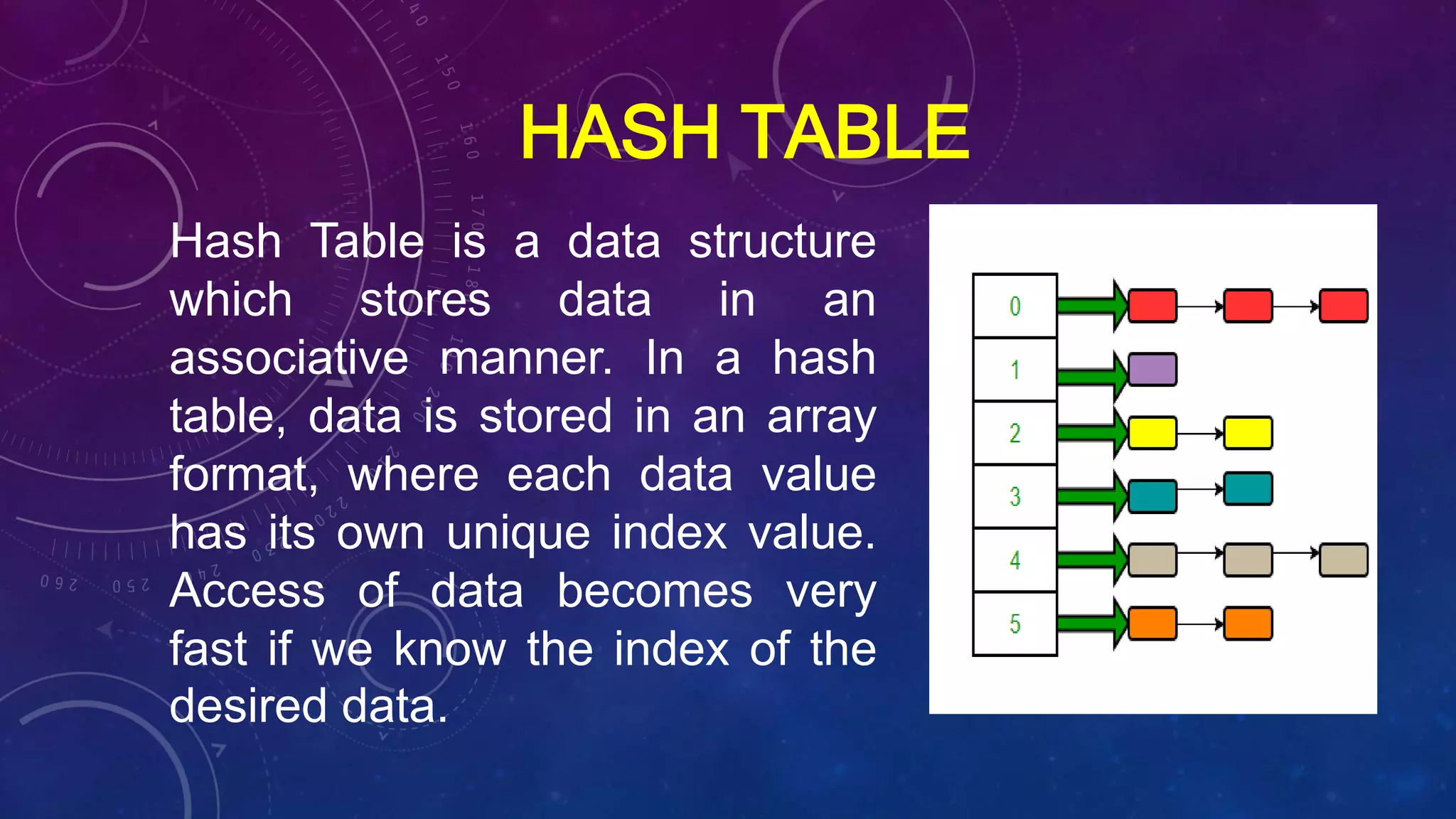
Hash Table is a data structure that stores data in an associative manner using an array format. Each data value has a unique index value. A hash function is used to compute an index, called a hash code, into an array of buckets from which the desired value can be retrieved. During lookup, the key is hashed and the resulting hash indicates where the corresponding value is stored. Collisions, where two keys hash to the same index, are handled using techniques like chaining or probing.




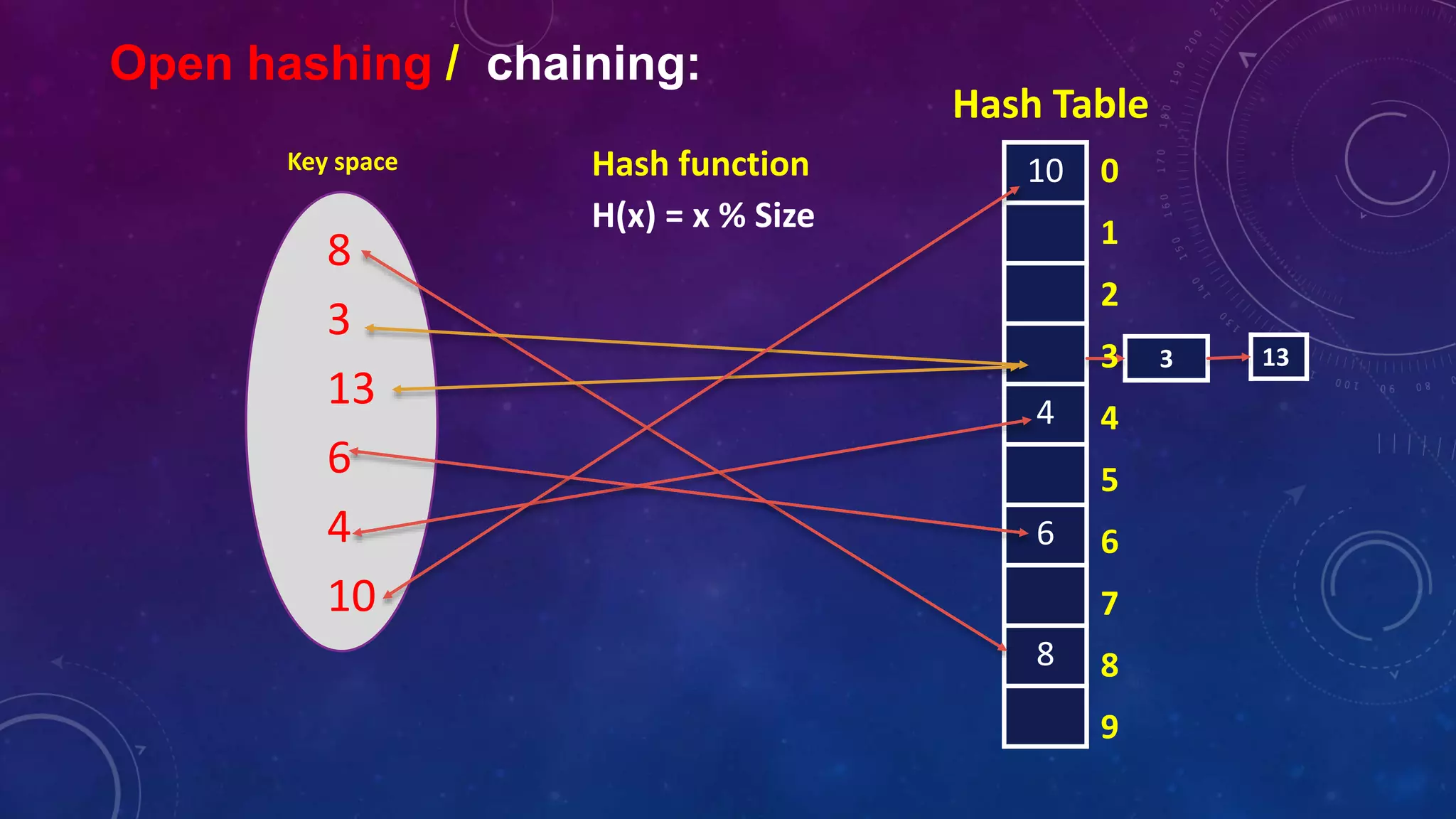
![Closed hashing / linear probing:
10
3
13
4
6
8
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
8
3
13
6
4
10
Key space
Hash function
H(x) = x % Size
Hash Table
H(x) = x % size
H’(x) = [ h (x) + f (i) ] % size
H’(13) = [ h (13) + f (0) ] % 10
= 3
H’(13) = [ h (13) + f (1) ] % 10
= 4
F(I) = I
I = 0,1,2,……](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hashtable2-220310180851/75/Hash-table-2-7-2048.jpg)
![Closed hashing / Quadradic Probing:
10
3
13
23
8
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
8
3
13
23
43
10
Key space
Hash function
H(x) = x % Size
Hash Table
H(x) = x % size
H’(x) = [ h (x) + f (i) ] % size
H’(23) = [ h (23) + f (0) ] % 10
= 3
H’(23) = [ h (23) + f (1) ] % 10
= (3+1) %10 = 4
H’(23) = [ h (23) + f (2) ] % 10
=(3 + 4 ) %10 = 7
F(I) = 𝐼2
0,1,2,……](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hashtable2-220310180851/75/Hash-table-2-8-2048.jpg)
![program to implement hashing with
chaining
class Hash
{
int BUCKET; // No. of buckets
// Pointer to an array containing buckets
list<int> *table;
public:
Hash(int V); // Constructor
// inserts a key into hash table
void insertItem(int x);
// deletes a key from hash table
void deleteItem(int key);
// hash function to map values to key
int hashFunction(int x) {
return (x % BUCKET);
}
void displayHash();
};
void Hash::deleteItem(int key)
{
// get the hash index of key
int index = hashFunction(key);
// find the key in (index)th list
list <int> :: iterator i;
for (i = table[index].begin();
i != table[index].end(); i++) {
if (*i == key)
break;
}
// if key is found in hash table, remove it
if (i != table[index].end())
table[index].erase(i);
}
// function to display hash table
void Hash::displayHash() {
for (int i = 0; i < BUCKET; i++) {
cout << i;
for (auto x : table[i])
cout << " --> " << x;
cout << endl;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hashtable2-220310180851/75/Hash-table-2-9-2048.jpg)
![// Driver program
int main()
{
// array that contains keys to be mapped
int a[] = {15, 11, 27, 8, 12};
int n = sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]);
// insert the keys into the hash table
Hash h(7); // 7 is count of buckets in
// hash table
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
h.insertItem(a[i]);
// delete 12 from hash table
h.deleteItem(12);
// display the Hash table
h.displayHash();
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hashtable2-220310180851/75/Hash-table-2-10-2048.jpg)