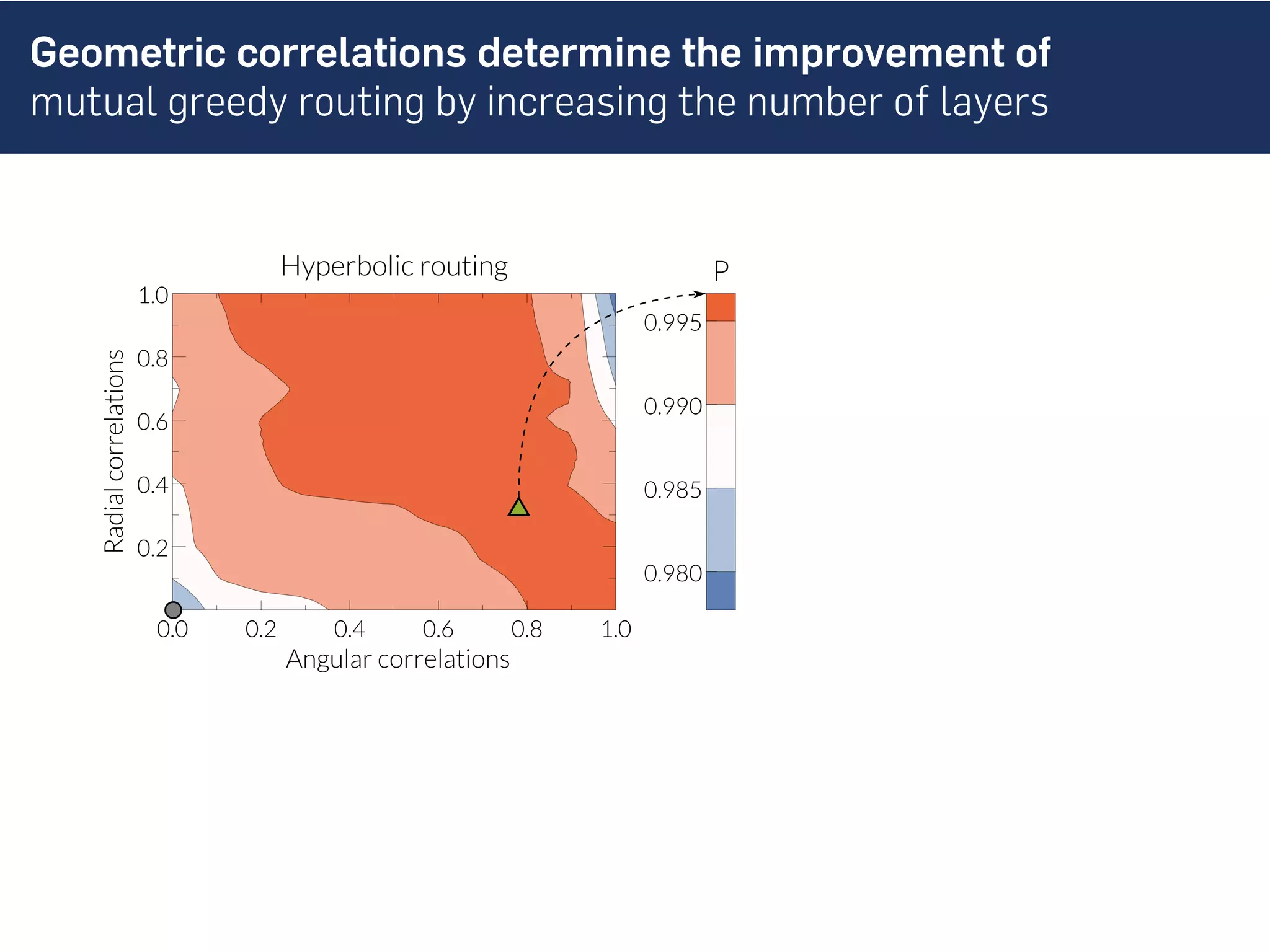
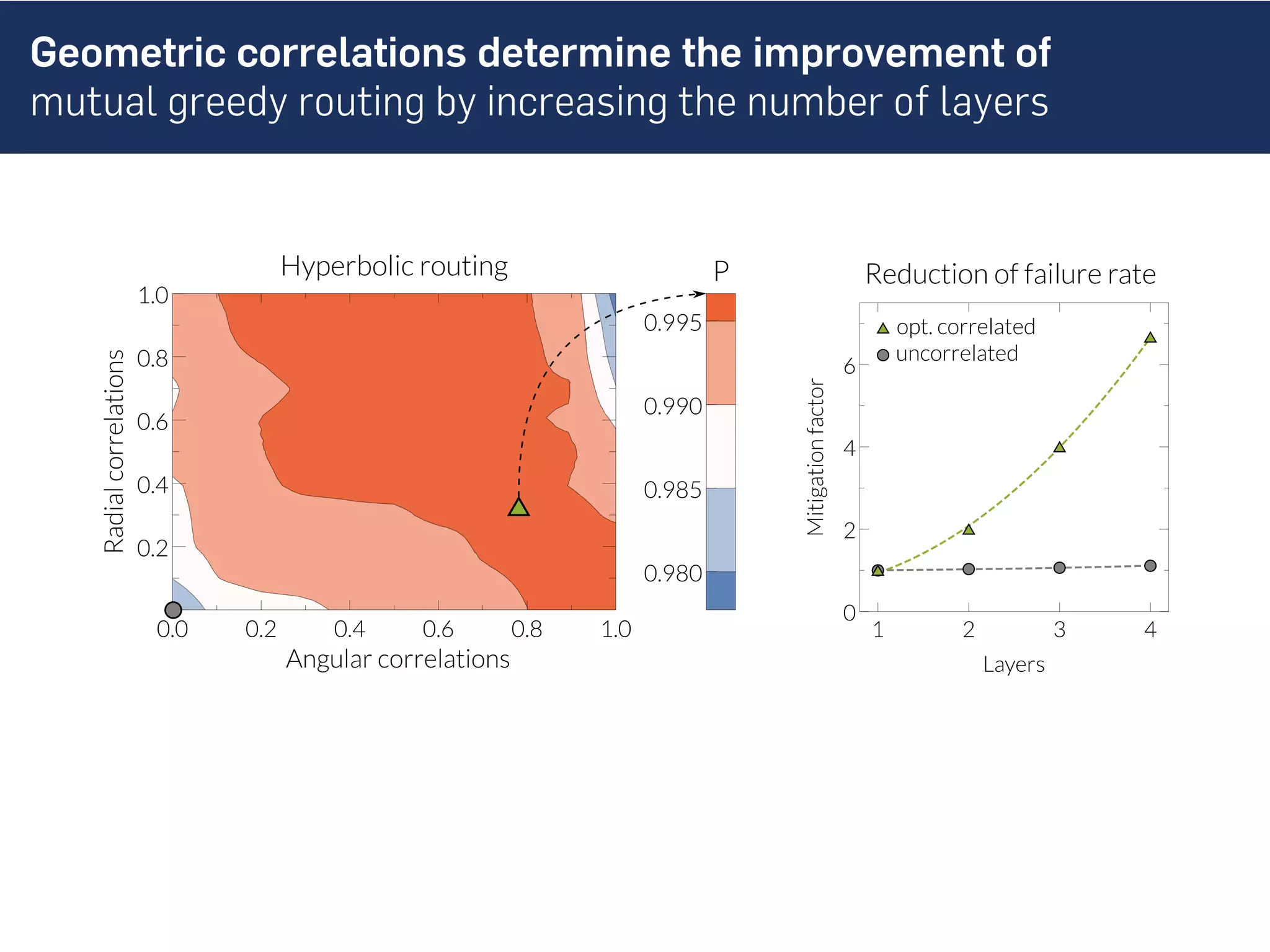
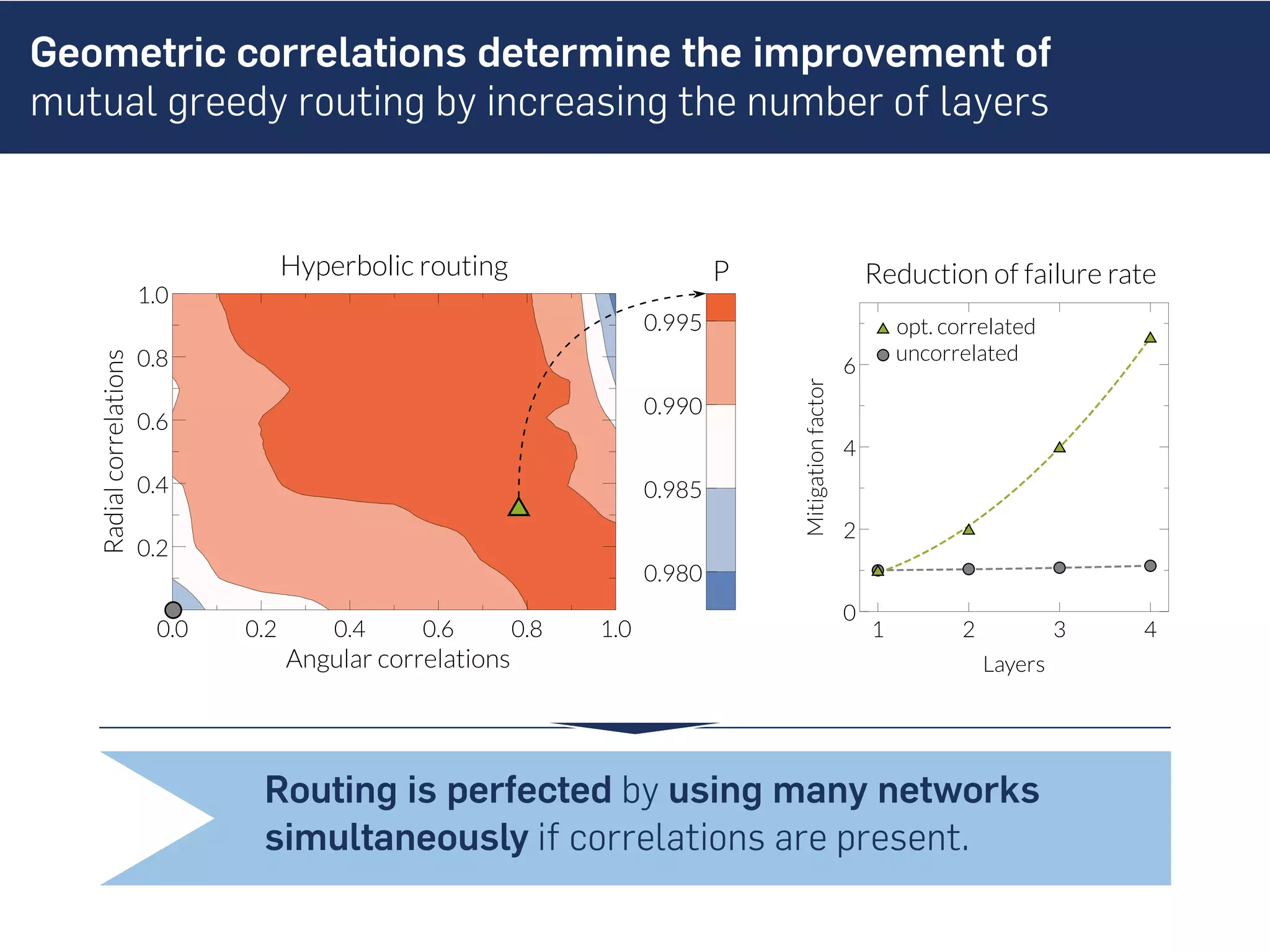
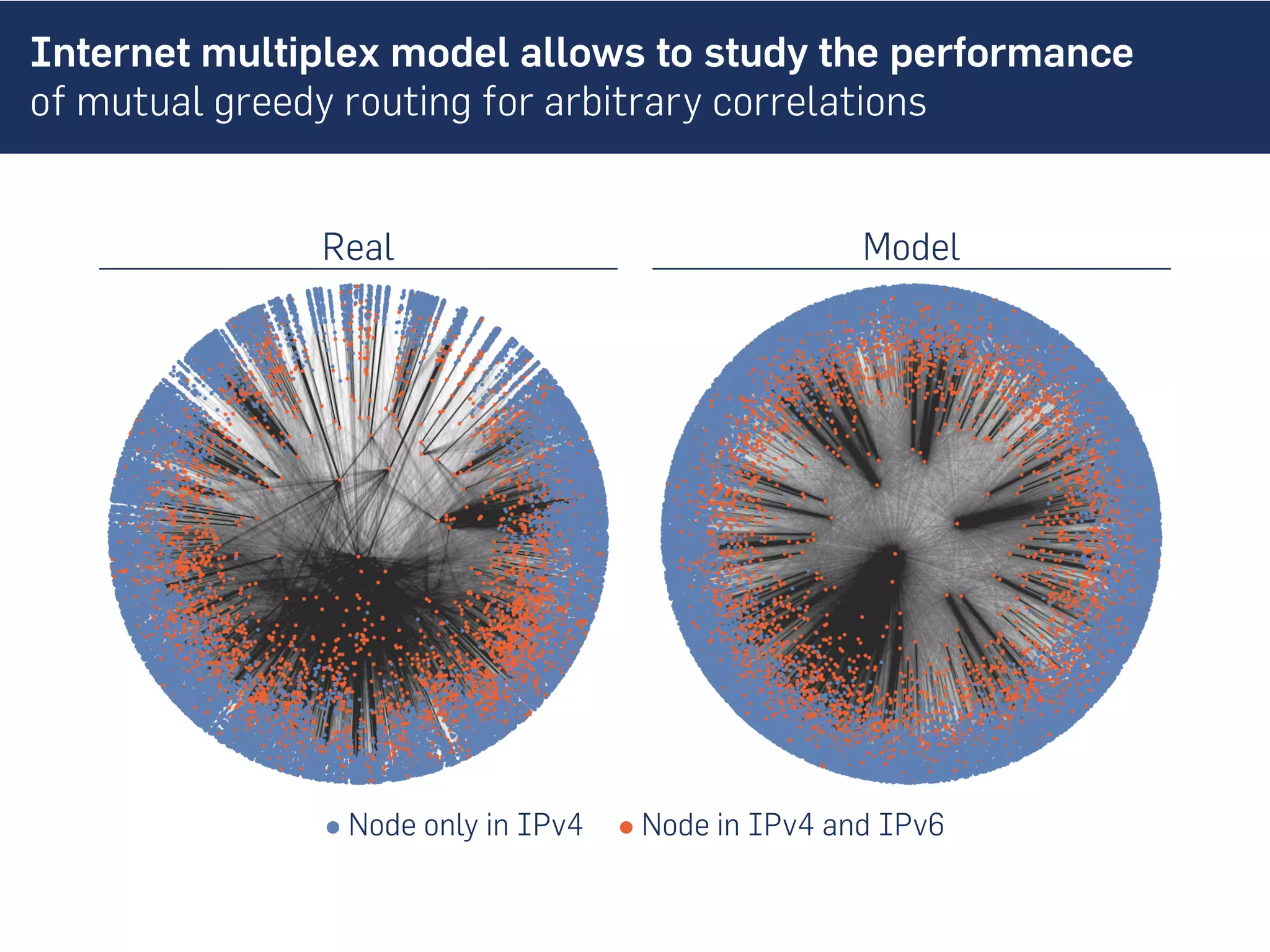
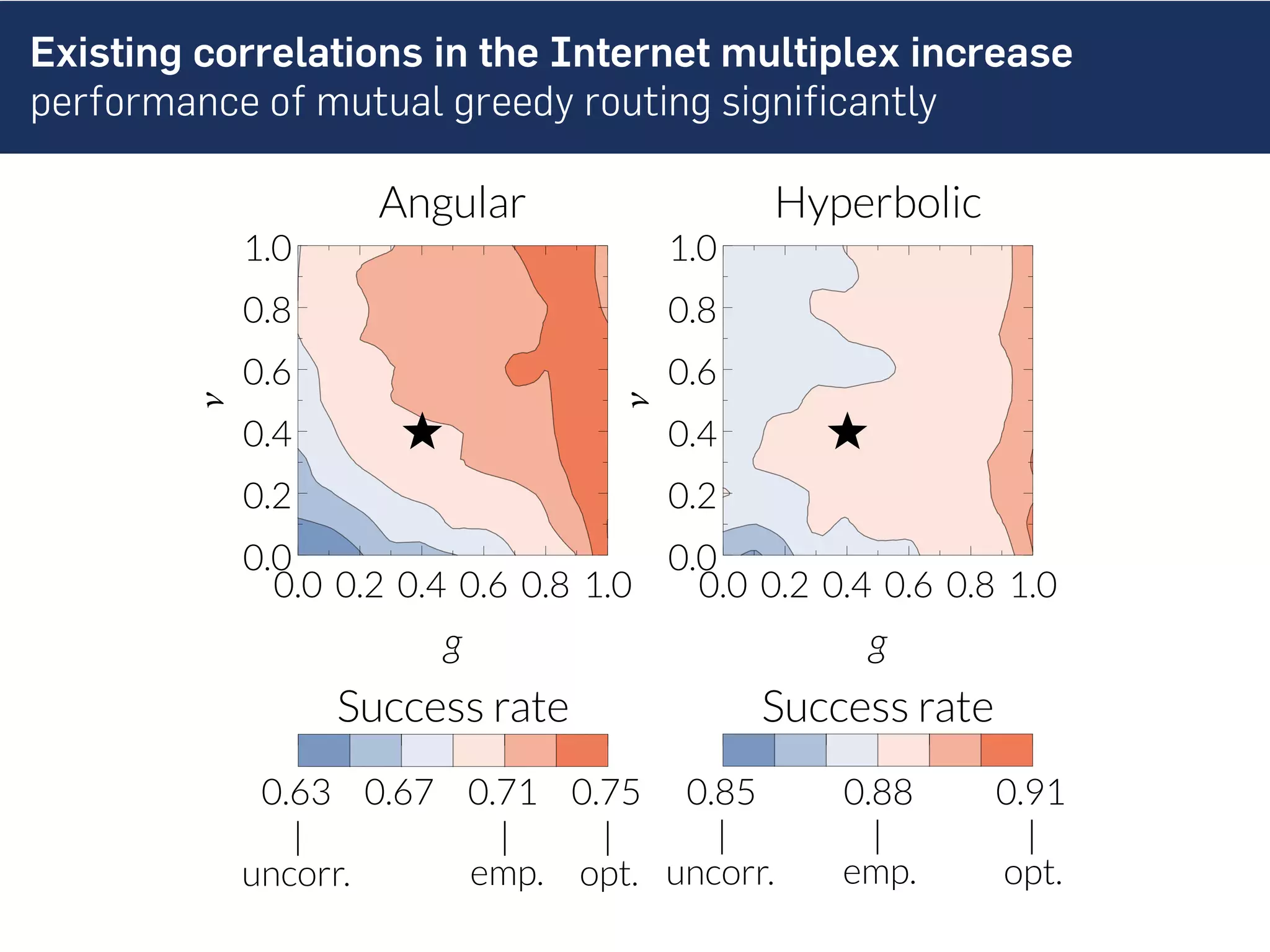
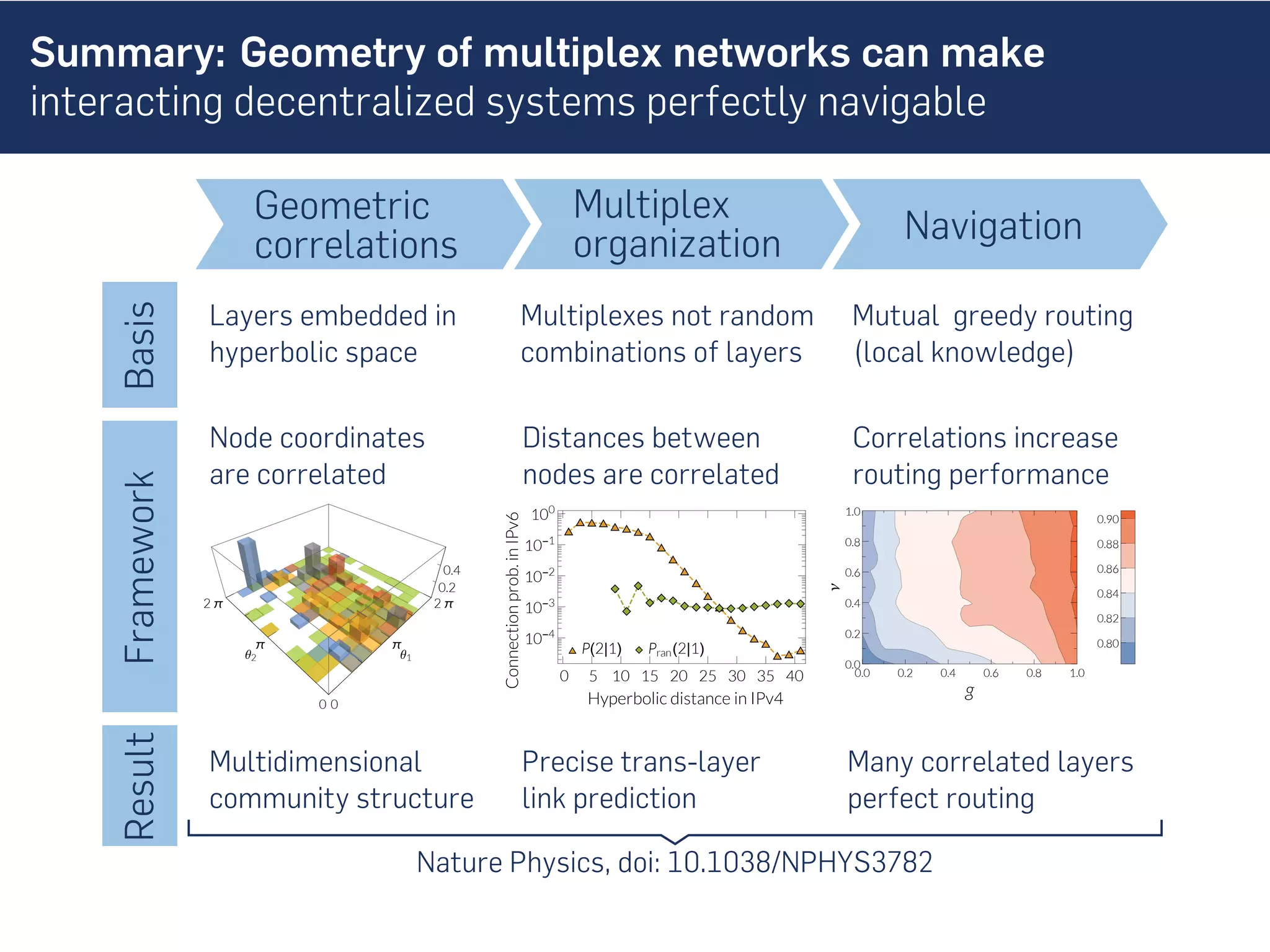
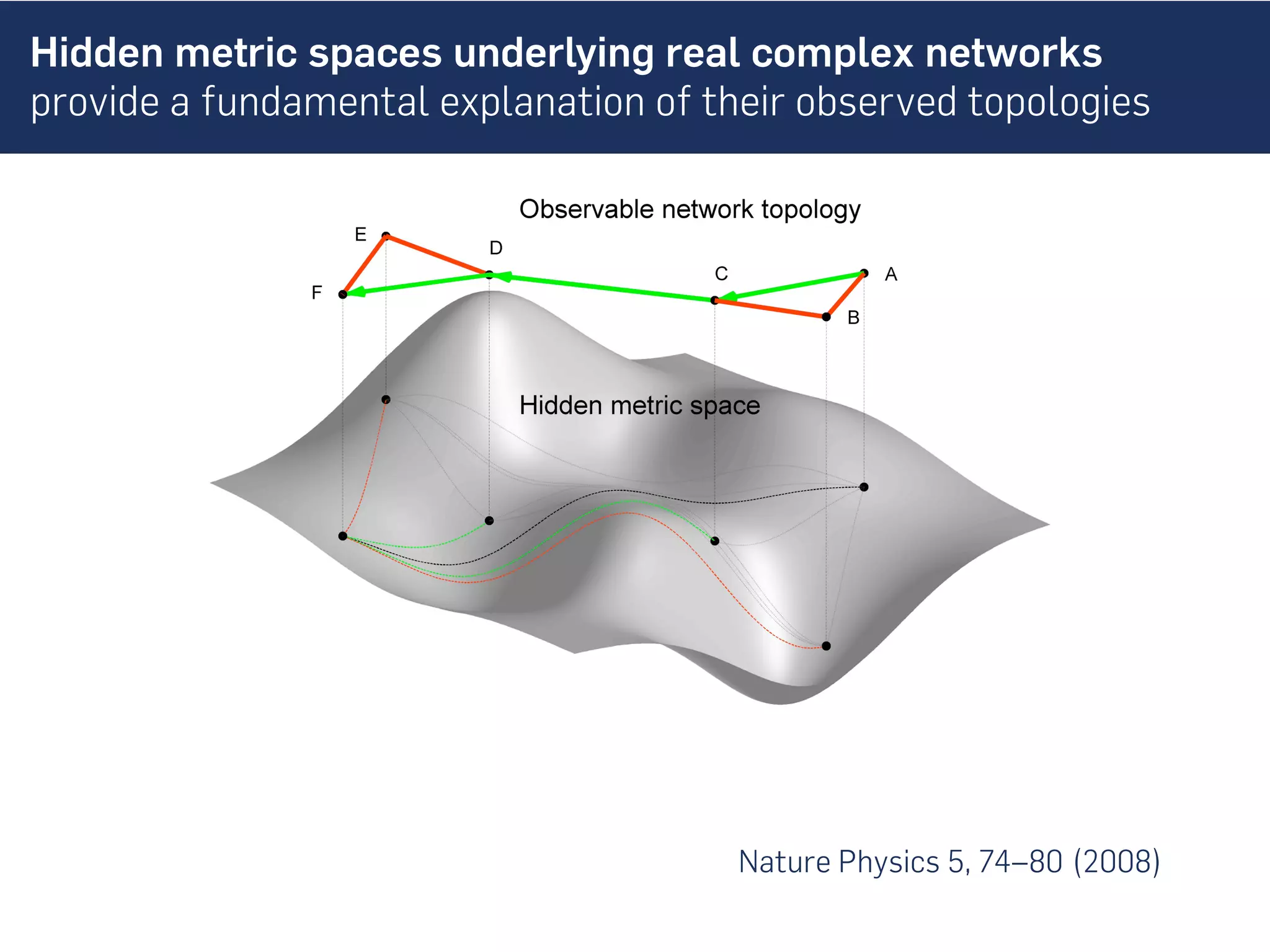
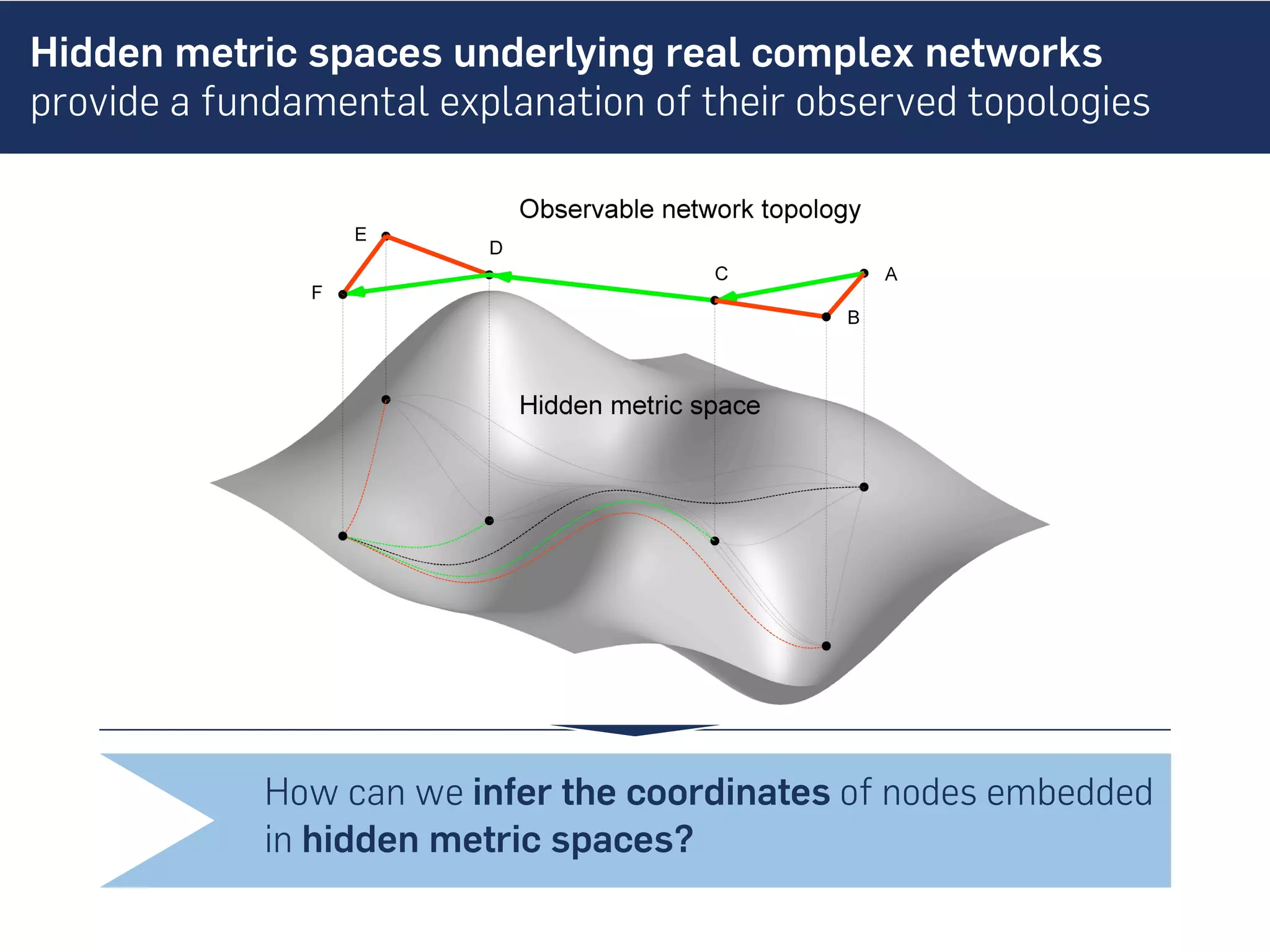
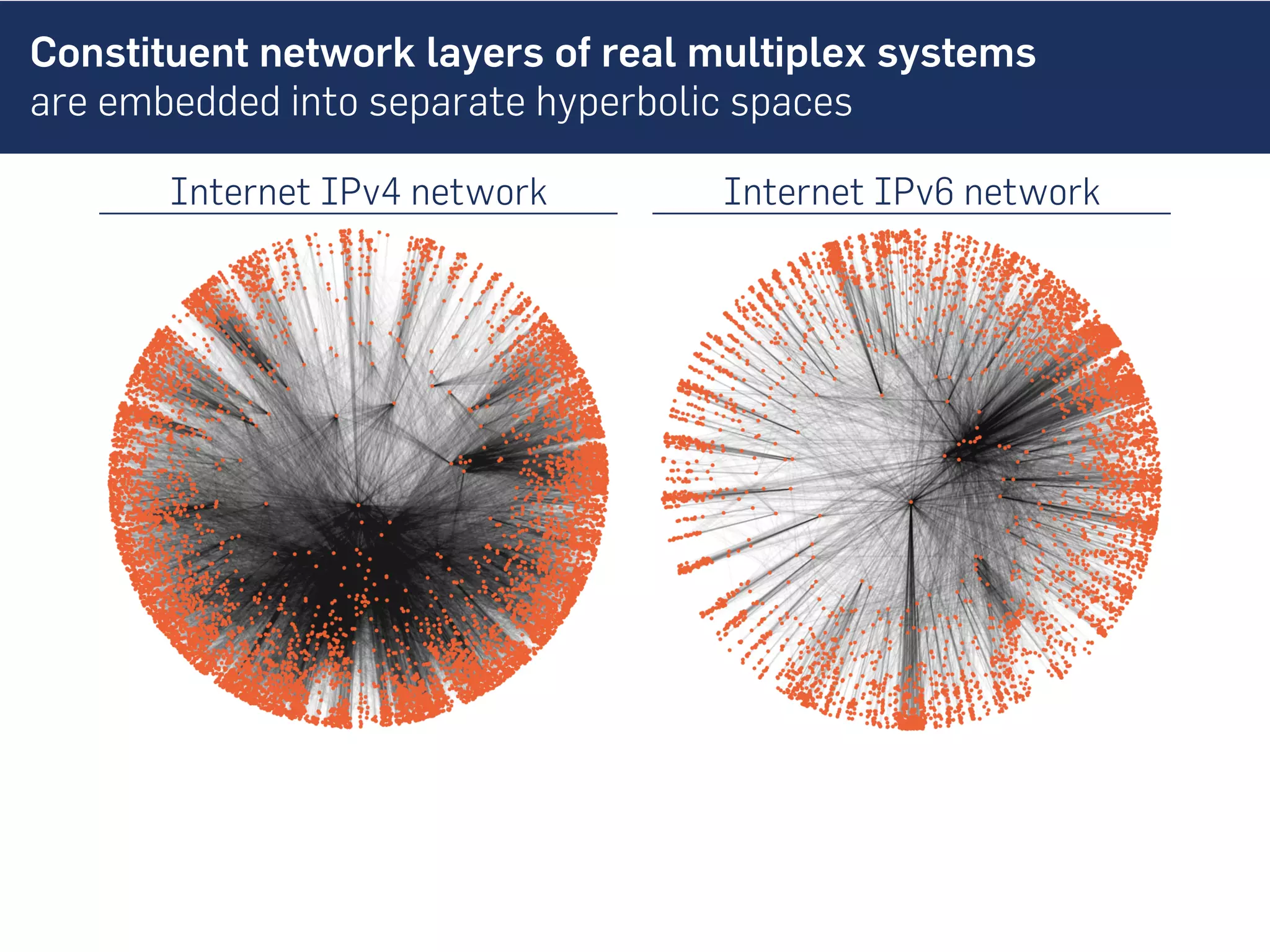
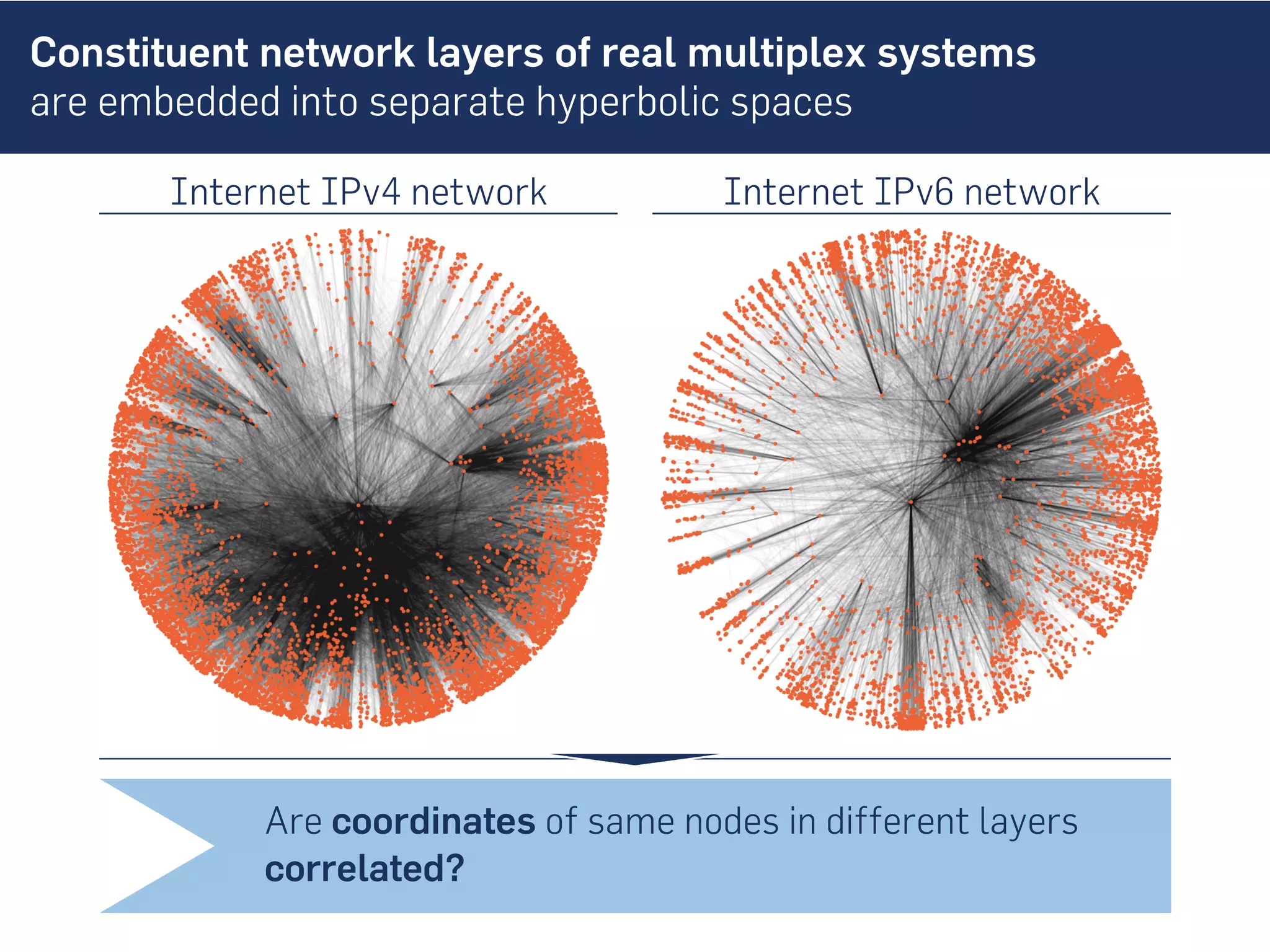
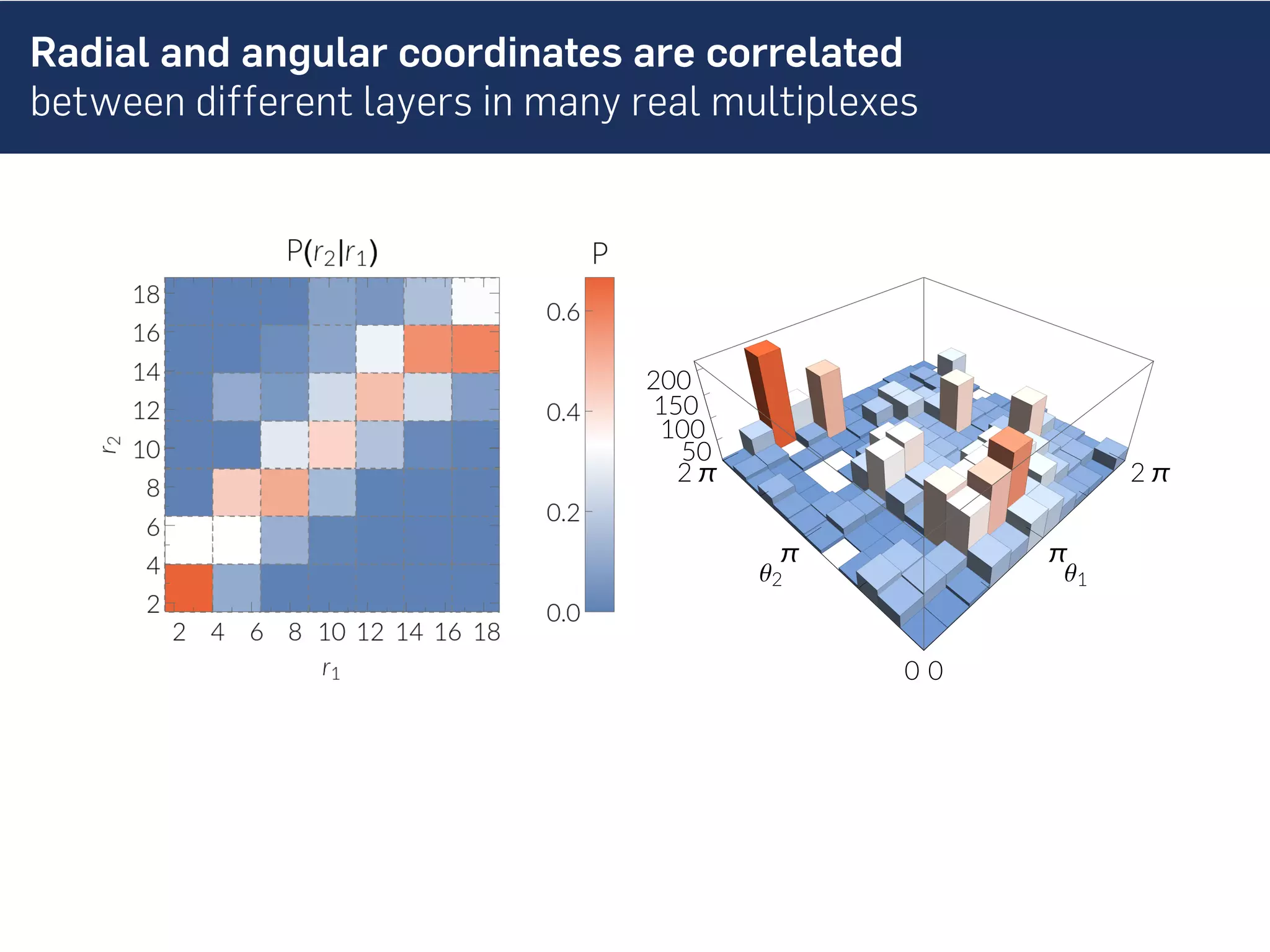
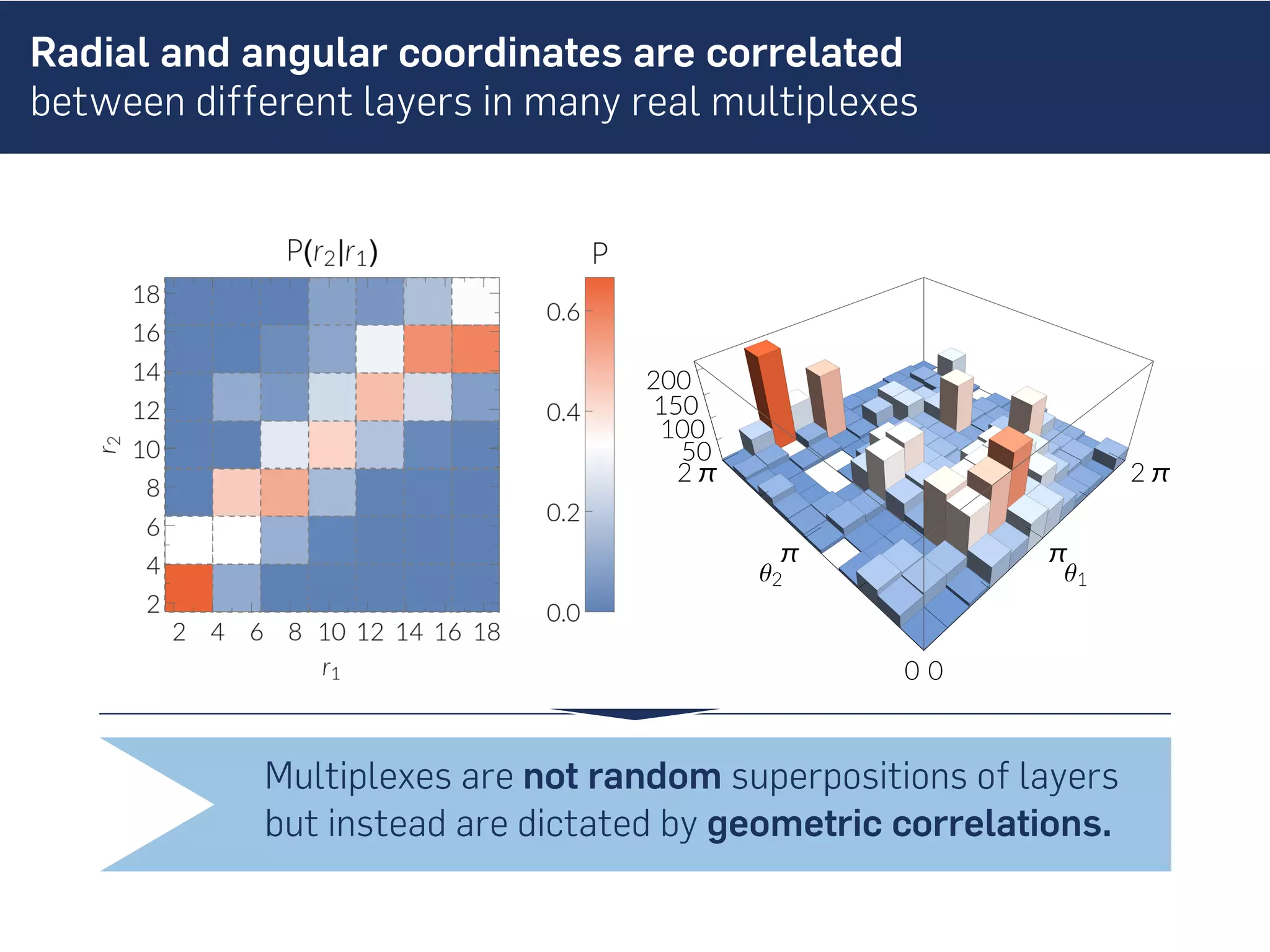
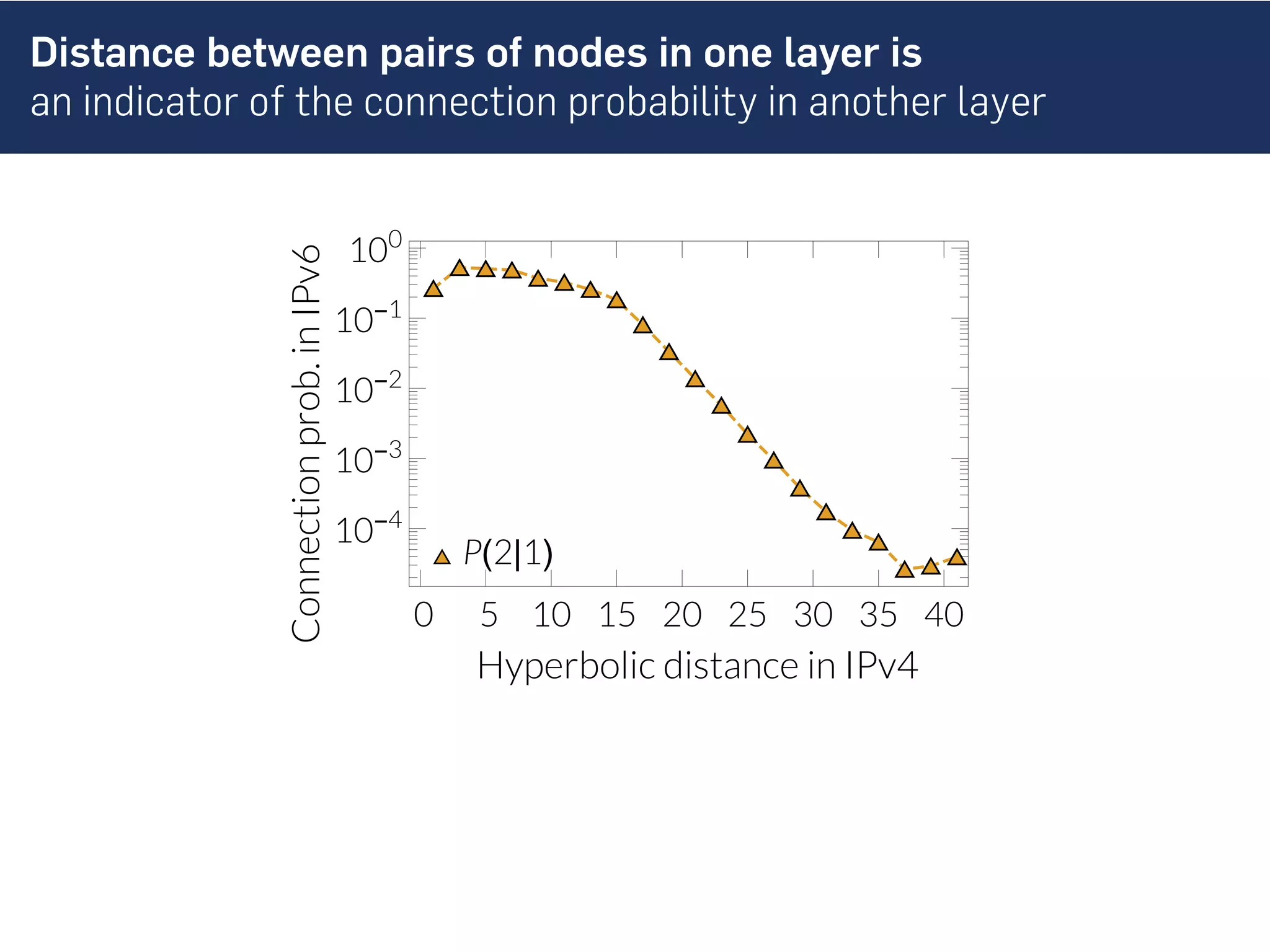
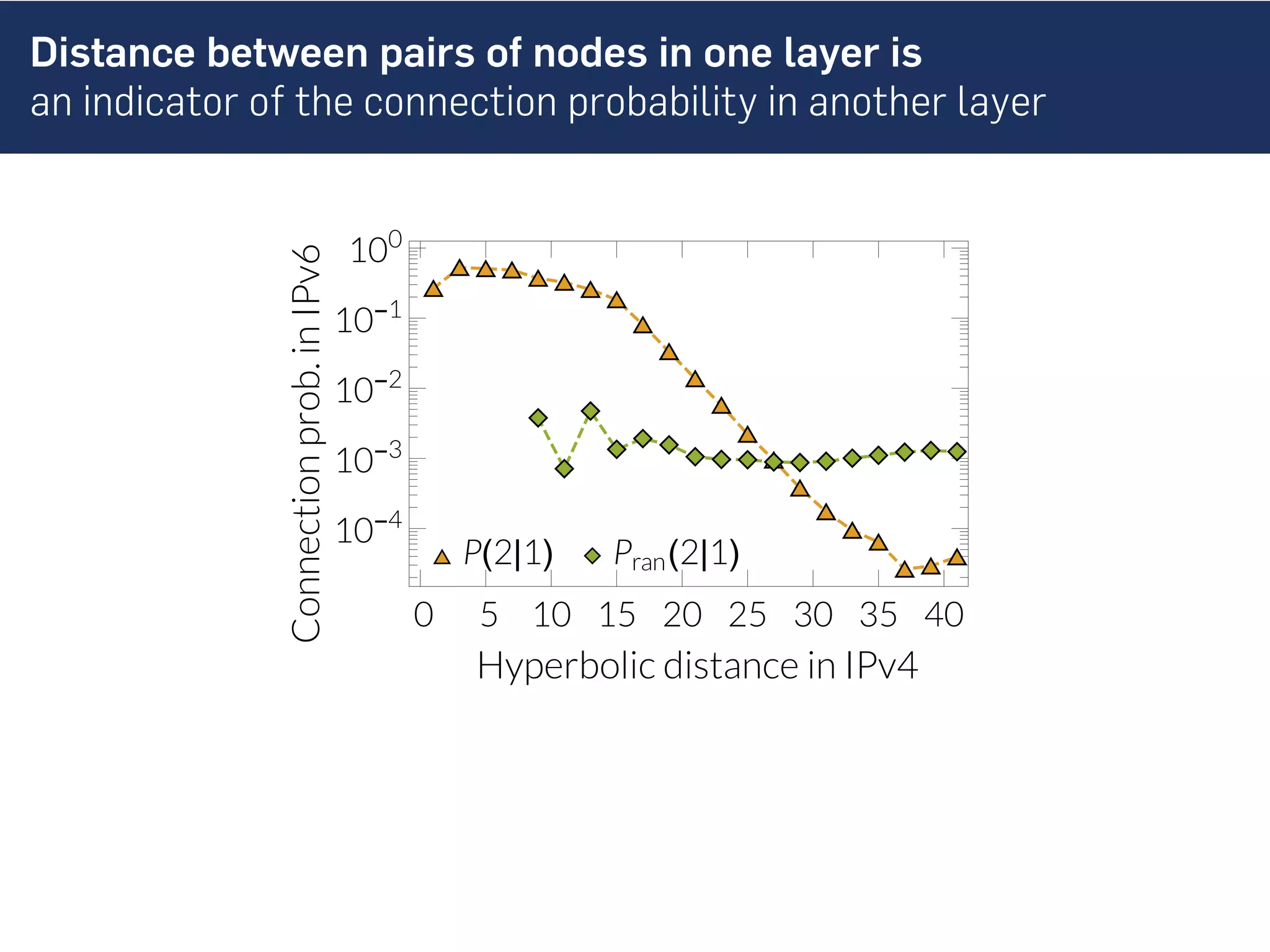
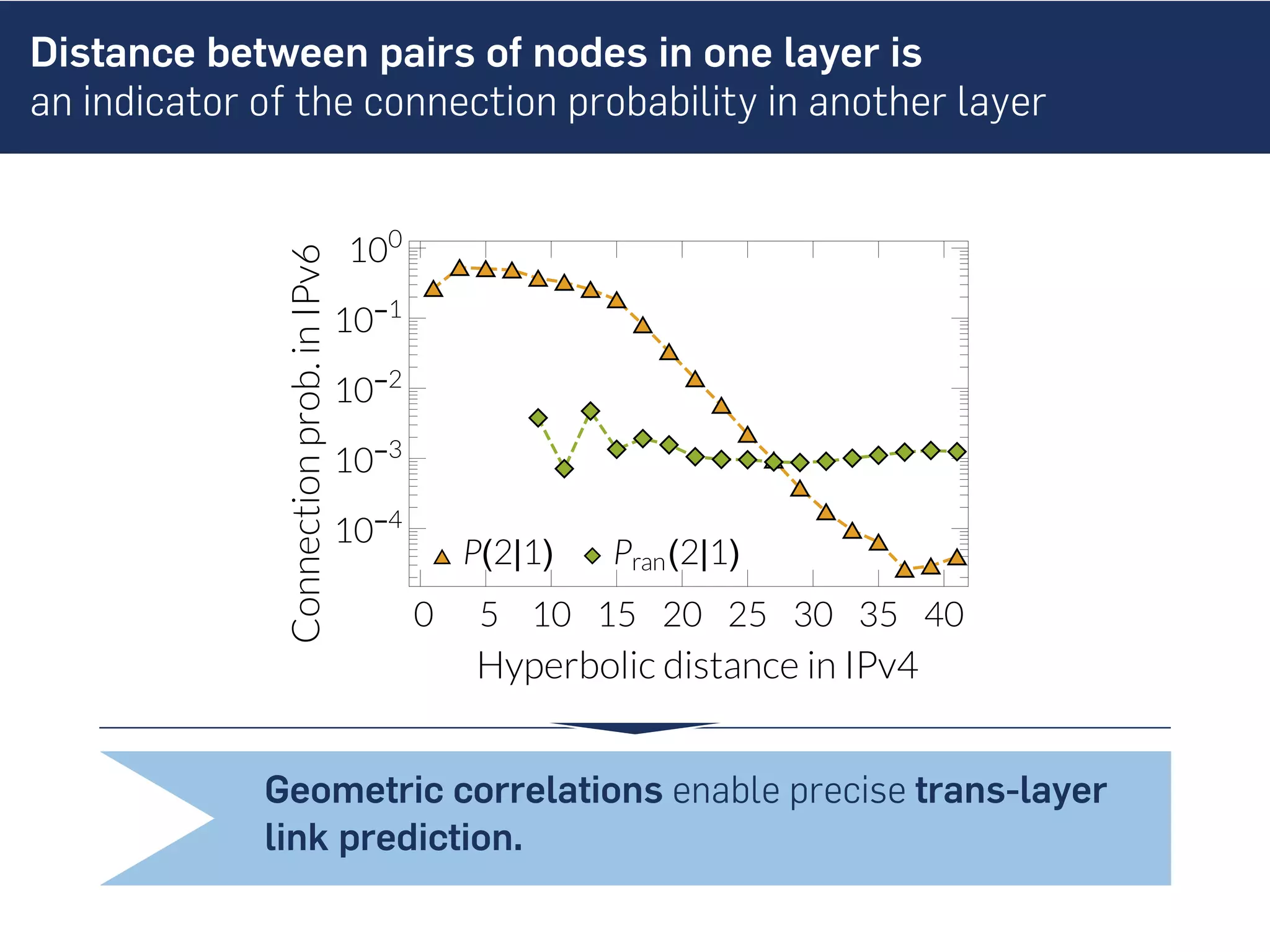
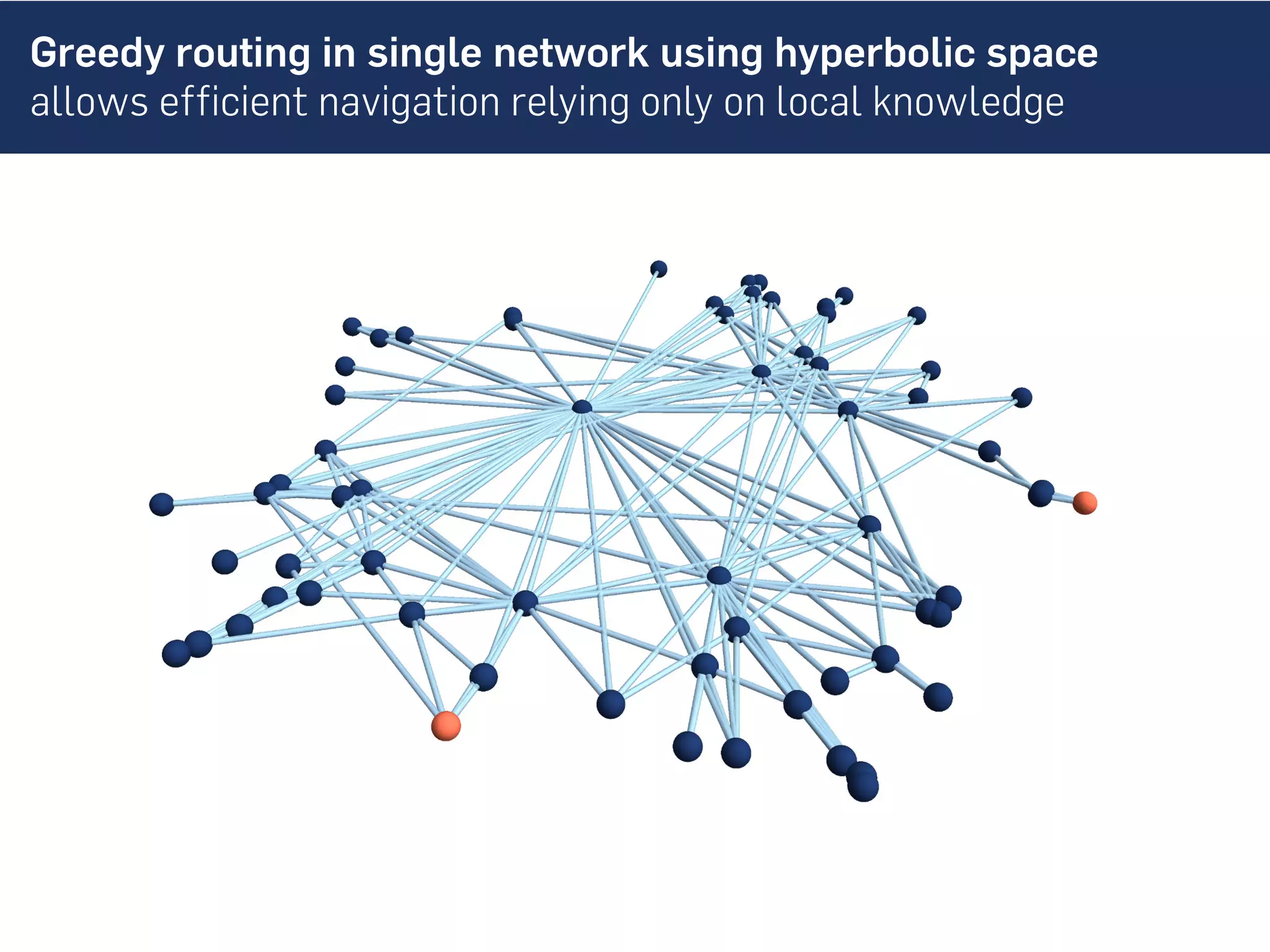
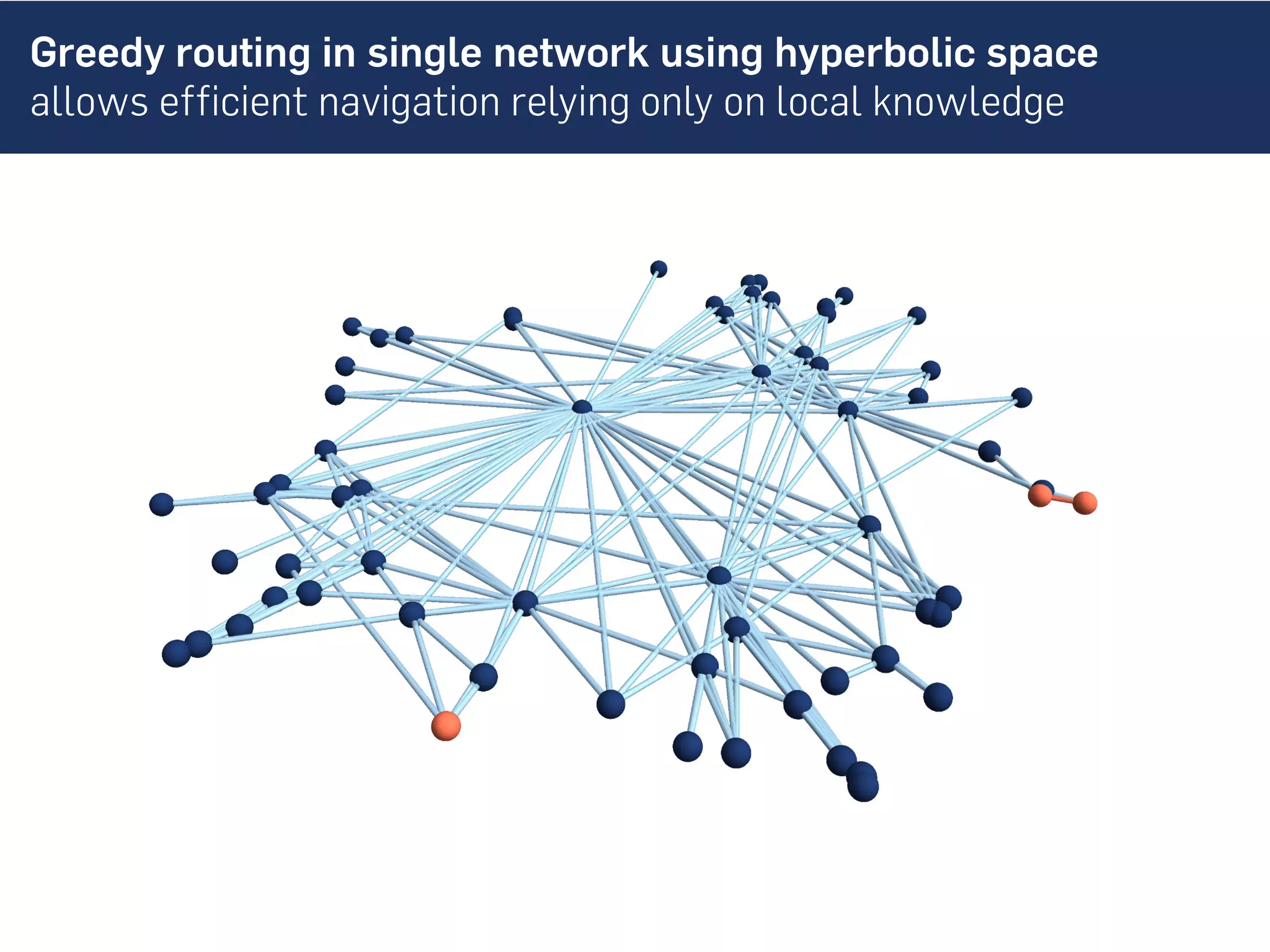
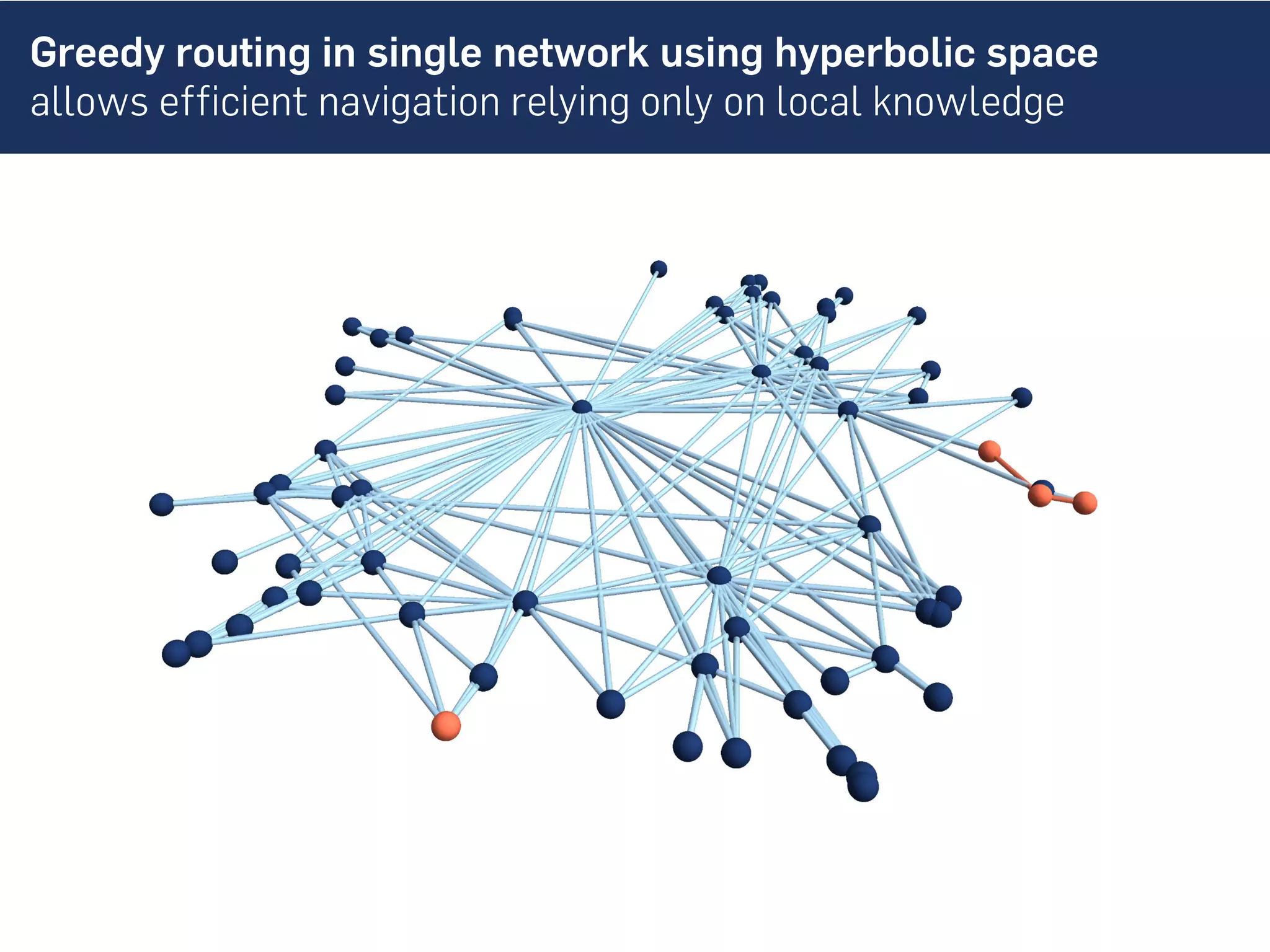
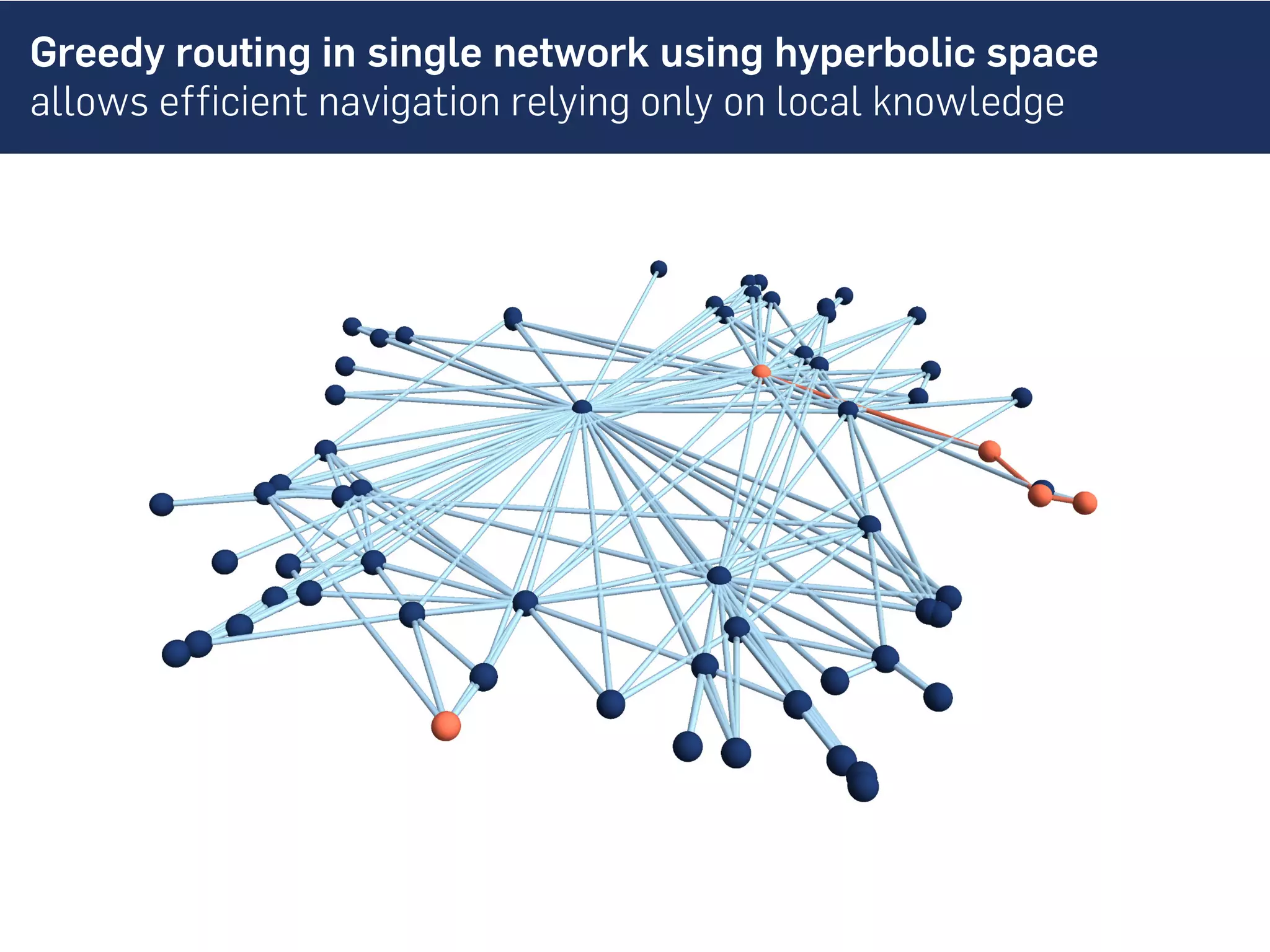
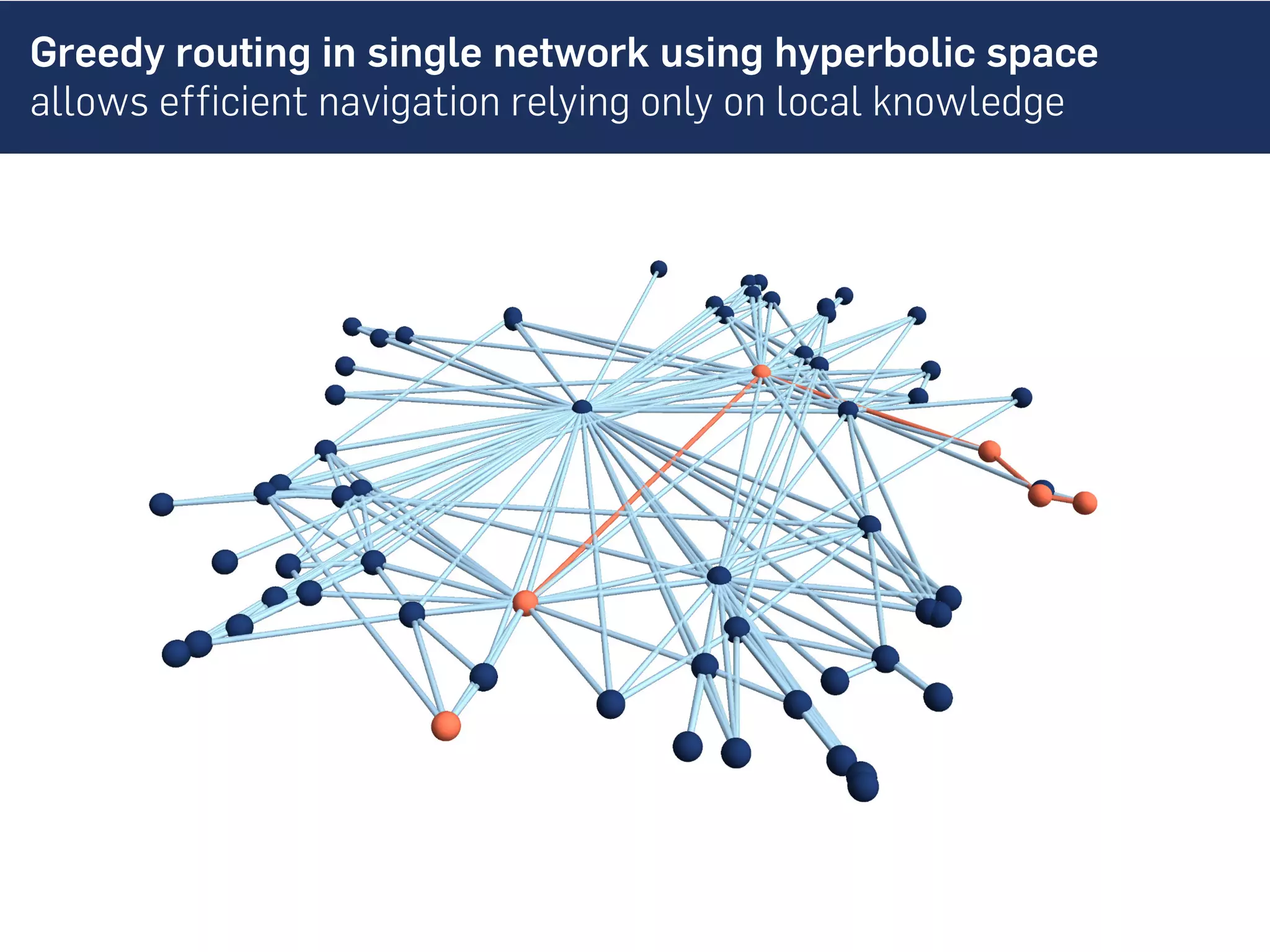
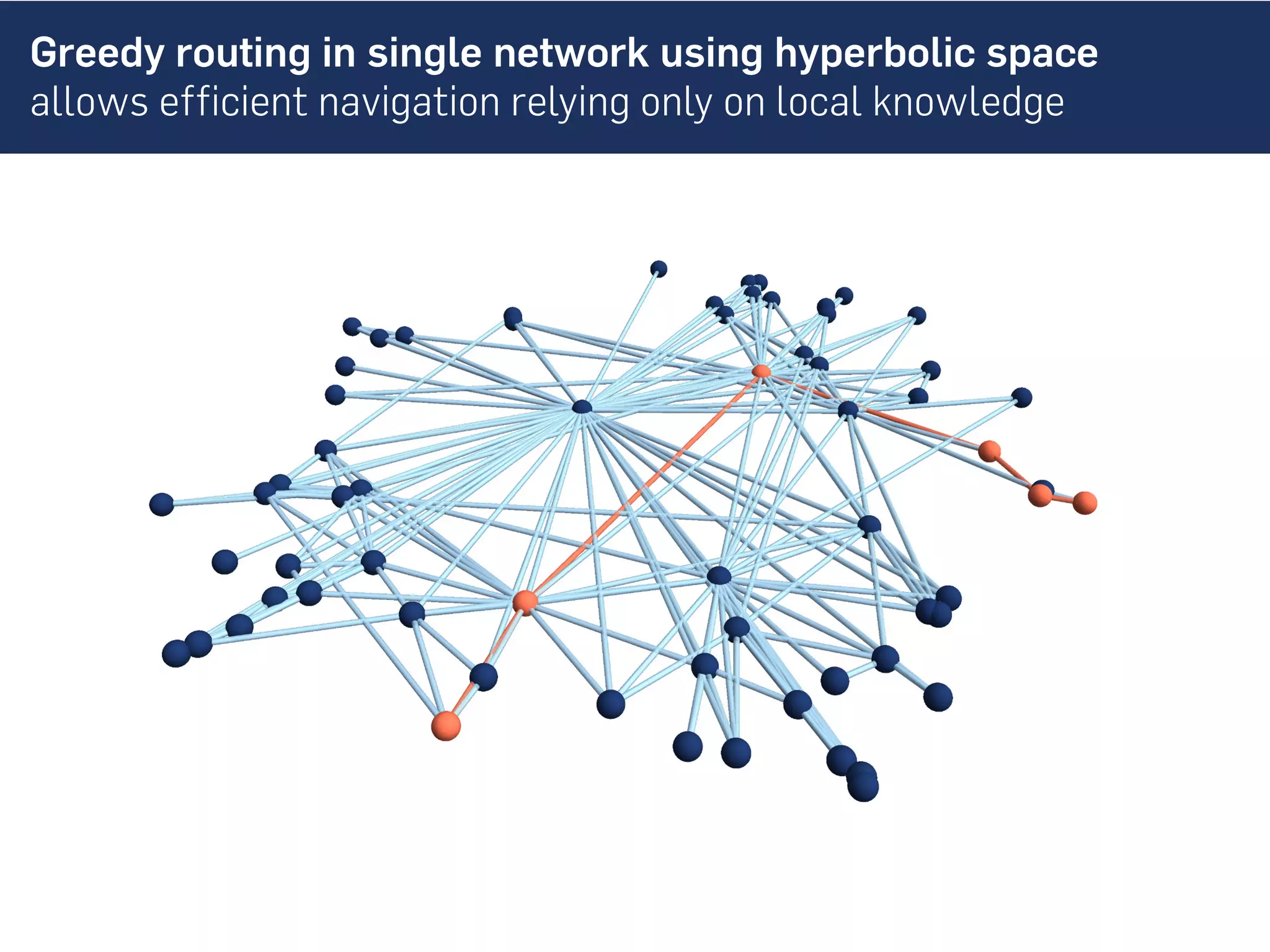
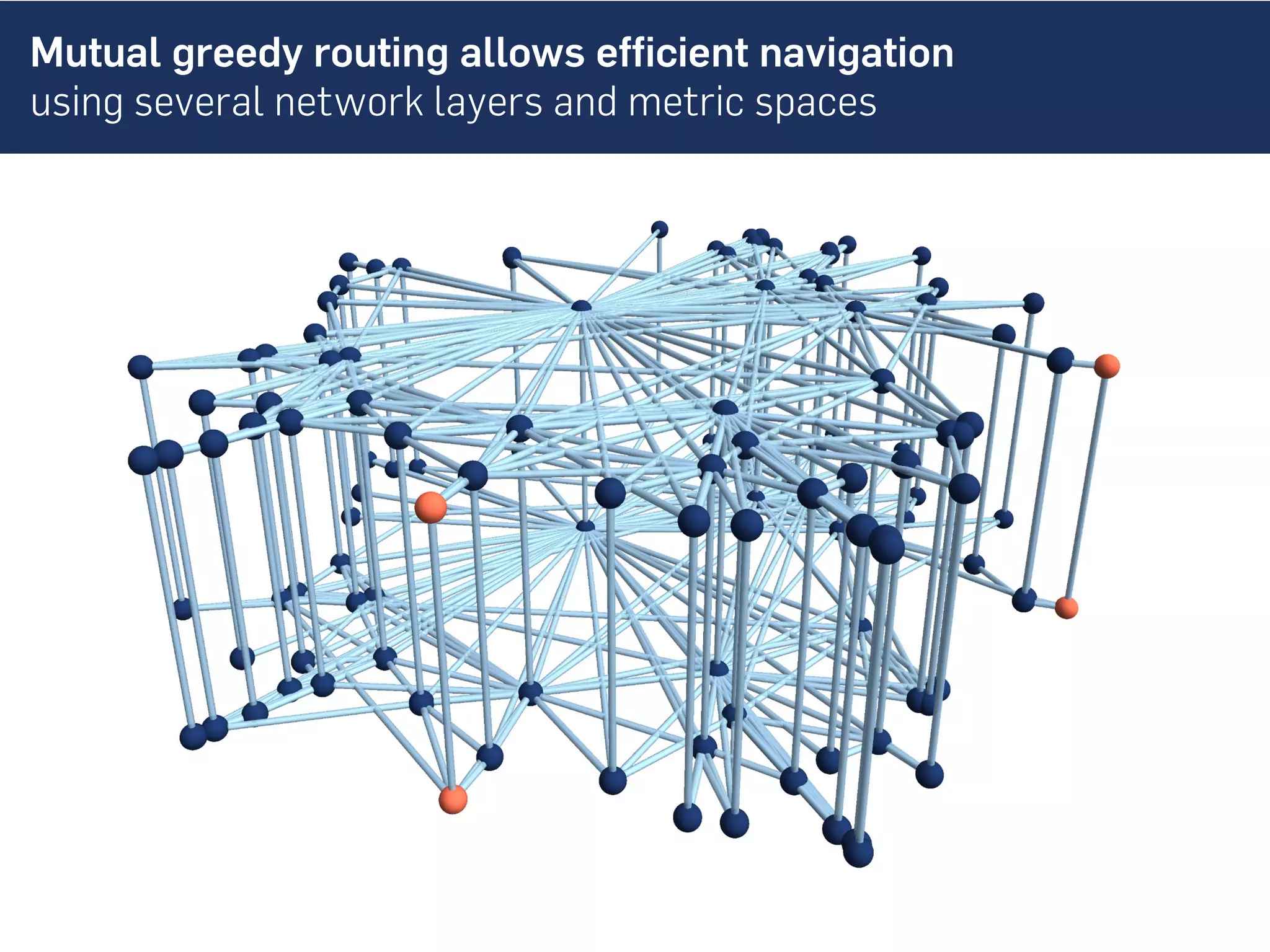
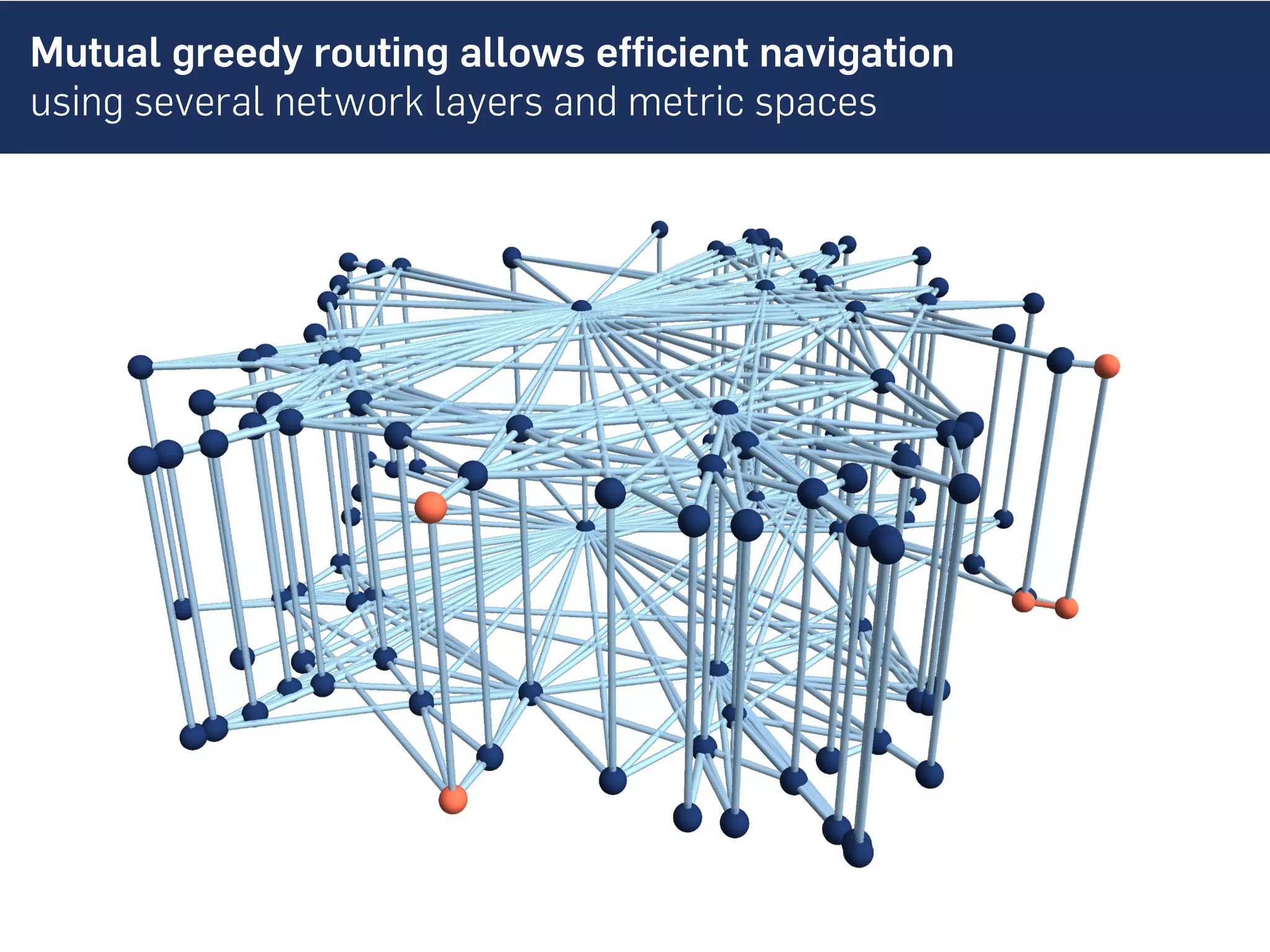
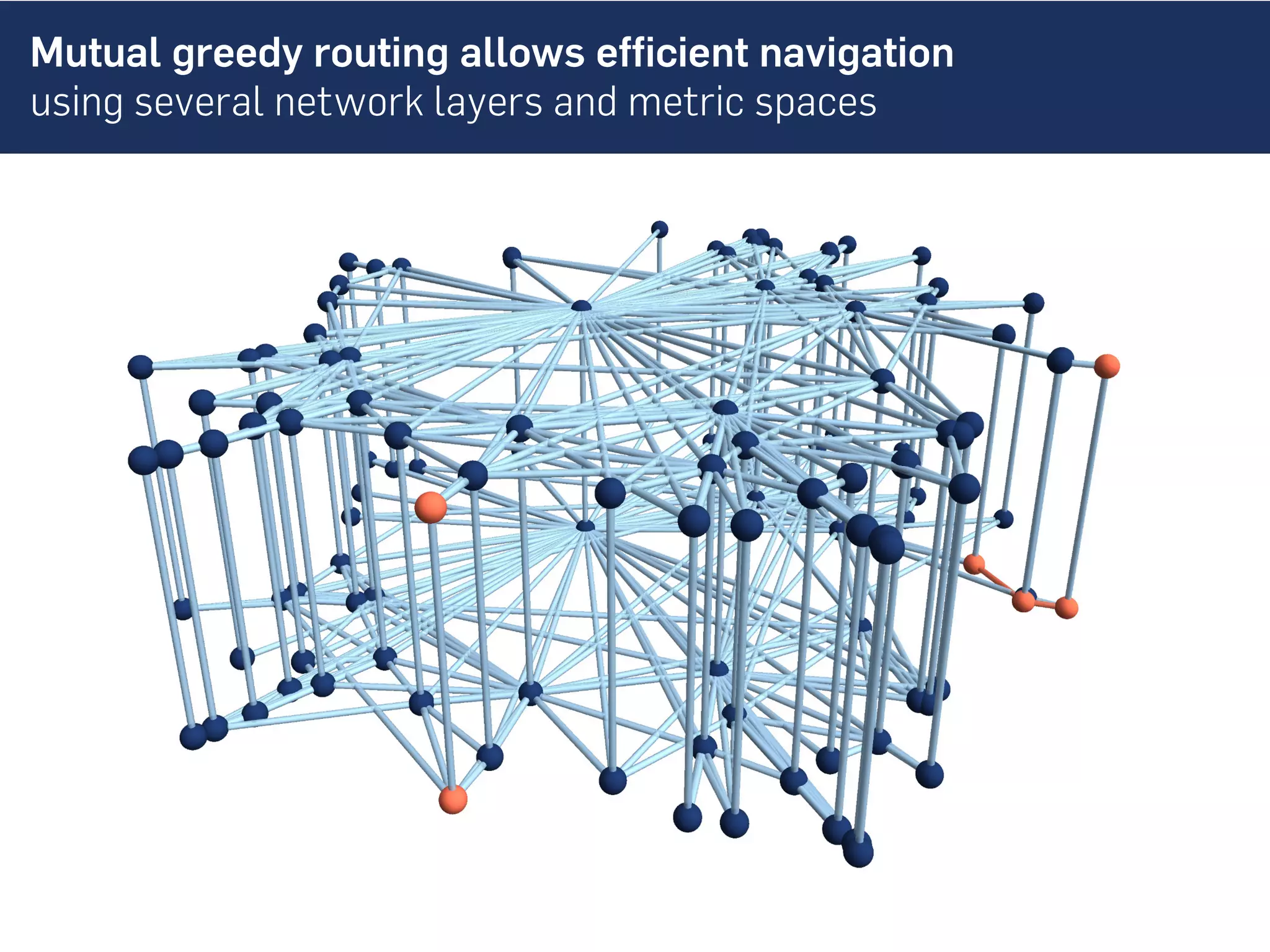
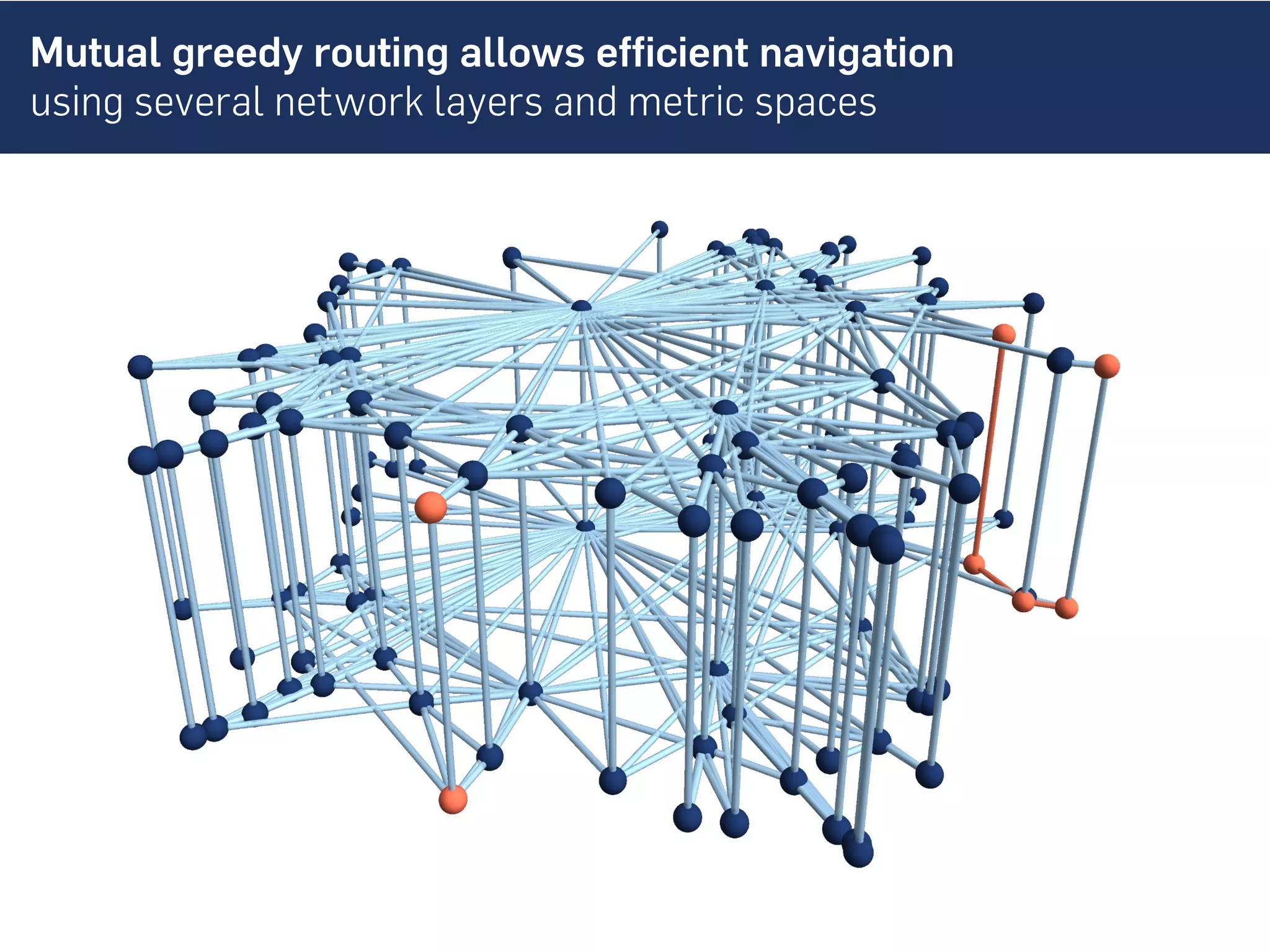
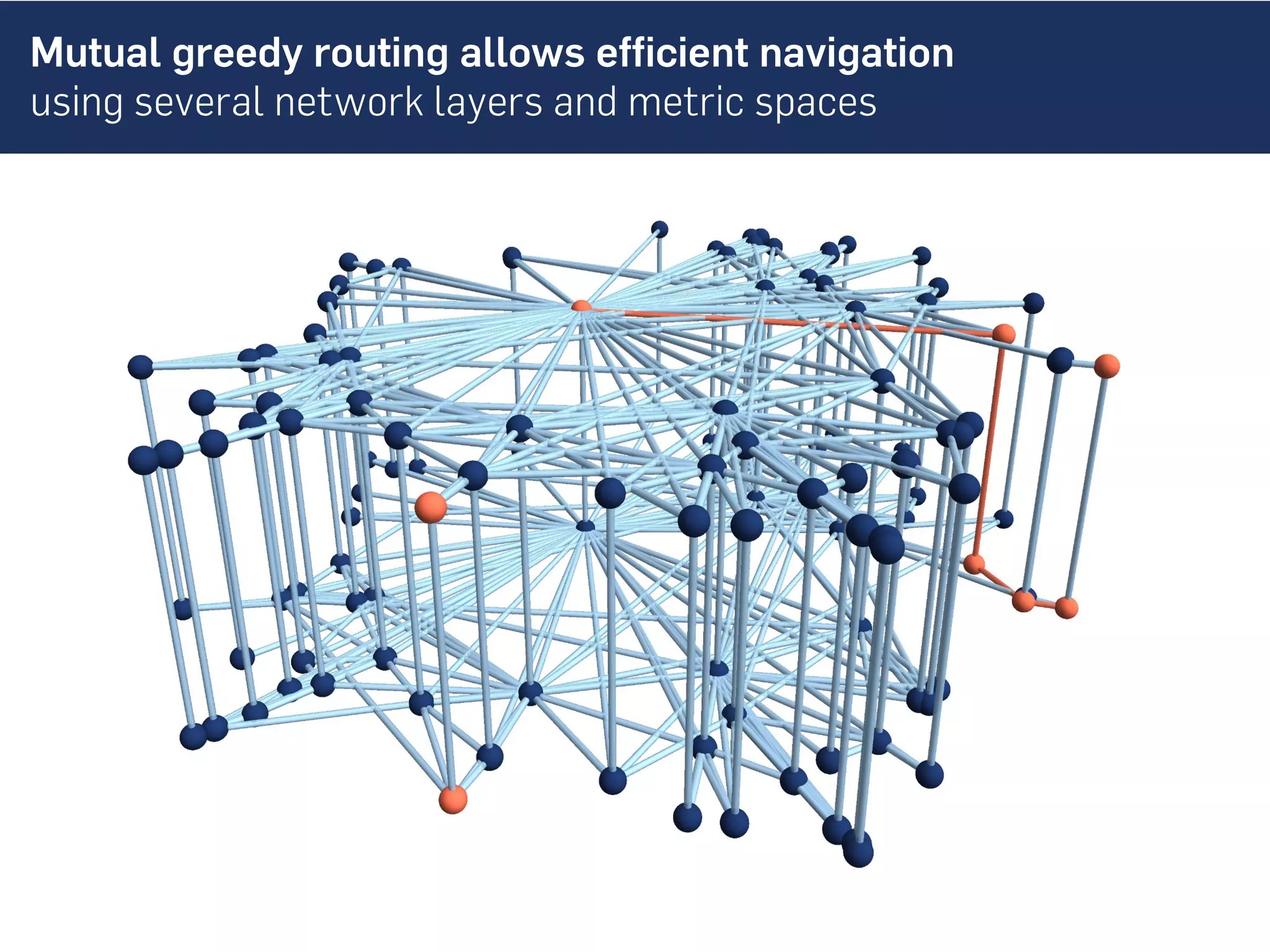
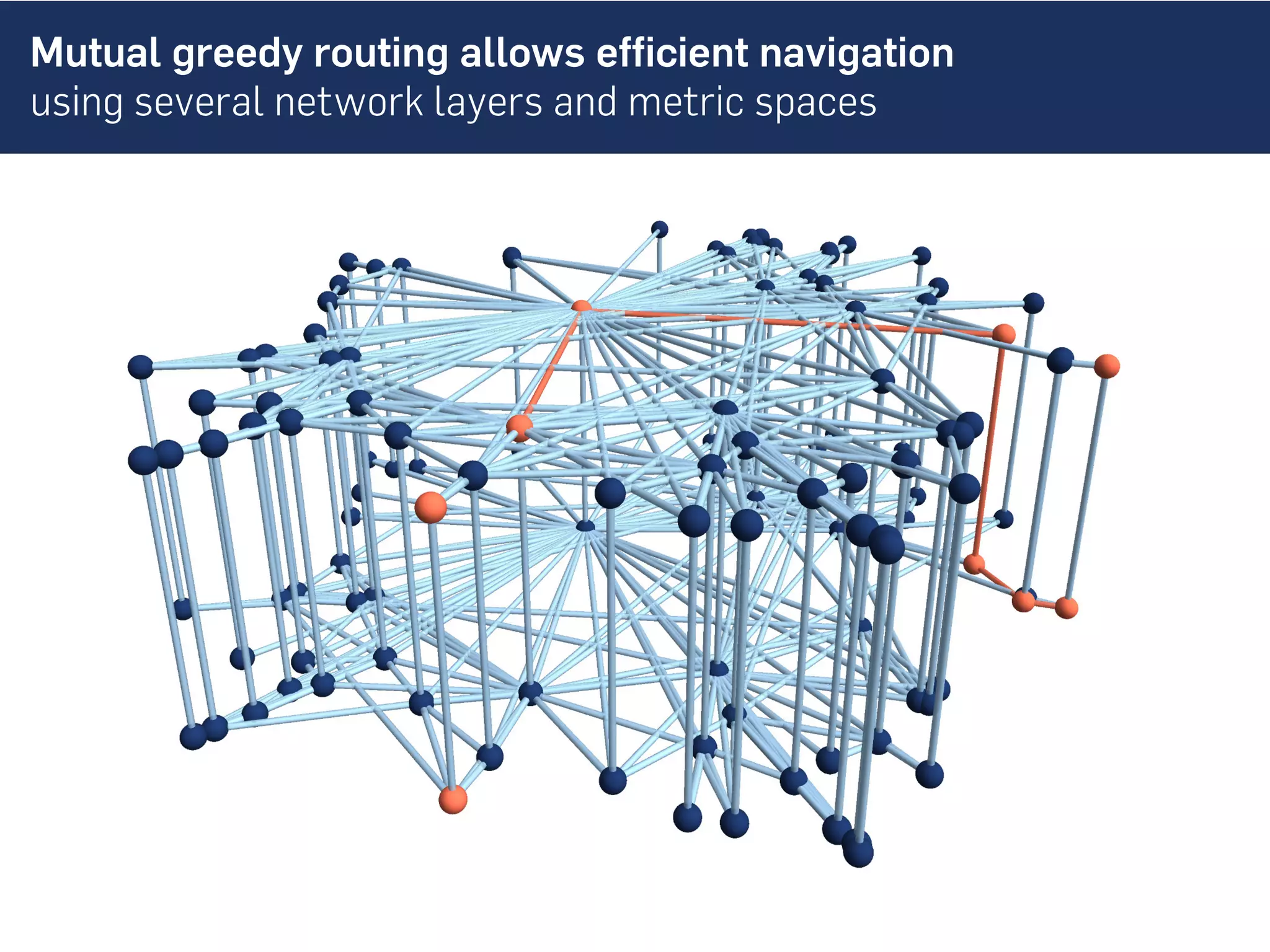
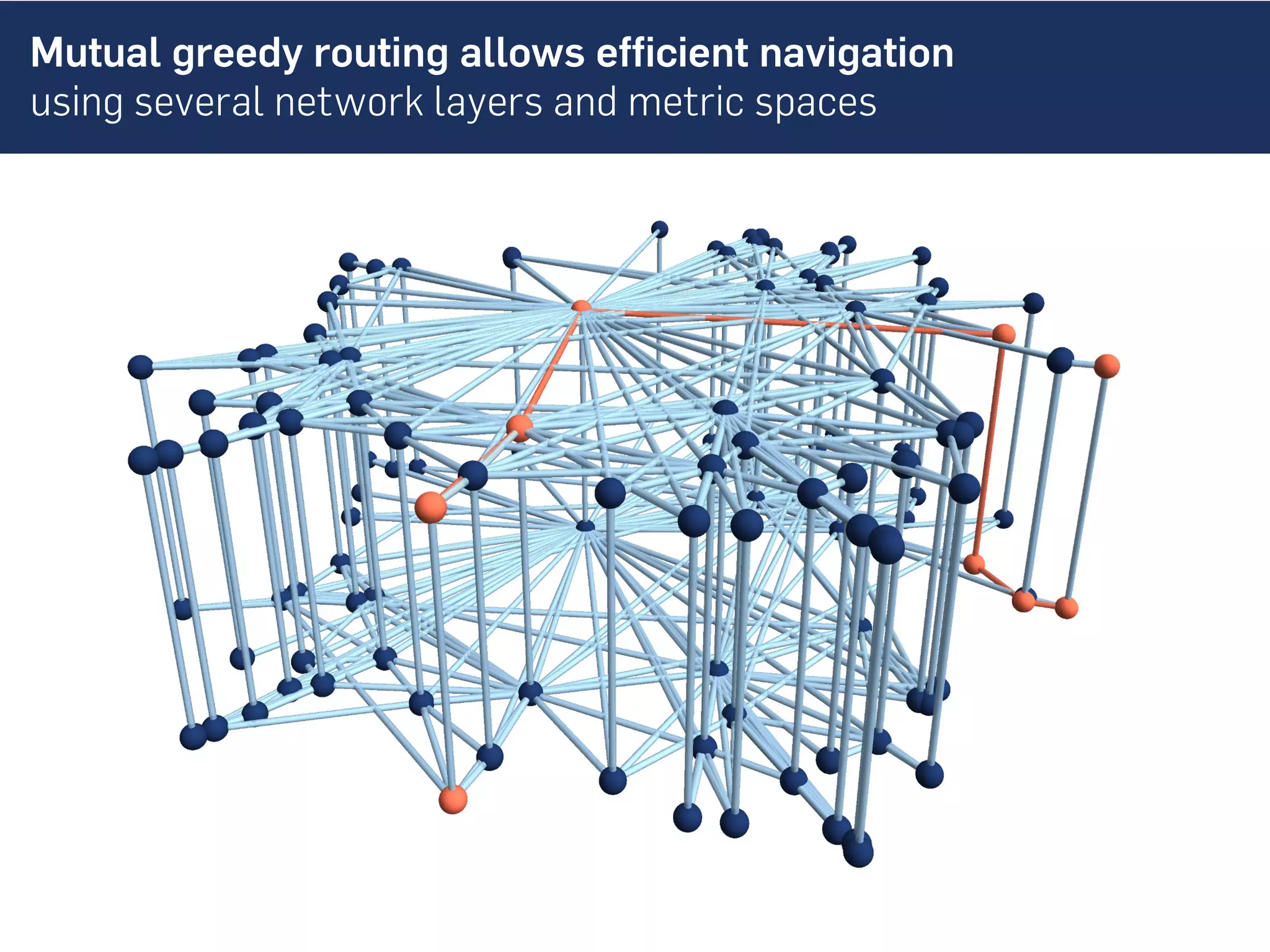
This document discusses the role of hidden geometric correlations in real multiplex networks, proposing that the structure and interaction of these networks can be understood through hyperbolic geometry. It highlights the relationship between node coordinates across layers, demonstrating that correlated distances influence connection probabilities and routing efficiency. The findings suggest that the geometry of multiplex networks can enhance navigation and performance in decentralized systems by improving routing methods such as mutual greedy routing.





![Hyperbolic geometry emerges from Newtonian model
and similarity × popularity optimization in growing network
S1
p(κ) ∝ κ−γ
r = 1
1+
[
d(θ,θ′)
µκκ′
]1/T
PRL 100, 078701](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dpgmultiplex-160713210306/75/Hidden-geometric-correlations-in-real-multiplex-networks-9-2048.jpg)
![Hyperbolic geometry emerges from Newtonian model
and similarity × popularity optimization in growing network
S1 H2
p(κ) ∝ κ−γ ri = R − 2 ln κi
κmin
r = 1
1+
[
d(θ,θ′)
µκκ′
]1/T p(xij) = 1
1+e
xij−R
2T
PRL 100, 078701 PRE 82, 036106](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dpgmultiplex-160713210306/75/Hidden-geometric-correlations-in-real-multiplex-networks-10-2048.jpg)
![Hyperbolic geometry emerges from Newtonian model
and similarity × popularity optimization in growing network
S1 H2 growing
1
2
3
p(κ) ∝ κ−γ ri = R − 2 ln κi
κmin t = 1, 2, 3 . . .
r = 1
1+
[
d(θ,θ′)
µκκ′
]1/T p(xij) = 1
1+e
xij−R
2T
mins [s × ∆θst]
PRL 100, 078701 PRE 82, 036106 Nature 489, 537–540](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dpgmultiplex-160713210306/75/Hidden-geometric-correlations-in-real-multiplex-networks-11-2048.jpg)



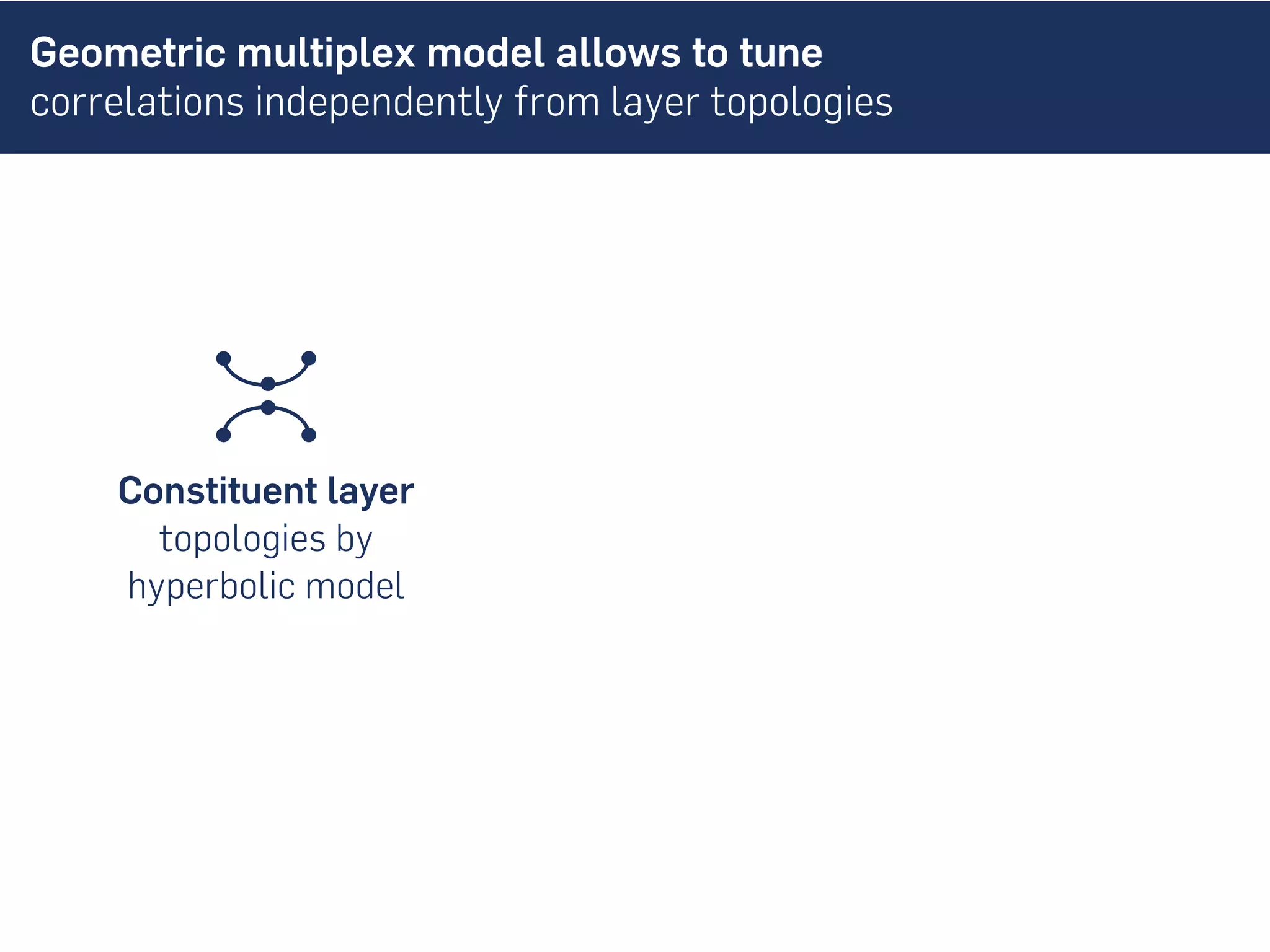
![Geometric multiplex model allows to tune
correlations independently from layer topologies
Constituent layer
topologies by
hyperbolic model
Radial correlations
controlled by
ν ∈ [0, 1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dpgmultiplex-160713210306/75/Hidden-geometric-correlations-in-real-multiplex-networks-40-2048.jpg)
![Geometric multiplex model allows to tune
correlations independently from layer topologies
Constituent layer
topologies by
hyperbolic model
Radial correlations
controlled by
ν ∈ [0, 1]
Angular corr.
controlled by
g ∈ [0, 1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dpgmultiplex-160713210306/75/Hidden-geometric-correlations-in-real-multiplex-networks-41-2048.jpg)