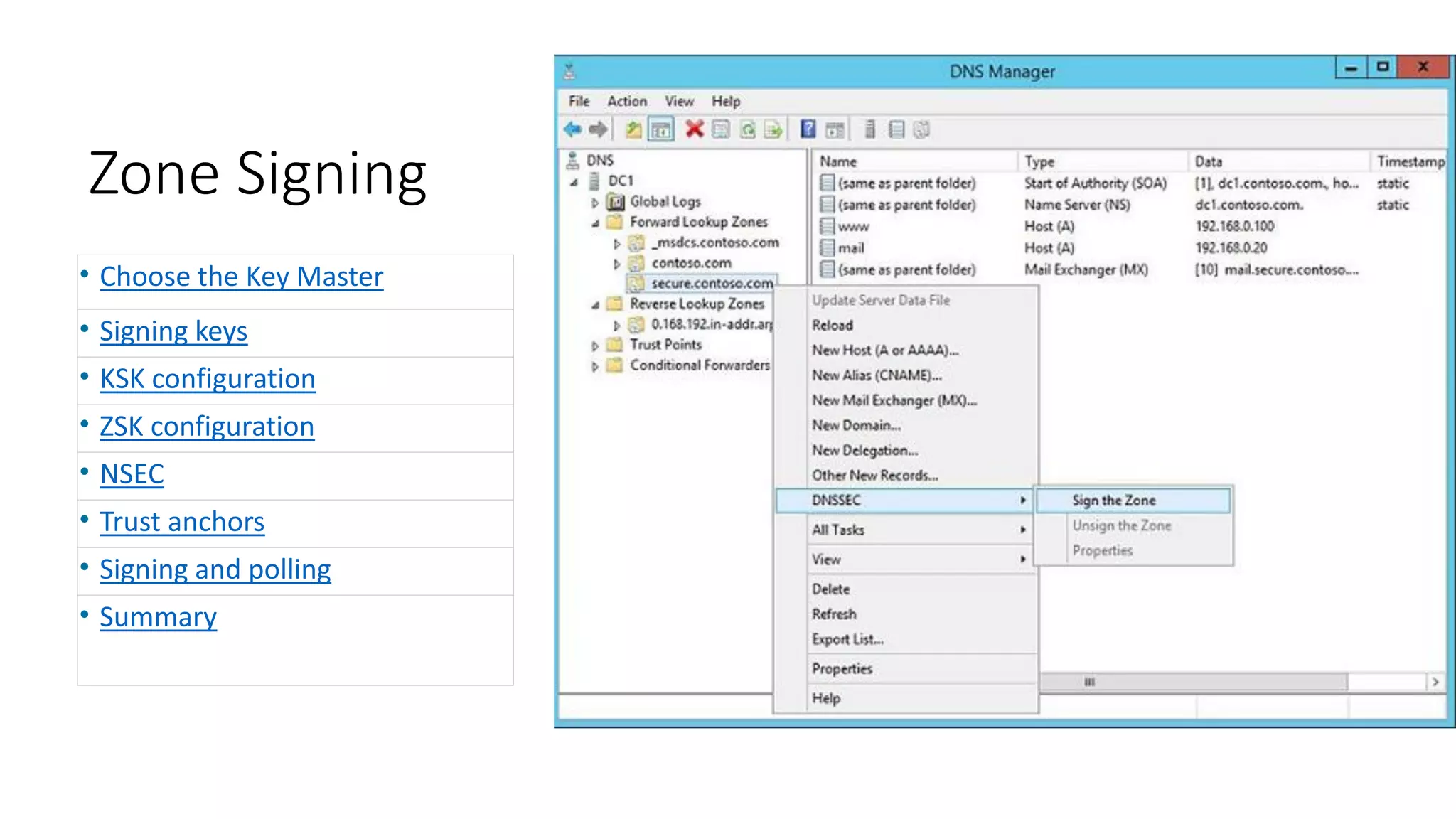
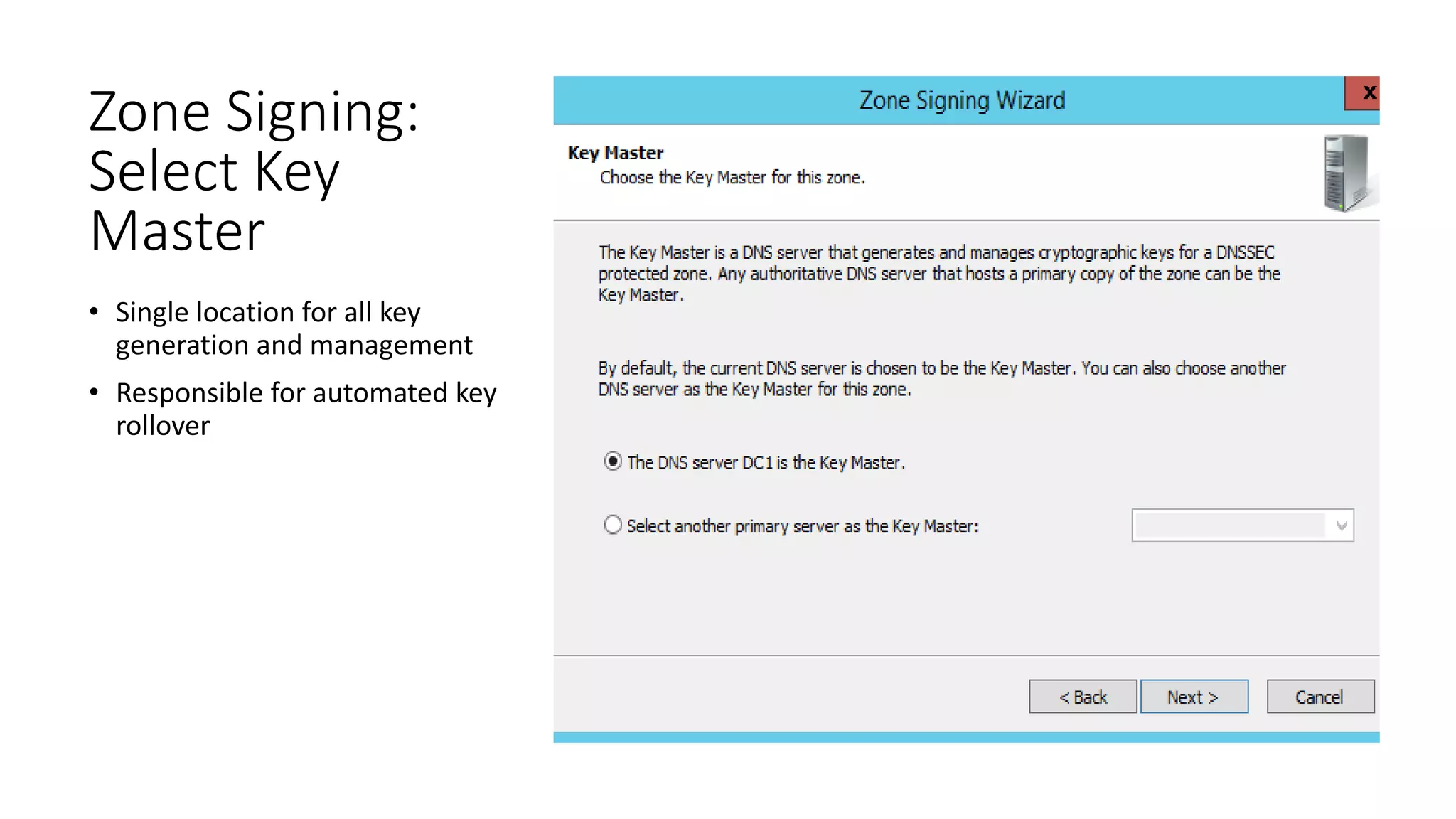
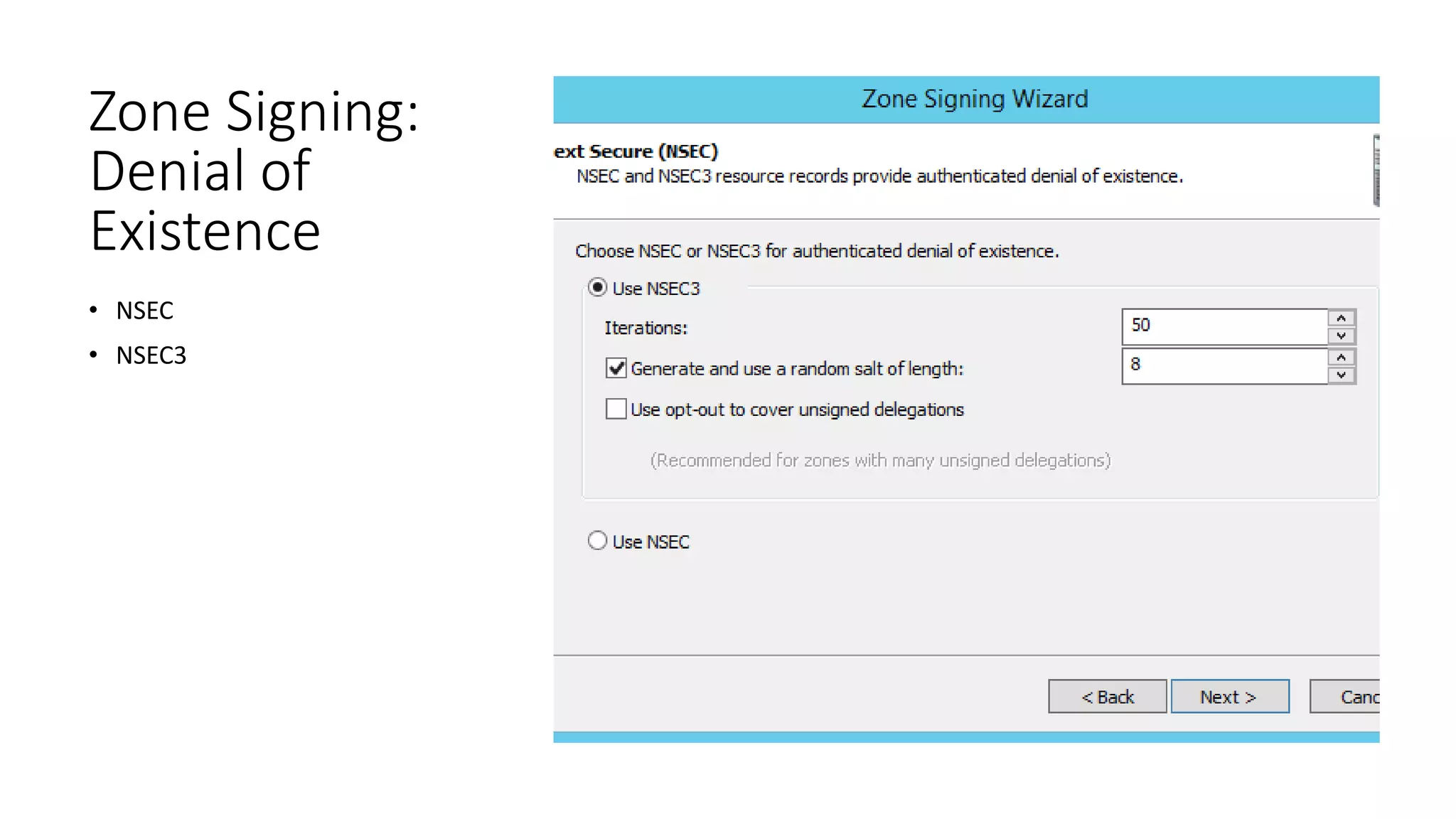
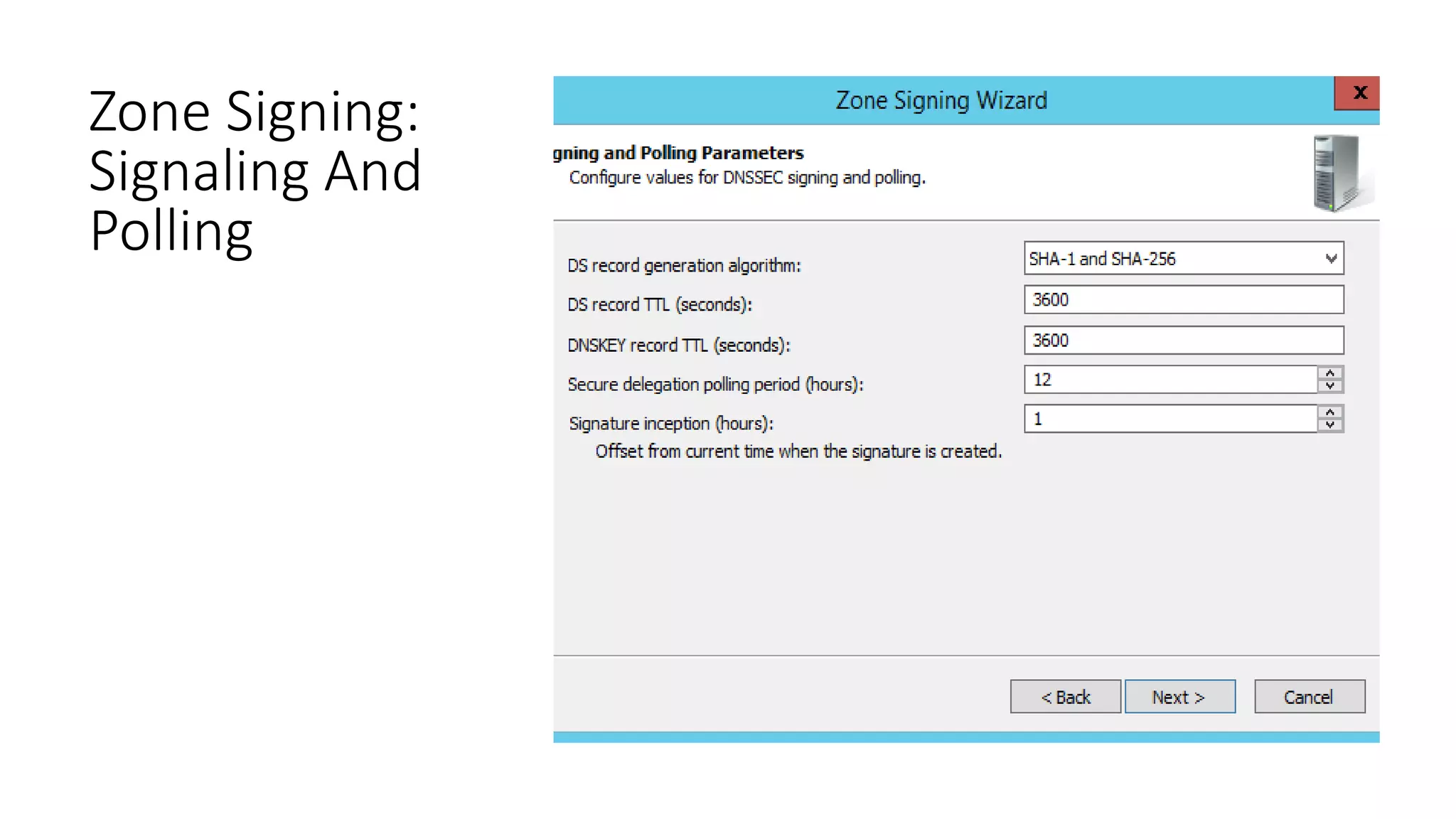
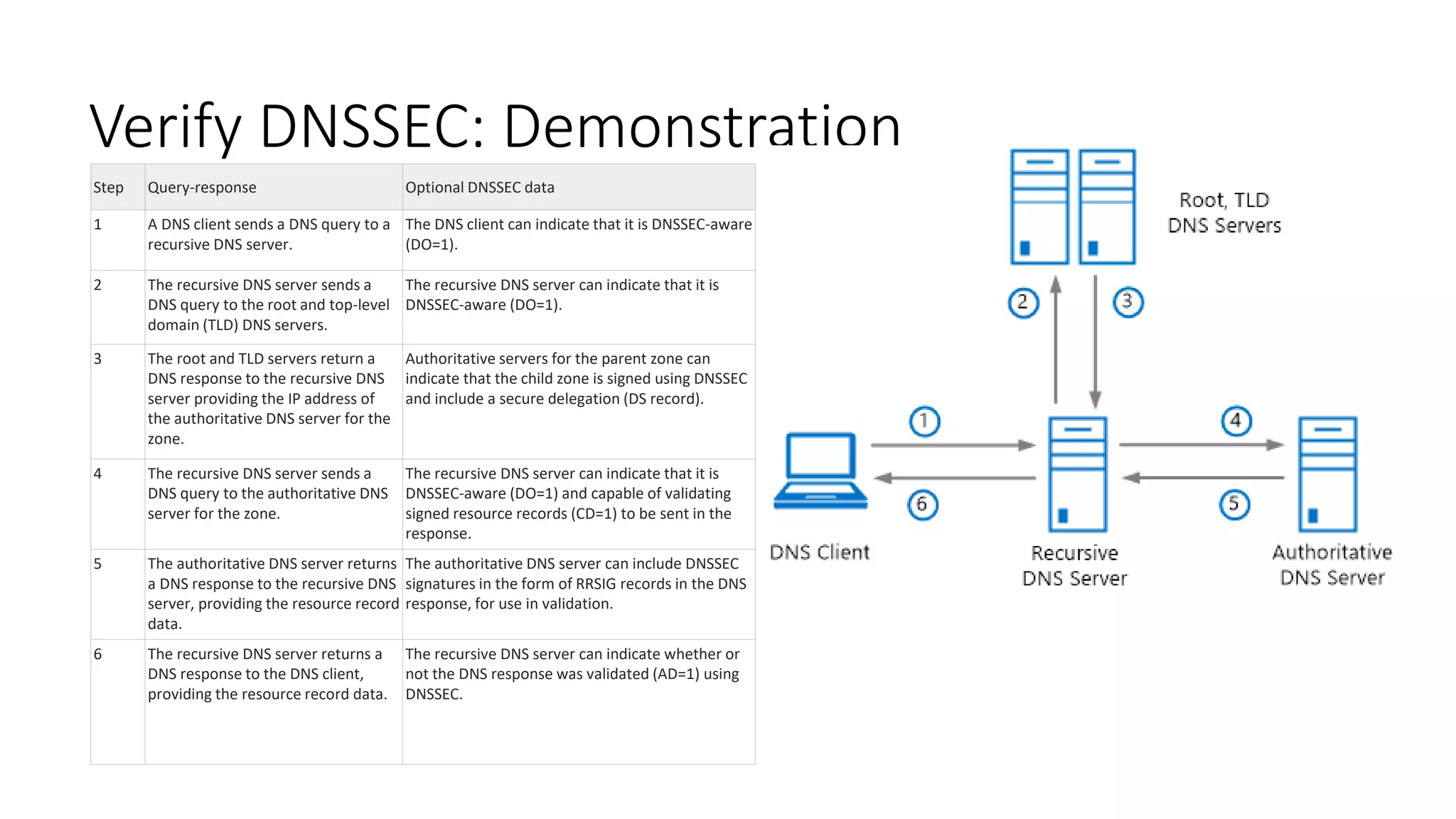
This document discusses DNSSEC configuration in Windows DNS servers. It covers choosing a key master to generate and manage keys, configuring key signing keys (KSK) and zone signing keys (ZSK), setting denial of existence such as NSEC, importing and exporting trust anchors, and verifying DNSSEC through demonstration of the query and response process between DNS clients, servers, and zones. Powershell commands are provided for automating DNSSEC signing and key management.