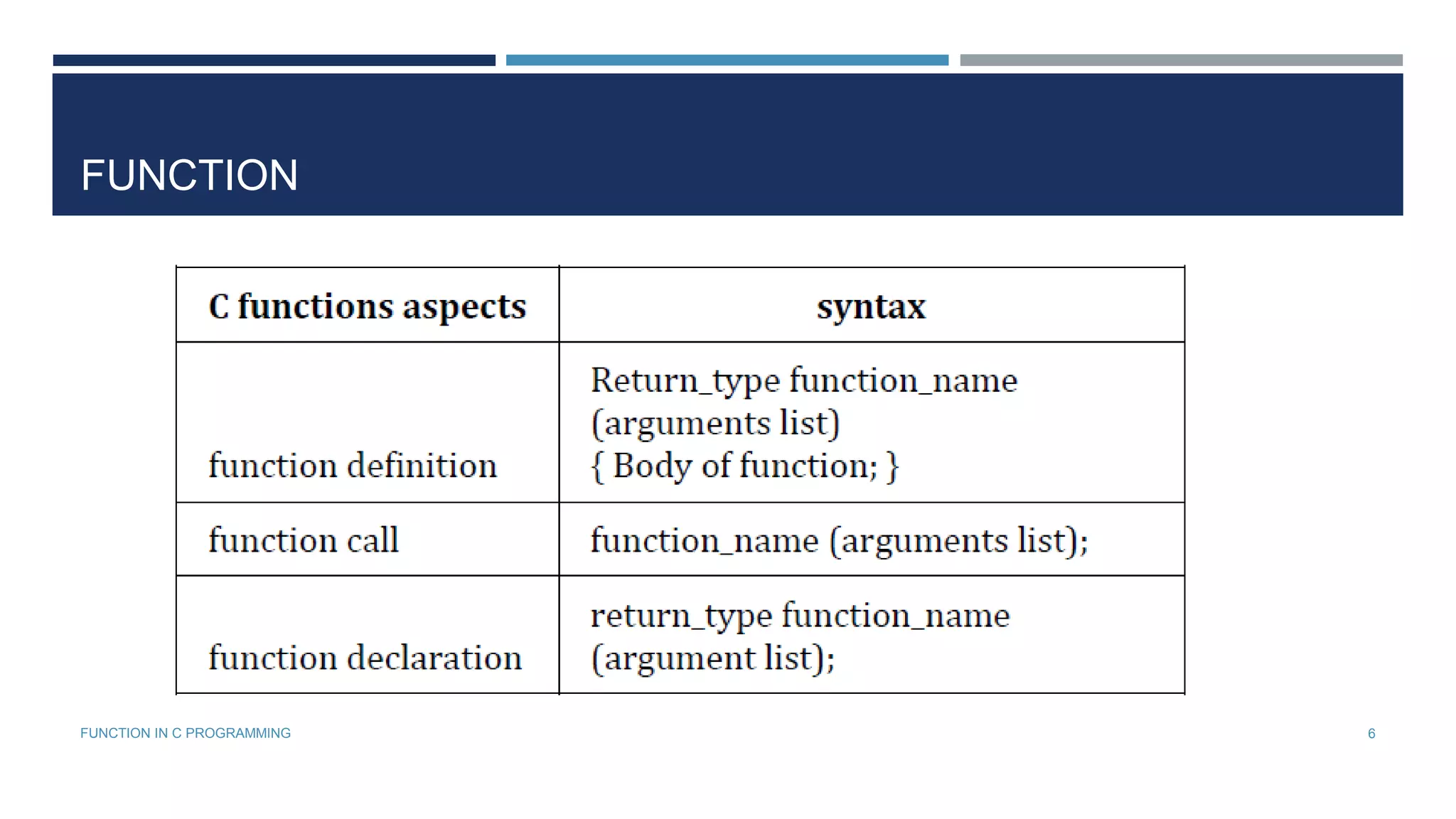
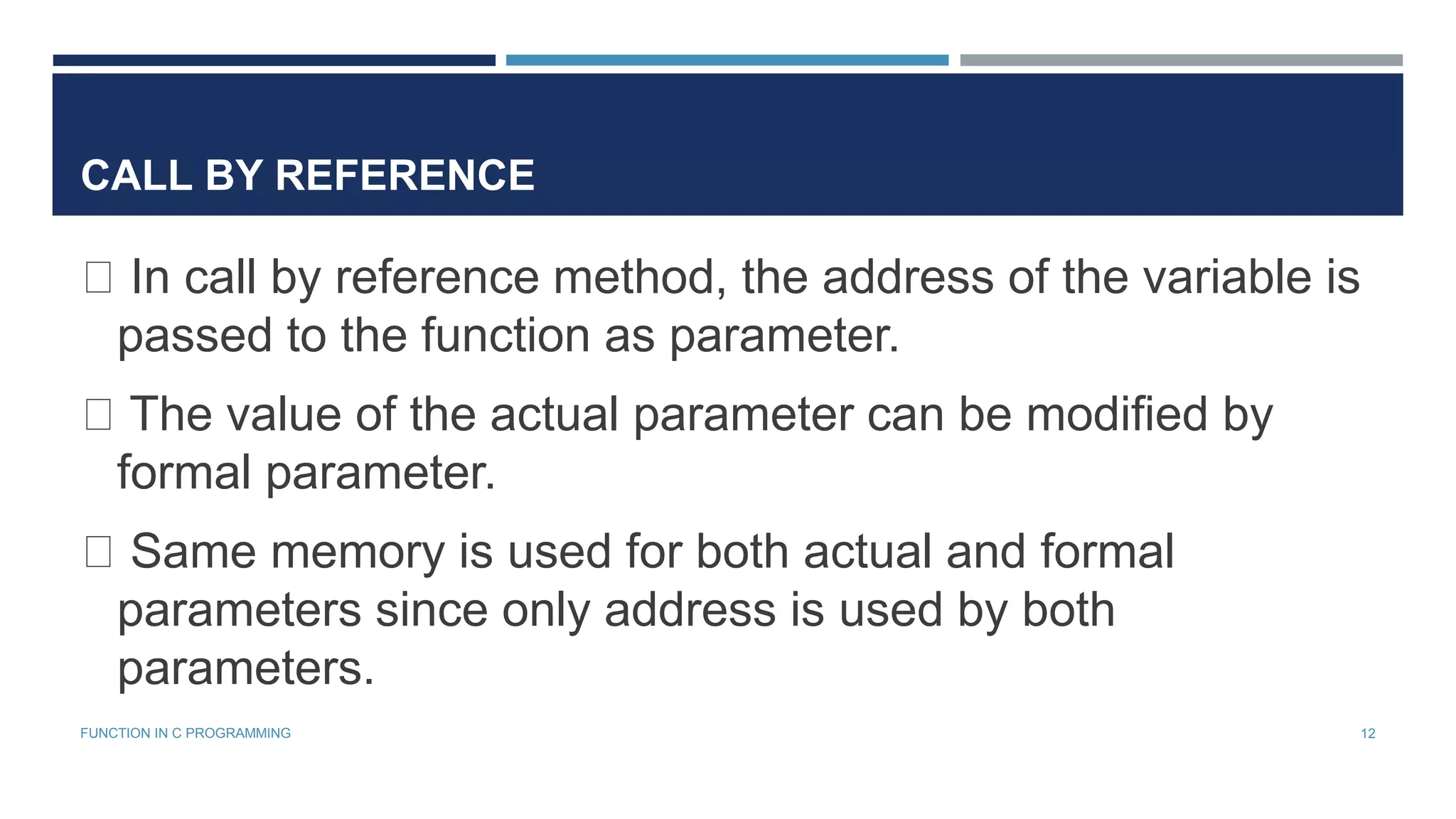
The document provides an overview of C functions, covering their definition, types, and utility in programming. It details the concepts of call by value and call by reference, along with examples demonstrating their usage. Additionally, the document discusses recursion in C programming, illustrating its principles and applications.