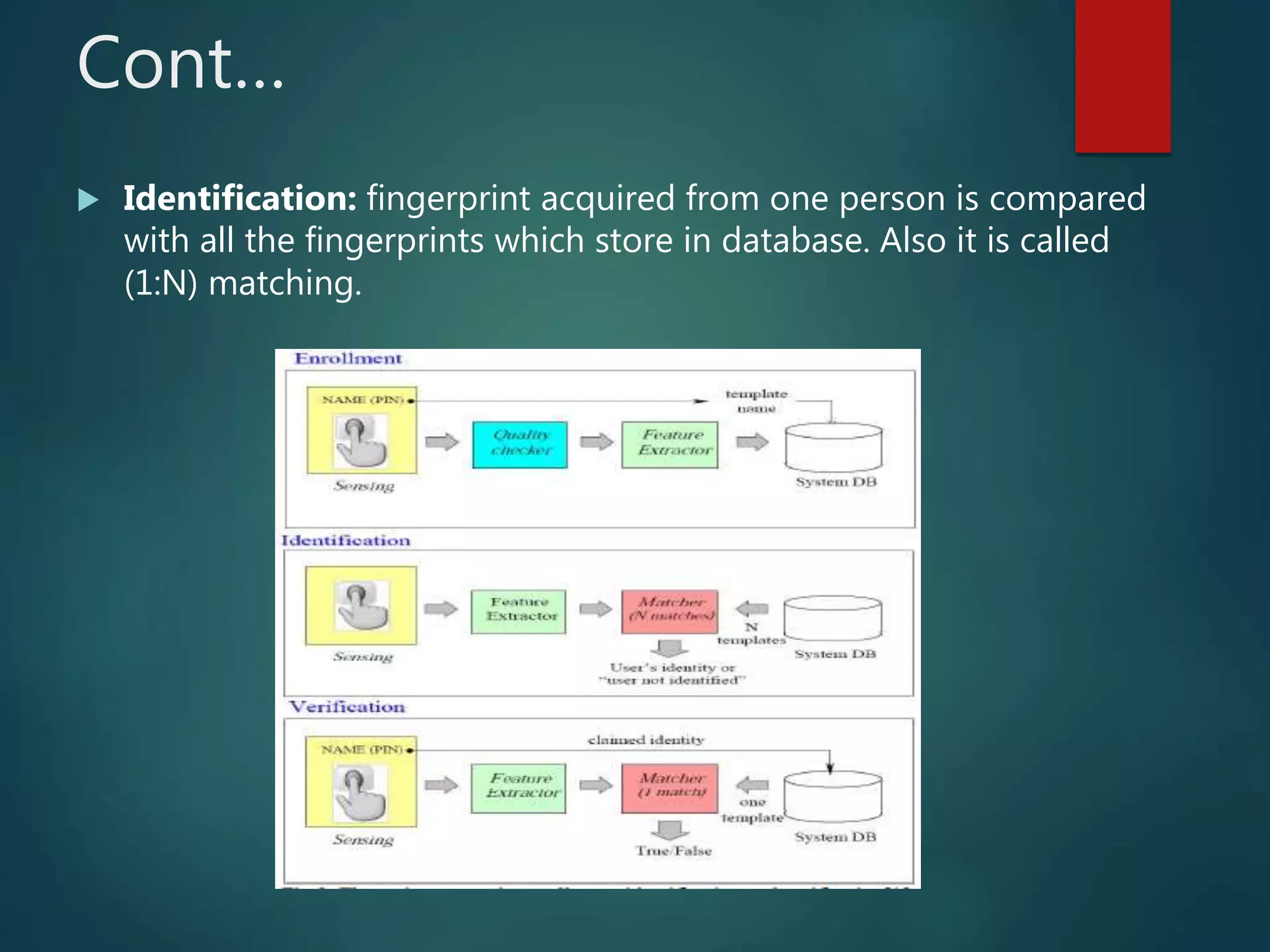
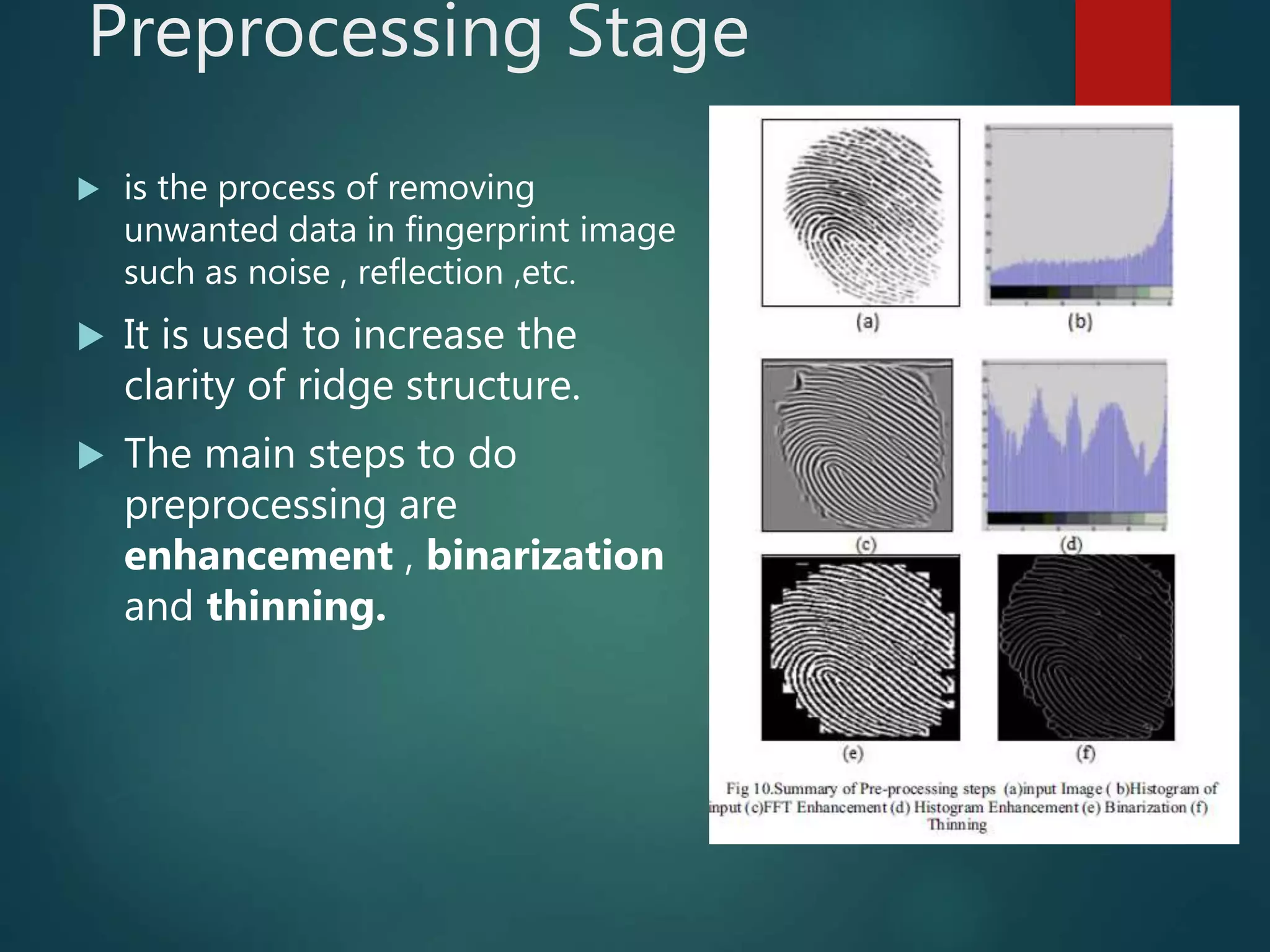
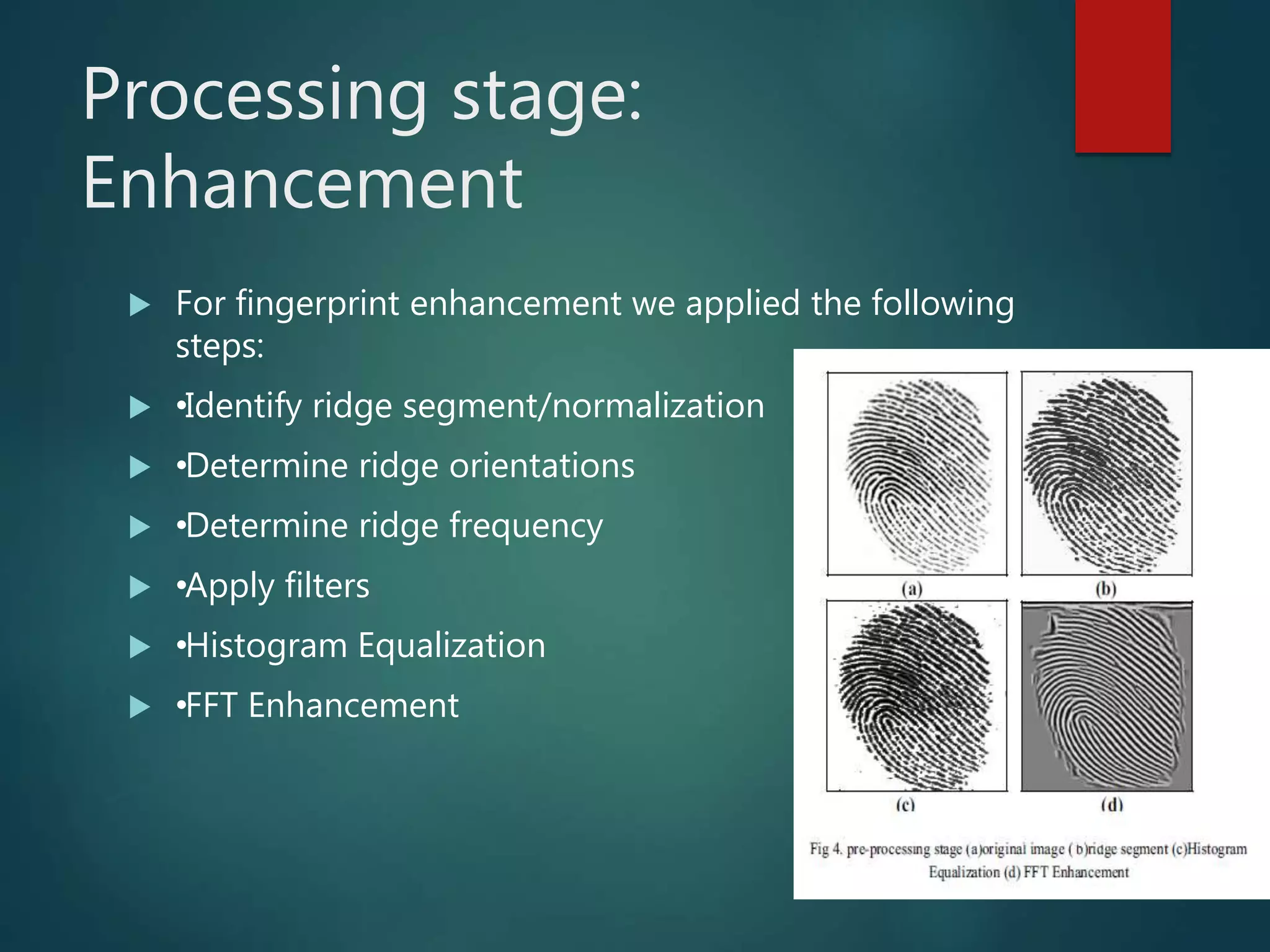
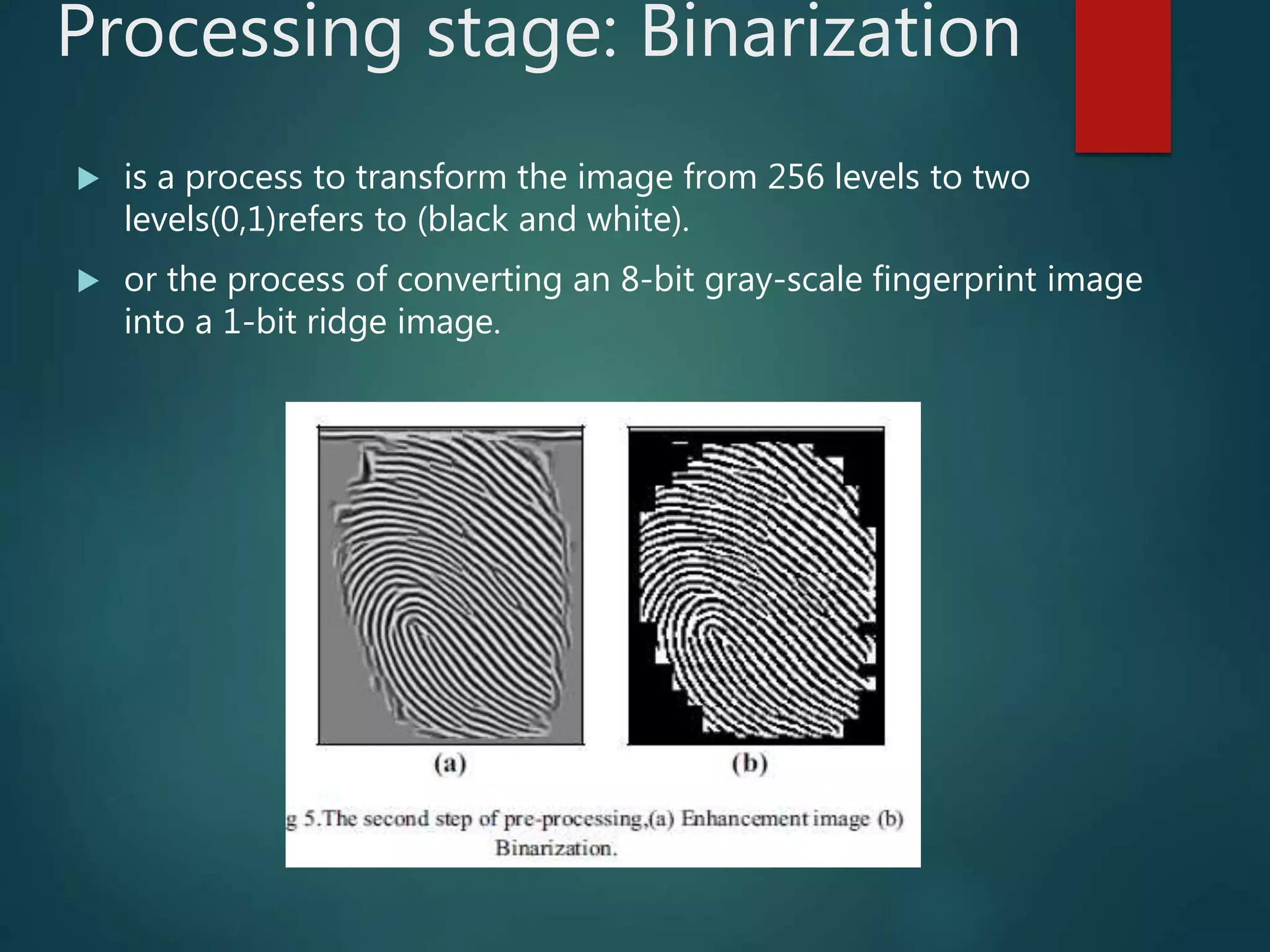
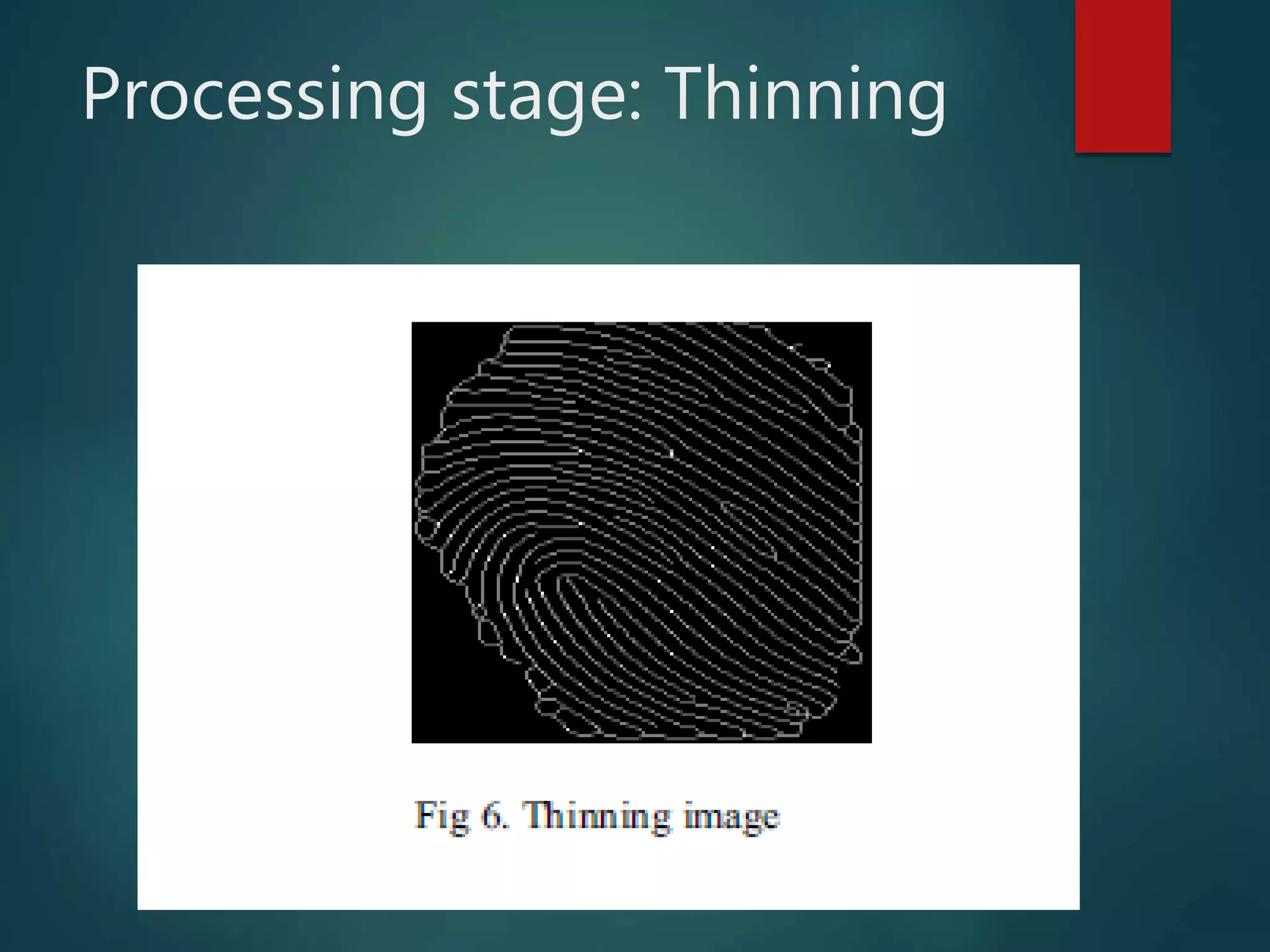
This document provides an overview of fingerprint recognition. It discusses key terms like minutiae points and fingerprint features. It describes the four main stages of fingerprint recognition: acquisition, preprocessing, feature extraction, and matching. The preprocessing stage enhances images through techniques like binarization and thinning. Feature extraction locates ridges, valleys and minutiae. The matching stage compares input fingerprints to templates to verify or identify individuals. The document provides details on minutiae, fingerprint patterns, and the verification and identification processes used in fingerprint recognition systems.