Embed presentation
Downloaded 10 times







GSM is a digital cellular network standard that was developed in 1982. It has a three-layer architecture consisting of the mobile station, the base station subsystem, and the network switching subsystem. GSM provides telecommunication services as well as data services and supplementary services. Some advantages of GSM include better speech quality, support for data transmission, and international roaming. However, GSM also has some disadvantages such as potential security issues and less efficient use of spectrum compared to newer technologies.
Introduction to GSM as the Global System for Mobile Communications.
Key discussion points include what GSM is, its architecture, services, advantages, and disadvantages.
GSM's history dates back to 1982, established to standardize mobile communications in Europe.
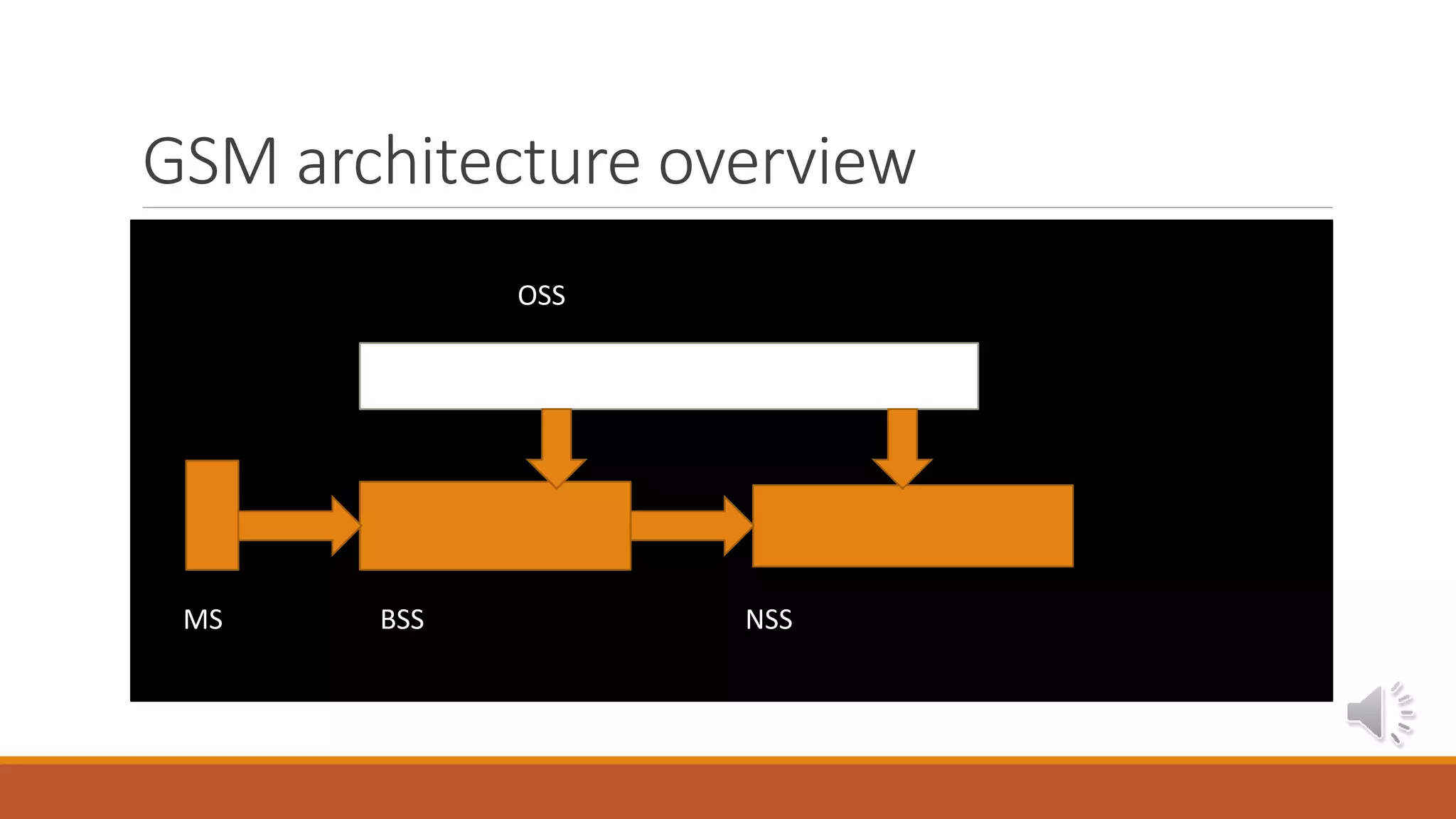
Overview of GSM architecture involving Operational Support Systems (OSS), Mobile Station (MS), Base Station System (BSS), and Network Switching Subsystem (NSS).
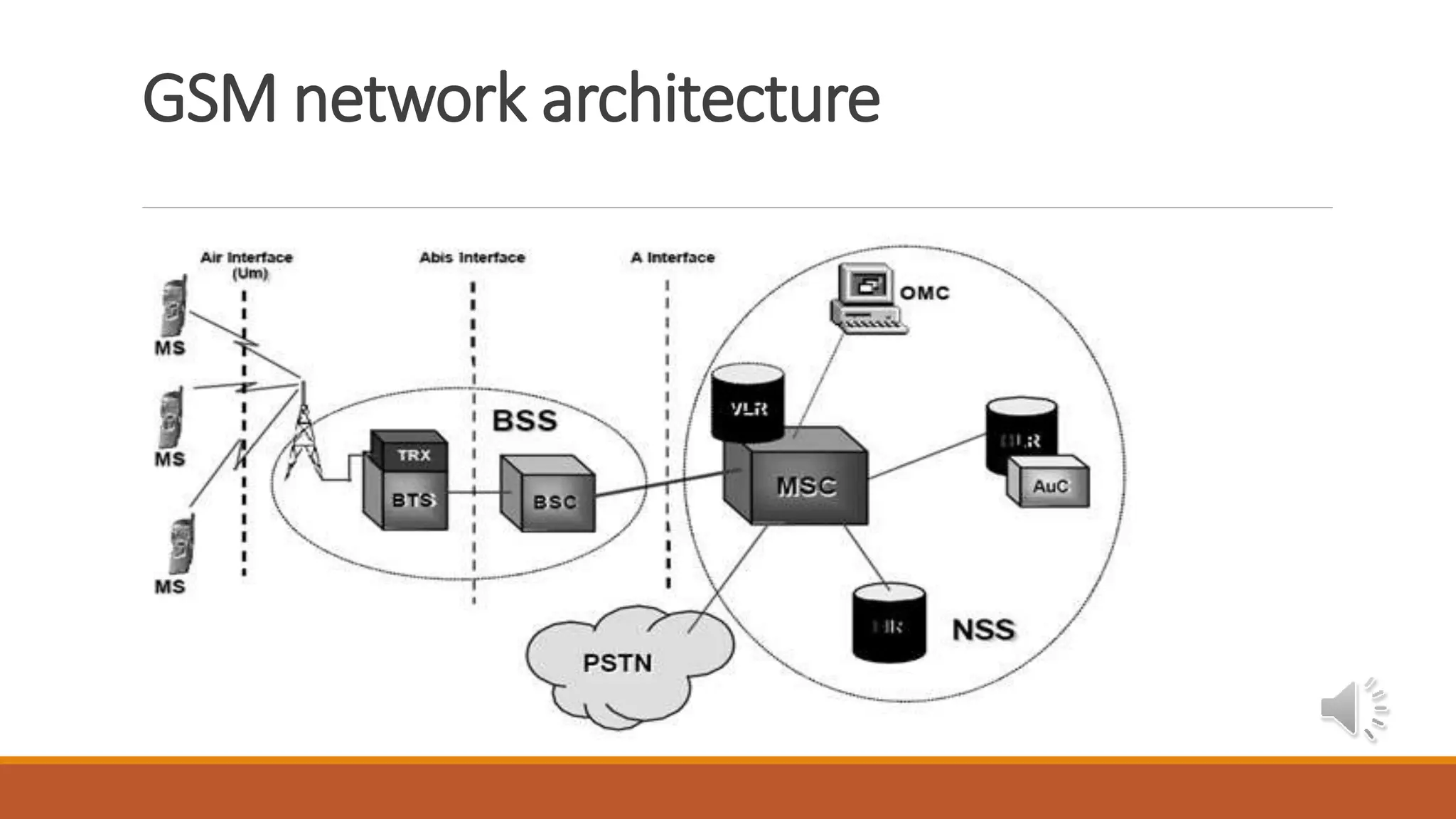
Detailed layout and design of the GSM network architecture.
Three main types of GSM services: Tele-service, Data Services, and Supplementary services.
Advantages include better speech quality and international roaming; disadvantages involve security issues and efficiency.
References and links provided for further information on GSM architecture and related topics.







