Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

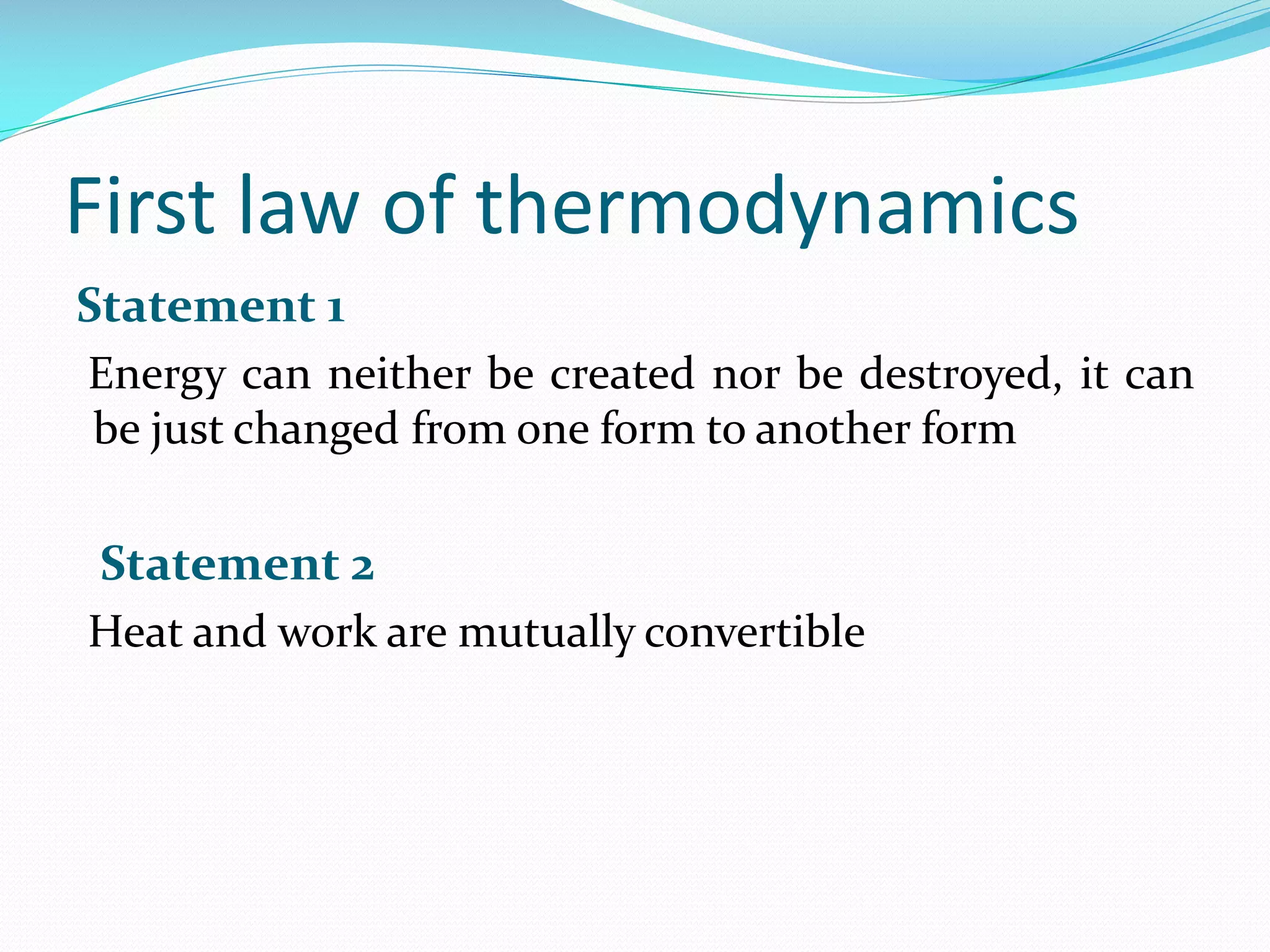
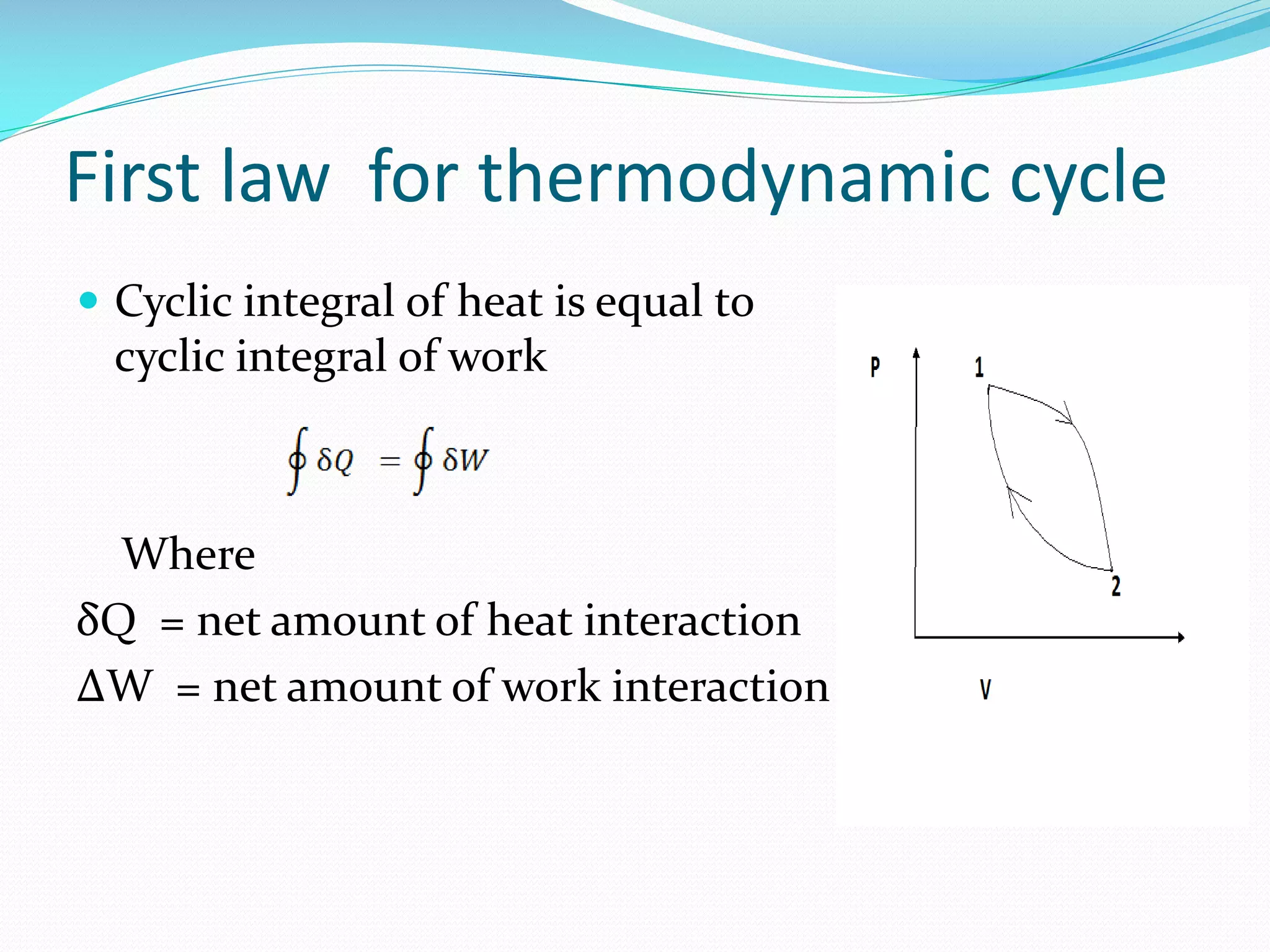
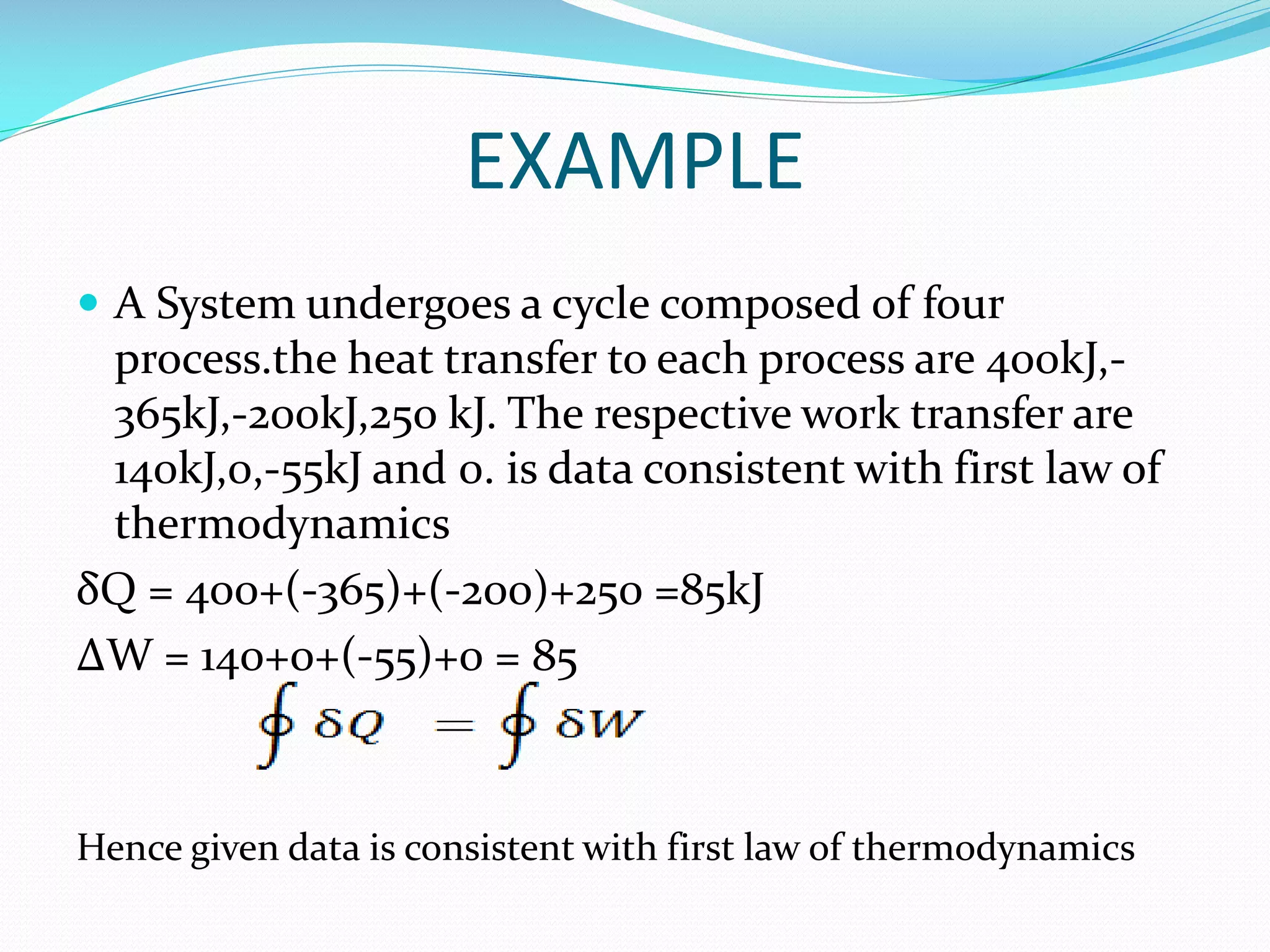
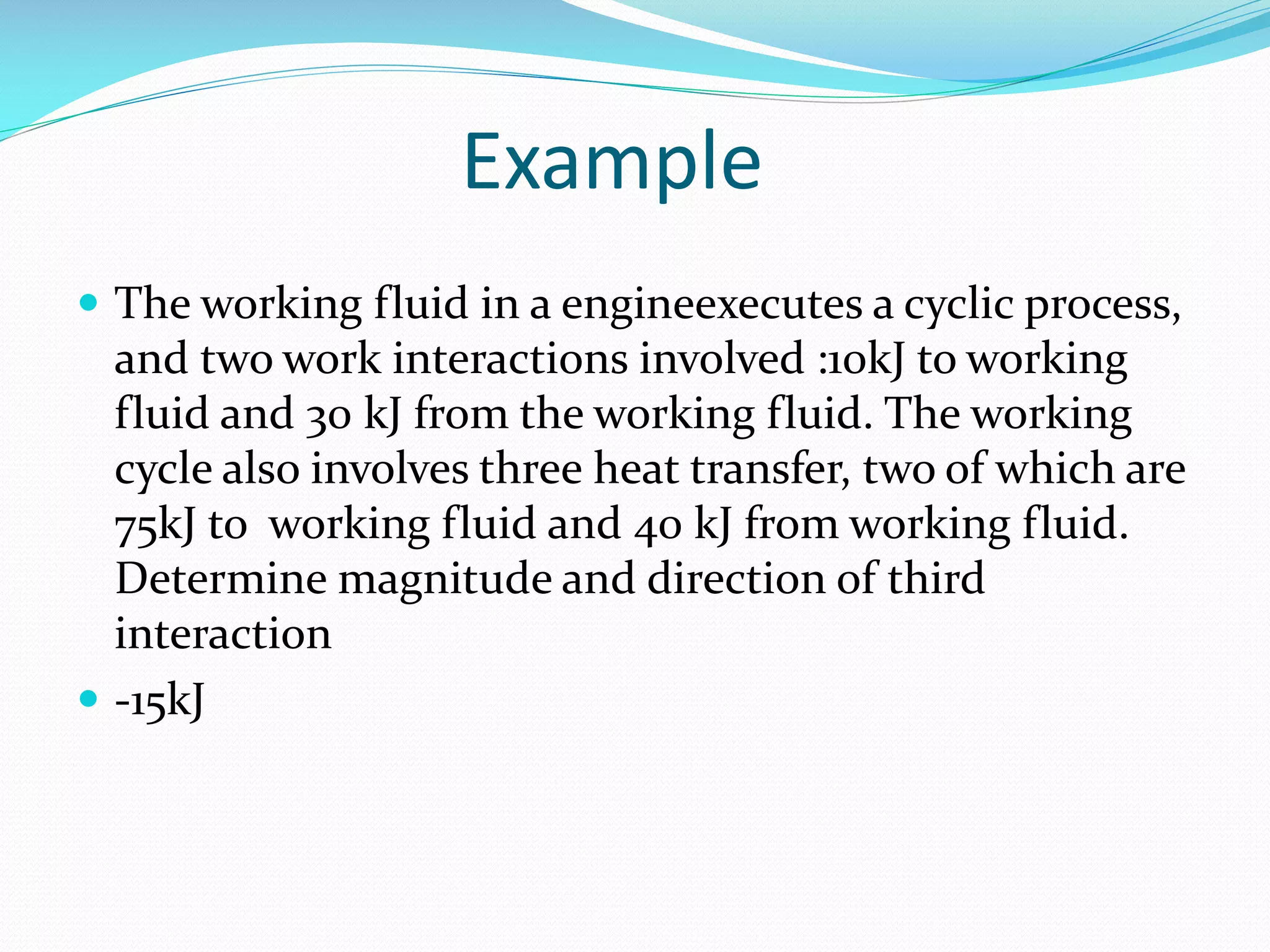


1. The first law of thermodynamics states that energy can be changed from one form to another, but cannot be created or destroyed. Heat and work are mutually convertible. 2. For a cyclic thermodynamic process, the net heat transfer equals the net work transfer. The first law must be satisfied at each step of the cycle. 3. Examples demonstrate using the first law to determine consistency of heat and work transfers for cyclic processes, and to calculate the magnitude and direction of heat transfer needed to satisfy the first law for a given work interaction and change in internal energy.
Introduction to the first law of thermodynamics presented by Er. R.P. Ojha.
The first law states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed, and highlights heat and work conversion.
Describes the cyclic nature of thermodynamic processes where the net heat equals the net work done.
A cycle example shows heat and work transfers totaling 85 kJ, demonstrating consistency with the first law.
An engine example calculates the third interaction from given work and heat exchanges, resulting in -15 kJ.
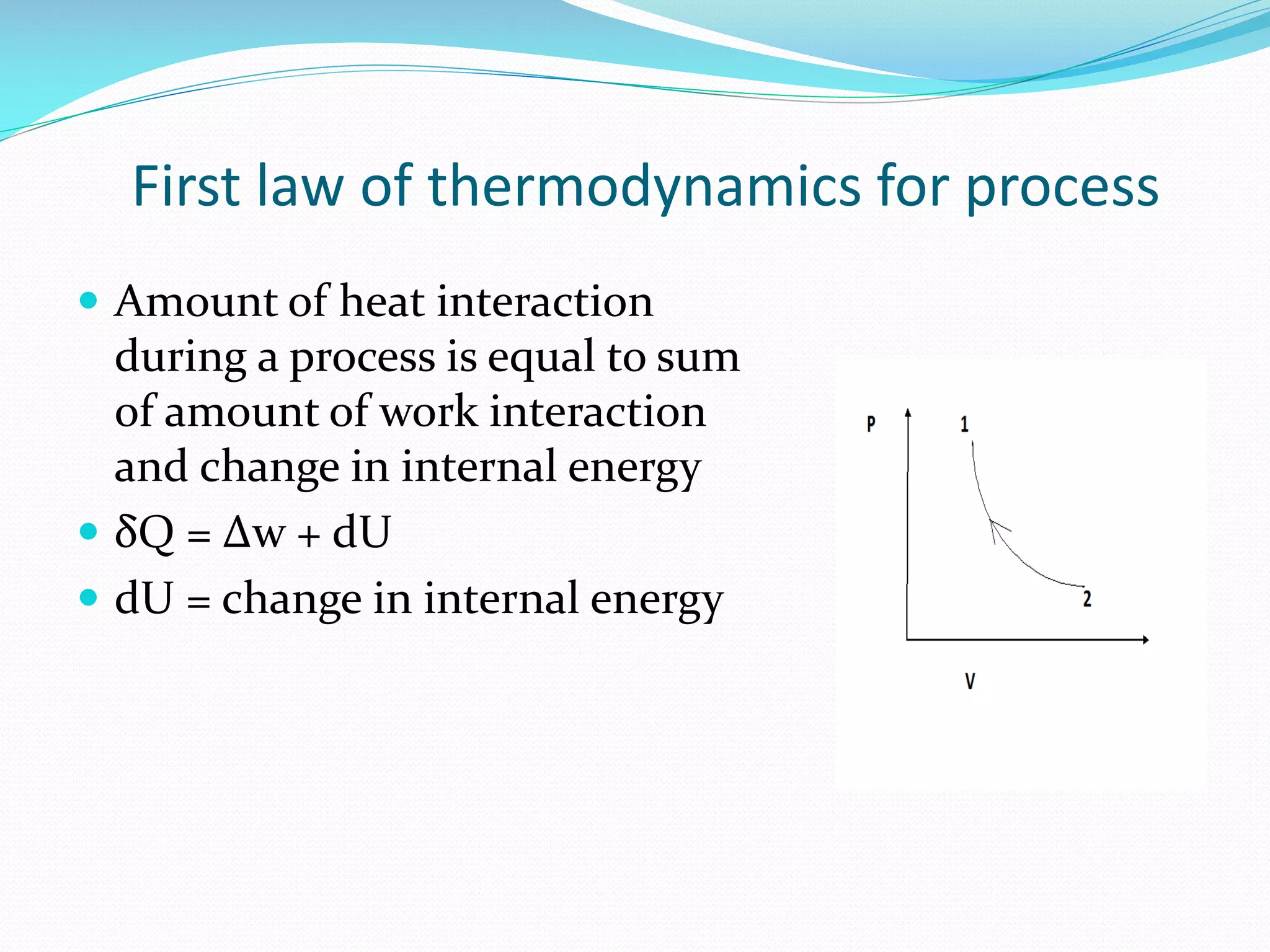
States that heat interaction in a process equals work done plus change in internal energy, represented by a specific equation.
Calculates change in specific internal energy during a compression process, with values leading to 240 J/kg.






