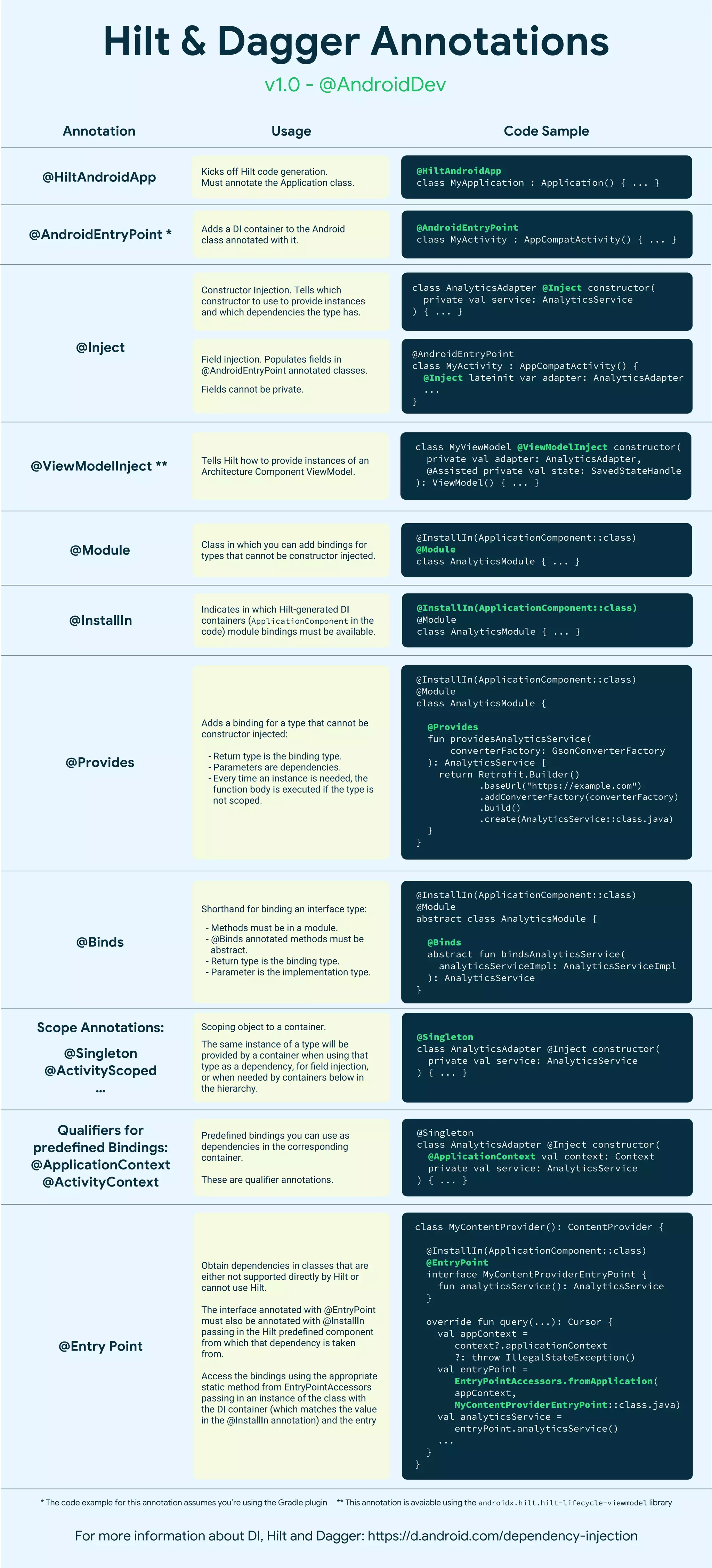
Hilt is an Android dependency injection library that uses annotation processing to generate code that implements dependency injection based on the annotated code. The document provides examples of Hilt annotations like @HiltAndroidApp, @AndroidEntryPoint, @ViewModelInject, @Inject, @Module, @Binds, @Provides, and scope annotations that allow declaring dependencies and how they are satisfied through constructor injection, field injection, and modules. It also describes how to access Hilt dependencies in classes not directly supported by Hilt using the @EntryPoint annotation.