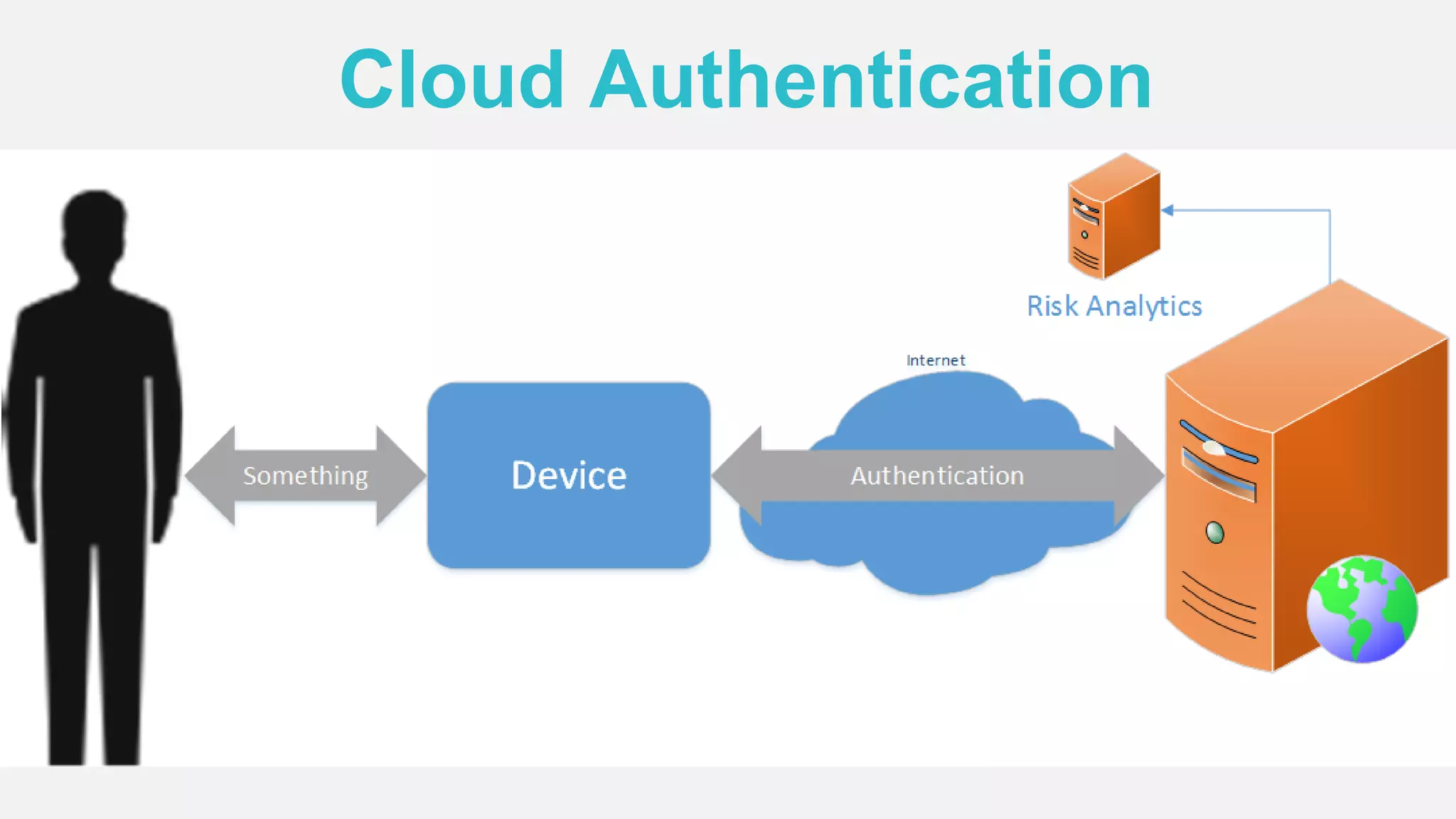
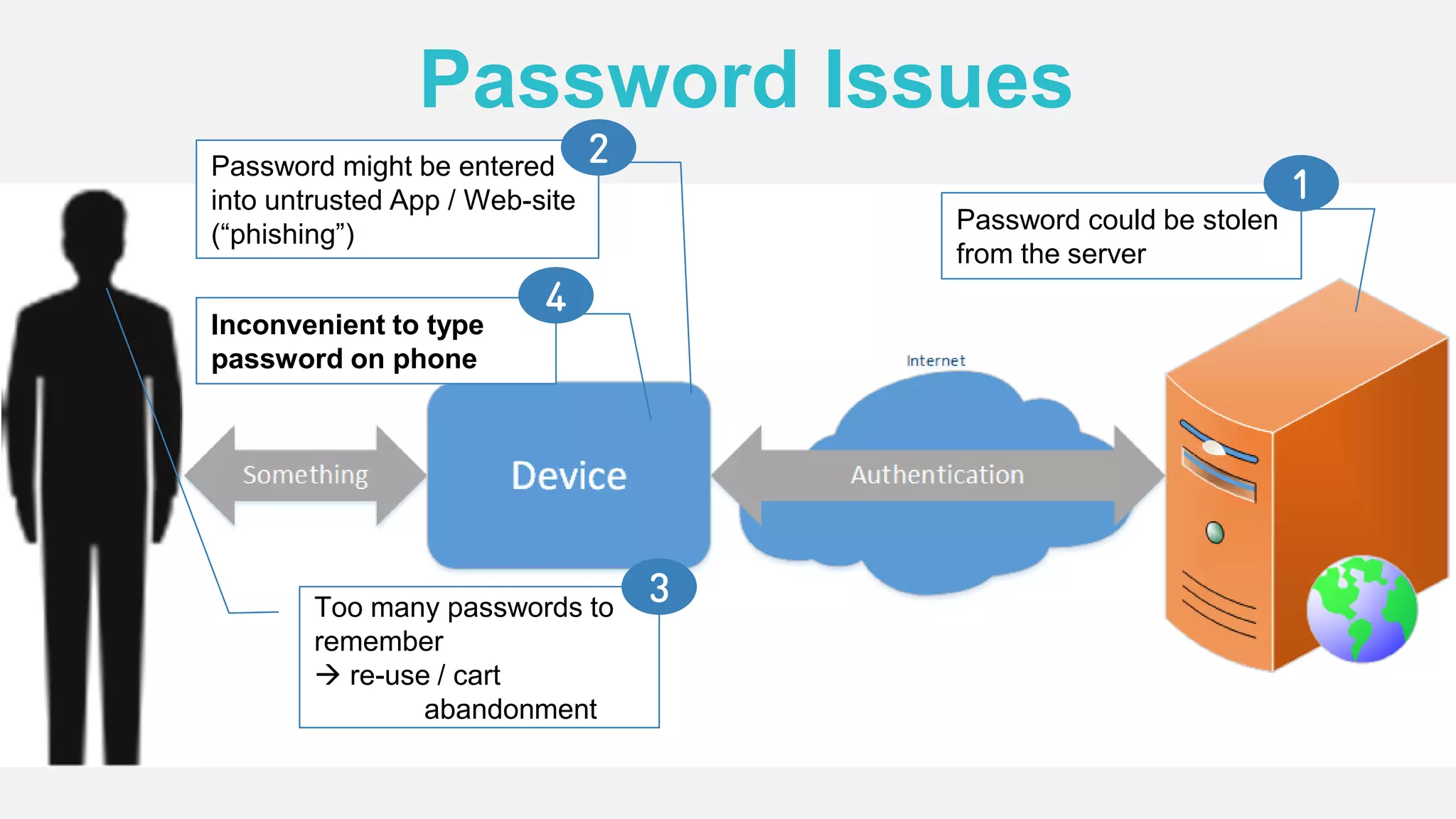
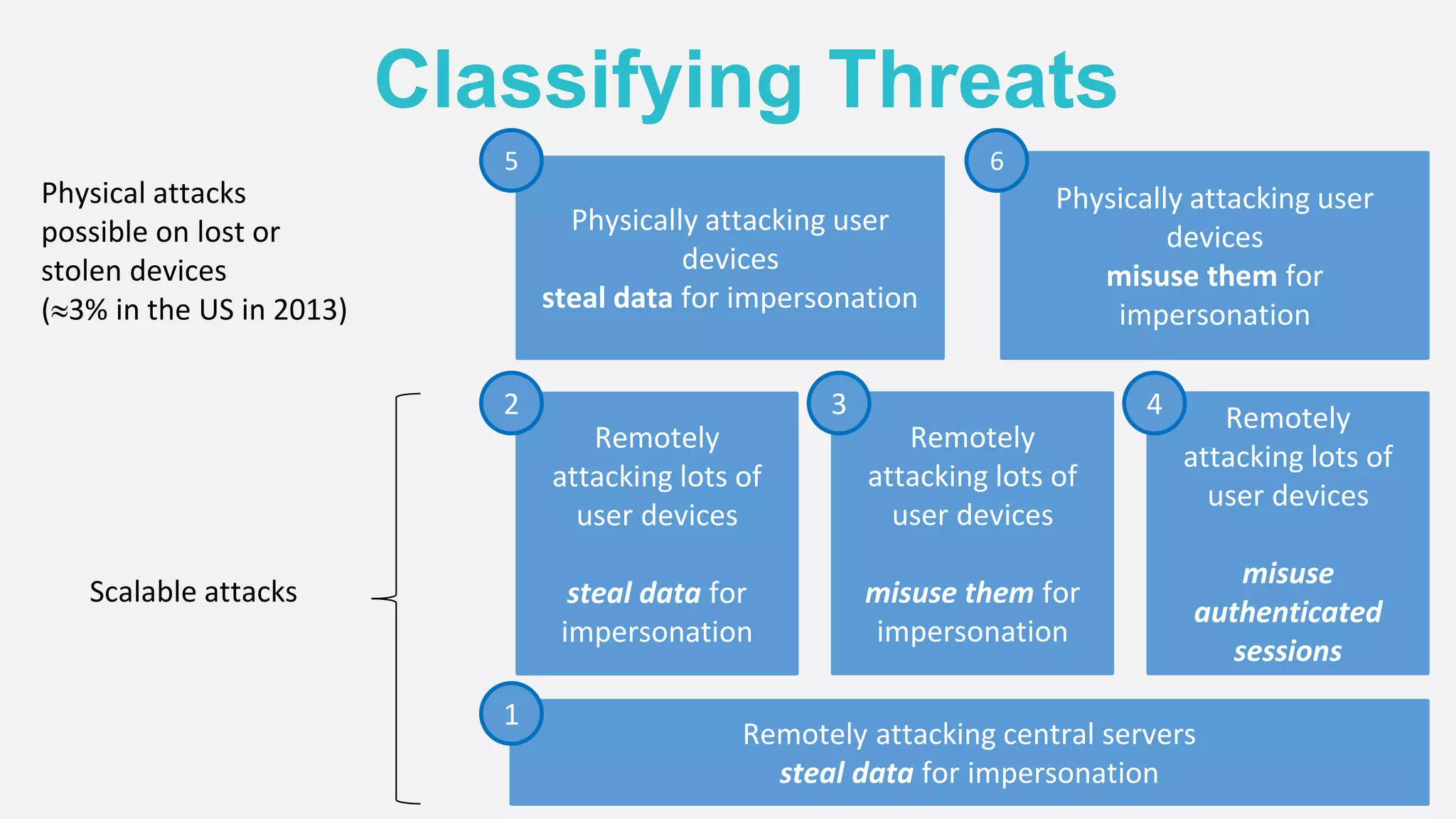
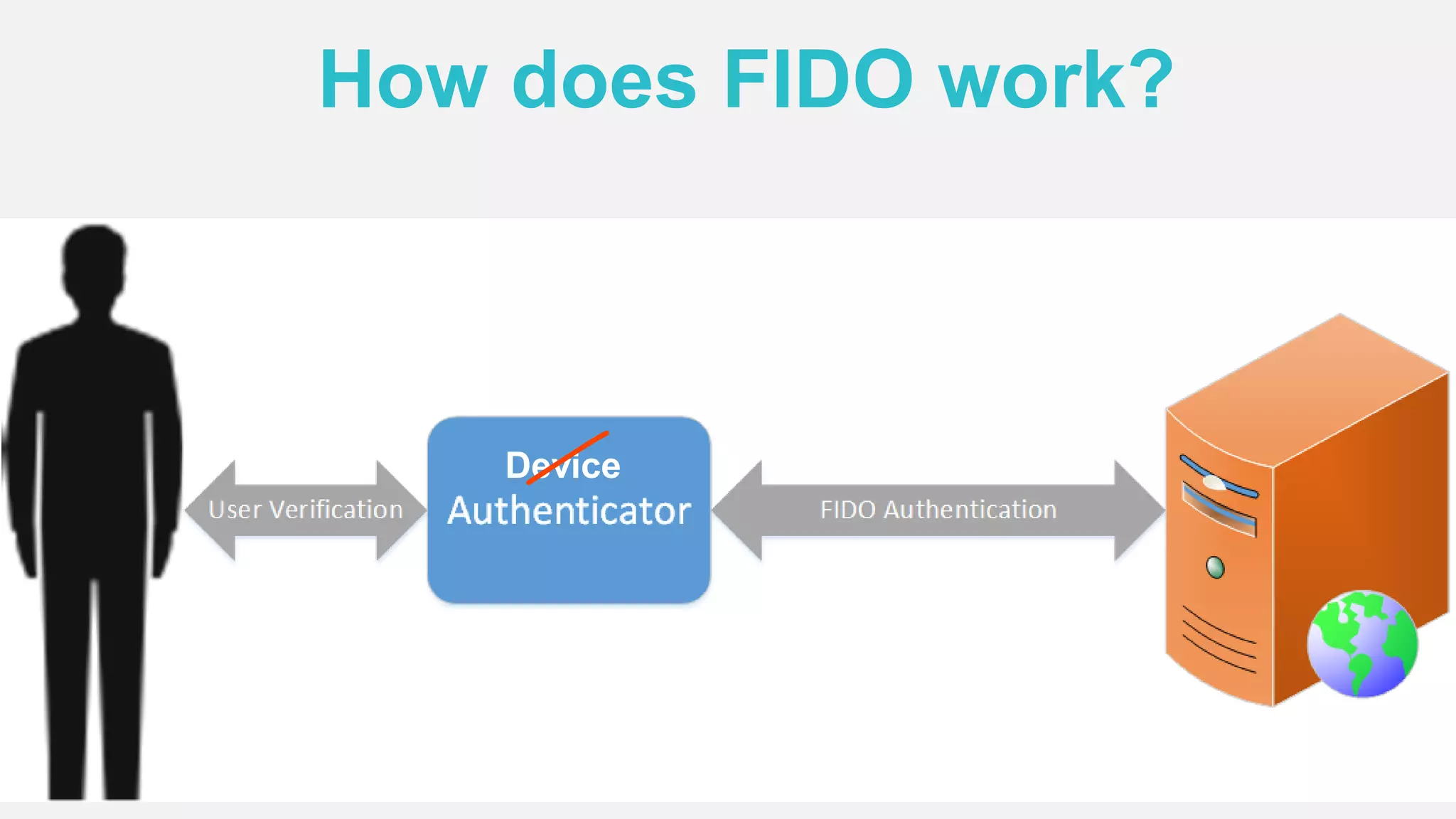
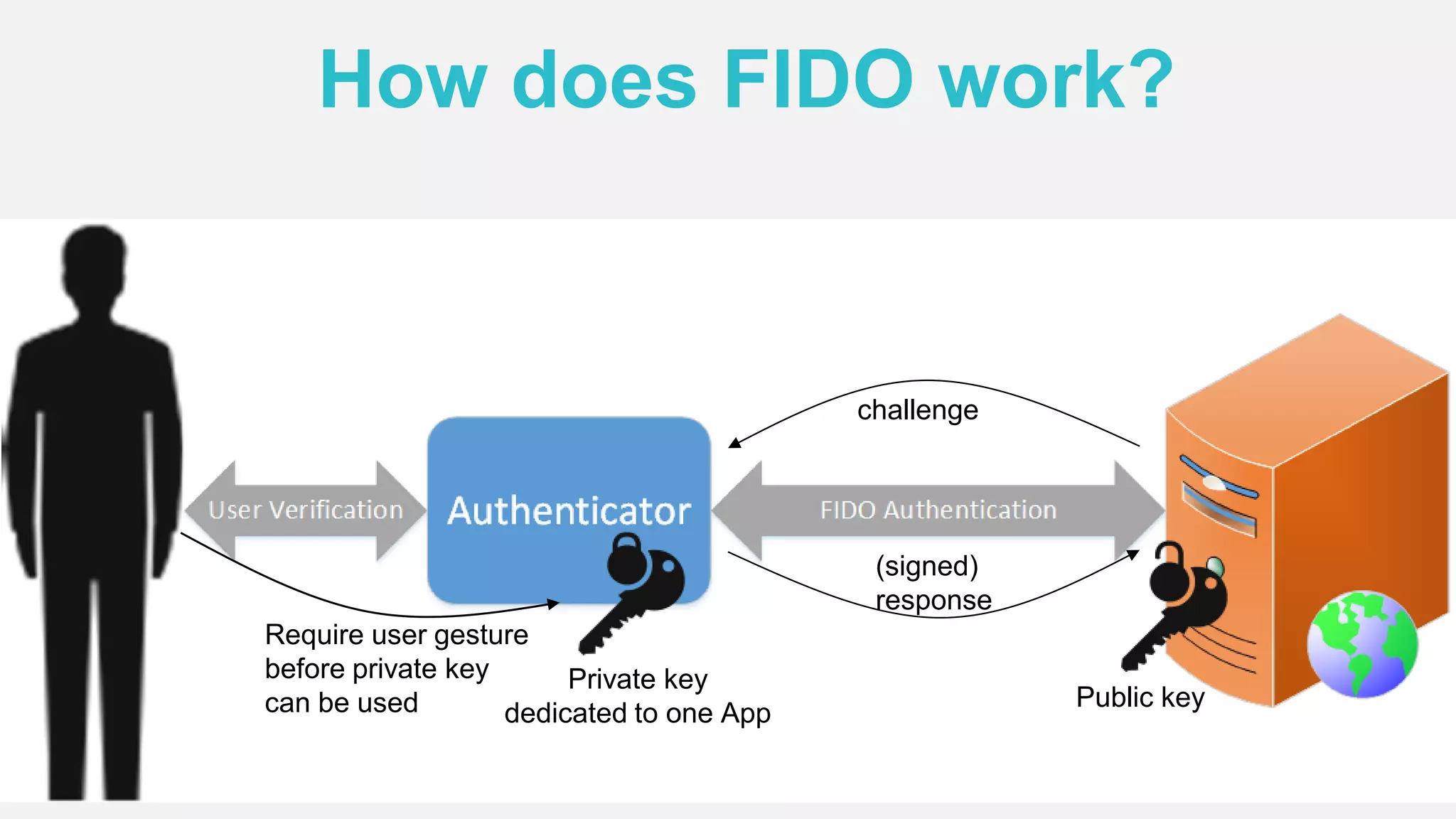
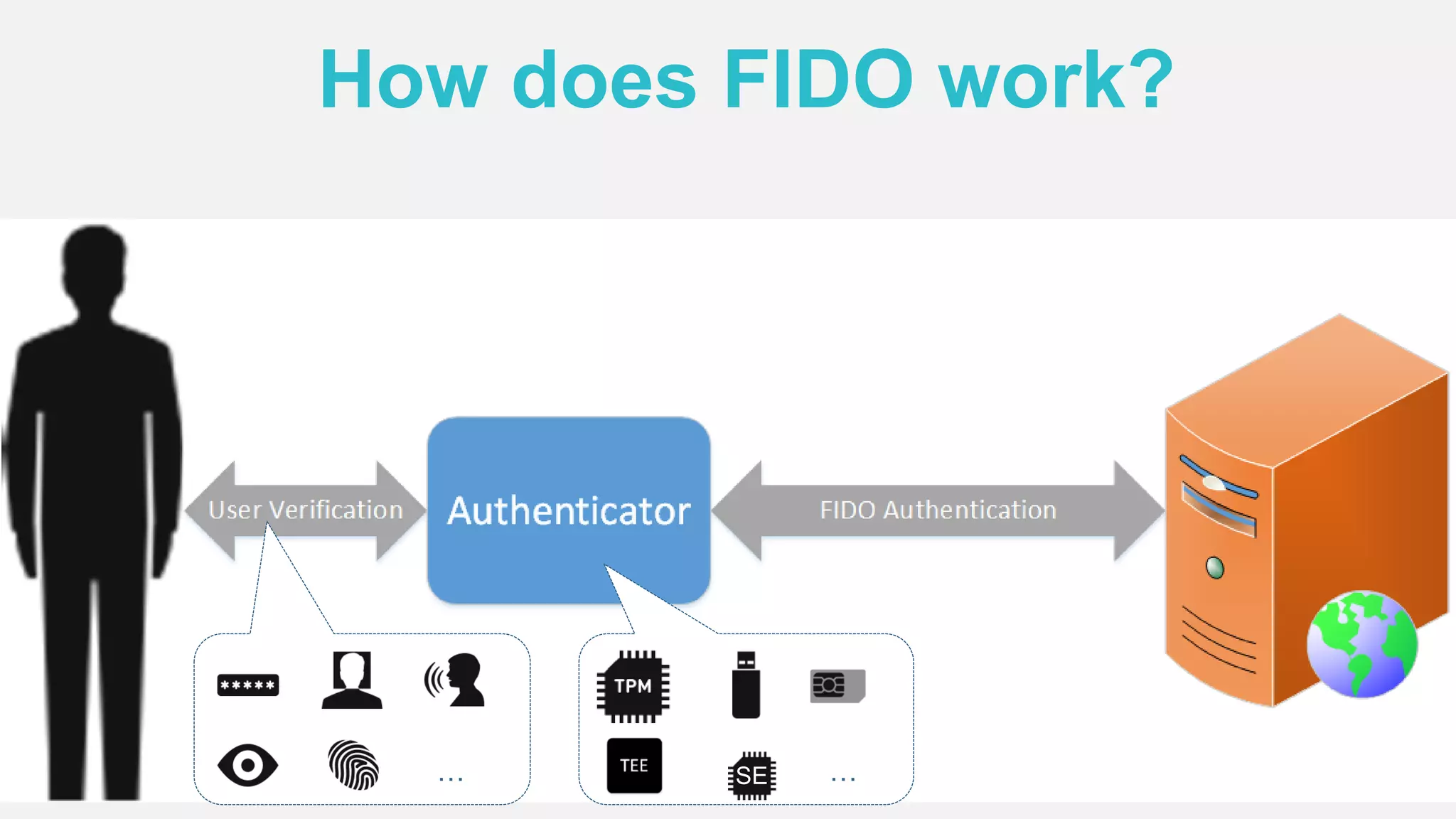
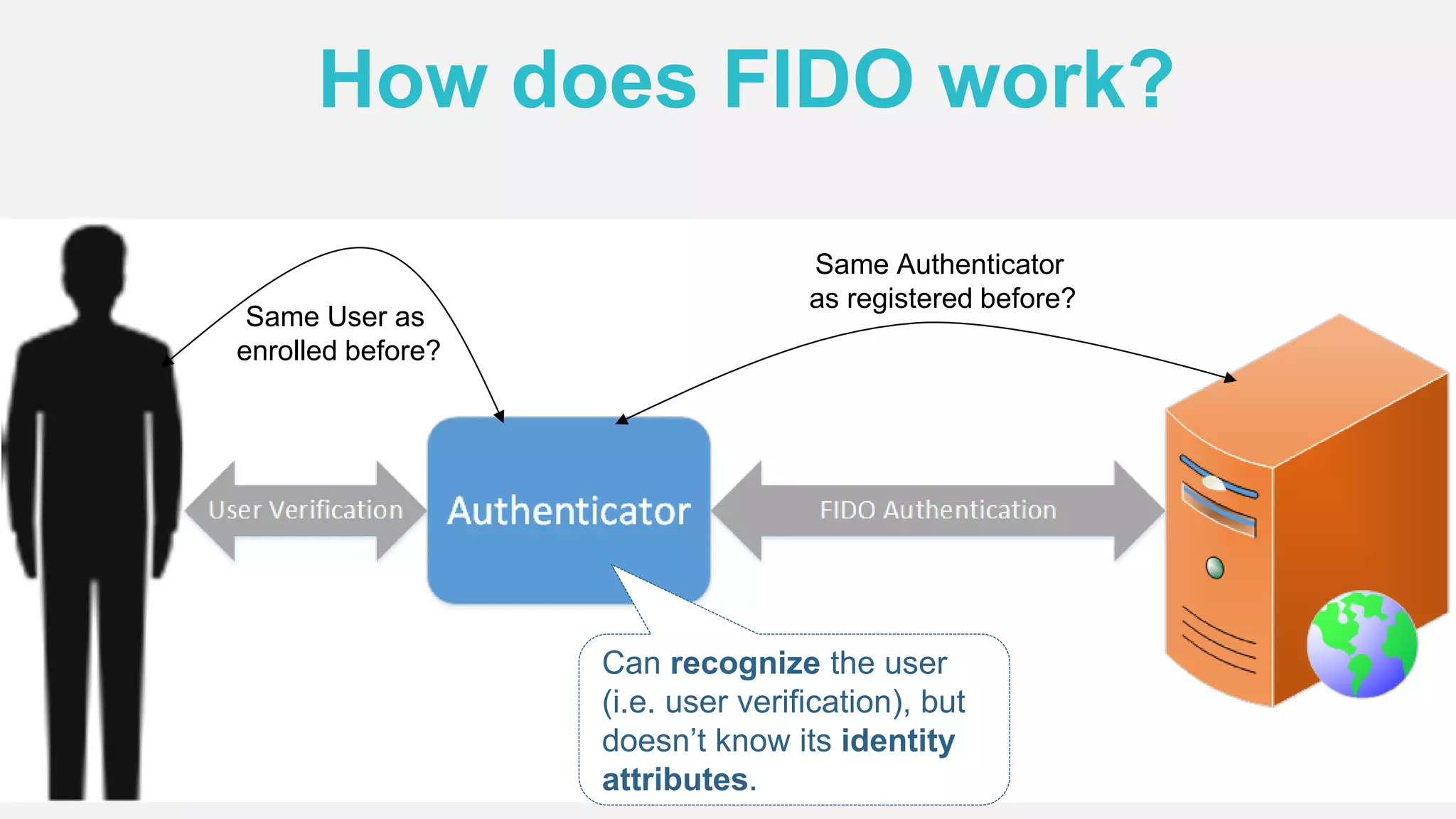
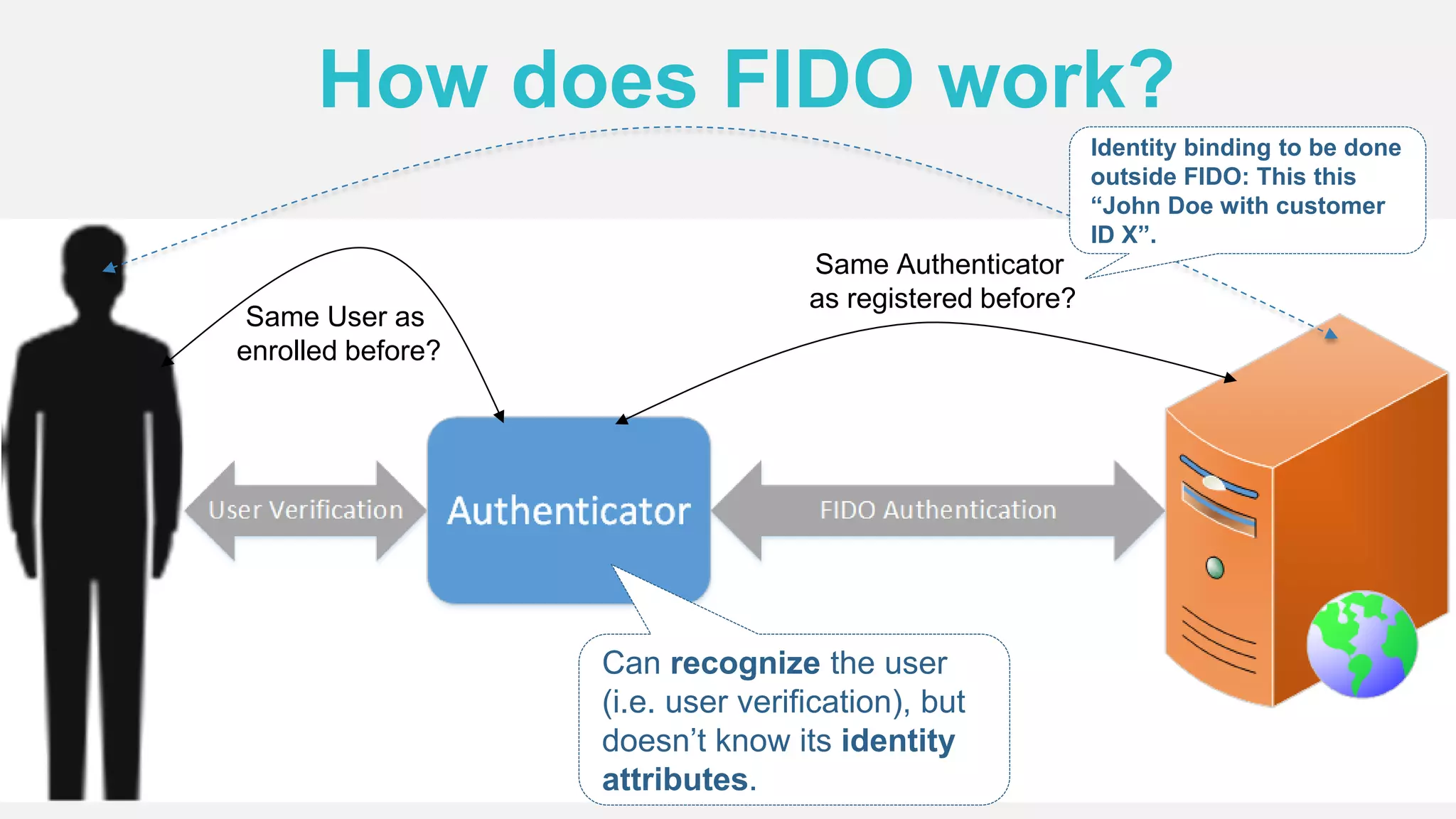
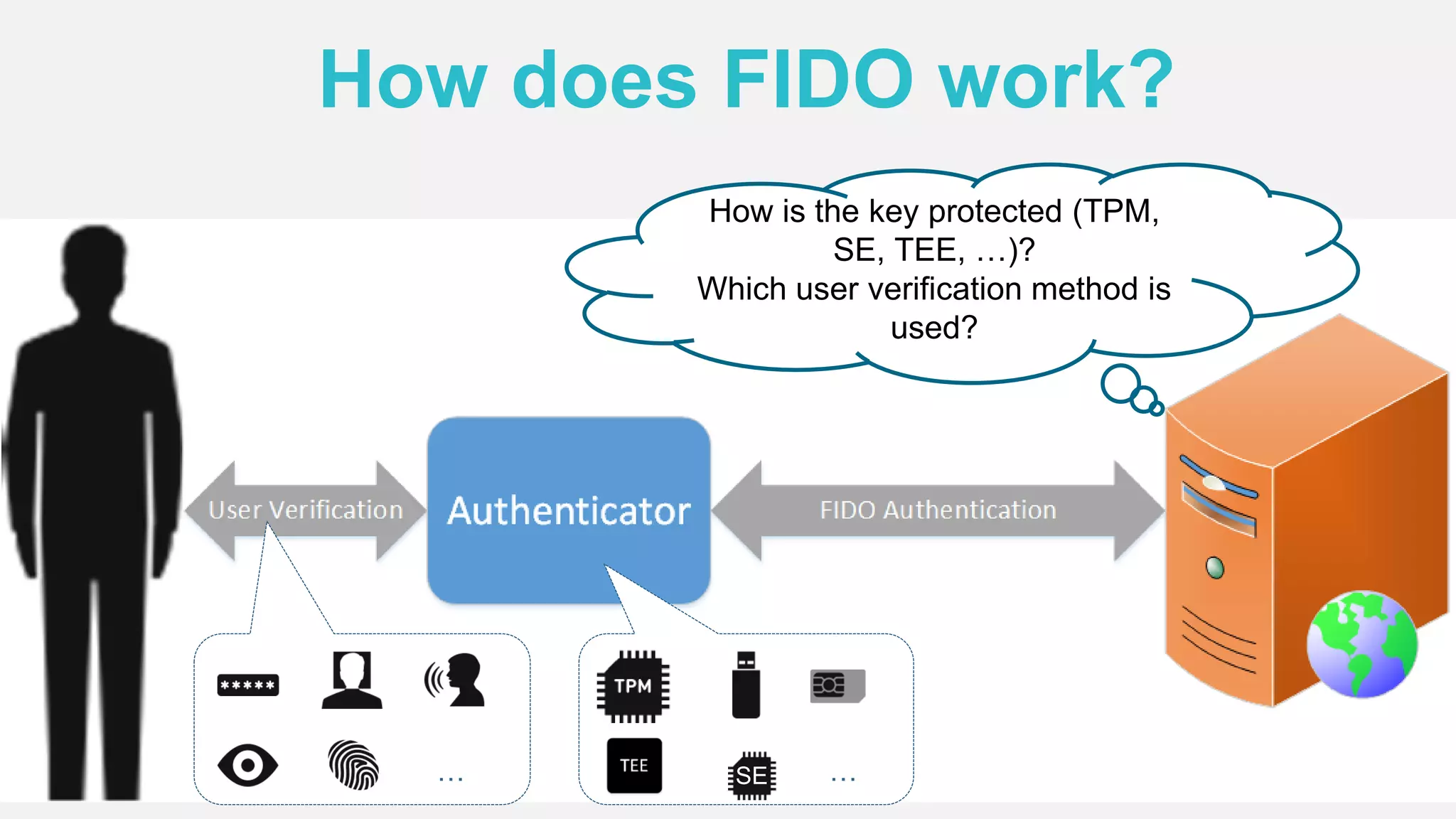
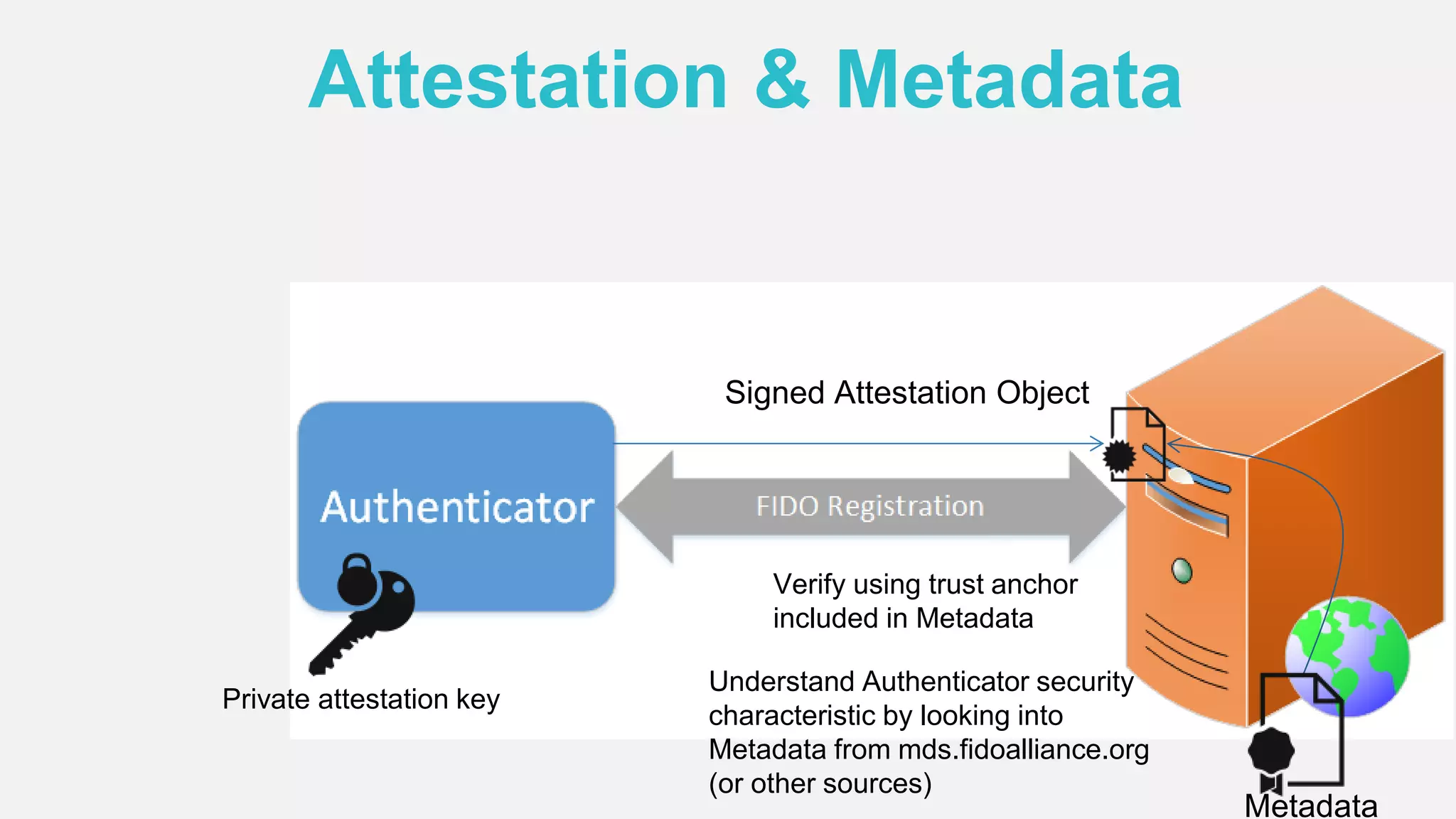
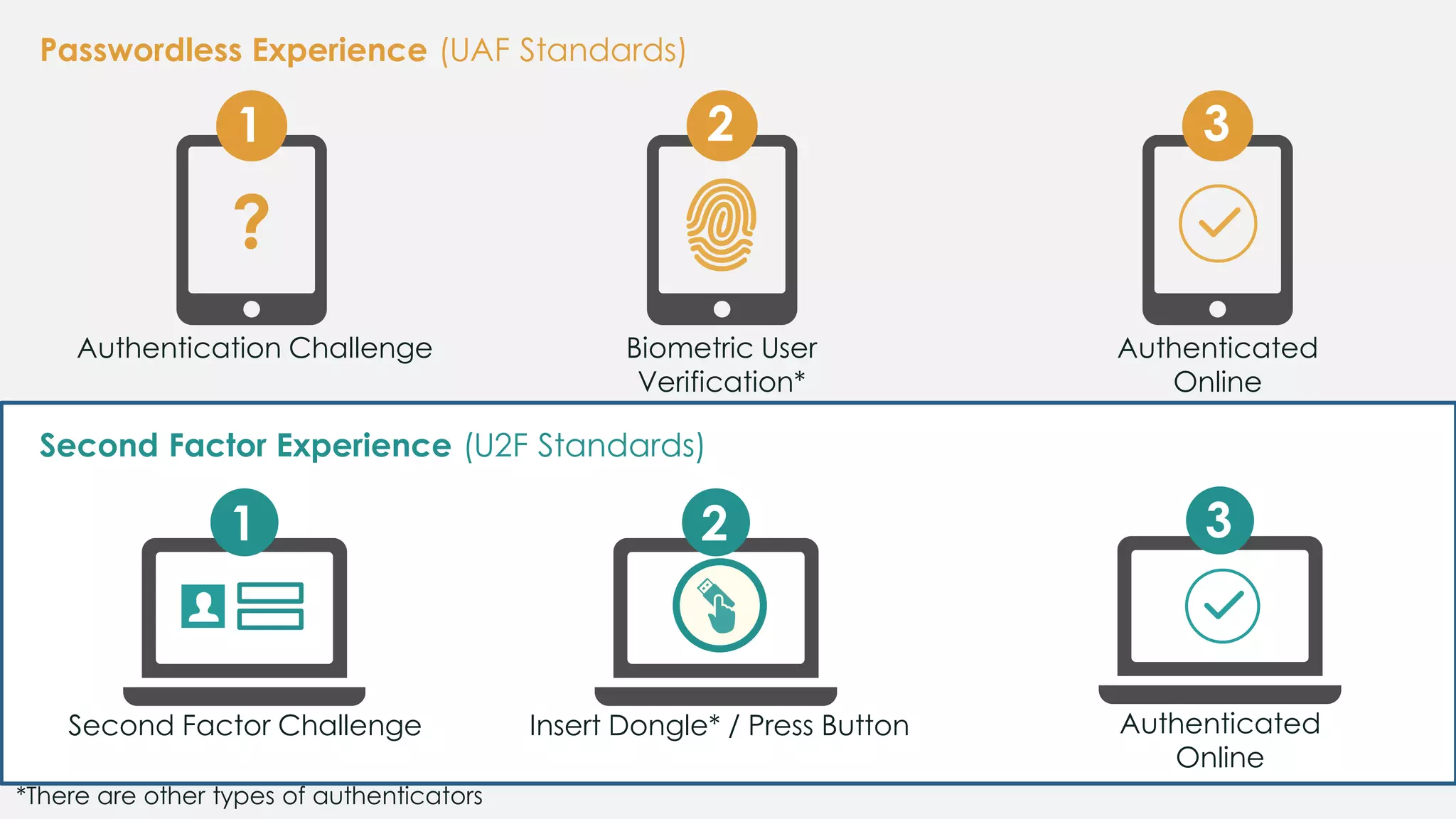
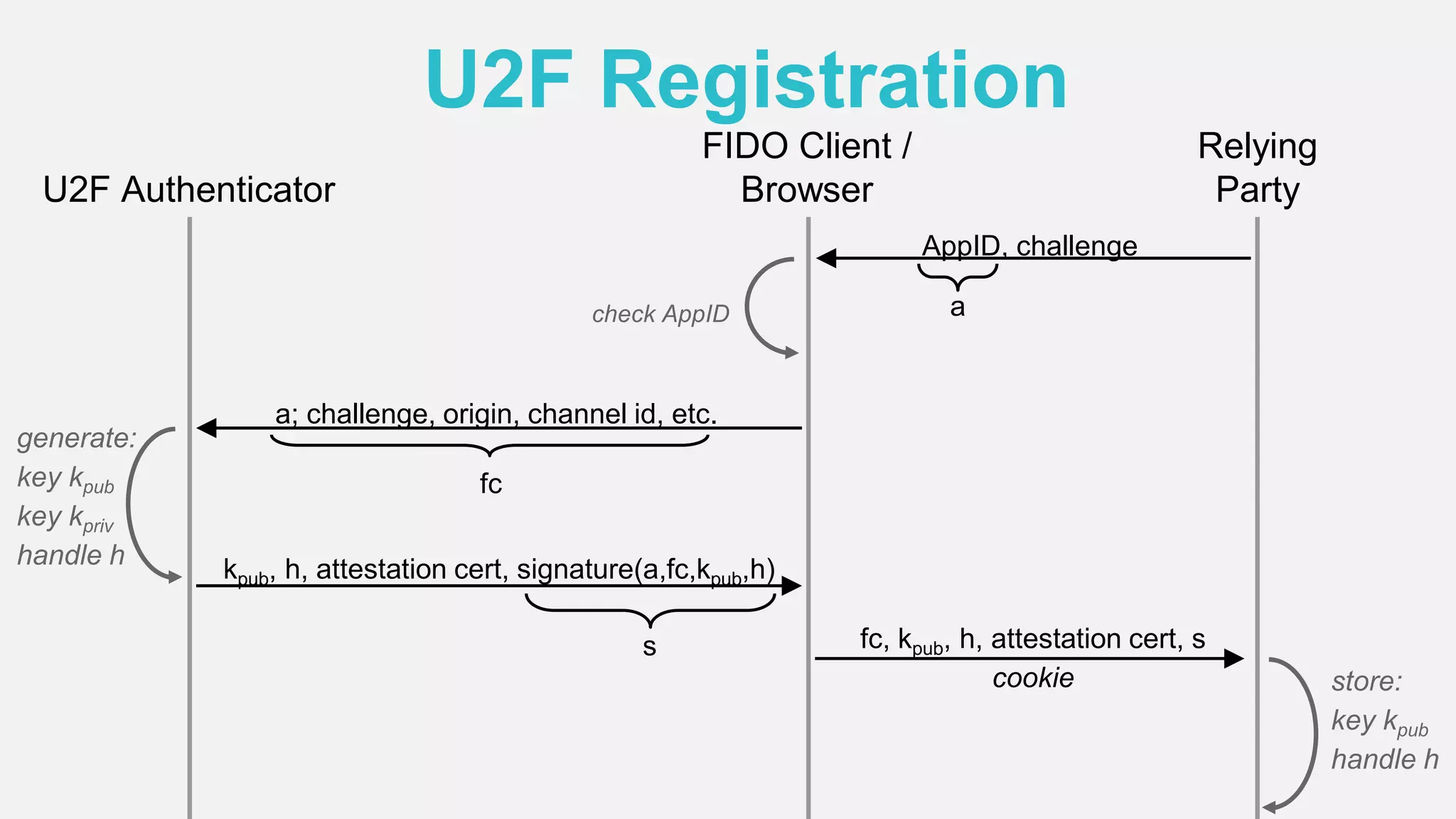
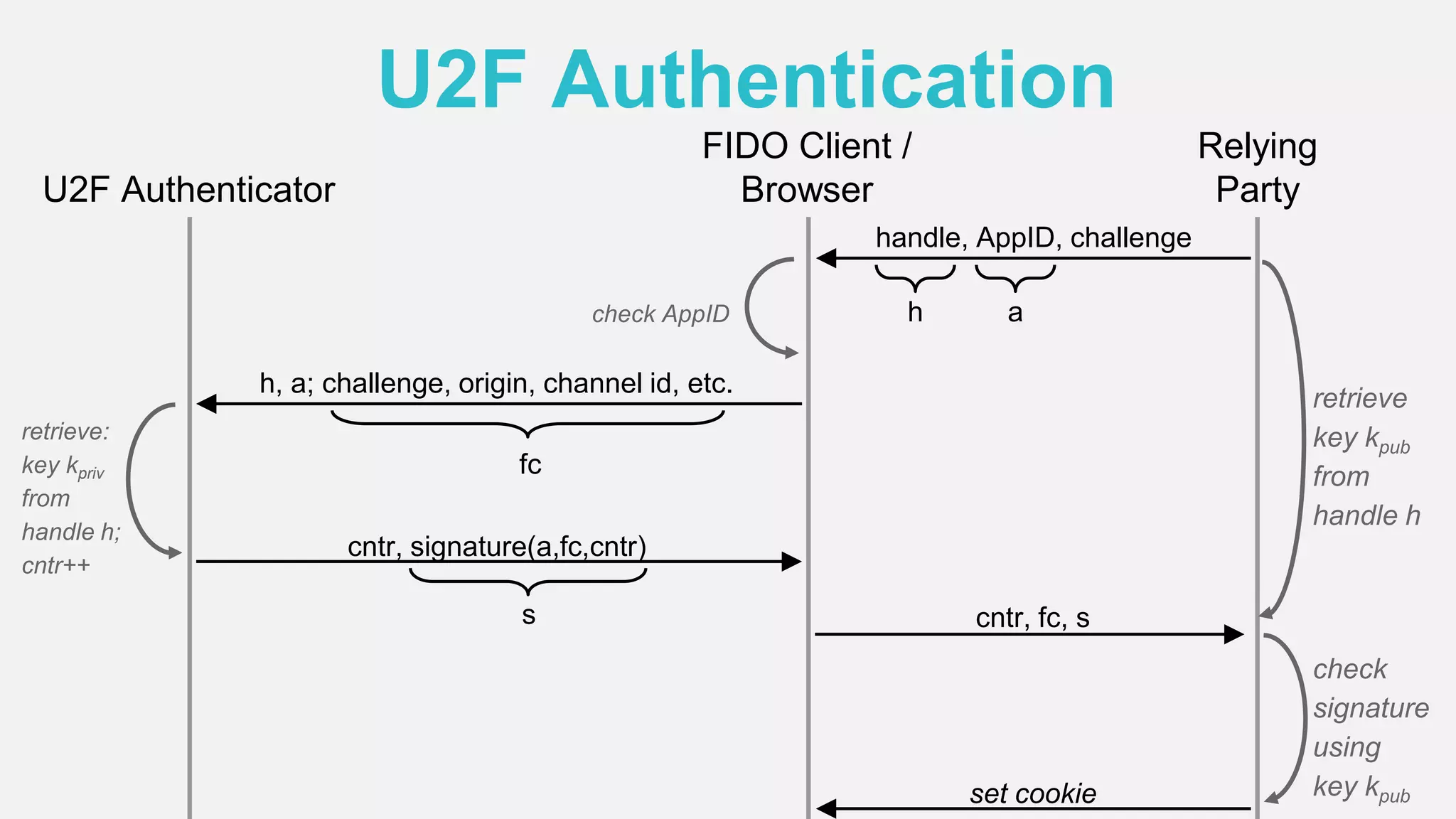
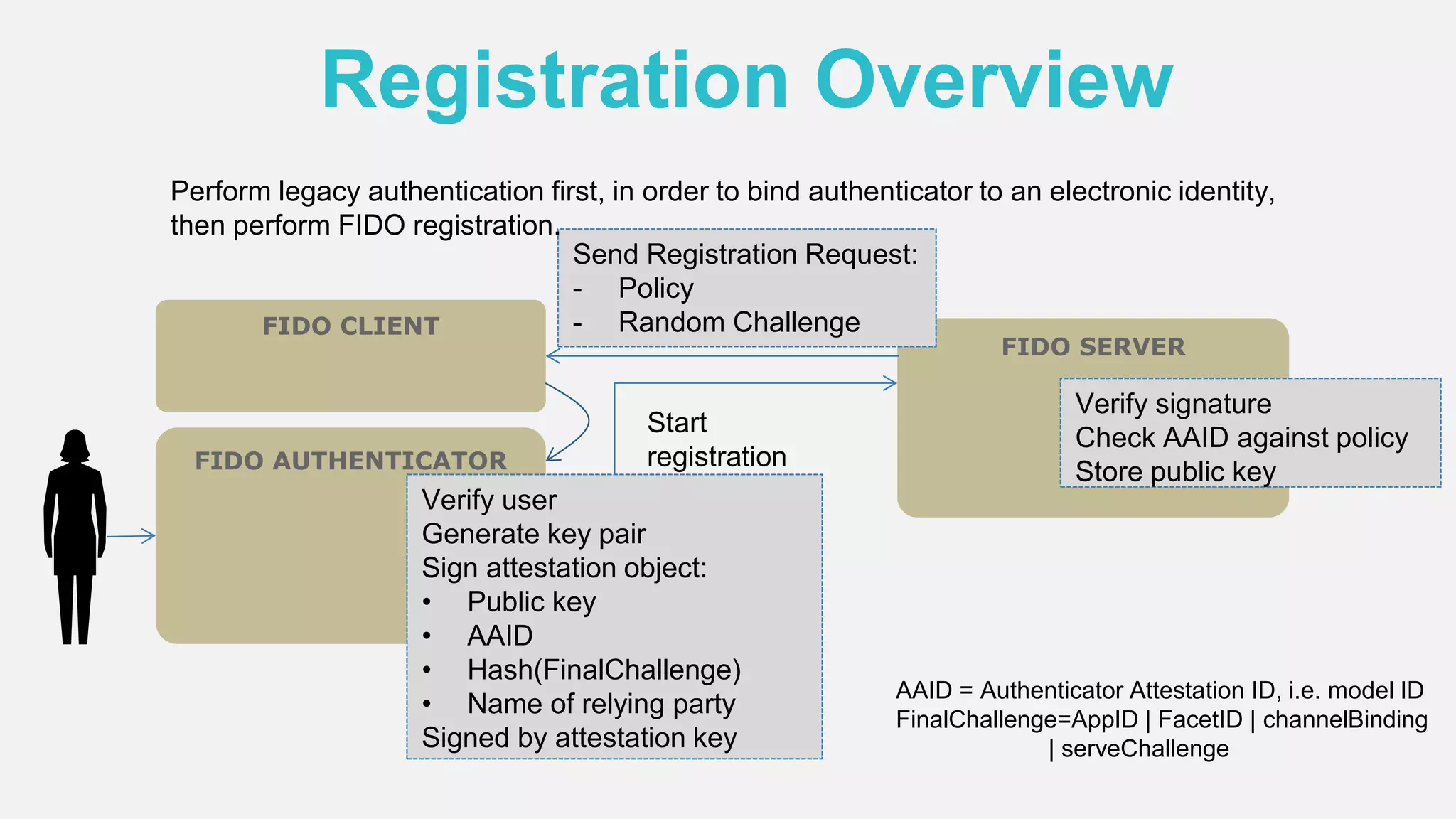
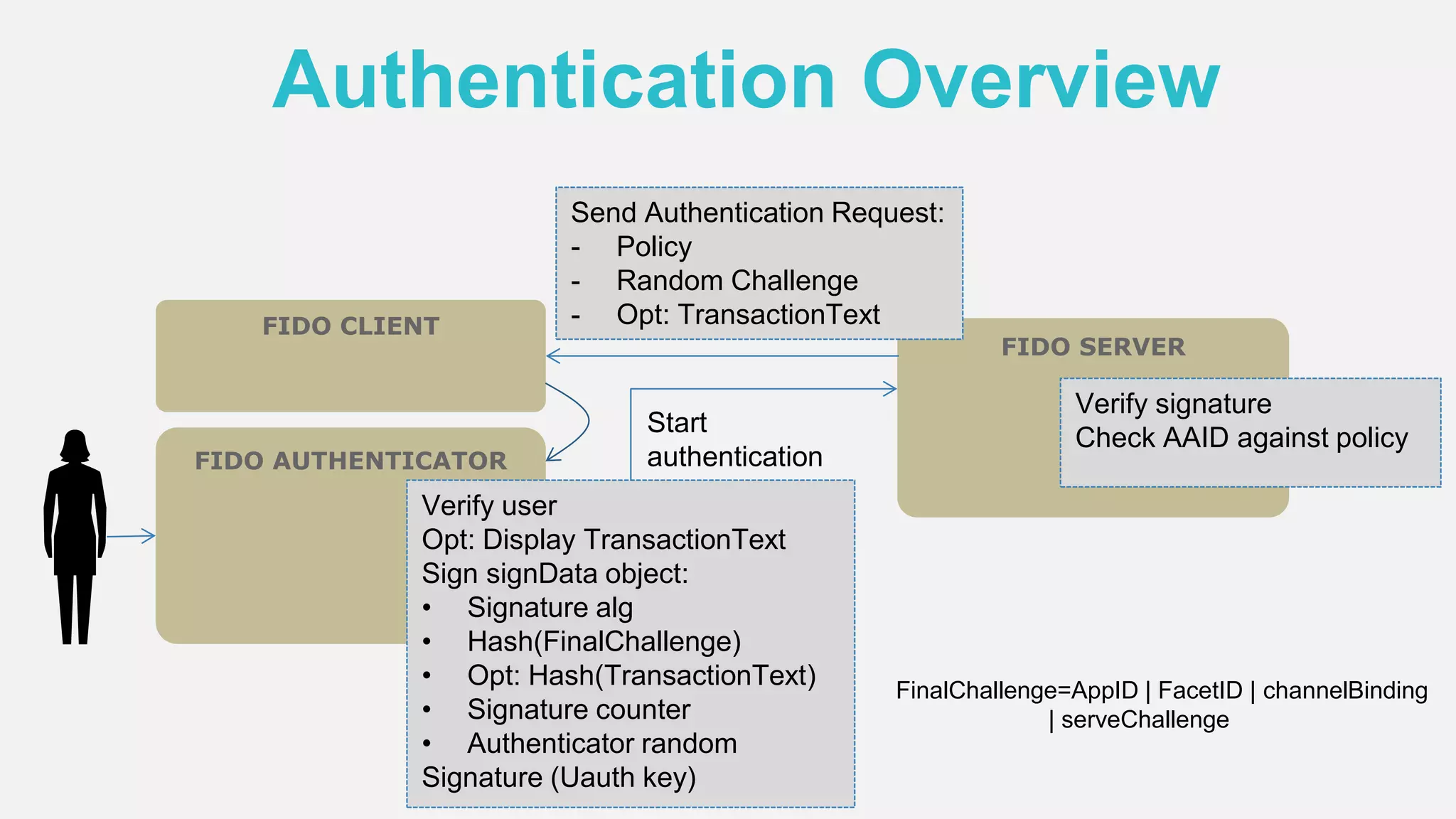
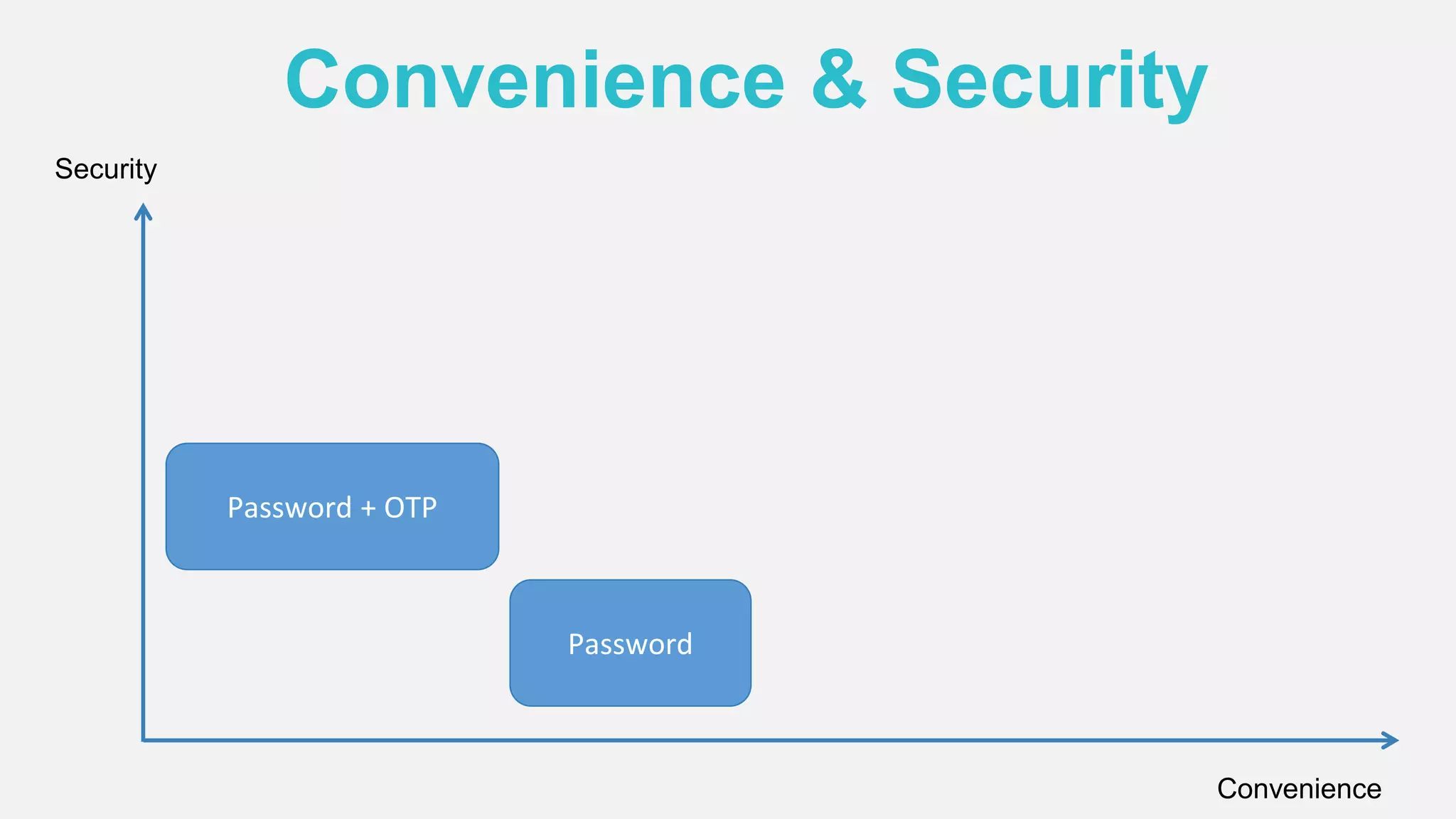
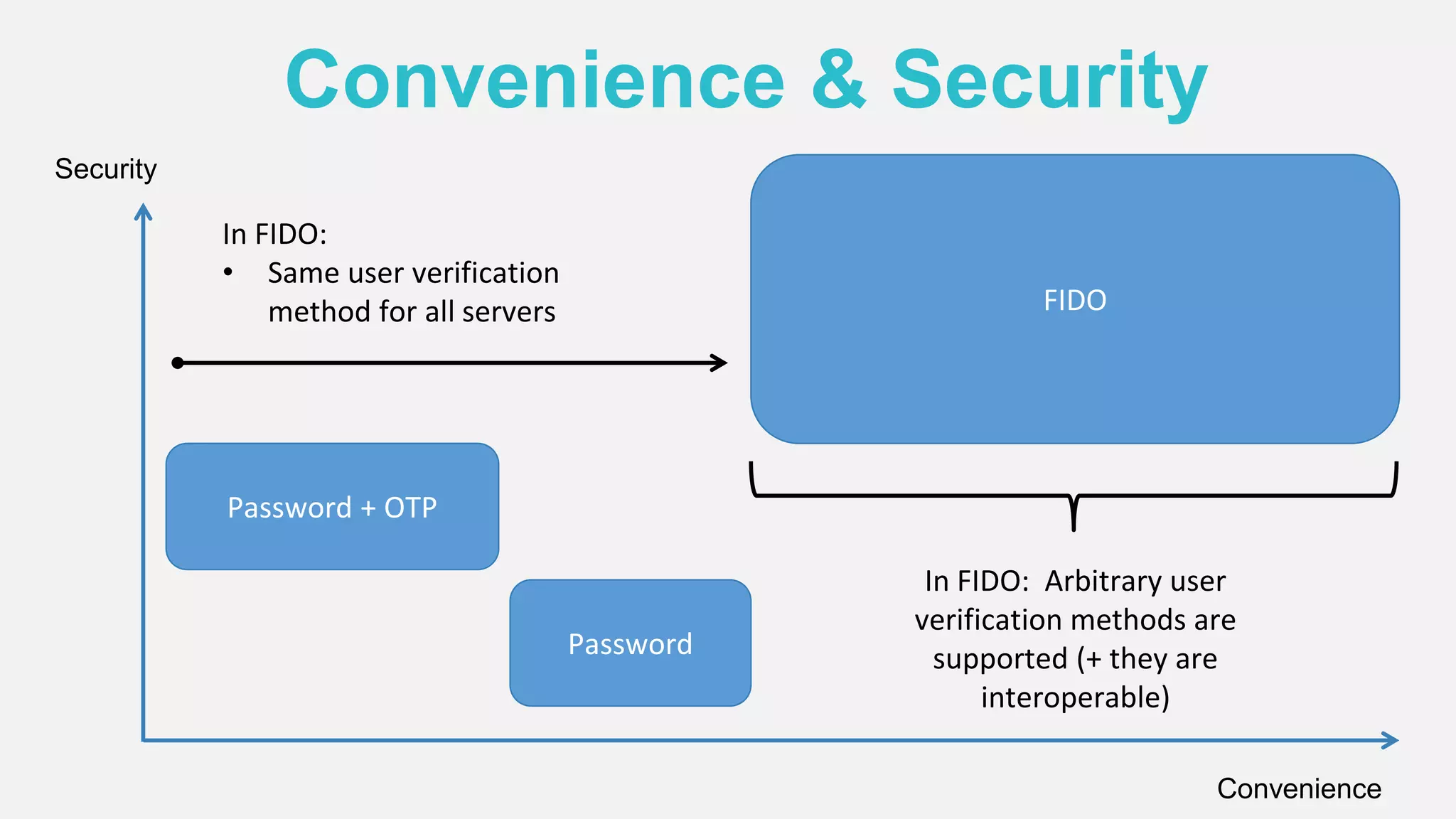
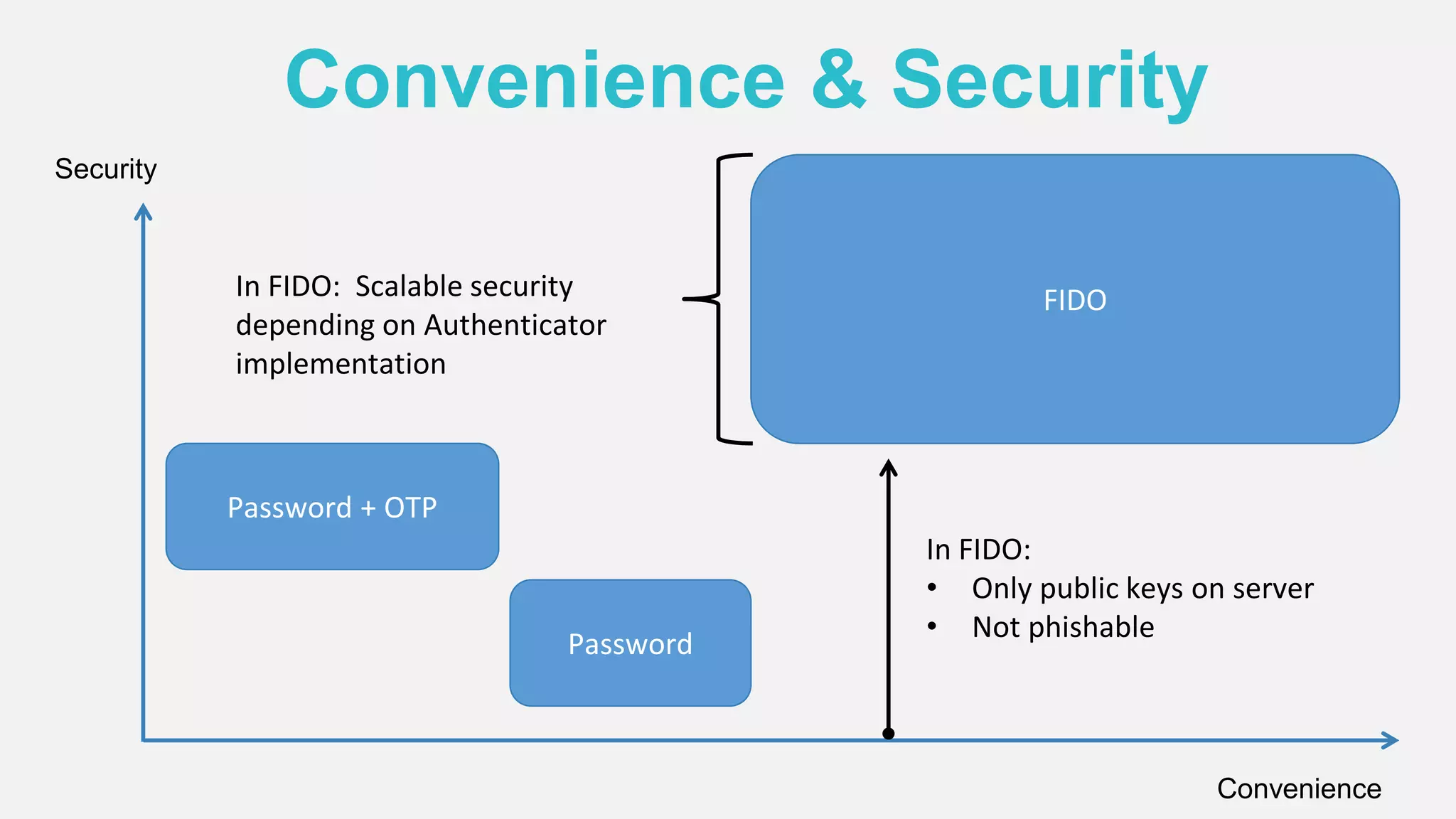
The document discusses the security issues surrounding traditional authentication methods, highlighting vulnerabilities such as phishing and password theft. It introduces the FIDO (Fast Identity Online) framework, which utilizes public key cryptography to enhance authentication security by separating user verification from authentication. The FIDO protocol supports various user verification methods and aims to provide a passwordless experience while ensuring convenience and security.