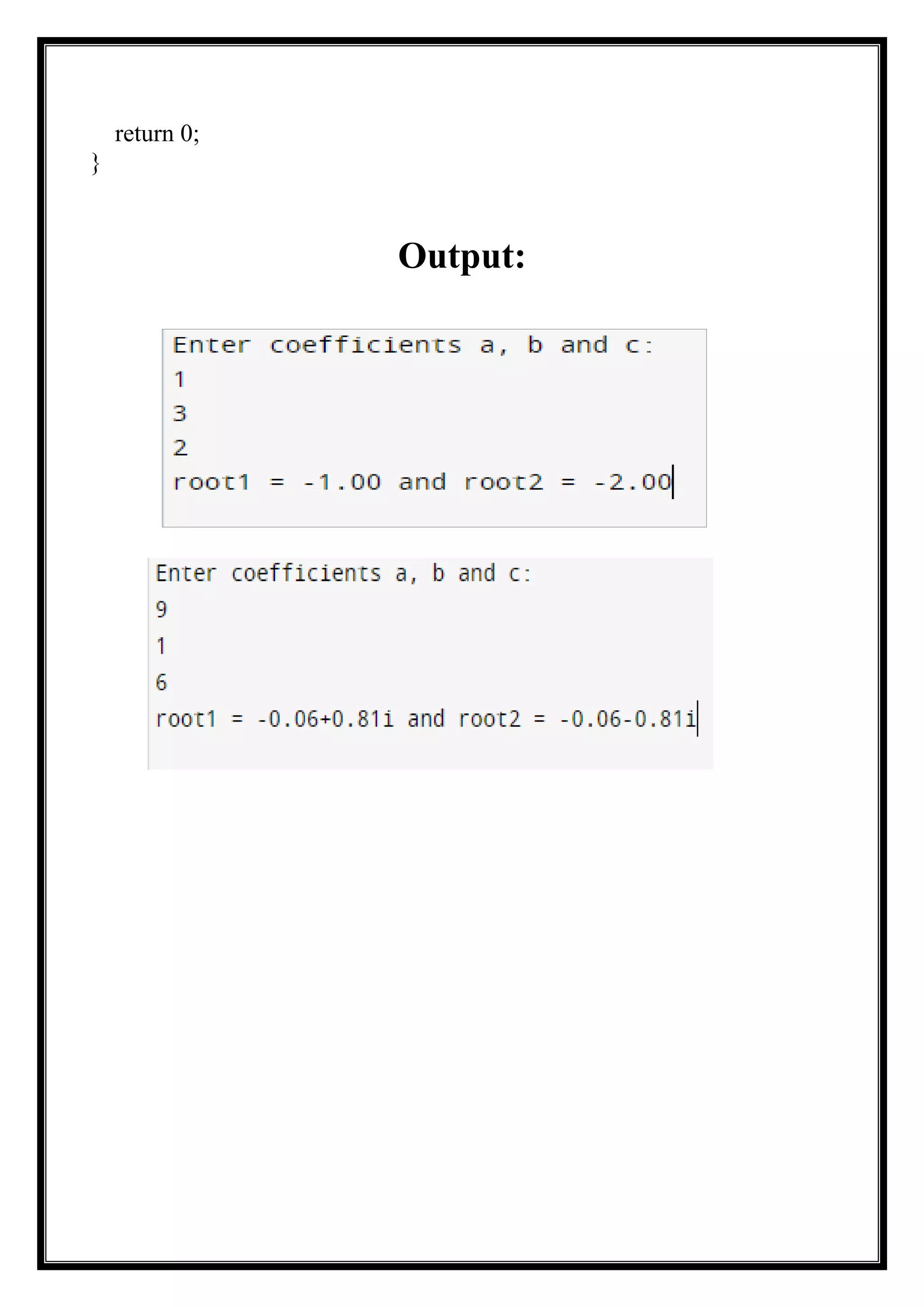
This document contains a lab report submitted by Syed Fuzail (Adm. No. 22SCSE1011555) to Dr. Monika Jain. The report details 6 lab sheets completed as part of an Exploration with CAS-I course. Each lab sheet contains multiple programming questions/problems where the student is asked to write C code to perform tasks like printing text, performing mathematical operations, taking user input, conditional checking, etc. For each question, the student provides the C code program followed by the output. The programs demonstrate the student's proficiency with basic C programming concepts.