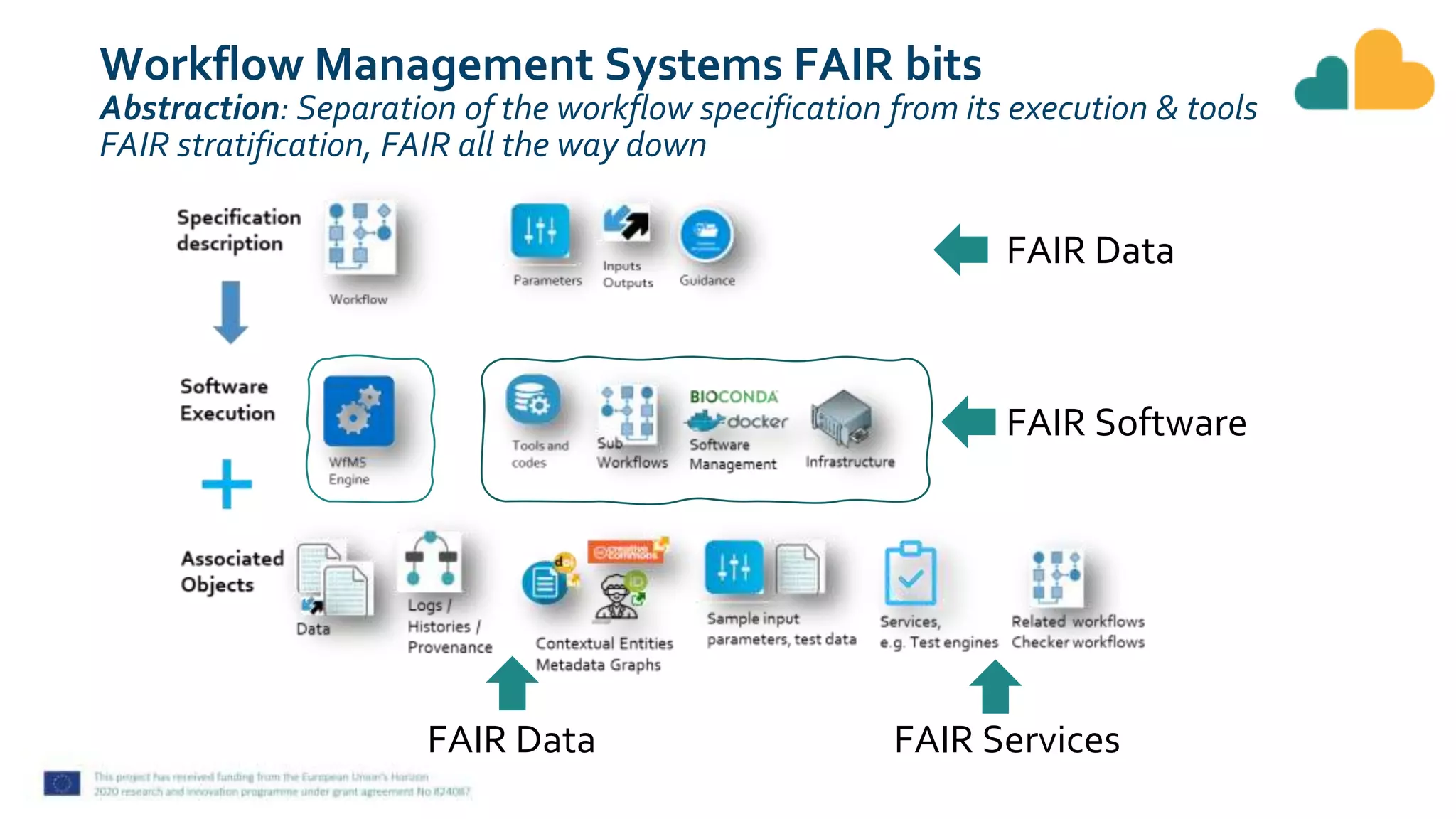
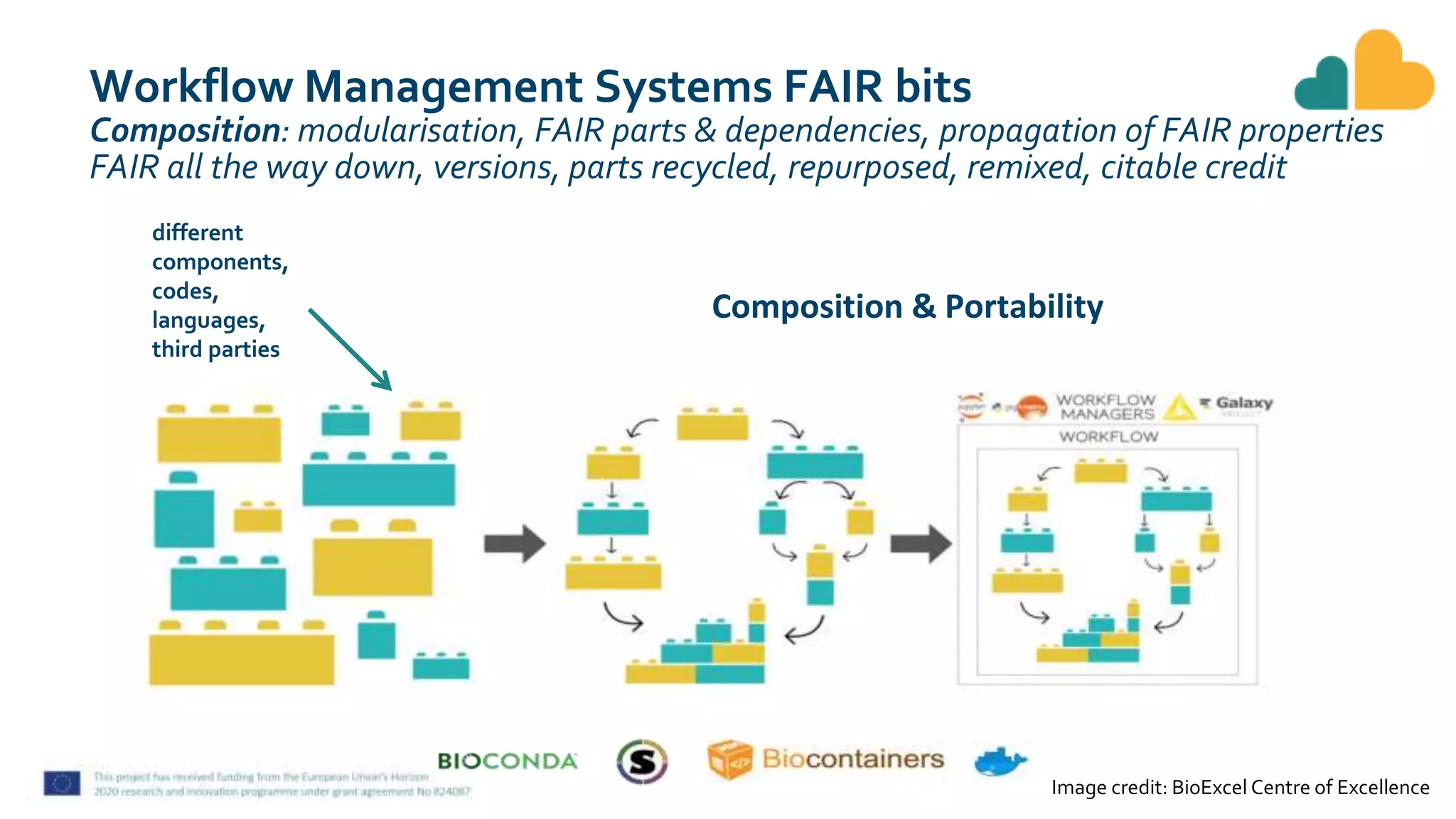
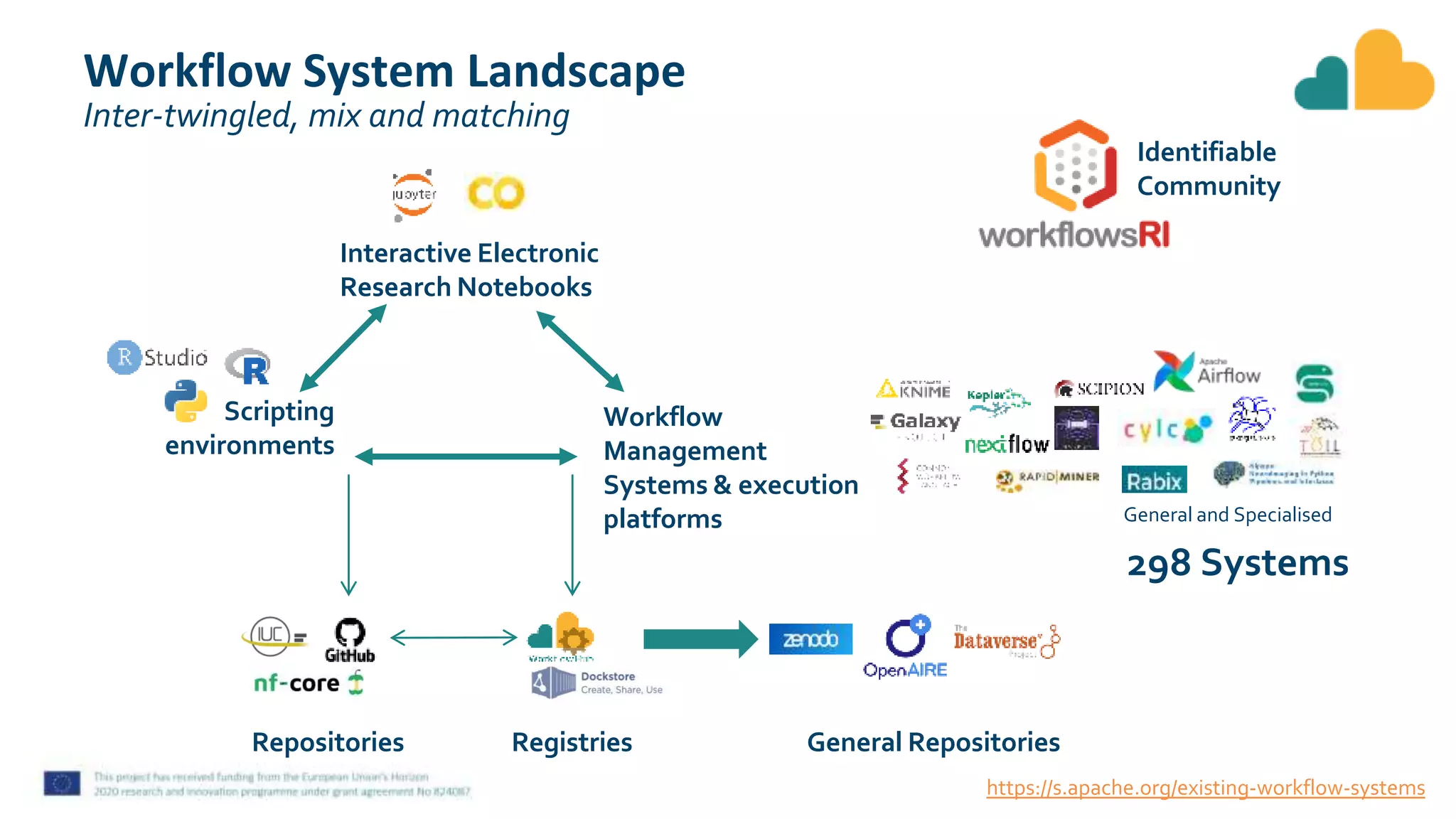
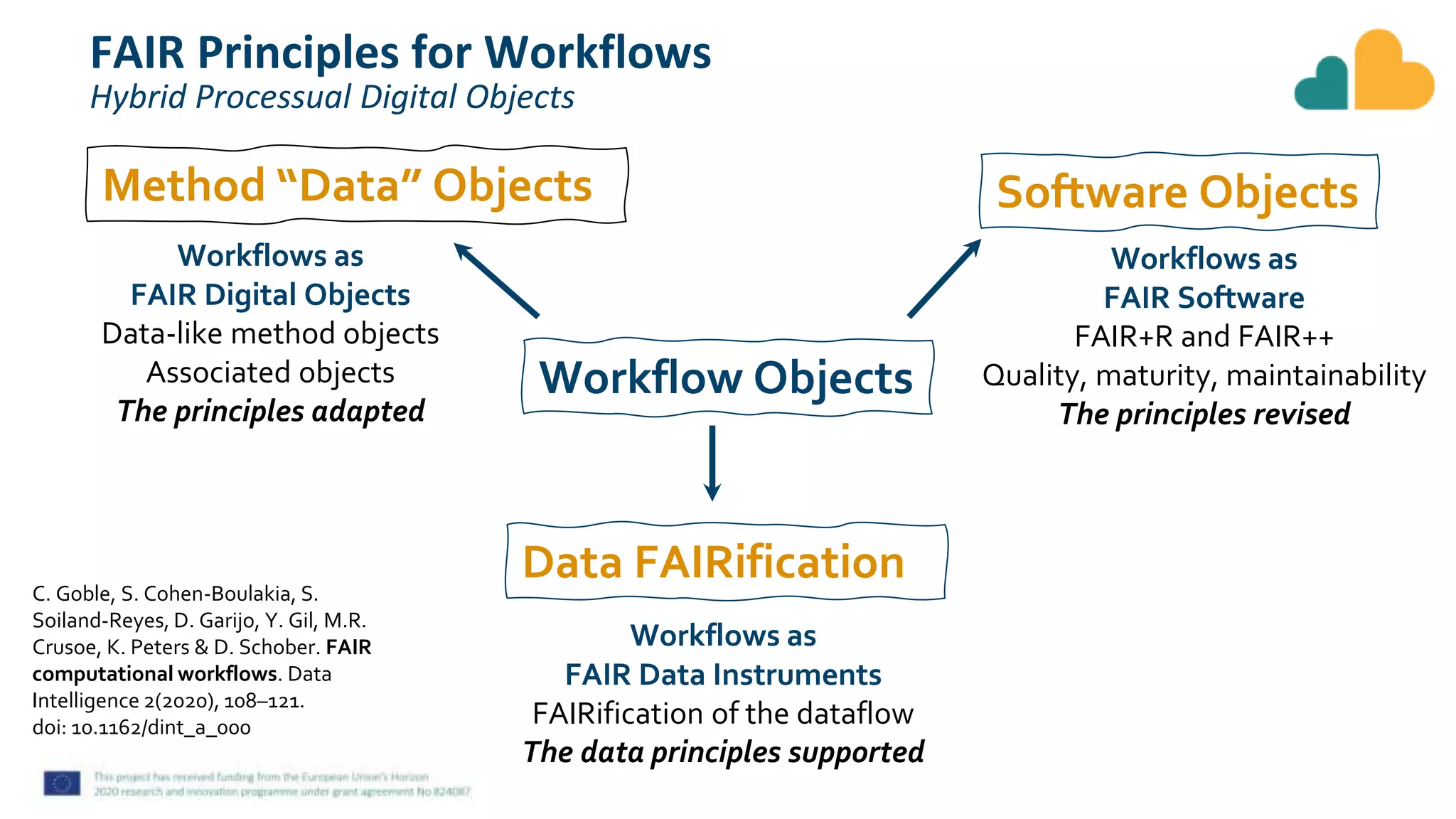
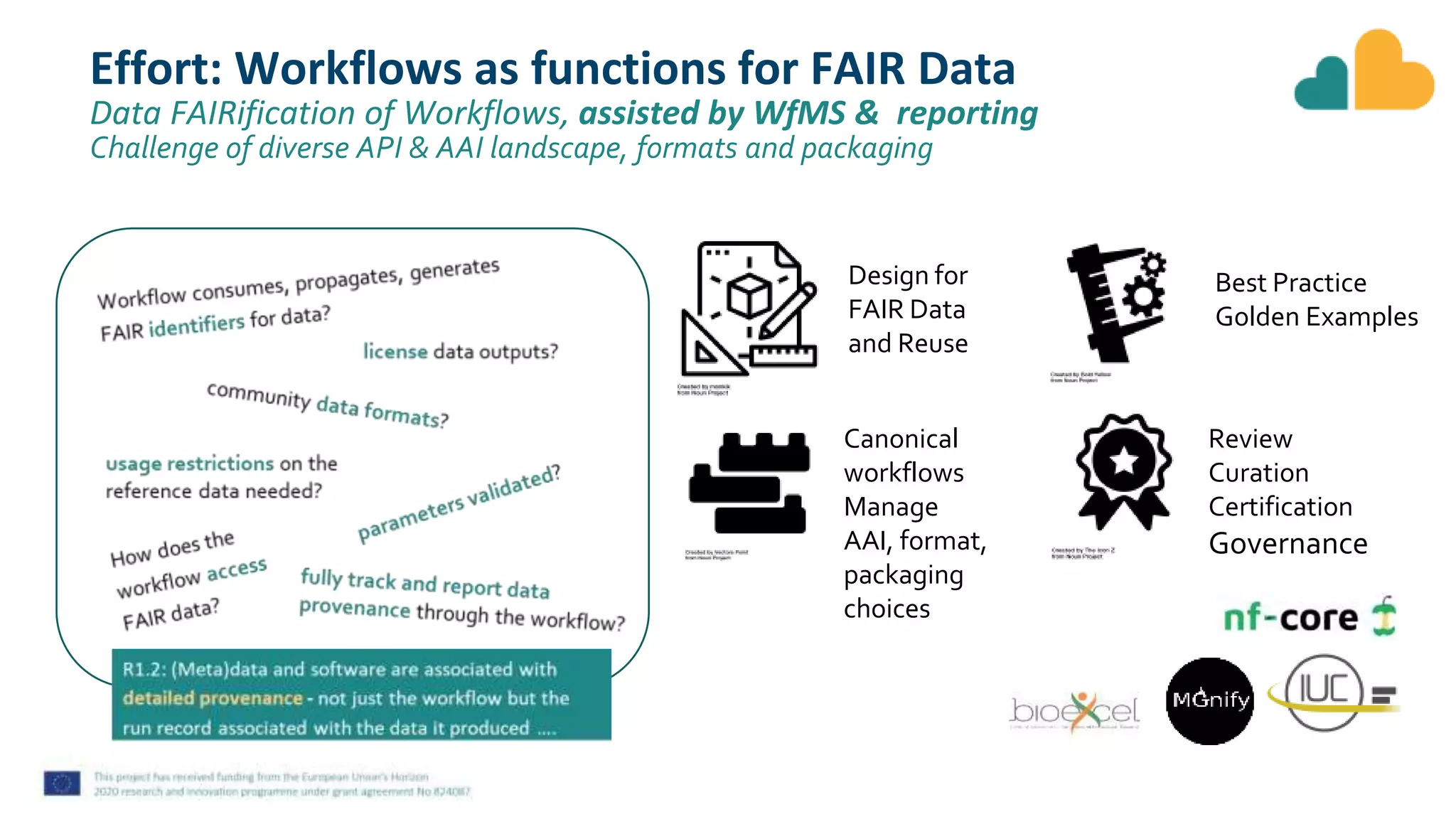
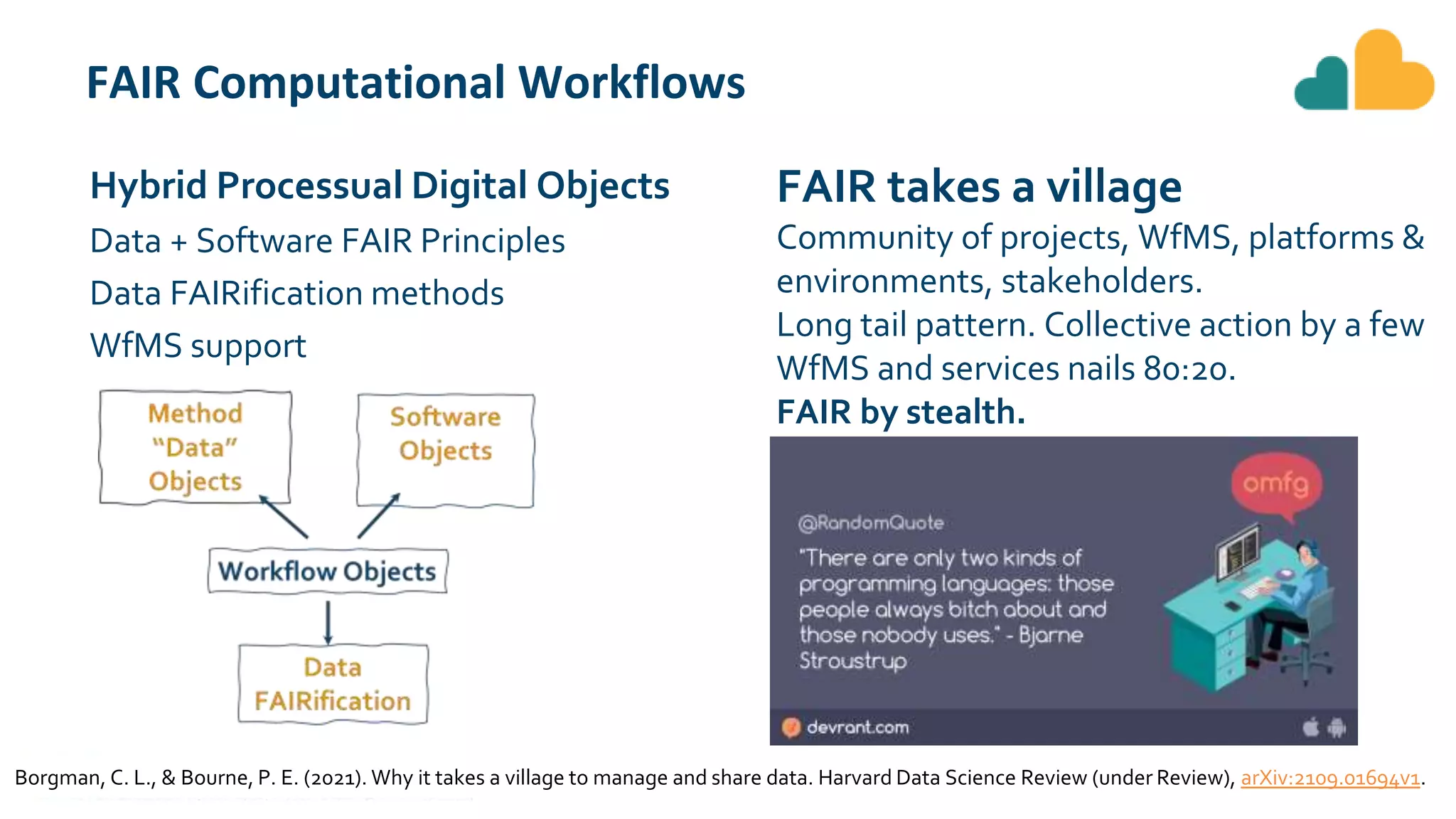
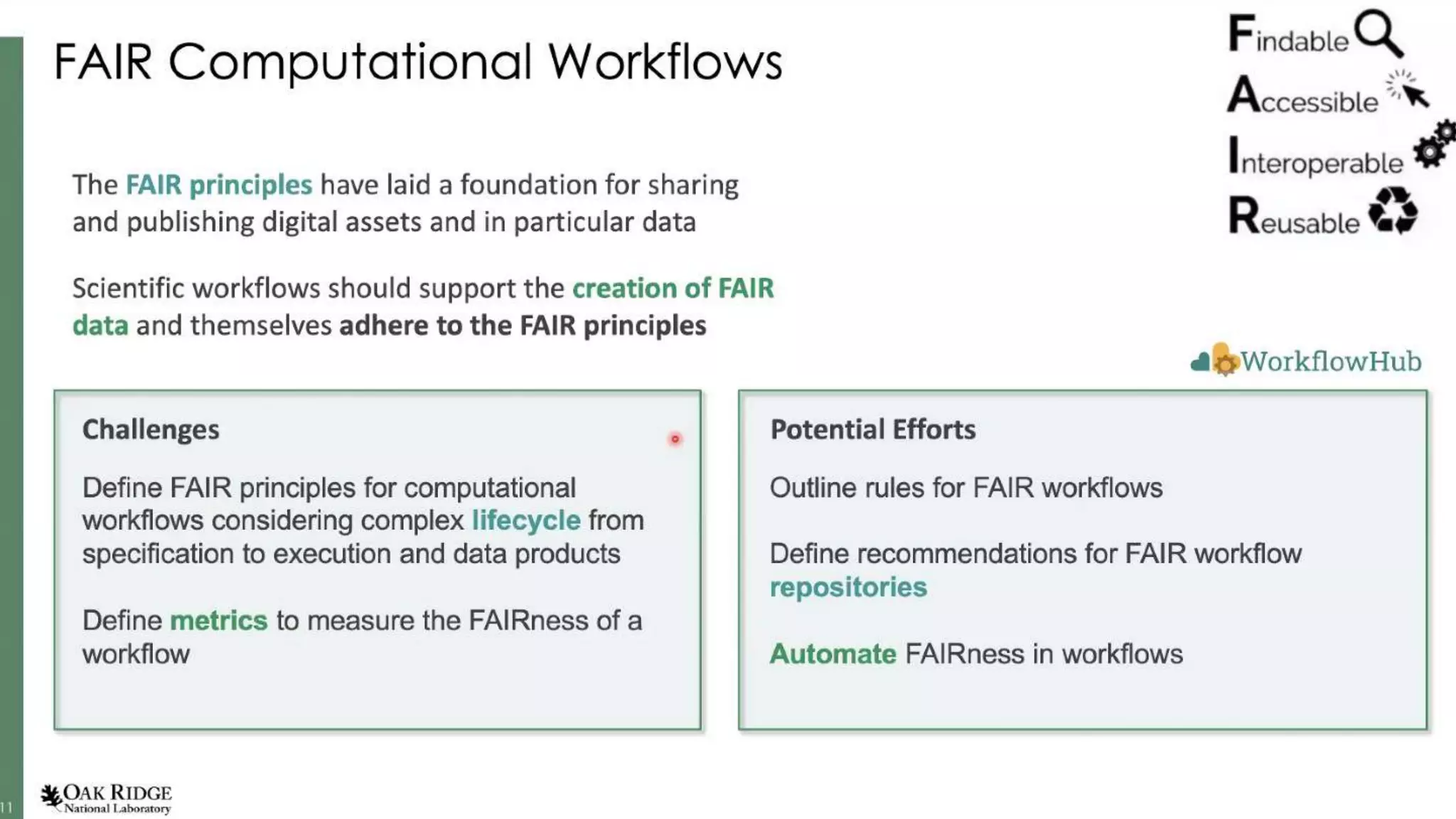
The document discusses fair computational workflows in data-intensive bioscience, emphasizing the importance of fair data and workflows for effective coordination and execution of complex data-related tasks. It outlines various components and systems that contribute to creating, sharing, and managing workflows, including metadata standards and best practices for interoperability and reusability. The document highlights the collaborative efforts within the research community to enhance workflow management systems and ensure quality and accessibility of bioinformatics tools.
![Computational Workflows for Data intensive Bioscience
prepare, analyze, and share increasing volumes of complex data
CryoEM Image Analysis
Metagenomic Pipelines
Protein Ligand
Simulation
[Adam Hospital]
[Rob Finn]
[Carlos Oscar Sorzano Sanchez]
Nature 573, 149-150 (2019)
https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-019-02619-z
Multi-step processes to
coordinate and execute multiple
codes and handle data and
processing dependencies
Typically Data flows
Benefit from FAIR data with
machine processable metadata
A precise description
A special kind of software](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fair-workflows-ieeeescience2021-goble-211108115131/75/FAIR-Computational-Workflows-2-2048.jpg)