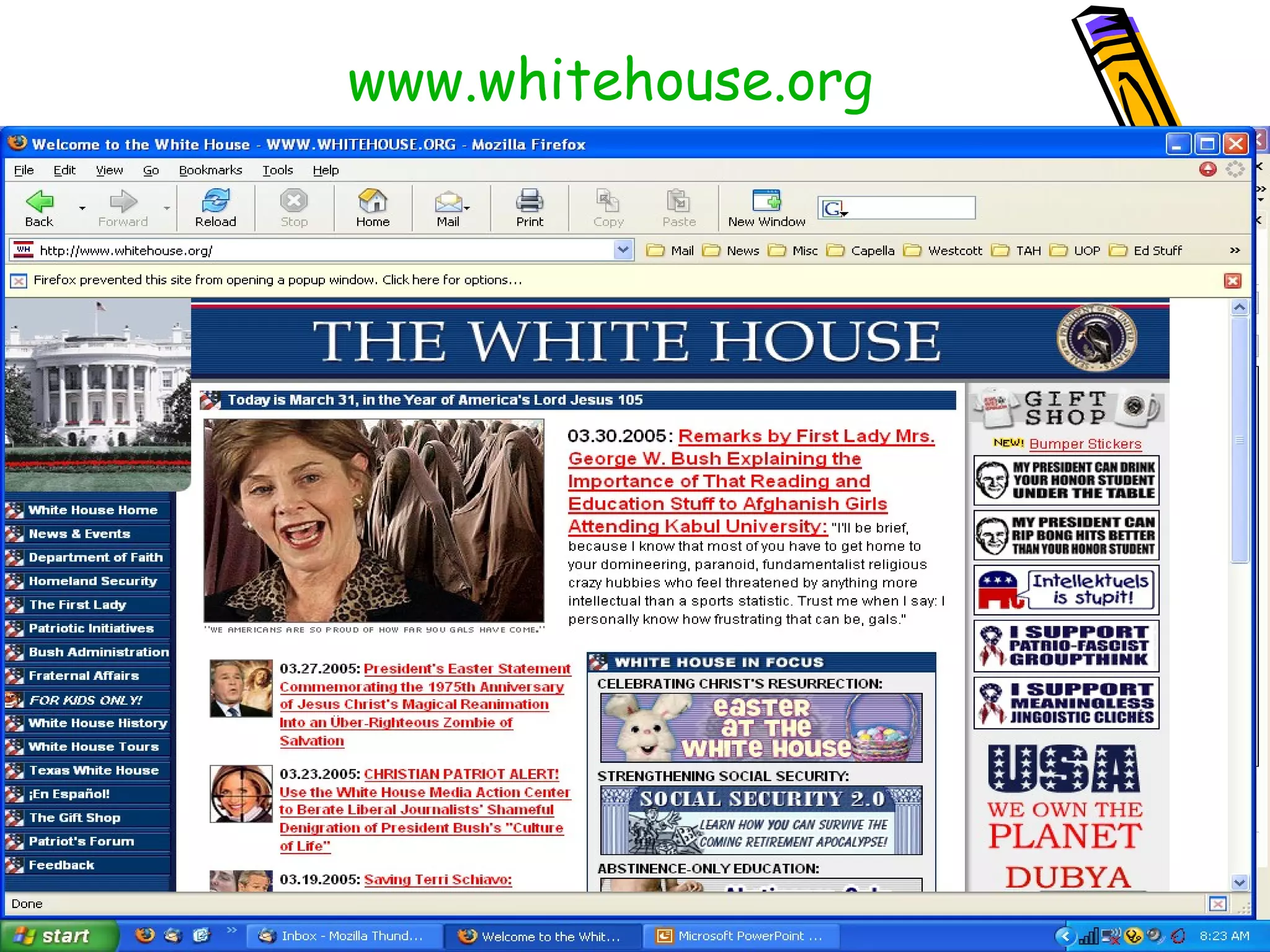
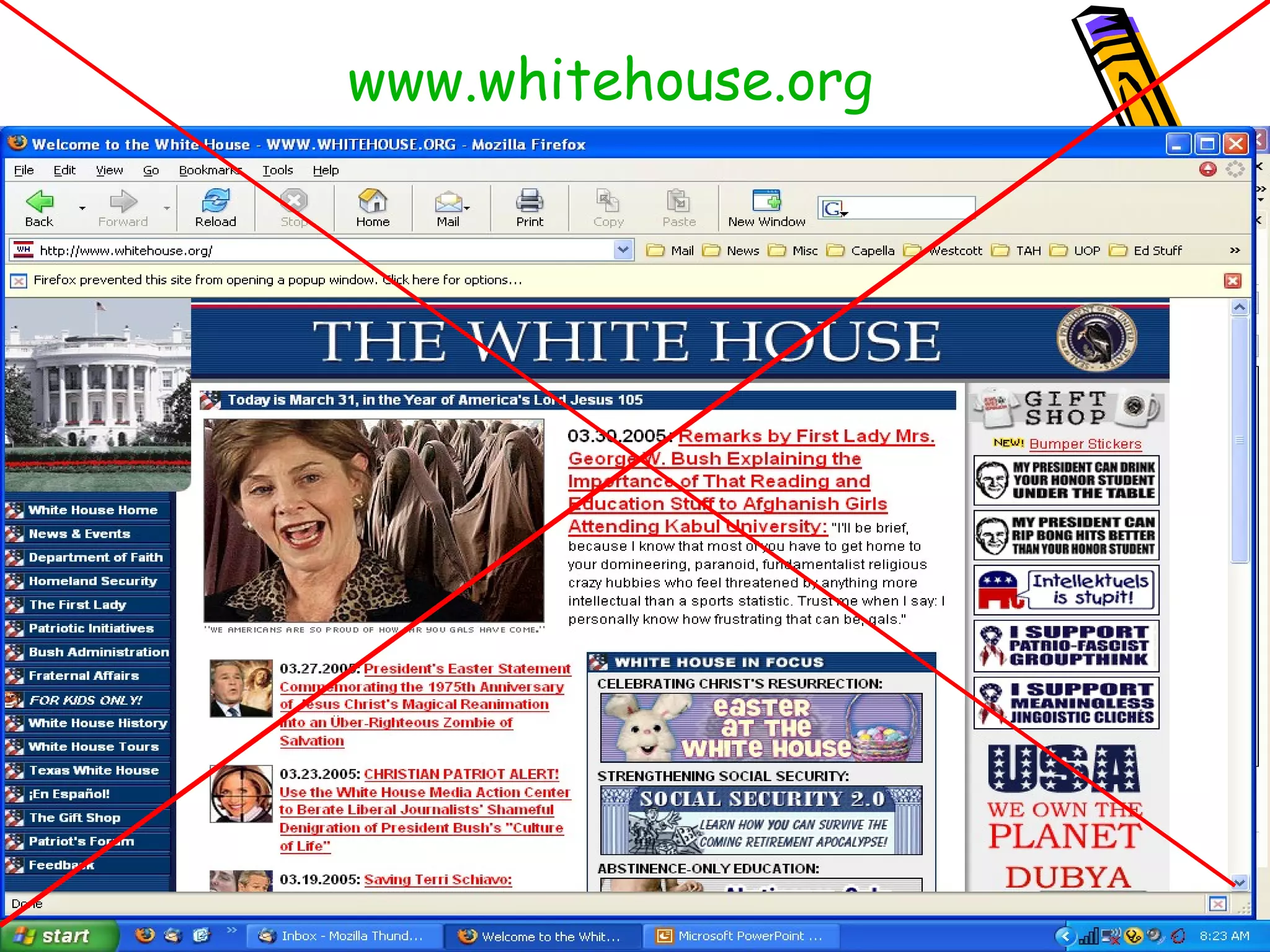
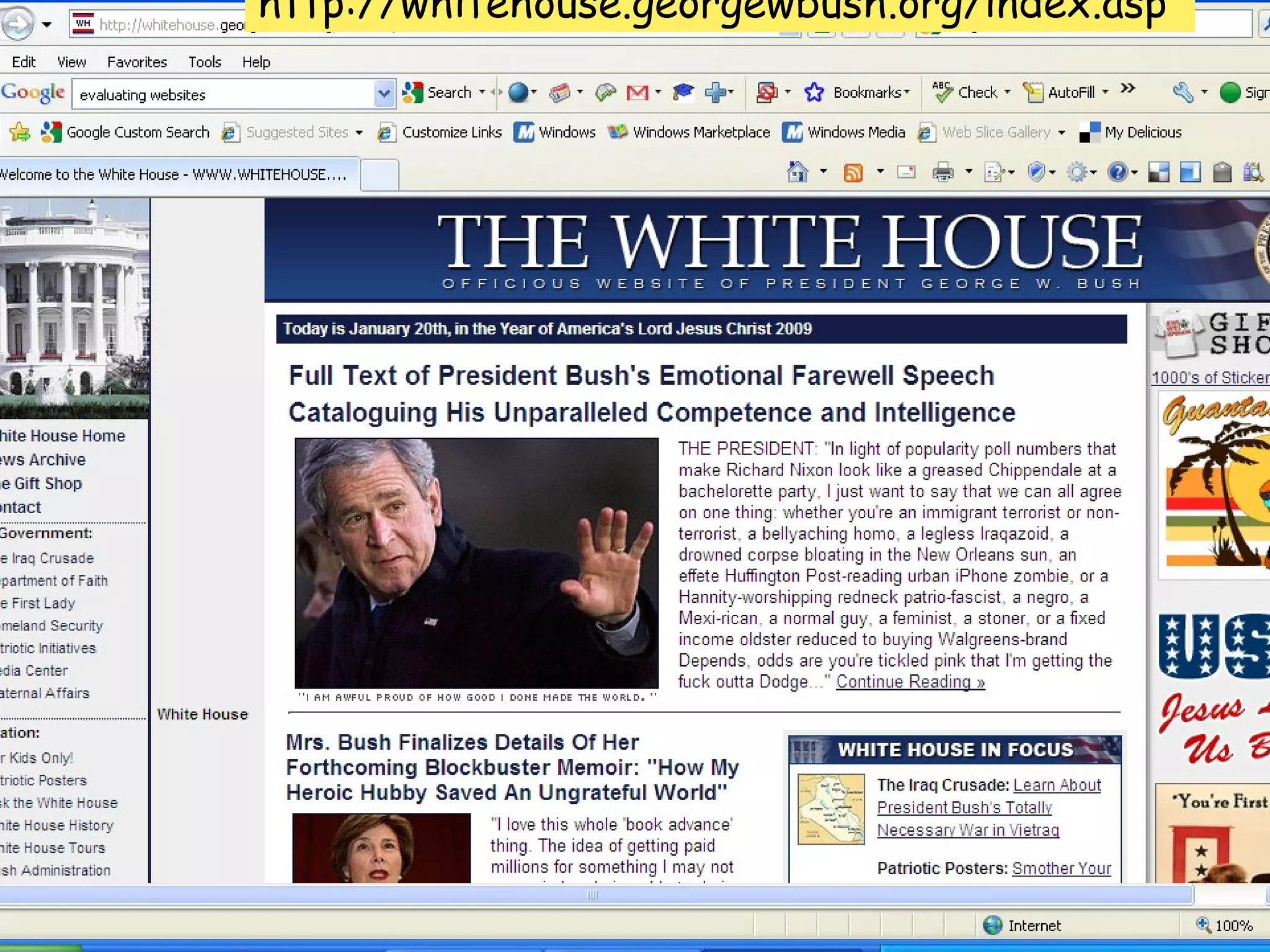
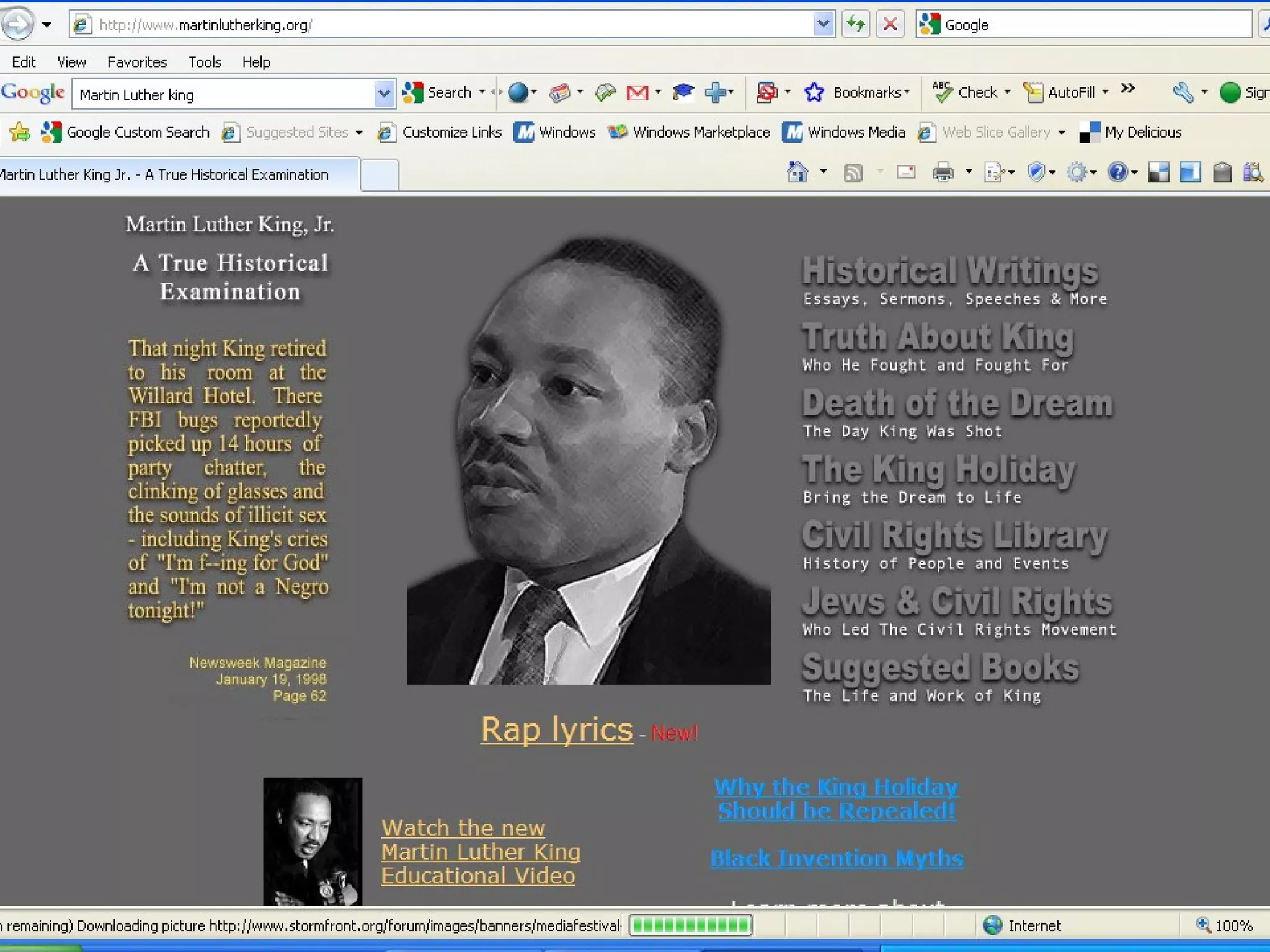
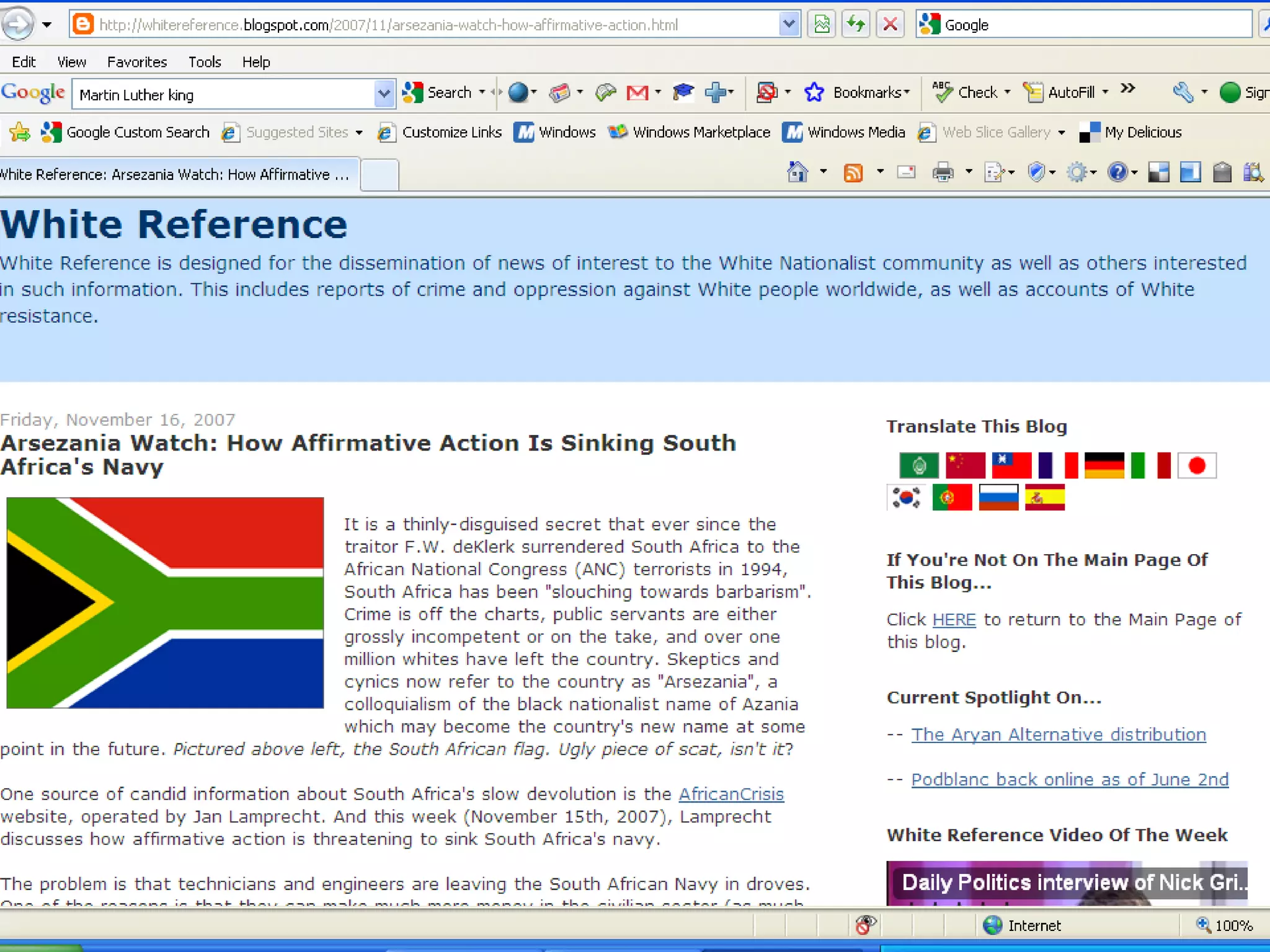
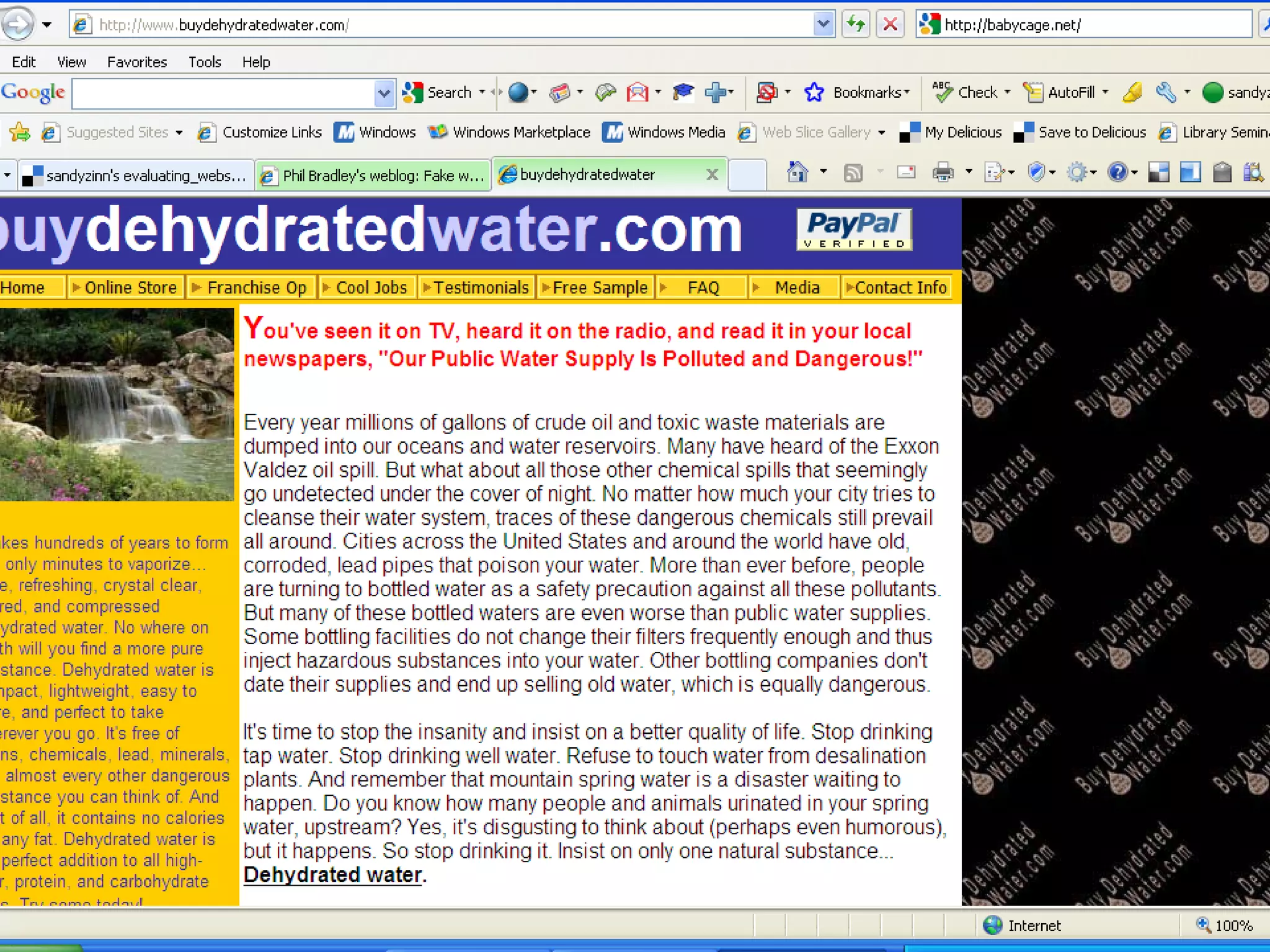
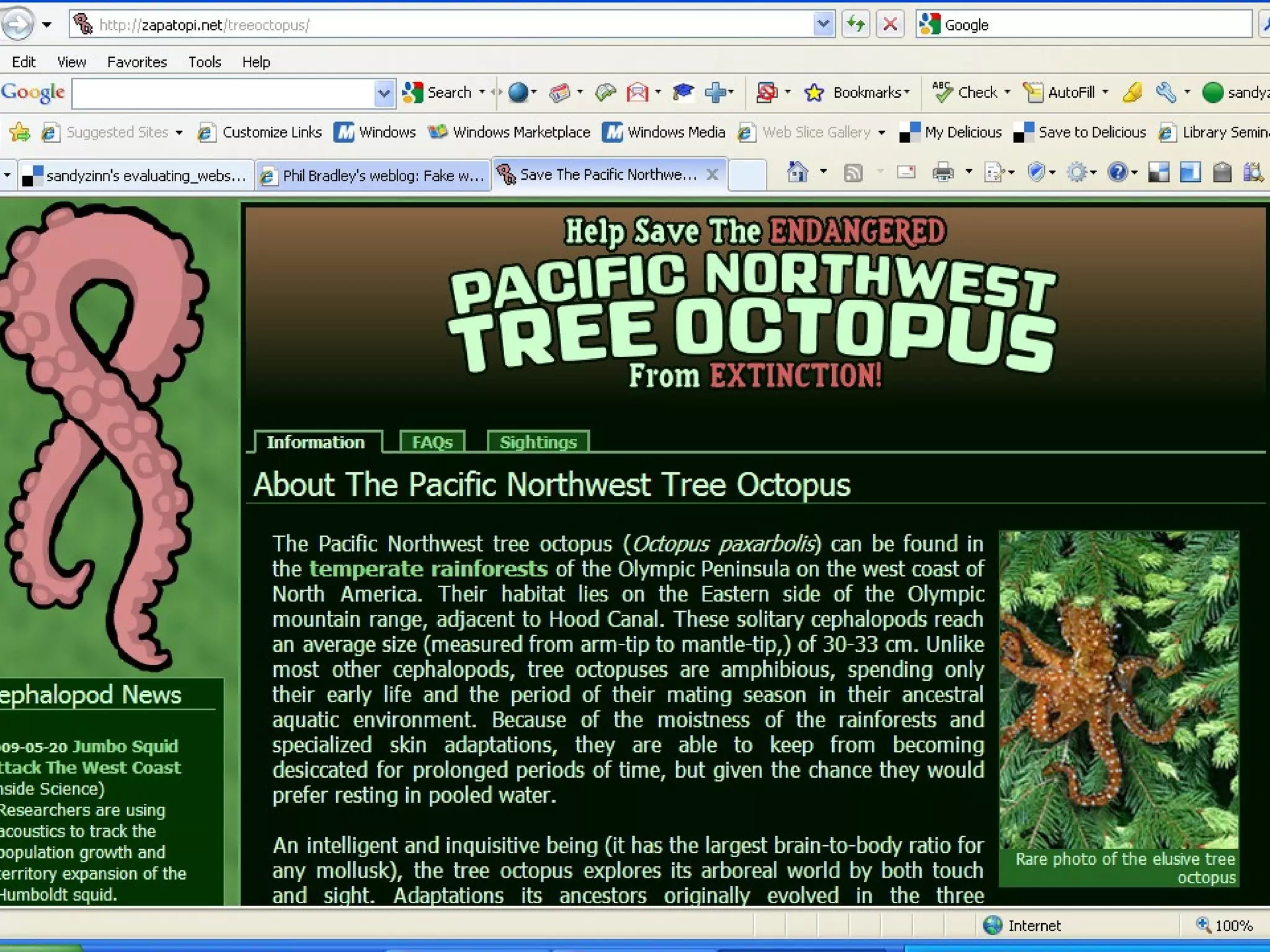
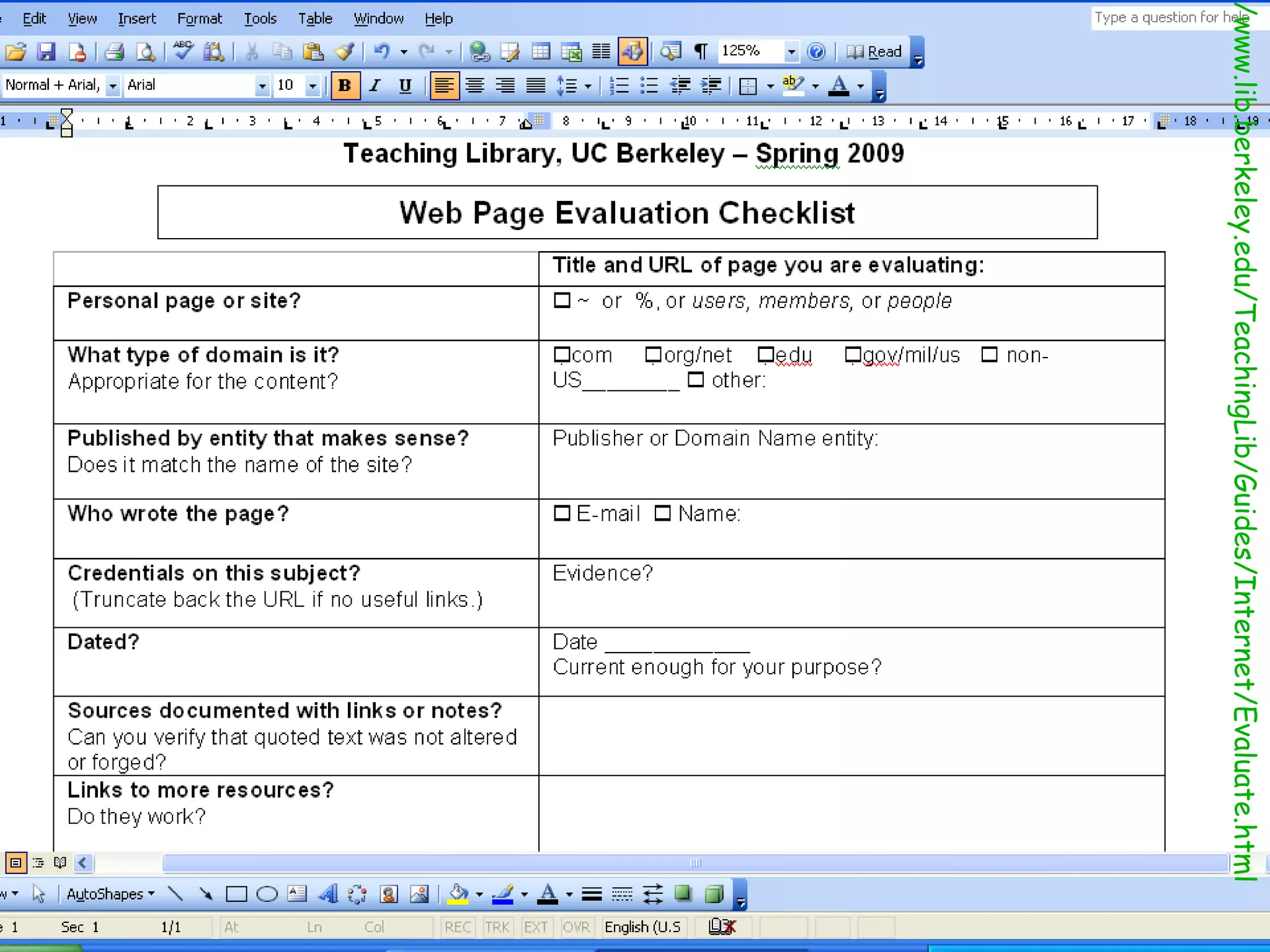
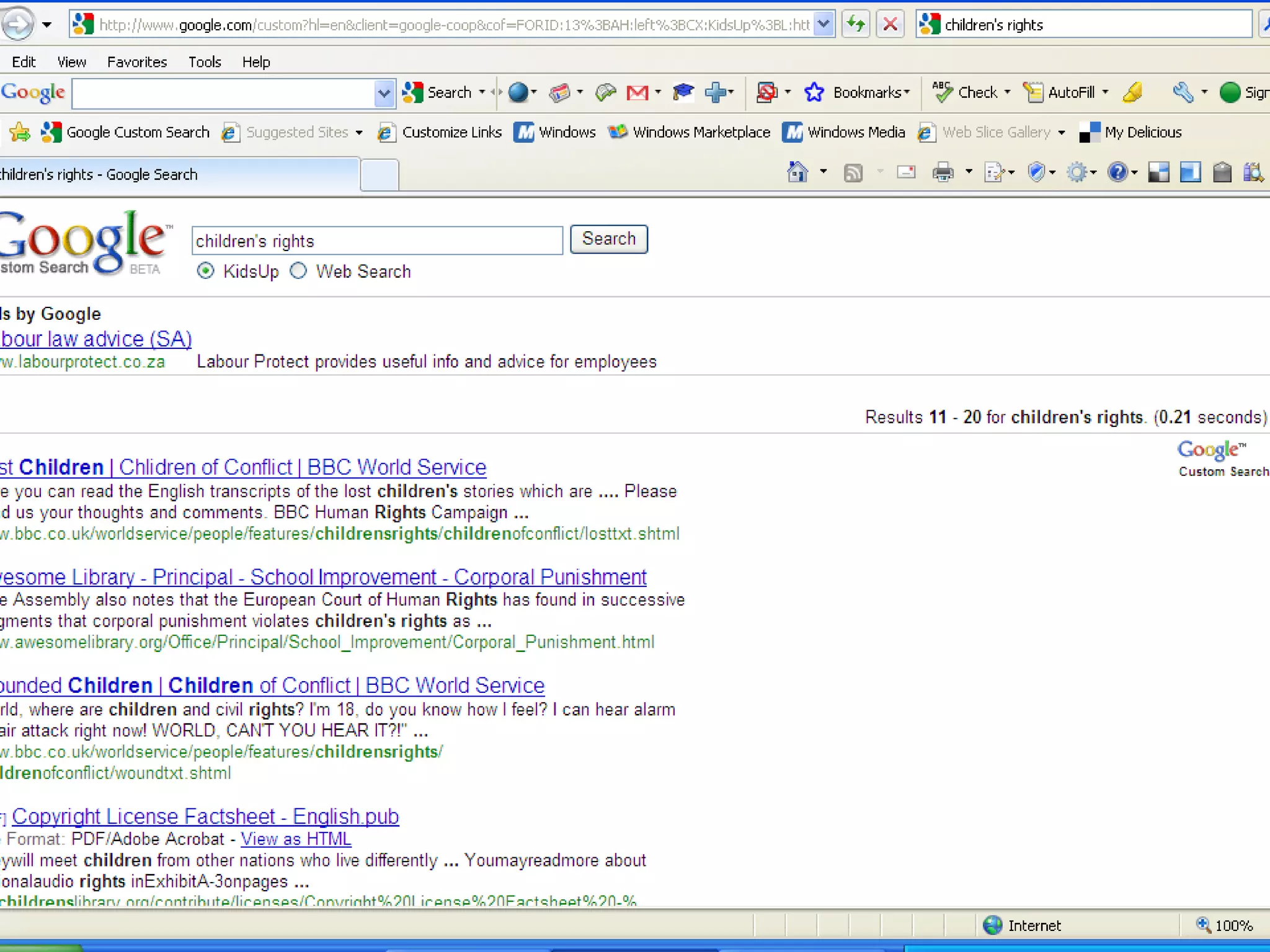
The document discusses the importance of evaluating websites for learners and provides criteria and tools that teachers can use to evaluate websites. It notes that with the amount of information on the web, evaluating websites is important to find credible sources and prevent learners from accessing inappropriate content. It then provides detailed criteria for teachers to use to evaluate websites, including evaluating the authority, content, and design of websites. Lastly, it discusses alternatives to evaluating websites like using specialized search engines designed for kids and creating a customized search engine.































![For example Foods Standards Agency (2003). What is BSE? [Online]. Available http:// www.foodstandards.gov.uk/bse [Accessed 4 April 2006]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2009evaluatingwebsitesforlearners-090604043628-phpapp01/75/Evaluating-Websites-For-Learners-51-2048.jpg)
![Thank You! Questions? Contact: [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2009evaluatingwebsitesforlearners-090604043628-phpapp01/75/Evaluating-Websites-For-Learners-52-2048.jpg)