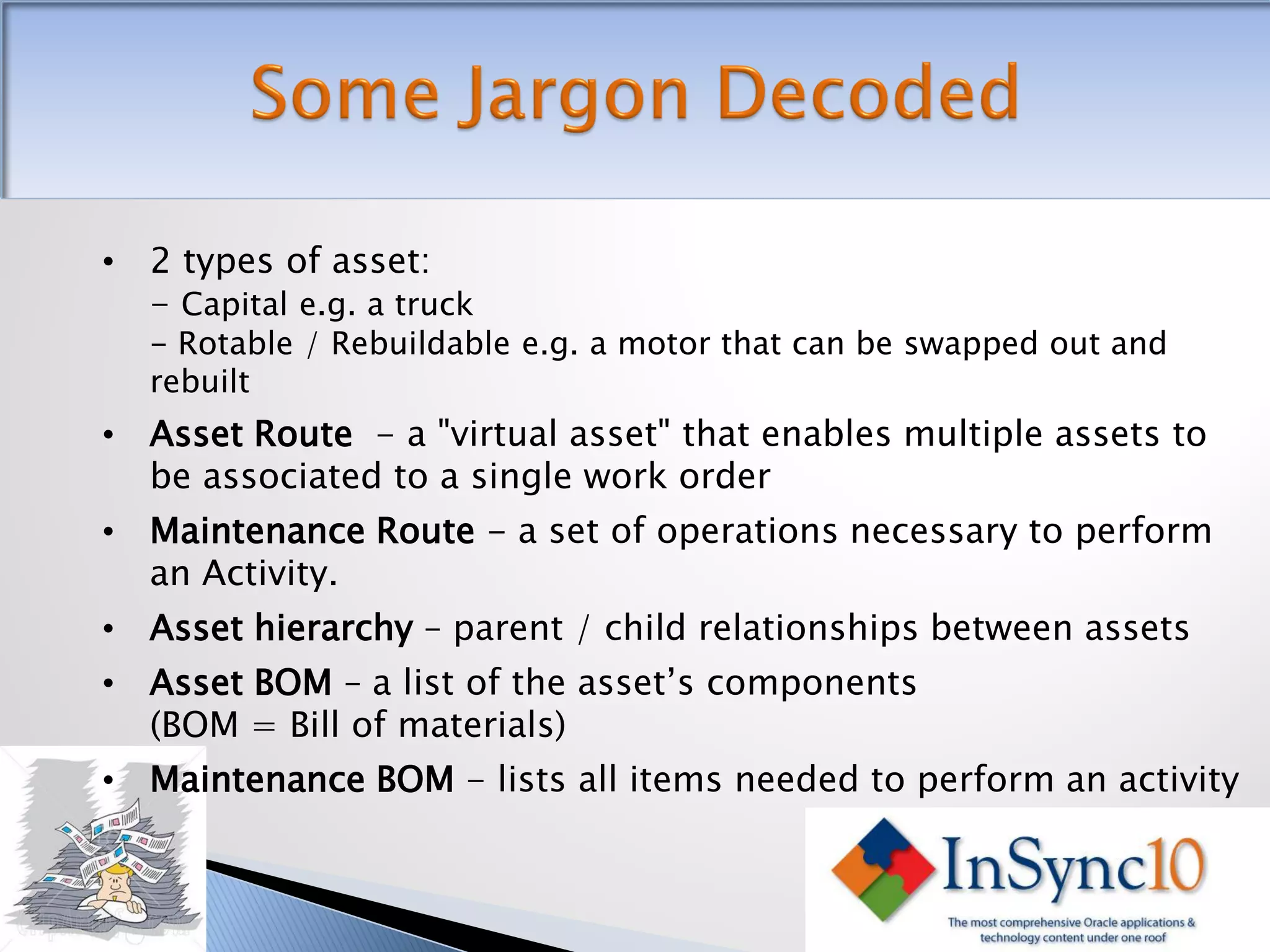
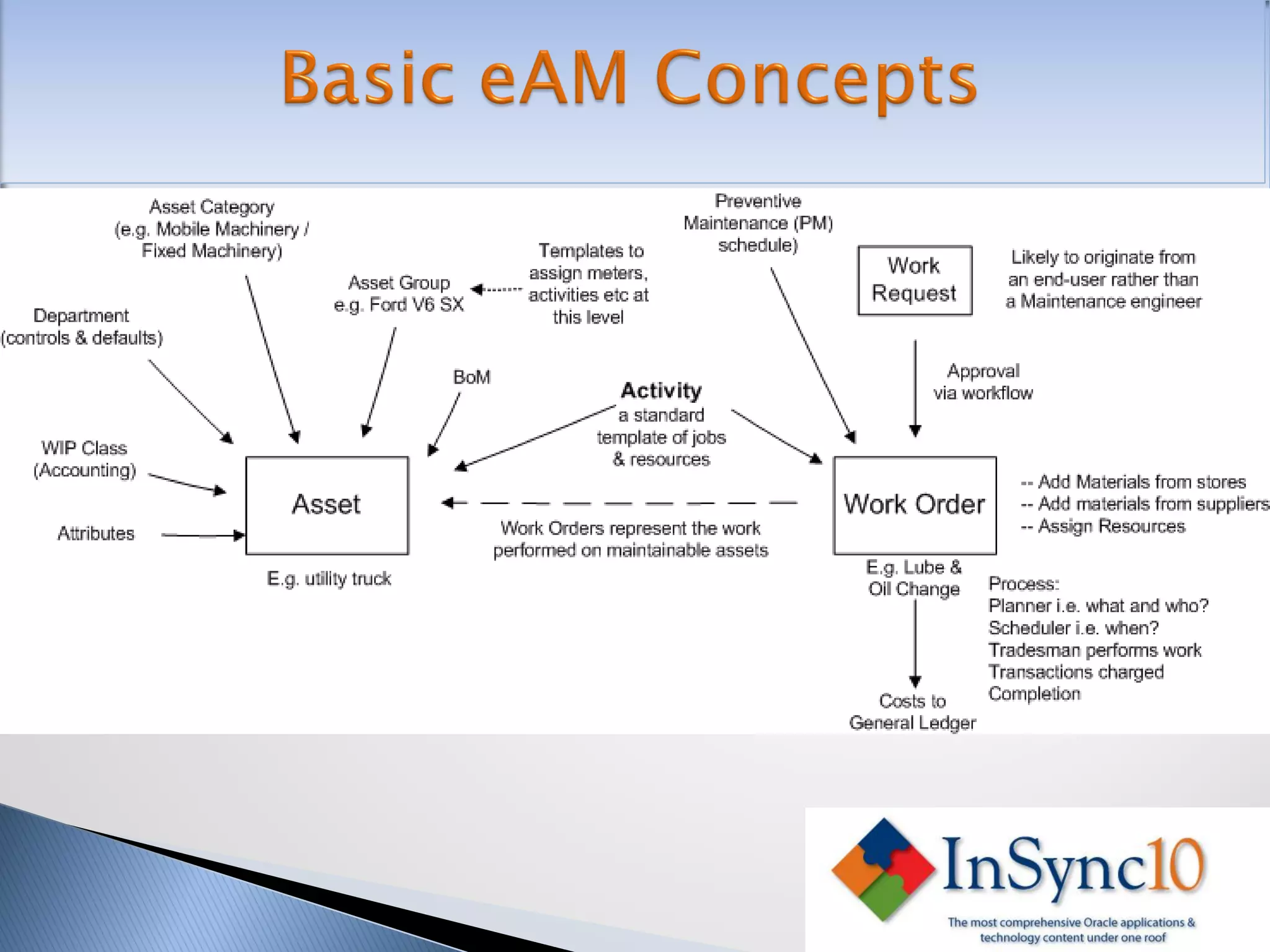
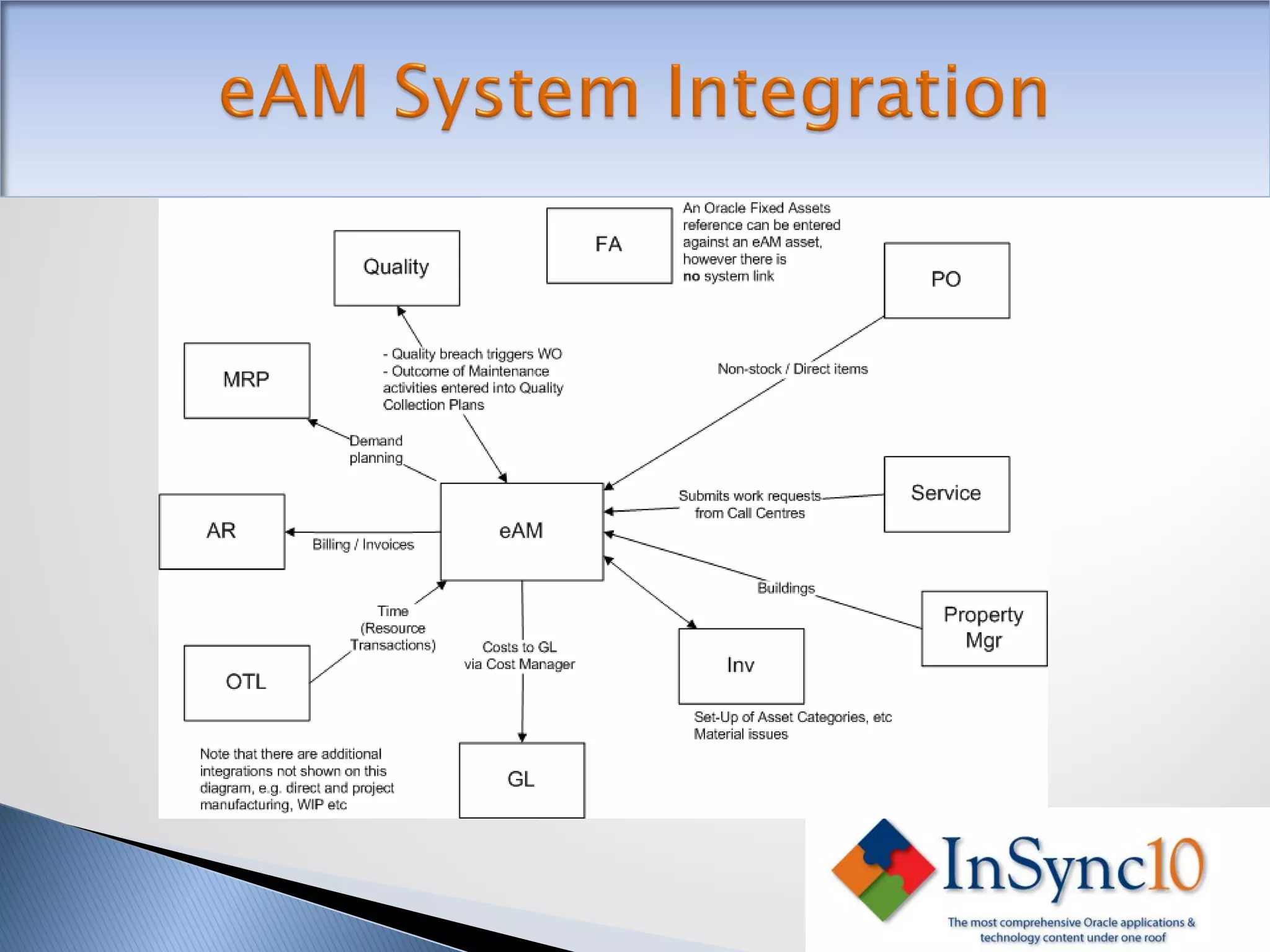
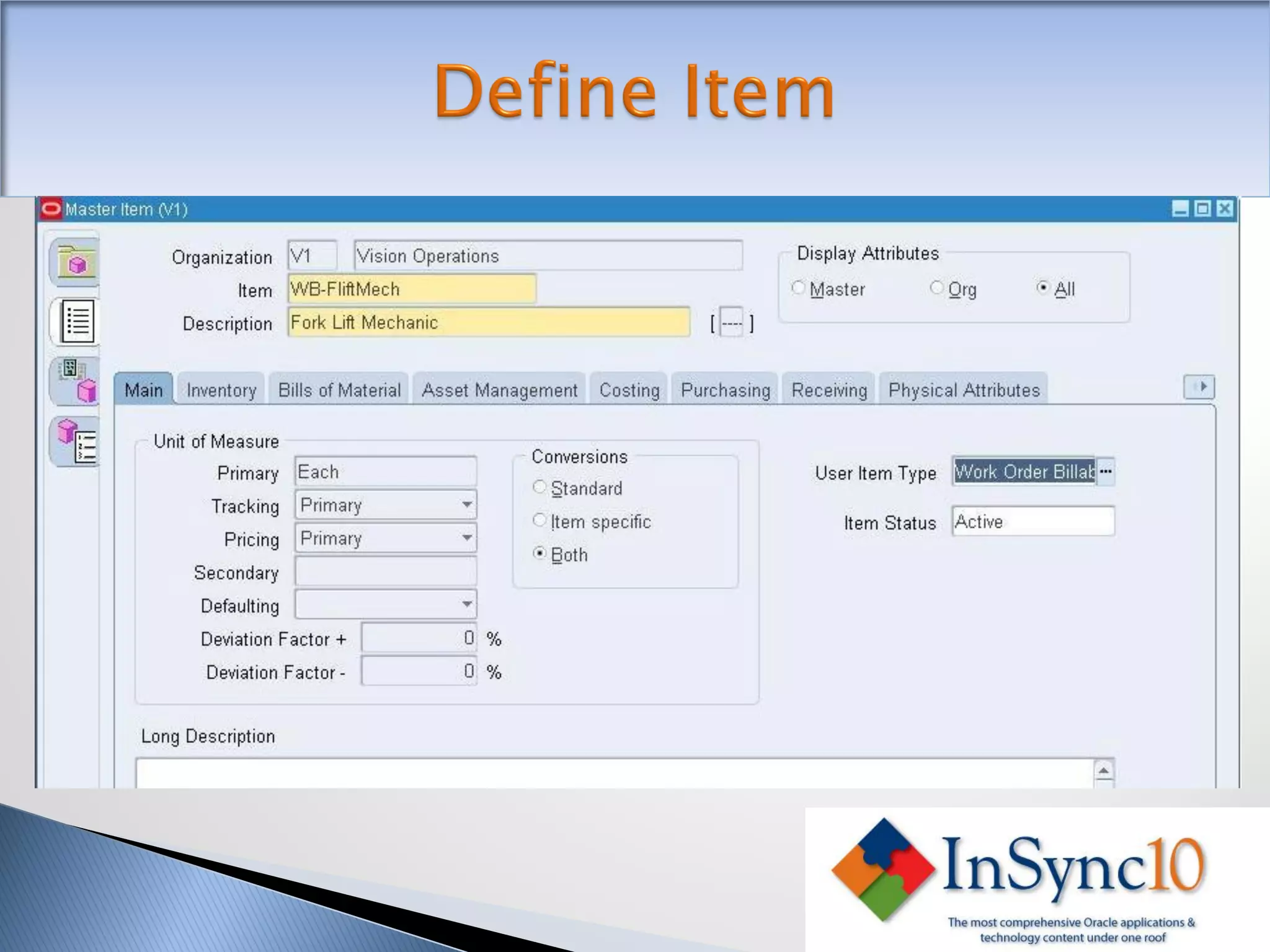
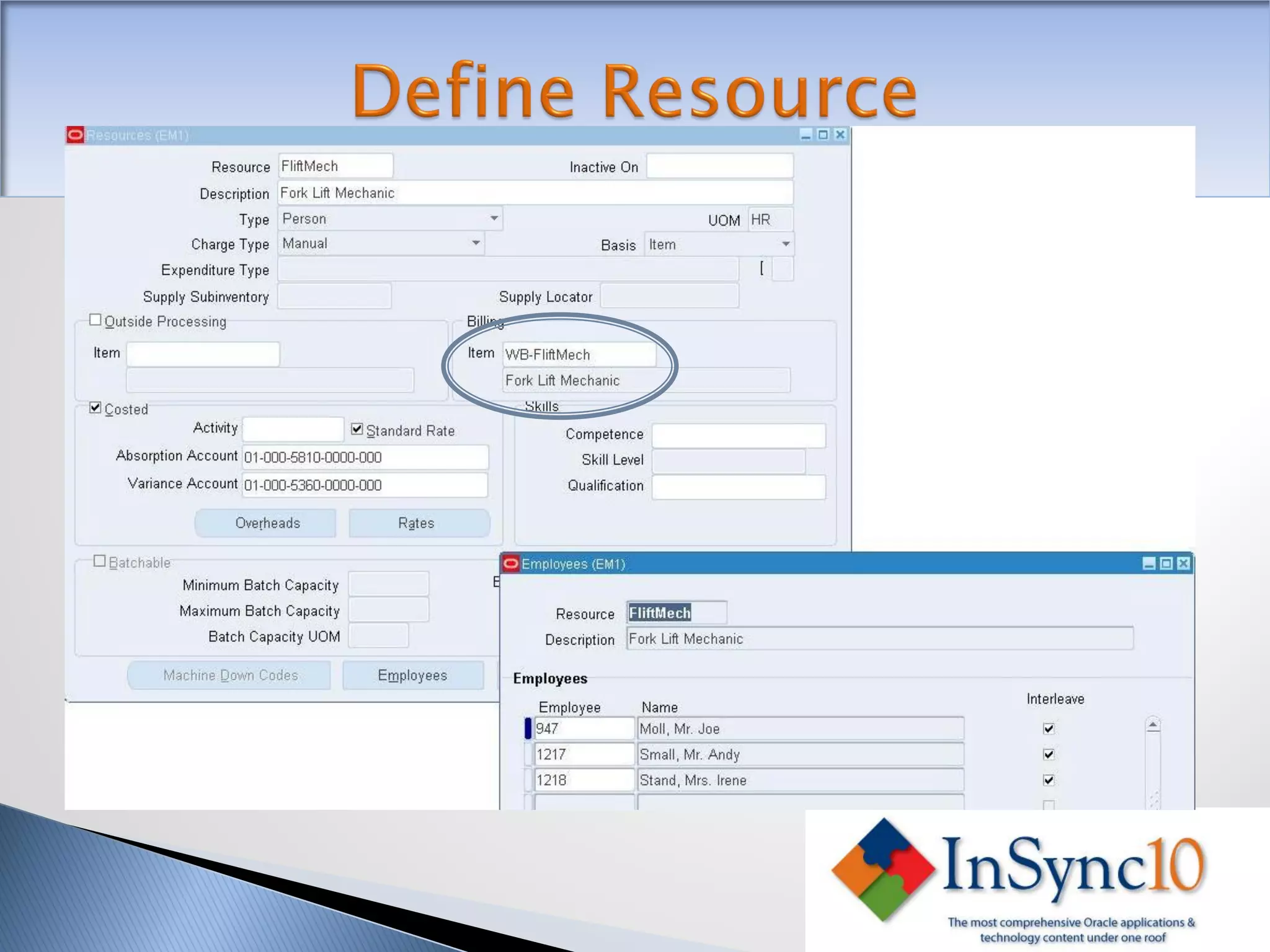
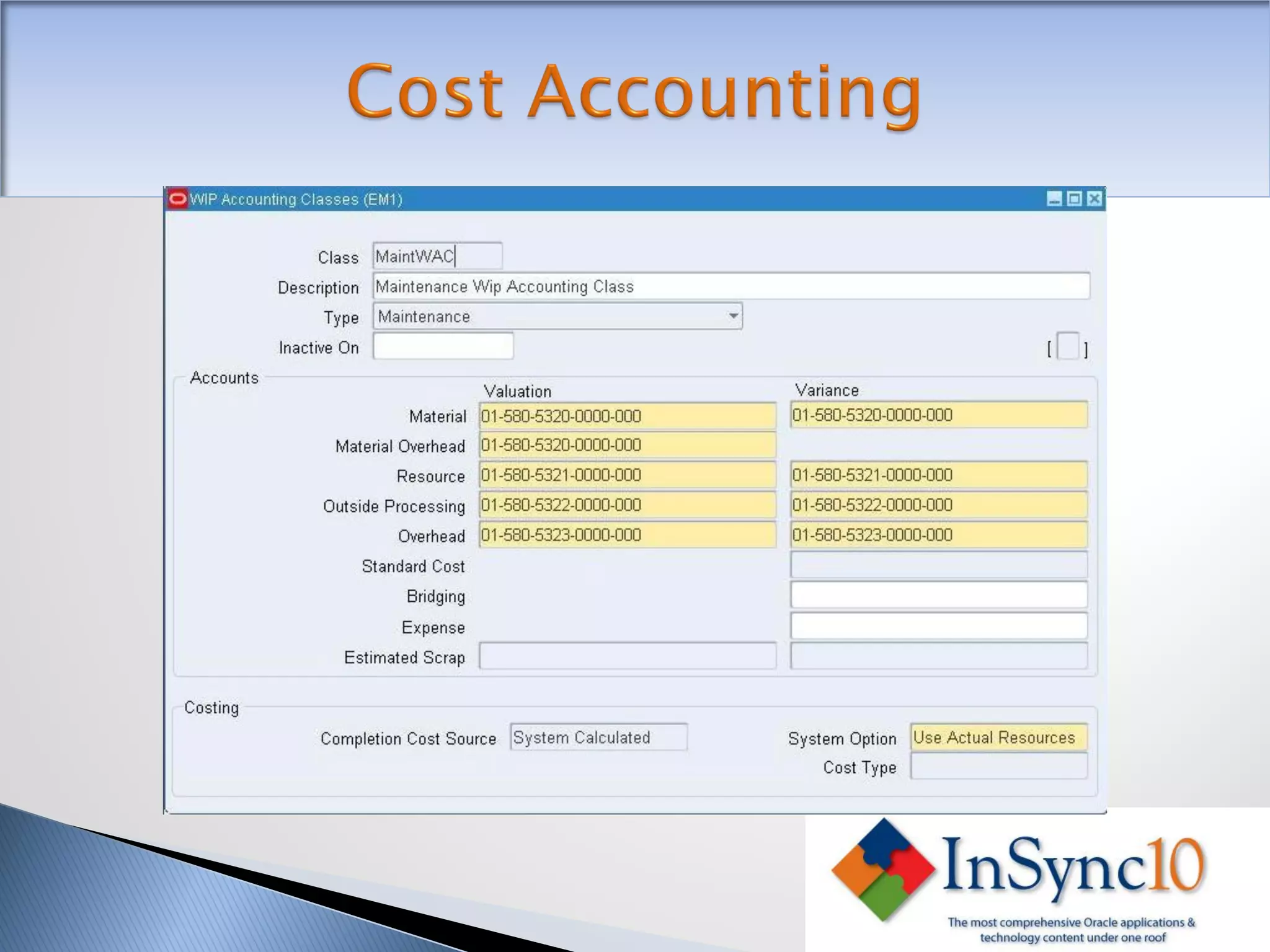
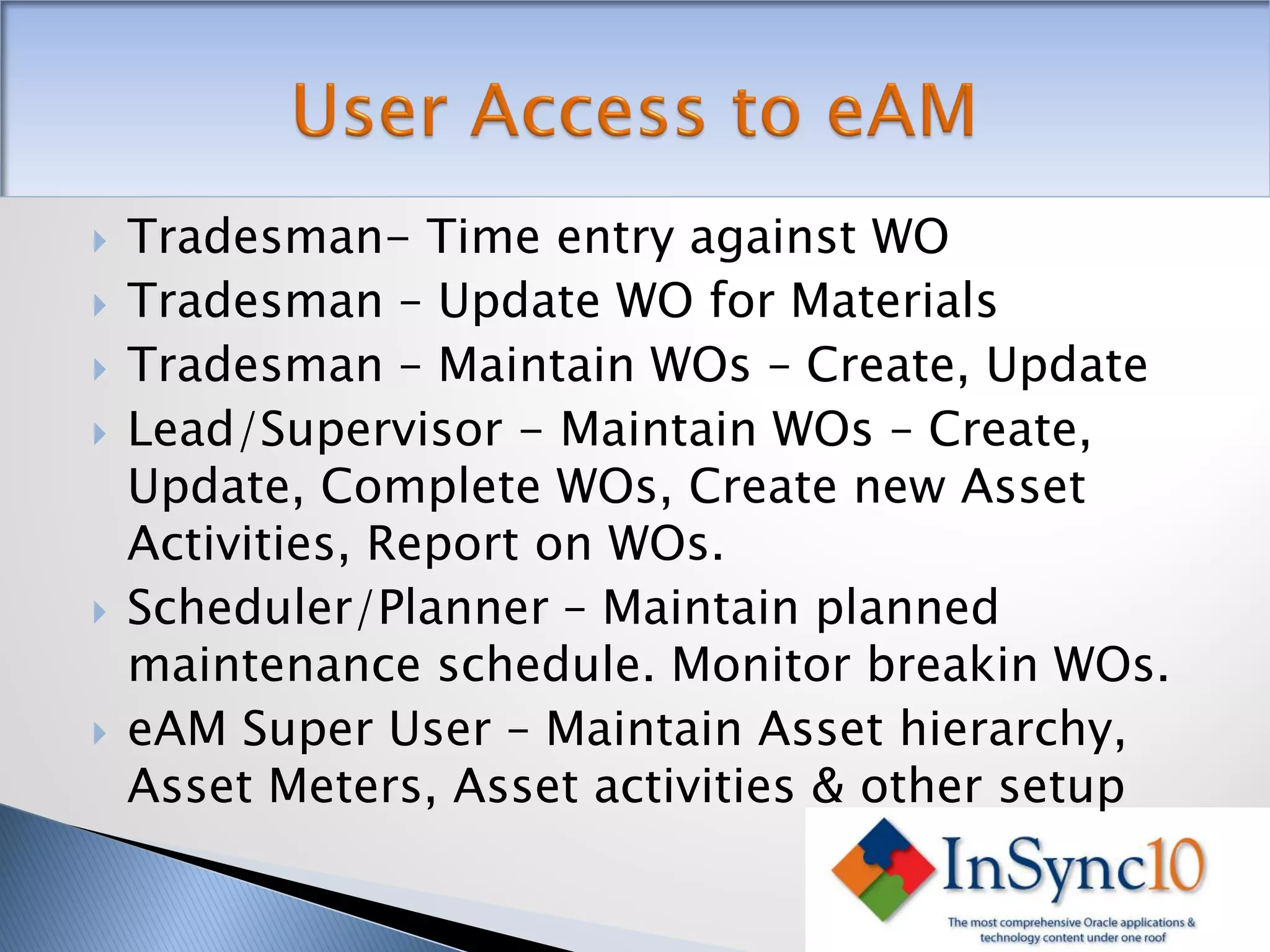
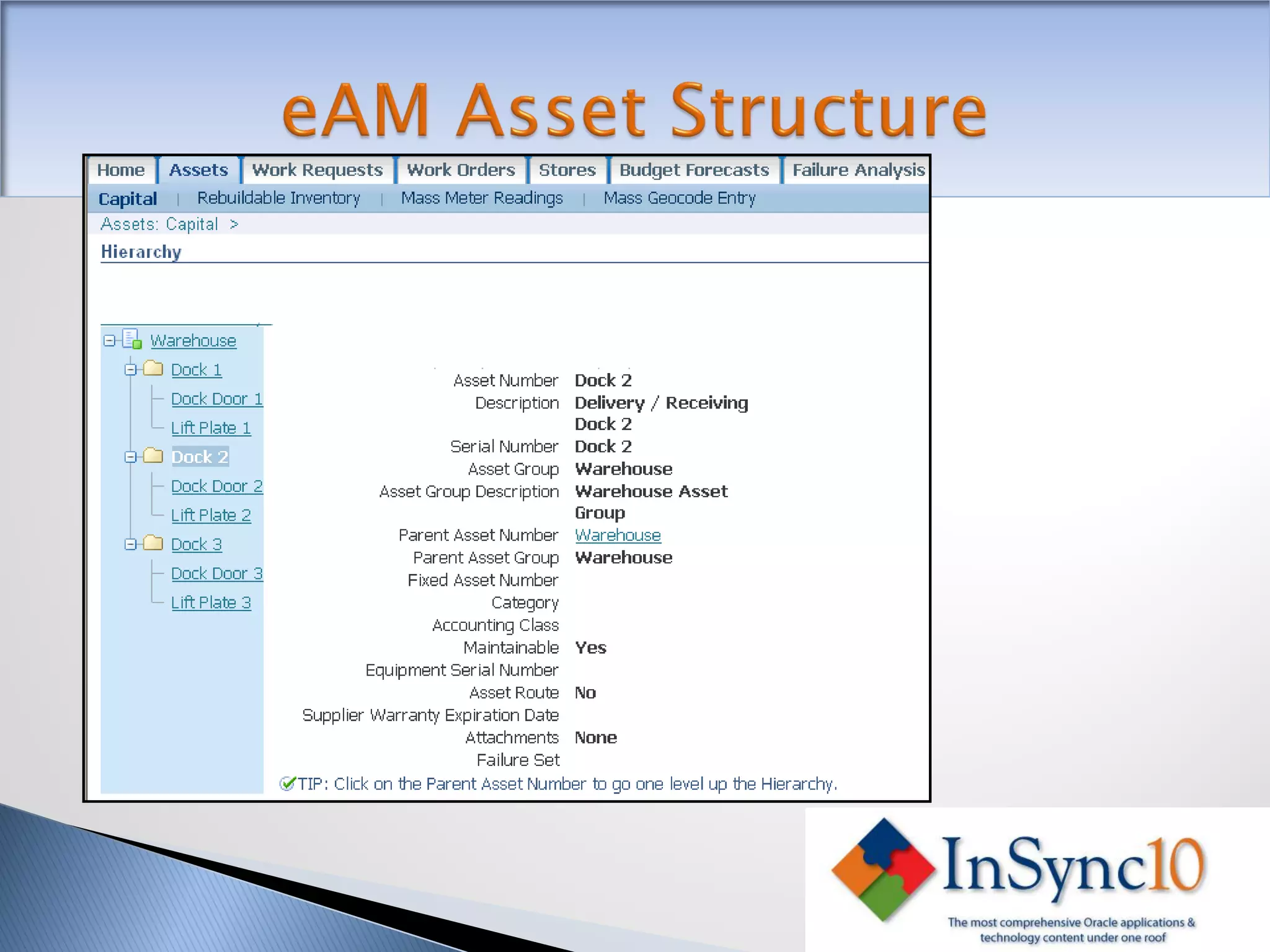
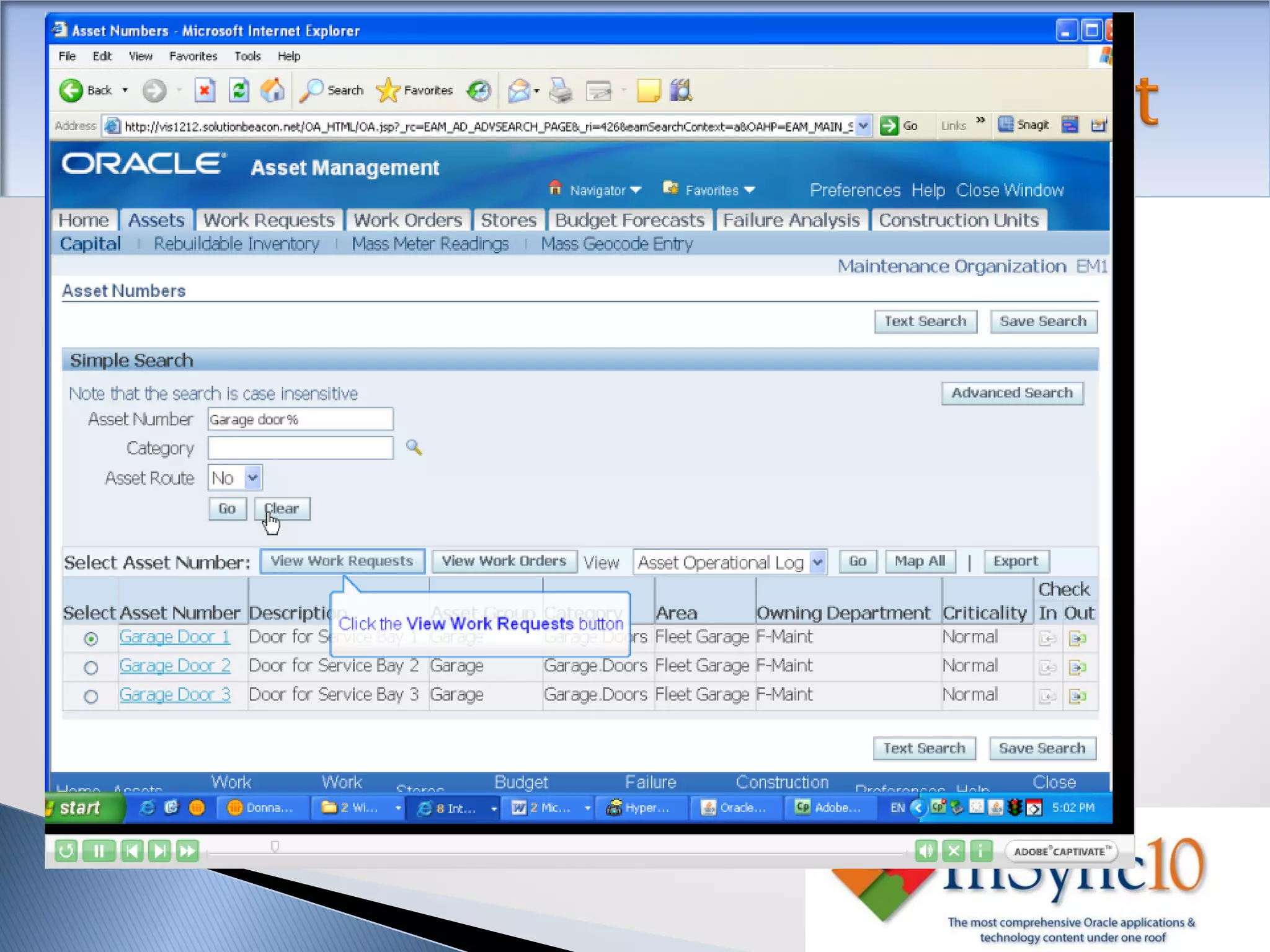
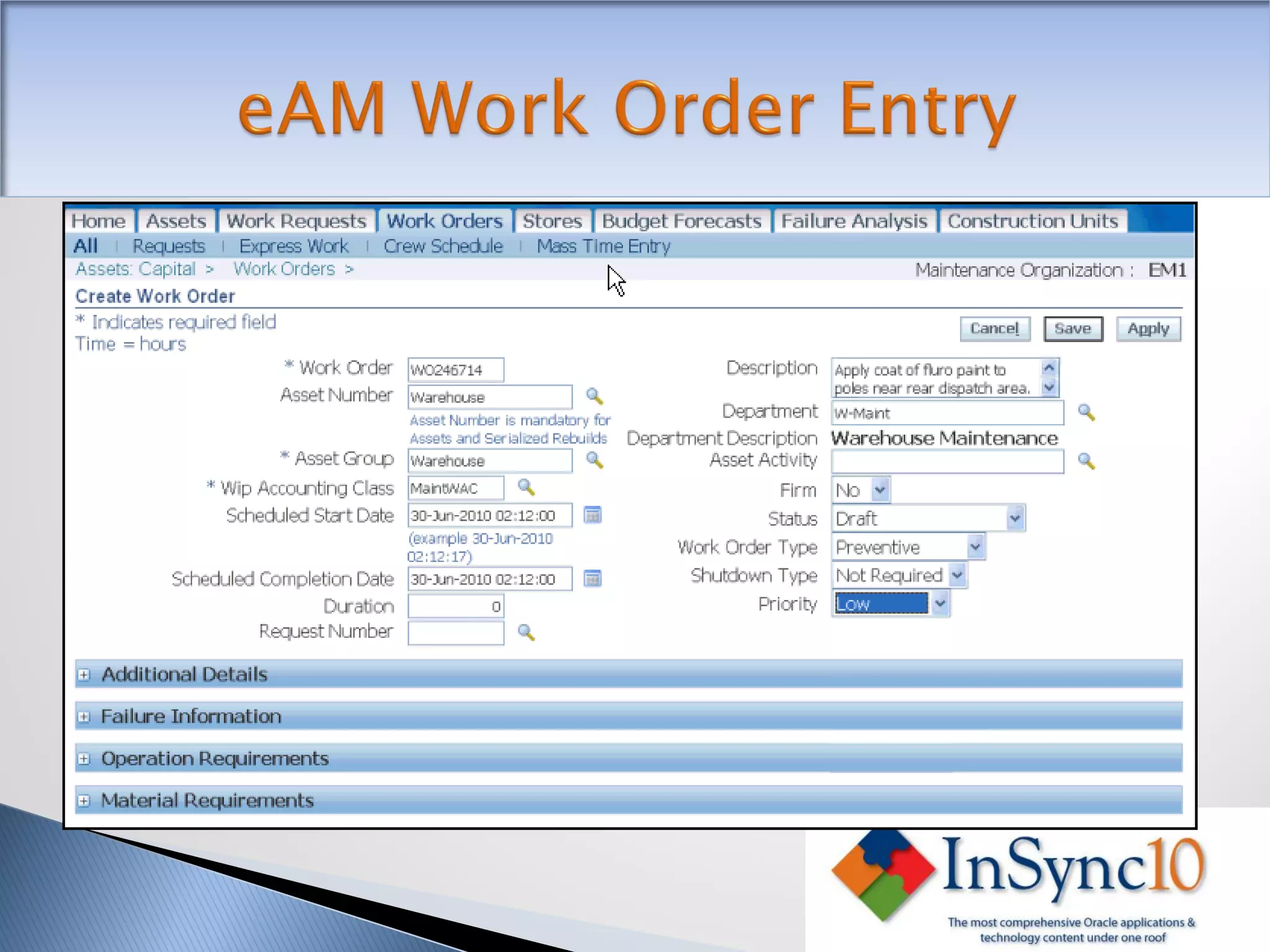
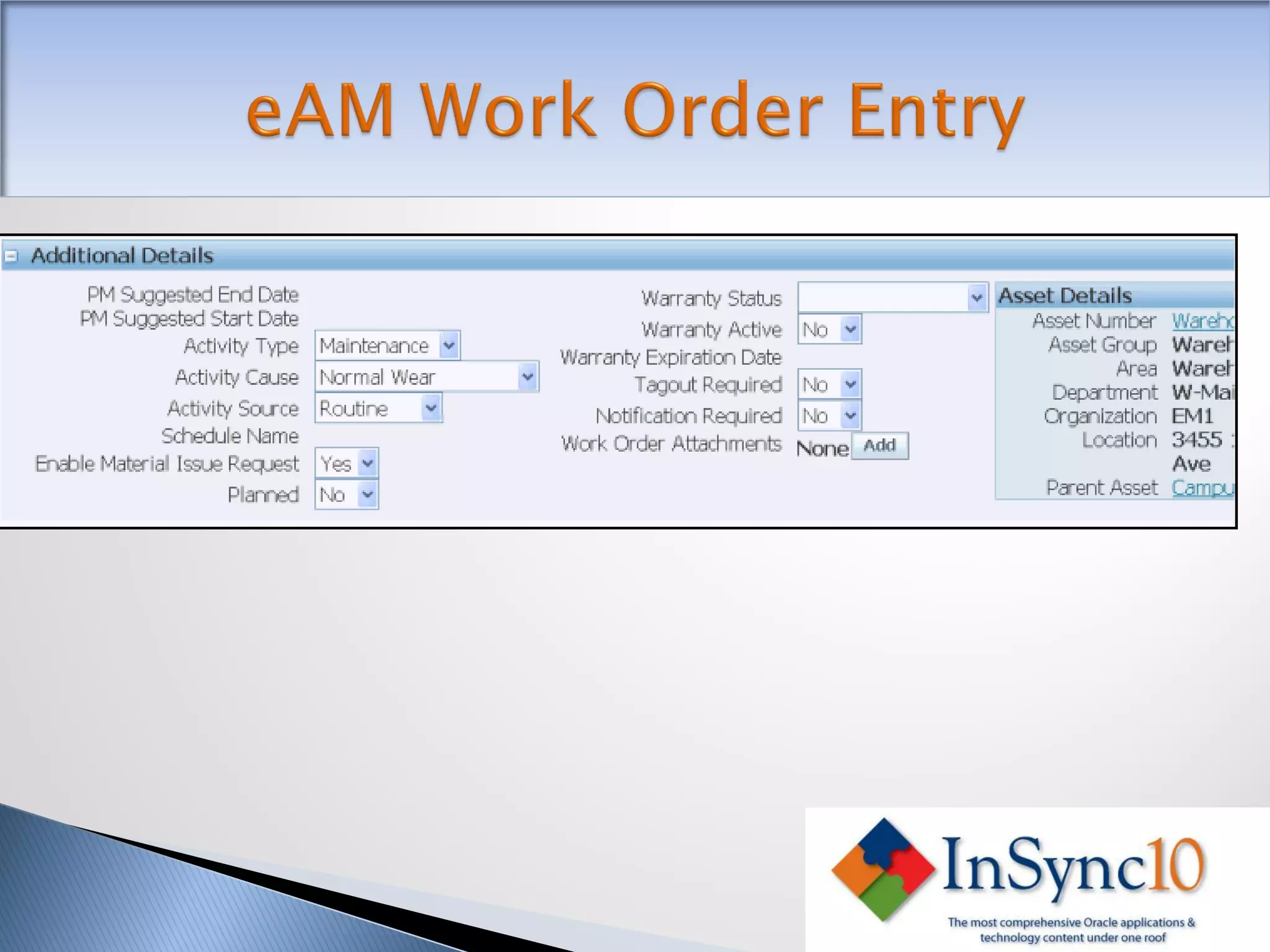
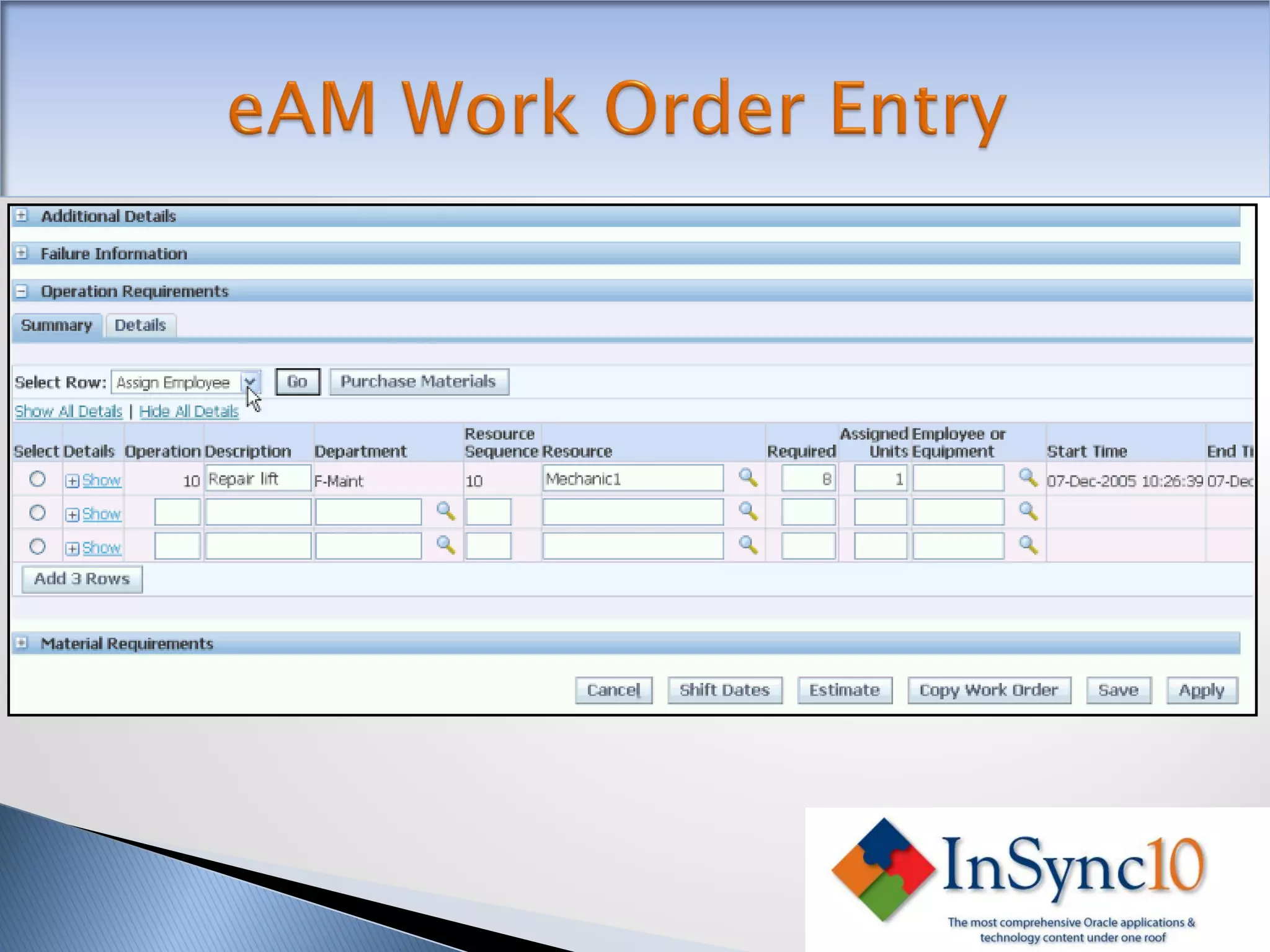
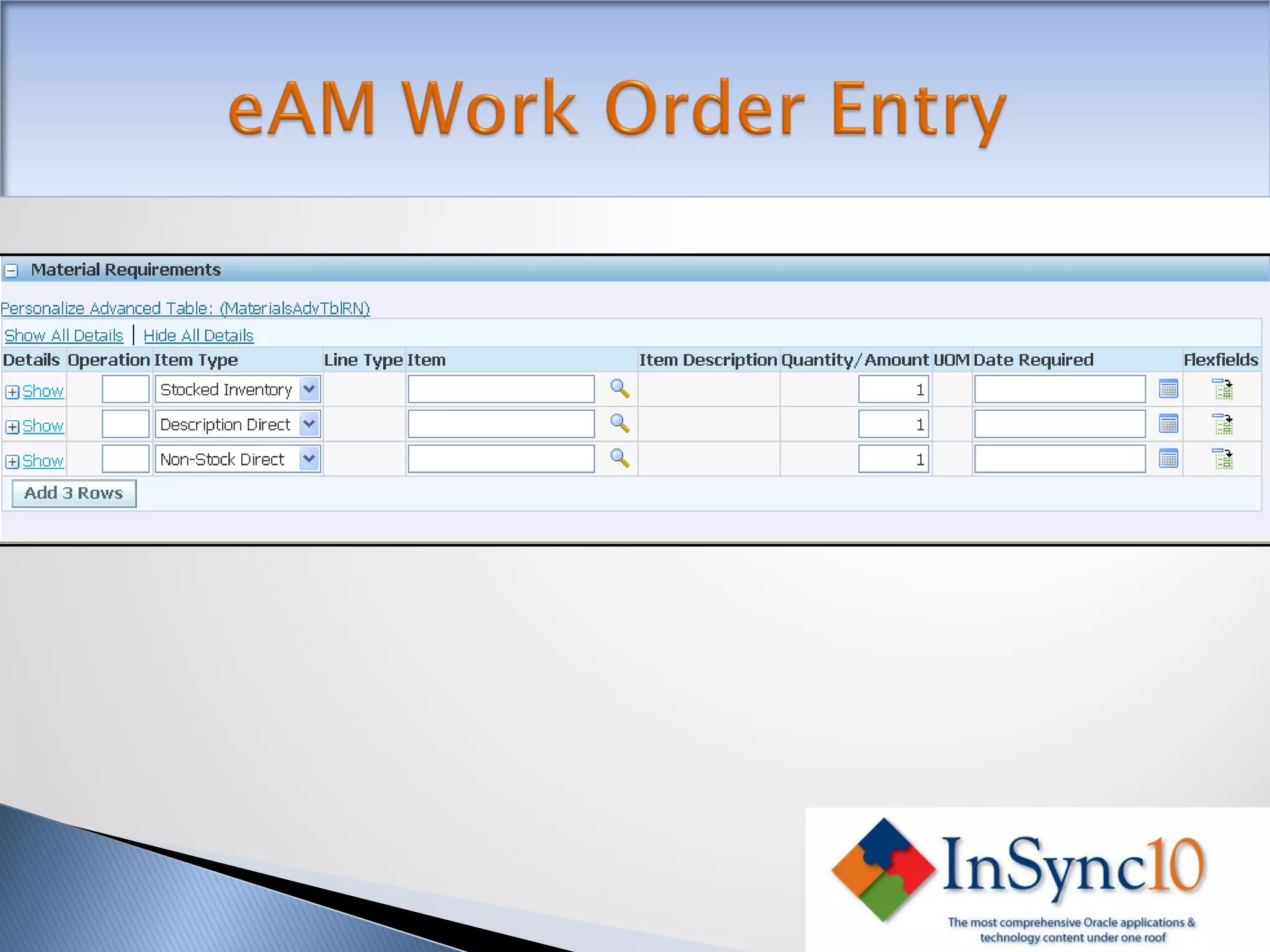
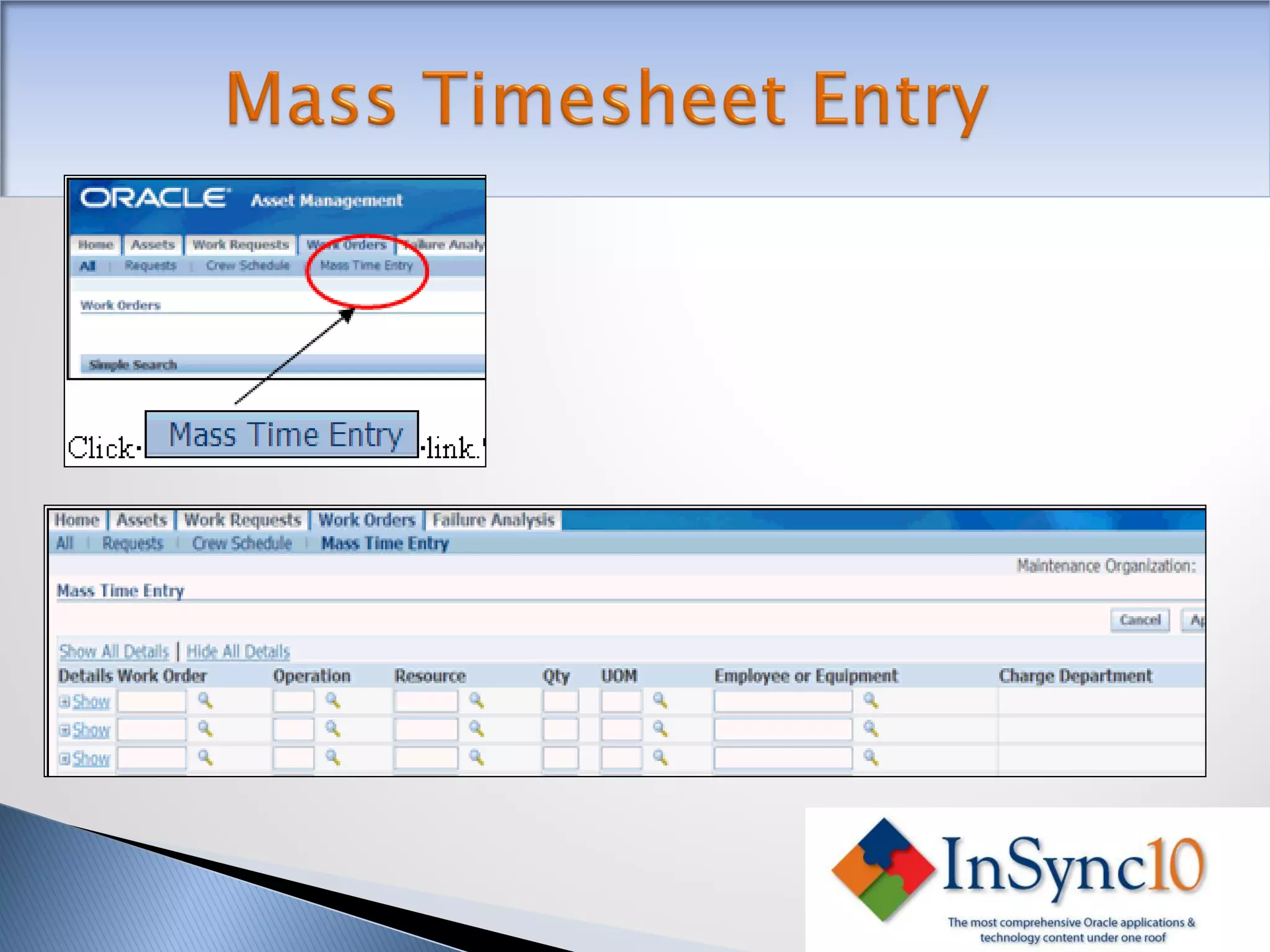
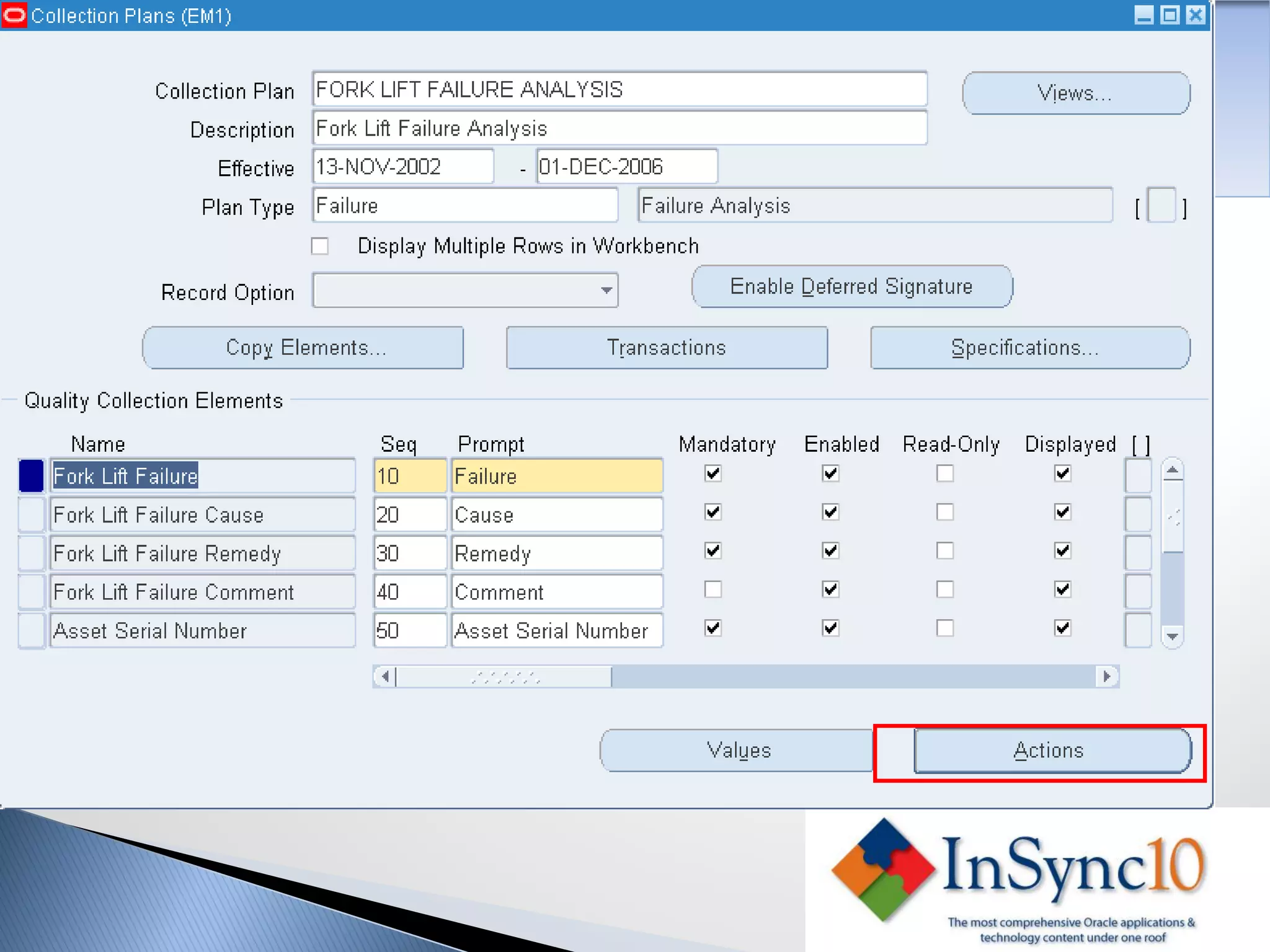
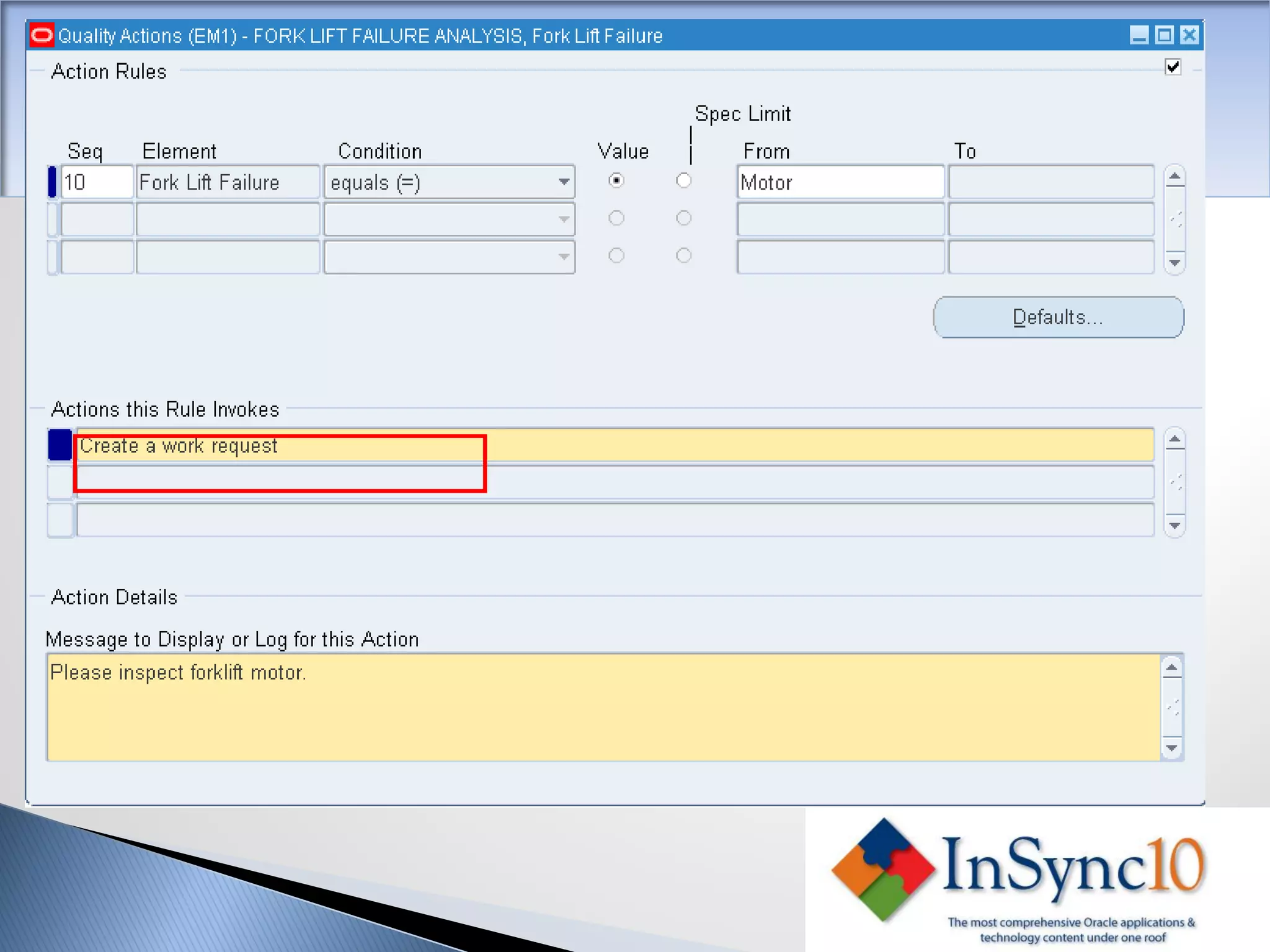
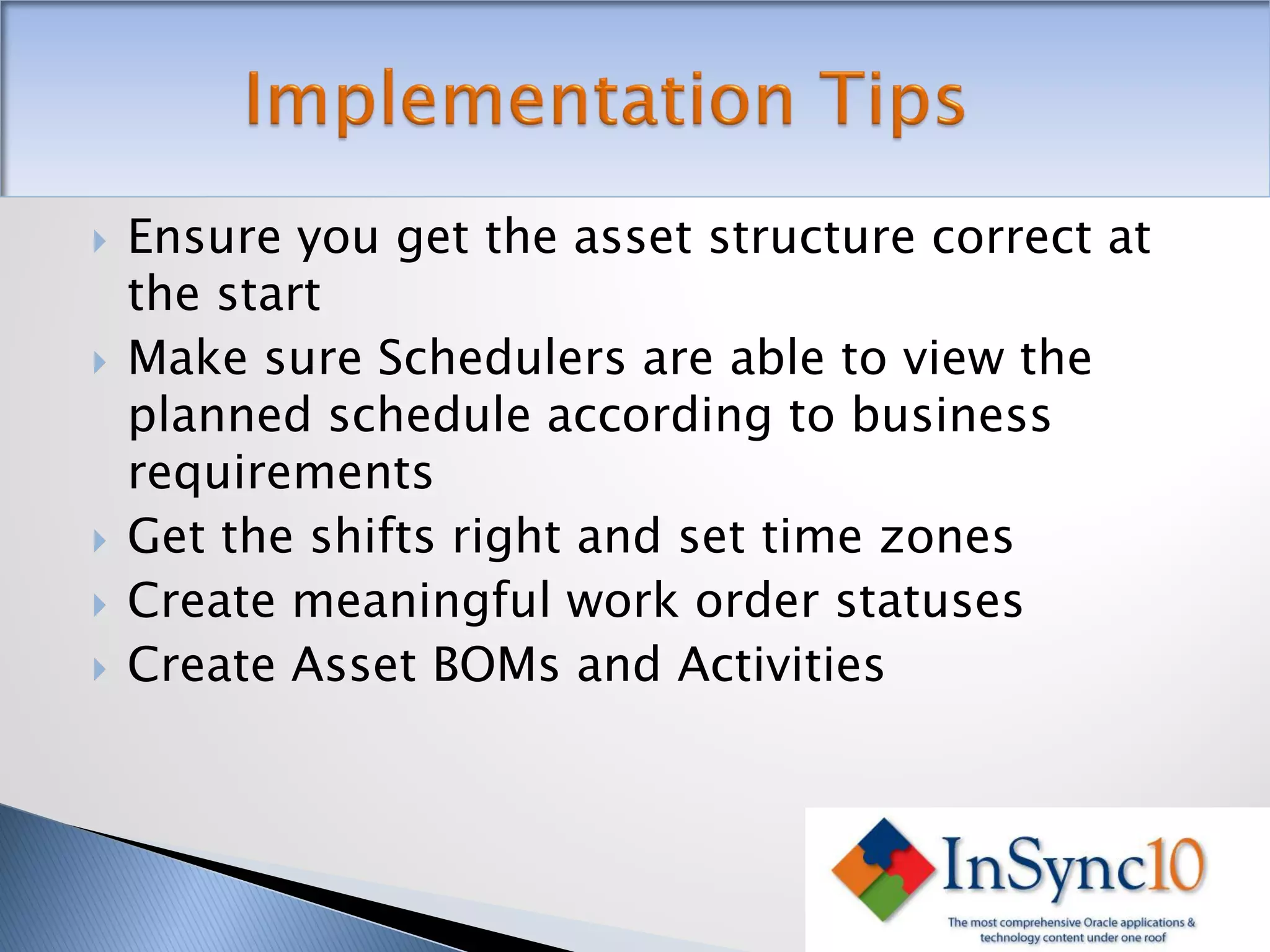
Enterprise Asset Management (eAM) provides an integrated solution for managing, scheduling, and accounting for maintenance of equipment and machinery. It allows organizations to track maintenance costs more efficiently than via spreadsheets. eAM manages assets with a hierarchy and relationships between parent and child assets. It also handles work orders, activities, and interactions between maintenance, procurement, and accounting functions. Successful implementation requires alignment with business needs, testing, training tailored to roles, and ensuring key setup elements like the asset structure and maintenance schedules meet requirements.