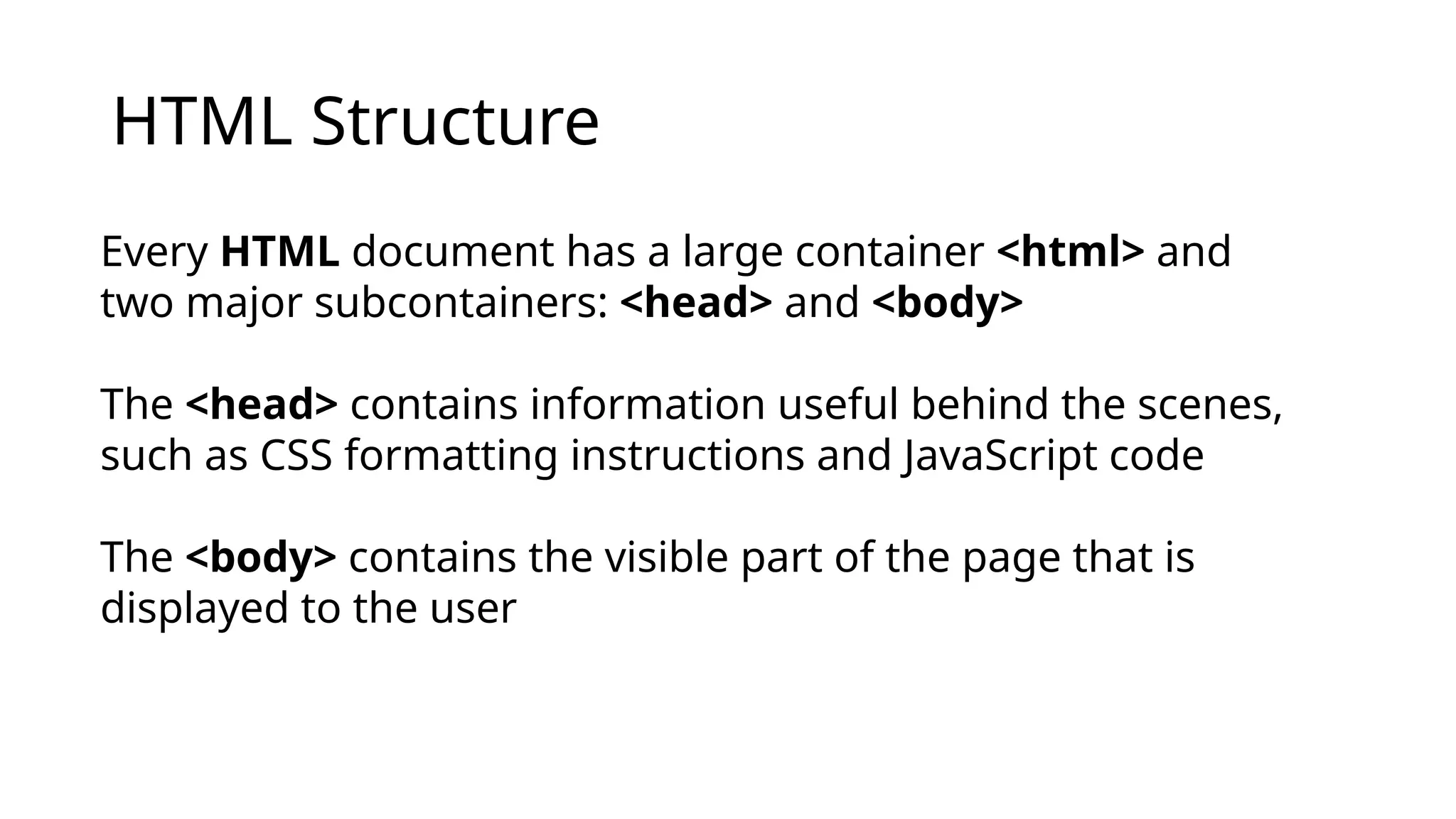
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) is a markup language used to create web pages and consists of a structure defined by elements like <html>, <head>, and <body>. It utilizes tags to denote content and can be enhanced with attributes, while modern web development separates styling (CSS) and interactivity (JavaScript) from HTML. The document also outlines the evolution of HTML from its first version in 1993 to the latest HTML5 in 2014, highlighting key features and updates introduced with each version.