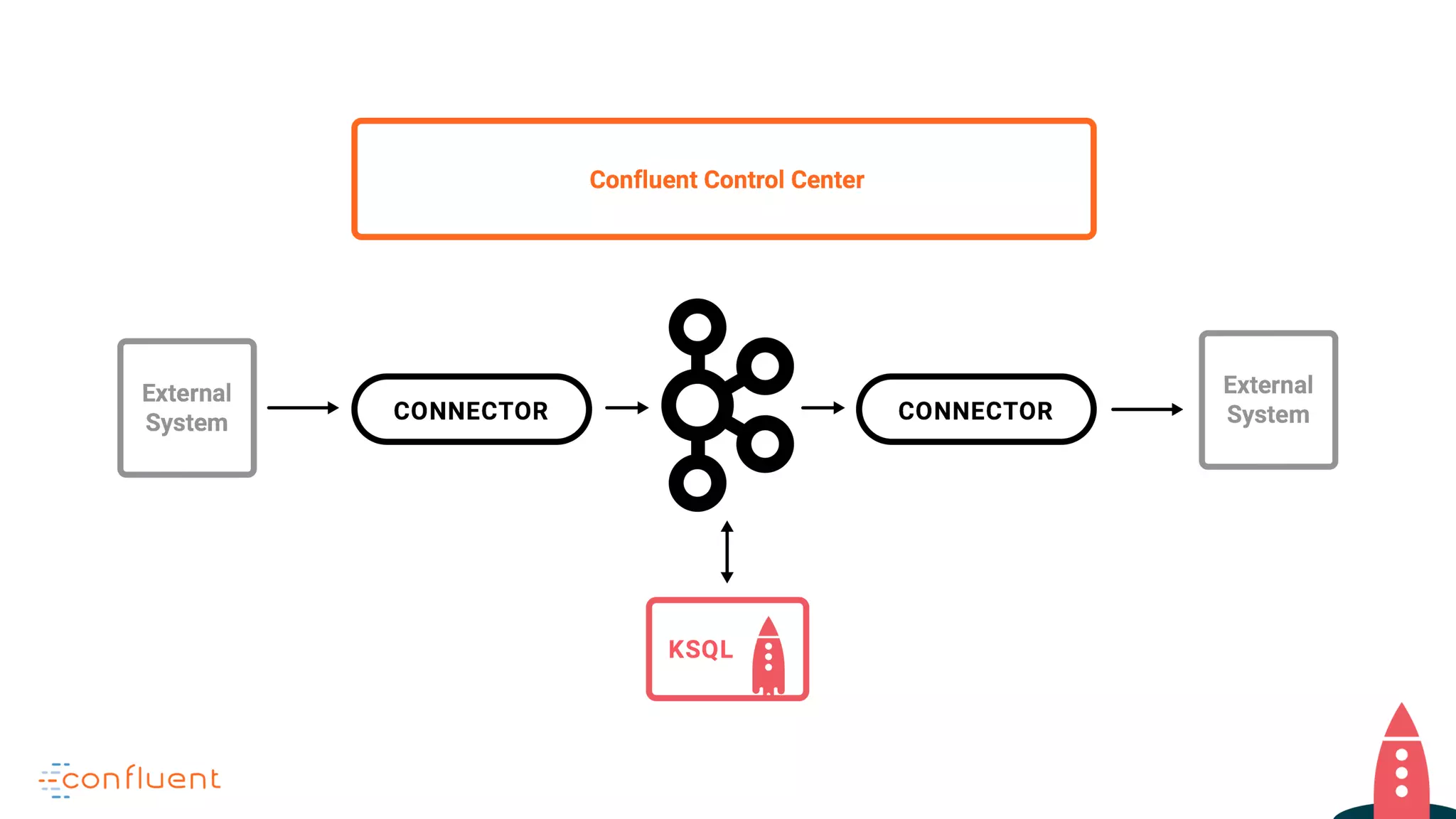
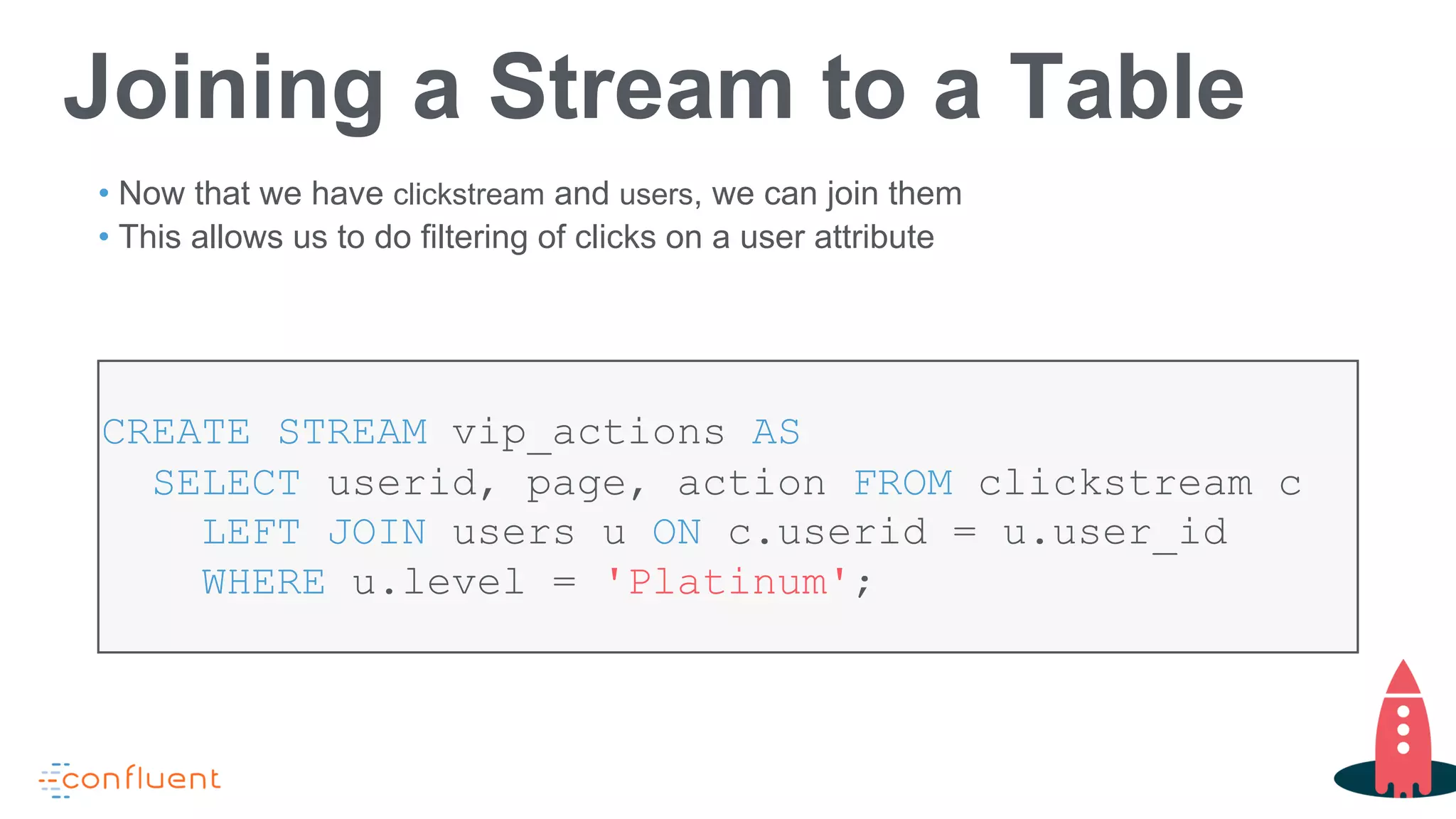
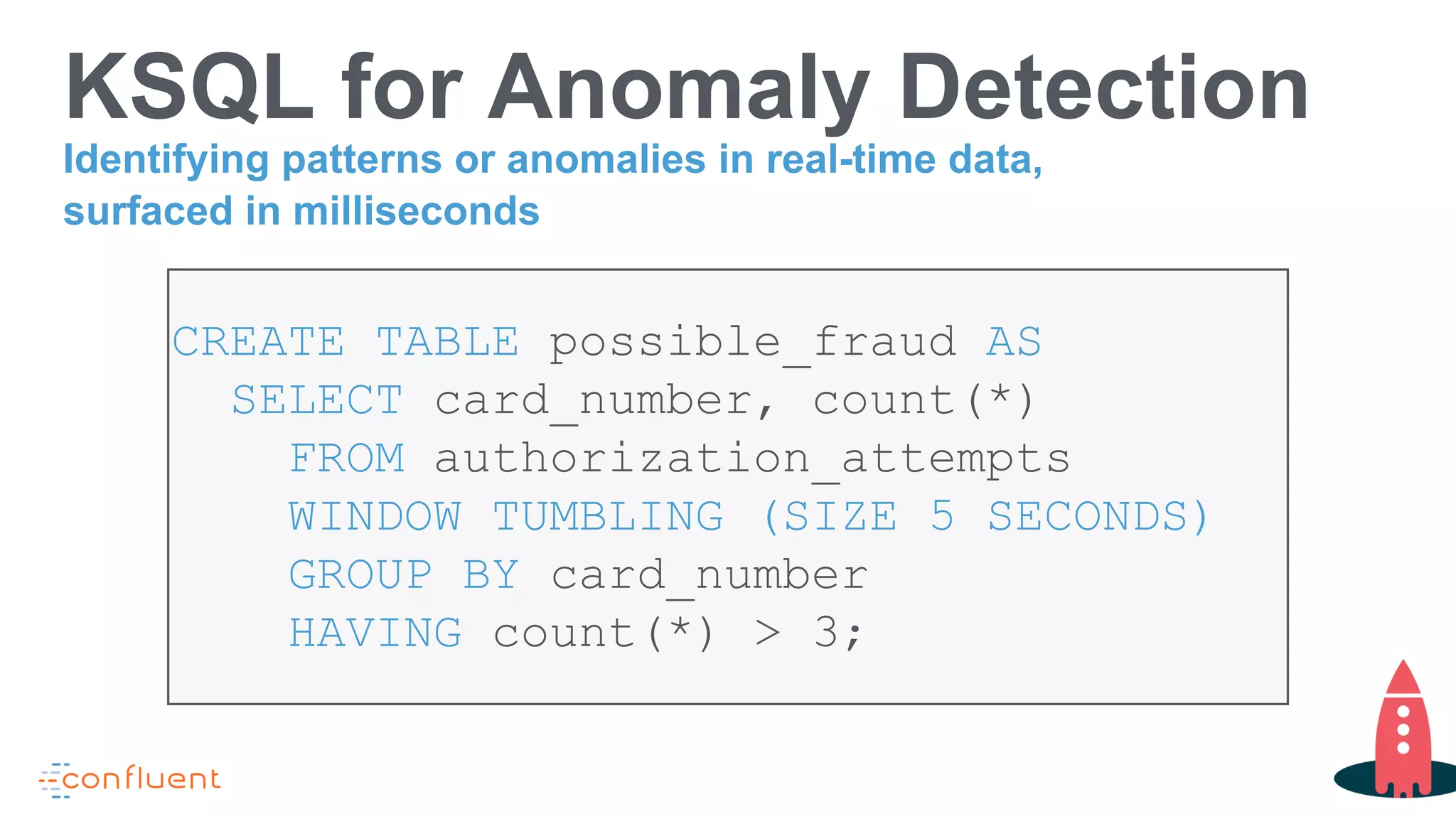
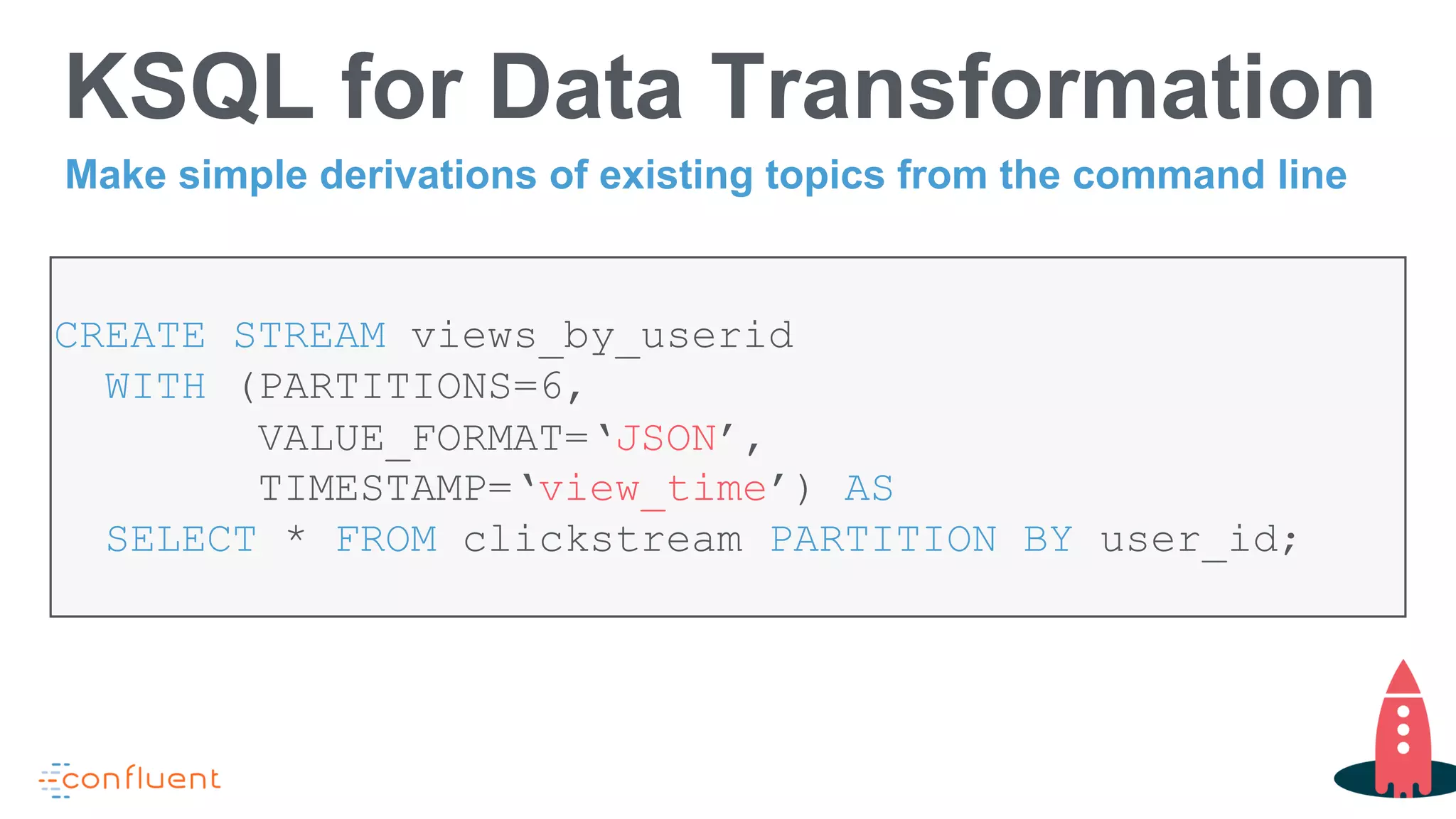
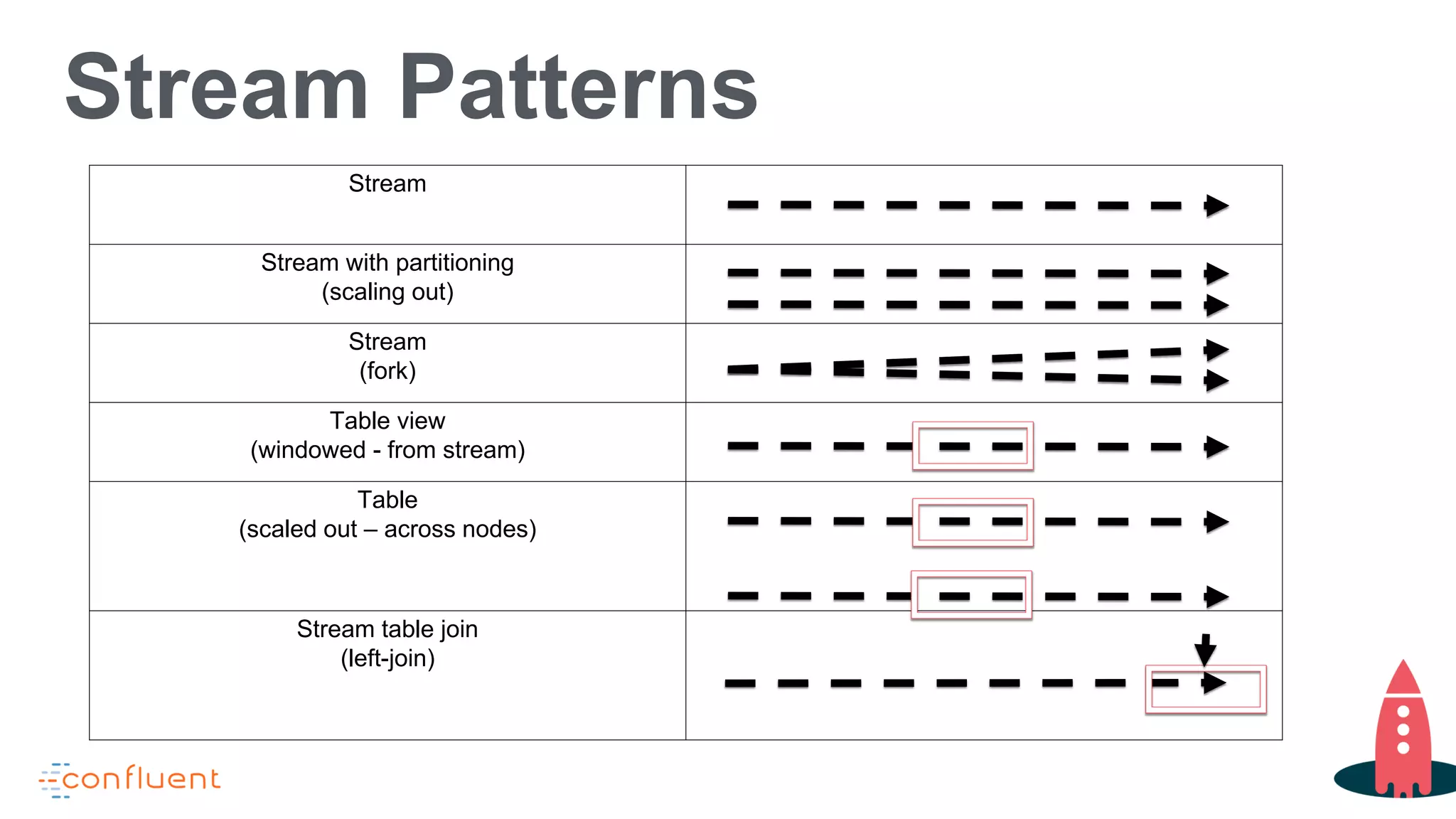
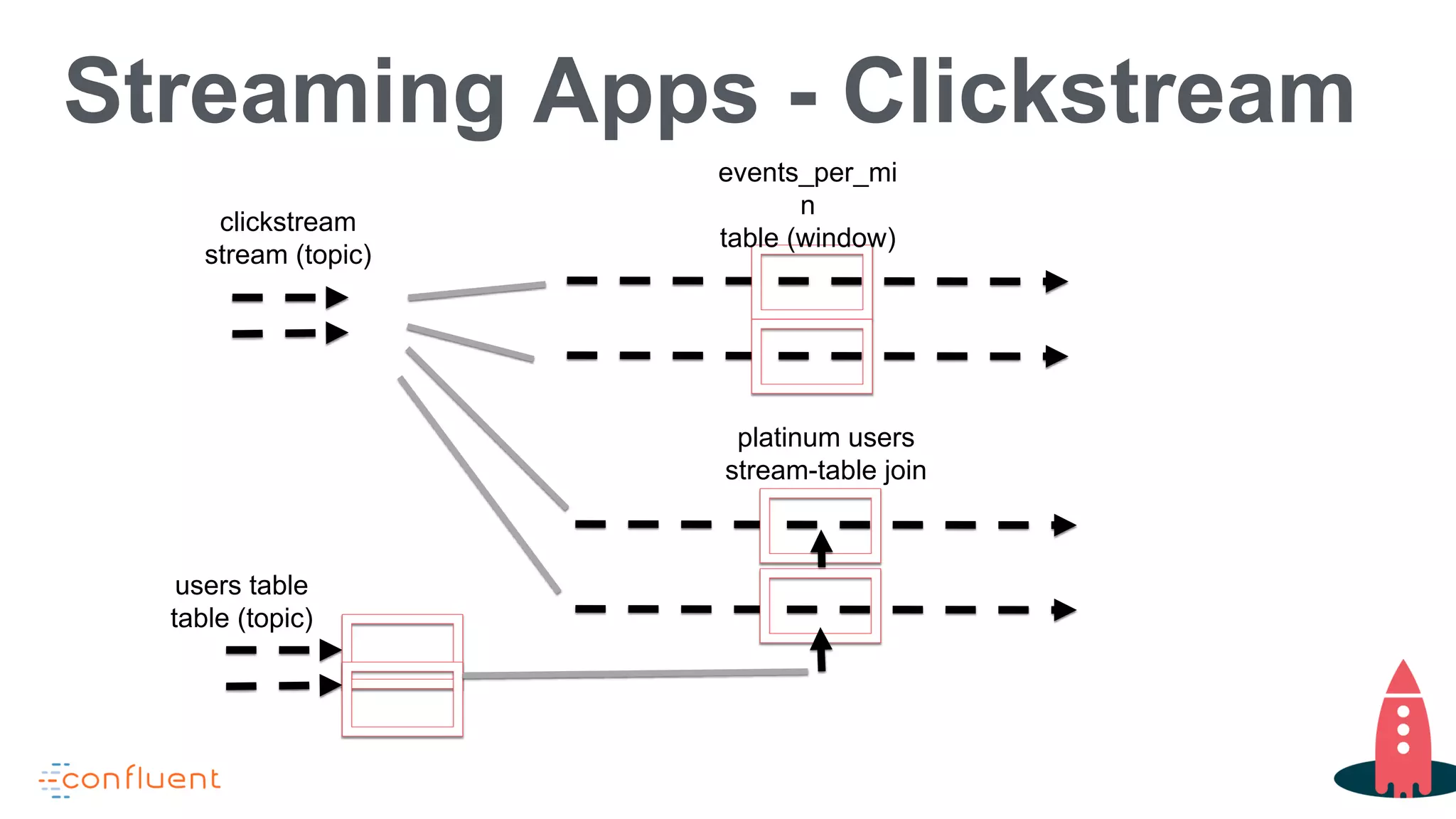
This document discusses KSQL, a streaming SQL engine for Apache Kafka. It begins by explaining some key KSQL concepts like streams, tables, queries, and windowing. It then provides examples of creating streams and tables from Kafka topics, exploring data in streams and tables, and joining streams to tables. Finally, it outlines some common usage patterns for KSQL like streaming ETL, anomaly detection, real-time monitoring, and data transformation. Throughout there are code examples demonstrating how to execute these patterns using the KSQL declarative language.