Recommended
PPTX
PPTX
Computer language 6th standard 201 .pptx
PPTX
Computer Language -by VarunThapa.pptx
PPTX
Presentation of the Computer language.pptx
PPTX
class 10 :Chapter 2 Programming in C language
PPTX
Programming_Languages_Presentation.pptx.
PPT
Software Engineering : Computer basics - Introduction to computer
PPTX
PPTX
Programming languages of computer
PPTX
Introduction To Computer Programming
PPT
porgrammingymtmutmtmtmtmtmsymxmsrmyytmsts
PPT
Vahida Akhter.ppt regardung computer languages
PPT
Programming language basics.ppt Computer Science
PPTX
Levels of programming languages
PPTX
introduction to programming languages
PPTX
Introduction-to-Computer-Languages.pptxx
PPT
English de lenguaje de programacion
PPTX
PPTX
Development of computer languages
PPTX
maincse-150510153437-lva1-app6892 (1).pptx
PPTX
Lec21&22.pptx programing language and there study
PPTX
Lab1 Launching into the world of programming.pptx
PPTX
Computer Languages & its genearations.pptx
PPTX
PPT
High level languages representation
PPTX
PPTX
Computer language of a computer system.pptx
PPTX
Programming Languages of Importance in Modern Academics & Industries
PPTX
Benefits of Online and analysis Systems.pptx
PPTX
terminal command2.pptx with good explanation
More Related Content
PPTX
PPTX
Computer language 6th standard 201 .pptx
PPTX
Computer Language -by VarunThapa.pptx
PPTX
Presentation of the Computer language.pptx
PPTX
class 10 :Chapter 2 Programming in C language
PPTX
Programming_Languages_Presentation.pptx.
PPT
Software Engineering : Computer basics - Introduction to computer
PPTX
Similar to HIGH-LEVEL PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE PPT.pptx
PPTX
Programming languages of computer
PPTX
Introduction To Computer Programming
PPT
porgrammingymtmutmtmtmtmtmsymxmsrmyytmsts
PPT
Vahida Akhter.ppt regardung computer languages
PPT
Programming language basics.ppt Computer Science
PPTX
Levels of programming languages
PPTX
introduction to programming languages
PPTX
Introduction-to-Computer-Languages.pptxx
PPT
English de lenguaje de programacion
PPTX
PPTX
Development of computer languages
PPTX
maincse-150510153437-lva1-app6892 (1).pptx
PPTX
Lec21&22.pptx programing language and there study
PPTX
Lab1 Launching into the world of programming.pptx
PPTX
Computer Languages & its genearations.pptx
PPTX
PPT
High level languages representation
PPTX
PPTX
Computer language of a computer system.pptx
PPTX
Programming Languages of Importance in Modern Academics & Industries
More from farsankadavandy
PPTX
Benefits of Online and analysis Systems.pptx
PPTX
terminal command2.pptx with good explanation
PPTX
Colorful Fun Mind Map Infographic Template Instagram Post.pptx
PPTX
RELATIONAL MODEL CONCEPTS.pptx with good explanation
PPT
422_114_216_module_1-inroduction-1.ppt with detailed notes and explanation
PPTX
Entity Relationship Diagram – ER Diagram in DBMS.pptx
PPTX
filepermission.pptx with detailed notes ,high quality
PPTX
Module 1 part 2.pptx with clear notes and explanation
Recently uploaded
PPT
atomic structure2.ppt qwgdwgdwidgqwuidg wdhwgdwgwydg qwgdwydgwydg87
PDF
Glass Facade Treatments and designs in architecture
DOCX
Leadership as a Catalyst How Nutrition Leadership Influences Health Financing...
PDF
Interpretability and Explainability Module 4.pdf
PDF
The Gemini Advantage: A Strategic Overview of Google’s Multimodal AI Ecosystem
PPTX
Summary of 2025 Change Capability Survey Results.pptx
PPT
Data Structures in java programing and ICT.ppt
PDF
Google Gemini Learning Guide - Generating Text, Vision Model, and Embeddings ...
PPTX
Correlation-Regression analysis -16.11.25.pptx
PDF
2= https___10-0-0-0-1.ph_.pdf10.0.0.0.1,
PDF
From Microsoft SCOM to Dashboards | Grafana, SquaredUp, Power BI, Azure Workb...
PPTX
Chinese economy in the era a modern world
PDF
2022.05.20_Presentazione_Luca-Ginnari-Satriani_Impurities.pdf
PPTX
2B.Carbon-Neutral Technologies and Negative Emission Strategies for Net-Zero ...
PPTX
Data_Analysis_Plan-corrected-Biostatistics.pptx
PPTX
ammonia process.pptx Amisha Group 7.pptxAmisha Group 7.pptxAmisha Group 7.pptx
PPTX
Engineering Project Proposal by Slidesgo.pptx
PPTX
MULTIPLE REGRESSION AND CORRELATION OF IMPORTS, THE NATIONAL INCOME AND RELAT...
PDF
Starting with SPSS.pdf spss software by ibm
PPTX
spam detacting system.pptx for mca students
HIGH-LEVEL PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE PPT.pptx 1. 2. 3. 4. DEFINITION
High-Level Language = Programming language with English-like
words & symbols.
Easy to read, write, and understand.
Examples: Python, Java, C, C++, JavaScript.
5. HISTORY
i. 1950s → FORTRAN (first HLL).
ii. 1960s → COBOL, BASIC.
iii. 1970s–1980s → C, Pascal, Ada.
iv. 1990s → C++, Java, Python.
v. Today → Swift, Kotlin, Go, Rust
6. FEATURES OF HLL
Simple, human-friendly syntax.
Portable across systems.
Structured programming support.
Rich libraries and functions.
Machine-independent.
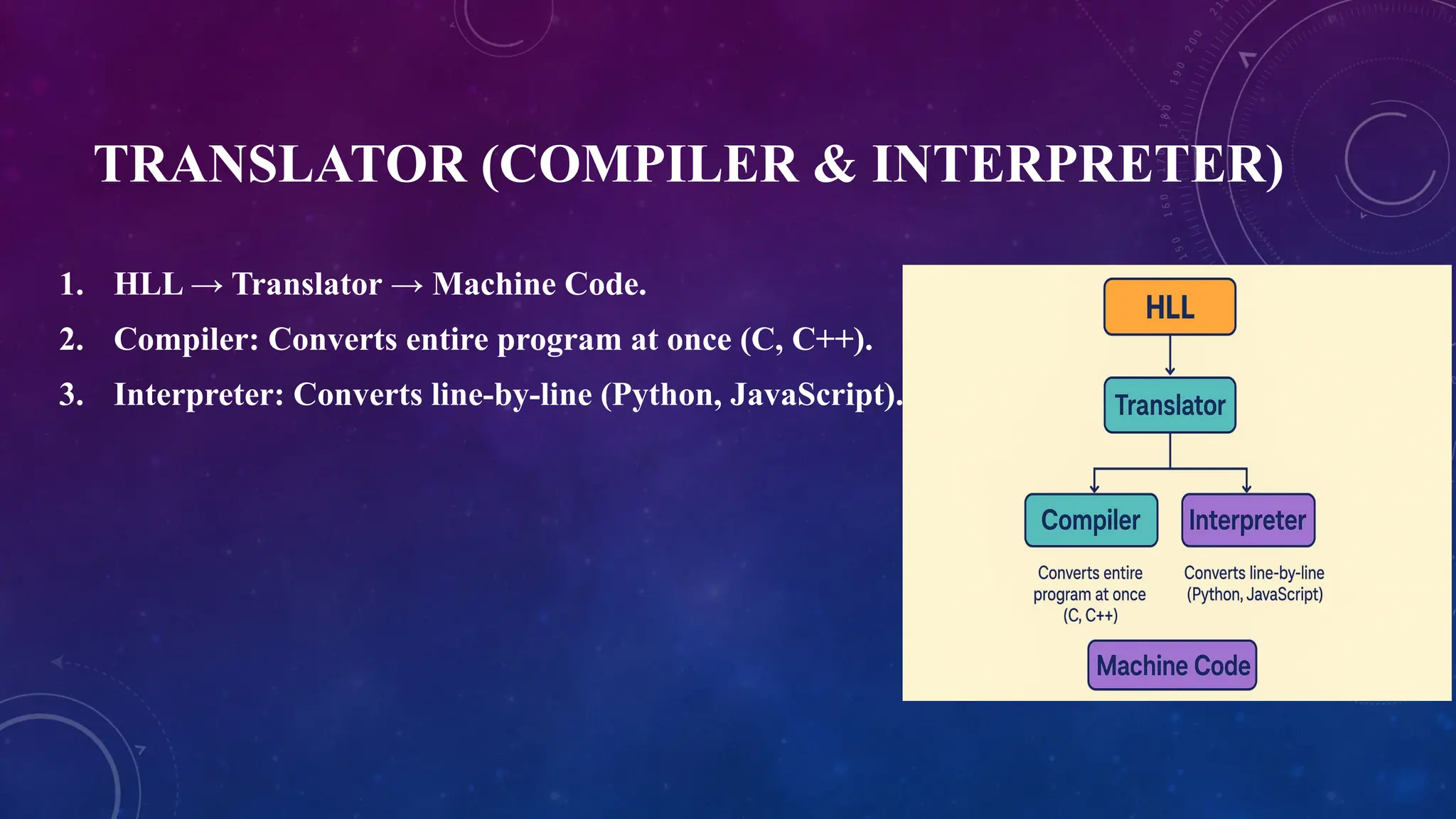
7. TRANSLATOR (COMPILER & INTERPRETER)
1. HLL → Translator → Machine Code.
2. Compiler: Converts entire program at once (C, C++).
3. Interpreter: Converts line-by-line (Python, JavaScript).
8. ADVANTAGES
Easy to learn & use.Faster program development.
Debugging and maintenance easier.
One program works on many platforms.
Supports complex applications.
9. 10. APPLICATIONS
Python – AI, ML, Data Science.
C/C++ – Operating systems, Games.
Java – Web & Mobile apps.
JavaScript – Websites.
C# – Windows apps, Games.
11. 12.