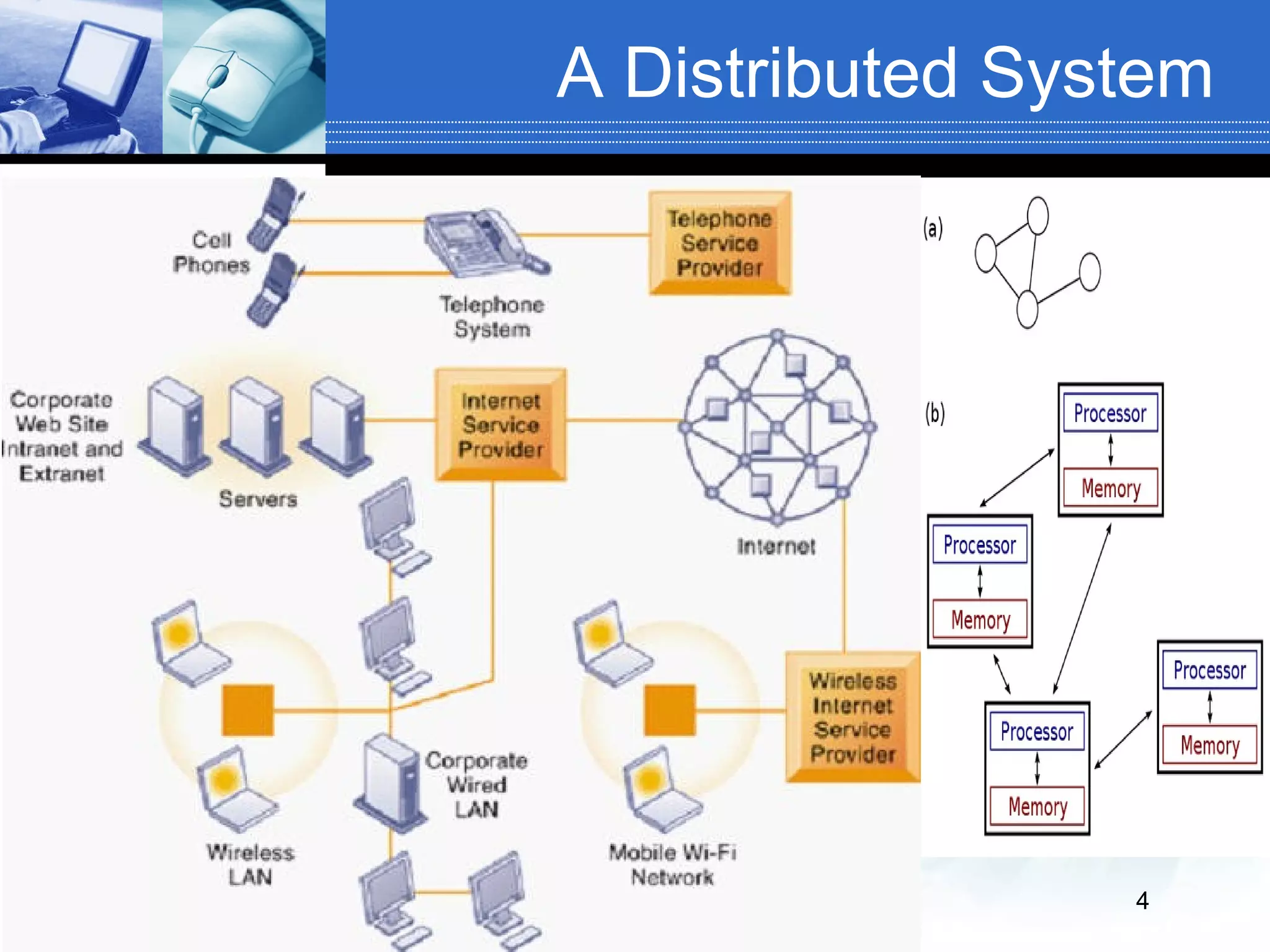
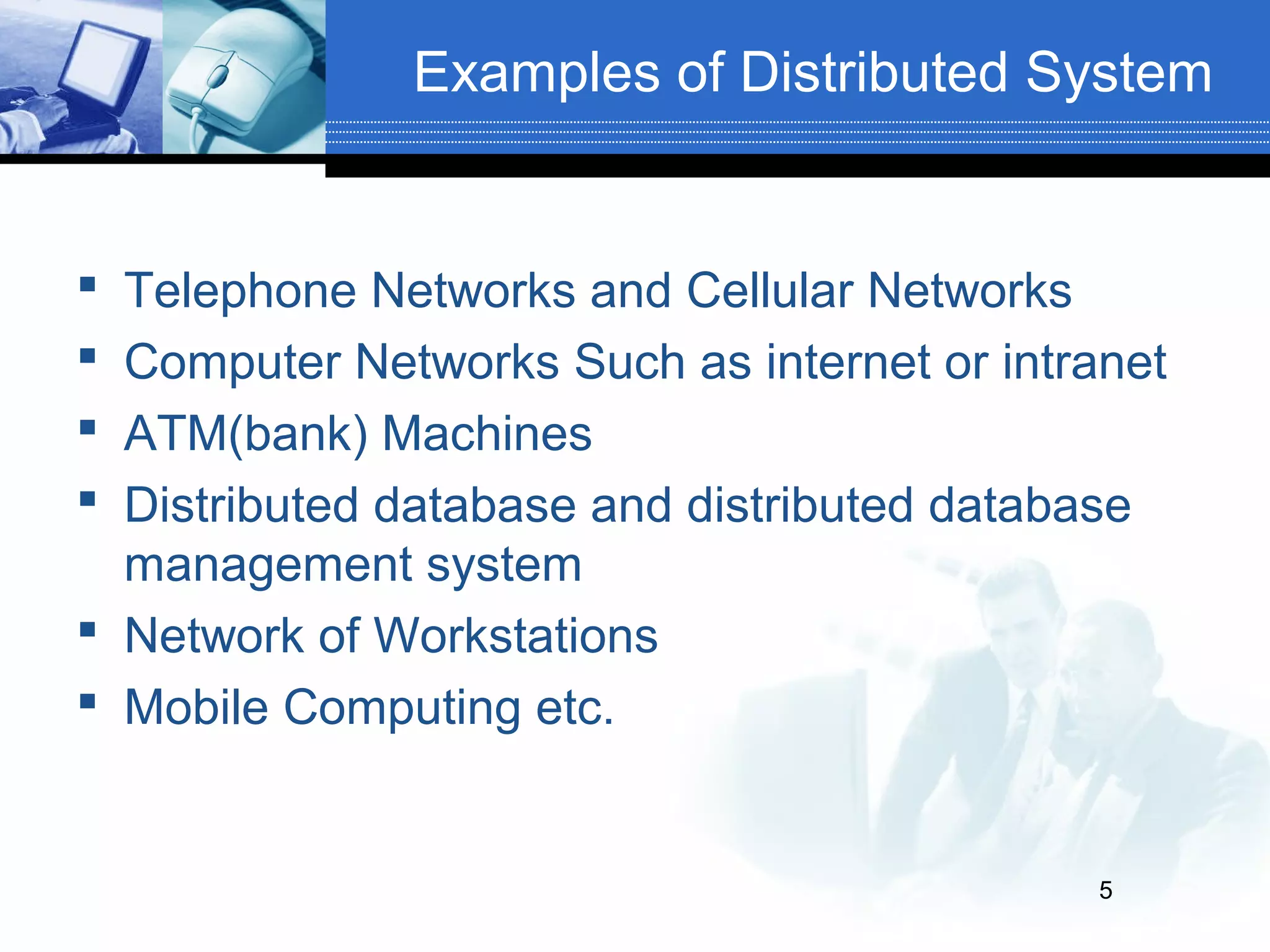
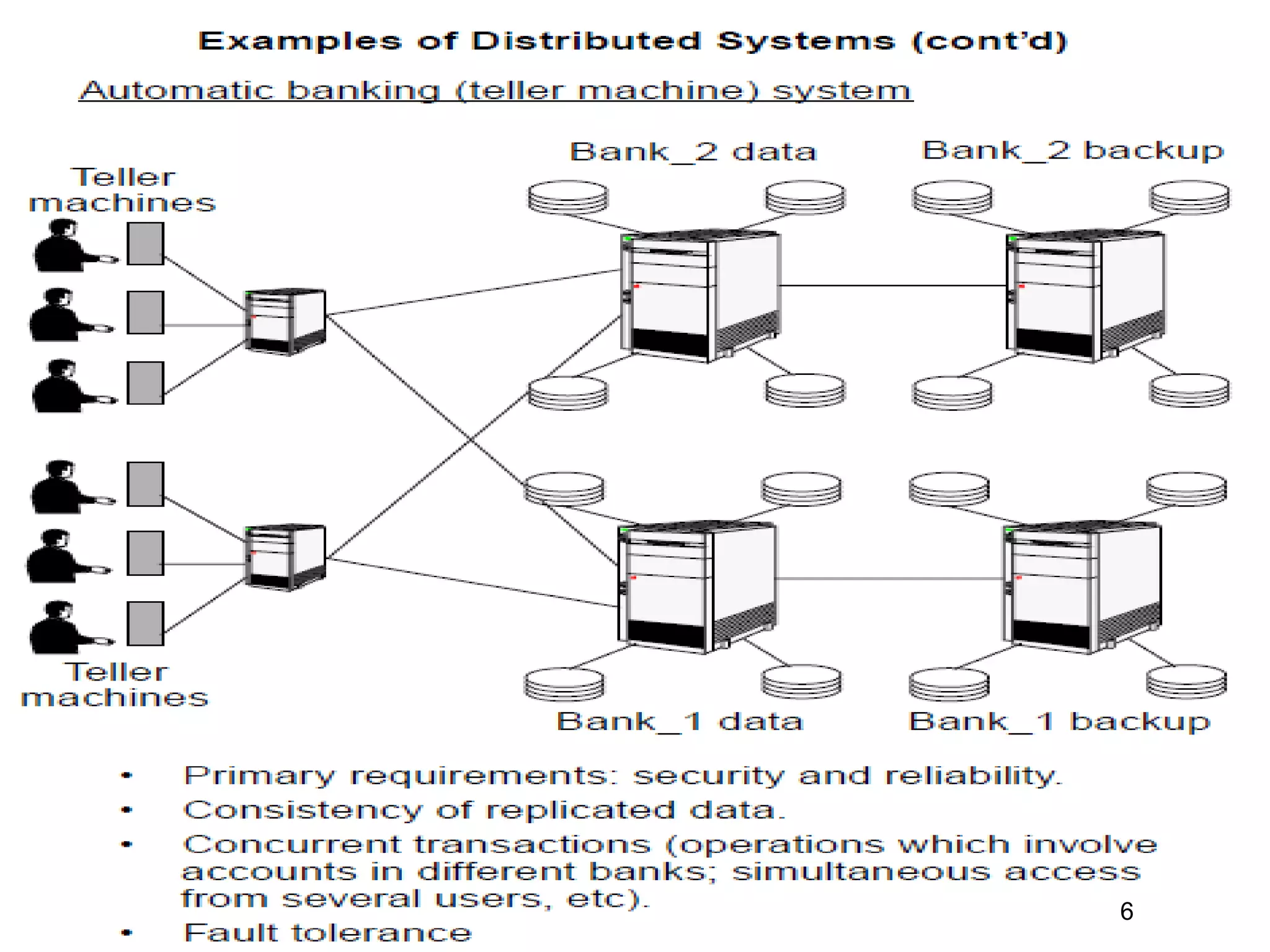
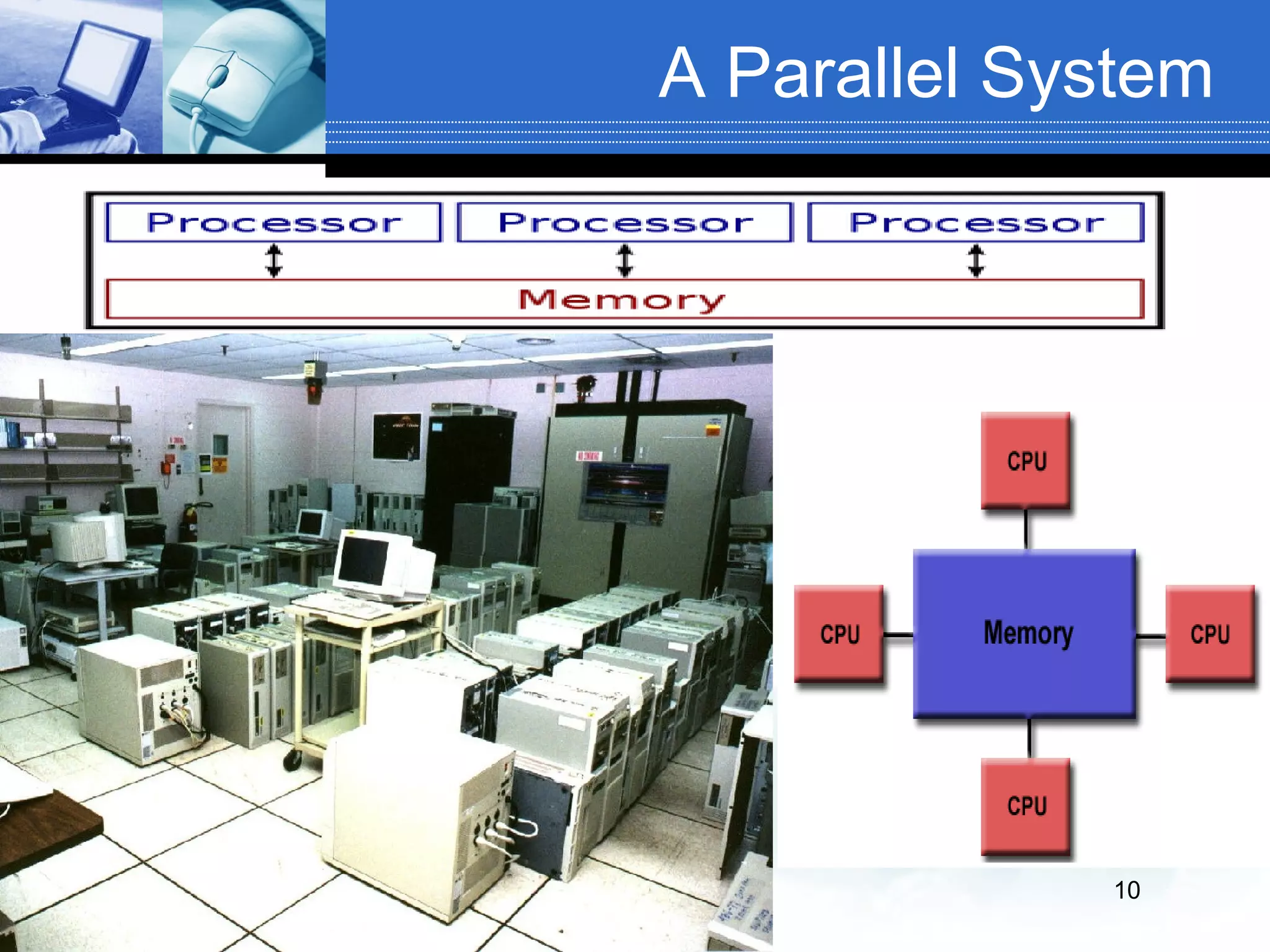
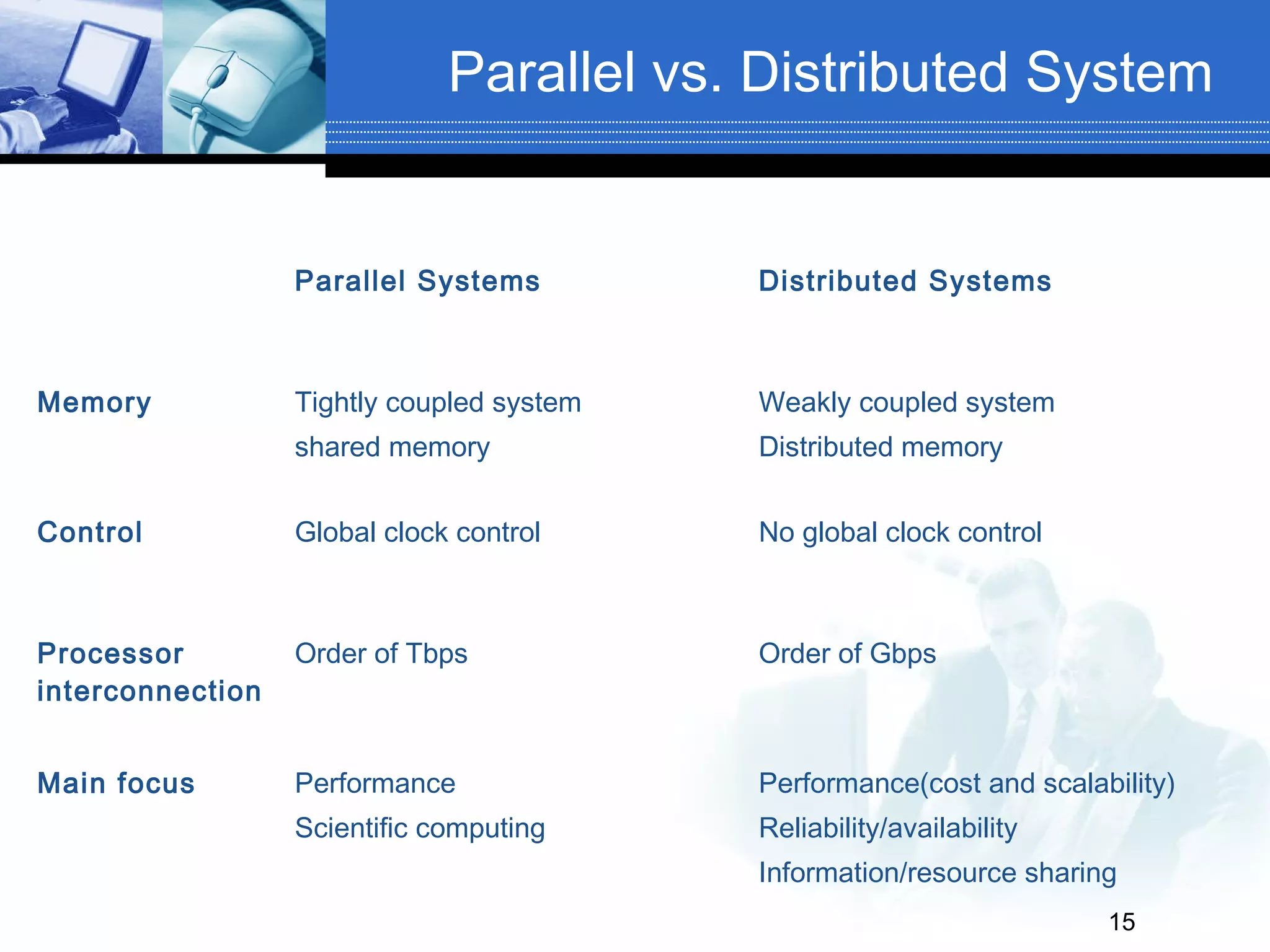
The document defines distributed and parallel systems. A distributed system consists of independent computers that communicate over a network to collaborate on tasks. It has features like no common clock and increased reliability. Examples include telephone networks and the internet. Advantages are information sharing and scalability, while disadvantages include difficulty developing software and security issues. A parallel system uses multiple processors with shared memory to solve problems. Examples are supercomputers and server clusters. Advantages are concurrency and saving time, while the main disadvantage is lack of scalability between memory and CPUs.