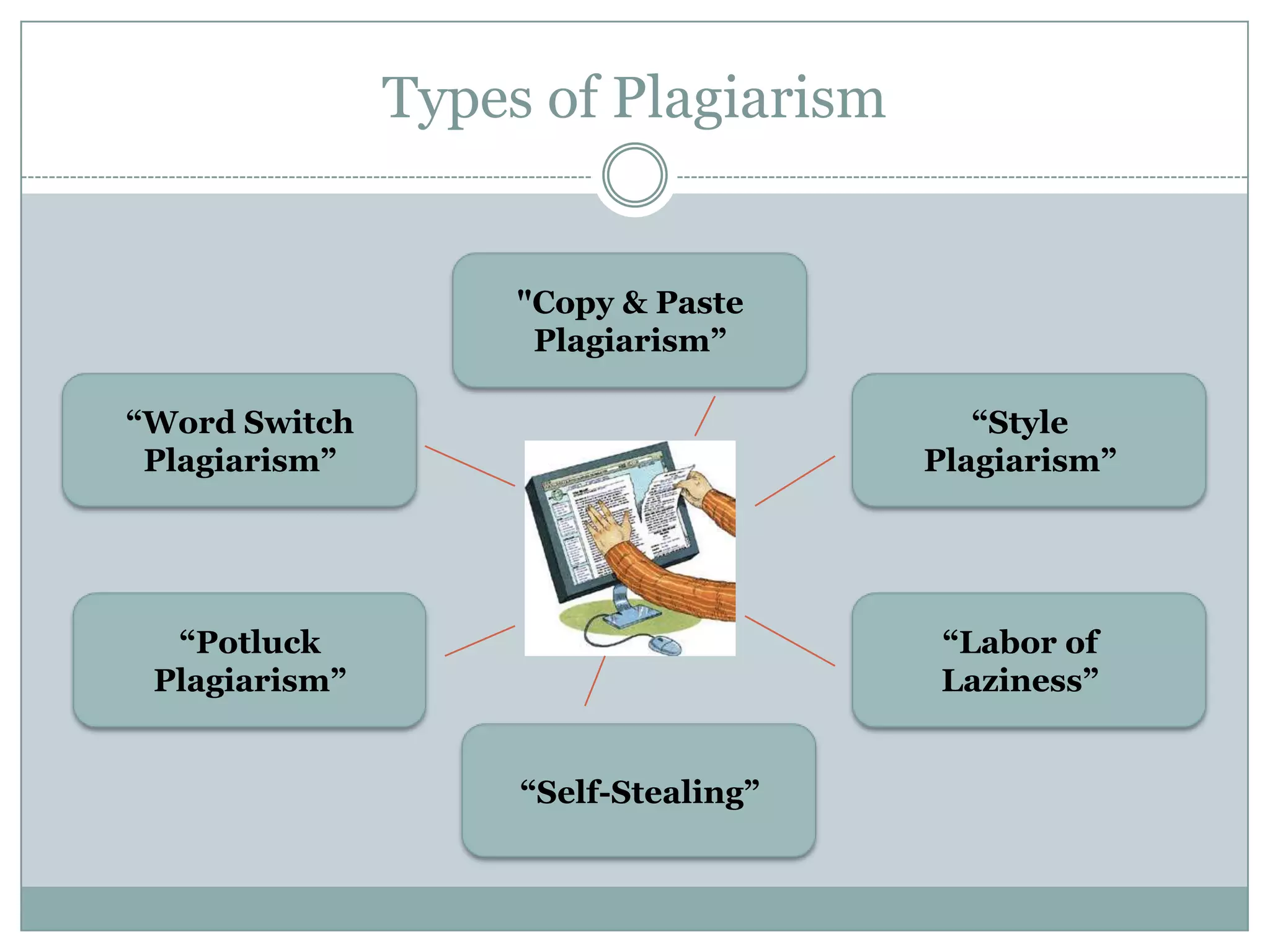
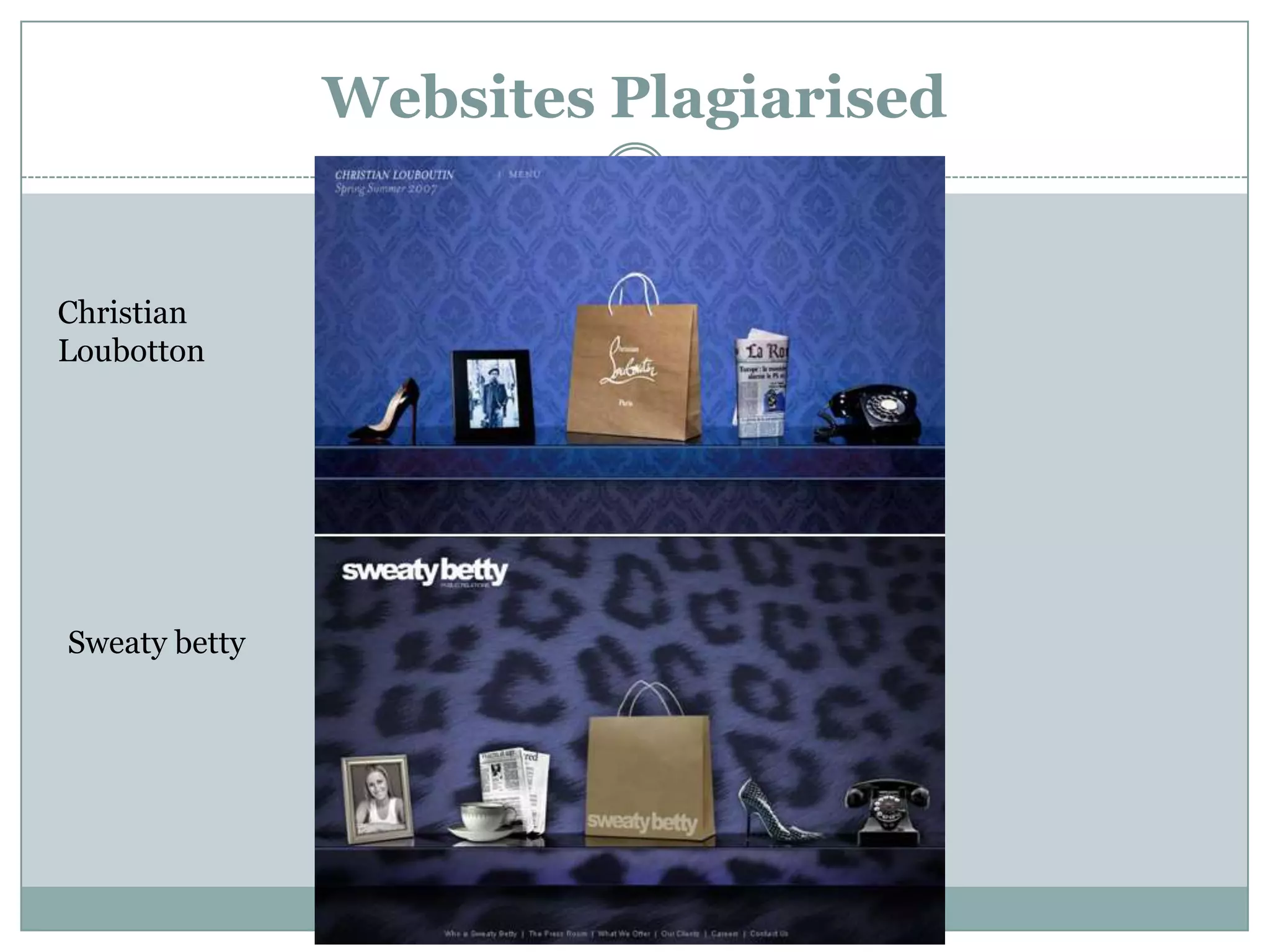
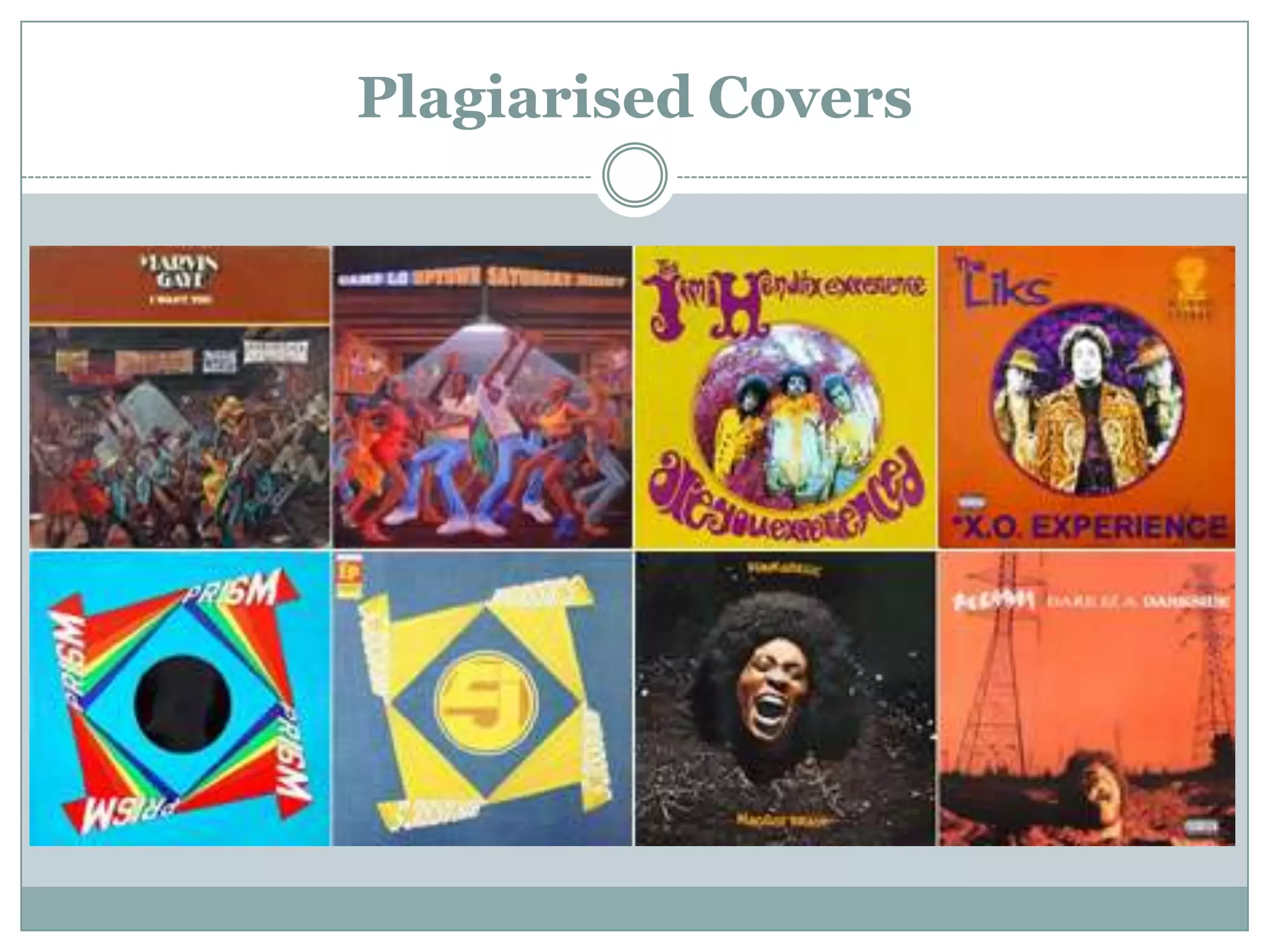
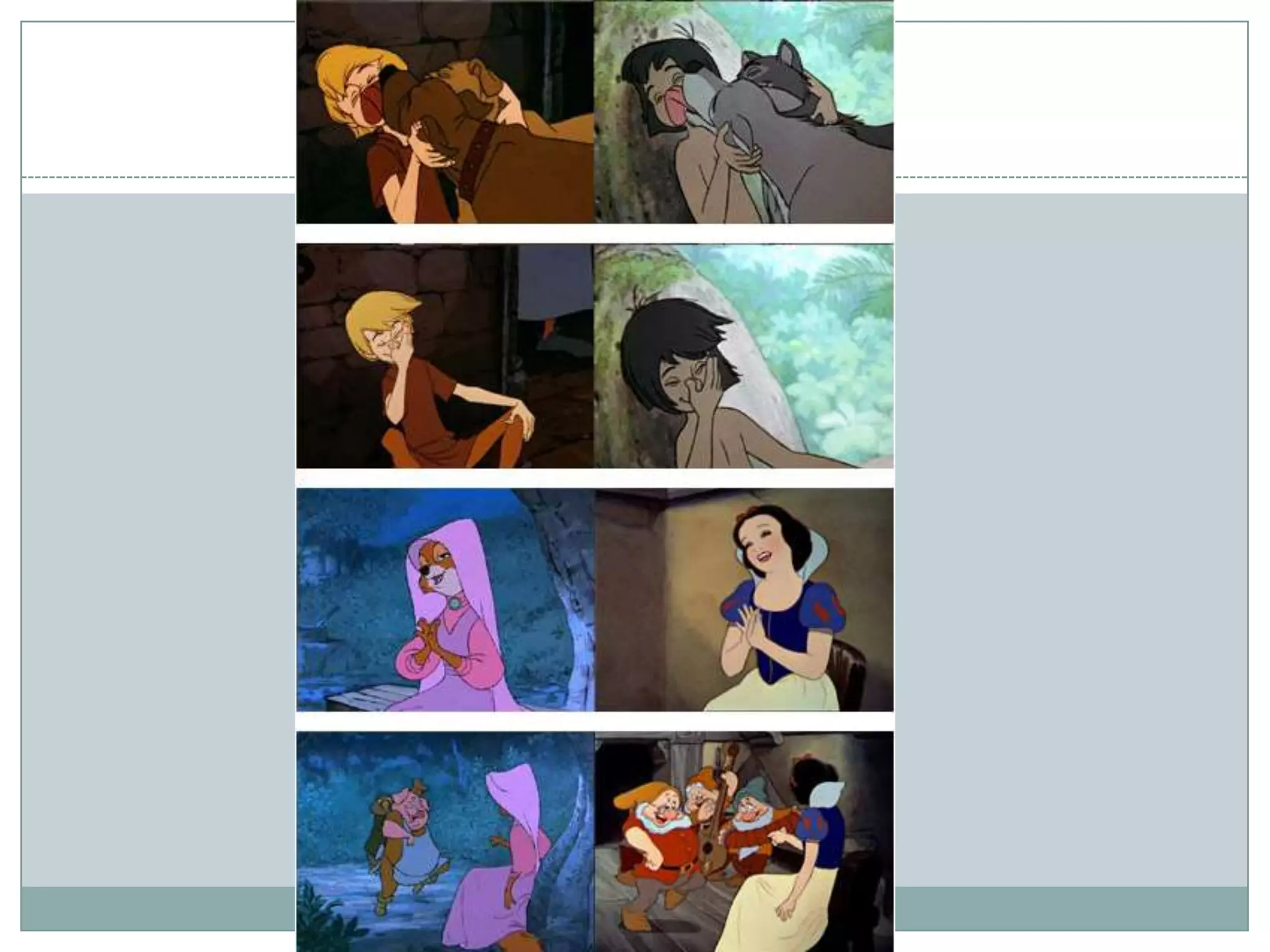
This document discusses plagiarism and how to avoid it in academic work. It defines plagiarism as passing off someone else's work as your own. The types of plagiarism include copy-paste plagiarism, switching around words, using another's ideas without credit, and self-plagiarism. To avoid plagiarism, you should cite all sources using styles like APA or MLA and create reference lists. When paraphrasing, you should change the wording and sentence structure. Common knowledge does not need to be cited. The document provides examples of properly citing different source types and using software tools to easily create reference lists.