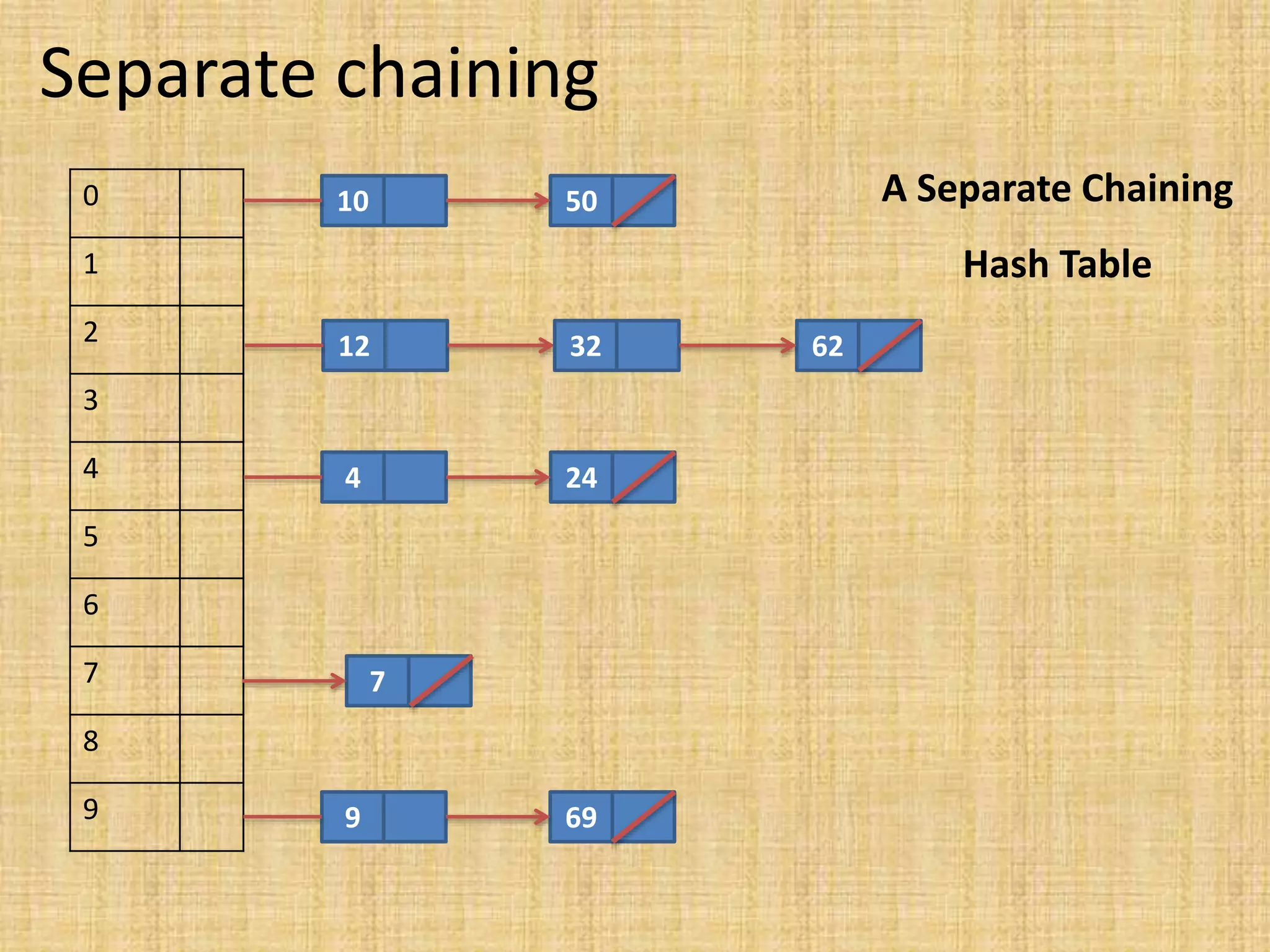
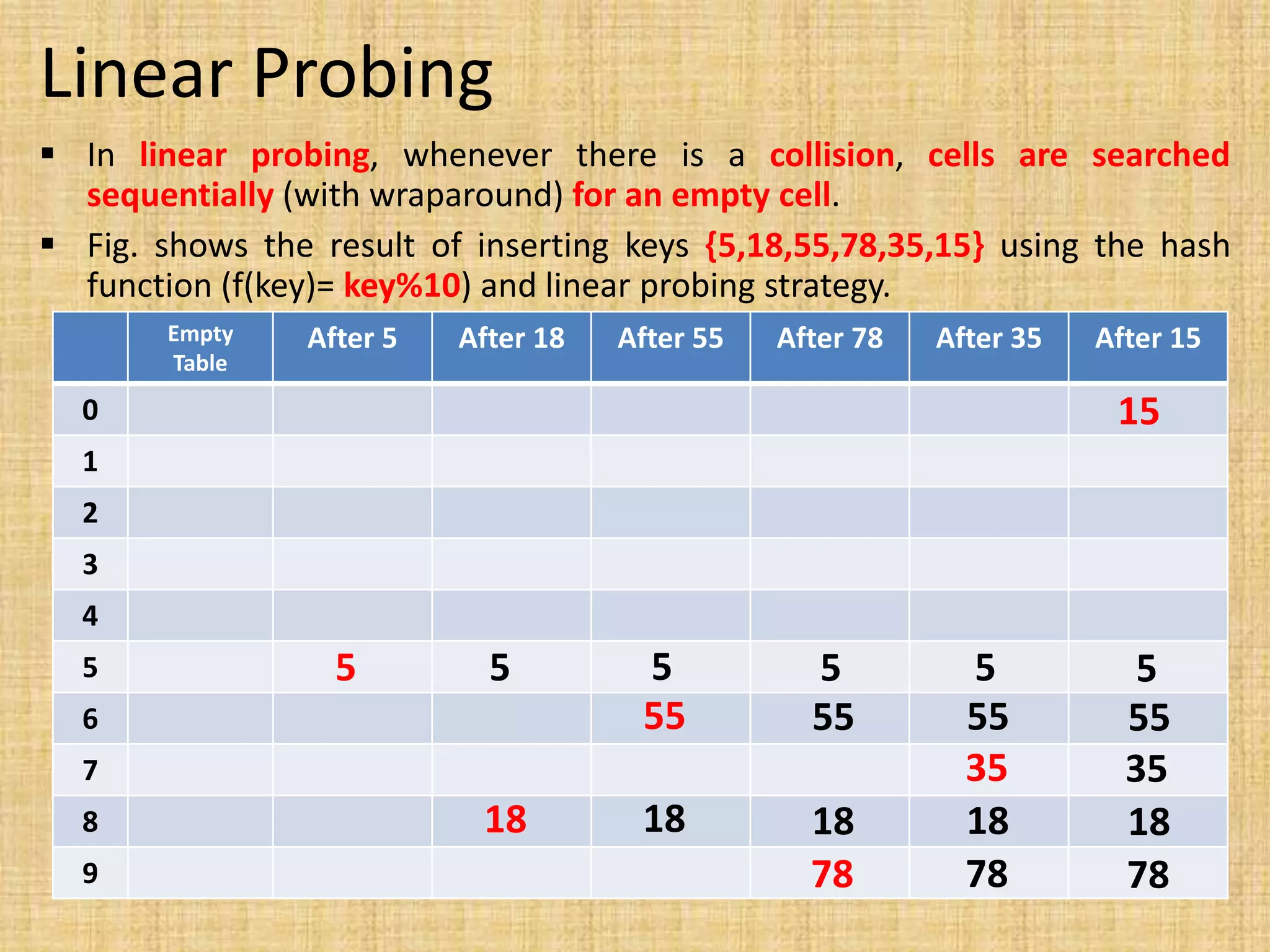
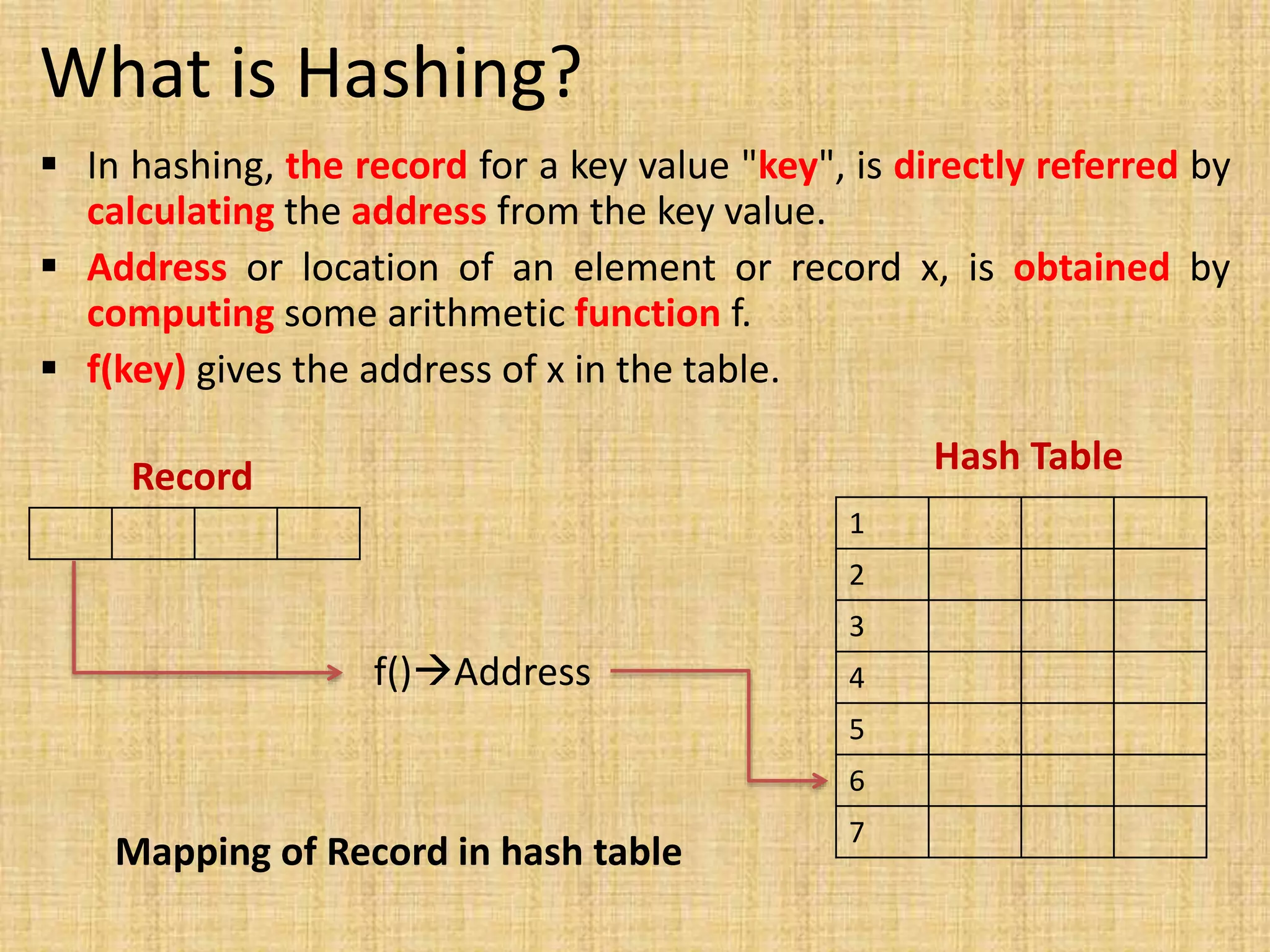
Hashing is a technique for storing data in an array-like structure that allows for fast lookup of data based on keys. It improves upon linear and binary search by avoiding the need to keep data sorted. Hashing works by using a hash function to map keys to array indices, with collisions resolved through techniques like separate chaining or open addressing. Separate chaining uses linked lists at each index while open addressing resolves collisions by probing to alternate indices like linear, quadratic, or double hashing.



![Open Hashing Data Structure
The basic idea is that the records [elements] are partitioned into
B classes, numbered 0,1,2 … B-1
A Hashing function f(x) maps a record with key x to an integer
value between 0 and B-1
Each bucket in the bucket table is the head of the linked list of
records mapped to that bucket
0
1
.
.
.
B-1
Bucket
Table
List of Elements
The open hashing
data organization](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hashing1-230208052233-50750de2/75/Hashing-pptx-5-2048.jpg)