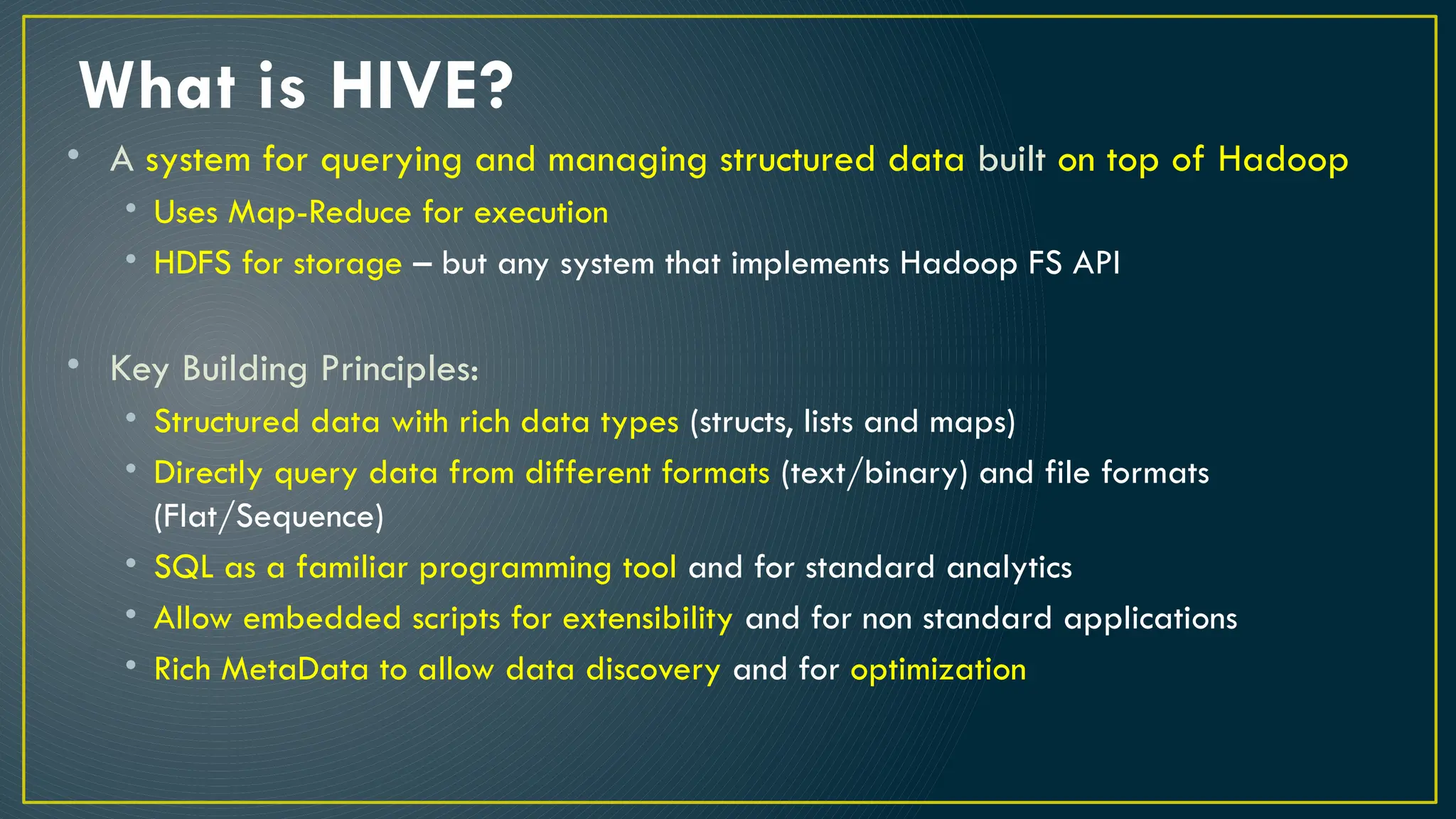
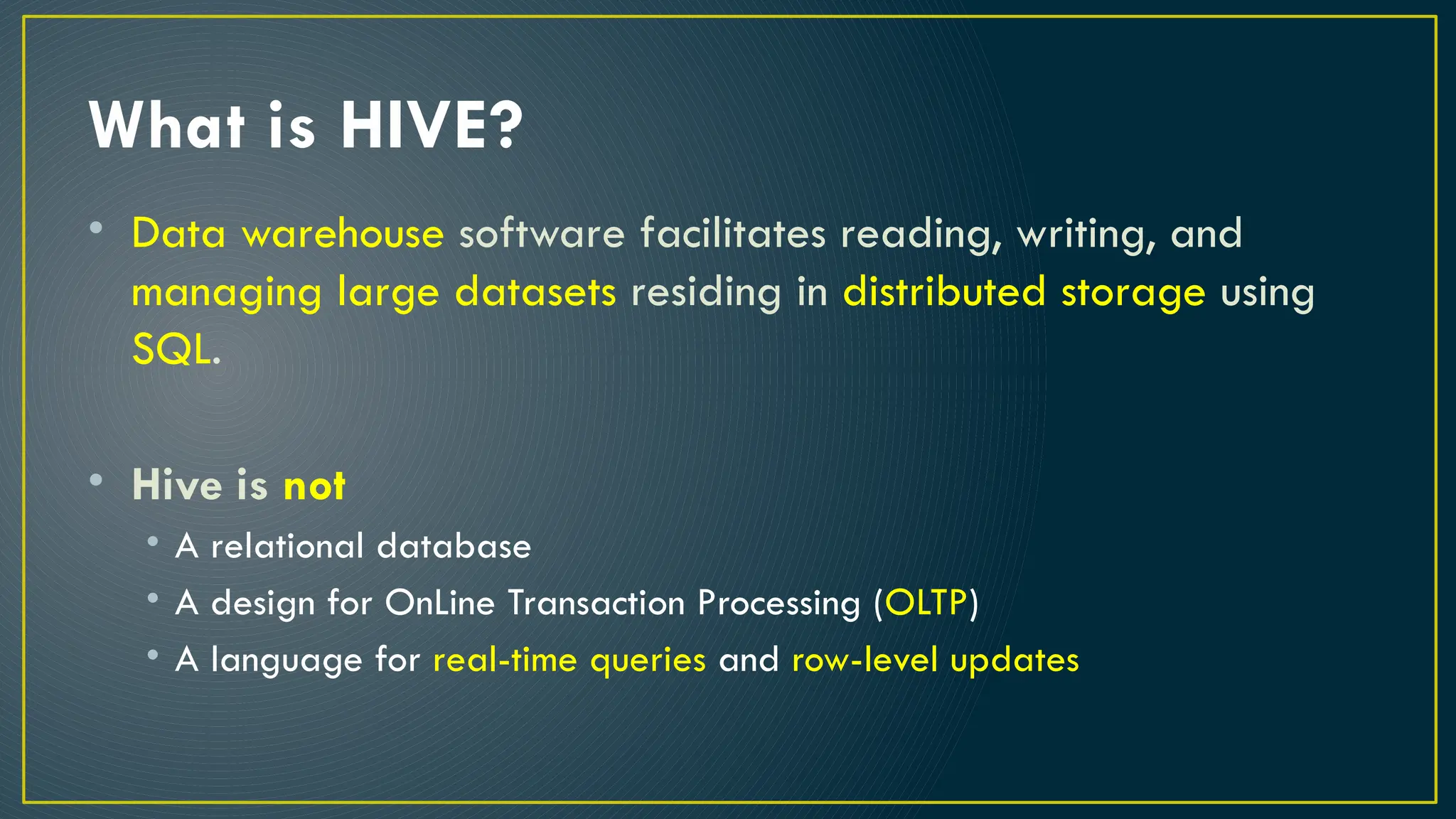
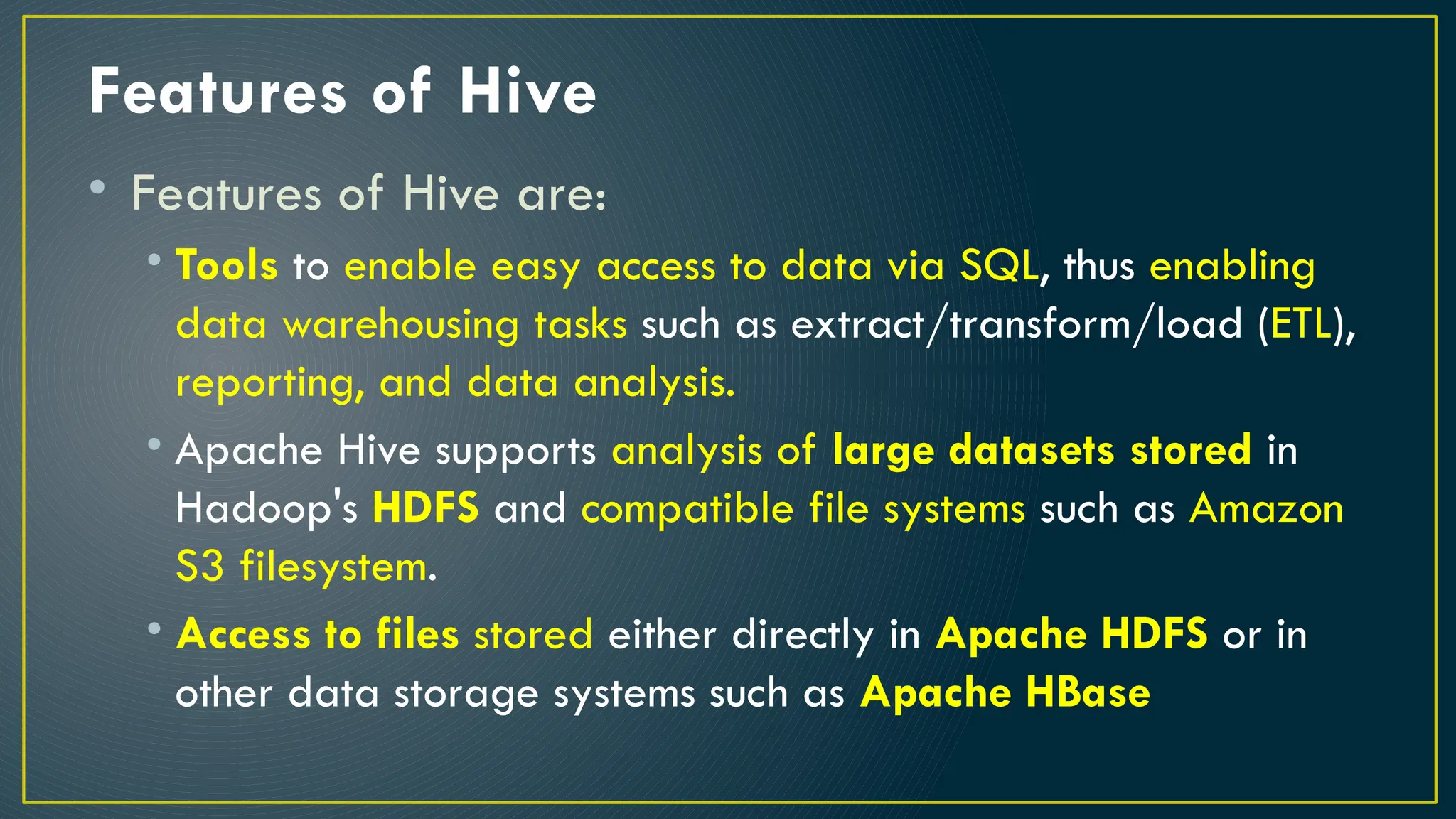
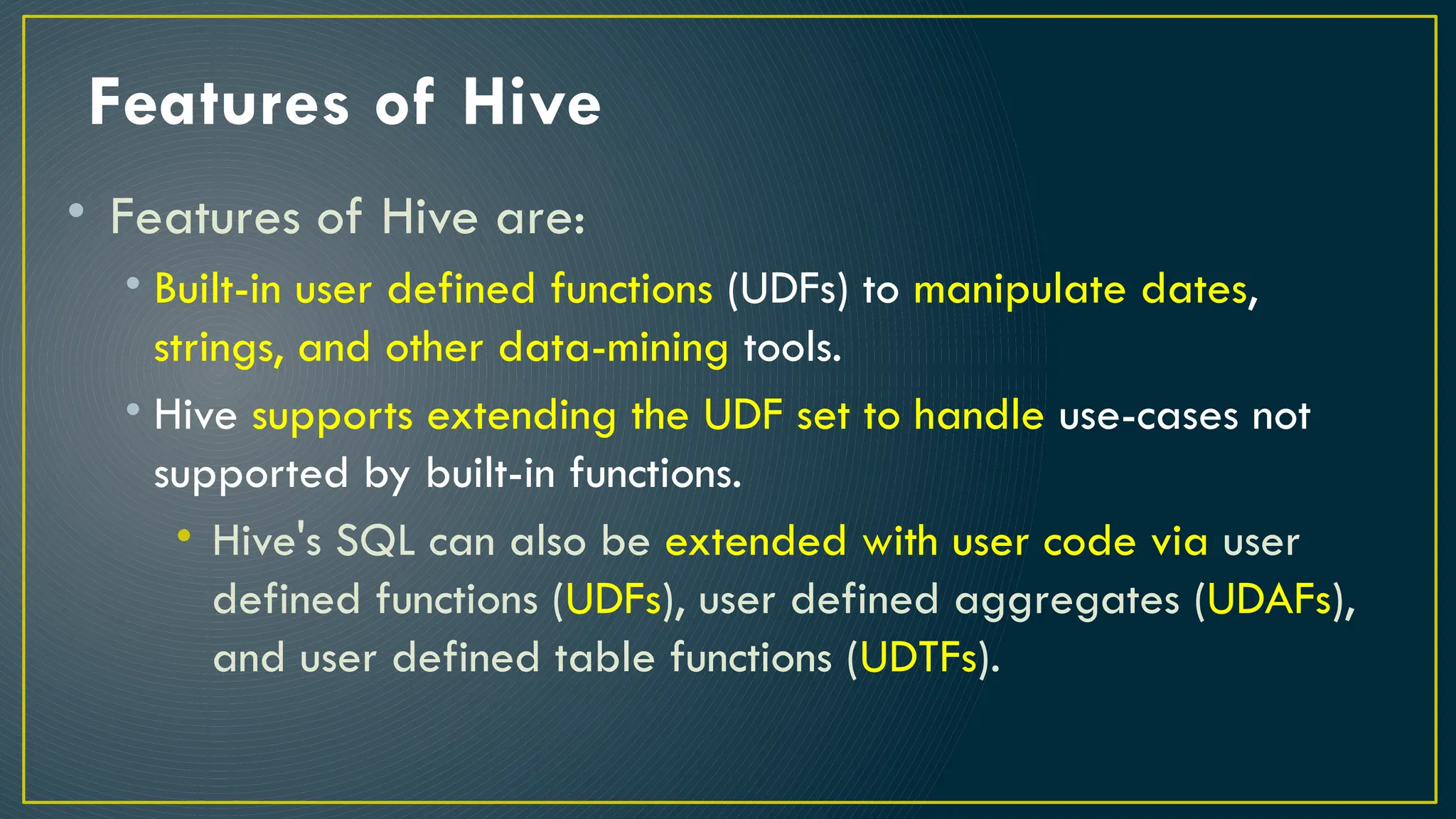
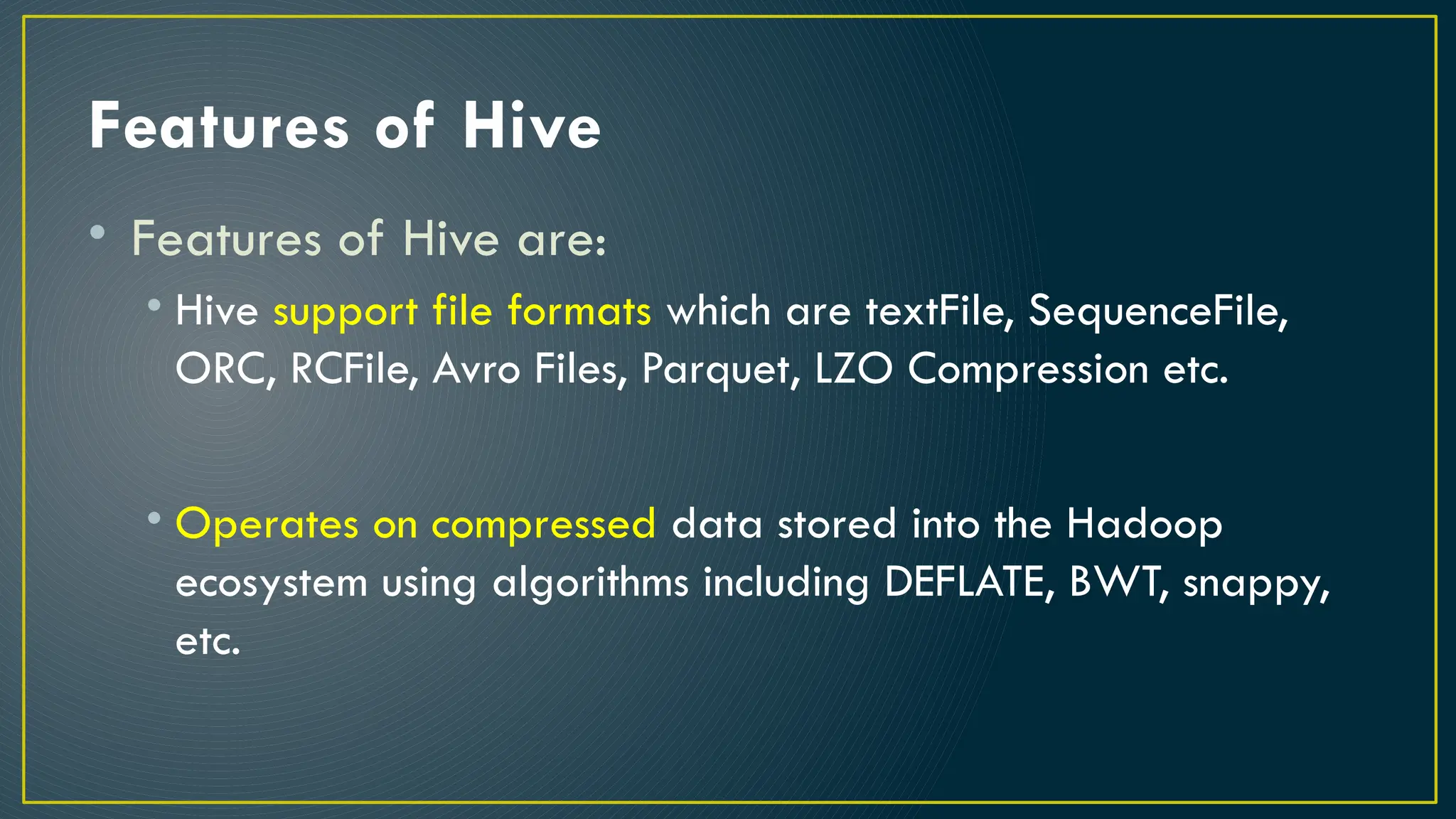
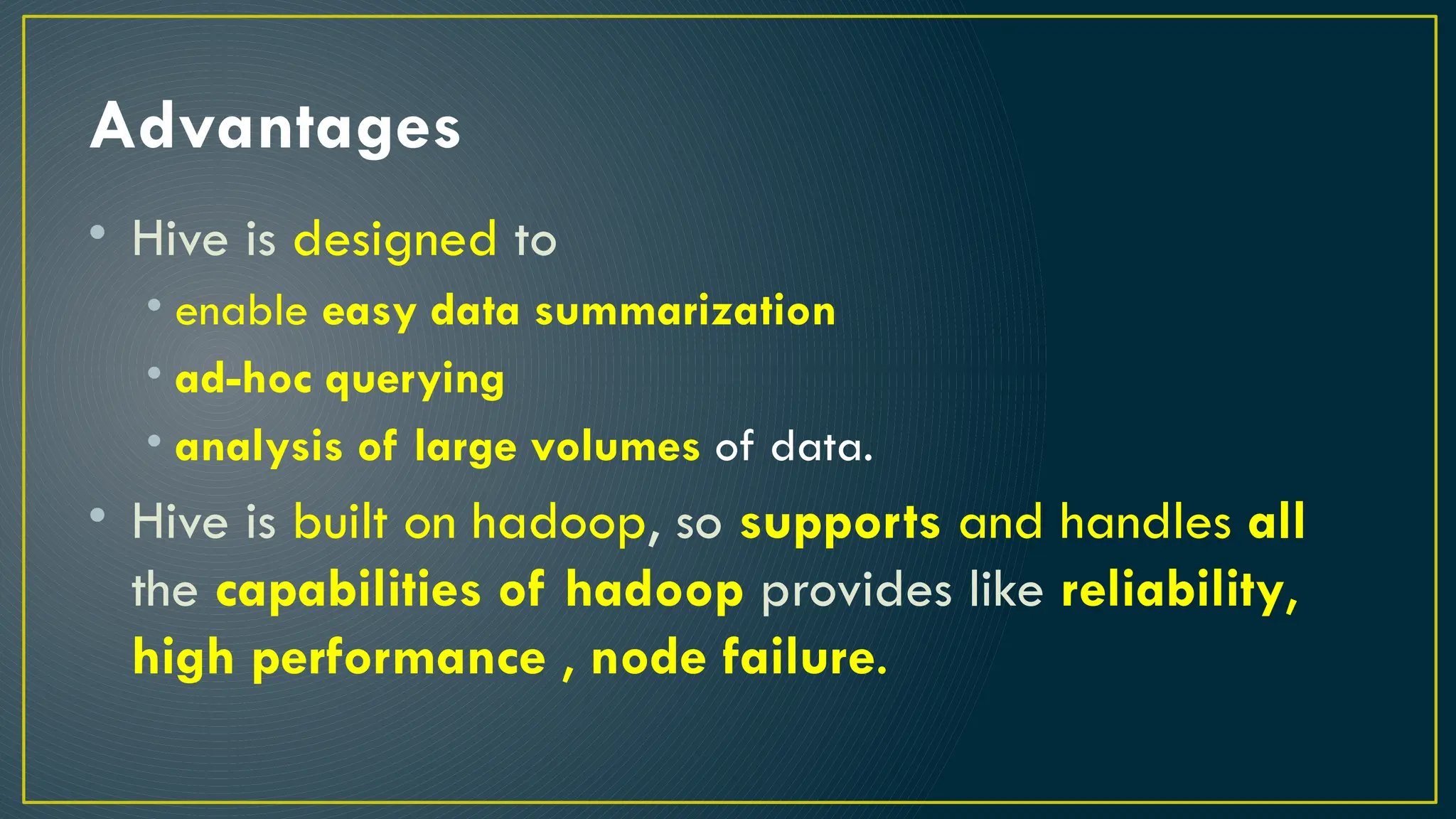
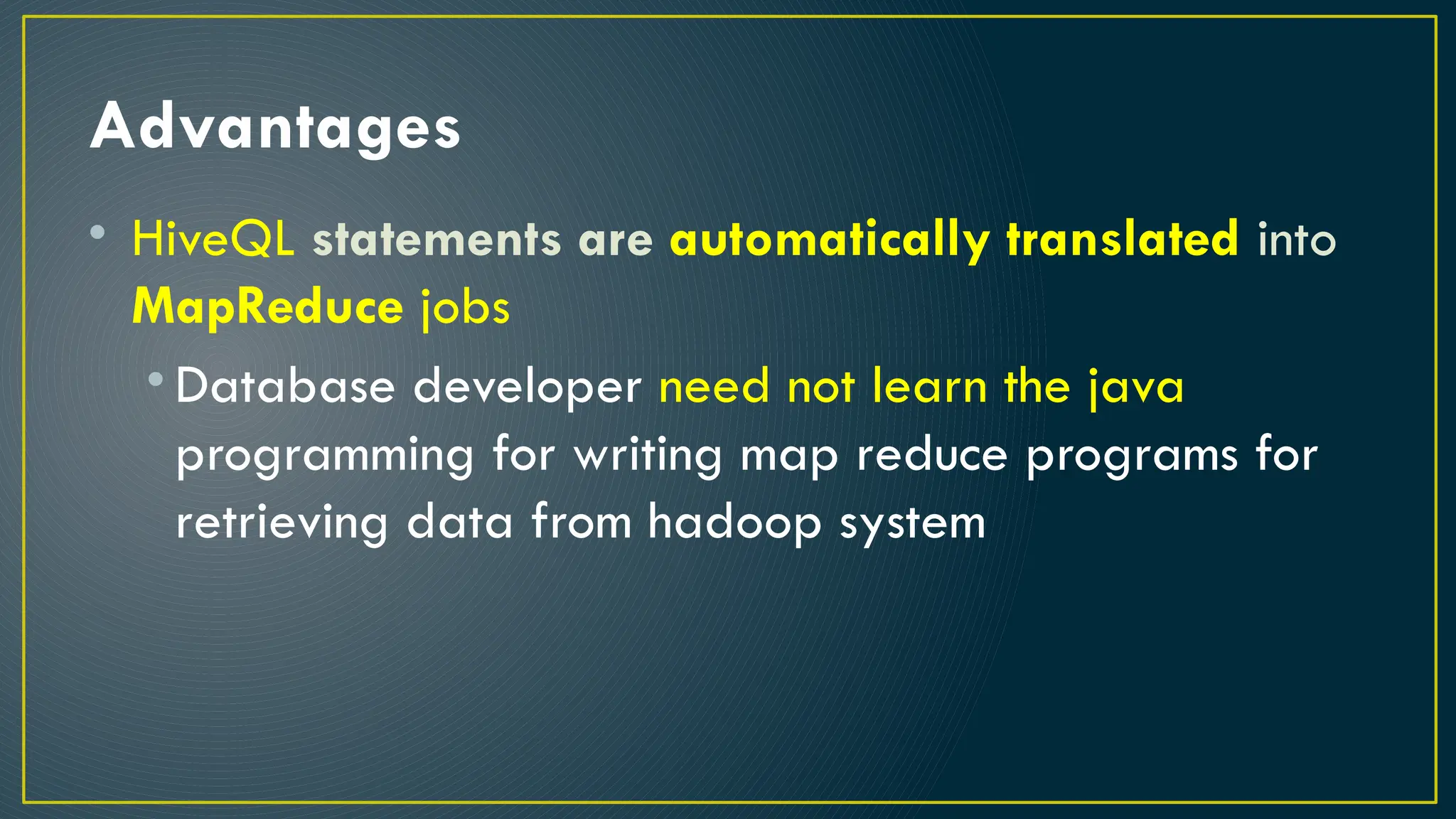
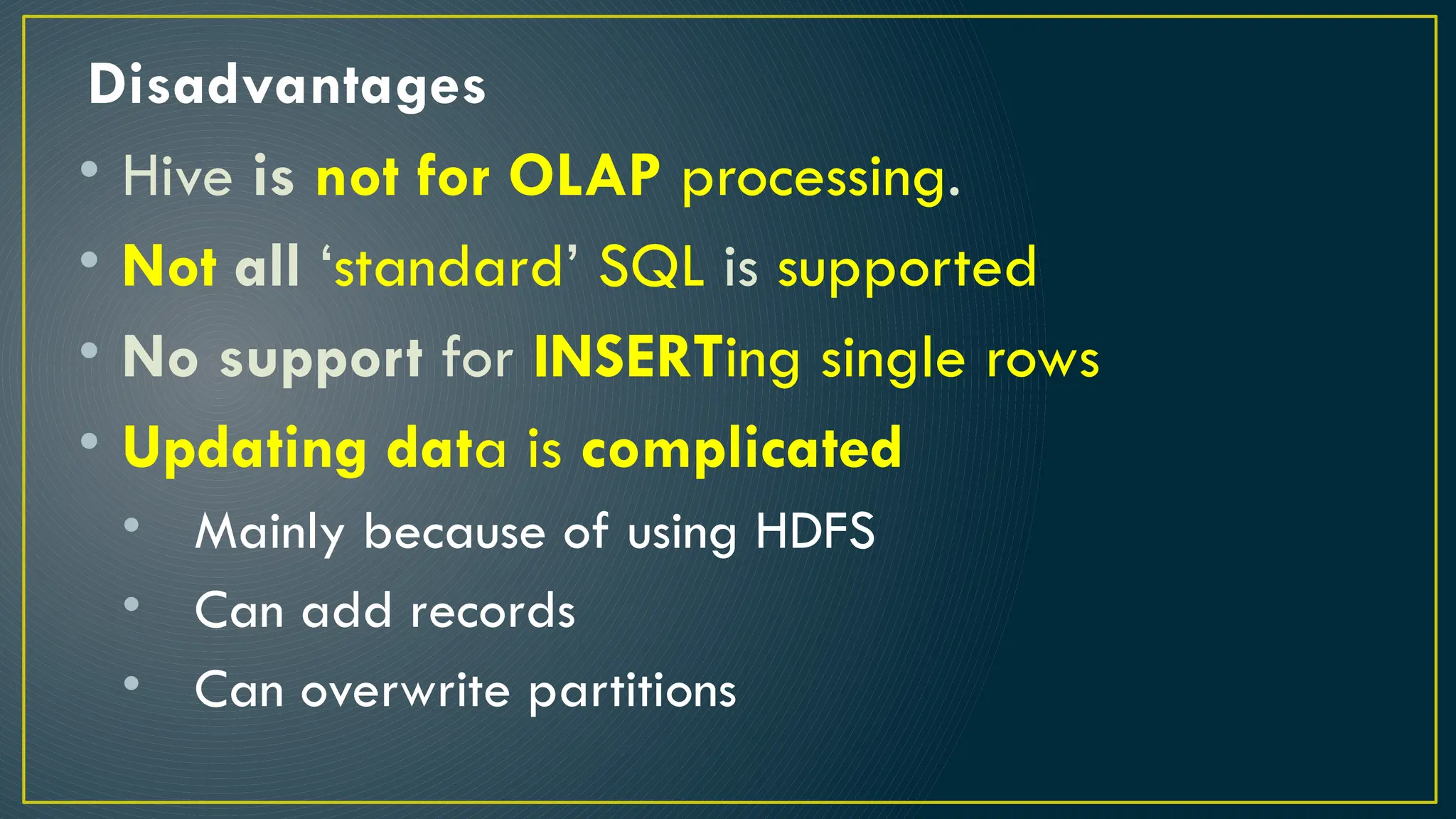
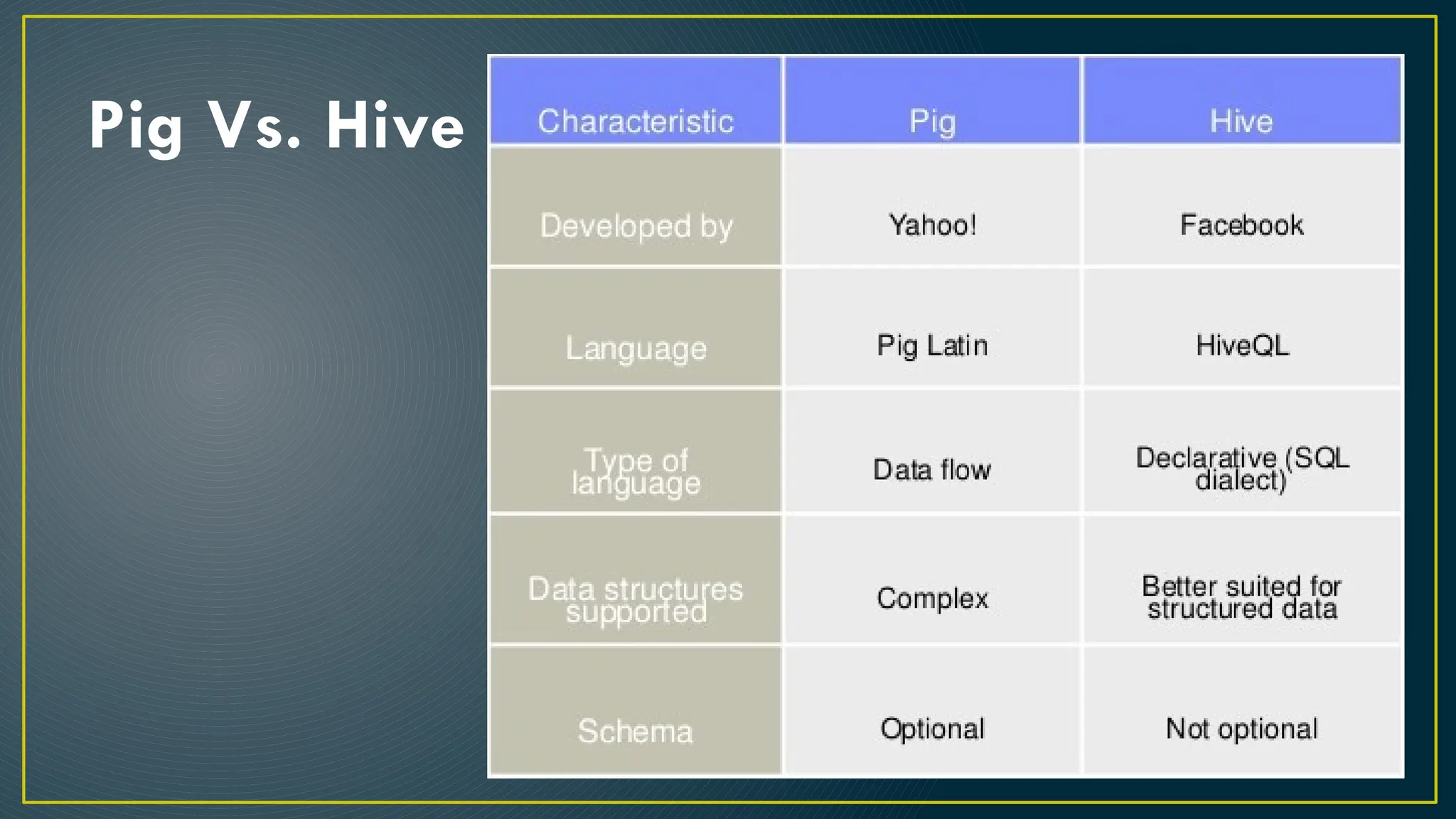
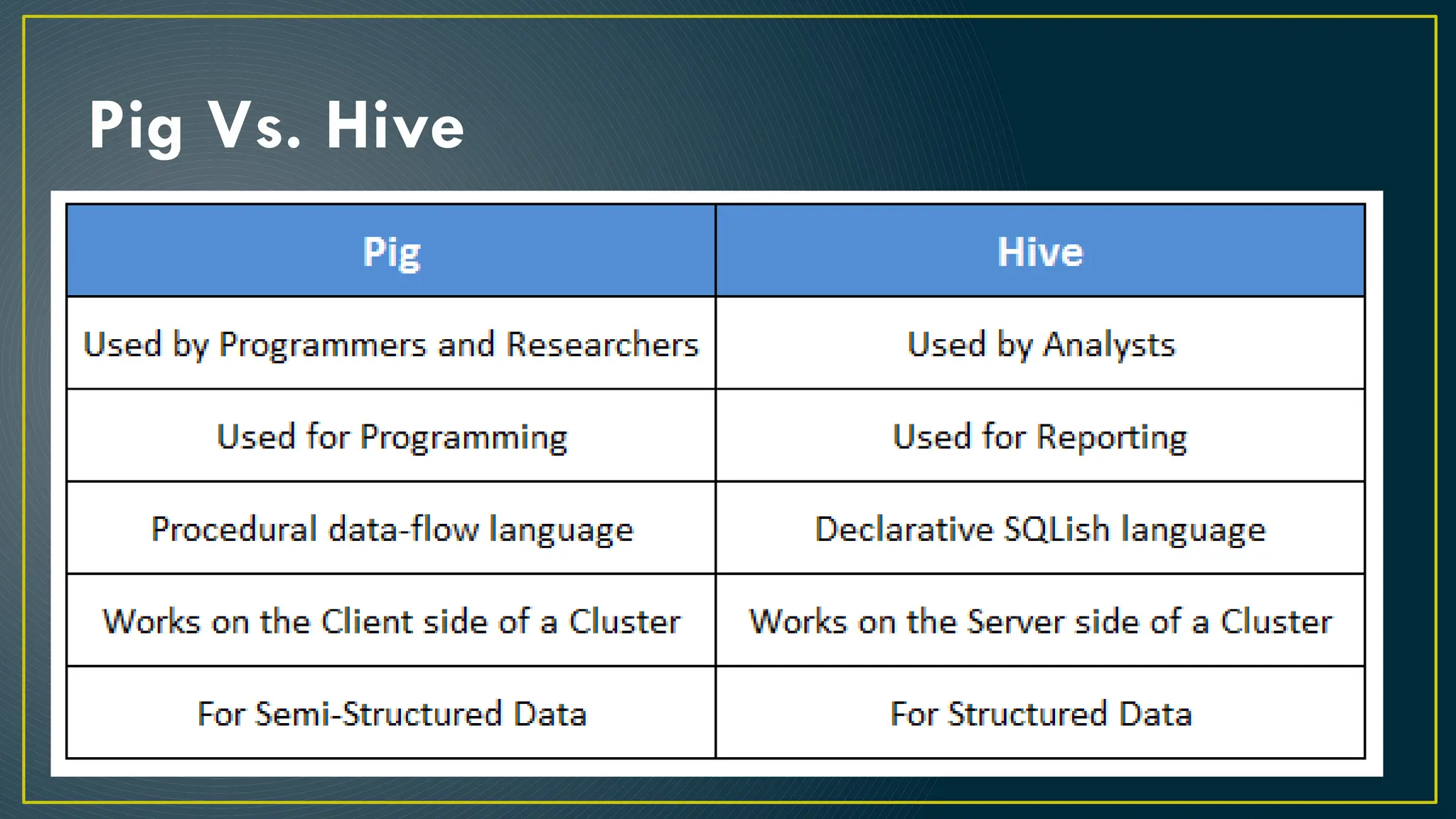
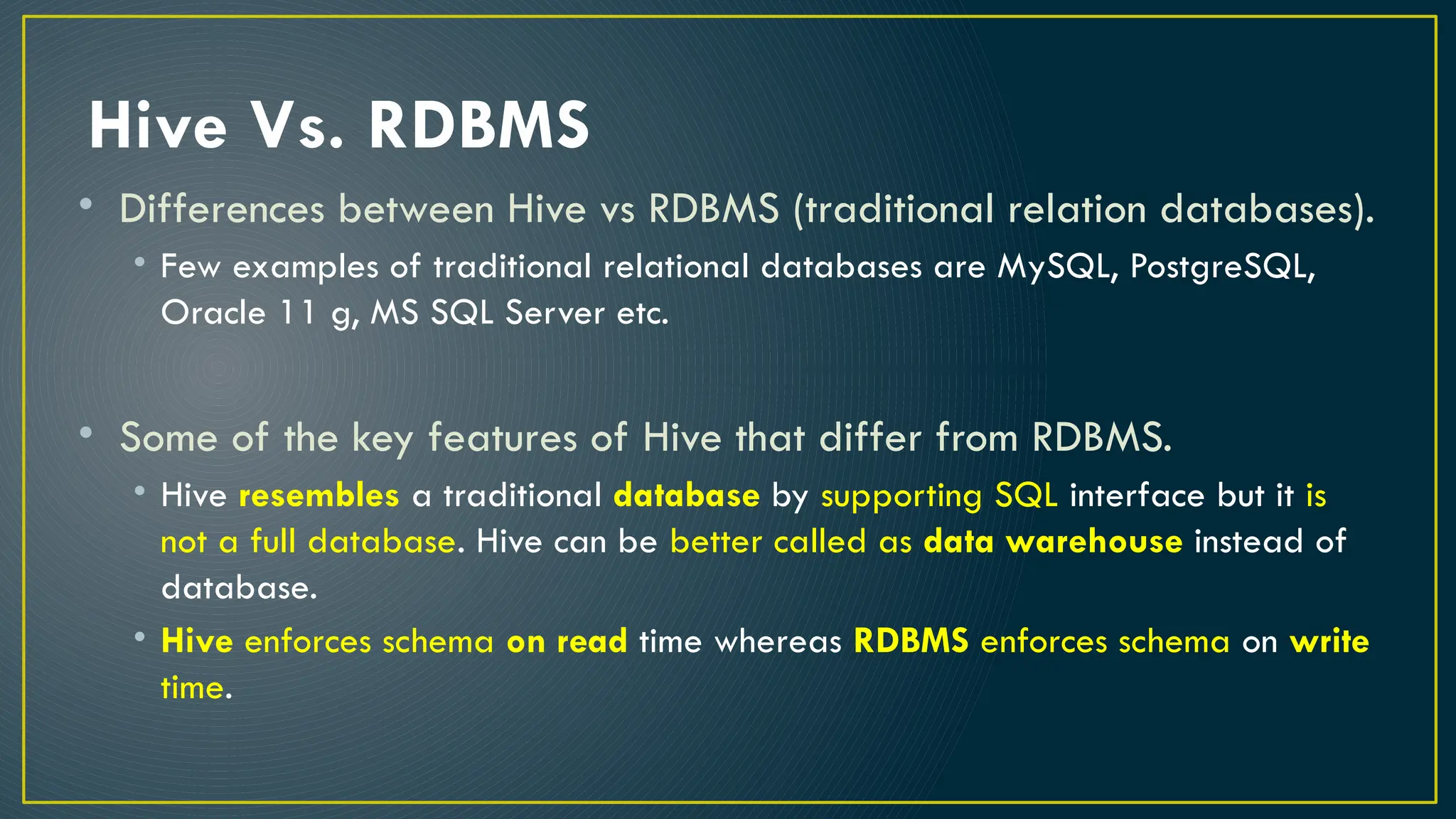
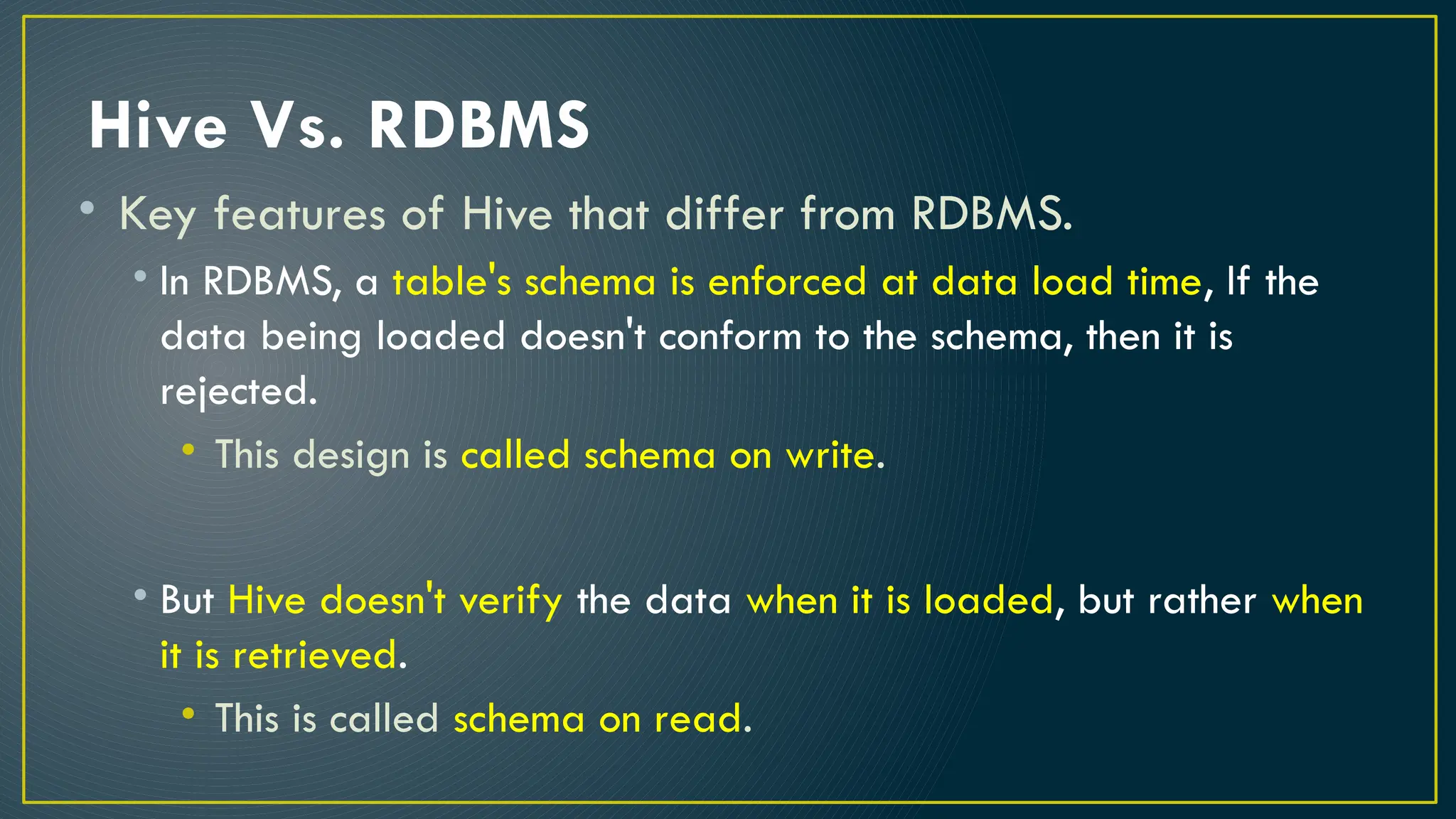
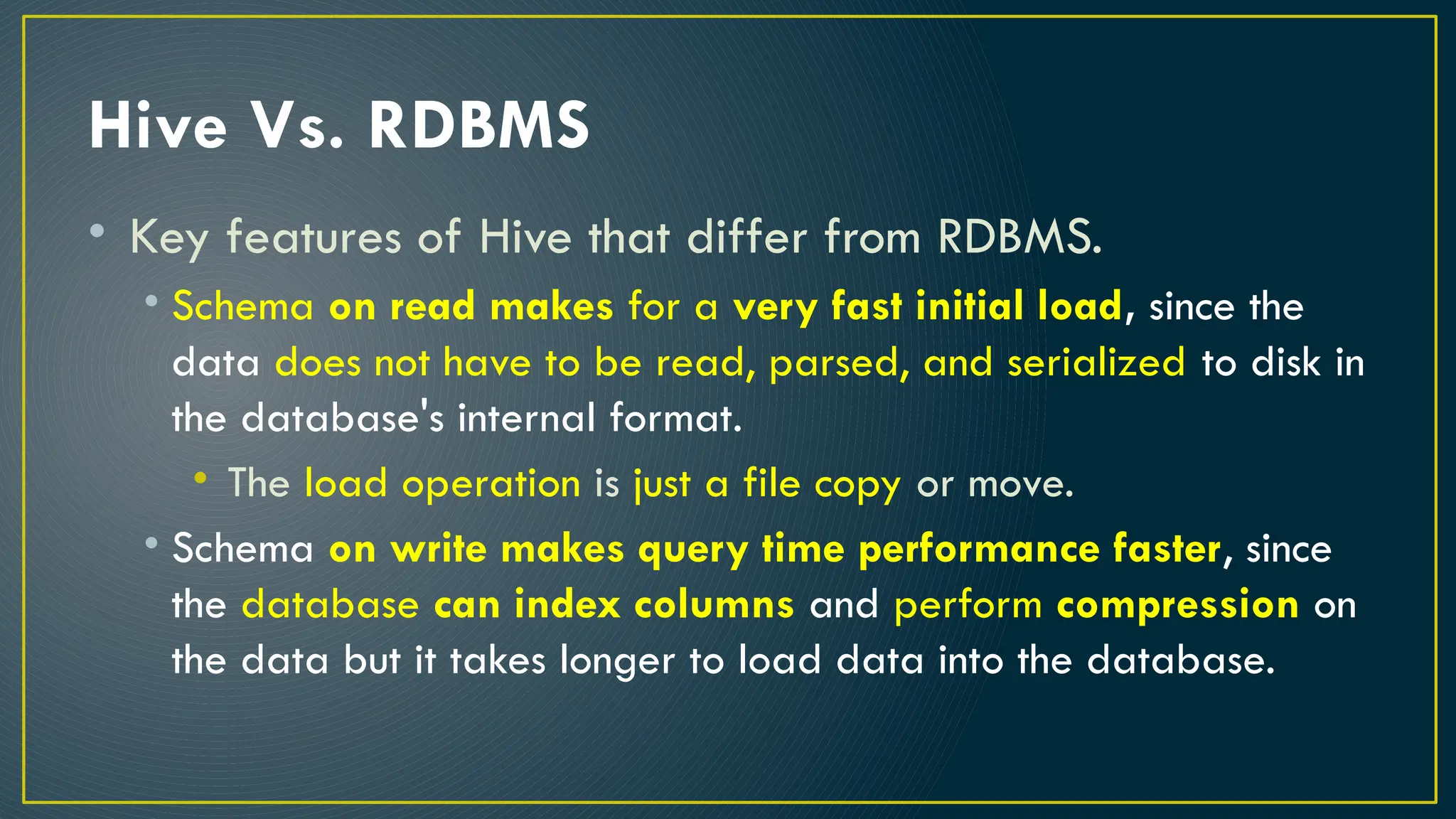
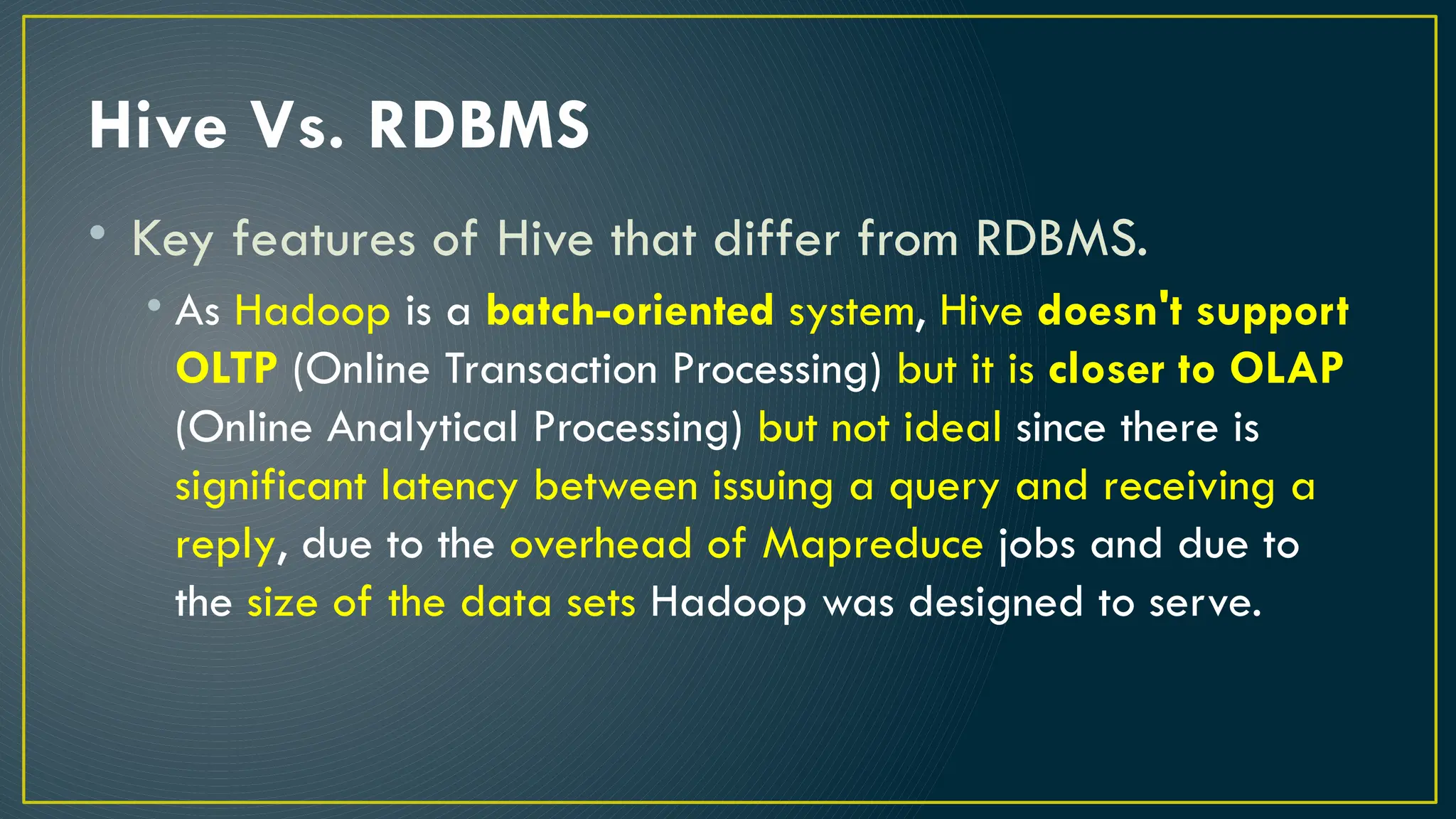
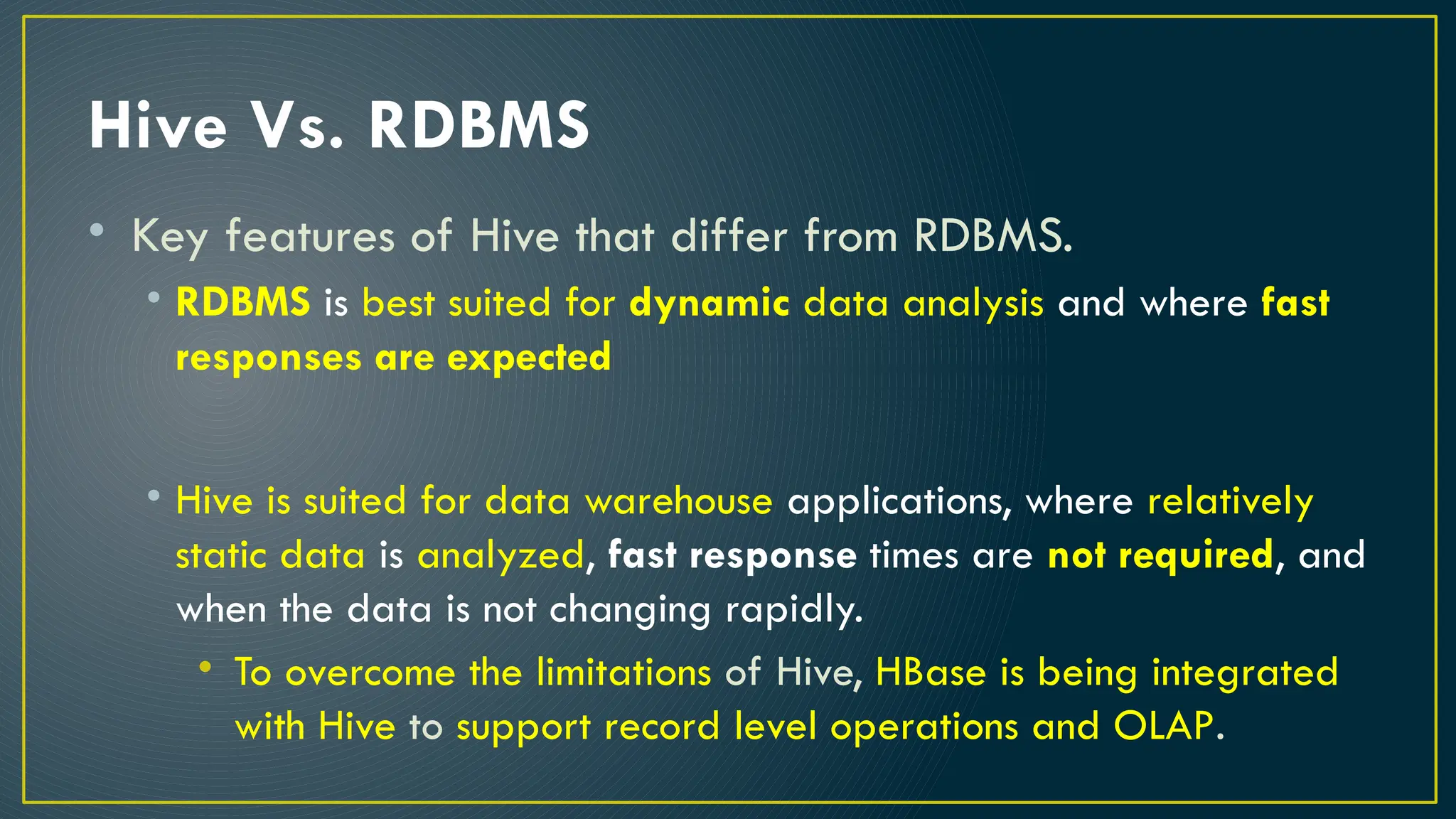
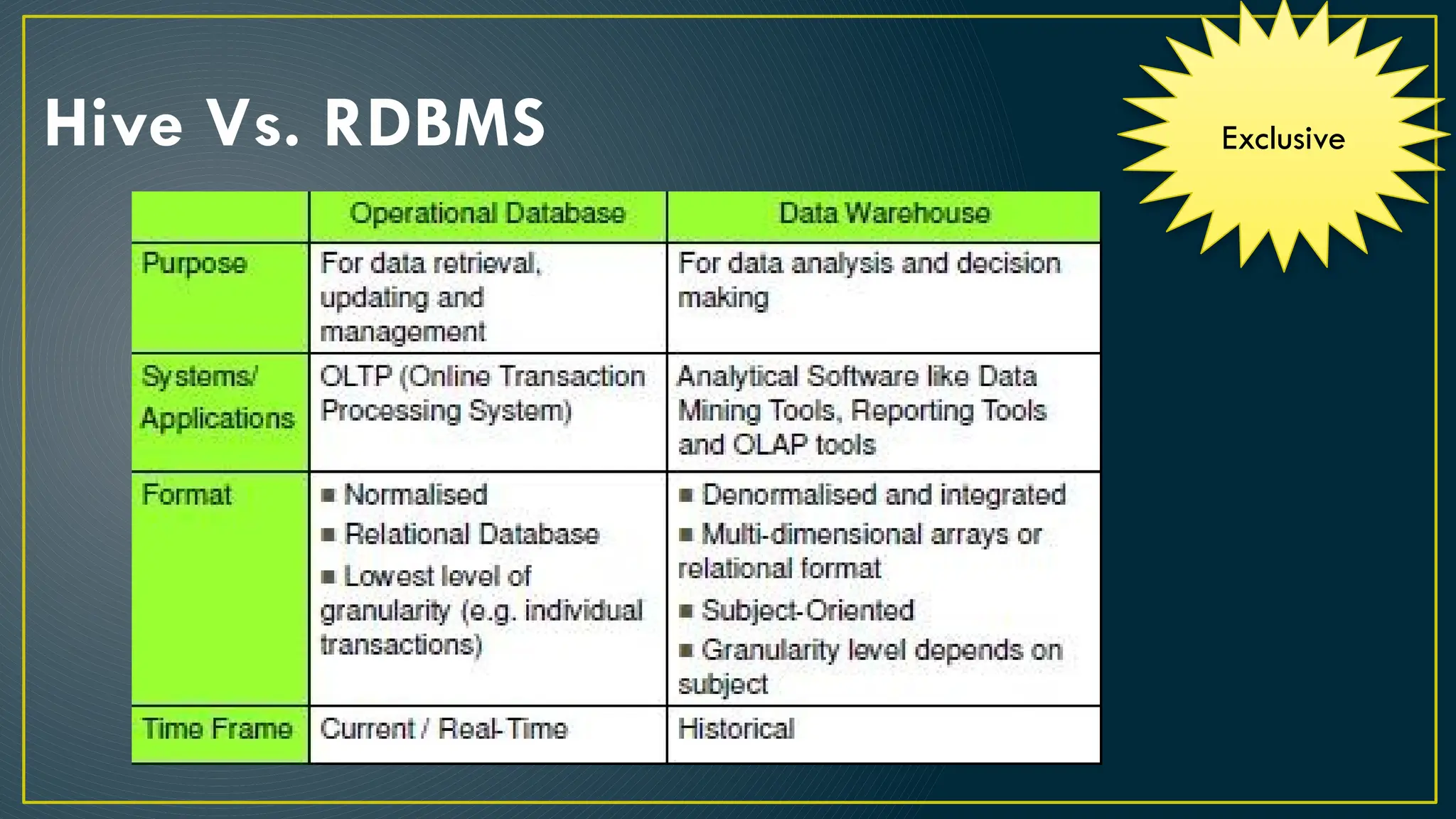
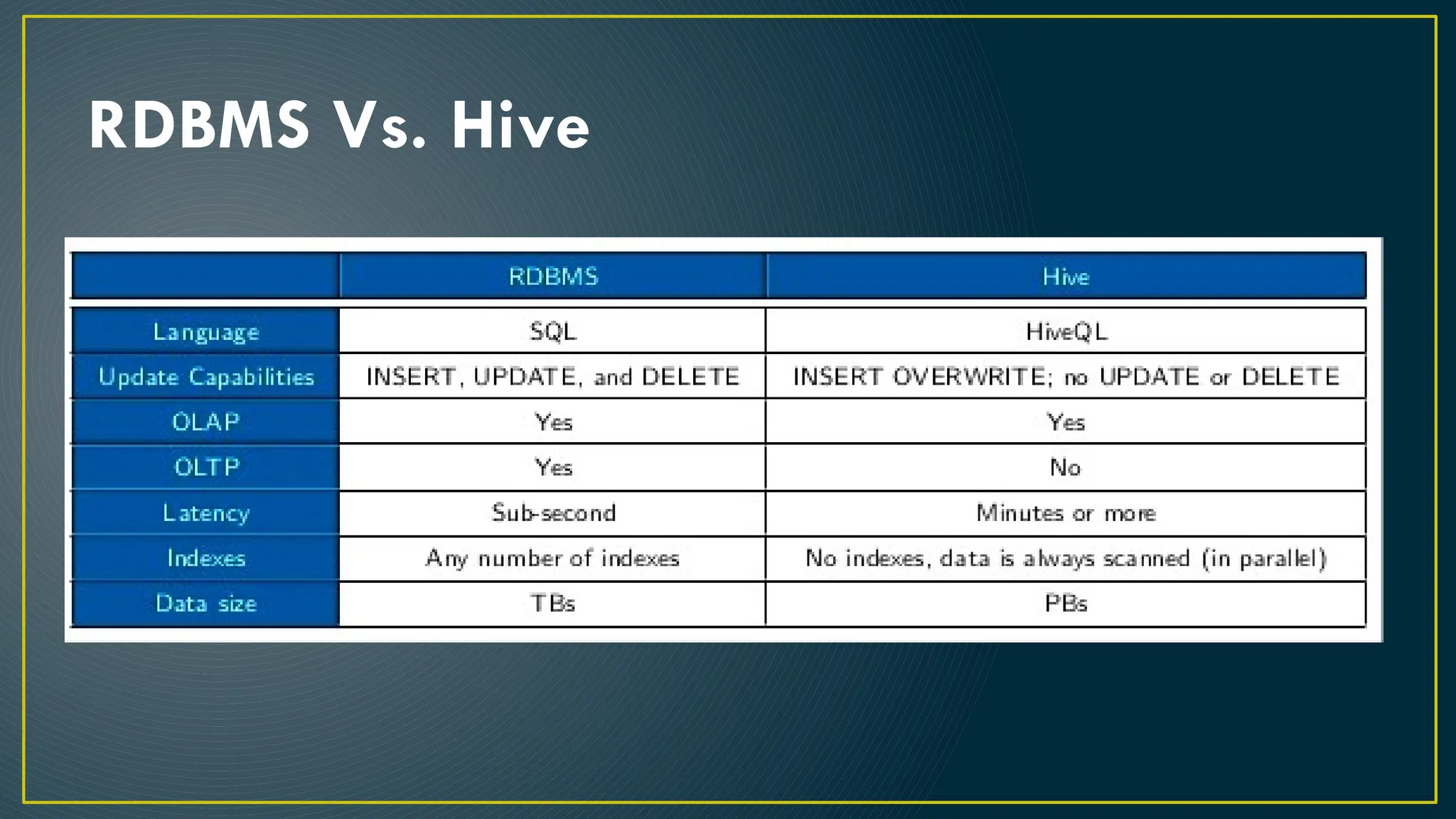
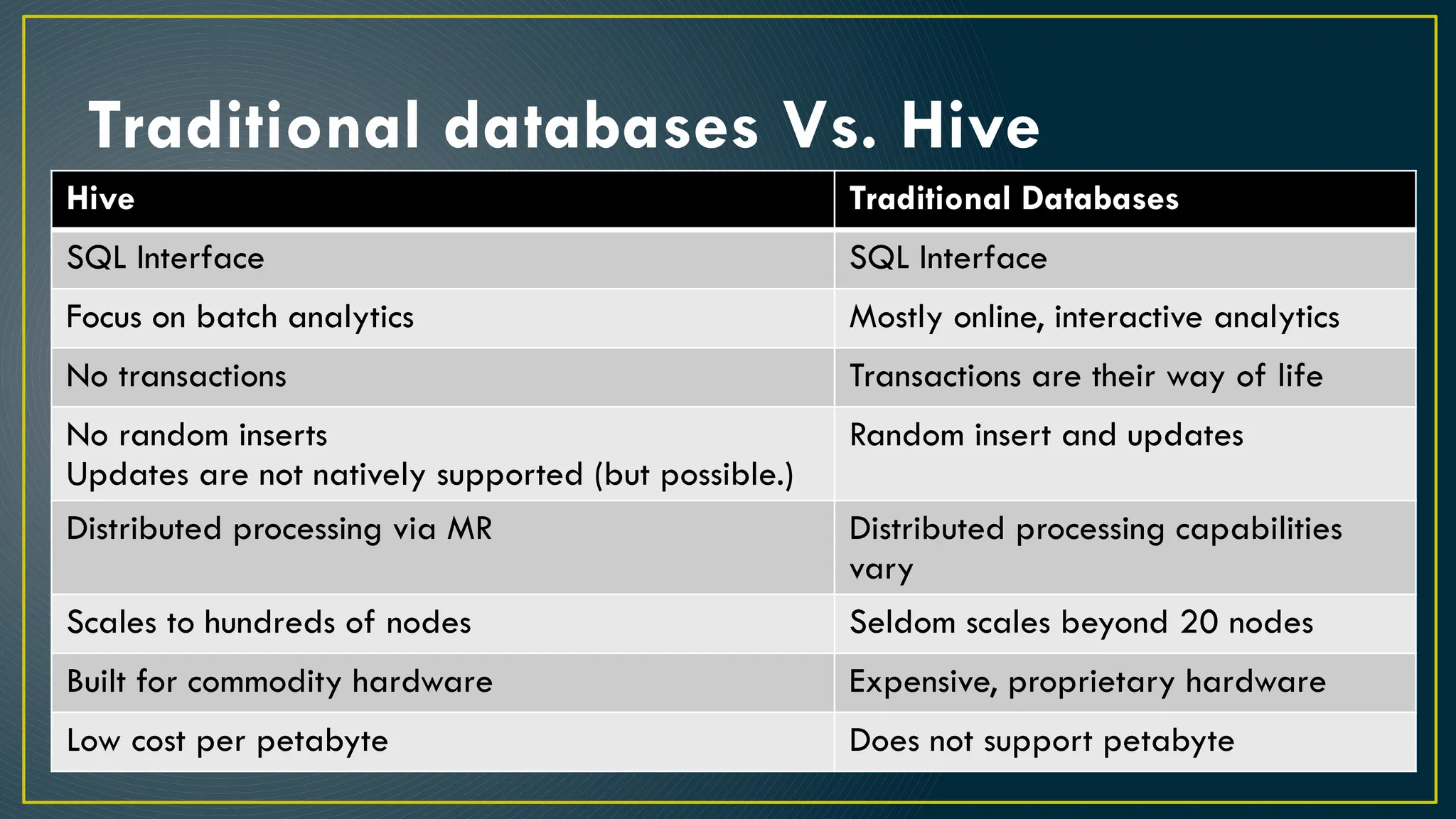
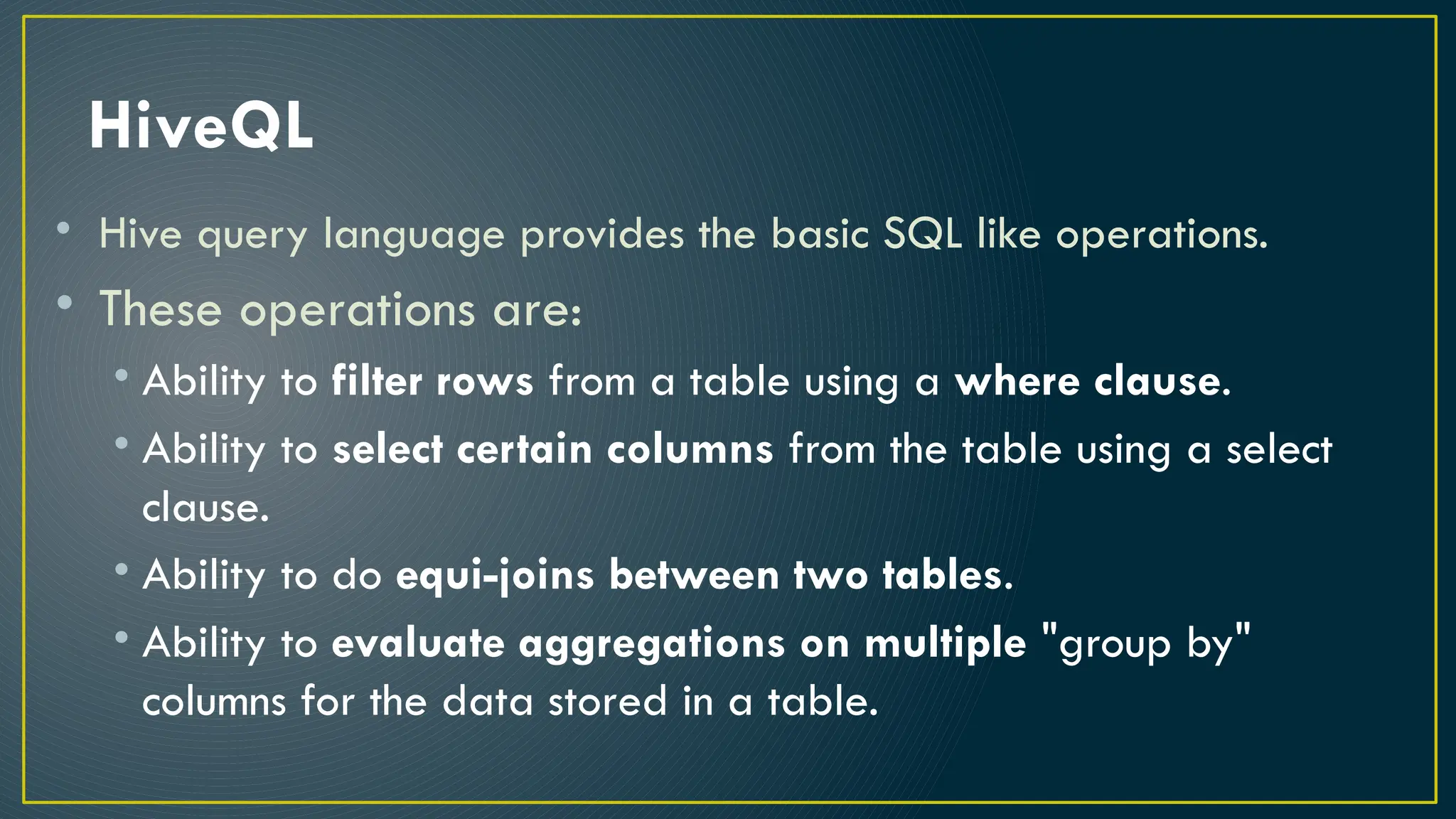
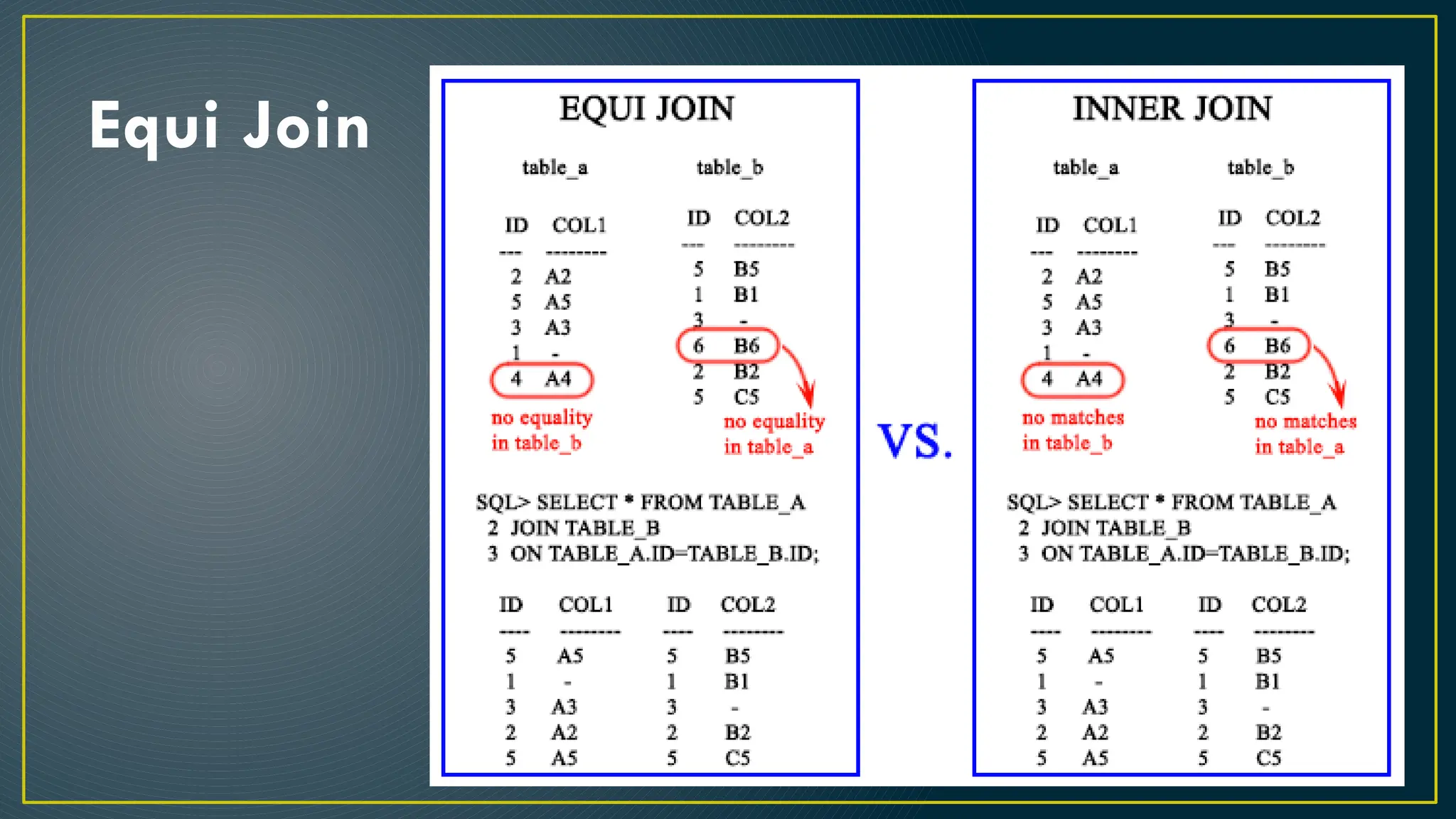
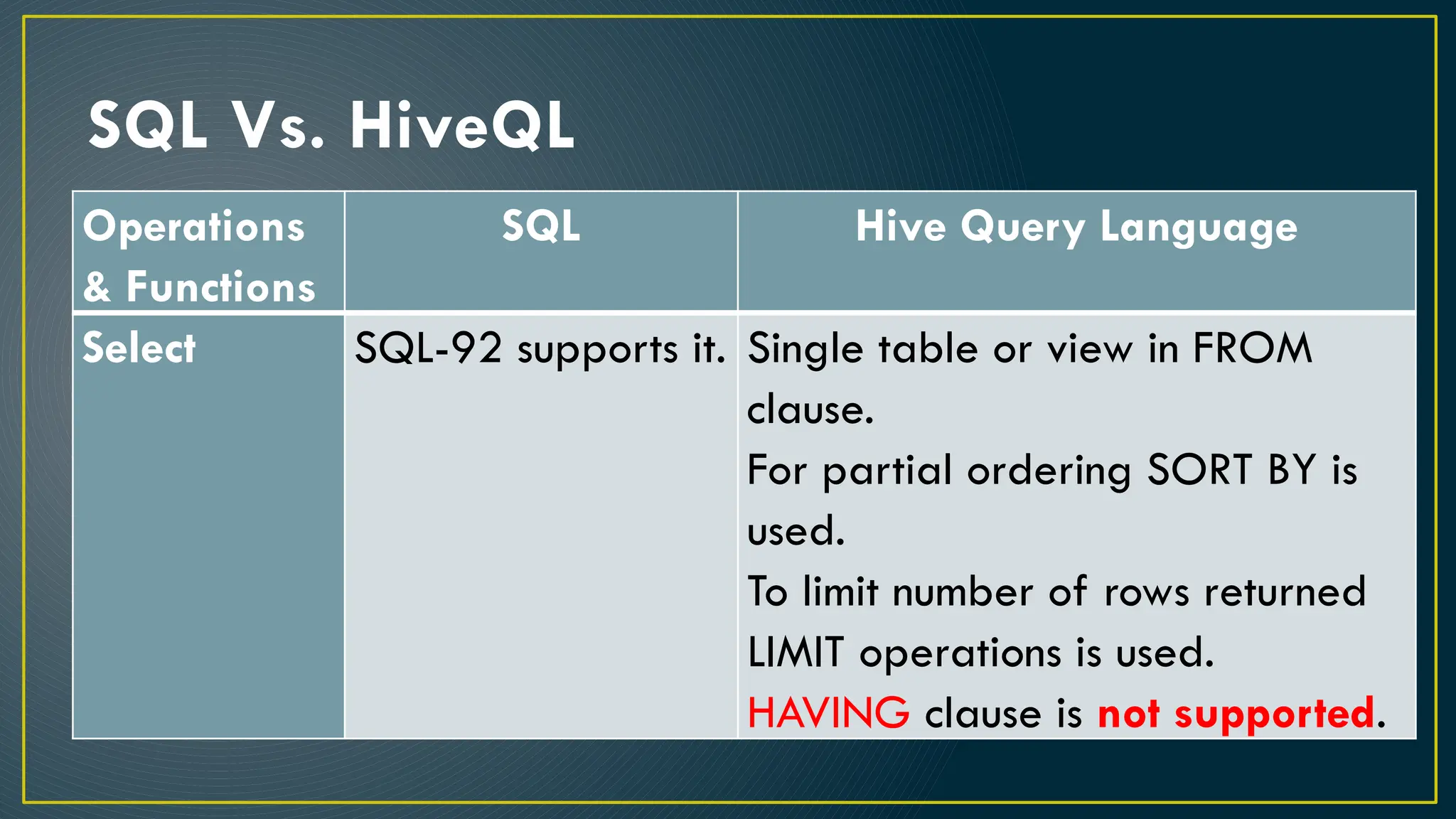
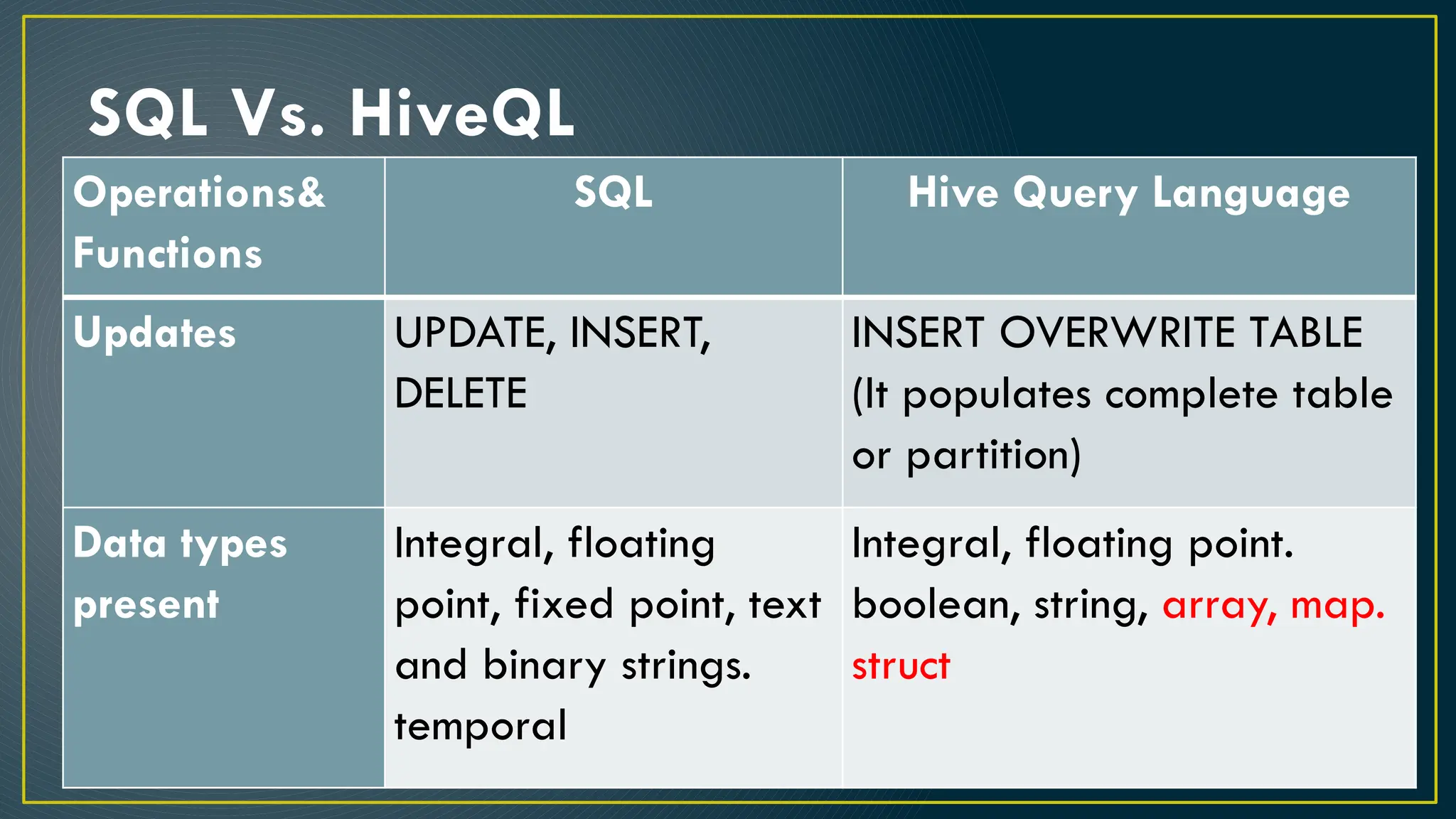
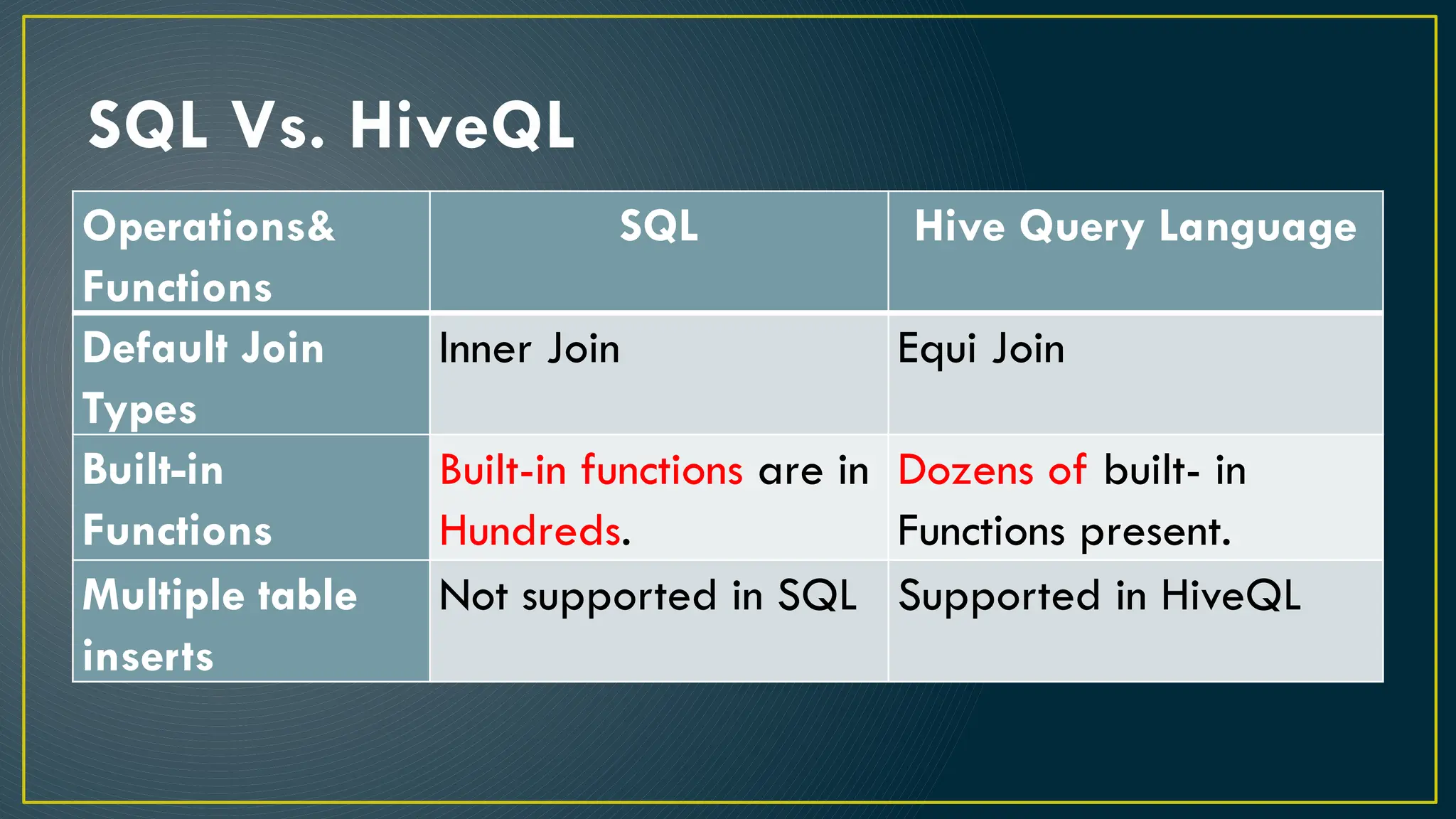
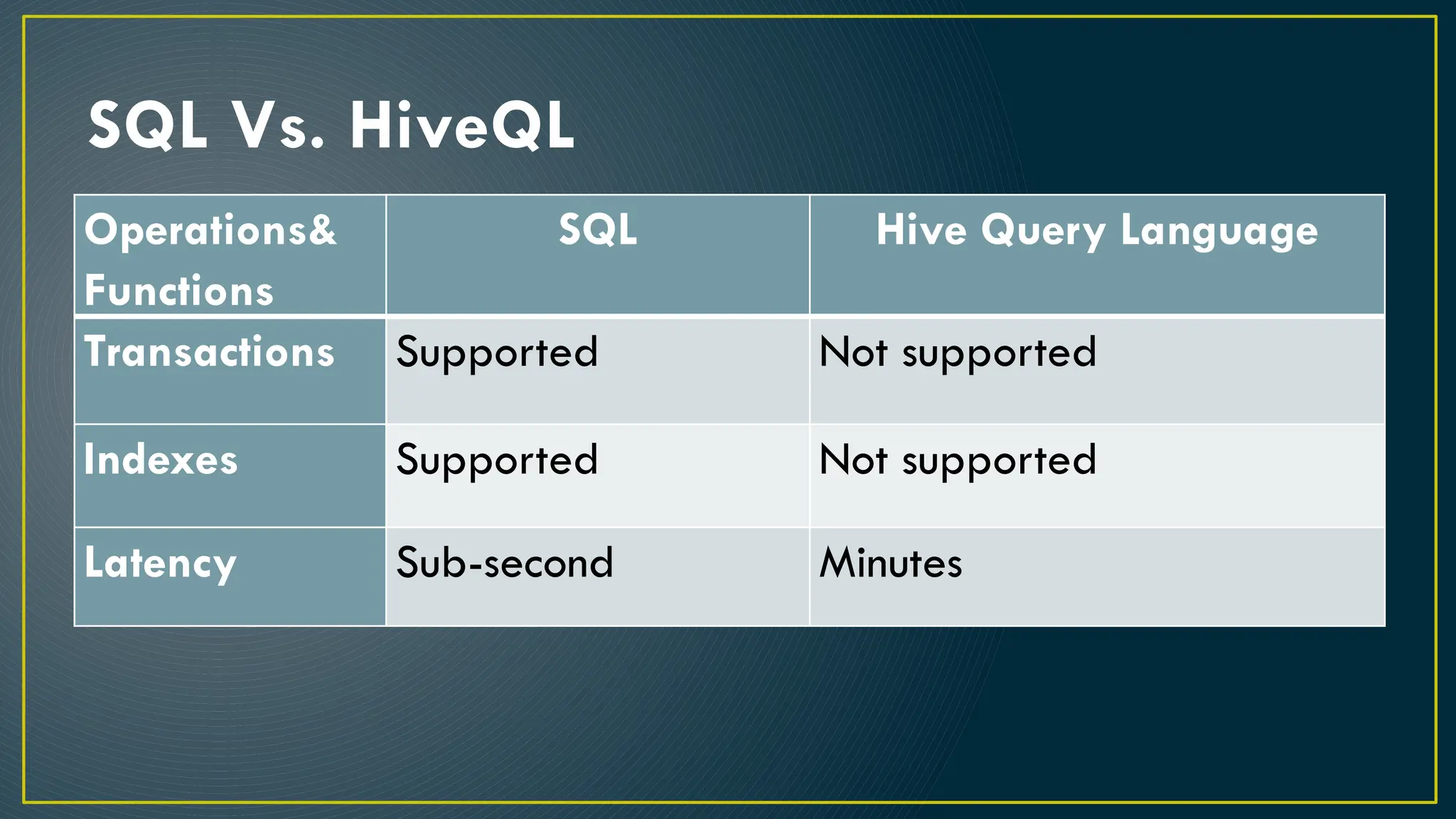
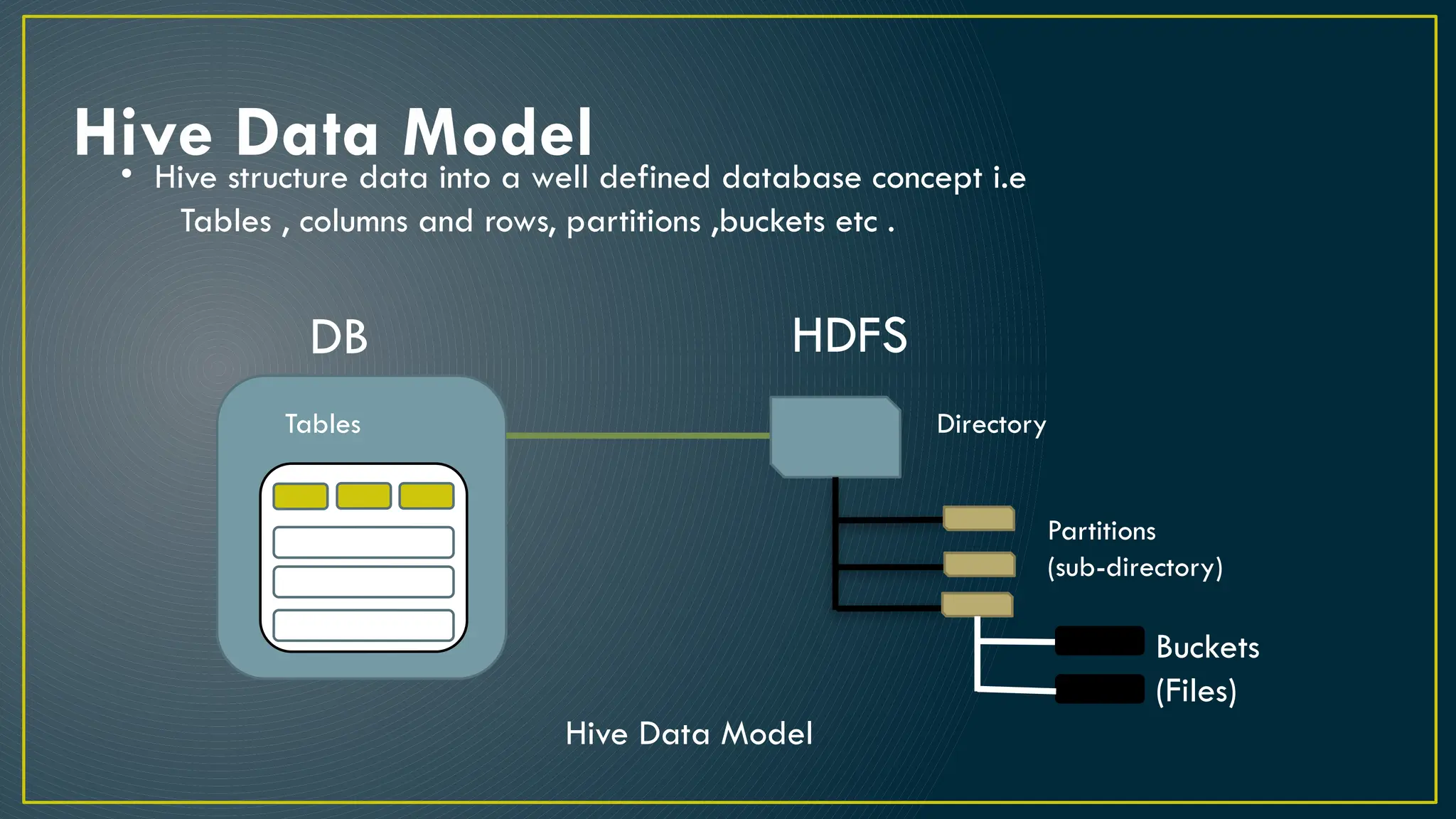
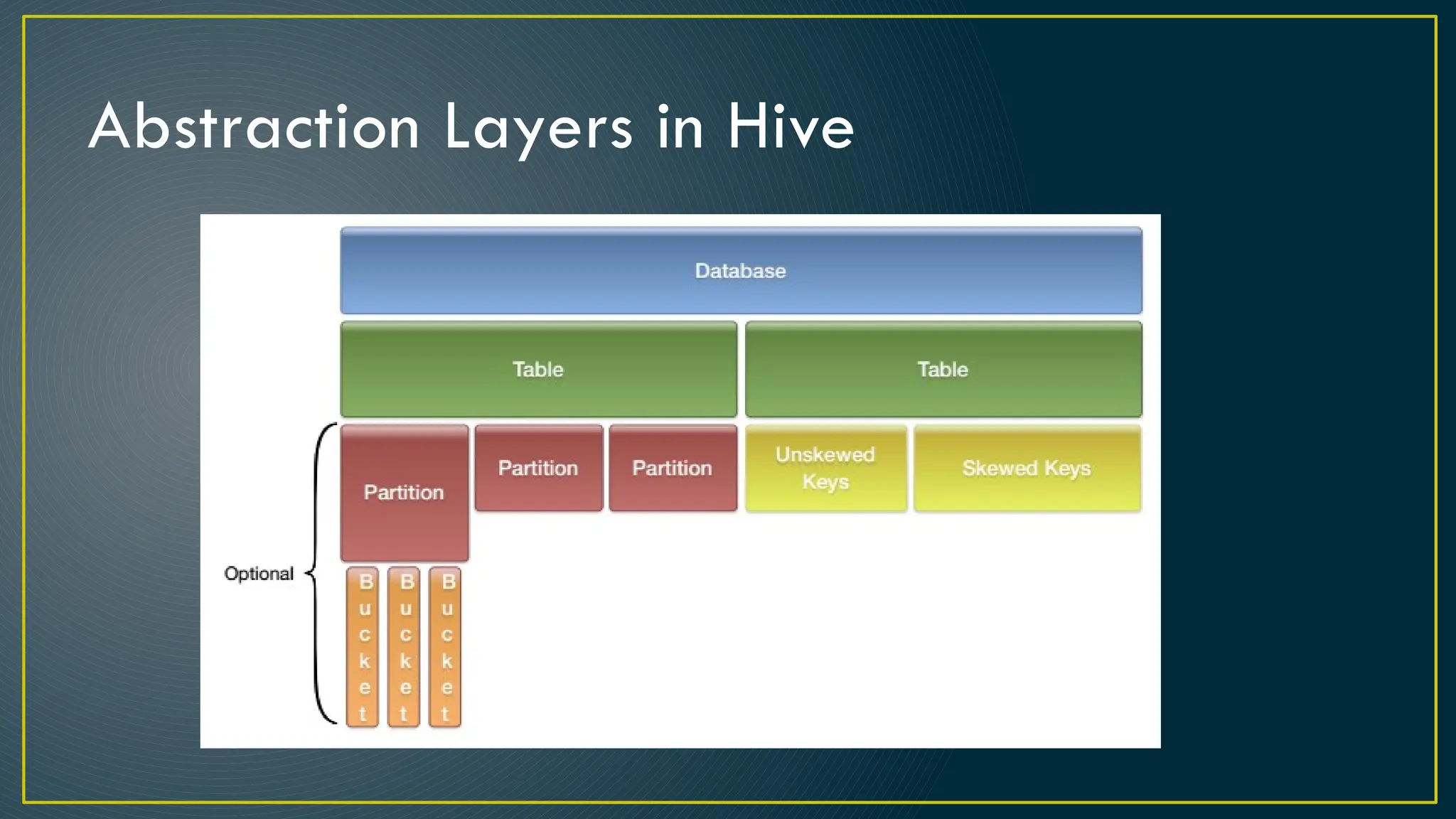
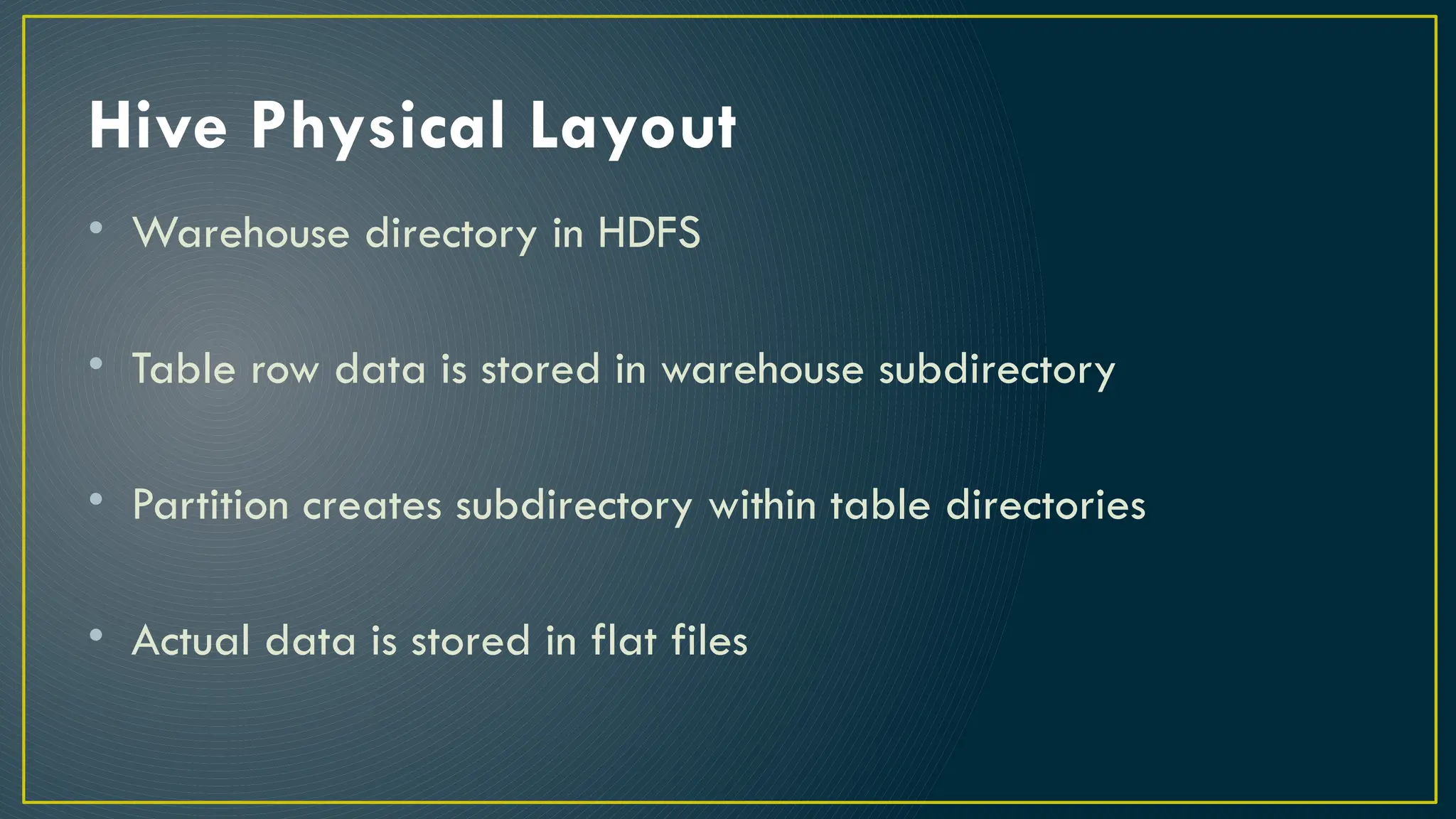
Hive is a data warehousing framework built on top of Hadoop, enabling analysts to query large datasets using SQL-like syntax without extensive programming knowledge. It supports various data formats and provides features for data management, including user-defined functions and support for external tables. However, Hive is not designed for online transaction processing and has limitations with real-time data access and row-level updates.