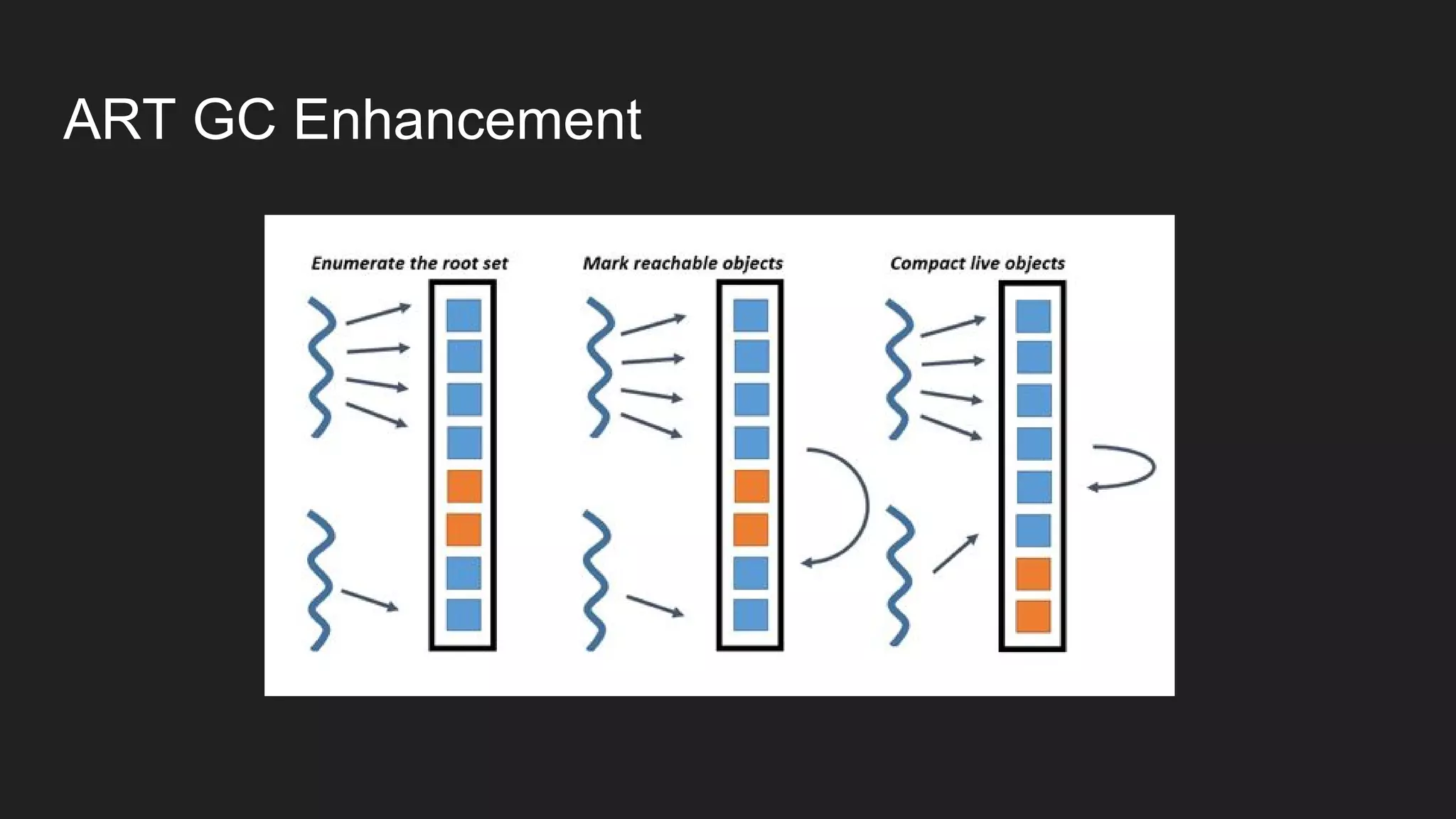
The document discusses Android memory management and how to avoid memory leaks and OutOfMemoryErrors. It covers topics like application memory restrictions, process priority, garbage collection in Dalvik and ART, detecting and avoiding memory leaks, and tools for analyzing memory usage like adb, Android Monitor, Eclipse MAT, and LeakCanary. The document provides tips on how to avoid memory leaks such as not keeping long-lived references and implementing cancellation policies, and how to avoid OutOfMemoryErrors such as using bitmaps efficiently, recycling bitmaps, avoiding unnecessary object creation, and coordinating with the system using onTrimMemory().