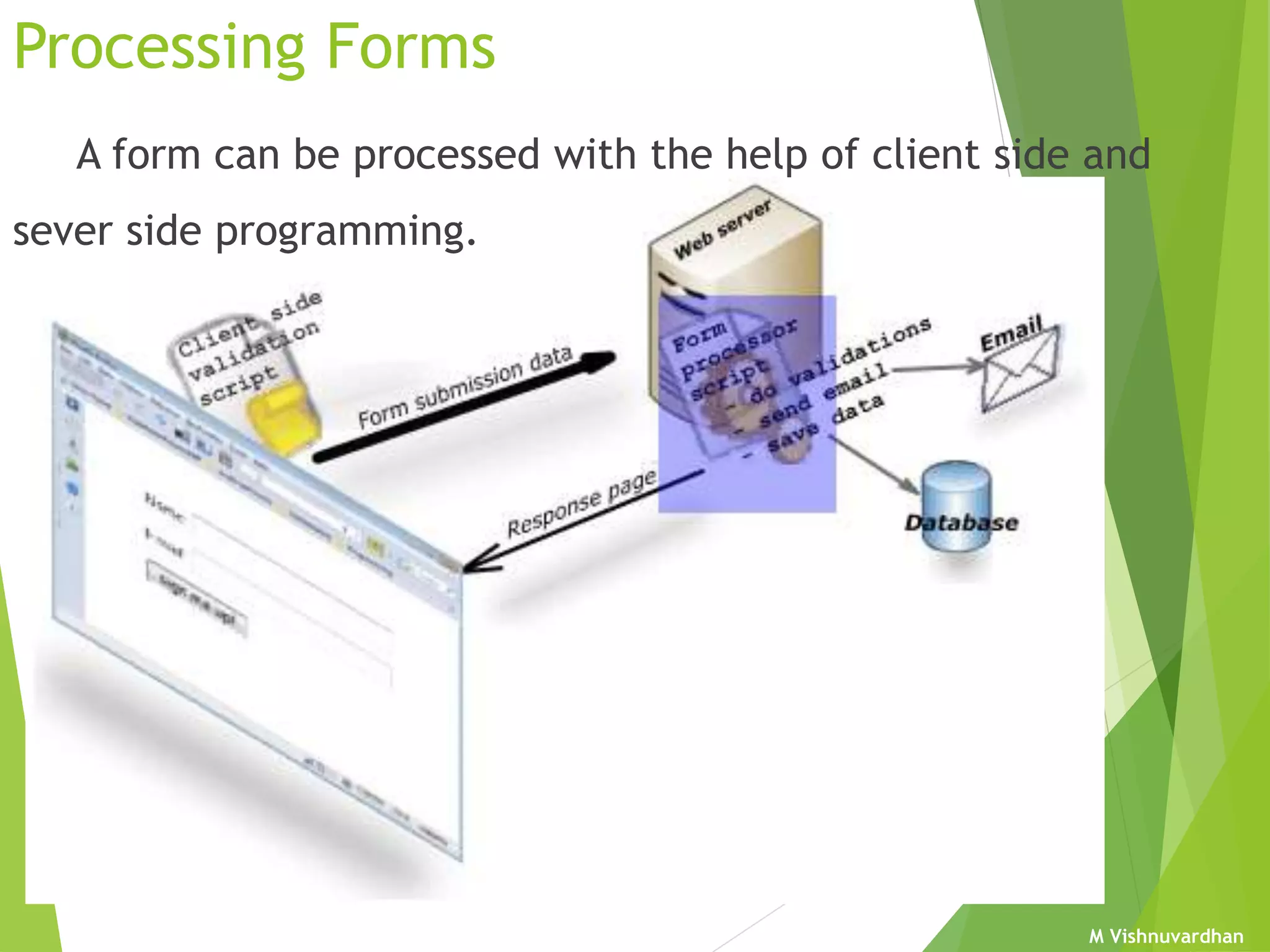
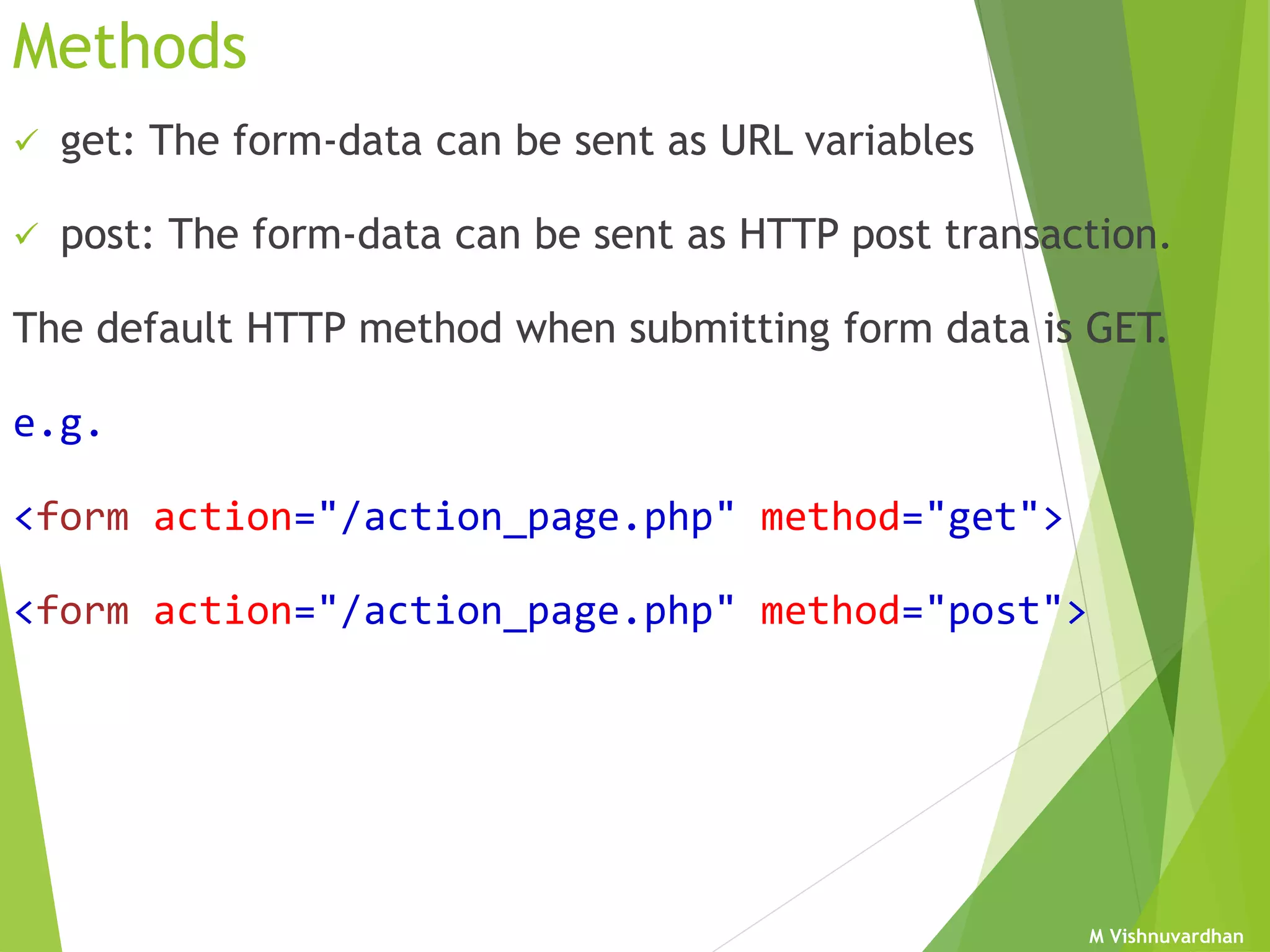
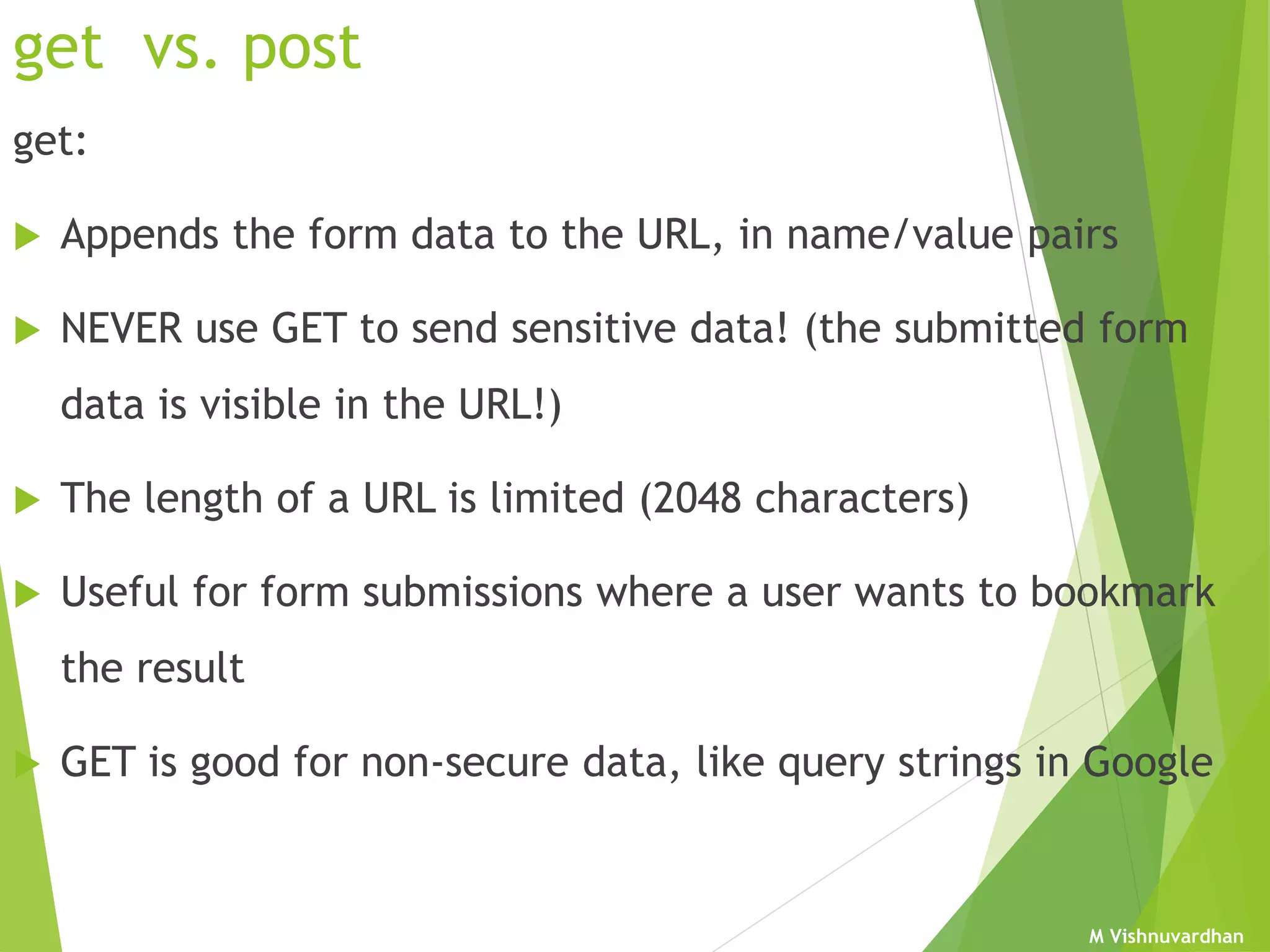
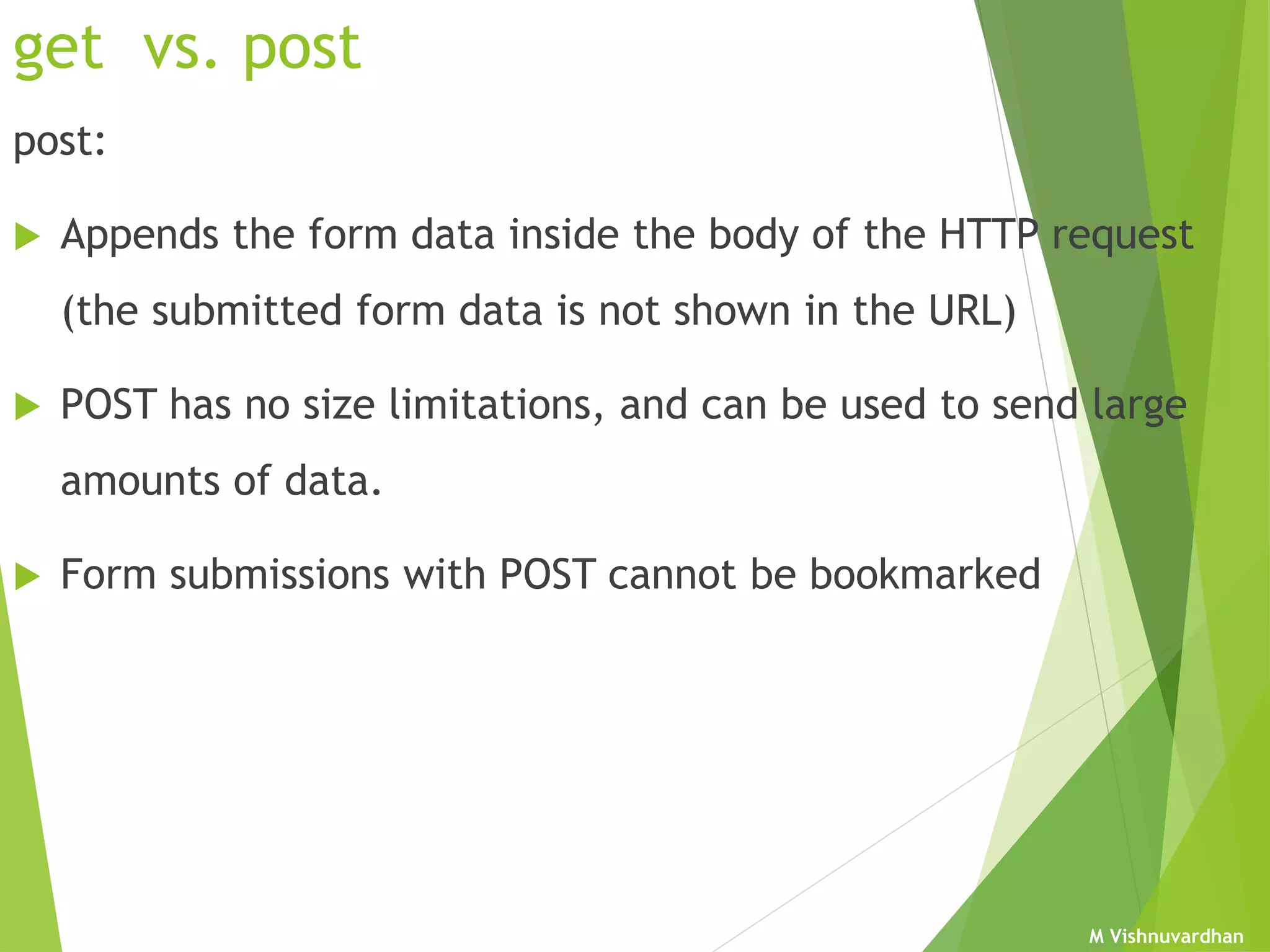
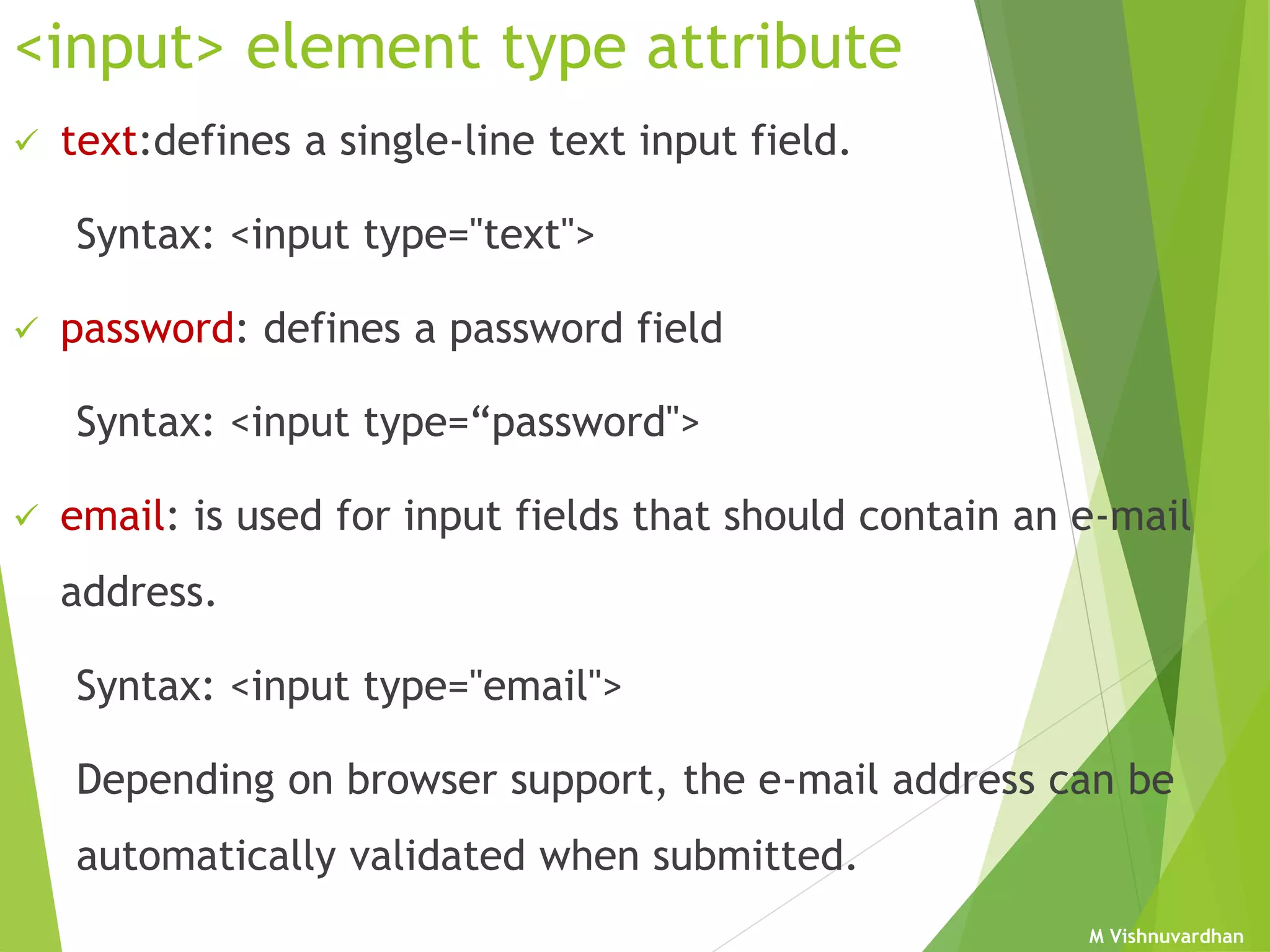
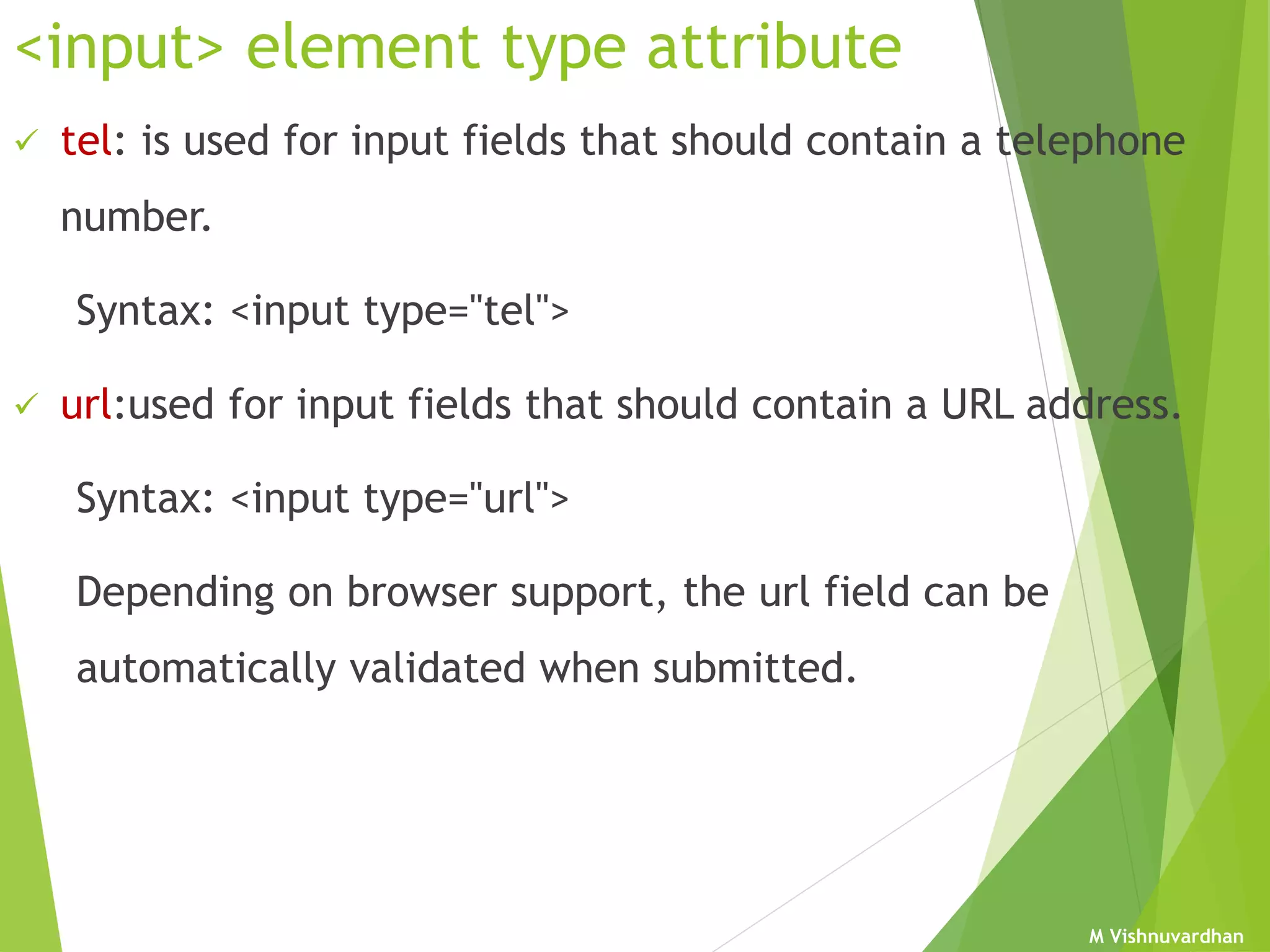
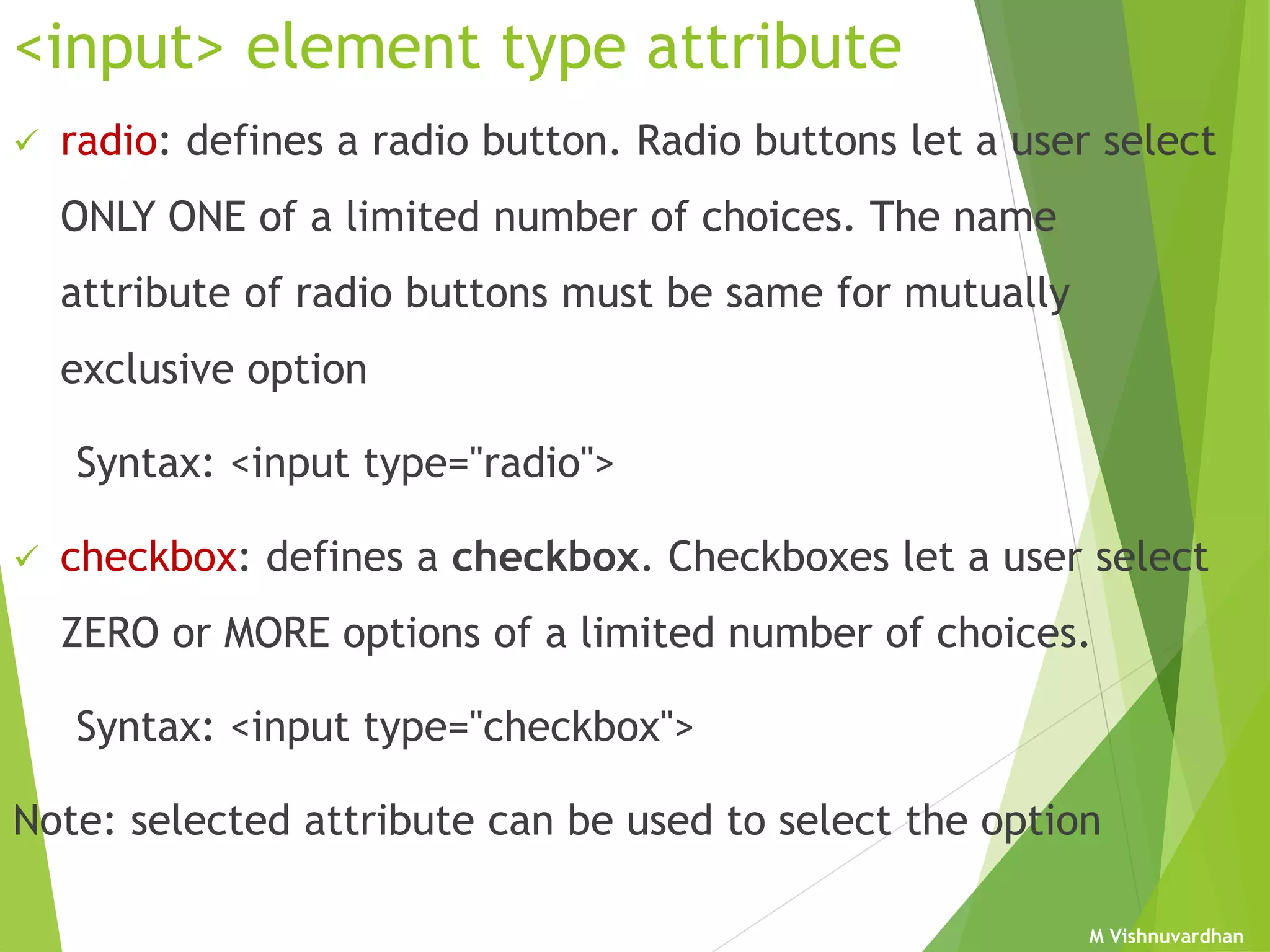
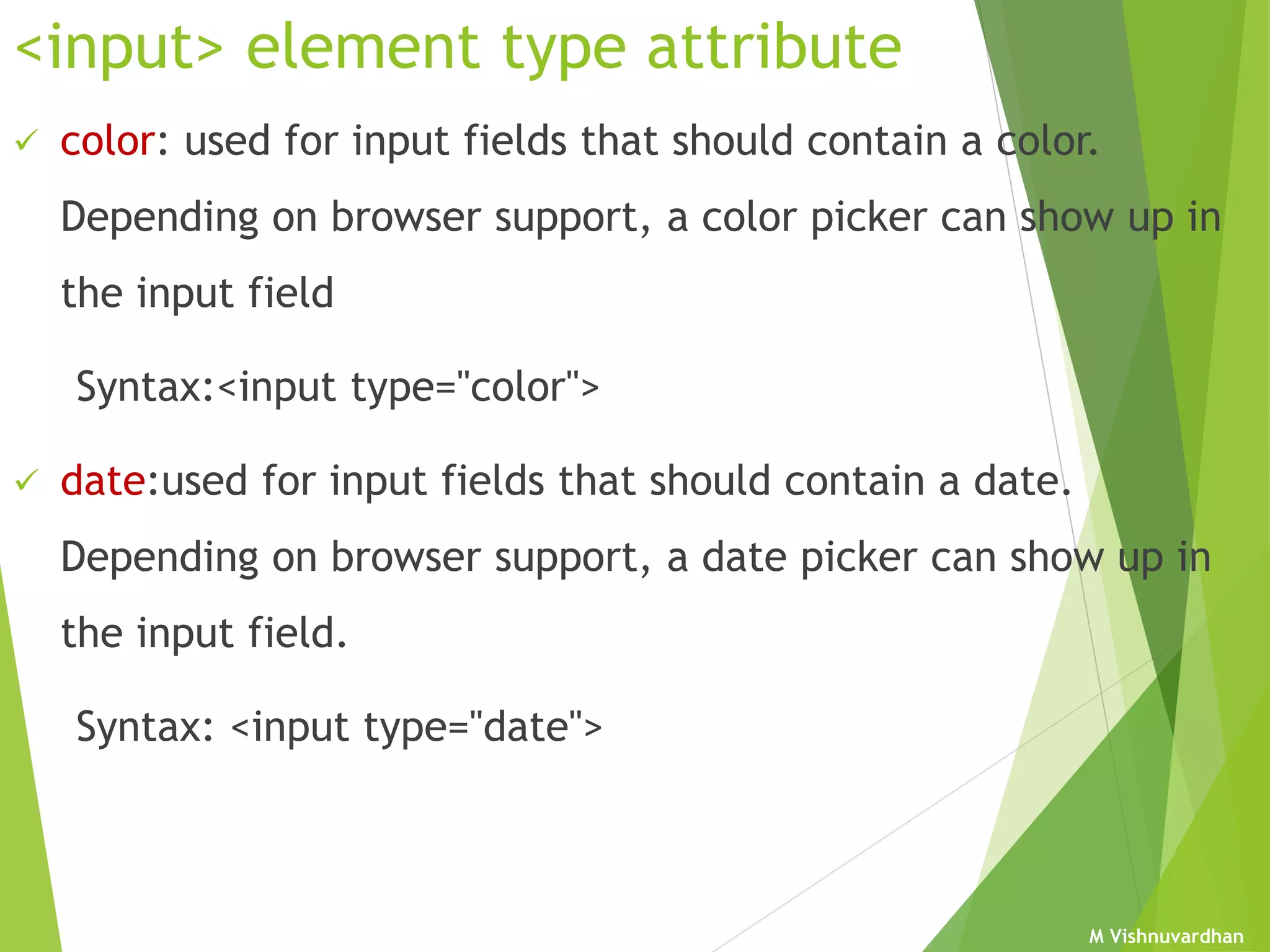
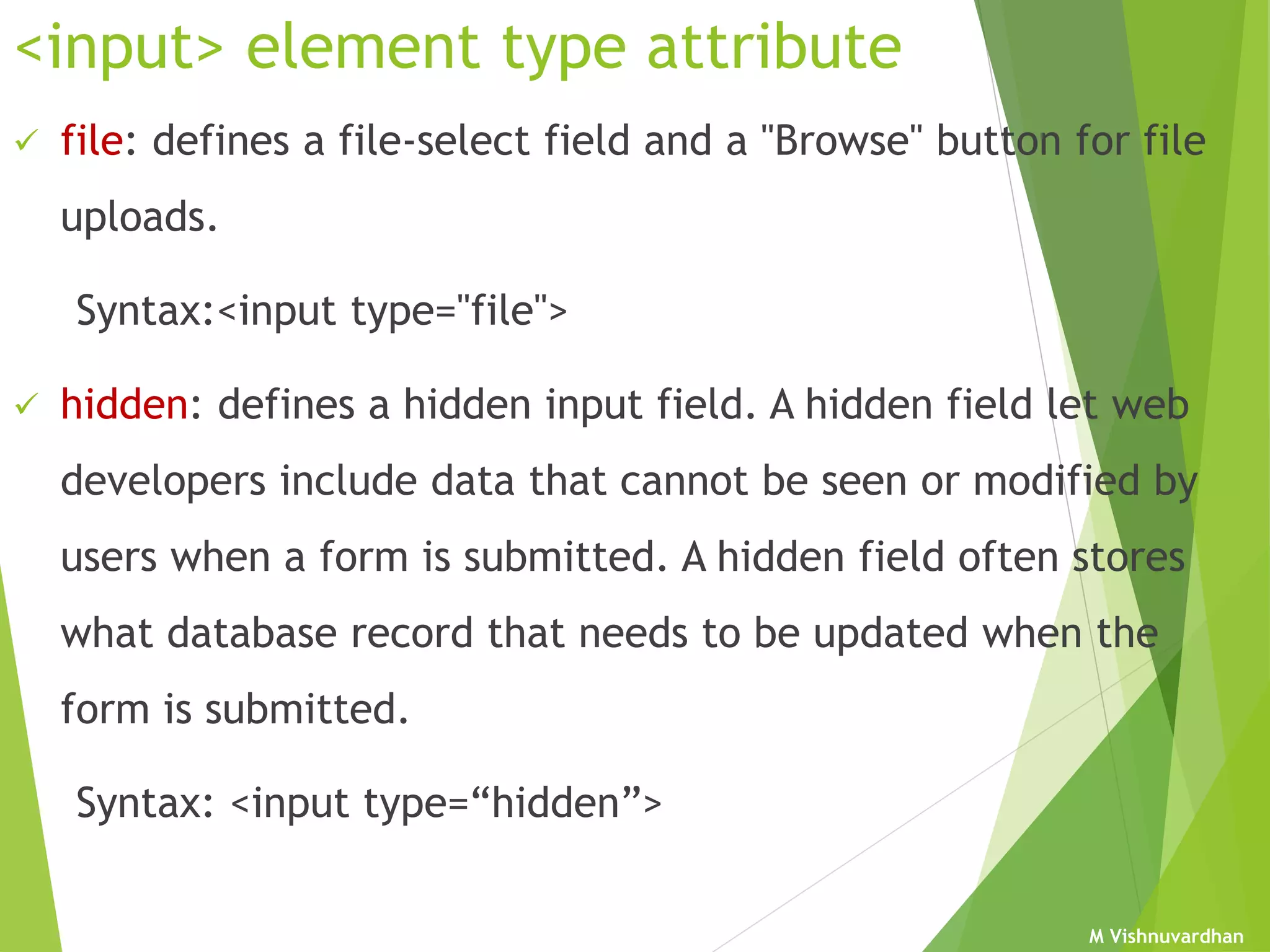
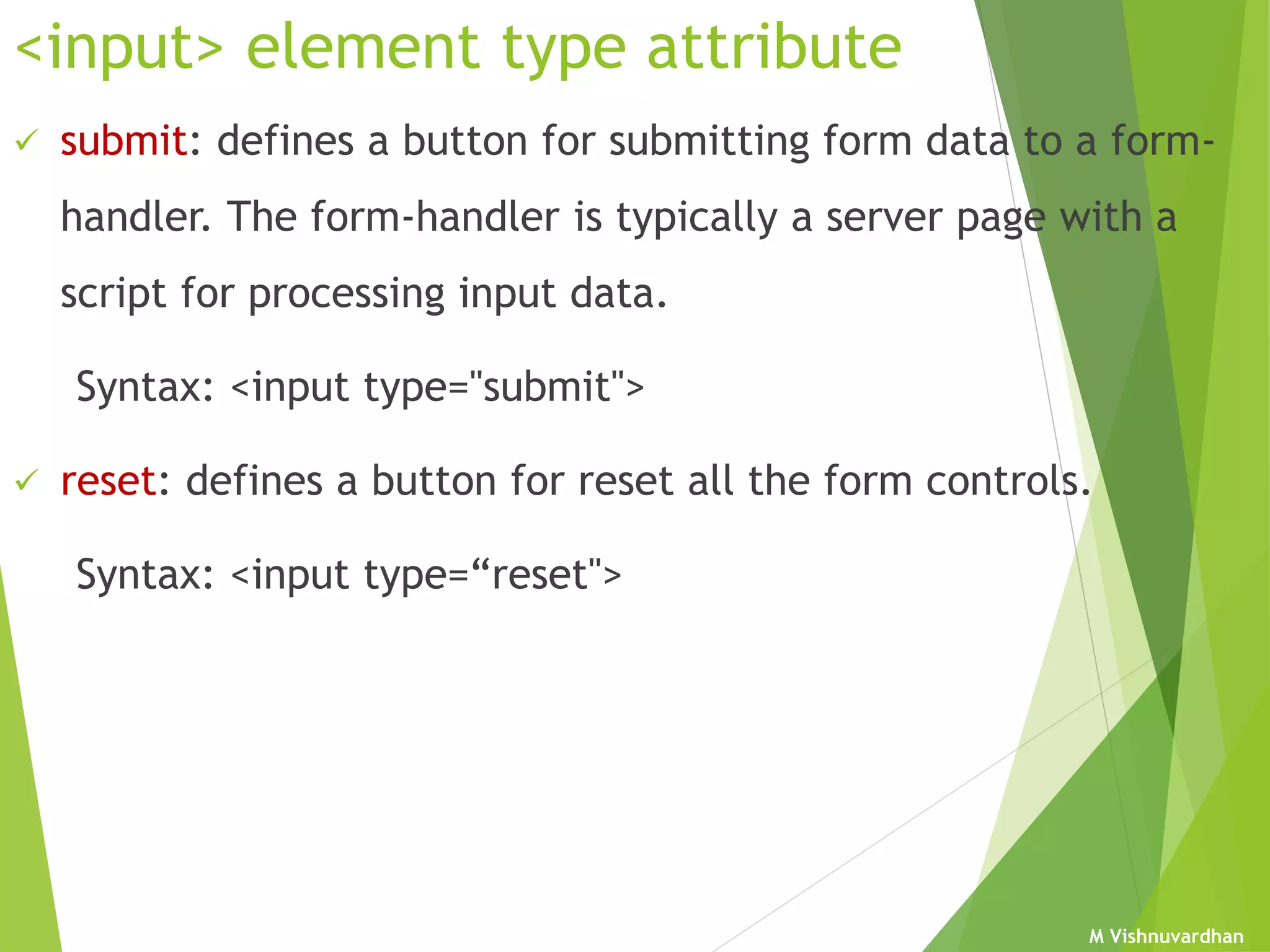
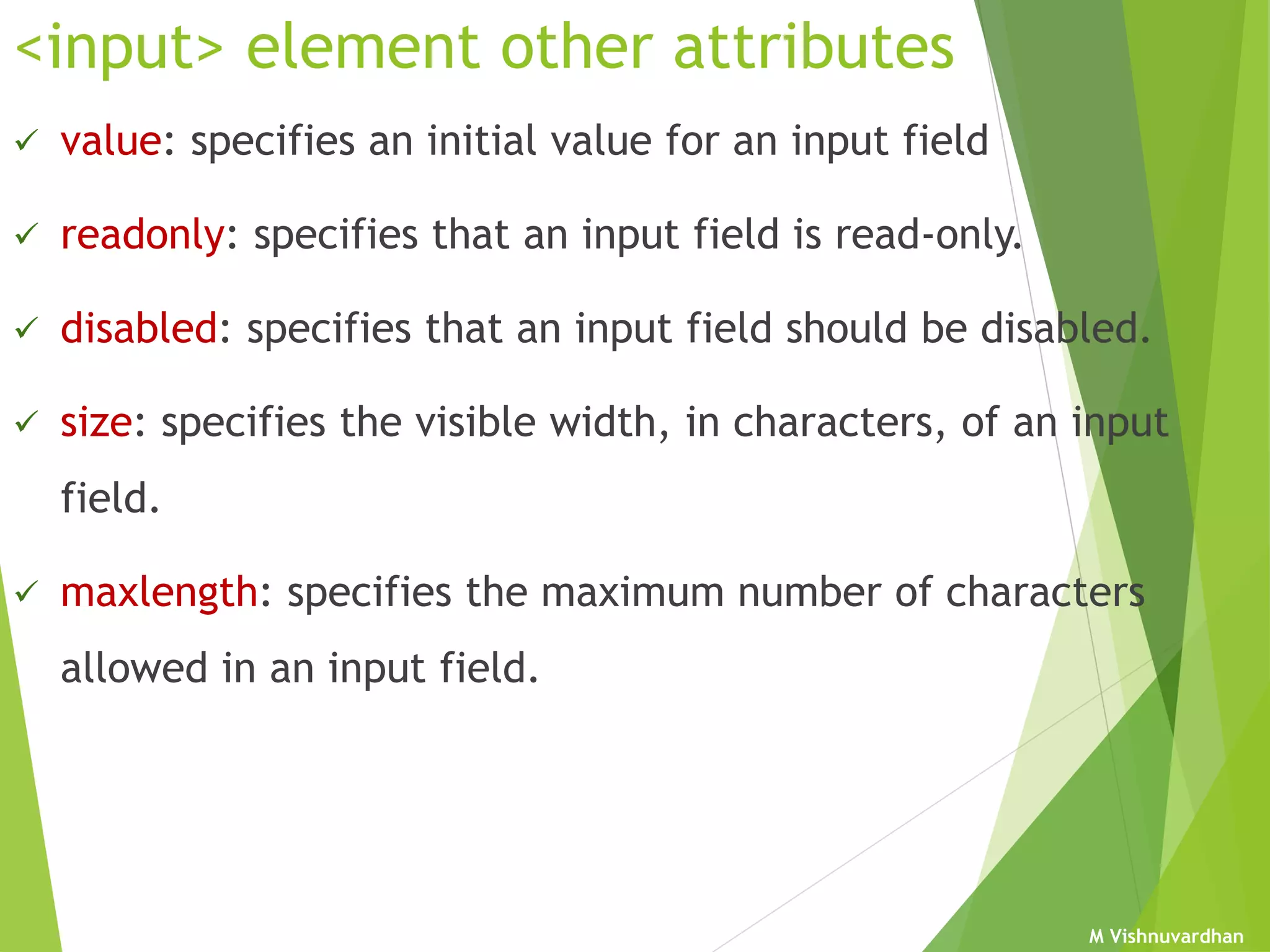
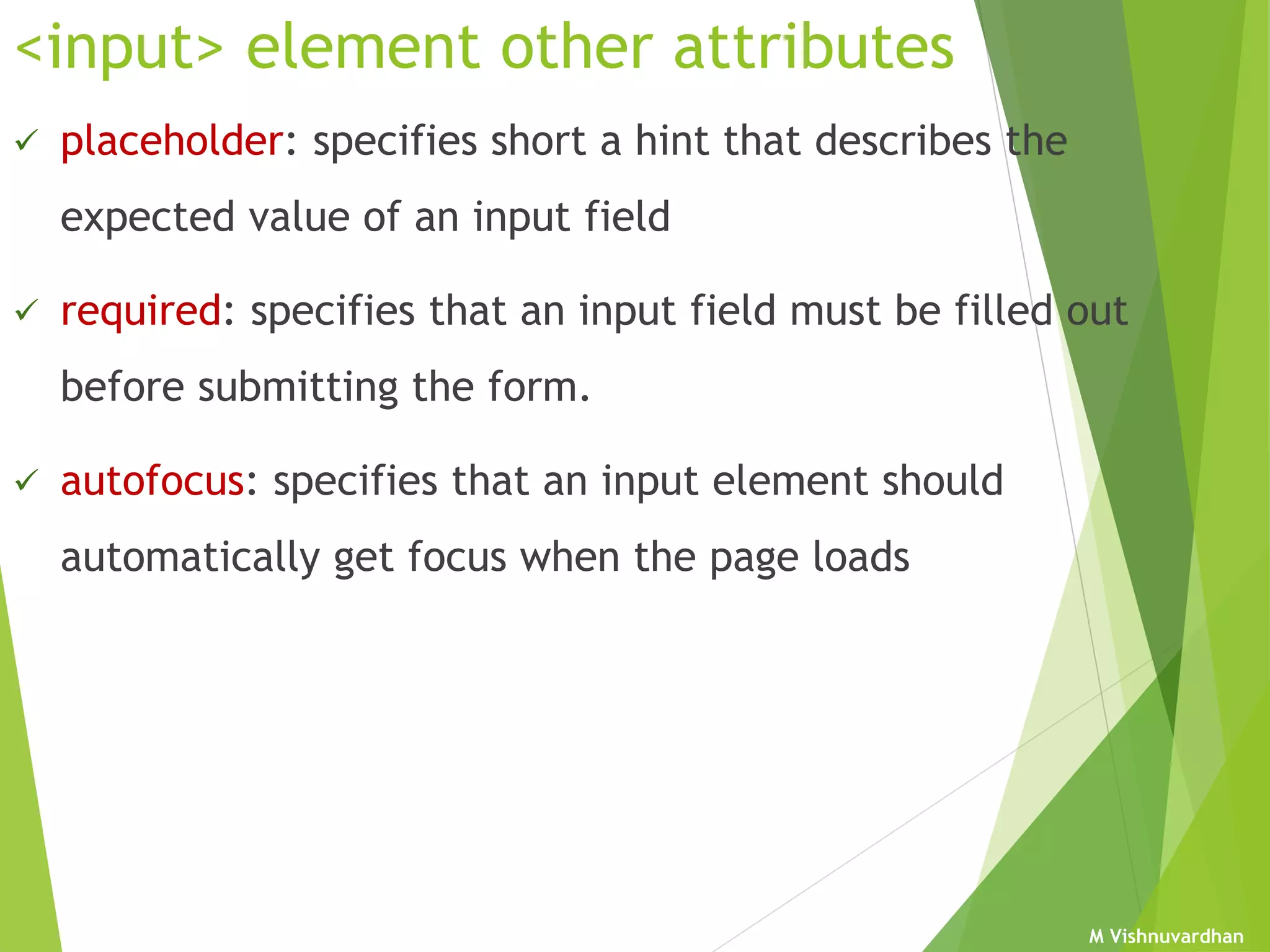
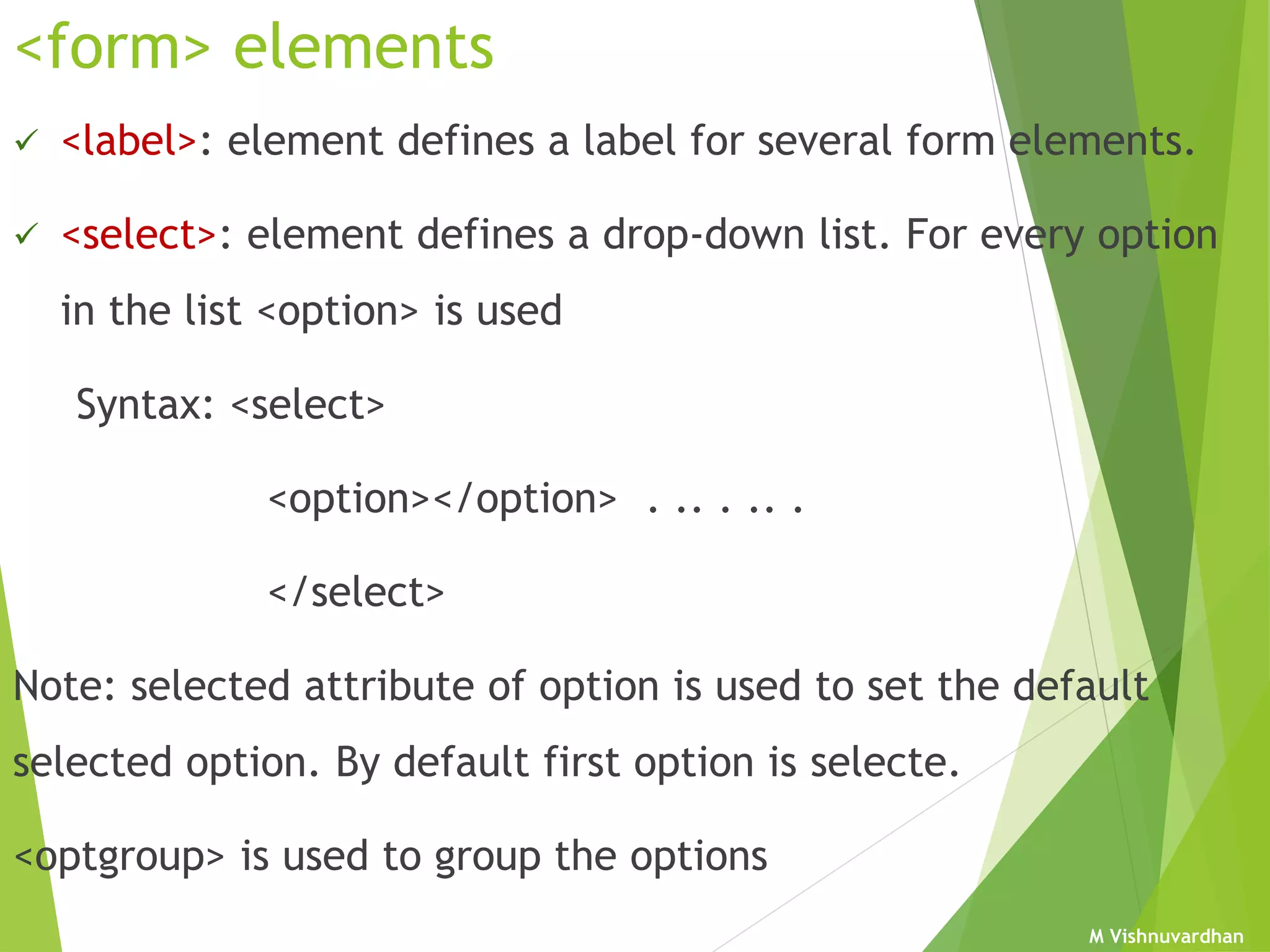
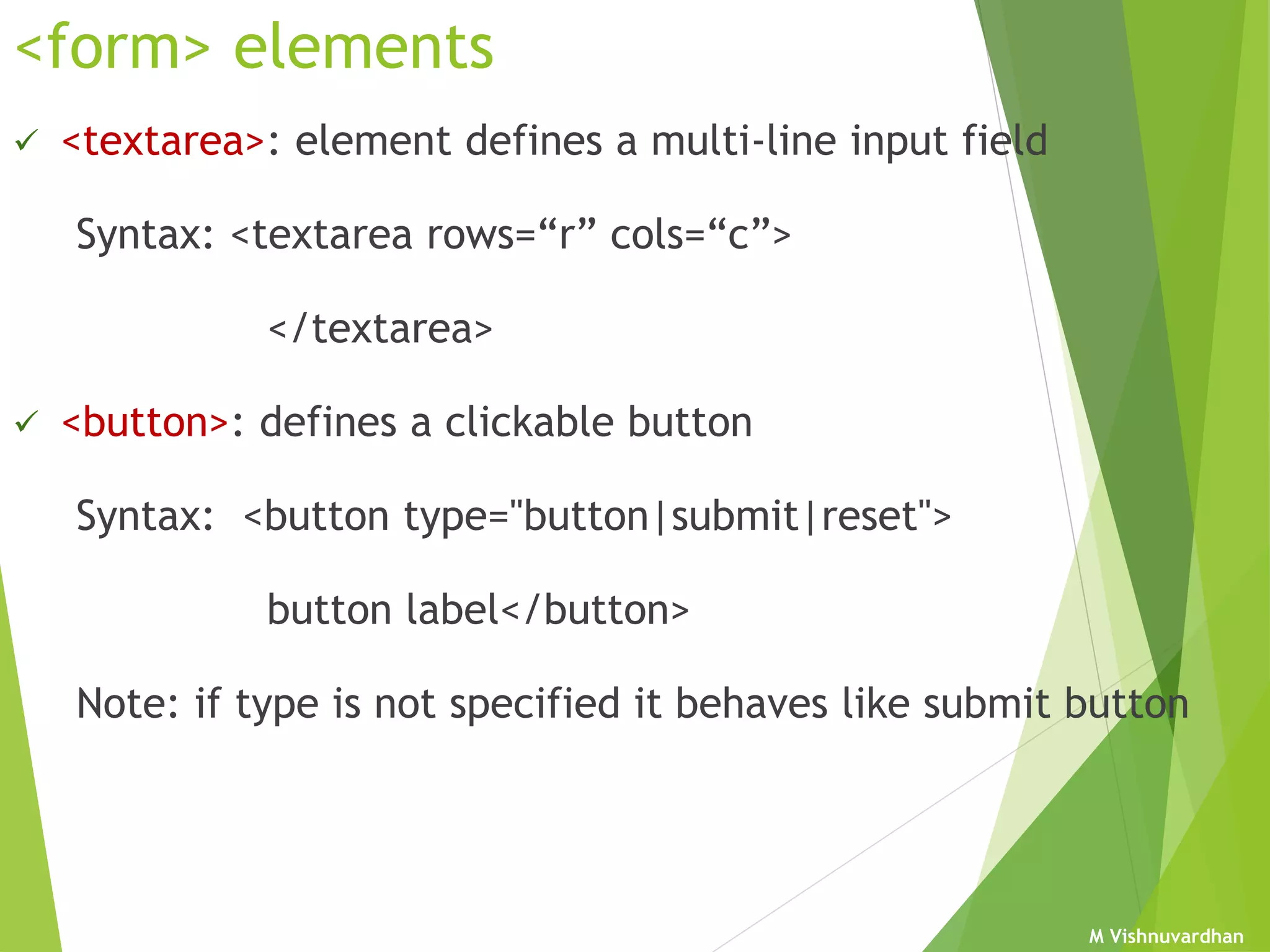
An HTML form is used to collect user input and consists of form fields, labels, and buttons. Forms can be processed using client-side programming, which performs tasks within the browser, or server-side programming, which runs on the server. Common client-side languages include JavaScript and CSS, while common server-side languages include PHP, ASP.NET, and Python. The <form> tag creates an HTML form and contains input elements like text fields, checkboxes, and submit buttons. Forms are submitted using either the GET or POST method, with POST being preferable for sensitive data since it does not display submitted values in the URL.