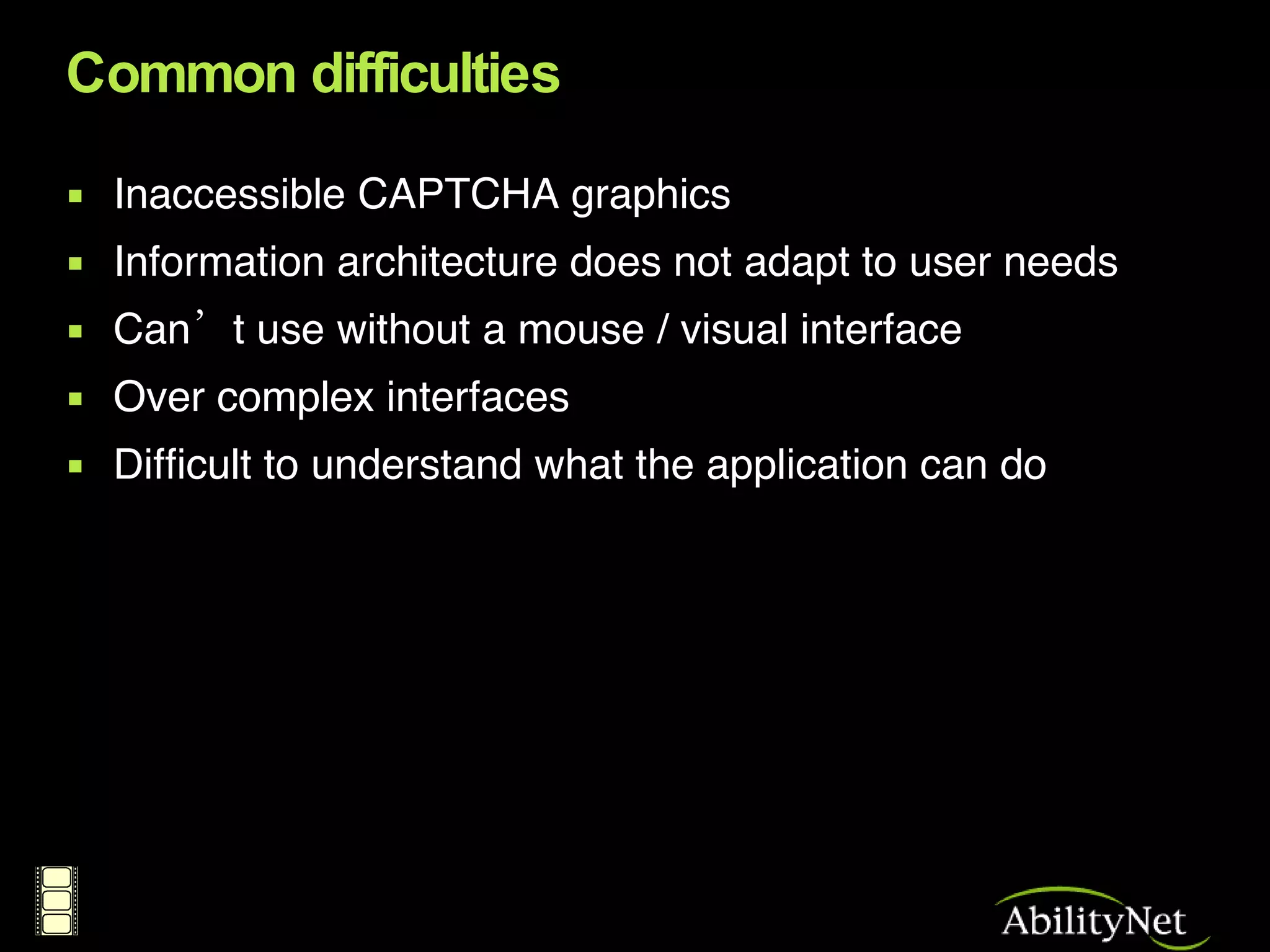
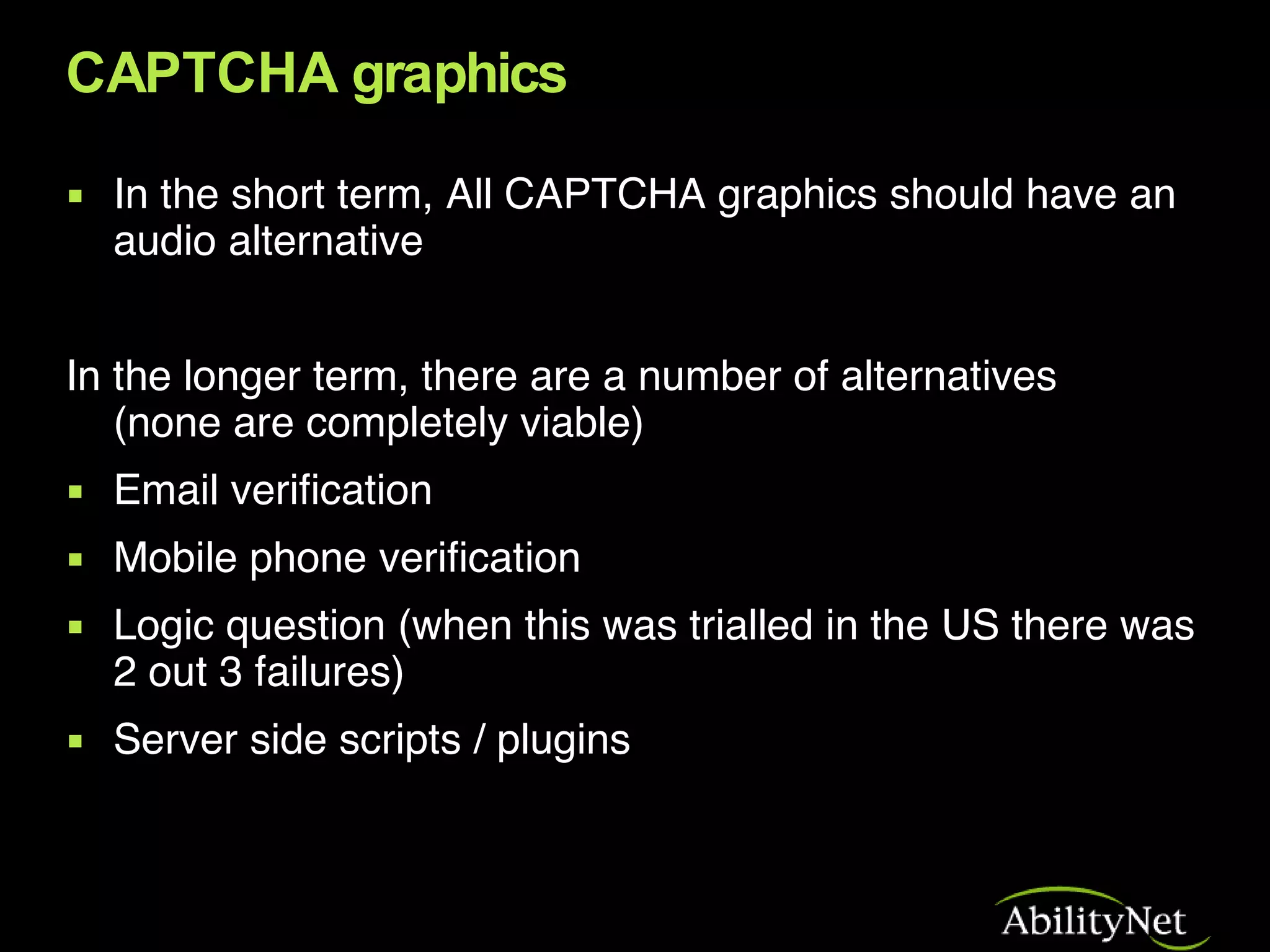
The document discusses the importance of accessibility in web 2.0 applications and social media sites. As users interact with websites in new complex ways, it is important that people with disabilities can also participate and contribute content. However, many current web 2.0 sites have accessibility issues that prevent disabled users from fully interacting with the content. The document provides recommendations to make web 2.0 more inclusive such as providing audio alternatives for images, semantic structure for user-generated content, and accessible authoring tools.




















![Thankyou GeekGirls! [email_address] With thanks: Damon Rose, BBC Ouch Ian Forrester, BBC Backstage Christian Heilmann, Yahoo Our testers: David, Hazel, Chris Lottie Poulton, Camera Di, Julia, Johann, AbilityNet](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geekgirls-1214573144203027-9/75/Girl-Geek-Dinners-with-IT4Communities-AbilityNet-24-2048.jpg)