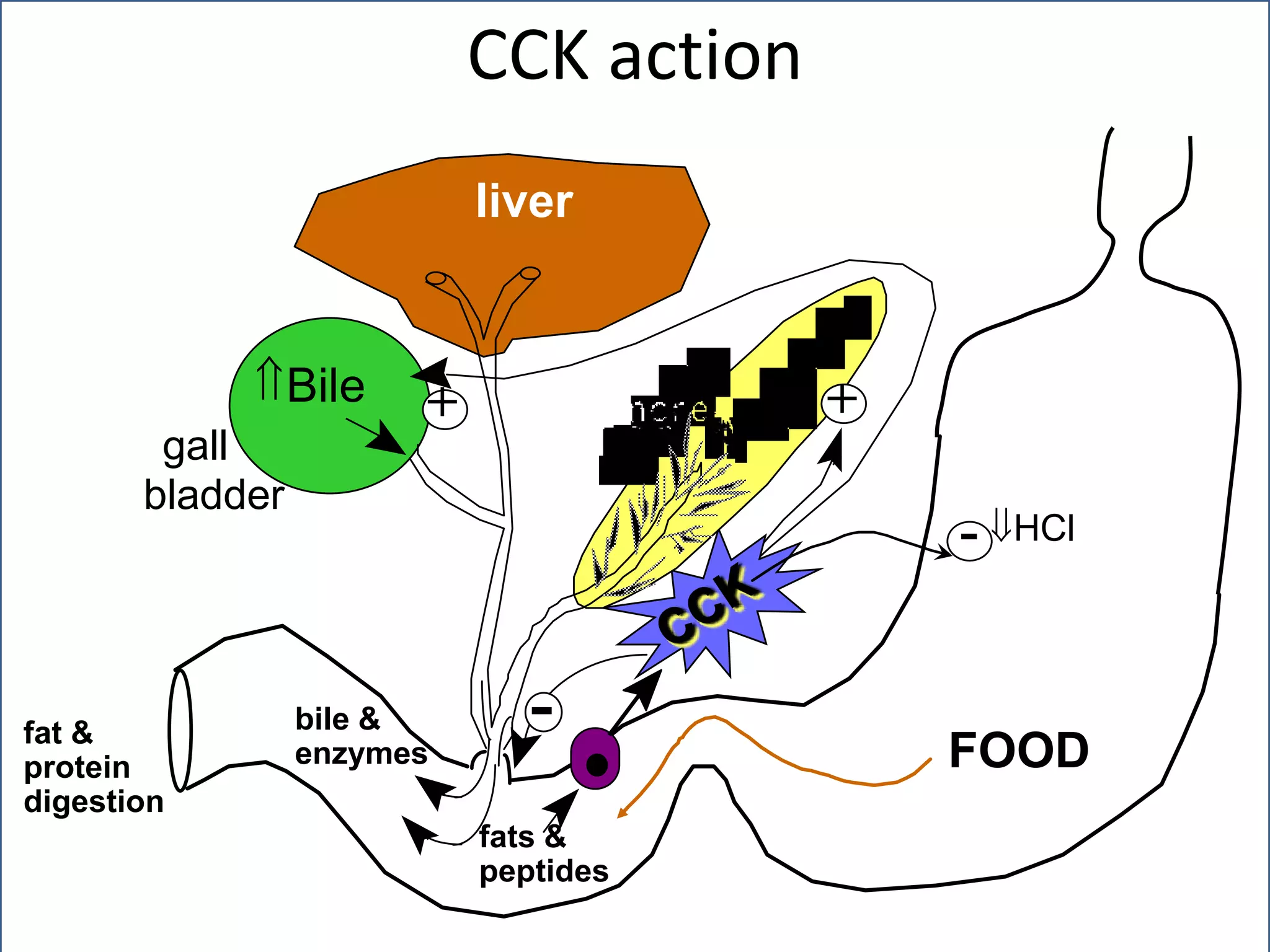
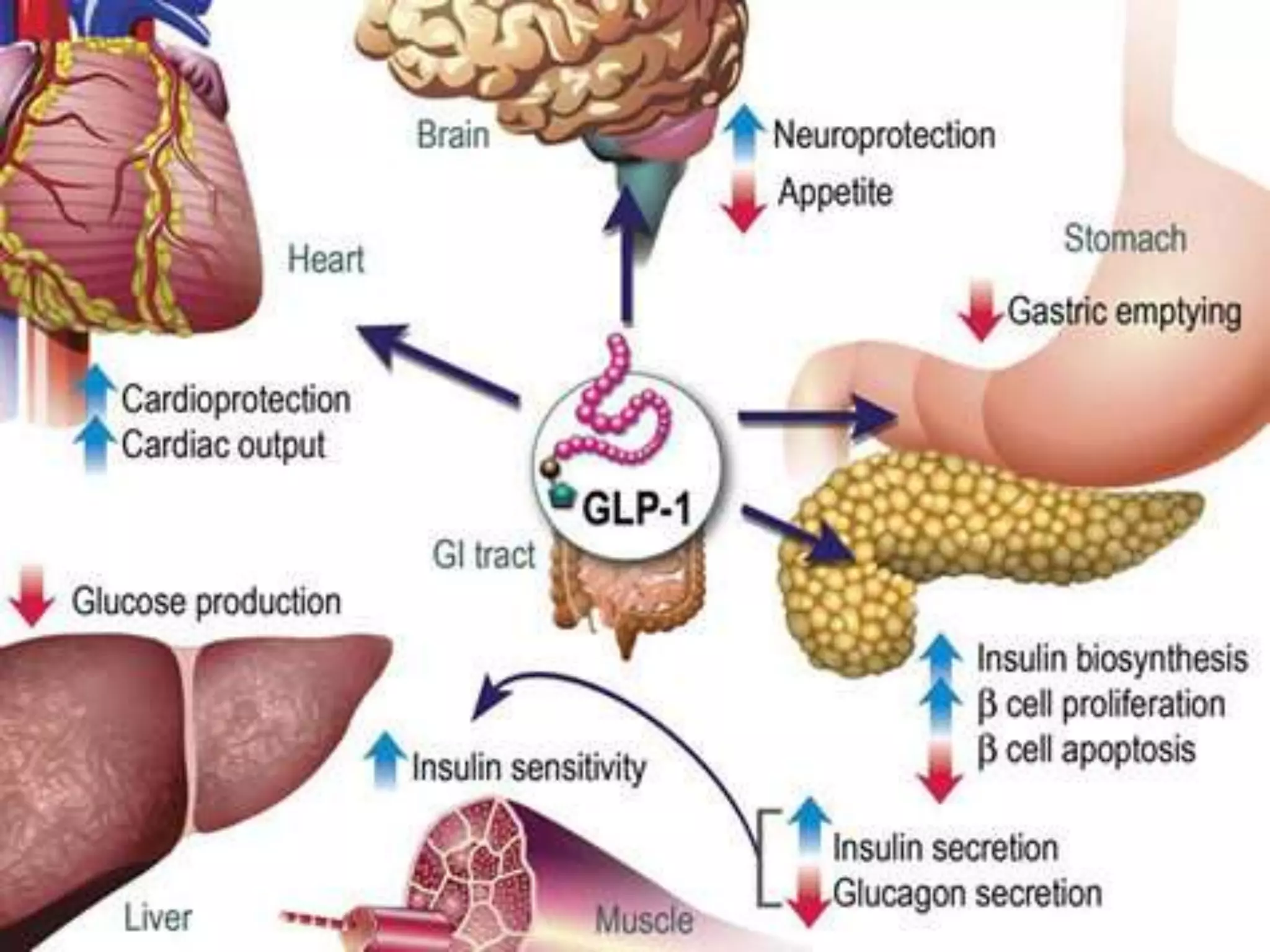
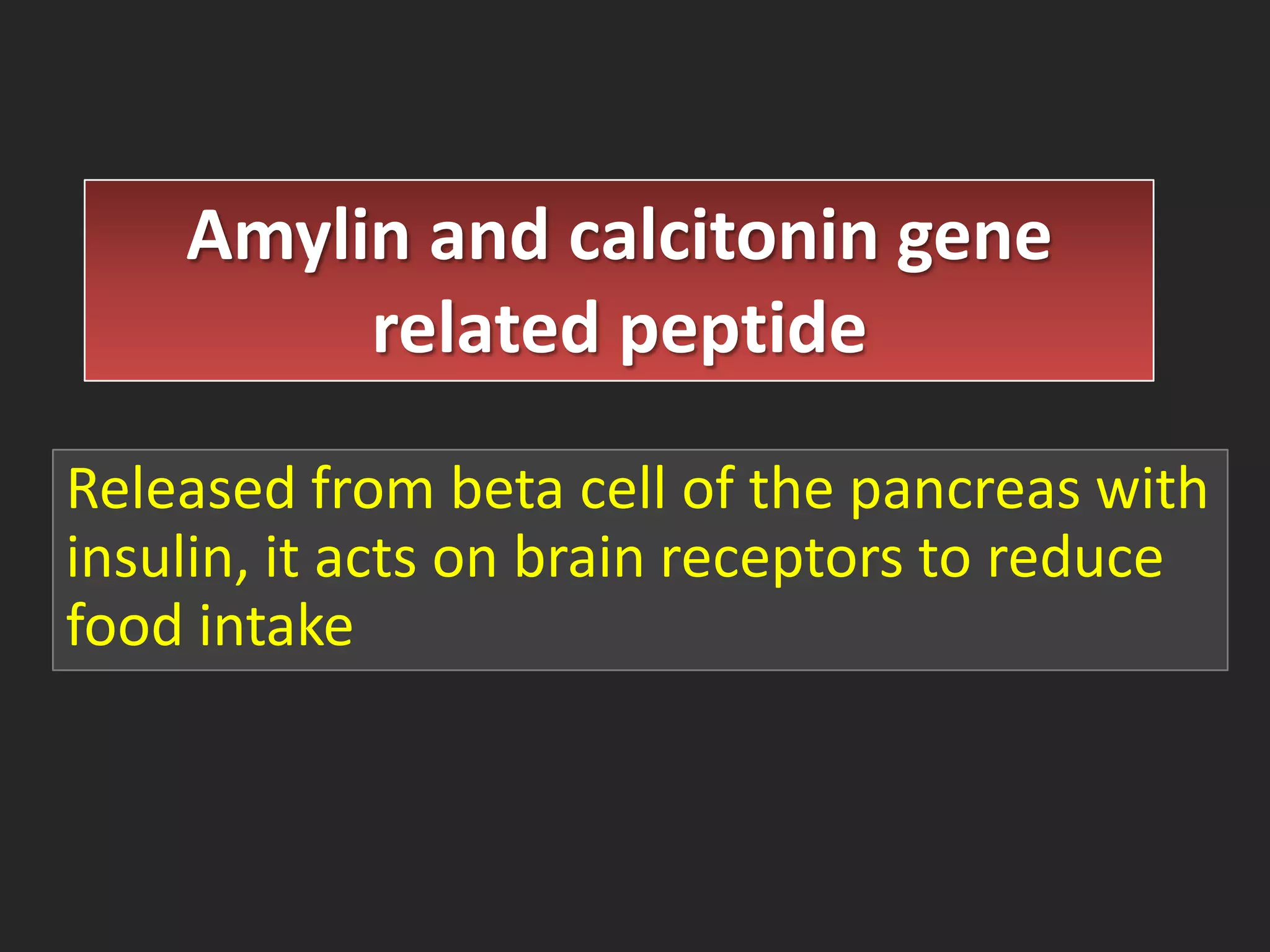
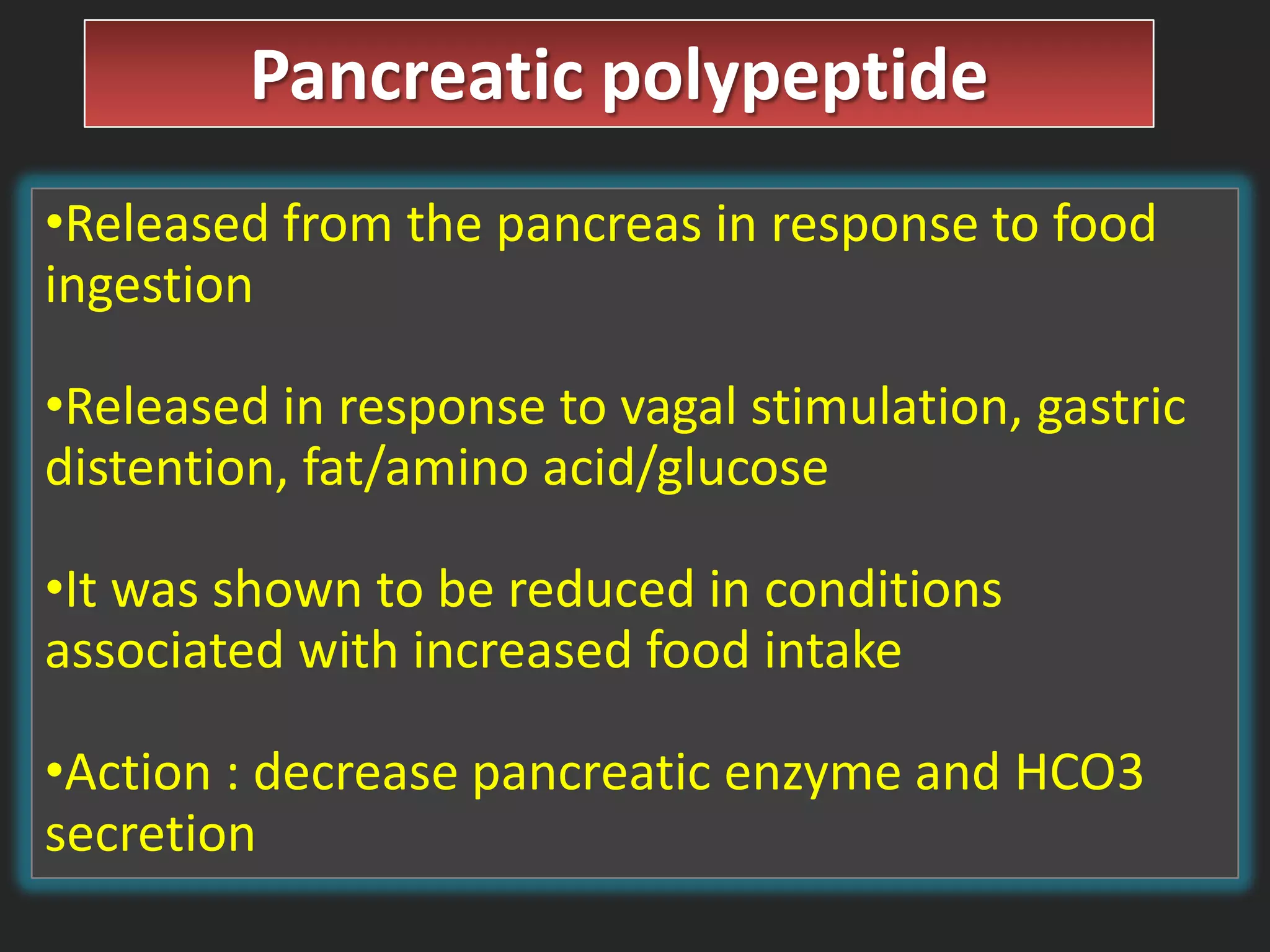
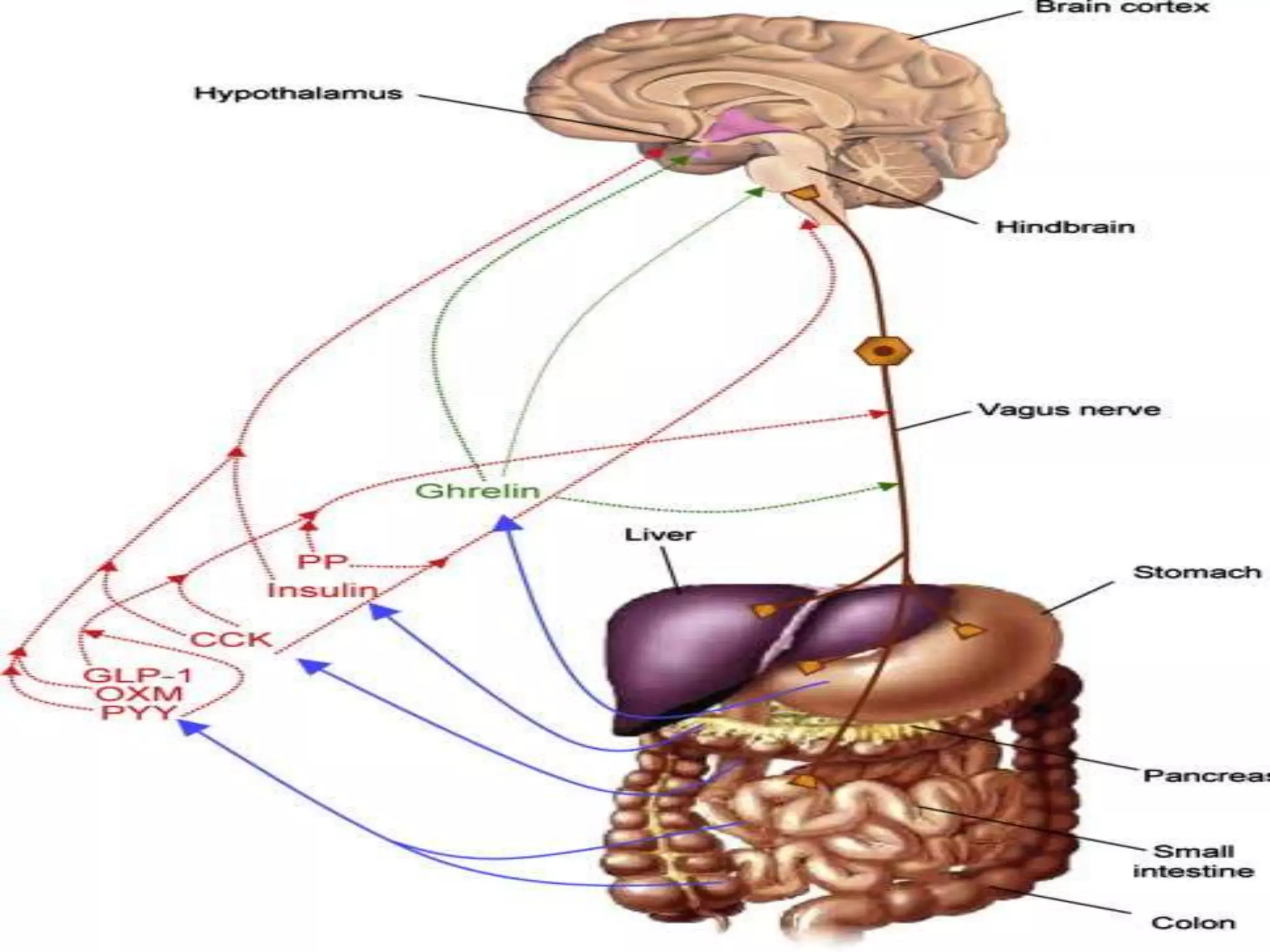
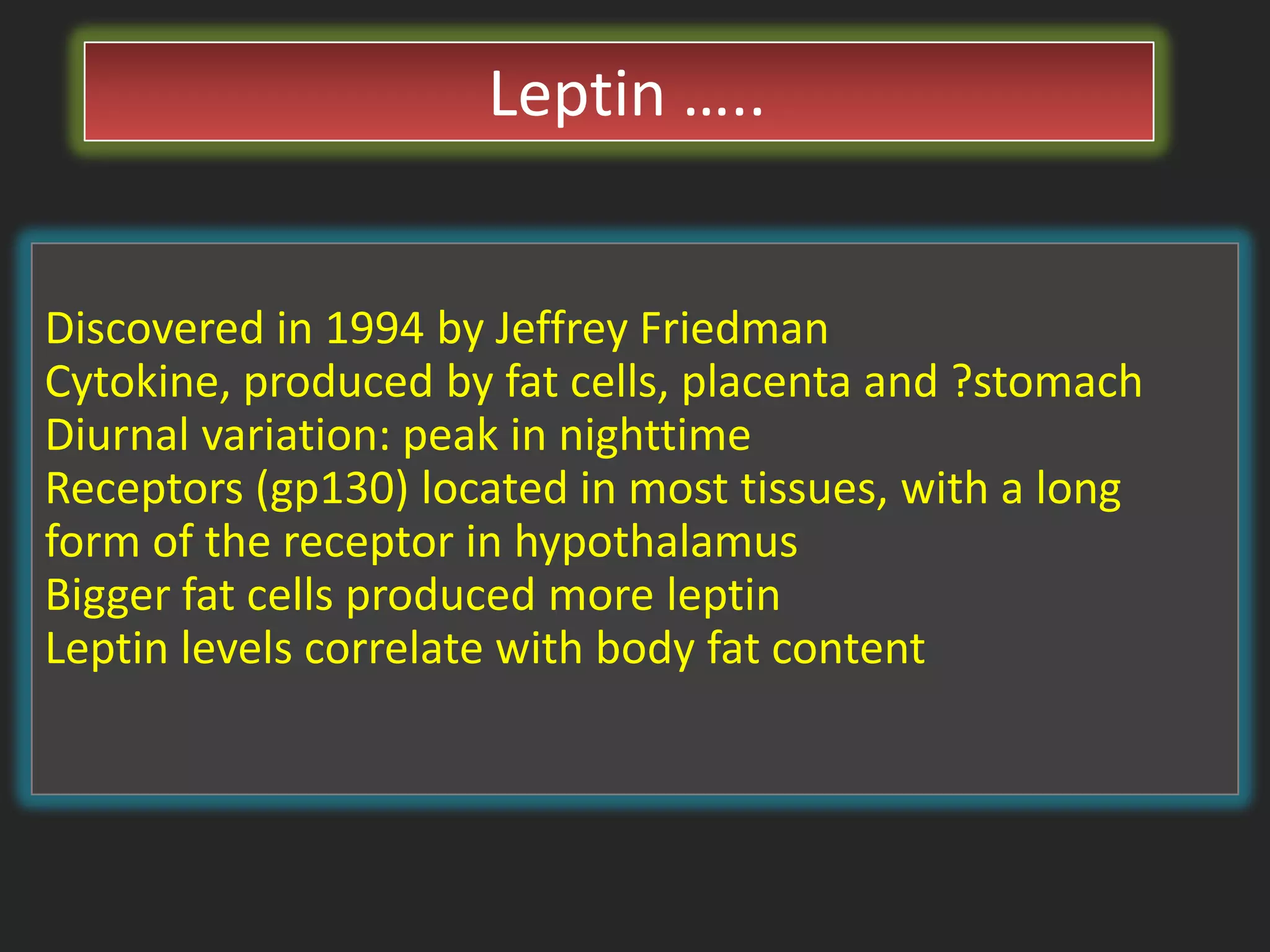
Short term satiety is regulated by mechano- and chemoreceptors in the stomach and small intestine that signal fullness after eating. Hormones like CCK, GLP-1, PYY are also involved in short term regulation by being released from the gut in response to food intake. Long term satiety is regulated by hormones like leptin released by adipose tissue and signals fullness over longer periods based on fat stores. Both short term gut signals and long term adipose signals need to work together to properly regulate long term energy balance and food intake.