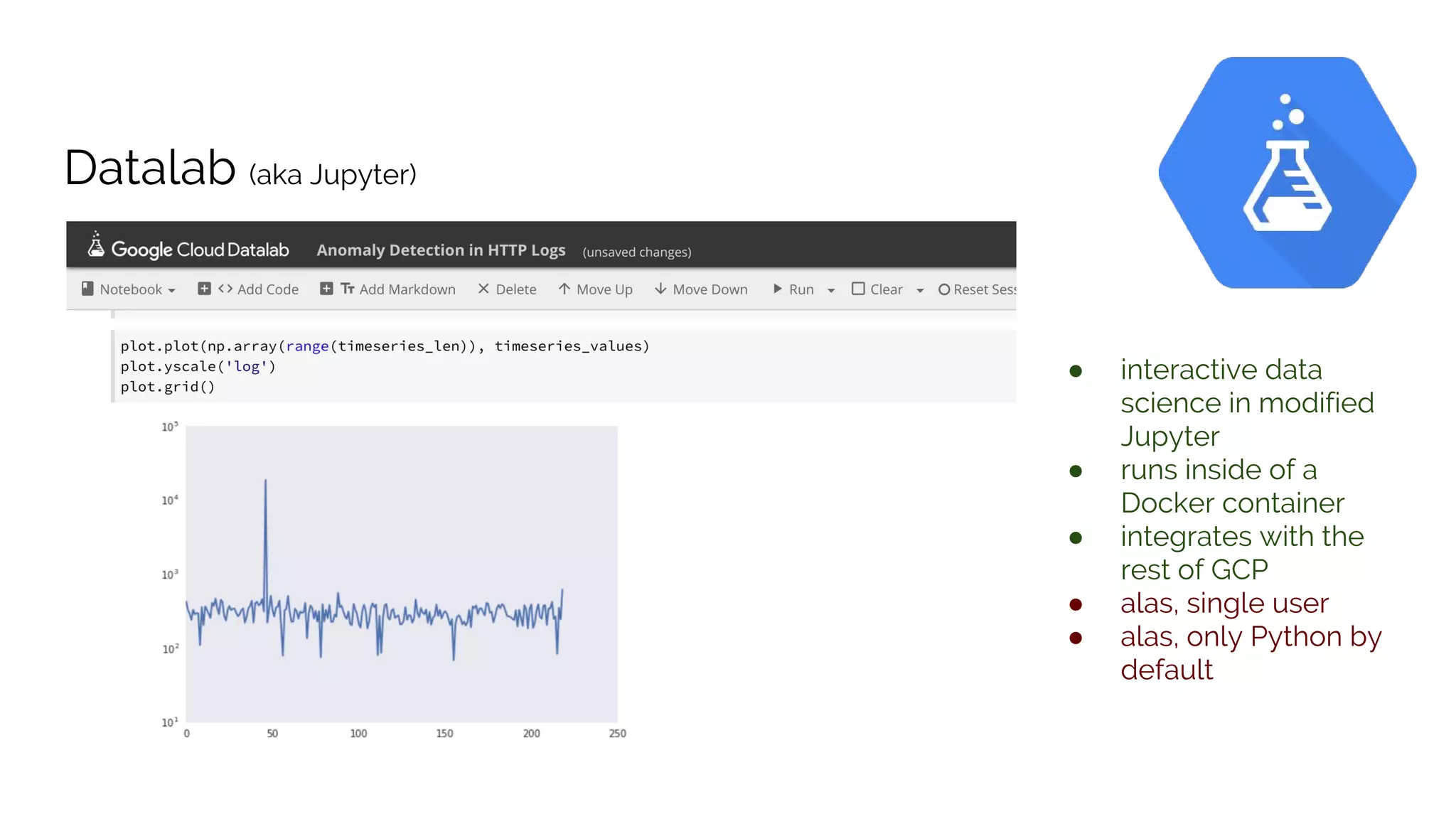
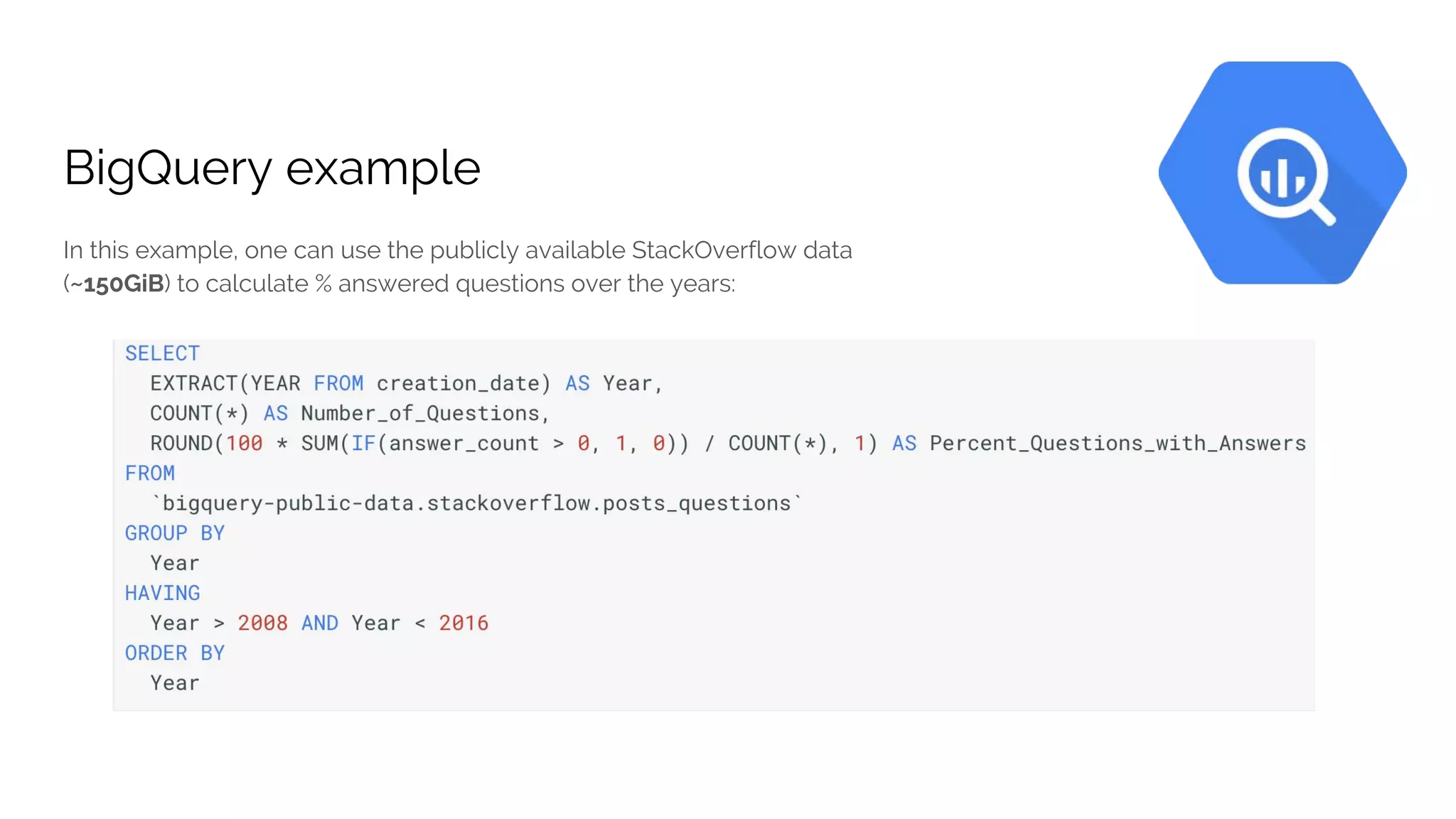
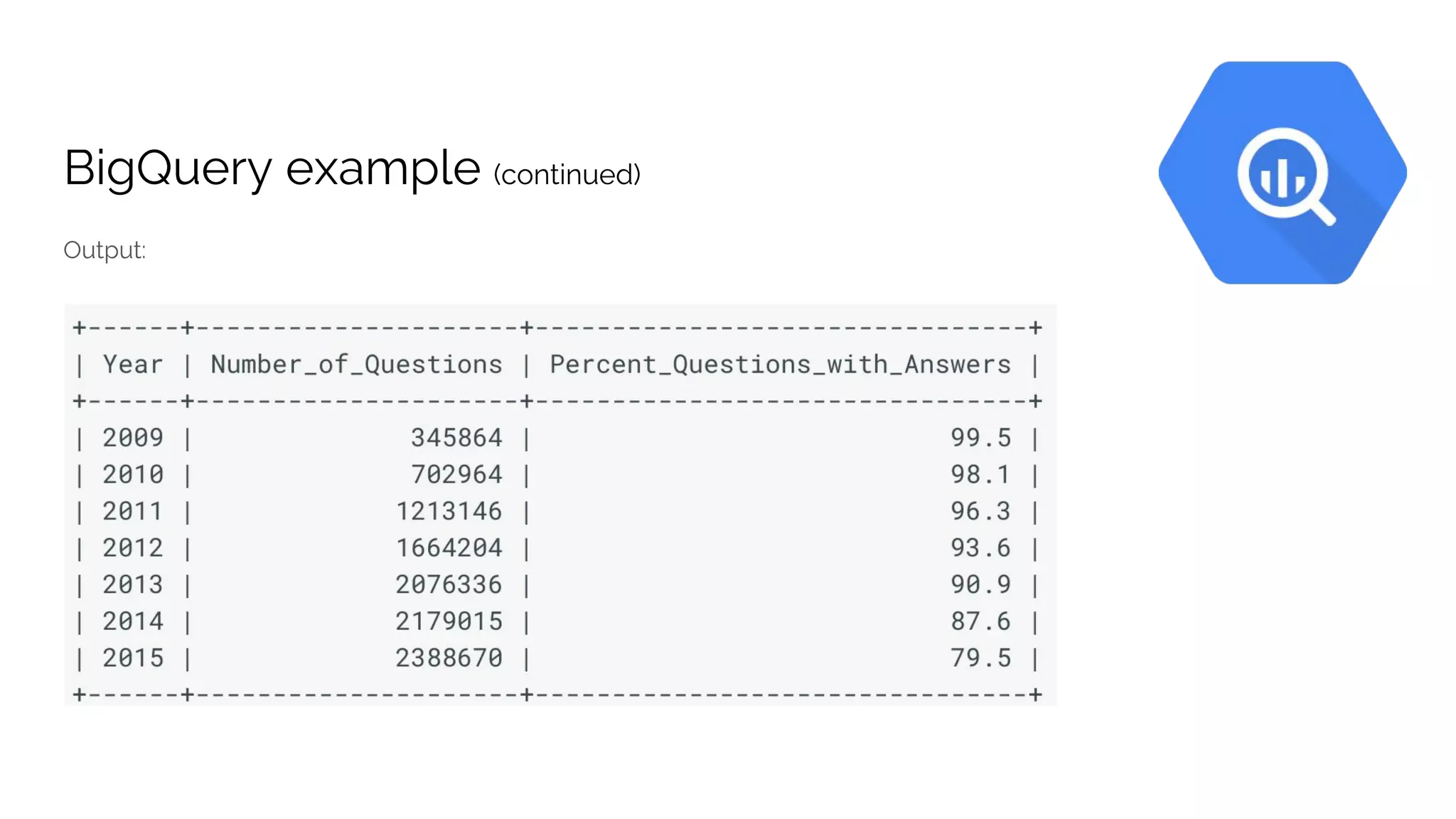
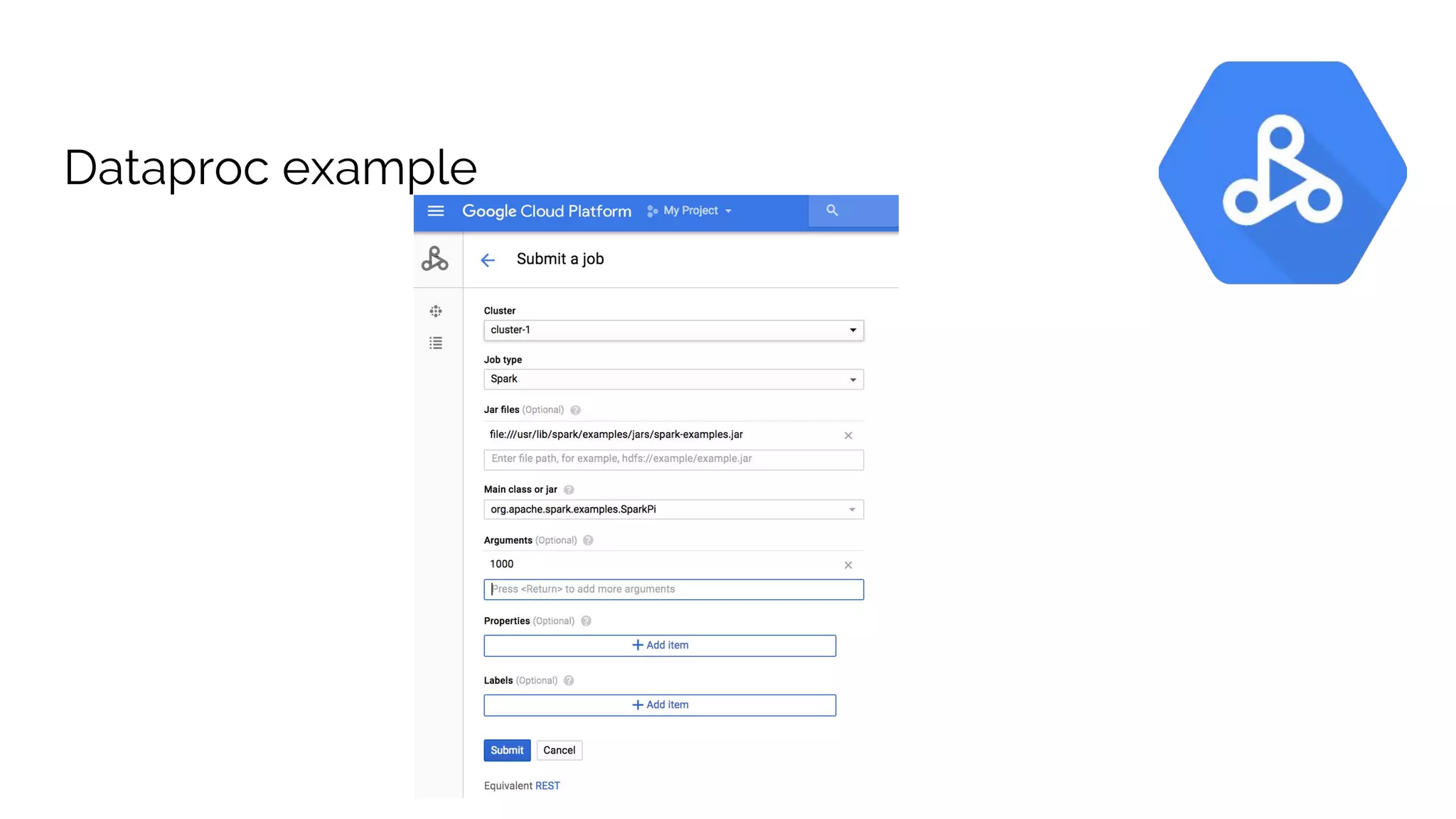
The document discusses the advantages of using Google Cloud Platform (GCP) for data science, highlighting benefits such as scalability, reproducible infrastructure, and integration with community tools. It details various GCP services like BigQuery, Dataflow, and Dataproc, and their functionalities in data processing and machine learning. The talk also touches upon interactive data science using Datalab and provides examples of leveraging GCP for projects such as predicting birth weight using Apache Spark.
![Google Cloud Platform
for Data Science teams
Barton Rhodes [@bmorphism]
Senior Data Scientist at Pandata [pandata.co]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2017-09-16-gcp-data-science-170918234658/75/Google-Cloud-Platform-for-Data-Science-teams-1-2048.jpg)