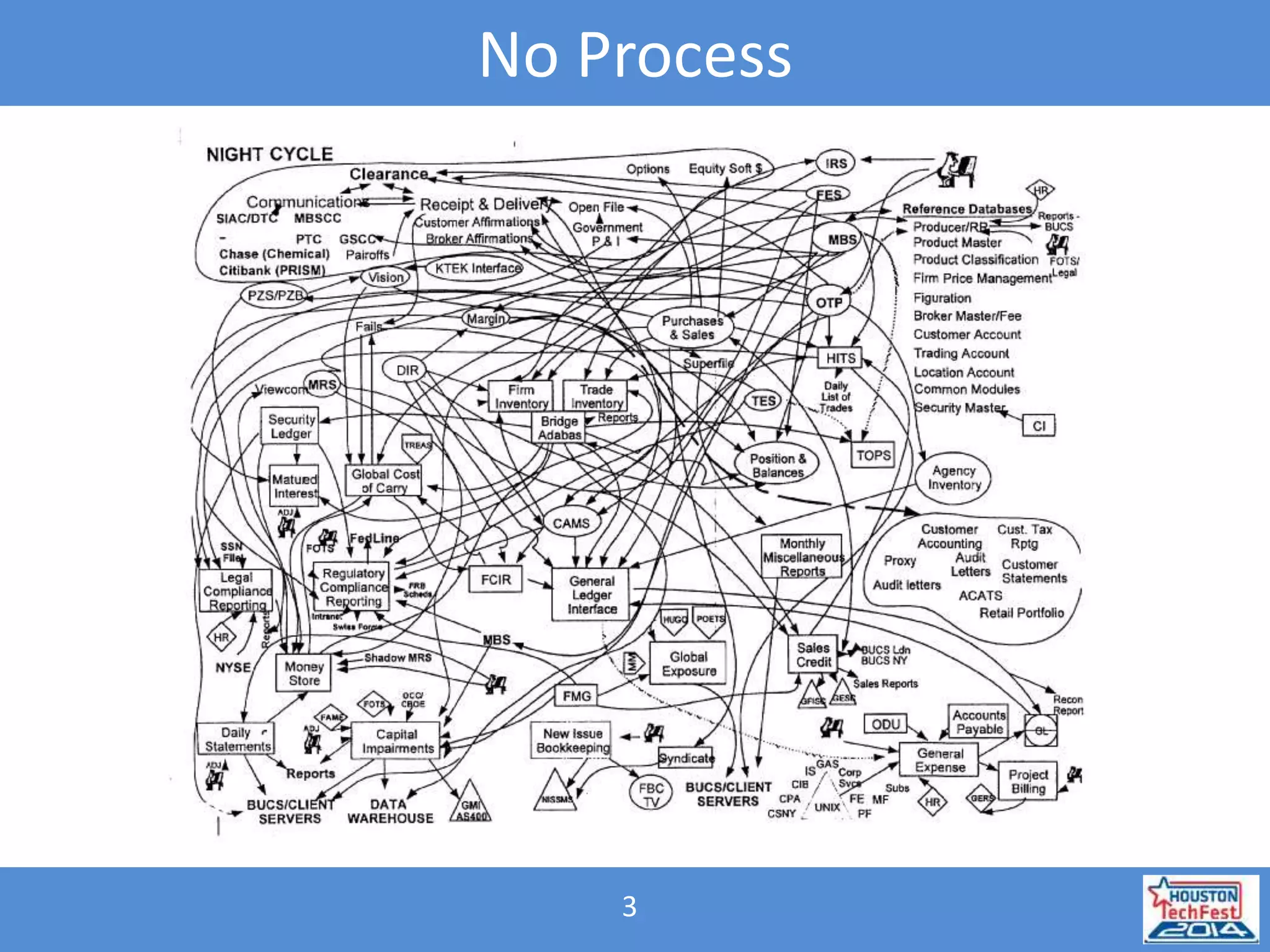
This document discusses managing SharePoint projects using Agile and Team Foundation Server (TFS). It introduces Agile project management processes like Scrum and compares them to traditional waterfall processes. It describes setting up process templates in TFS, including the Agile and Scrum templates. It then covers various Agile concepts like product backlogs, sprints, stand-up meetings, and retrospectives and how they relate to planning and executing SharePoint projects in TFS.