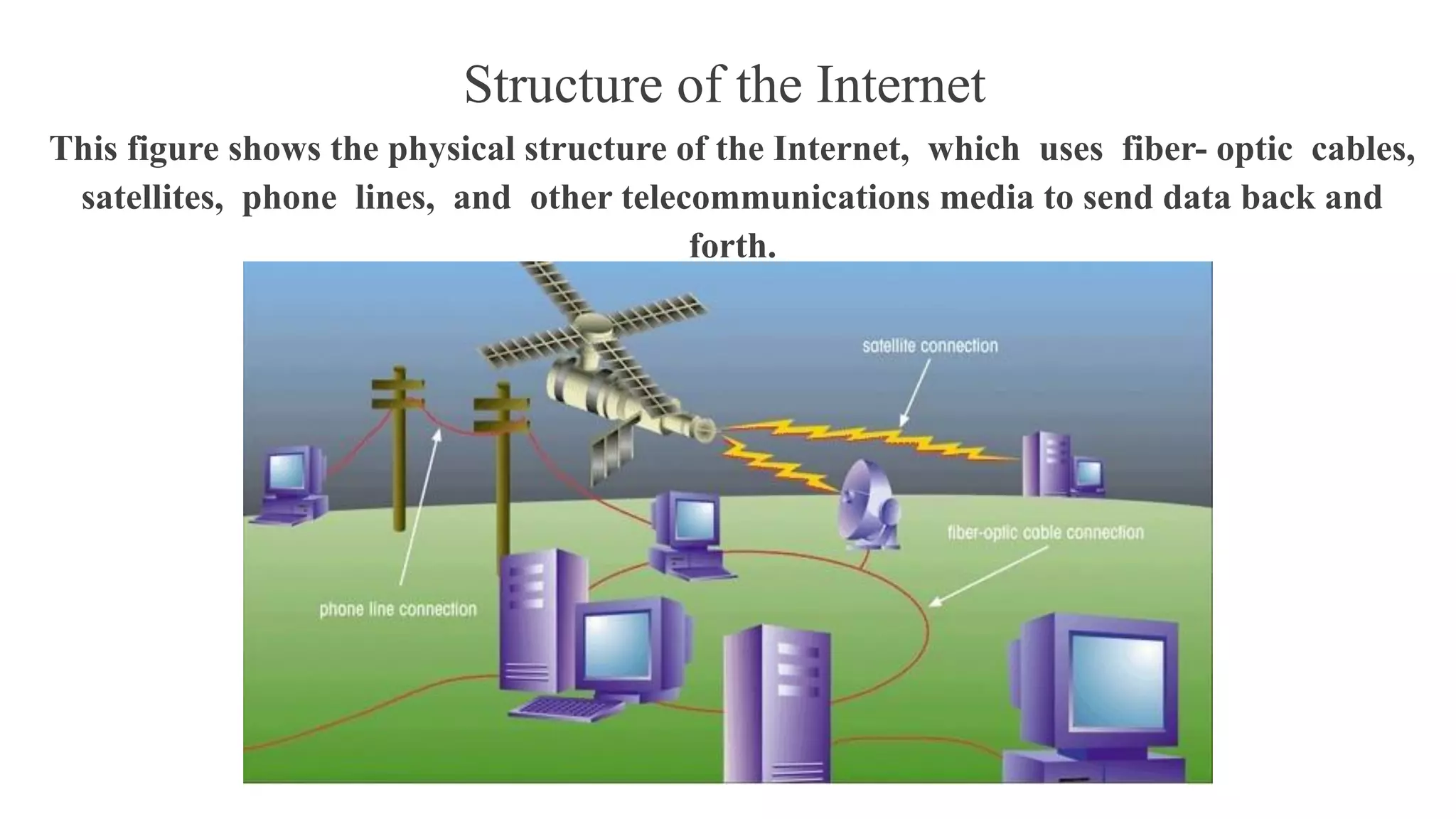
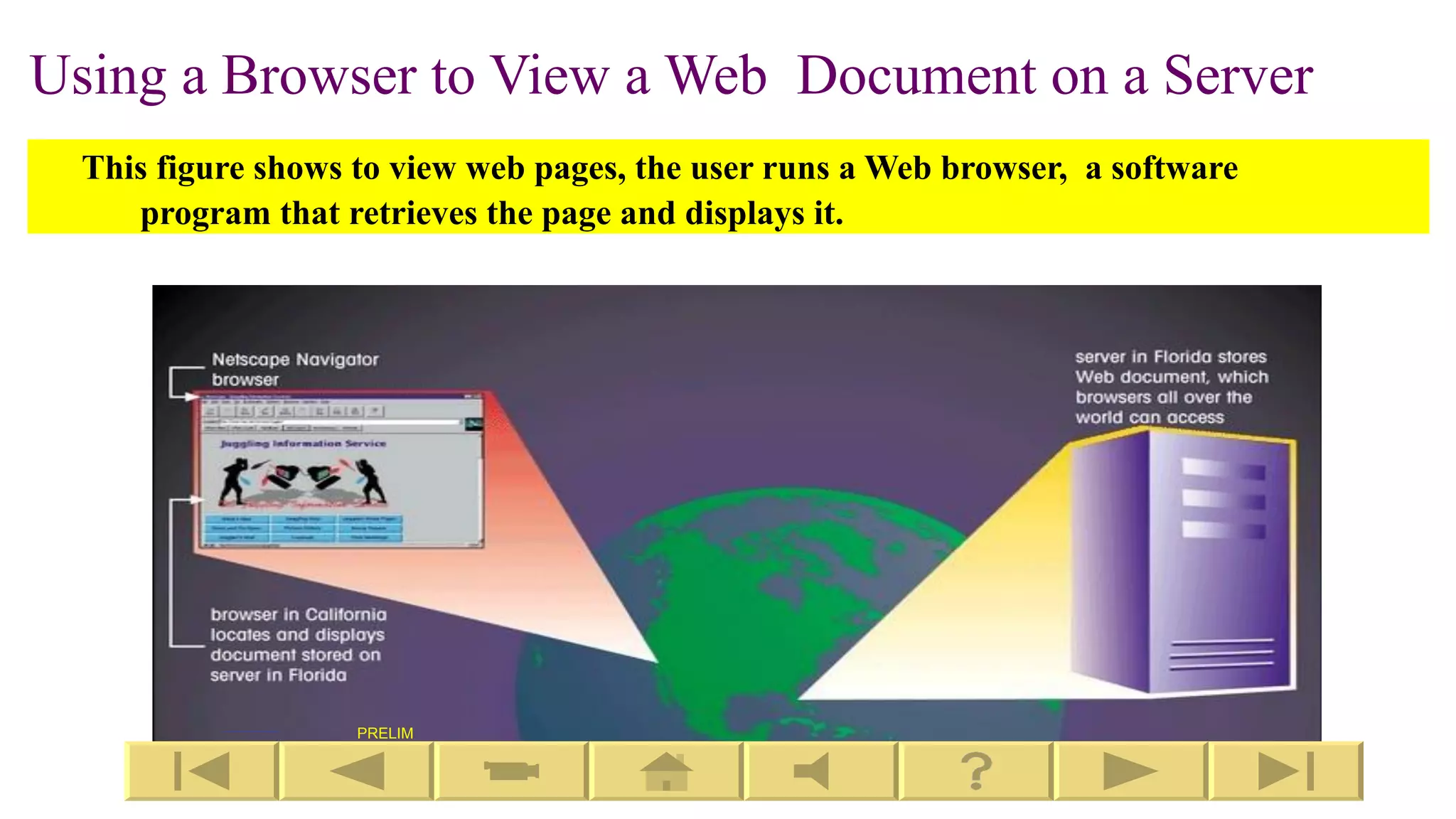
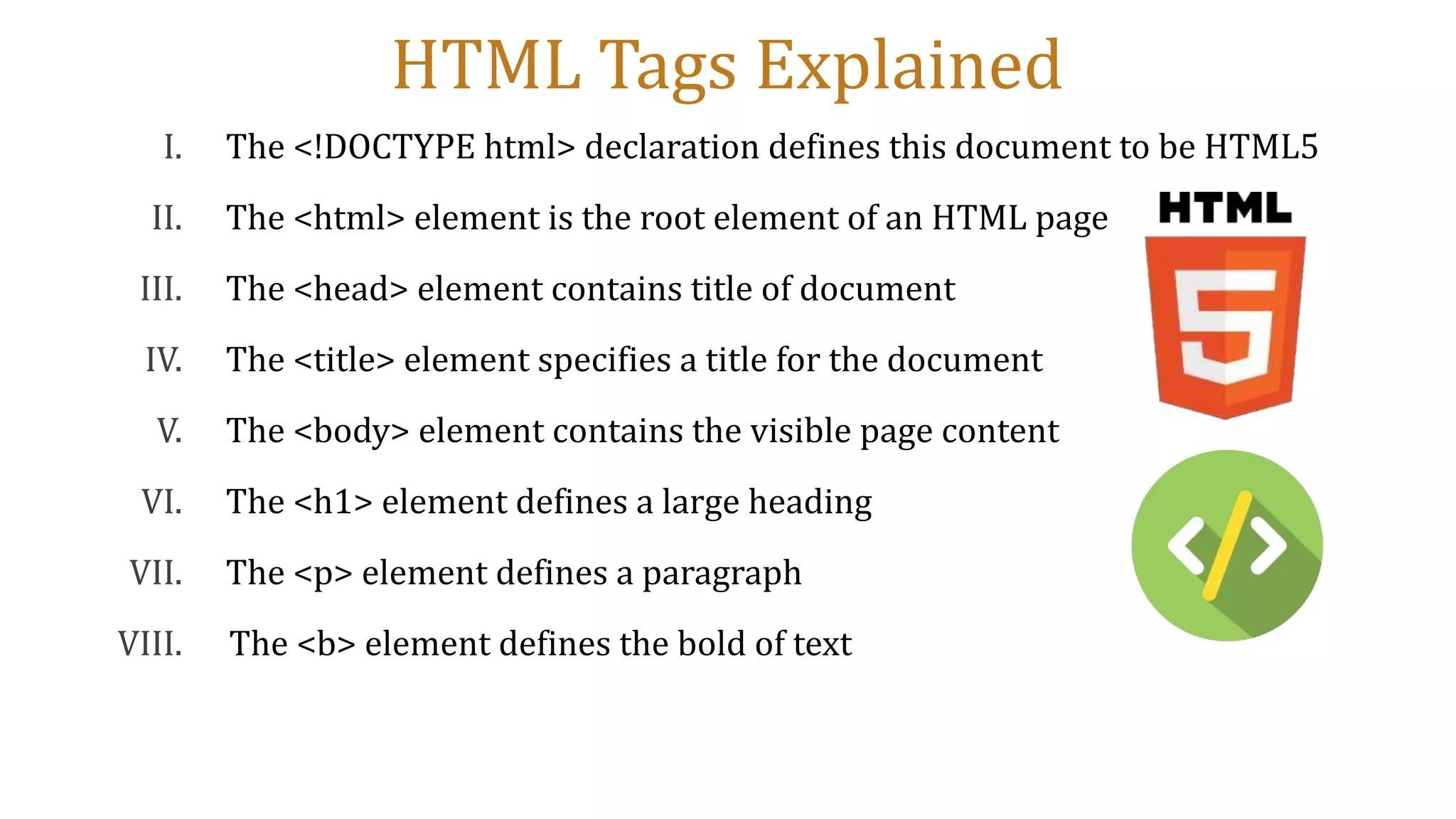
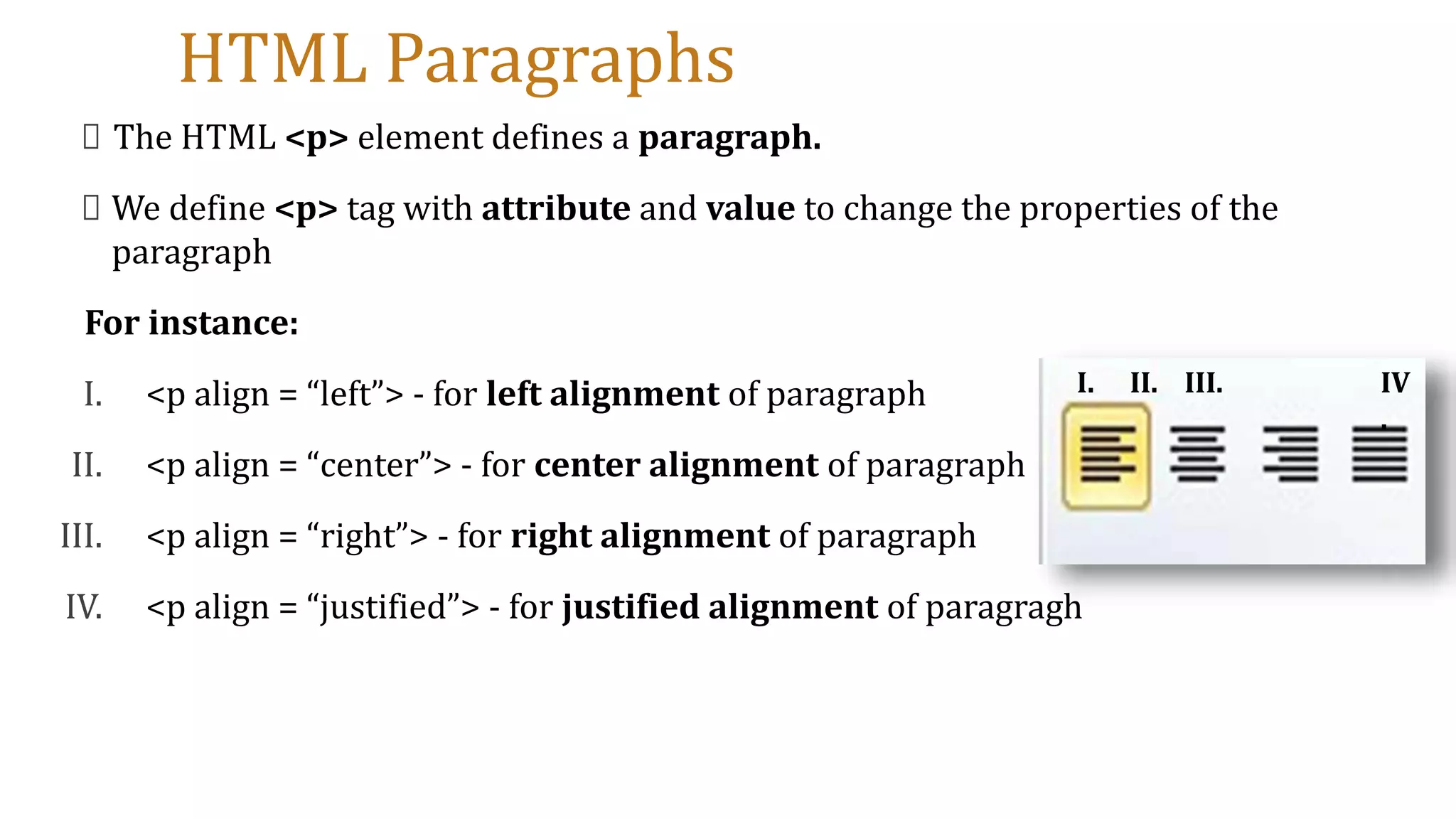
This document provides an introduction to designing web pages using HTML. It explains that a web page is stored on a web server and viewed using a web browser. It then discusses key HTML elements like tags, headings, paragraphs, images and attributes that are used to structure and style the content and appearance of web pages. The document gives examples of common HTML tags and how they are used to define the structure of a web page, add headings, format text, and insert images.