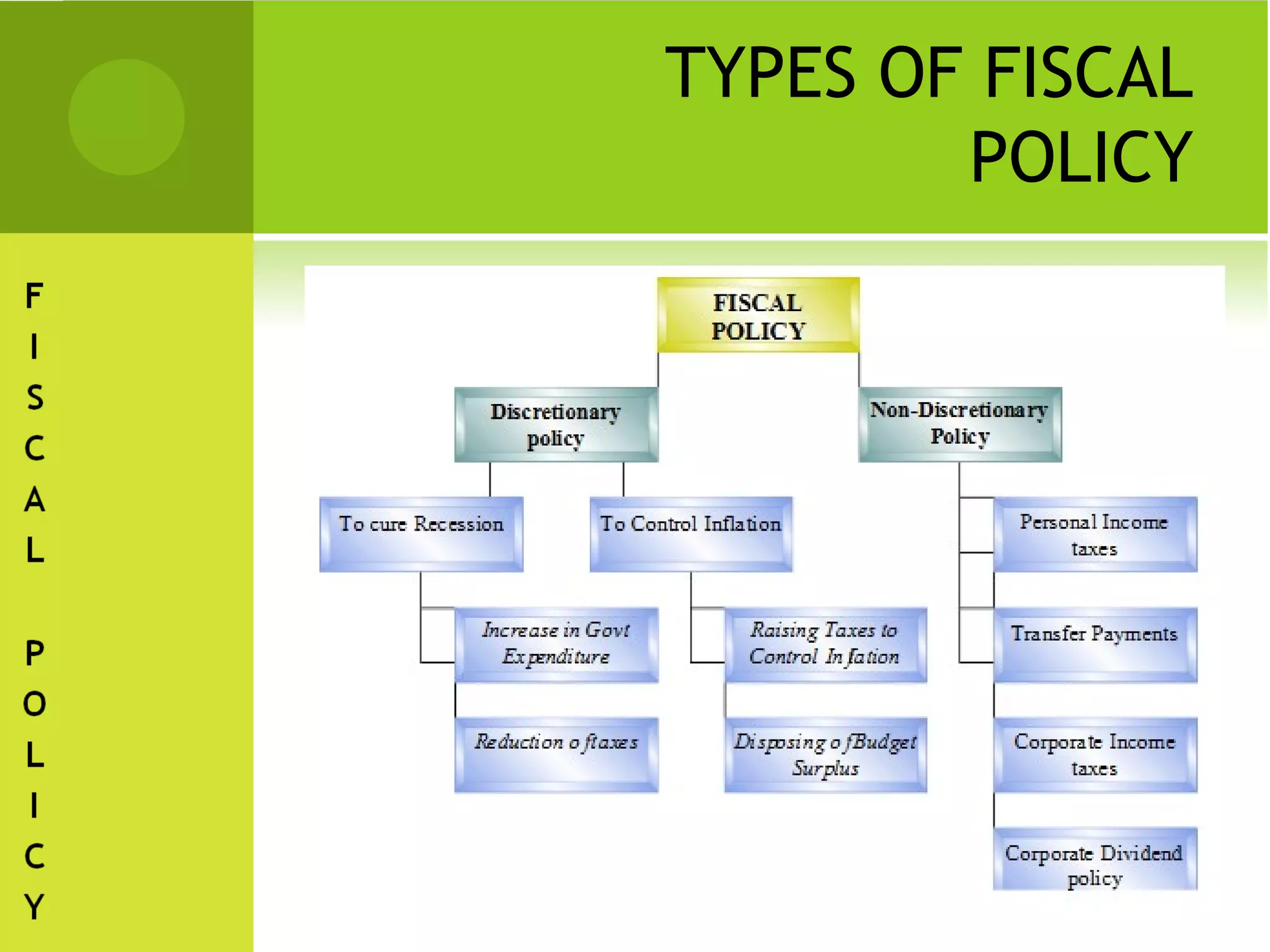
The document discusses fiscal policy as the government's tool for managing budget, revenue, and expenditure to foster economic growth and stability. It highlights Malaysia's approach to fiscal policy, emphasizing the balance between public and private sector roles, implementation adjustments for efficiency, and the importance of monitoring development projects. The conclusion asserts that a more expansive fiscal policy is expected to maintain a surplus without causing budget deficits, suggesting a strong government sector support for public goods and services.