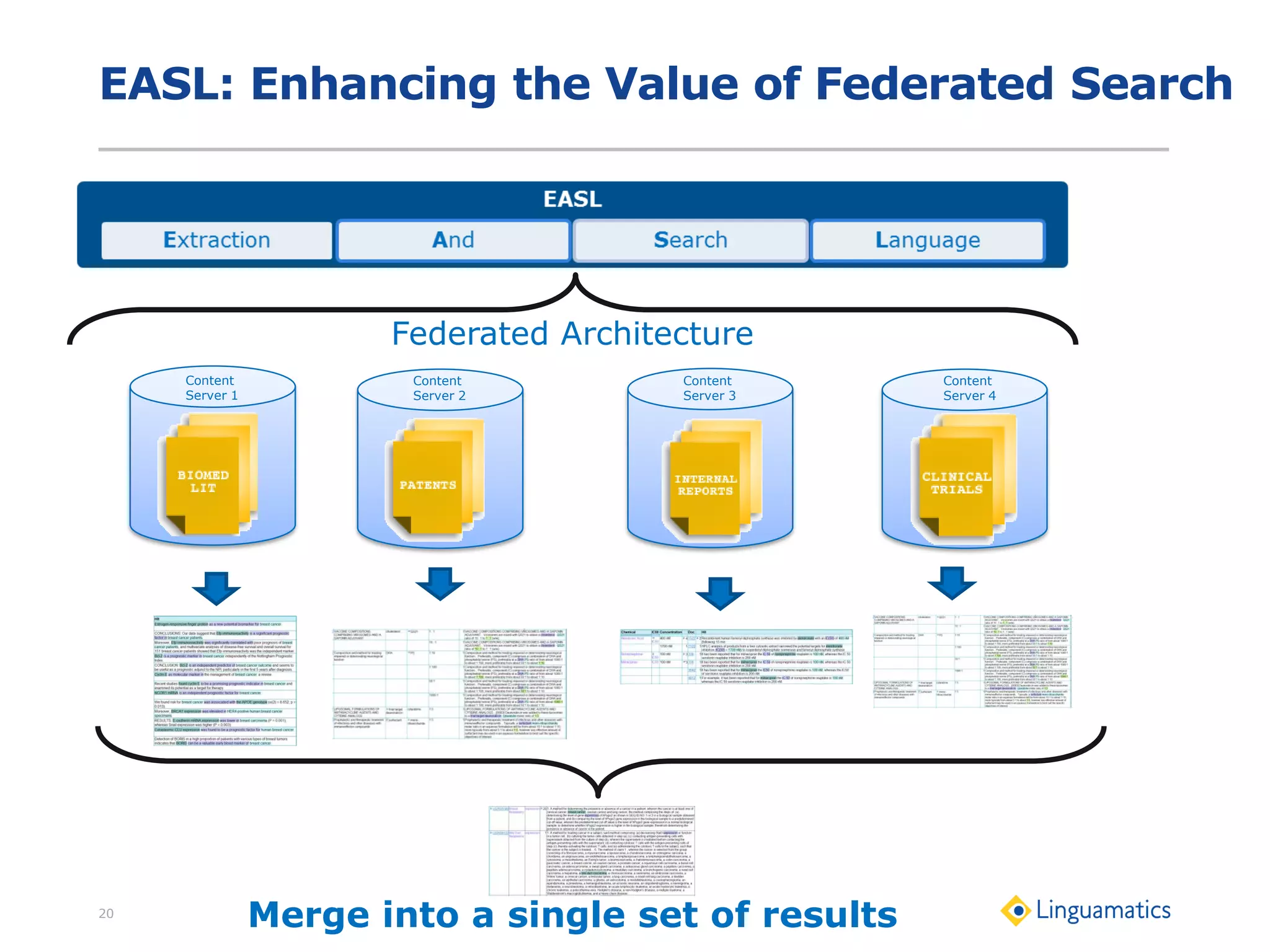
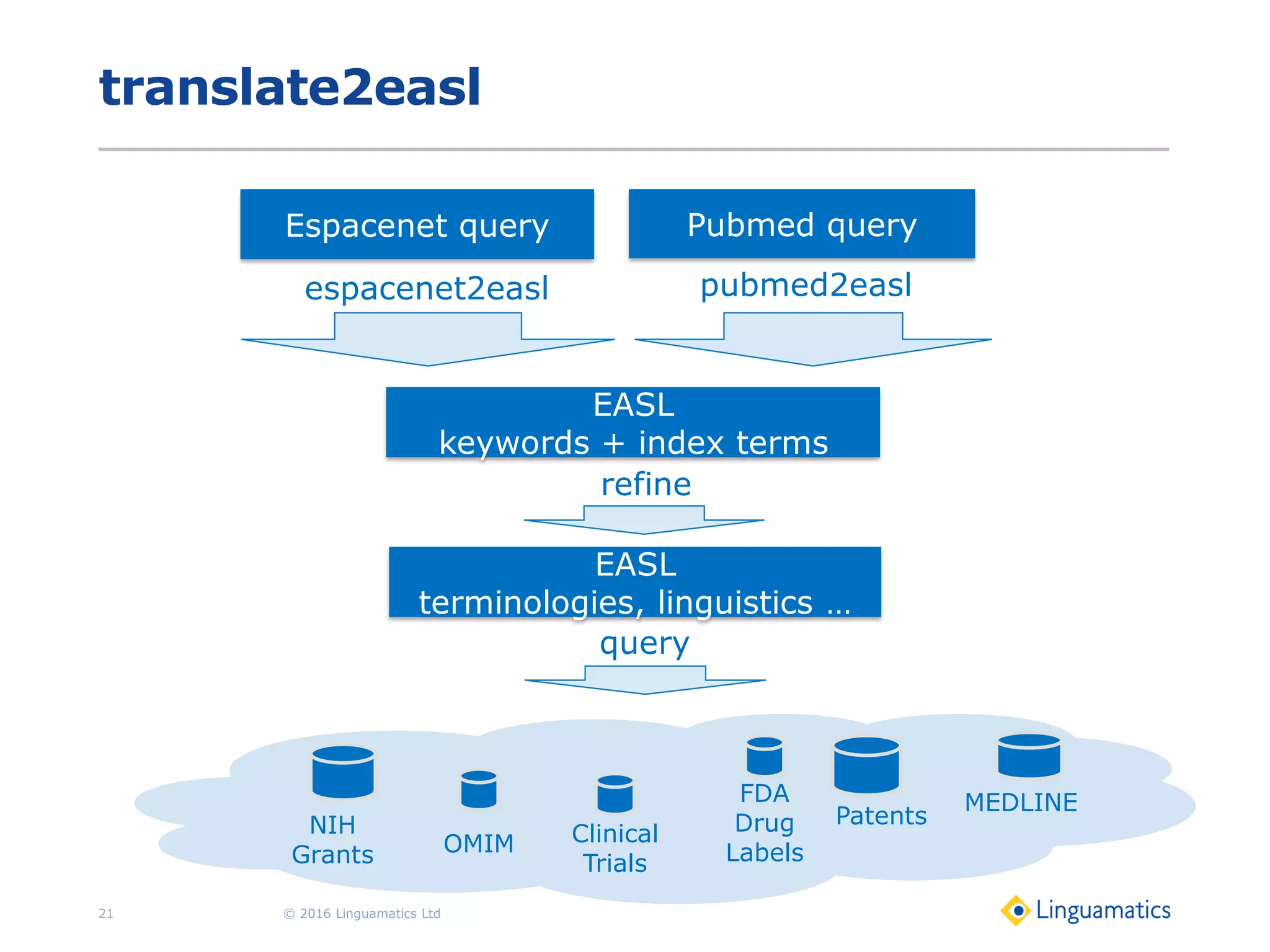
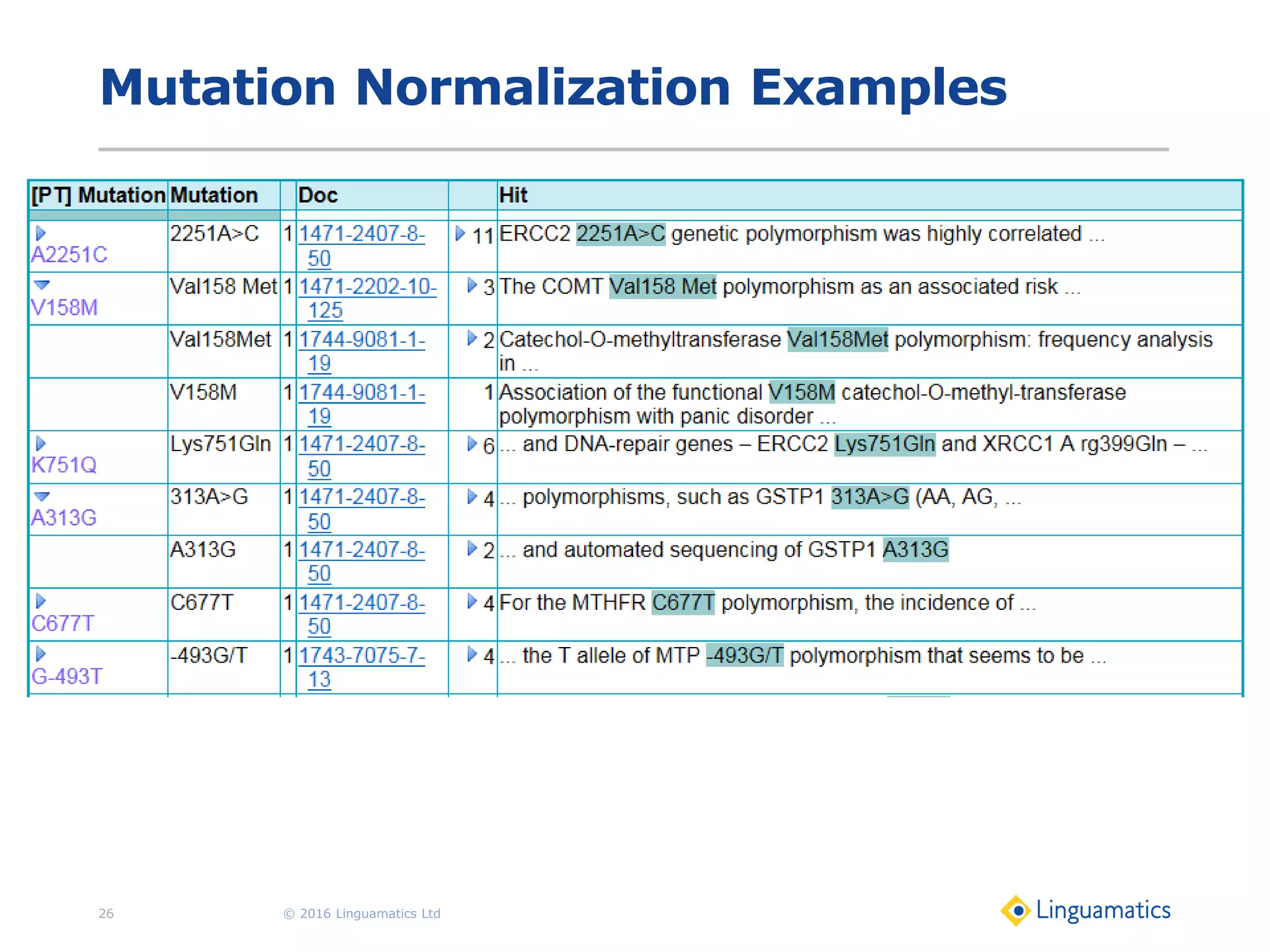
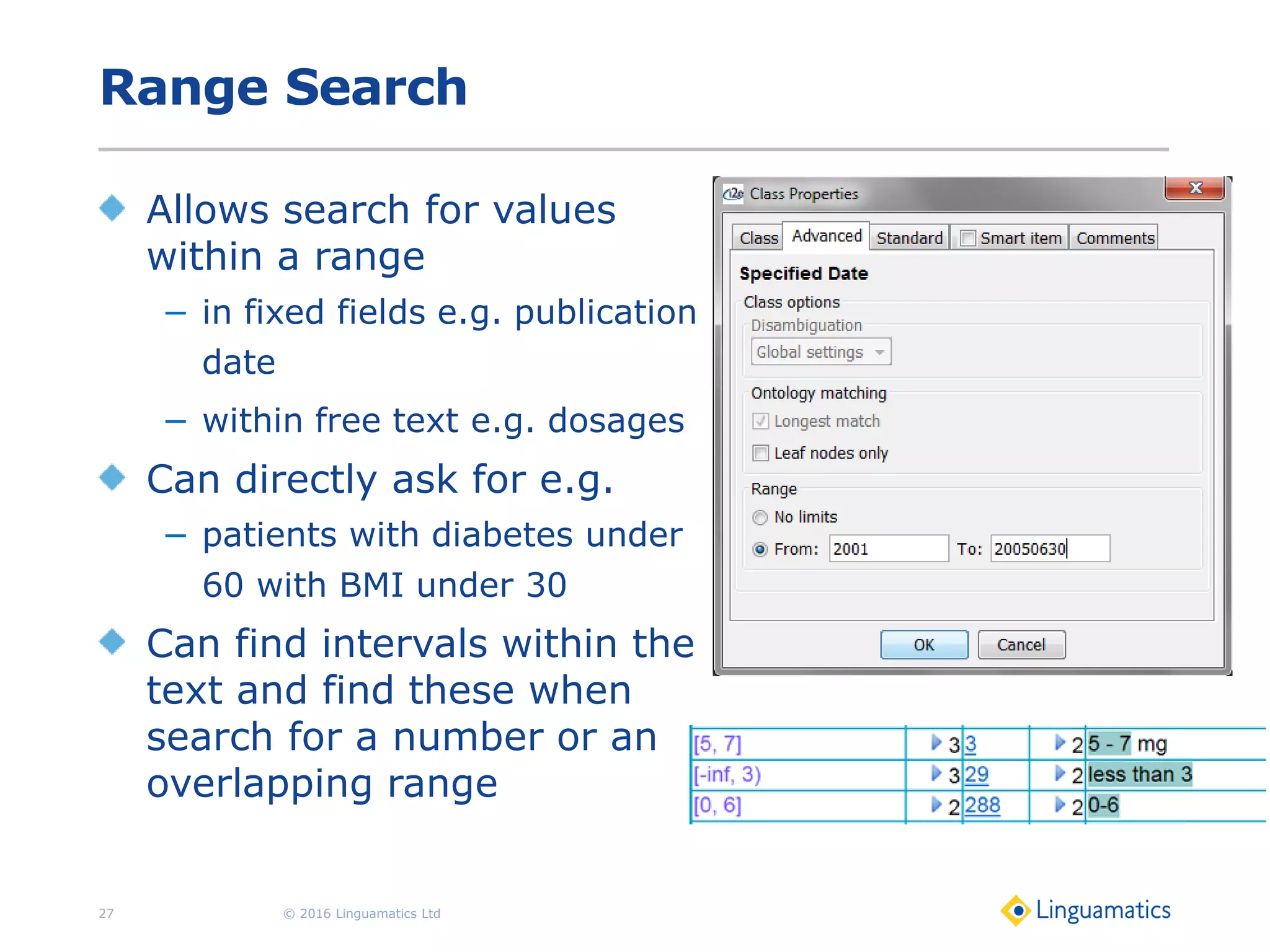
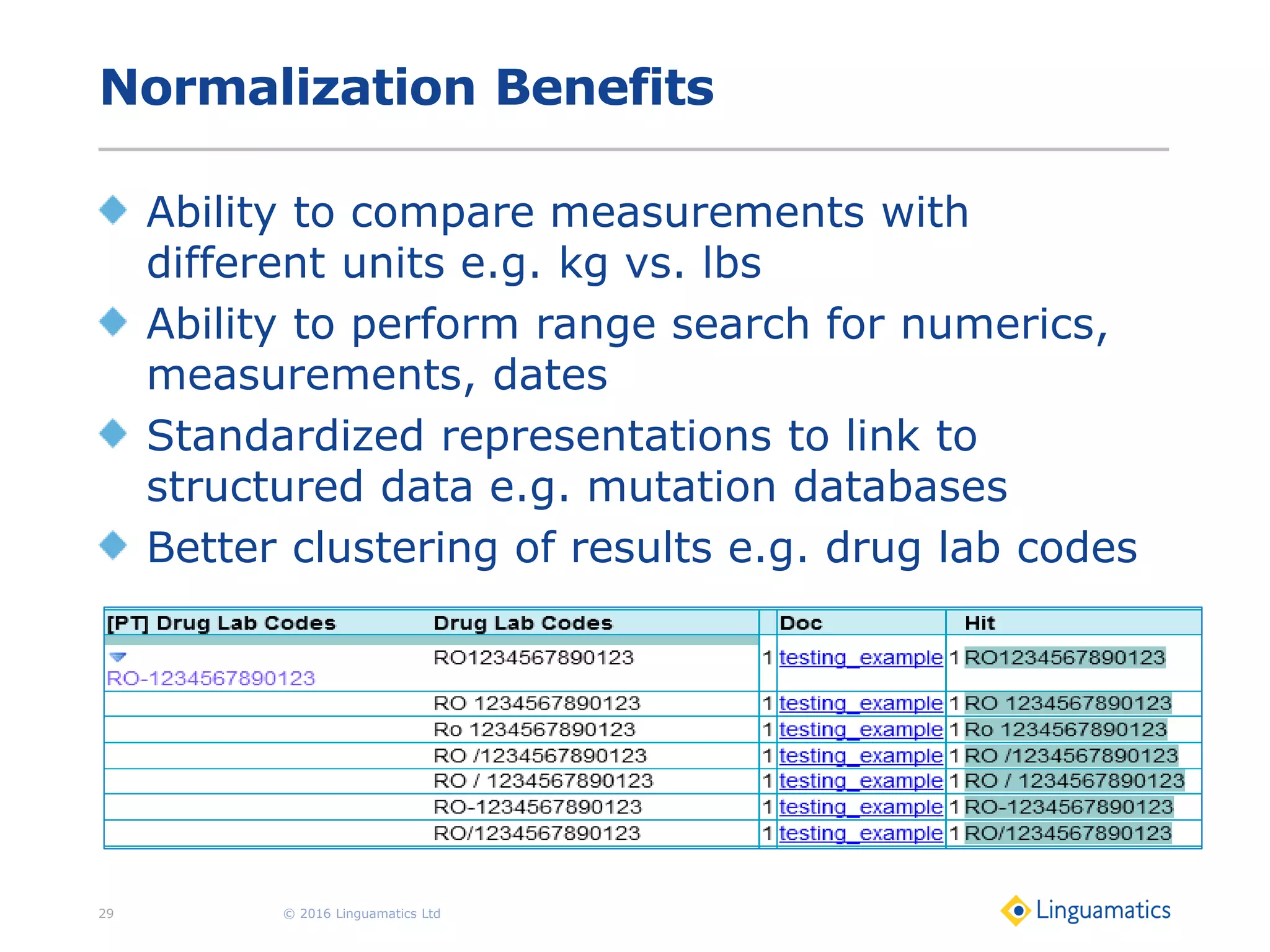
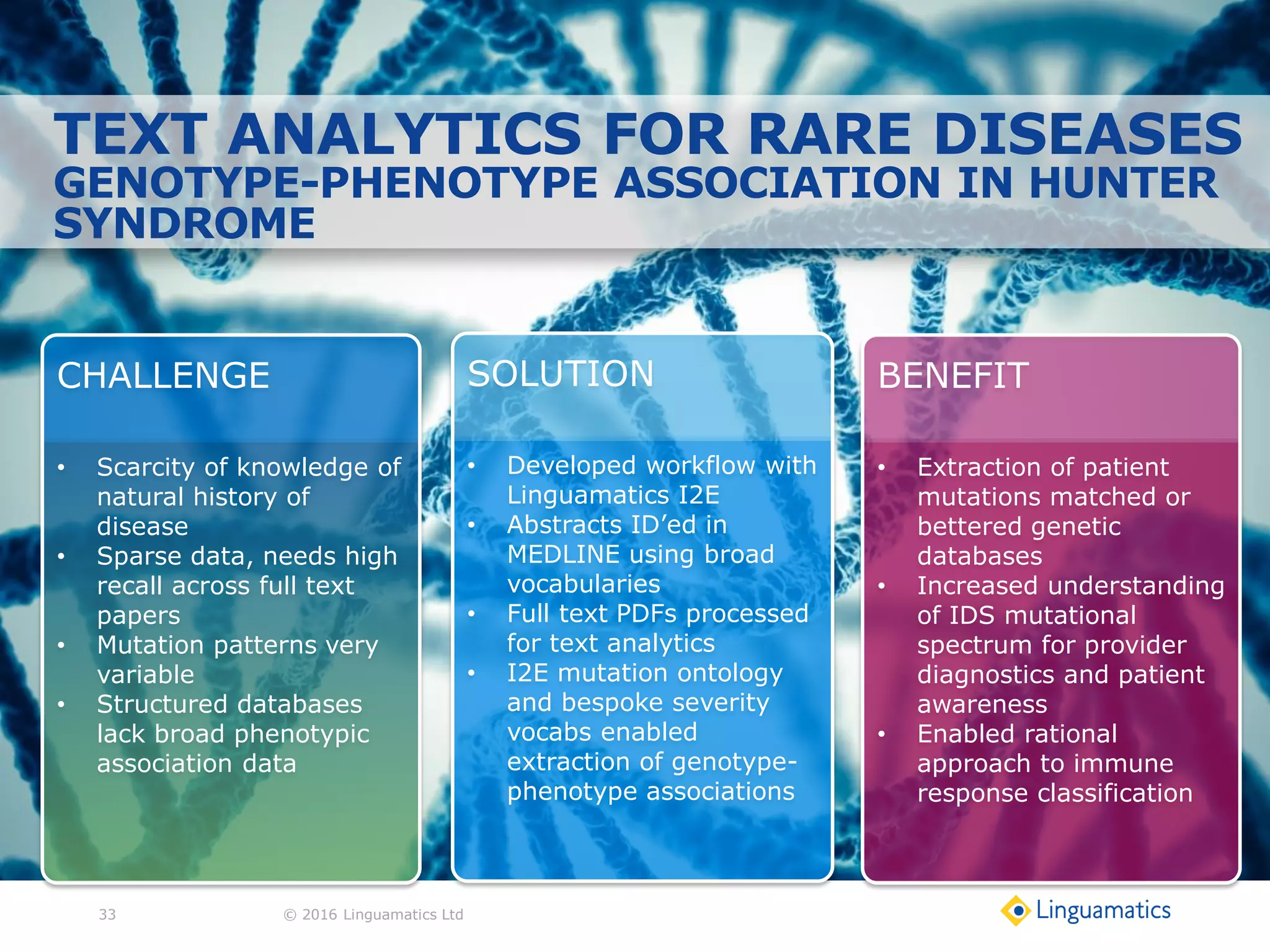
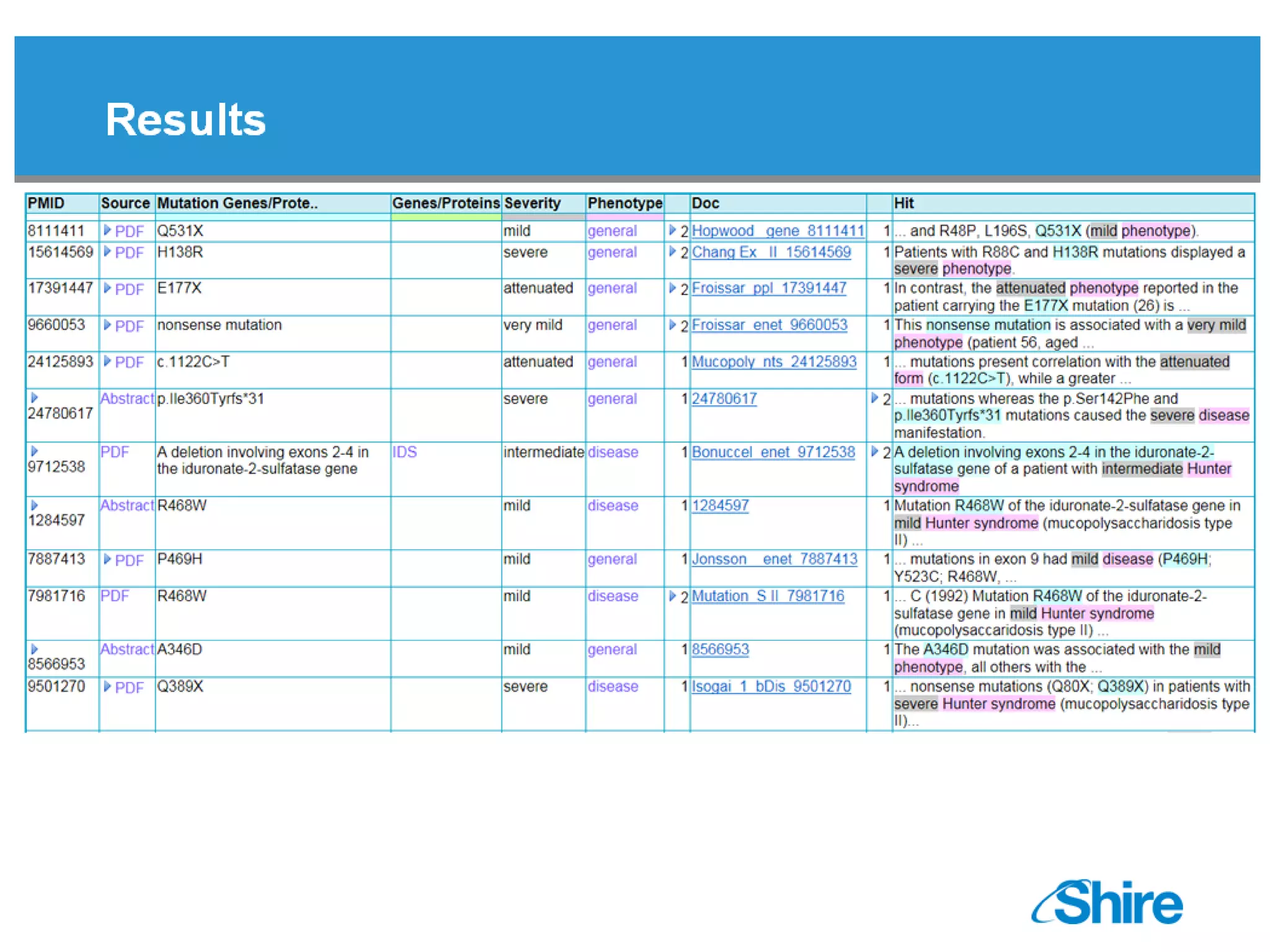
The document discusses the integration of text mining in various fields, emphasizing its importance in handling unstructured data, particularly in healthcare. It highlights challenges in normalizing diverse data inputs, such as gene mutations and various numerical forms, and proposes the use of natural language processing (NLP) to extract structured insights. The benefits of utilizing enhanced normalization methods and the extraction and search language (EASL) for efficient data analysis are also presented.